1. Introduction
In 2019, a new coronavirus known as SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) erupted throughout the world causing the highly contagious illness coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) [
1]. Multiple variants of SARS-CoV-2 have been identified, of which a few are considered variants of concern due to their propensity to increase transmissibility or virulence [
2]. As per World Health Organization (WHO), there was an increase in the number of new COVID-19 cases by 52% during the 28-day period from Nov 20, 2023 to Dec 17, 2023 as compared to the previous 28-day period, with over 8,50,000 new cases reported globally [
3]. As of Feb 2024, India has witnessed >44 million cases and >0.53 million deaths due to COVID-19 [
4]. India is the most impacted country, ranking second to the United States of America (USA) in terms of the number of cases, and third to USA and Brazil in terms of deaths [
5].
SARS-CoV-2 enters the respiratory tract via the nose and causes an infection through a series of events including binding to the nasal epithelial cells, entering the nasal epithelial cells via the host receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2), undergoing local replication and transmission after entry, as well as causing the infection of ciliated cells in the upper respiratory tract [
6]. Early signs and symptoms of COVID-19 infection include fever, headache, sore throat, and loss of smell and taste. In adults a significant reduction in CD8+ and CD4+ T-cells in the primary stages of the disease when encountered with the virus is observed. The decrease in the T-cells leads to the acute respiratory distress syndrome for approximately 7–10 days which further causes the fast viral replication phase of the disease, resulting in release of a storm of pro-inflammatory cytokines, initiating chemokine responses, and infiltration of inflammatory cells [
1]. So as to prevent the progression of the disease at early infection phase wherein the viral load is highest in the nose and nasopharynx, the applicability of nasal spray with an active substance that inhibits virus entry and replication may stop or delay the progression of the disease to the lower respiratory system and reduce the transmission to uninfected individuals [
7].
Azelastine hydrochloride nasal spray (concentration of 0.1% w/v) is currently an approved medicinal product to treat allergic rhinitis. Several studies have explored azelastine’s potential as a promising drug repurposing candidate to reduce SARS-CoV-2 viral load and infection rates [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. The mechanism of azelastine in exerting the antiviral effect may involve its direct action on viruses, host cell pro-viral factors, and on the virus-induced host response [
14]. Azelastine nasal spray might be used as an instant approach in the initial stage of COVID-19 infection to prevent nasal colonization with SARS-CoV-2; therefore, it may have a great effect in preventing the viral spread from the nasopharynx to lungs [
13].
The first clinical dose finding proof-of-concept study in subjects tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 was the German CARVIN trial [
15]. The study results provided the first human data showing that azelastine hydrochloride 0.1% nasal spray indeed may be effective in accelerating the reduction of virus load in the nasal cavity and improving COVID-19 symptoms in subjects. Therefore, to further understand the impact of azelastine hydrochloride in treating SARS-CoV-2 infected subjects, the present phase II study (CARVIN-II) was planned based upon the positive outcome of the phase II dose finding study [
15]. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical safety and efficacy of azelastine nasal spray in Indian subjects tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 with mild symptoms and not requiring hospitalization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
In this multi-center, phase II, randomized, prospective, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled efficacy and safety study, non-hospitalised Asian subjects with mild COVID-19 infection, who were detected positive with rapid antigen test (RATs), were randomized to receive azelastine 0.1% nasal spray or placebo nasal spray.
Subjects self-administered two puffs of the nasal spray, with one puff per nostril each, five times daily, preferably at 3 hours intervals during the day, from day 2 to day 10. Daily administration on days 2-10 was not less than 3 application per nostril. On day 1 (day of inclusion of subject), at least two puffs per nostril were administered. On day 11 (last day of the study treatment), at least one application was completed before the Investigator’s visit. All subjects were provided with standard supportive treatment as per the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoH FW), Government of India [
16].
The study was initiated after protocol approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee or Institutional Review Board. A full list of Ethics Committees involved is provided in the
Supplementary Table S1. The study was carried out in compliance with the Good Clinical Practice, principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and all applicable local and national regulatory requirements. Prior to the start of the study, the clinical trial was registered in the Clinical Trials Registry-India (clinical trial ID: CTRI/2022/09/).
2.2. Participants
Male and female subjects ≥18 years of age, willing to provide nasopharyngeal swabs, with positive RAT for SARS-CoV-2 were enrolled from the general population and treated on the same day based on randomization. Subjects with blood oxygen levels nearing moderate Saturation of Peripheral Oxygen (SpO2) (<93%) were excluded.
Women of reproductive age agreeing to employ reliable contraceptive methods (including hormonal contraception, barrier methods or abstinence) until day 11 or those unable to bear children were enrolled. Pregnant or lactating women were not included into the study. All inclusion and exclusion criteria are listed in (
Supplementary Table S2). Subjects required to possess the ability to give informed consent and self-administer the nasal spray.
2.3. Randomization and Masking
A total of 294 subjects with mild COVID-19 were randomized in 1:1 ratio to receive either azelastine (1 mg/mL) nasal spray plus standard supportive care or a matching placebo nasal spray plus supportive care using a computer-generated randomization scheme (
Supplementary Table S3).
The randomization was simple and there was no restriction on randomization, such as blocking and block size. All participants, care providers, and assessors were blinded after assignment to interventions. Randomization and blinding were achieved using unique serial numbers and coded treatment kits, along with sealed emergency envelopes containing treatment sequences. An independent biostatistician (randomizer) was involved in the generation of the random allocation sequence. Individual sites were responsible for the enrollment of participants. The investigational products were packed and labelled by the Sponsor and were assigned to the participants.
2.4. Procedures
After obtaining the informed consent, a thorough clinical history, physical examination, measurement of vital signs and laboratory parameters including SpO2 levels were conducted for evaluation and eligibility assessment.
Samples for RATs were collected for the detection of COVID-19. All subjects detected positive on the RAT were enrolled and the treatment was initiated on the same day, as per the randomization schedule. Simultaneously, samples nasopharyngeal swabs (for RT-PCR test as confirmatory diagnosis of COVID-19) were collected on the same day. The RT-PCR positive subjects, regardless of symptoms, were continued in the study; RT-PCR negative subjects were considered a screen failure. Subjects were randomly assigned to one of the two treatment groups and given a blinded study medication with instructions on how to self-administer each dose. The nasal spray bottles for both the groups were identical. The azelastine formulation included 1 mg/mL of azelastine hydrochloride (i.e., 0.1%) in a solution containing various excipients (disodium edetate, hypromellose, disodium phosphate dodecahydrate, citric acid sodium chloride, and water), while the visually identical placebo had the same excipients minus the active drug.
The study comprised 6 visits over a period of 30 days. Visit 1 (day 1) serves as the screening/baseline/treatment visit, followed by subsequent visits: Visit 2 (days 3+1), Visit 3 (days 6+1), Visit 4 (days 11+1 - End of Treatment [EOT]), and follow-up visits: Visit 5 (days 15+1), and Visit 6 (days 30+1- End of Study). In case of persistent symptoms, another follow-up visit was to be scheduled on day 60 (±1 day).
Clinical condition of participants was assessed by the investigators using the WHO 11-category ordinal score ranging from a score of 0 to 10, classifying the subject’s status as uninfected, mild, moderate, or severe. Additionally, the alteration in subject status was displayed as the variance between the temperature and blood SpO2 measurements at each visit compared to their respective baseline measurements.
The treatment phase spanned 11 days, and data for quantitative RT-PCR, severity of symptoms, and safety assessment including adverse events (AEs) and change in laboratory parameters like blood oxygen levels and temperature were collected on day 1, day 3, day 6 and day 11. The study procedures and assessments schedule are provided in (
Supplementary Table S4).
2.5. Efficacy Outcomes
The study's primary endpoints focused on assessing the rate of COVID-19-related hospitalization in subjects with SARS-CoV-2 infection between the treatment and control groups up to day 11 and determining the reduction in mean virus load via quantitative RT-PCR using nasopharyngeal swabs from baseline (day 1) to day 3, day 6, and day 11.
Secondary endpoints included the proportion of subjects exhibiting a 10-fold decrease in virus load, tracking changes in symptom severity using MoH checklist, assessing subjects’ status with an 11-category scale proposed by WHO, and determining the proportion of subjects achieving negative conversion of SARS-CoV-2 via RT-PCR as well as time to cure. All the above endpoints were evaluated from baseline [day 1] to day 3, day 6, and day 11.
Exploratory analysis was conducted to analyse subjects with initial cycle threshold (Ct) values below <20 and <25, and assess them based on their vaccination status, grouping them into categories of not vaccinated and those who received one, two, or three doses of the vaccine.
2.6. Safety Outcomes
Safety and tolerability of azelastine nasal spray treatment (secondary endpoints) included the assessment of adverse events (AEs) post-randomization until day 30. Safety parameters included AEs, vital signs, physical examination, and laboratory results. The variations from the initial measurements in vital signs and laboratory parameters including the SpO2 and temperature levels were assessed on baseline (day 1) to day 3, day 6, and day 11.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Primary and secondary efficacy analyses were performed on both safety and per protocol (PP) population. All safety analyses were performed using the safety analysis set. For reporting of demographics and frequency of ongoing medical information full analysis set (FAS) was used.
The primary outcome of COVID-19-related hospitalization (and not due to co-morbid conditions) was analyzed through logistic regression to ascertain the efficacy of the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray. This rate measured the proportion of subjects confirmed with SARS-CoV-2 and subsequently hospitalised at specific visits compared to the total subjects present at that visit.
The second primary endpoint which compared the reduction in mean virus load (area under the curve [AUC] analysis) between two treatment groups was performed using Chi square test for categorical variables, and continuous variables were analyzed using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) with the relevant covariates (baseline, visit, and treatment). The change from baseline was determined by subtracting the virus load at follow-up visits from the baseline value, considering log-transformed virus load measurements. The AUC was calculated using a linear trapezoidal rule, incorporating all time points including unscheduled ones from days 1, 3, 6, and 11. Any potential post-hoc situations would prompt adjustments in the analysis method, potentially involving model-based simulations for the primary outcome variable if necessary. All tests were two-sided, maintaining a 5% significance level. Two-group comparisons were examined with the Kruskal-Wallis test.
Safety analyses were carried out on the entire set of randomized participants who had been administered a minimum of one dose of the study drug or placebo (Safety Analysis Set) and included AEs, vital signs, physical examinations, and laboratory findings. Descriptive statistics were used to summarise vital signs and laboratory data for continuous parameters.
All analyses were performed using the statistical software package SAS® version 9.4 or higher (SAS Institute Inc., USA). No interim analysis was planned.
The sample size was calculated based on the viral load mean values observed in a previously performed phase II study (CARVIN). The viral load mean values observed in the CARVIN study for azelastine 0.1% group at baseline and day 11 were 6.52 log10 copies/mL [±1.94 Standard deviation (SD)] and 2.36 log10 copies/mL (±2.12 SD), respectively. Corresponding values noted in the control group were 6.30 log10 copies/mL (±2.11 SD) and 2.75 log10 copies/mL (±1.82 SD), respectively. A two-sided α = 0.05 and a power of 80%, a sample size of 126 subjects per treatment group was calculated. Anticipating a drop-out rate of 15%, the aim was to randomize 290 subjects in total (145 subjects per treatment group) to result in 126 subjects per group completing the study and being eligible for analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Subject Disposition
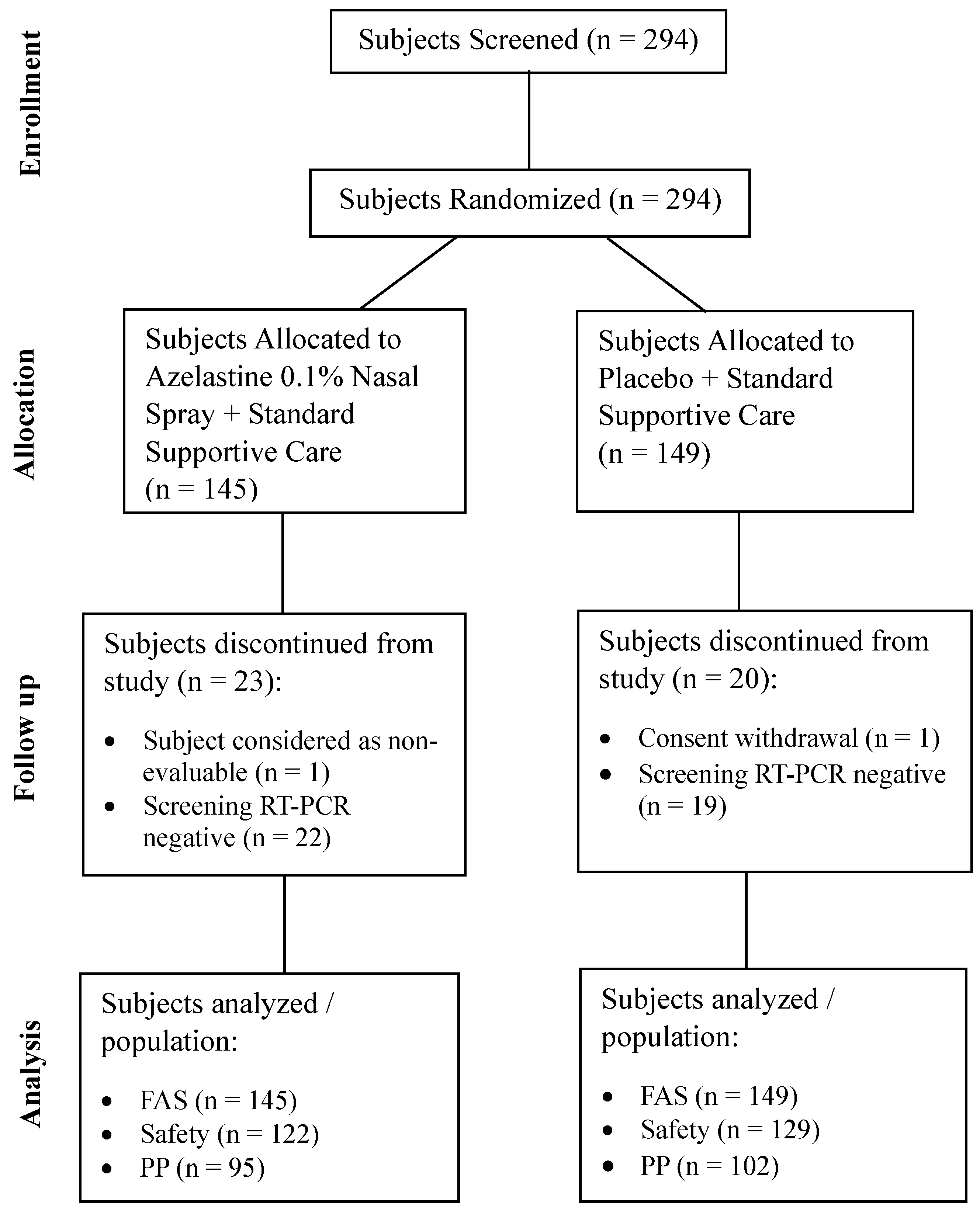
The study was conducted at 10 sites in India commencing on Sep 27, 2022 (first participant first visit) and concluding on May 16, 2023 (last participant last visit). A total of 294 subjects were screened. All screened subjects were randomized in 1:1 ratio to azelastine 0.1% nasal spray or placebo group. Of the 294 subjects, 251 (85.4%) completed the study and were included in the safety population. A total of 43 (14.6%) subjects discontinued from the study and did not receive even one dose of the study medication. The reasons for discontinuation were “a negative RT-PCR screening result reported post-randomization” in 22 (15.2%) subjects in the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray group and 19 (12.8%) subjects in the placebo group, followed by “withdrawn consent” in one subject (0.7%) in the placebo group and “subject considered as non-evaluable” in 1 subject (0.7%) in the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray group (
Figure 1).
Abbreviation: FAS=Full Analysis Set; PP=Per-protocol; RT-PCR=Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction; FAS: FAS Population included data from all randomized subjects regardless of the treatment actually received; Safety: All subjects who received at least 1 dose of randomized IMP, or Placebo and for whom any post-dose data were available included in the safety analysis set.
Per Protocol: All subjects from safety analysis set completing the study without major protocol deviations and had their baseline RT-PCR report as positive were included in the PP analysis set.
Of those 251 subjects, 54 (21.5%) subjects reported at least one major protocol deviation/violation, hence a total of 197 (78.5%) subjects were included in the PP population. Of those 197 subjects, 95 (48.2%) subjects belonged to the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray treatment group, and 102 (51.8%) subjects belong to the placebo group. Mean treatment compliance was >90% and comparable between both groups.
3.2. Subjects’ Baseline Characteristics
Both groups had comparable baseline and demographic characteristics, thus excluding a systematic bias and allowing a very good comparability of treatment effects. Of the 251 subjects included in the safety population, 153 (61.0%) were male, the mean (SD) age of all subjects was 39.9 (15.11) years, and all the subjects (100.0%) were Asian (
Table 1). Two doses of COVID-19 vaccine were received by 38.5% subjects in the azelastine 0.1% group and 34.1% in the placebo group. The frequency of ongoing medical information (subject health information) in FAS was similar between the two groups [14 subjects (9.7%) in the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray treatment group vs. 13 subjects (8.7%) in the placebo group]. The most frequent medical history of subjects by system organ class (SOC) and preferred terms (PT) were hypertension (4.8%) and diabetes mellitus (3.4%) (
Supplementary Table S5).
3.3. Efficacy
3.3.1. Rate of COVID-19 Related Hospitalization
The primary efficacy endpoint was hospitalization due to COVID-19 infection (and not due to comorbid conditions). There was no incidence of COVID-19 related hospitalization in subjects with SARS-CoV-2 infection in both treatment groups.
3.3.2. Viral SARS-CoV-2 RNA Load Reduction
The second primary endpoint was to compare the reduction in the mean virus load between the two treatment groups. On the log-transformed scale, the mean virus load value (genEq/mL log
10) at baseline was higher in the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray treatment group as compared to that in the placebo group (log
10 6.32 vs. log
10 6.20). The log-transformed mean virus load was adjusted to median and then corrected at zero. There was a significant reduction in the mean virus load in both groups during the 11 treatment days as compared with baseline. The reduction in virus load in the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray group was significantly higher than the reduction in the placebo group at day 11 (log
10 5.93 vs. log
10 5.85, p=0.0041). Similar results were observed at day 3 (log
10 2.80 vs. log
10 2.62, p<0.0001) and day 6 (log
10 5.05 vs. log
10 4.94, p=0.0013) (
Table 2).
Evaluation of the AUC value based on simulated log-transformed virus load values showed that the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray treatment group exhibited a greater AUC value 1014.960±35.2527, referring to a greater decrease in viral load, compared to the placebo group with an AUC value 982.977±31.6776 (p<0.0001) (
Table 3).
The median time to cure was similar between both groups (225 hours; hazard ratio and 95% Confidence Interval [CI]: 0.32 [0.83, 2.32]; p=0.2161) (
Supplementary Table S6).
3.4. Exploratory Analysis for Robustness of the Primary Endpoint
Robustness of the primary efficacy endpoint (decrease in mean virus load) was checked by exploratory analysis. Subgroups (i.e., initial Ct value <20 and <25 as well as based on vaccination status [not vaccinated and one/two/three dose(s) of vaccine]) were also checked by exploratory analysis. There was a significant reduction in mean virus load in both the treatment groups at day 3, day 6 and day 11 when compared to baseline (p<0.0001) for all subgroup populations (initial Ct value <20 and <25; vaccination status: not vaccinated and one/two/three dose of vaccine). Additionally, exploratory analysis was also performed on the PP population. Results of the efficacy endpoints (decrease in mean virus load and AUC assessment for virus load) with PP population were comparable to the results obtained in the safety population which indicated that there was no impact of protocol deviations/violations on the efficacy analysis results, i.e. superior efficacy of treatment (azelastine 0.1% nasal spray) over control (placebo nasal spray) is supported through this sensitivity analysis.
3.4.1. Subjects Demonstrating a 10-Fold Decrease in SARS-CoV-2 Virus Load
The proportion of subjects that demonstrated a 10-fold decrease in virus load of SARS-CoV-2 was comparable at all subsequent visits between both groups (
Supplementary Table S7).
3.4.2. Subjects with Negative Conversion of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR
The proportion of subjects with negative conversion of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR was increased gradually at all subsequent visits when compared to baseline in both groups. The proportion of subjects with negative RT-PCR results were comparable between the two groups at day 3, day 6 and day 11. More than 90% of subjects were found negative in RT-PCR test results at day 11 in both treatment groups (
Supplementary Table S8).
3.4.3. Change in Symptom Severity (Based on MoH FW Checklist)
The analysis of symptoms severity (symptom score based on MoH FW checklist) in both groups at baseline showed that the patients were predominantly mildly symptomatic (i.e., anorexia, cough, diarrhea or gastrointestinal upset, fever, headache, loss of smell, loss of taste, malaise, nausea, sore throat or throat irritation, vomiting, and weakness). During the treatment, both groups showed clear improvements in the severity of symptoms, and the majority of symptoms were resolved at day 11 in both groups. However, azelastine 0.1% nasal spray treatment was associated with significant improvement in fever (p=0.0046), weakness (p=0.0012) and hypoxia (p<0.0001) compared to placebo group.
None of the subjects showed symptoms of mild COVID-19, as outlined by the MoH FW, Government of India, during Visit 6 (day 30±1 day). Therefore, no further follow-up visit (to be scheduled on day 60 (±1 day)) had to be arranged.
3.4.4. Change in Subject Status (Based on WHO’s 11-Category Ordinal Score)
The subject status was assessed using an 11-category ordinal score as proposed by the WHO which allows classification of the subject’s status as uninfected, mild, moderate, or severe (Score: 0 to 10). The mean ordinal score proposed by WHO clinical progression scale was similar at baseline between the two groups (Score 2). The mean ordinal score was decreased significantly (p<0.0001) at day 3, day 6, day 11 and day 15 in both groups as compared with baseline. At day 6, the mean ordinal score was almost “0” (0.4 in both groups) which reflects that there was no viral RNA detected and clear improvement in subject’s clinical status (
Supplementary Table S9).
3.5. Safety
The number of subjects that reported at least one adverse event (AE) and overall incidence of AEs were similar between the two groups. A total of 79 subjects (31.5%) experienced at least one AE (total incidence of AEs=99). A total of 39 subjects (32.0%) in the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray treatment group and 40 subjects (31.0%) in the placebo group reported 48 and 51 AEs respectively. All AEs were considered as treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) in both groups. All 39 subjects (32.0%) in the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray treatment group reported only mild AEs. One subject (0.8%) in the placebo group reported moderate AE in the study and the remaining 40 subjects (31.0%) reported mild AEs. In both groups, all the AEs were not related to the investigational treatment. There was no action taken with study medication due to AEs and all AEs were recovered/resolved in both treatment groups. There was no serious adverse event (SAE) reported in the study (
Supplementary Table S10).
The most common AEs reported by the subjects (≥5%) in both groups were asthenia in 28 (11.2%) followed by nausea in 21 (8.4%), myalgia in 18 (7.2%), and headache in 16 (6.4%) subjects (
Table 4). There was no death or other significant AE reported in either of the treatment groups.
There were no clinically significant changes in vital signs (i.e., diastolic blood pressure, pulse rate, respiration rate, and systolic blood pressure) at post baseline visit when compared to baseline in both treatment groups. However, clinically significant changes were observed in SpO2 which increased gradually at post baseline visits (day 3, day 6, day 11, day 15 and day 30) and temperature decreased at post baseline visits (day 3, day 6, and day 11) when compared to baseline visit (day 1) in both groups. The mean change in SpO2 at day 11 from baseline was identical in both groups (1.0% in both groups). Similarly, the mean change in temperature at day 11 from baseline was comparable between the two groups (-2.1°F in the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray treatment group and -2.2°F in the placebo group).
There were no clinically relevant trends observed in the majority of haematology, biochemistry, and urinalysis laboratory parameters at day 11 and day 15 when compared to baseline in both groups. Majority of the subjects in both groups had either normal or abnormal clinically not significant laboratory results at day 11 and day 15. Overall, based on the safety results of the study it was concluded that azelastine 0.1% nasal spray was safe and well-tolerated by the subjects.
4. Discussion
COVID-19 starts with the infection of the nasal mucosa and the nasopharynx; therefore, application of locally acting antiviral agents appears to be particularly promising. The obtainability of a self-administrable nasal spray may reduce subsequent viral transmission and thus offers great advantage for the community [
17]. For instance, nitric oxide (NO) and the preventive application of a hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) nasal spray have shown to reduce the viral load in adult subjects with mild COVID-19 infections [
18,
19]. Meanwhile NO and HPMC nasal sprays appear to act via rather unspecific mechanisms – HPMC by forming a physical barrier on the mucosal surface and NO by nitrosylation of proteins – the well-established antihistaminic OTC-drug azelastine appears to exhibit pharmacological antiviral properties via specific interactions with viral and host target proteins. So far, azelastine has been suggested to inhibit the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the nasal mucosa by binding to the ACE-2 receptor, furthermore by inhibiting the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 as well as the host cell’s sigma-1 receptor, therewith facilitating both viral entry and replication-inhibiting effects [
11,
12]. Azelastine was furthermore found to inhibit inflammation and intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) upregulation induced by viral infections, effects that may contribute to the antiviral activity observed also against non-coronaviruses [
14].
In the present study, subjects were eligible for treatment after confirmation of positive RT-PCR test, and if enrolled no later than 48 h after swab sampling. It is anticipated that virus load is at peak during the initial phase of the disease, considering the current study setting wherein the treatment with azelastine started during the symptomatic phase of the disease; this scenario corresponds to current COVID-19 treatment regimens (e.g., with monoclonal antibodies or antiviral substances) which are usually started at ≤5–7 days upon start of symptoms, and are still efficacious. Indeed, the strongest decrease in viral load was seen in this trial within the first days of treatment with azelastine nasal spray, as was observed already previously [
15].
The study reported no incidence of COVID-19 related hospitalization in both treatment groups up to day 11, indicating overall rather mild courses of the disease in this trial. The outcome of the primary efficacy endpoint in this study is far better than the study conducted by Sinha et al.[
20], where 9 (1.48%) molnupiravir plus standard of care treated and 26 (4.26%) standard of care alone treated subjects required hospitalization. Similarly, in a phase III, double-blind study conducted by Jayk Bernal et al. [
21] in non-hospitalised, unvaccinated subjects with mild-to-moderate, laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 infection, the risk of hospitalization for any cause or death through day 29 was lower with molnupiravir (28/385 [7.3%]) than with placebo (53/377 [14.1%]).
The second primary endpoint (decrease in mean virus load) was measured as the virus load change from baseline and virus load AUC based on the qRT-PCR values. The review of the study data revealed an unexpected baseline imbalance in the outcome variables virus load and log-transformed virus load between the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray and placebo treatment group. Thus adjusted baseline values were centered at zero for both groups to assess within- and between-treatment significance. The Longitudinal ANCOVA model’s fixed effects were used to simulate normal random samples for treatment effects and variances, transforming outcome variables as needed.
The study population in the current study had an initial mean virus load of log
10 6.26 ± 1.16 genEq/mL which was lesser than more recently reported SARS-CoV-2 virus load values, and the rate of negative testing’s increased earlier as compared to the first phase II clinical trial investigating the efficacy of azelastine nasal spray [
15]. This observation may be explained with a) the evolution of the virus (meanwhile the alpha variant was dominating during conduction of the referenced phase II clinical trial [
15], omicron variants dominated during this clinical trial), b) very likely with the much higher rate of preceding infections and vaccinations, causing an earlier and specific antiviral immune-response in patients included into this trial, and c) potentially also due to the different populations included into both studies (dominantly European vs. Asian populations, respectively). Self-administered azelastine 0.1% nasal spray in this study, had a statistically significant greater mean reduction in SARS-CoV-2 RNA log
10 copies/mL over the 11 days of treatment compared to placebo. The results of mean reduction in virus load observed in this study are in line with the results of Tandon et al. [
22] where self-administered NO nasal spray (six times daily as two puffs per nostril for seven days; 0.45 mL solution/dose) was associated with a significantly better reduction in the mean virus load throughout the treatment period compared to subjects treated with placebo. Similarly, in the phase II CARVIN study, azelastine nasal spray 0.1% three times daily for 11 days of treatment was associated with greater virus load reduction compared to placebo (p=0.007) [
15]. Meanwhile the NO nasal spray was administered six times daily, azelastine 0.1 % nasal spray was applied three times daily in the study of Klussmann et al. [
15] and five times daily in the reported study, based on a pharmakometric analysis of the CARVIN data indicating a greater benefit of a five-fold application per day [
23].
In the present study, the mean AUC assessment for virus load over the 11-day treatment period was significantly greater in the azelastine 0.1% nasal spray treatment group as compared to the placebo group (1014.960 vs. 982.977, p<0.0001). The results (azelastine 0.1% group AUC value: 24.14±13.12 vs. placebo group AUC value: 18.89±4.70, p=0.007) of the earlier phase II CARVIN study [
15] were coherent with the present study.
Throughout the treatment, there were noticeable improvements in symptom severity for both groups in this trial, with most symptoms resolving by day 11. At day 11, the mean ordinal score proposed by WHO was 0.1 in both groups which proves that there was no viral RNA detected. This underlines the overall mild course of disease in the observed population and could be cautiously interpreted as an indication of a fundamental decrease in the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections.
This is furthermore supported, since in the present study, over 90% of subjects in both groups were tested negative for RT-PCR by day 11, which is a much higher rate than observed in the previous phase II study [
15], wherein the negative PCR results appeared earlier and more frequently in the azelastine treated groups, with 48.2% of patients exhibiting a negative result by day 11 in the 0.1% azelastine group versus only 23.1% of the patients in the placebo group.
Future research approaches of locally applied antiviral agents could therefore focus on the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infections rather than on reducing the symptoms of the already increasingly mild courses of the disease, considering that even after mild acute infections there is still a high rate of long-lasting COVID symptoms.
Generally, treatment with azelastine appeared safe in SARS-CoV-2 positive subjects: no SAEs or death were reported in the current study, and the number of AEs were comparable between groups. These observations are similar to the previous phase II CARVIN study where subjects receiving either azelastine nasal spray or placebo had comparable AEs with no safety concerns [
15]. The comparable compliance between treatment groups (90.8% in azelastine 0.1% nasal spray vs. 92.5% in placebo group) further supported the observation that the tolerability of the investigational medicinal products did not negatively impact treatment adherence.
The present study showed both strengths and limitations. Thus, eligibility criteria were designed carefully to investigate a clearly defined, homogeneous study population of low-risk subjects with a narrow age range. In addition, intervals between swab sampling were short and the overall number of performed RT-PCR tests was high to allow a very close determination of the virus clearance. Furthermore, we cannot rule out the possibility that the placebo contributed to viral clearance, leading to an overall underestimation of azelastine’s treatment effect. Rinsing and diluting effects as well as the formation of a physical barrier (HPMC is one ingredient of the formulation) might have contributed to such effects.
5. Conclusions
Overall, no incidence of COVID-19 related hospitalization, accompanied by significant reduction in viral load and improvements in symptom severity in this study support the use of azelastine 0.1% nasal spray in subjects tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 with mild symptoms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org: Table S1: List of IECs or IRBs; Table S2: Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria; Table S3: Randomisation Procedure; Table S4: Study Procedures and Assessments Schedule; Table S5: Ongoing Medical Information (Subject Health Information) – FAS Population; Table S6: Time to Cure (Safety Population) ; Table S7: Proportion of Subjects Demonstrating a 10-fold Decrease in Virus Load of SARS-CoV-2 (Safety Population) ; Table S8: Shift from Baseline in RT-PCR Results Across Visits (Safety Population); Table S9: Change in Subject Status Using an 11-Category Ordinal Score as Proposed by the World Health Organisation (WHO) (Safety Population); Table S10: Overall Summary of Adverse Events (Safety Population)
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.M., M.F. and F.H.; methodology, P.M. and R.J.; software, R.J.; validation, R..J.; formal analysis, P.M, D.G., C.S., B.S., R.J.; investigation, CARVIN-II study group; resources, P.M., R.J. and F.H.; data curation, R.J..; writing—original draft preparation, R.J.; writing—review and editing, P.M. and all involved authors; supervision, P.M.; project administration, P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The Clinical Trial was funded by URSAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by all involved Institutional Review Boards and Ethics Committees. A full list of the Institutional Review Boards and Ethics Committees involved is provided in the
Supplementary Table S1. The study was conducted in accordance with the Good Clinical Practice, the Declaration of Helsinki, and all applicable local and national regulatory requirements.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy restrictions. The study protocol is available in the appendix.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all CARVIN-II Study Group Investigators: Rajas Walinjkar, Seven Hills Healthcare Pvt. Ltd., Mumbai, India; Sachin Shivnitwar, Lifepoint Multispeciality Hospital, Pune, India; Deepak Siddavaram, Saideep Healthcare and Research Pvt. Ltd., Ahmednagar, India; Govardhan Rao MV, Excel Hospital, Secunderabad, India; Sandeep Laxman Dandin, Belagavi Institute Of Medical Sciences, Belagavi, India; Rajesh Jagannath Khayallapa, D.Y. Patil Medical College, Kolhapur, India; Sandeep Jain, Tagore Hospital and Research Center, Jaipur, India; Mohd Zaki Siddiqui, MLB Medical College, Jhansi, India; Rakesh Patil, Kkasturi Medicare Pvt Ltd., Mumbai, India; Ajit Avhad, Indus Diabetes and Obesity Centre, Thane, India. The authors acknowledge Parveen Kumar, PharmaLex India Pvt. Ltd., Noida, India for providing manuscript writing support. The authors acknowledge the clinical research organization involved in the study Jehangir Clinical Development Center, Maharashtra, India.
Conflicts of Interest
Peter Meiser, Michael Flegel, Dorothea Groß, Charlotte Steinmetz and Barbara Scherer are employed at URSAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH, Frank Holzer is the CEO of URSAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH, the sponsor of the clinical trial. Rajesh Jain is employed at PharmaLex India Pvt. Ltd, the CRO which organized this trial.
References
- Panahi, Yunes, Armita Mahdavi Gorabi, Sona Talaei, Fatemeh Beiraghdar, Abolfazl Akbarzadeh, Vahideh Tarhriz, and Hassan Mellatyar. "An Overview on the Treatments and Prevention against Covid-19." Virology Journal 20, no. 1 (2023): 23. [CrossRef]
- Cascella M, Rajnik M, and et al. Aleem A. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (Covid-19) [Updated 2023 Aug 18]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.
- update, World Health Organization: COVID-19 epidemiological. "World Health Organization: Covid-19 Epidemiological Update " https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update---22-december-2023.
- COVID-19, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. "Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. Covid-19." https://www.mohfw.gov.in/.
- Balasubramani, Karuppusamy, Venkatesh Ravichandran, Kumar Arun Prasad, Mu Ramkumar, Sulochana Shekhar, Meenu Mariya James, Naveen Kumar Kodali, Sujit Kumar Behera, Natarajan Gopalan, Rakesh Kumar Sharma, Devojit Kumar Sarma, M. Santosh, Aditya Prasad Dash, and Praveen Balabaskaran Nina. "Spatio-Temporal Epidemiology and Associated Indicators of Covid-19 (Wave-I and Ii) in India." Sci Rep 14, no. 1 (2024): 220. [CrossRef]
- Parasher, Anant. "Covid-19: Current Understanding of Its Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and Treatment." Postgraduate Medical Journal 97, no. 1147 (2020): 312-20. [CrossRef]
- Killingley, Ben, Alex J. Mann, Mariya Kalinova, Alison Boyers, Niluka Goonawardane, Jie Zhou, Kate Lindsell, Samanjit S. Hare, Jonathan Brown, Rebecca Frise, Emma Smith, Claire Hopkins, Nicolas Noulin, Brandon Löndt, Tom Wilkinson, Stephen Harden, Helen McShane, Mark Baillet, Anthony Gilbert, Michael Jacobs, Christine Charman, Priya Mande, Jonathan S. Nguyen-Van-Tam, Malcolm G. Semple, Robert C. Read, Neil M. Ferguson, Peter J. Openshaw, Garth Rapeport, Wendy S. Barclay, Andrew P. Catchpole, and Christopher Chiu. "Safety, Tolerability and Viral Kinetics During Sars-Cov-2 Human Challenge in Young Adults." Nature Medicine 28, no. 5 (2022): 1031-41. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Li, Rong-juan Pei, Heng Li, Xin-na Ma, Yu Zhou, Feng-hua Zhu, Pei-lan He, Wei Tang, Ye-cheng Zhang, Jin Xiong, Shu-qi Xiao, Xian-kun Tong, Bo Zhang, and Jian-ping Zuo. "Identification of Sars-Cov-2 Entry Inhibitors among Already Approved Drugs." Acta Pharmacol Sin 42, no. 8 (2021): 1347-53. [CrossRef]
- Ghahremanpour, M. M., J. Tirado-Rives, M. Deshmukh, J. A. Ippolito, C. H. Zhang, I. Cabeza de Vaca, M. E. Liosi, K. S. Anderson, and W. L. Jorgensen. "Identification of 14 Known Drugs as Inhibitors of the Main Protease of Sars-Cov-2." ACS Med Chem Lett 11, no. 12 (2020): 2526-33. [CrossRef]
- Jain, R., and S. Mujwar. "Repurposing Metocurine as Main Protease Inhibitor to Develop Novel Antiviral Therapy for Covid-19." Struct Chem (2020): 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Odhar, H. A., S. W. Ahjel, Aama Albeer, A. F. Hashim, A. M. Rayshan, and S. S. Humadi. "Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulation of Fda Approved Drugs with the Main Protease from 2019 Novel Coronavirus." Bioinformation 16, no. 3 (2020): 236-44. [CrossRef]
- Reznikov, L. R., M. H. Norris, R. Vashisht, A. P. Bluhm, D. Li, Y. J. Liao, A. Brown, A. J. Butte, and D. A. Ostrov. "Identification of Antiviral Antihistamines for Covid-19 Repurposing." Biochem Biophys Res Commun 538 (2021): 173-79. [CrossRef]
- Konrat, R., H. Papp, J. Kimpel, A. Rössler, V. Szijártó, G. Nagy, M. Madai, S. Zeghbib, A. Kuczmog, Z. Lanszki, T. Gesell, Z. Helyes, G. Kemenesi, F. Jakab, and E. Nagy. "The Anti-Histamine Azelastine, Identified by Computational Drug Repurposing, Inhibits Infection by Major Variants of Sars-Cov-2 in Cell Cultures and Reconstituted Human Nasal Tissue." Front Pharmacol 13 (2022): 861295. [CrossRef]
- Fischhuber, K., Z. Bánki, J. Kimpel, N. Kragl, A. Rössler, A. Bolze, B. Muellauer, J. Angerer, G. Nagy, E. Nagy, and V. Szijarto. "Antiviral Potential of Azelastine against Major Respiratory Viruses." Viruses 15, no. 12 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Klussmann, Jens Peter, Maria Grosheva, Peter Meiser, Clara Lehmann, Eszter Nagy, Valéria Szijártó, Gábor Nagy, Robert Konrat, Michael Flegel, Frank Holzer, Dorothea Groß, Charlotte Steinmetz, Barbara Scherer, Henning Gruell, Maike Schlotz, Florian Klein, Paula Aguiar de Aragão, Henning Morr, Helal Al Saleh, Andreas Bilstein, Belisa Russo, Susanne Müller-Scholtz, Cengizhan Acikel, Hacer Sahin, Nina Werkhäuser, Silke Allekotte, and Ralph Mösges. "Early Intervention with Azelastine Nasal Spray May Reduce Viral Load in Sars-Cov-2 Infected Patients." Sci Rep 13, no. 1 (2023): 6839. [CrossRef]
- (Dte.GHS), AIIMS/ ICMR-COVID-19 National Task Force/Joint Monitoring Group. "Aiims/ Icmr-Covid-19 National Task Force/Joint Monitoring Group (Dte.Ghs) Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India. Clinical Guidance for the Syndromic Management of Suspected Covid–19 Cases." https://dghs.gov.in/WriteReadData/News/202104290258250563281SyndromicapproachforCOVID-19.pdf.
- Marc, Aurélien, Marion Kerioui, François Blanquart, Julie Bertrand, Oriol Mitjà, Marc Corbacho-Monné, Michael Marks, and Jeremie Guedj. "Quantifying the Relationship between Sars-Cov-2 Viral Load and Infectiousness." eLife 10 (2021): e69302. [CrossRef]
- Winchester, Stephen, Sarah John, Kashif Jabbar, and Isaac John. "Clinical Efficacy of Nitric Oxide Nasal Spray (Nons) for the Treatment of Mild Covid-19 Infection." Journal of Infection 83, no. 2 (2021): 237-79. [CrossRef]
- Shmuel, Klang, Megiddo Dalia, Lapidot Tair, and Naparstek Yaakov. "Low Ph Hypromellose (Taffix) Nasal Powder Spray Could Reduce Sars-Cov-2 Infection Rate Post Mass-Gathering Event at a Highly Endemic Community: An Observational Prospective Open Label User Survey." Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy 19, no. 10 (2021): 1325-30. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S., K. N, V. K. Suram, S. S. Chary, S. Naik, V. B. Singh, M. K. Jain, C. P. Suthar, S. Borthakur, V. Sawardekar, N. Sk, N. Reddy, L. Talluri, P. Thakur, M. Reddy, M. Panapakam, and R. Vattipalli. "Efficacy and Safety of Molnupiravir in Mild Covid-19 Patients in India." Cureus 14, no. 11 (2022): e31508. [CrossRef]
- Bernal, Angélica Jayk, Monica M. Gomes da Silva, Dany B. Musungaie, Evgeniy Kovalchuk, Antonio Gonzalez, Virginia Delos Reyes, Alejandro Martín-Quirós, Yoseph Caraco, Angela Williams-Diaz, Michelle L. Brown, Jiejun Du, Alison Pedley, Christopher Assaid, Julie Strizki, Jay A. Grobler, Hala H. Shamsuddin, Robert Tipping, Hong Wan, Amanda Paschke, Joan R. Butterton, Matthew G. Johnson, and Carisa De Anda. "Molnupiravir for Oral Treatment of Covid-19 in Nonhospitalized Patients." New England Journal of Medicine 386, no. 6 (2022): 509-20. [CrossRef]
- Tandon, Monika, Wen Wu, Keith Moore, Stephen Winchester, Yuan-Po Tu, Christopher Miller, Rahul Kodgule, Amol Pendse, Shabbir Rangwala, and Shashank Joshi. "Sars-Cov-2 Accelerated Clearance Using a Novel Nitric Oxide Nasal Spray (Nons) Treatment: A Randomized Trial." The Lancet Regional Health - Southeast Asia 3 (2022).
- Dings, C., P. Meiser, F. Holzer, M. Flegel, D. Selzer, E. Nagy, R. Mösges, J. P. Klussmann, and T. Lehr. "Pharmacometric Modeling of the Impact of Azelastine Nasal Spray on Sars-Cov-2 Viral Load and Related Symptoms in Covid-19 Patients." Pharmaceutics 14, no. 10 (2022). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).