Submitted:
30 October 2024
Posted:
31 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Prostate Cell Lines
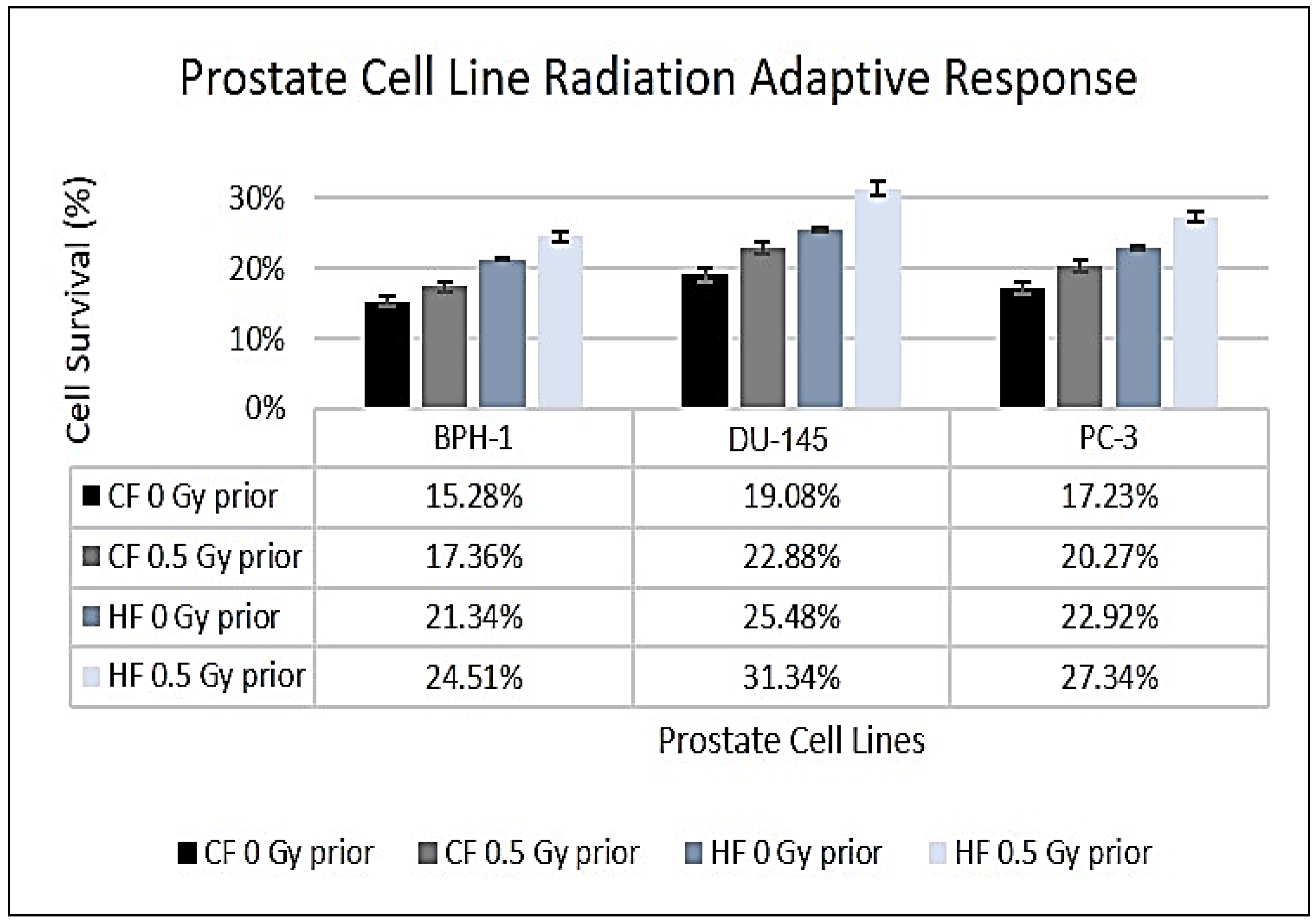
2.2. Doubling time, Adaptive Response and Clonogenic Survival Assay (CSA)
2.3. Biological Effective Dose (BED)
2.4. Split Dose Experiment and the Clonogenic Survival Assay
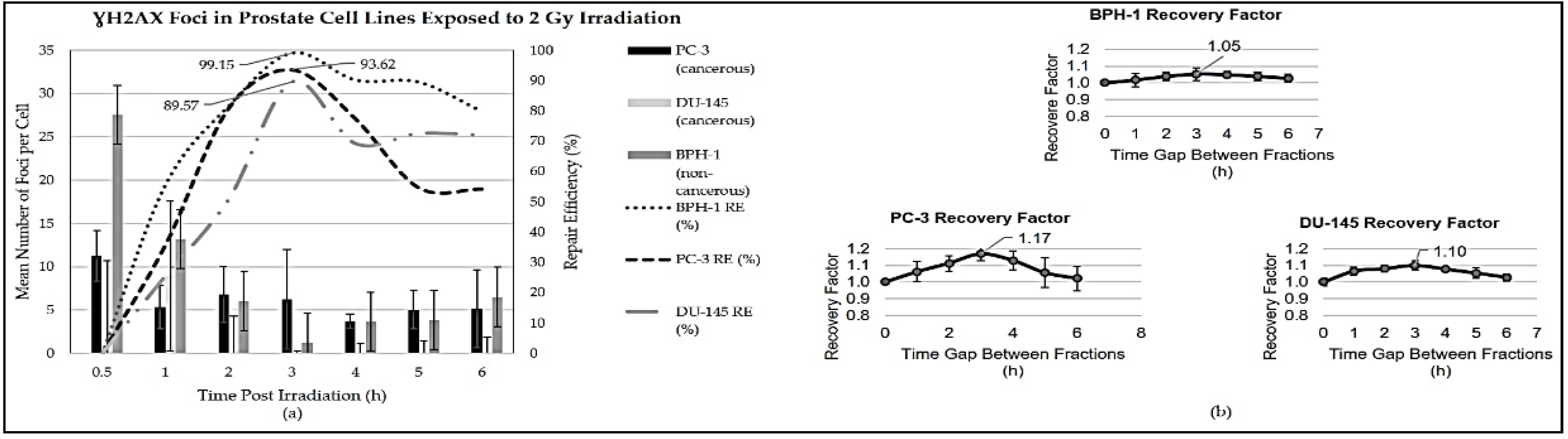
2.5. Gamma-H2AX Foci Assay
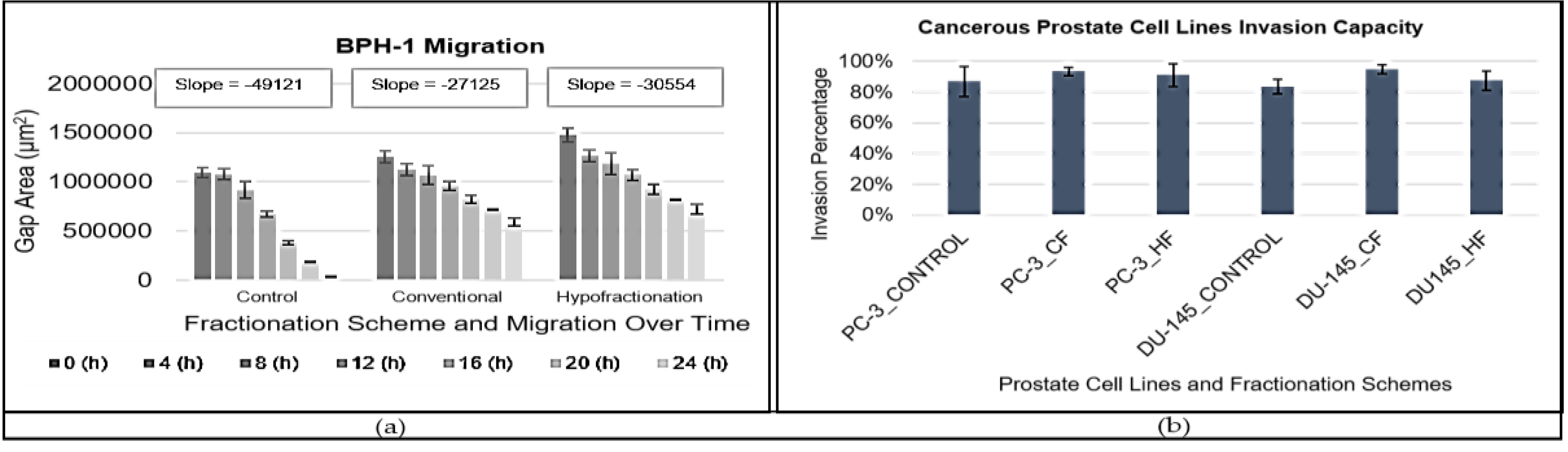
2.6. Migration Assay
2.7. Invasion Assay
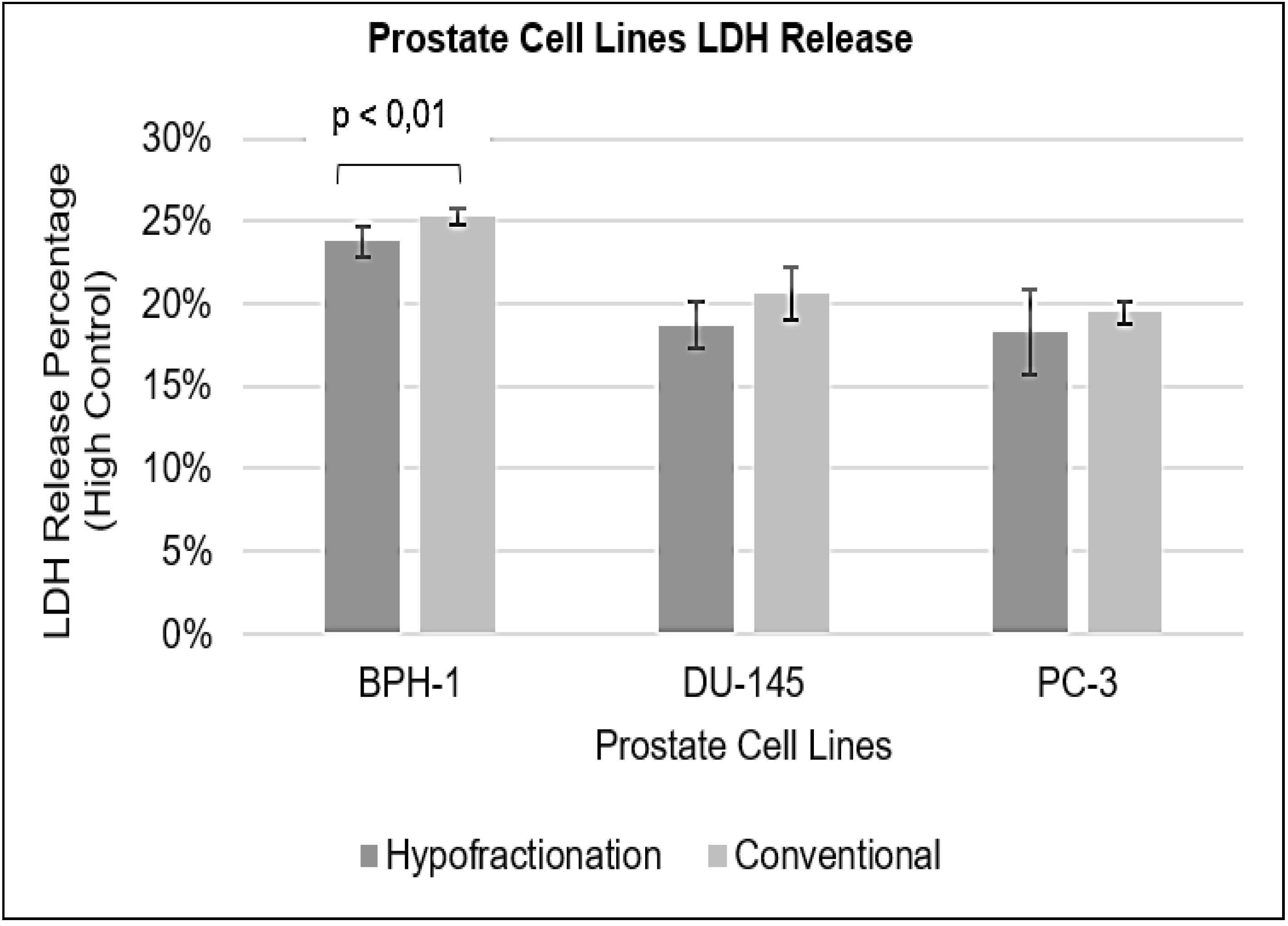
2.7. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimisation of Comparable Treatment Regimens and Adaptive Doubling Time
3.2. Surviving Fraction and Adaptive Response
3.3. Prostate Cell Line Migration and Invasion
3.4. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Musekiwa, A.; Moyo, M.; Mohammed, M.; Matsena-Zingoni, Z.; Twabi, H.S.; Batidzirai, J.M.; Singini, G.C.; Kgarosi, K.; Mchunu, N.; Nevhungoni, P.; Silinda, P. Mapping evidence on the burden of breast, cervical, and prostate cancers in Sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review. Frontiers in Public Health 2022, 10, 908302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, N.D.; Tannock, I.; N'Dow, J.; Feng, F.; Gillessen, S.; Ali, S.A.; Trujillo, B.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Attard, G.; Bray, F.; Compérat, E. The Lancet Commission on prostate cancer: planning for the surge in cases. The Lancet 2024, 403, 1683–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnet, N.G.; Benson, R.J.; Williams, M.V.; Peacock, J.H. Improving cancer outcomes through radiotherapy: Lack of UK radiotherapy resources prejudices cancer outcomes. British Medical Journal 2000, 320, 198–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasinska, A. The contribution of women to radiobiology: Marie Curie and beyond. Reports of Practical Oncology and Radiotherapy 2016, 21, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, F.; Abdel-Wahab, S.; Filipovic, N.; Jeremic, B. Radiation therapy. [CrossRef]
- Ndlovu, N. Radiotherapy treatment in cancer control and its important role in Africa. Ecancermedicalscience 2019, 13, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, V.; Boldrini, L.; Mariani, S.; Massaccesi, M. Role of radiation oncology in modern multidisciplinary cancer treatment. Molecular Oncology 2020, 14, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, A.M.; Pompos, A.; Timmerman, R.; Jiang, S.; Story, M.D.; Pistenmaa, D.; Choy, H. The role of hypofractionated radiation therapy with photons, protons, and heavy ions for treating extracranial lesions. Frontiers in Oncology 2016, 5, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insley, B.; Hsu, I.C.; Cunha, J.A.M. Paradigm shift in radiation treatment planning over multiple treatment modalities. Journal of Medical Physics 2021, 46, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feofanova, N.; Geraldo, J.M.; Andrade, L.M.D. Radiation oncology in vitro: trends to improve radiotherapy through molecular targets. BioMed Research International 2014, 2014, 461687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibamoto, Y.; Miyakawa, A.; Otsuka, S.; Iwata, H. Radiobiology of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy: what are the optimal fractionation schedules? Journal of Radiation Research 2016, 57, i76–i82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuryak, I.; Hall, E.J.; Brenner, D.J. Optimized Hypofractionation Can Markedly Improve Tumor Control and Decrease Late Effects for Head and Neck Cancer. Radiation Oncology Biology 2019, 104, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, K.; Mukherjee, S. When Less is More: The Rising Tide of Hypofractionation. Clinical Oncology (Royal College of Radiologists (Great Britain)) 2022, 34, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizarro, F.; Hernández, A. Optimization of radiotherapy fractionation schedules based on radiobiological functions. The British Journal of Radiology 2017, 90, 20170400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.D.; Gao, D.; Redfern, A.; Thompson, E.W. Controversies around epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer metastasis. Nature Reviews Cancer 2019, 19, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochbati L, Vanderpuye V, Moujahed R, Rejeb M Ben, Naimi Z, Olasinde T. Cancer care and COVID-19: tailoring recommendations for the African radiation oncology context. Ecancermedicalscience 2020, 14, 1144.
- Swanson, W.; Kamwa, F.; Samba, R.; Ige, T.; Lasebikan, N.; Mallum, A.; Ngoma, T.; Sajo, E.; Elzawawy, A.; Incrocci, L.; Ngwa, W. Hypofractionated radiotherapy in African cancer centers. Frontiers in Oncology 2021, 10, 618641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabucci, L.; Cornacchione, P.; Boldrini, L.; Pasini, D.; Dinapoli, L.; Smiljanic, L.; Valentini, V.; Dinapoli, N. Radiotherapy during the COVID-19: a review about management and treatment strategies. Reports of Practical Oncology and Radiotherapy 2022, 27, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.; Chappell, R.; Ritter, M. Is alpha/beta for prostate tumors really low? International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics 2001, 50, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearnaley, D.; Syndikus, I.; Mossop, H.; Khoo, V.; Birtle, A.; Bloomfield, D.; Graham, J.; Kirkbride, P.; Logue, J.; Malik, Z.; Money-Kyrle, J. Conventional versus hypofractionated high-dose intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer: 5-year outcomes of the randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 CHHiP trial. The Lancet Oncology 2016, 17, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.R. , Dignam, J. J., Amin, M., Bruner, D., Low, D., Swanson, G.P., Shah, A., D'Souza, D., Michalski, J.M., Dayes, I. and Seaward, S.A. NRG Oncology RTOG 0415: A randomized phase III non-inferiority study comparing two fractionation schedules in patients with low-risk prostate cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016, 4, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar]
- Van Leeuwen, C.M.; Oei, A.L.; Crezee, J.; Bel, A.; Franken, N.A.P.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Kok, H.P. The alpha and beta of tumours: a review of parameters of the linear-quadratic model, derived from clinical radiotherapy studies. Radiation Oncology 2018, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.S.; Lasley, F.D.; Das, I.J.; Mendonca, M.S.; Dynlacht, J.R. Normal Tissue Radiation Response BT - Basic Radiotherapy Physics and Biology. In: Chang DS, Lasley FD, Das IJ, Mendonca MS, Dynlacht JR, editors. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2021, 261–272. [CrossRef]
- Janopaul-Naylor, J.R.; Shen, Y.; Qian, D.C.; Buchwald, Z.S. The Abscopal Effect: A Review of Pre-Clinical and Clinical Advances. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, I.M.; Attalla, E.M.; El-Gohary, M.I. Impact of 3D conformal and Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy on secondary cancer risk for patients with early prostate cancer. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 2022, 15, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, R.F.; Howell, R.W.; Song, H.; Baechler, S.; Sgouros, G. Redefining relative biological effectiveness in the context of the EQDX formalism: implications for alpha-particle emitter therapy. Radiation Research 2014, 181, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.J.; Prise, K.M. Mechanistic modelling of radiation responses. Cancers 2019, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, W.; Schmidt, M. Normal Tissue Radiobiology. In: Brahme ABTCBP, editor. Oxford: Elsevier; 2014: 75–95. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect. 9780. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, R.B. Effect of heterogeneous radiosensitivity on the survival, alpha beta ratio and biological effective dose calculation of irradiated mammalian cell populations. Clinical and Translational Radiation Oncology 2017, 4, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J.; Nilsson, P.; Gleisner, K.S. On the biologically effective dose (BED)-using convolution for calculating the effects of repair: I. Analytical considerations. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2013, 58, 1507–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopewell, J.W.; Millar, W.T.; Lindquist, C.; Nordström, H.; Lidberg, P.; Gårding, J. Application of the concept of biologically effective dose (BED) to patients with vestibular schwannomas treated by radiosurgery. Journal of Radiosurgery and SBRT 2013, 2, 257–271. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, W.T.; Hopewell, J.W.; Paddick, I.; Lindquist, C.; Nordström, H.; Lidberg, G.; Gårding, J. The role of the concept of biologically effective dose (BED) in treatment planning in radiosurgery. Physica Medica 2015, 31, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A.; Beltran, C.J.; Furutani, K.M. Clonogenic Survival RBE Calculations in Carbon Ion Therapy: The Importance of the Absolute Values of α and β in the Photon Dose-Response Curve and a Strategy to Mitigate Their Anticorrelation. Quantum Beam Science 2023, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, N.A.P.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; Van Bree, C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nature Protocols 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahnreich, S.; Ebersberger, A.; Kaina, B.; Schmidberger, H. Biodosimetry Based on γ-H2AX Quantification and Cytogenetics after Partial- and Total-Body Irradiation during Fractionated Radiotherapy. Radiation Research 2015, 183, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Ren, S.; Yu, S.; Pan, H.; Li, T.; Ge, S.; Zhang, J.; Xia, N. Methods favoring homology-directed repair choice in response to CRISPR/Cas9 induced-double strand breaks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuijens, A.C.; Oei, A.L.; van Oorschot, B.; Visser, J.; van Os, R.M.; Moerland, D.; Franken, N.A.; Rasch, C.R.; Stalpers, L.J. Gamma-H2AX foci decay ratio as a stronger predictive factor of late radiation toxicity than dose-volume parameters in a prospective cohort of prostate cancer patients. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics 2022, 112, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Someya, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Nakamura, A.J.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kitagawa, M.; Gocho, T.; Mafune, S.; Ikeuchi, Y.; Tauchi, H.; Sakata, K.I. Prediction of late adverse events in pelvic cancer patients receiving definitive radiotherapy using radiation-induced gamma-H2AX foci assay. Journal of Radiation Research 2023, 64, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, L.; Gadea, G.; Roux, P. Control of cell migration: a tumor suppressor function for p53? Biology of the Cell 2006, 98, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, F.R.; Janes, S.M.; Giangreco, A. Epithelial cell migration as a potential therapeutic target in early lung cancer. European Respiratory Review 2017, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porporato, P.E.; Dhup, S.; Dadhich, R.K.; Copetti, T.; Sonveaux, P. Anticancer targets in the glycolytic metabolism of tumors: a comprehensive review. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2011, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez, A.; Shental, O.; Tchebiner, J.Z.; Laufer-Perl, M.; Wasserman, A.; Sella, T.; Guzner-Gur, H. Diagnostic and prognostic value of very high serum lactate dehydrogenase in admitted medical patients. Israel Medical Association Journal 2014, 16, 439–443. [Google Scholar]
- Bok, R.; Lee, J.; Sriram, R.; Keshari, K.; Sukumar, S.; Daneshmandi, S.; Korenchan, D.E.; Flavell, R.R.; Vigneron, D.B.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Seth, P. The role of lactate metabolism in prostate cancer progression and metastases revealed by dual-agent hyperpolarized 13C MRSI. Cancers 2019, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Banerjee, D. Lactate Dehydrogenases as Metabolic Links between Tumor and Stroma in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelizzari, G.; Basile, D.; Zago, S.; Lisanti, C.; Bartoletti, M.; Bortot, L.; Vitale, M.G.; Fanotto, V.; Barban, S.; Cinausero, M.; Bonotto, M. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) response to first-line treatment predicts survival in metastatic breast cancer: first clues for a cost-effective and dynamic biomarker. Cancers 2019, 11, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouten, R.M.; Dalgard, C.L.; Soltis, A.R.; Slaven, J.E.; Day, R.M. Transcriptomic profiling and pathway analysis of cultured human lung microvascular endothelial cells following ionizing radiation exposure. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 24214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Distel, L.V.R.; Neuhuber, W. Caffeic Acid, Quercetin and 5-Fluorocytidine-Functionalized Au-Fe3O4 Nanoheterodimers for X-ray-Triggered Drug Delivery in Breast Tumor Spheroids. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Guo, H.; Chen, W.; Ding, T. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy and Conventional Radiotherapy Induce Cytoskeleton Extension and Enlargement of Cell Morphology in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Dose-Response 2021, 19, 15593258211064499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, S.; Shibamoto, Y.; Iwata, H.; Murata, R.; Sugie, C.; Ito, M.; Ogino, H. Compatibility of the linear-quadratic formalism and biologically effective dose concept to high-dose-per-fraction irradiation in a murine tumor. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics 2011, 81, 1538–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wan, C.; Huang, J.; Yang, C.; Qin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, B.; Xu, S.; Wu, G.; Yang, K. In vitro radiobiological advantages of hypofractionation compared with conventional fractionation: early-passage NSCLC cells are less aggressive after hypofractionation. Radiation Research 2018, 190, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaccianoce, E.; Festuccia, C.; Dondi, D.; Guerini, V.; Bologna, M.; Motta, M.; Poletti, A. Characterization of prostate cancer DU145 cells expressing the recombinant androgen receptor. Oncology Research 2003, 14, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S. , Sun, Y. , Squires, J.M., Zhang, H., Oh, W.K., Liang, C.Z. and Huang, J. PC3 is a cell line characteristic of prostatic small cell carcinoma. The Prostate 2011, 71, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Moya, L.; Walpole, C.; Rae, F.; Srinivasan, S.; Seim, I.; Lai, J.; Nicol, D.; Williams, E.D.; Clements, J.A.; Batra, J. Characterisation of cell lines derived from prostate cancer patients with localized disease. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases 2023, 26, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, M.A.; Kilroy, G.E.; Johnson, J.R.; Lopez, M.J.; Moore, R.M.; Gimble, J.M. Cell growth characteristics and differentiation frequency of adherent equine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: adipogenic and osteogenic capacity. Veterinary Surgery 2006, 35, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Cha, S.H.; Kang, H.W.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Ko, K.B.; Lee, H.T. Effects of serial passage on the characteristics and chondrogenic differentiation of canine umbilical cord matrix derived mesenchymal stem cells. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences 2013, 26, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ediriweera, M.K.; Tennekoon, K.H.; Samarakoon, S.R. In vitro assays and techniques utilized in anticancer drug discovery. Journal of Applied Toxicology 2019, 39, 38–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, S.J. The linear quadratic model: Usage, interpretation and challenges. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2018, 64, 0–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, R.; Carabe-Fernandez, A. The radiobiology of conventional radiotherapy and its application to radionuclide therapy. Cancer Biology and Radiopharmaceuticals 2005, 20, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Cairncross, S.; Miles, X.; Engelbrecht, M.; du Plessis, B.; Bolcaen, J.; Fisher, R.; Ndimba, R.; Cunningham, C.; Martínez-López, W.; Schunck, C. An automated microscopic scoring method for the γ-H2AX foci assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Journal of Visualized Experiments (JoVE) 2021, 178, e62623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panek A, Miszczyk J. DNA repair processes in human lymphocytes irradiated with a 60-MeV proton radiotherapeutic beam. RAD Conference Proceedings 2019, 3, 10–14.
- Jayakumar, S.; Kunwar, A.; Sandur, S.K.; Pandey, B.N.; Chaubey, R.C. Differential response of DU145 and PC3 prostate cancer cells to ionizing radiation: Role of reactive oxygen species, GSH and Nrf2 in radiosensitivity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 2014, 1840, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövey, J.; Nie, D.; Tóvári, J.; Kenessey, I.; Tímár, J.; Kandouz, M.A.; Honn, K.V. Radiosensitivity of human prostate cancer cells can be modulated by inhibition of 12-lipoxygenase. Cancer Letters 2013, 335, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, M.; Bagley, A.F.; Zaidan, H.Y.; Yantasee, W. Augmenting the therapeutic window of radiotherapy: A perspective on molecularly targeted therapies and nanomaterials. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2020, 150, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Gao, X.; Lyu, F.; Sun, D. Mechanism of the DNA Damage Repair Gene Work on Elevated α/β Value after Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics 2019, 108, e526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, R. Role of p53 in Regulating Radiation Responses. Life 2022, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhong, R.; Sun, L.; Jia, J.; Ma, S.; Liu, X. Ionizing radiation-induced adaptive response in fibroblasts under both monolayer and 3-dimensional conditions. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0121289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.C.; Nguyen, E.V.; Niranjan, B.; Wu, Y.; Lim Kam Sian, T.C.; Horvath, L.G.; Taylor, R.A.; Daly, R.J. Cell-type-specific signaling networks impacted by prostate epithelial-stromal intercellular communication. Cancers 2023, 15, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabinejad, S.; Soleymanifard, S.; Sayyah, S.; Behnam Rasouli, F. High-dose Irradiation Stimulated Breast Tumor Microenvironment to Enhance Tumor Cell Growth and Decrease Tumor Cell Motility. Journal of Biomedical Physics and Engineering 2023, 13, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Cappa, T.; Kuhlenschmidt, T.; Kuhlenschmidt, M.; Saif, T. Specific and Non-Specific Adhesion in Cancer Cells with Various Metastatic Potentials BT - Mechanobiology of Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix Interactions. In: Wagoner Johnson A, Harley BAC, editors. Boston, MA: Springer US; 2011: 105–22. [CrossRef]
- Sideri, S. , Petragnano, F. , Maggio, R., Petrungaro, S., Catizone, A., Gesualdi, L., De Martino, V., Battafarano, G., Del Fattore, A., Liguoro, D. and De Cesaris. Radioresistance Mechanisms in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines Surviving Ultra-Hypo-Fractionated EBRT: Implications and Possible Clinical Applications. Cancers 2022, 14, 5504. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Graham, P.H.; Hao, J.; Bucci, J.; Cozzi, P.J.; Kearsley, J.H.; Li, Y. Emerging roles of radioresistance in prostate cancer metastasis and radiation therapy. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews 2014, 33, 469–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; DeMarco, V.G.; Nicholl, M.B. Resveratrol enhances radiation sensitivity in prostate cancer by inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting cell senescence and apoptosis. Cancer Science 2012, 103, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cell Line (Breast) |
Doubling Time (h) | Standard Deviation | Adaptive Doubling Time (h) | Standard Deviation (h) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPH-1 | 35.21 | 5.80 | 37.61 | 2.30 | p = 0.235 |
| PC-3 | 36.20 | 2.80 | 40.63 | 1.30 | p = 0.572 |
| DU-145 | 18.40 | 2.90 | 18.83 | 0.30 | p = 0.857 |
| Cell Line (Prostate) |
α (Gy−1) | β (Gy−2) | α/β Ratio | D50 (Gy) | P-value | RS | Conventional Fractionation | Hypofractionation | Biological Effective Dose (BED) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPH-1 (non-cancerous) |
0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00* | 2.7 ± 0.80 | 3.66 ± 0.10 | - | - | 2.00 Gy x 4 = 8.00 Gy with 3 hours gap | 4.93 Gy x 1 = 4.93 Gy | 13.93 Gy |
| PC-3 (cancerous) |
0.12 ± 0.00* | 0.03 ± 0.00* | 3.7 ± 0.90 | 3.21 ± 0.00* | 0.447 | 1.14 ± 0.00* | 2.00 Gy x 4 = 8.00 Gy with 3 hours gap | 5.15 Gy x 1 = 5.15 Gy | 14.67 Gy |
| DU-145 (cancerous) | 0.10 ± 0.00* | 0.04 ± 0.00* | 2.4 ± 0.80 | 3.10 ± 0.00* | 0.794 | 1.18 ± 0.00* | 2.00 Gy x 4 = 8.00 Gy with 3 hours gap | 4.85 Gy x 1 = 4.85 Gy | 12.32 Gy |
| Cell Lines | Single-Dose (Gy) | Intrinsic Survival (%) | Hypofractionation Survival (%) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPH-1 | 4.93 | 32.5 ± 3.5 | 21.3 ± 4.0 | 0.0012 |
| PC-3 | 5.15 | 24.3 ± 3.1 | 25.5 ± 2.0 | 0.5612 |
| DU-145 | 4.85 | 24.0 ± 4.0 | 22.9 ± 2.0 | 0.3148 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





