Introduction
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are somatic stem cells with potential for self-renewal, immunomodulation, and multilineage differentiation [
1]. The potential therapeutic applicability of stem cells has been empirically investigated for a range of conditions, such as acute myocardial infarction [
2], inflammatory bowel disease [
3], traumatic spinal cord injury [
4], diabetes melluitus [
5], and ageing frailty [
6,
7]. The beneficial effects of MSCs are thought to be caused not only by engraftment and differentiation, but also by the secretion of biologically active cells that exert beneficial effects on other cells [
1]. The trophic activities of MSCs include anti-fibrotic, immunomodulatory, anti-apoptotic, chemoattractive, neurogenic, and angiogenic properties [
1].
A recent article noted that, as of April 2023, despite 1,120 registered clinical trials for MSC therapy worldwide, only 12 MSC therapies have been approved by regulatory agencies for commercial application [
8]. There are recognised challenges in translating promising preclinical findings of MSC therapies into clinical trial results and then to the clinic [
8], but the immense potential for MSC therapies to transform the management of a wide range of conditions offers great promise to the medical and scientific communities worldwide.
Lifestyle-related diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidaemia, can damage the endothelium of major blood vessels, leading to the development of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE), ultimately leading to death [
9,
10]. Although animal studies have already shown that the intravenous administration of stem cells promotes vascular endothelial regeneration [
11], clinical research has confirmed that intravenous administration in humans can regenerate major blood vessels to a clinically meaningful extent, leading to reduced long-term complications and mortality rate. To our knowledge, no large clinical study has evaluated the risk factors for MACCEs in patients receiving MSC therapy for various indications. This study aimed to evaluate the mean MACCE-free period and potential risk factors for MACCE development in a population of patients receiving MSC therapy for various indications.
Results
Study Population and Setting
Study population characteristics are summarised in
Table 1. This study included 2,504 patients who received intravenous stem cells at the Omotesando Helene Clinic between October 2014 and December 2023. The average age of patients was 54.09 ± 11.65 years. Among the 2504 patients, 1276 (50.96%) were female, and 1225 (48.92%) were male; the sex details of three (0.12%) patients were missing. The total number of intravenous doses of mesenchymal stem cells administered in this group was 4,431, and the mean dose of stem cells received per participant was 1.49 ± 0.75 billion cells. The average length of follow-up was 15.88 ± 26.85 months. The nationality distribution of patients was as follows: 72% (n=1,802) were Chinese, 16% (n=402) Vietnamese, 6% (n=152) Japanese, and 6% (n=148) others, almost all of whom were from East or Southeast Asia.
Statistical Analysis
The indications for MSC administration varied (
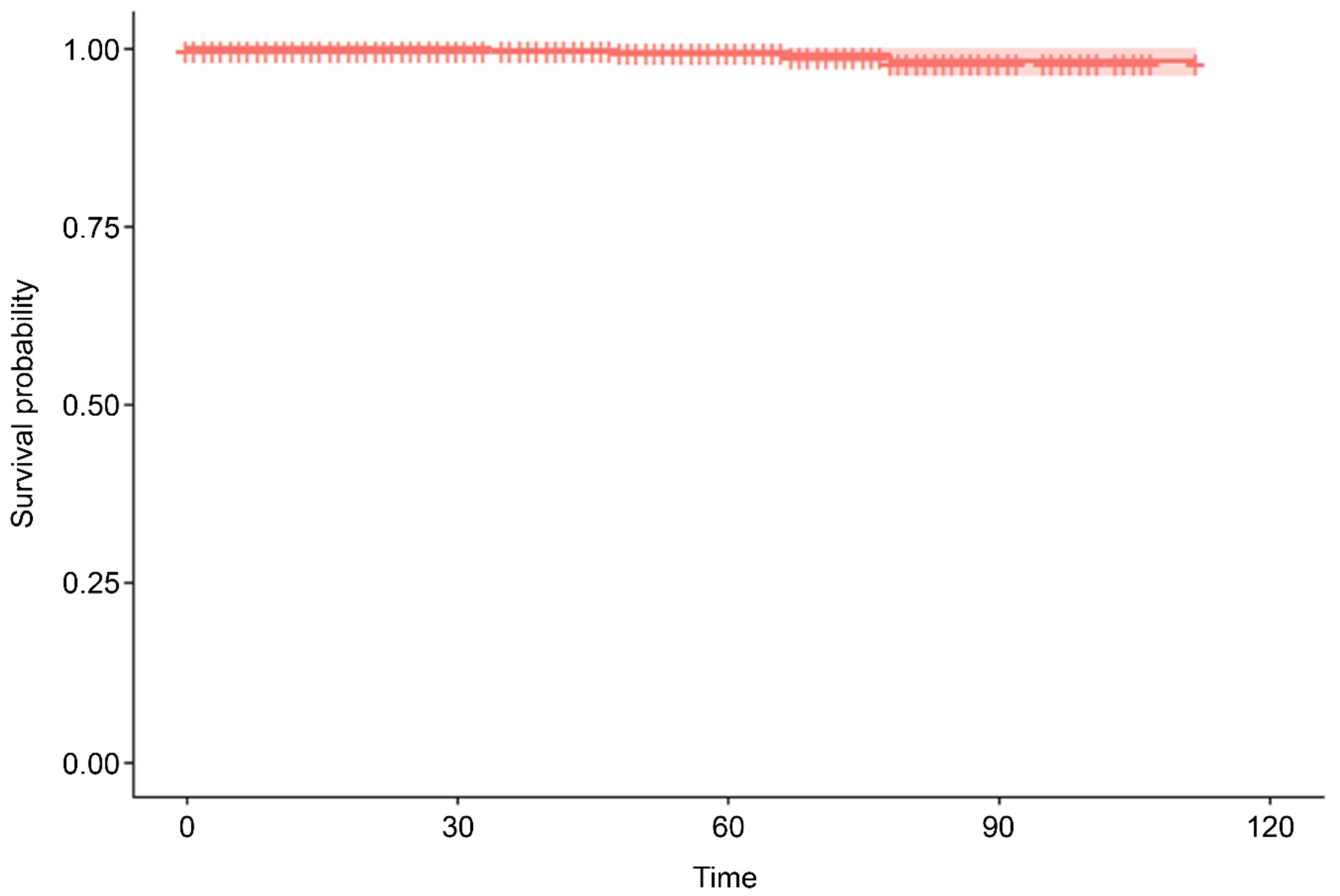
Table 1), but over two-thirds (n=1,700, 67.89%) received MSC therapy as an anti-aging therapy, of whom 712 were followed up. There were five MACCE and deaths during the mean observation period of 112 months (standard error = 0.435;
Table 2 and
Figure 1), including four deaths (one due to coronavirus disease 2019-related pneumonia, one due to an unrelated incident, one due to natural causes [old age], and one due to stroke) and an additional case of non-fatal stroke. This represents a MACCE rate of 0.20% during the follow-up period. In univariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis, an analysis of age, gender, and MSC dose revealed that only age was significantly associated with a risk of MACCE (hazard ratio = 1.124; 95% confidence interval = 1.04, 1.214; p = 0.0031;
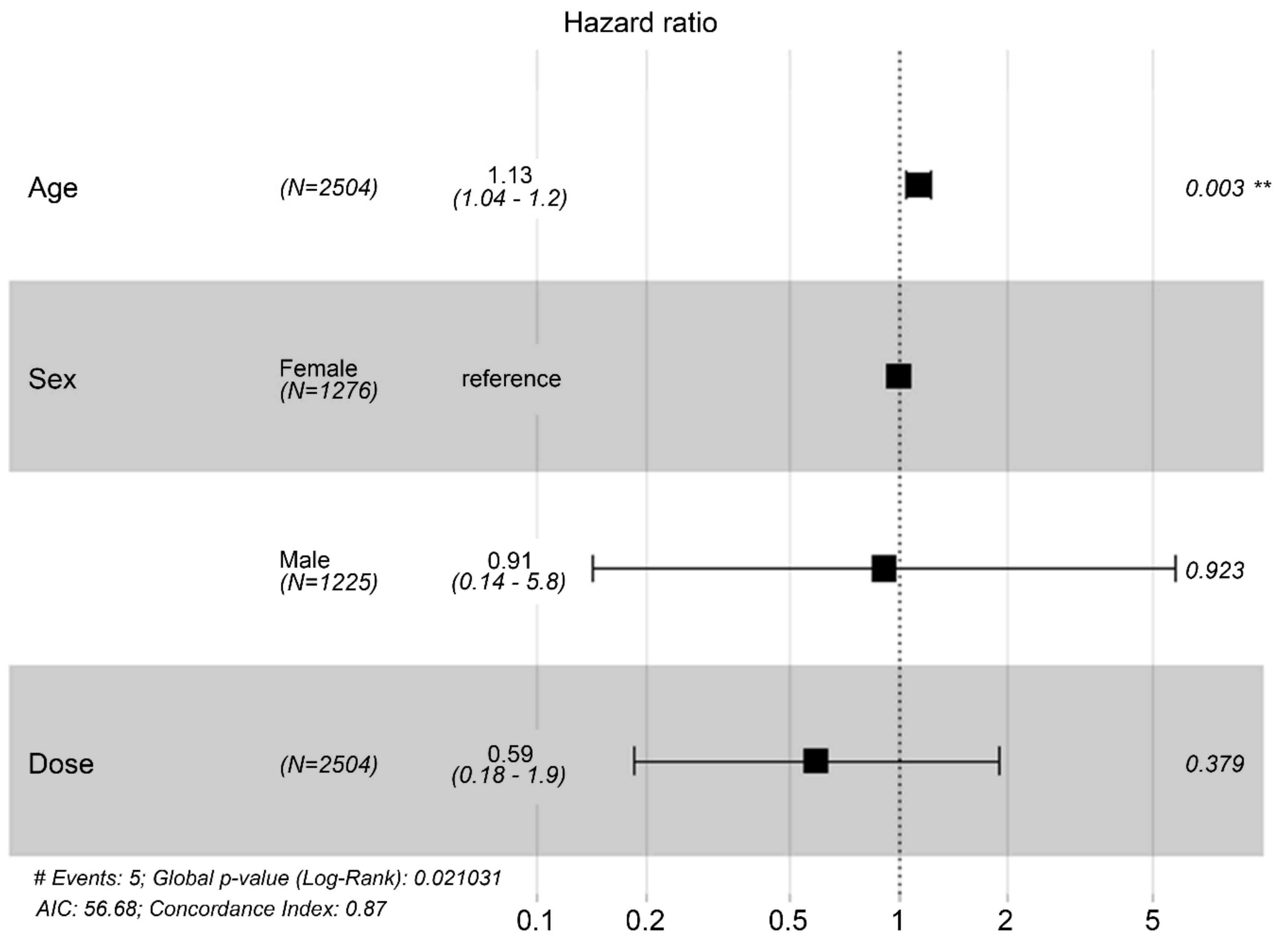
Table 3). Specifically, the risk of MACCE increases by 1.124 per unit increase in age. In a multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis including the same three variables, age remained significantly associated with MACCE risk (hazard ratio = 1.127; 95% confidence interval = 1.0418–1.219; p = 0.0029;
Table 4 and
Figure 2), such that the risk of MACCE increased by 1.127 with each unit increase in age. Sex and MSC dose remained non-significant in multivariate analysis.
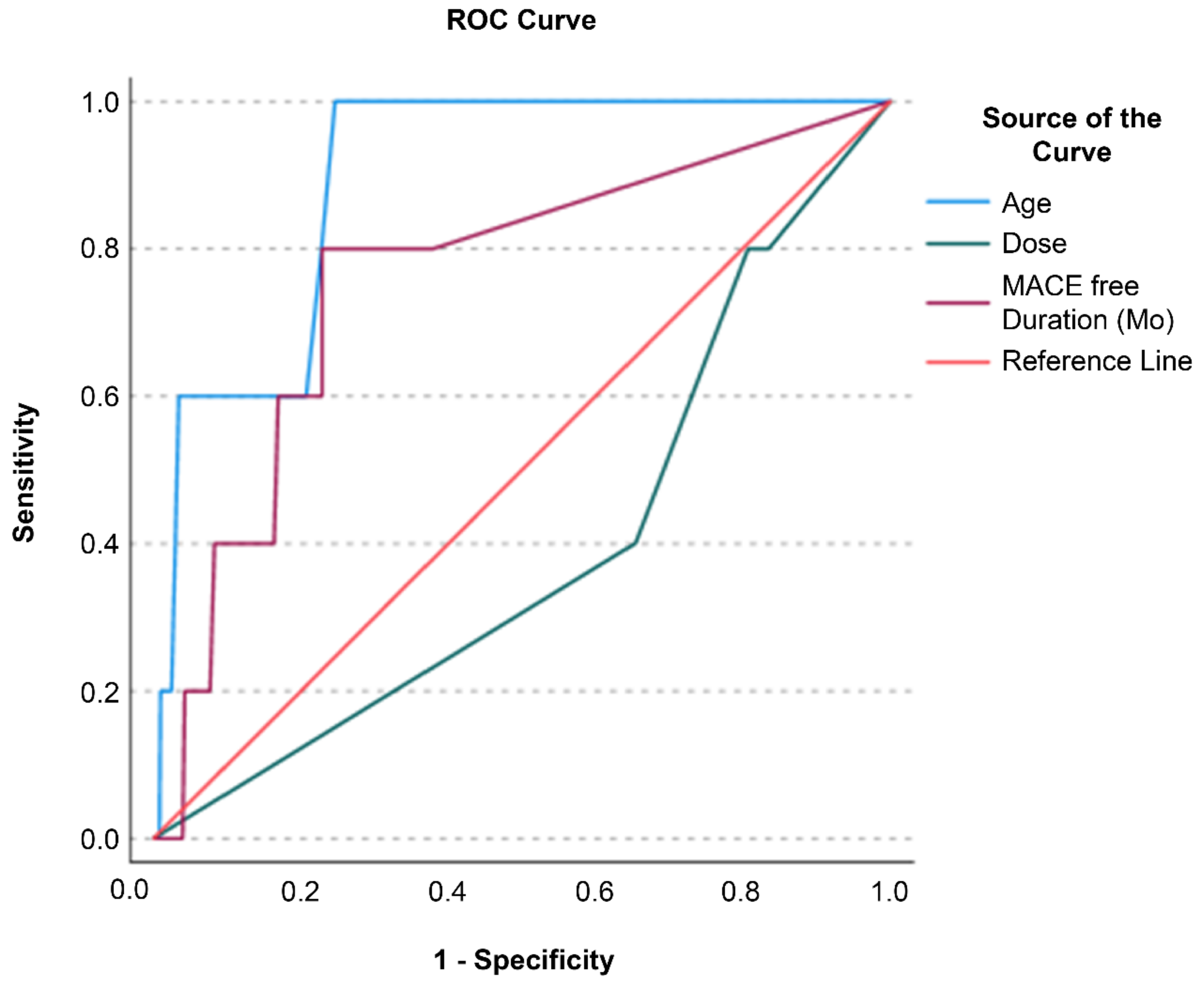
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to evaluate which of the variables age, MSC dose, and MACCE-free duration facilitated the classification of MACCE status (event vs. no event;
Figure 3). Age and MACCE-free duration were excellent for classifying MACCE status, with area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.895 (p <0.001, 95% confidence interval = 0.807–0.984) and 0.759 (p = 0.019, 95% confidence interval = 0.542–0.976), respectively. MSC dose, with an AUC of 0.394 (p = 0.377; 95% confidence interval = 0.158, 0.630), was not a significant predictor. Classifier evaluation metrics confirmed the superiority of age (Gini Index = 0.791; maximum Kolmogorov–Smirnov metric = 0.754; Kolmogorov–Smirnov metric cut-off = 61.50) and MACCE-free duration (Gini Index = 0.518; maximum Kolmogorov–Smirnov metric = 0.571; Kolmogorov–Smirnov metric cut-off = 33.50) over the MSC dose (Gini Index = -0.213; maximum Kolmogorov–Smirnov metric = 0.000; Kolmogorov–Smirnov metric cut-off = 3.00).
Adverse Effects
Most MSC therapy recipients (n=2484, 99.2%) experienced no adverse effects (
Table 1). The most common adverse event was insomnia (n=10, 0.4%), followed by disrupted menstrual cycles (n=4, 0.16%) and dizziness (n=2, 0.08%). Importantly, none of the adverse events were severe.
Discussion
This large, retrospective study of 2,504 individuals who received MSC therapy for various indications showed that stem cell therapy is safe and associated with a very low risk of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events over an average follow-up period of over 9 years. Multivariate analysis revealed that age was significantly associated with MACCE risk, and an AUC analysis of an ROC curve identified age and MACCE-free duration as significant predictors of MACCE status. Neither sex nor MSC dose was associated with MACCE risk. The adverse event rate was low (n=20/2504, 0.8%), and none of the reported adverse events were severe.
There has been great interest in the use of MSC therapies to treat a wide range of medical conditions [
2,
3,
4,
5], as well as the effects of aging frailty [
6,
7]. Inflammation plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of aging-related frailty and is referred to in this context as “inflammaging” [
12]. Inflammation is known to accelerate diseases associated with aging, including cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases that constitute MACCE [
12]. Evidence from a phase II trial of patients diagnosed with frailty administered intravenous human allogeneic MSCs found the treatment to be safe and to improve physical performance, as well as inflammatory biomarkers, including serum tumour necrosis factor alpha levels [
13]. In the current study, over two-thirds of the participants received MSC therapy as an anti-aging therapy, which holds promise as an application of MSC therapy to improve global health outcomes.
The current study had some limitations. First, its retrospective nature increases the risk of bias in the data collected; further prospective studies to corroborate our findings are warranted. Second, data on a matched control group are not available to demonstrate the potential MACCE-reducing benefits of MSC therapy. Future prospective studies should incorporate such a control group matched at baseline for risk factors associated with the development of MACCE, including cardiovascular risk factors [
9].
In conclusion, our study showed that stem cell therapy is safe in a large cohort of individuals and is associated with a low rate of major cardiac and cerebrovascular events. Further prospective randomised studies are warranted to confirm that MSC therapy reduces MACCE events relative to placebo in age- and cardiovascular risk-matched controls.
Methods
Study Design and Ethical Approval
In this single-centre, observational, retrospective cohort study, written informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to stem cell administration. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of our institution (Helene Ethical Committee; approval number: HCS-20140601).
Study Population and Setting
The study population comprised all adult patients who received their first intravenous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment between 28 October, 2014 and 18 December, 2023. Treatments were administered at the Omotesando Helene Clinic, a general medical clinic in Tokyo, Japan.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) confirmation of a physician’s diagnosis and opinion regarding the appropriateness of MSC administration, (2) patients aged at least 20 years at the time of obtaining consent, and (3) patients who provided written informed consent to participate in this study.
The single exclusion criterion was patients deemed unsuitable by the principal investigator or subinvestigator to participate in the study.
Treatment
In patients who received multiple doses, the date of administration was calculated from the date of the first dose. The dose of mesenchymal stem cells administered to each patient was not fixed and ranged from 100 million to 2 billion cells, with most patients receiving 1 or 2 billion cells. Dosing decisions were based on the physician’s diagnosis.
Each dose of mesenchymal stem cells was administered as a single intravenous dose and was not split. Culture-grown MSCs were dissolved in 200 mL of 0.9% saline and administered intravenously in an outpatient treatment room. The total time required for the administration of MSCs was approximately 1 h. Treatment was completed after 30 min, after which the medical staff monitored the patients for any abnormalities in their physical condition and confirmed that there were no abnormal vital signs or other irregularities. Post-administration monitoring was conducted by telephone or other means on the following day to check for complications during the acute phase.
Follow-Up
Clinical follow-up included medical record reviews, telephone, email conversations, and administration of questionnaires to patients, their families, and caregivers.
Endpoints
The primary endpoint of the study was the MACCE rate during the follow-up period, defined as a composite of all-cause mortality and non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI)/non-fatal stroke. The secondary endpoints included the occurrence of minor side effects such as fever, dizziness, insomnia, pruritus, and nausea.
Statistical Analyses
Categorical variables were represented as frequencies and percentages. Univariate Cox regression analyses were performed for each predictor to identify individual associations with MACCE risk. Multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to assess the associations between various factors and MACCE. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis was performed to evaluate the probability of MACCE-free status during the follow-up period. Patients who were alive but could not be followed up were censored as dropouts. ROC analysis was performed to test the classification ability to discriminate MACCE status among predictors. The classification ability was tested using AUC analysis. The classification ability of the model was evaluated using Gini’s Index and Maximum K-S value, and the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was performed to determine the optimal threshold value for predictors that could provide the best classification for MACCE status.
However, power calculations were not performed. The p-value threshold for statistical significance was set at p<0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using R version 4.3.2 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) and Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA), except for the ROC analysis, which was performed using SPSS (version 27.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. TM, NK, TI, YW, and YH treated the patients as attending physicians and contributed to the collection of clinical data on patients. TM prepared the materials and analyses, wrote the first draft of the manuscript and commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Informed Consent Statement
This study was approved by the Helene Ethical Committee (approval number: HCS-20140601). Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article.
Acknowledgments
Editorial support, in the form of medical writing, assembling tables, creating high-resolution images based on authors’ detailed directions, collating author comments, copyediting, fact checking, and referencing, was provided by Editage and Cactus Communications. This study received no funding.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare no financial or non-financial competing interests.
Code Availability: Not applicable
References
- Maldonado, V. V., et al. Clinical utility of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in regenerative medicine and cellular therapy. J. Biol. Eng. 17, 44 (2023).
- Clavellina, D., Balkan, W. & Hare, J. M. Stem cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction: mesenchymal stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Exp. Opin. Biol. Ther. 23, 951-967 (2023).
- Saadh, M. J., et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs)-based cell therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) therapy. Eur. J. Med. Res. 28, 47 (2023).
- Montoto-Meijide, R., Meijide-Faílde, R., Díaz-Prado, S. M., Montoto-Marqués, A. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in traumatic spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 11719 (2023).
- Mikłosz, A. & Chabowski, A. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells therapy as a new treatment option for diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 108, 1889-1897 (2023).
- Zhu, Y., Ge, J., Huang, C., Liu, H. & Jiang, H. Application of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for aging frailty: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Theranostics 11, 5675-5685 (2021).
- Schulman, I. H., Balkan, W. & Hare, J. M. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for aging frailty. Front. Nutr. 5, 108 (2018).
- Fernández-Garza, L. E., Barrera-Barrera, S. A., & Barrera-Saldaña, H. A. Mesenchymal stem cell therapies approved by regulatory agencies around the world. Pharmaceuticals 16, 1334 (2023).
- Liu, H., et al. The association of triglyceride-glucose index with major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events after acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Nutr. Diabetes, 14, 39 (2024).
- Wang, W. T., et al. Comparative effectiveness of blood pressure-lowering drugs in patients who have already suffered from stroke: traditional and Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Medicine 95, e3302 (2016).
- Evans, C. E., Iruela-Arispe, M. L., & Zhao, Y. Y. Mechanisms of endothelial regeneration and vascular repair and their application to regenerative medicine. Am. J. Pathol. 191, 52-65 (2021).
- Franceschi, C., et al. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 908, 244-254 (2000).
- Tompkins, B. A., et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate aging frailty: a phase ii randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 72, 1513-1522 (2017).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).