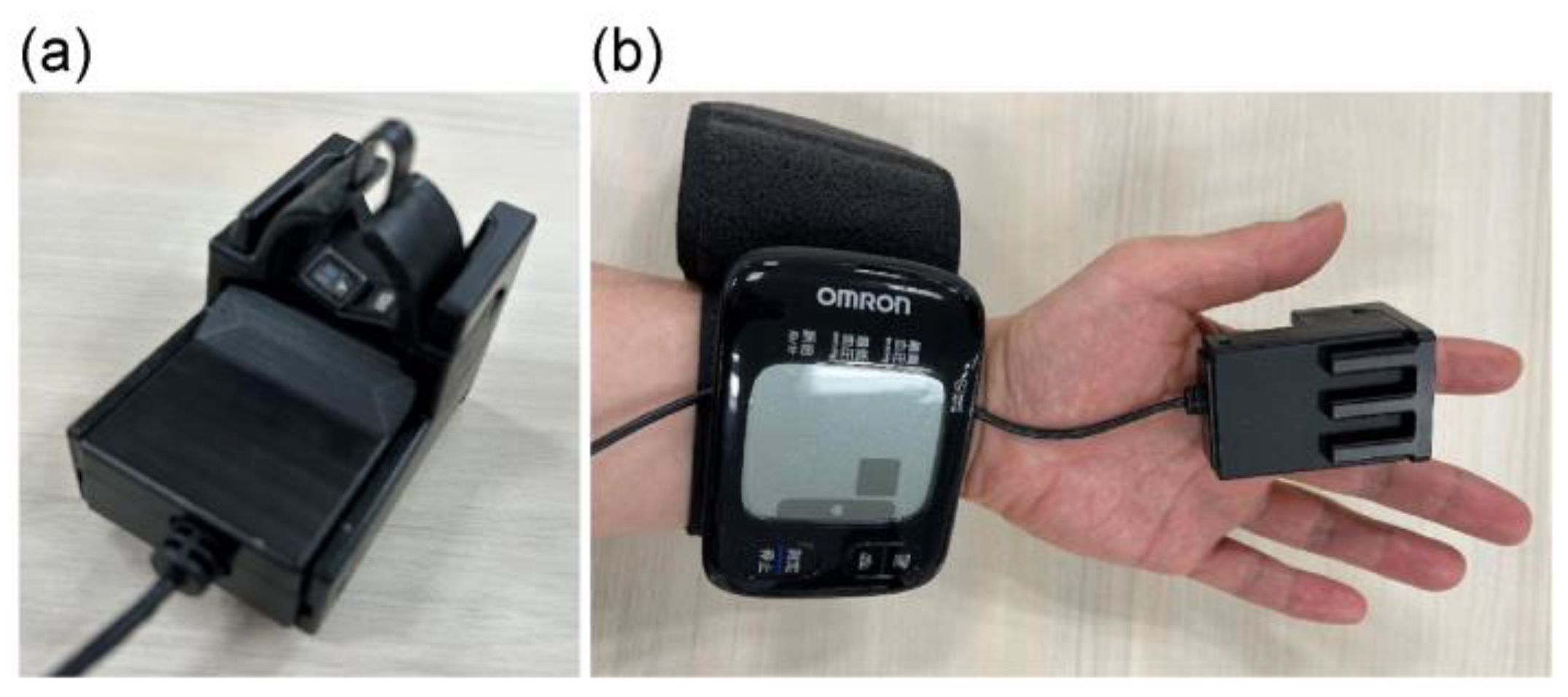
Because the photoplethysmography sensor noise increases when the device does not adhere to the skin, we manufactured a measurement tool that could adhere to the finger. The measurement tool was used to obtain photoplethysmograms from the subjects under multiple measurement conditions with varying peripheral hemodynamics. The wrist blood pressure was also measured under each condition. We also developed a program to calculate the plurality of feature values from the photoplethysmogram, the acquired photoplethysmogram being processed using this program.
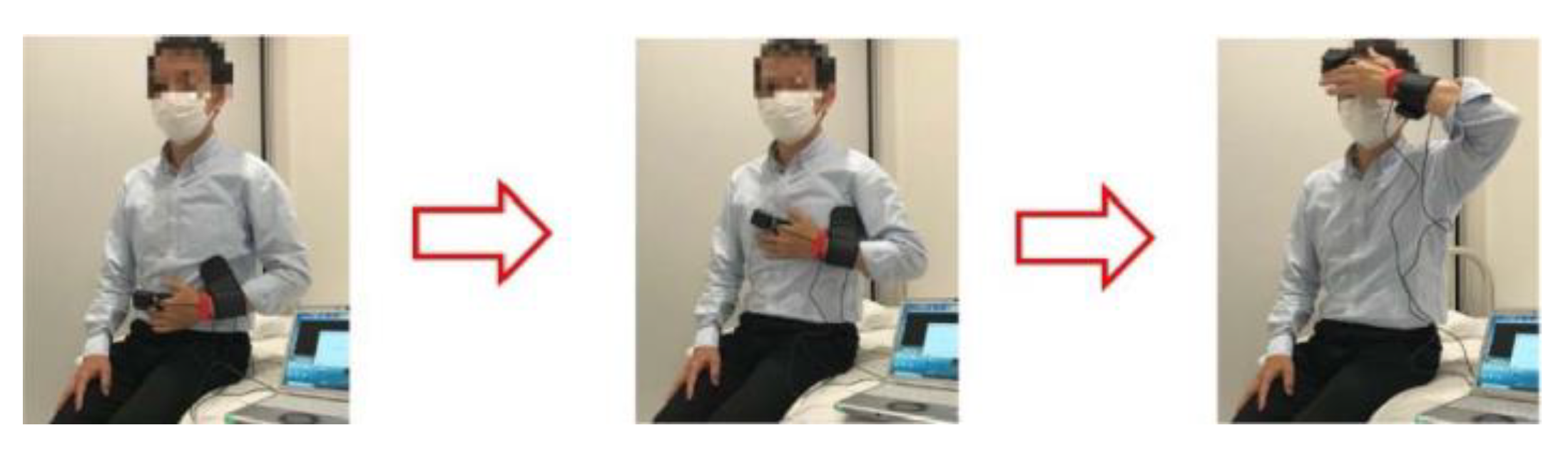
The left elbow was then cooled using a cooling agent, while the left hand was held at chest height. Photoplethysmogram and blood pressure measurements were taken after cooling for at least five minutes. First-order (velocity plethysmogram) and second-order (acceleration plethysmogram) differentiations were obtained from the three measured photoplethysmograms, and each was divided into beats using the program developed in this study.
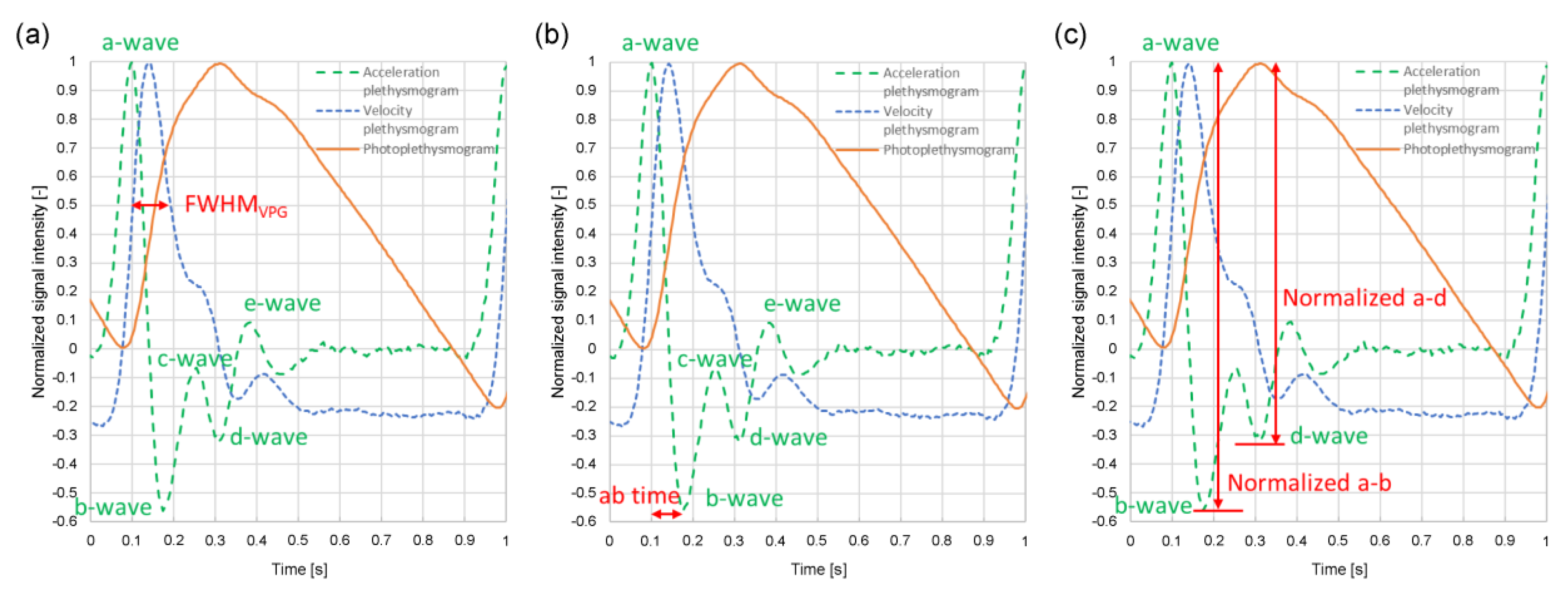
Figure 4 shows the feature values of the velocity and acceleration plethysmograms. The photoplethysmograms are shown as a solid line, the velocity plethysmograms as a dotted line, and the acceleration plethysmograms as a dashed line. Here, we refer to the half-width of the maximum peak of the velocity plethysmogram as the FWHM
VPG. The acceleration plethysmogram is generally called an
a-wave,
b-wave,
c-wave,
d-wave, or
e-wave; the
a-, c-, and
e-waves are positive peaks, whereas the
b- and
d-waves are negative peaks. The difference between the
a-wave and
b-wave peak times is called the
ab time. The signal intensity at the peak apex of the
a-wave to
e-wave can be set as
a-e, the difference between the
a-wave and
b-wave can be set as
a-b, and the difference between the
a-wave and
d-wave can be set as
a-d.
Figure 4 shows the photoplethysmogram, velocity plethysmogram, and acceleration plethysmogram normalized such that the maximum peak is 1. The normalized values are referred to as normalized
a-b and normalized
a-d.
2.1. Delay Time of Green a-Wave Peak from Near-Infrared a-Wave Peak
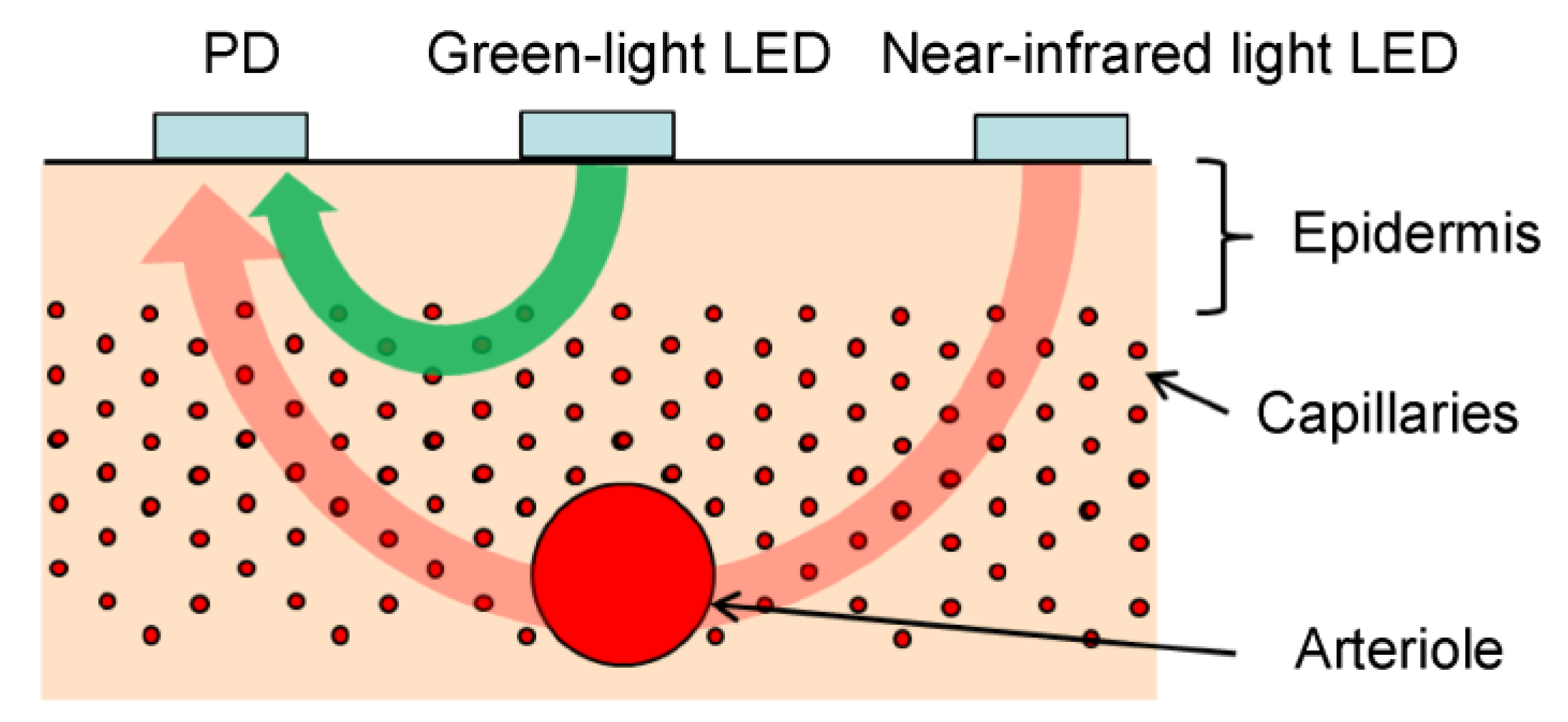
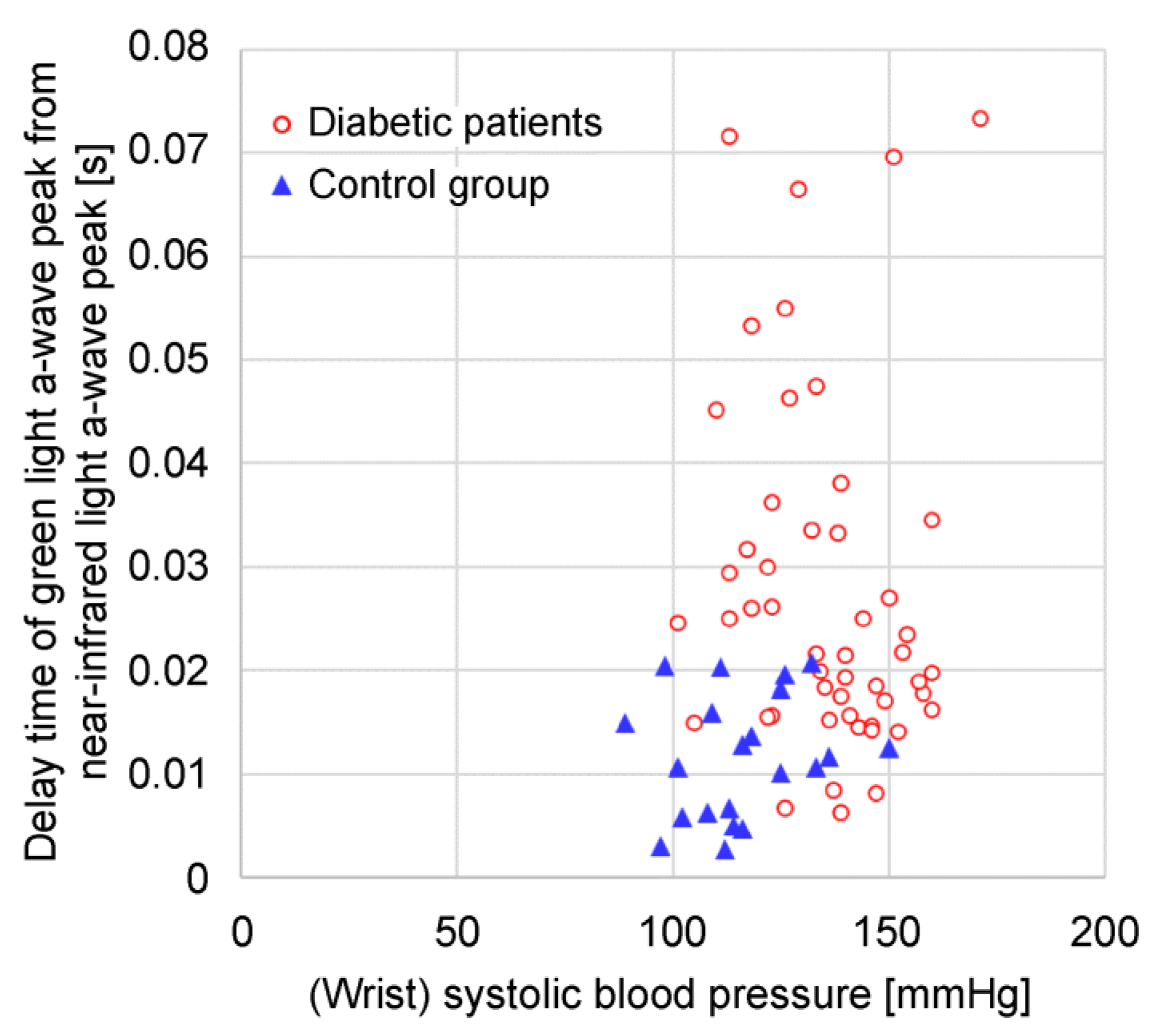
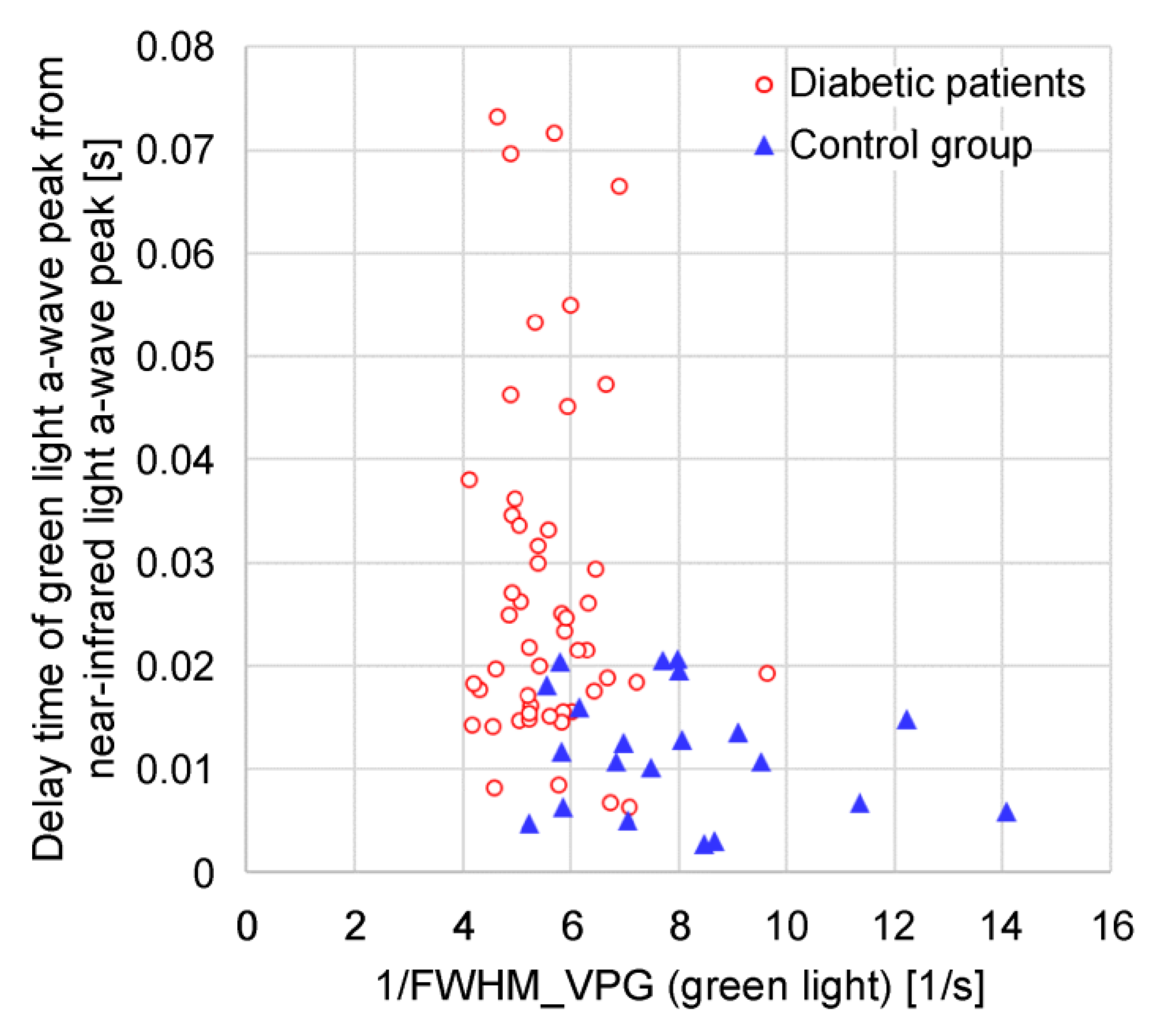
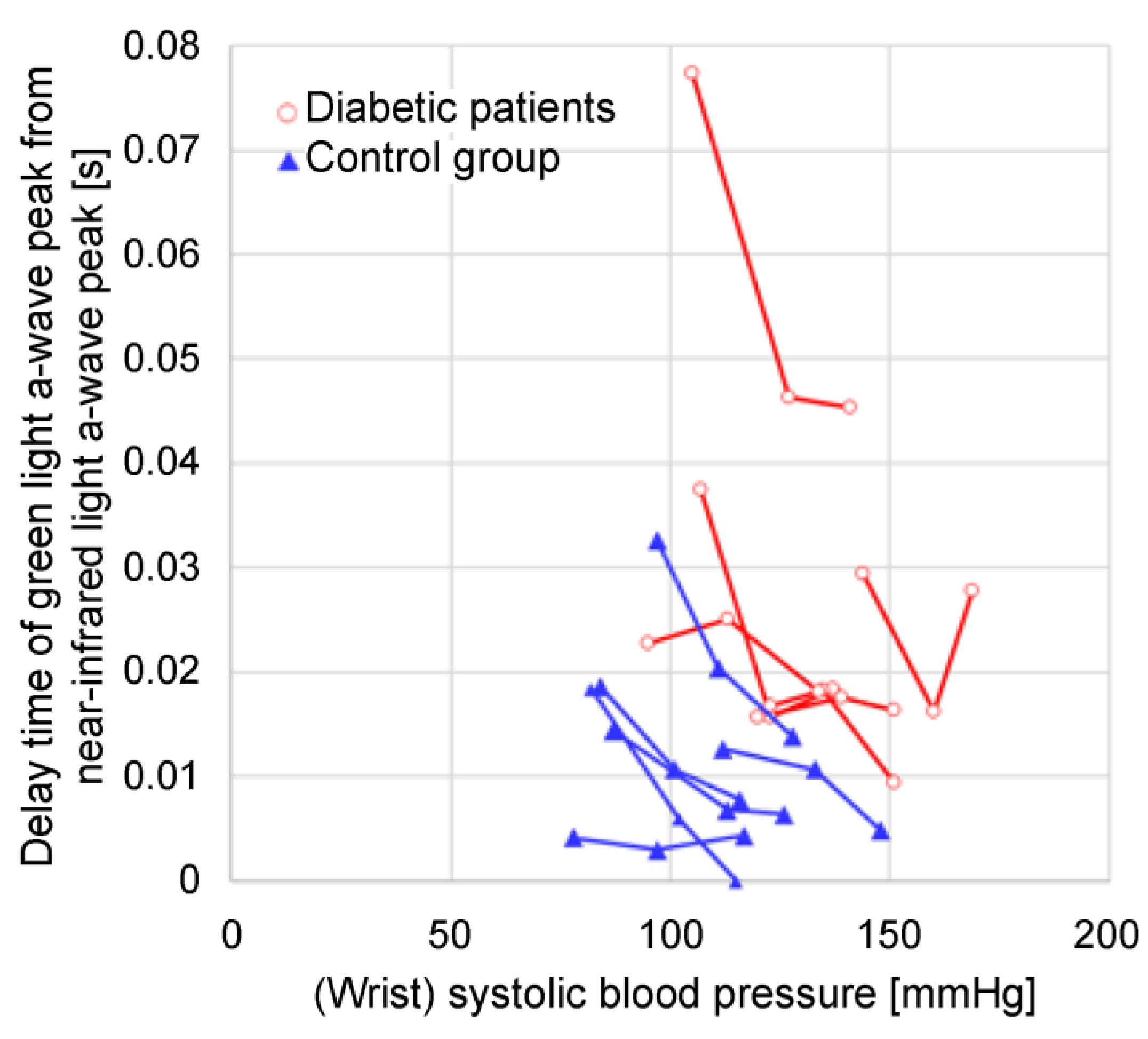
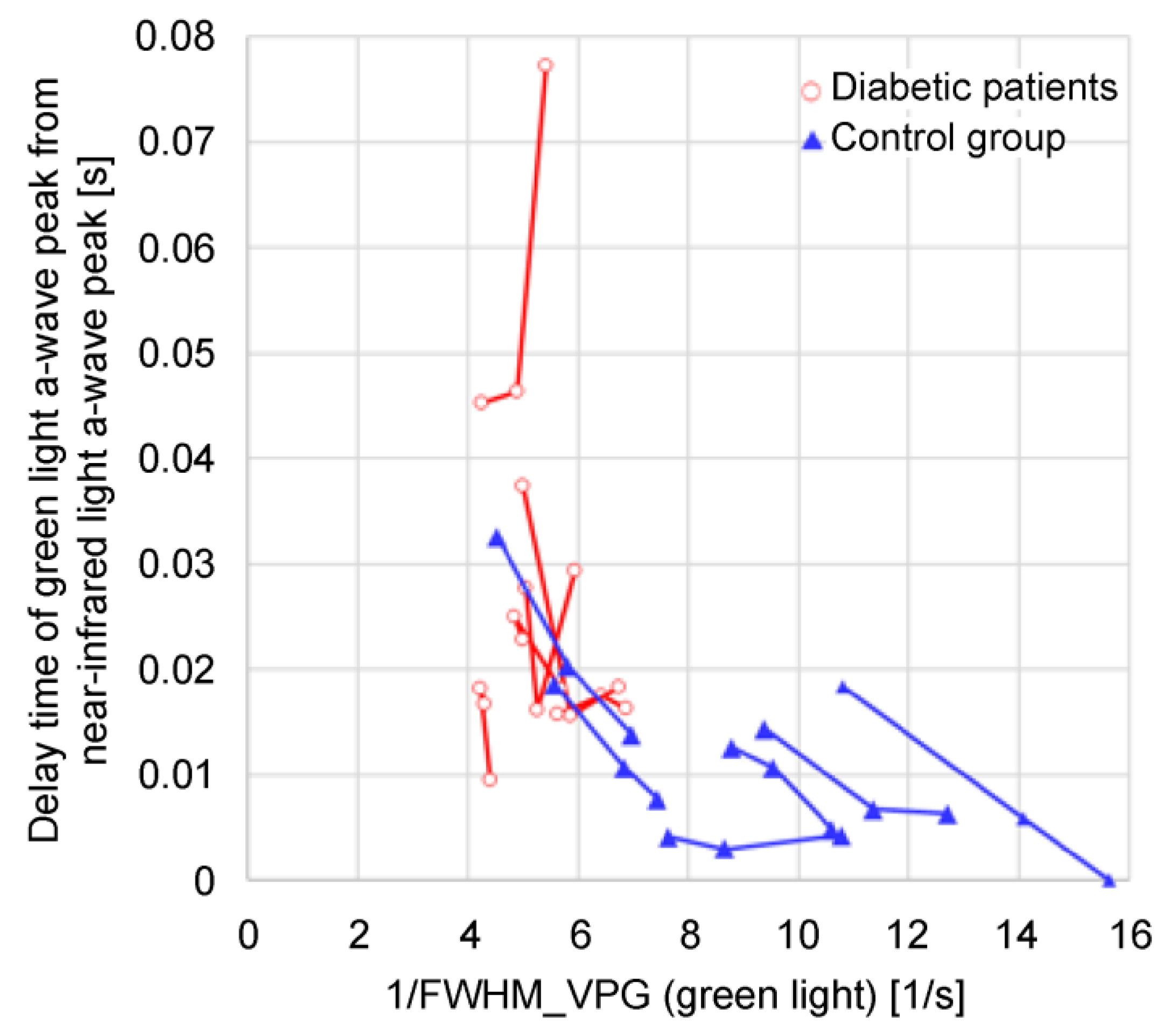
The photoplethysmograms of the near-infrared light and green light measured at the same measurement point were second-order differentiated, and their a-wave peak times were compared. The results showed that a delay occurred in the green a-wave peak relative to the near-infrared a-wave peak. It could be speculated that green light was strongly absorbed by the body, and the LED-PD distance was short (at approximately 2 mm); therefore, the information contained in the green light photoplethysmogram was mainly that of capillaries in the superficial skin area, whereas near-infrared light was relatively weakly absorbed by the body, reaching the deep skin area; therefore, the information contained included arterioles in addition to capillaries. The proposed design was such that by increasing the LED-PD distance to approximately 10 mm for near-infrared light, it would be difficult for information in superficial regions to reach the PD, and the ratio of information in deep regions would increase. In other words, the time delay between the green light a-wave peak and the near-infrared light a-wave peak corresponds to the time required for the pulse wave to reach the superficial region of the skin.
Figure 5 shows the optical paths of the green and near-infrared light received by the PD. Skin tissue is a light scatterer, and the LED light incident on the skin spreads in all directions as it is scattered within the skin. The arrows in
Figure 5 do not represent the light emitted from the LED but rather the penetration depth of the light received by the PD.
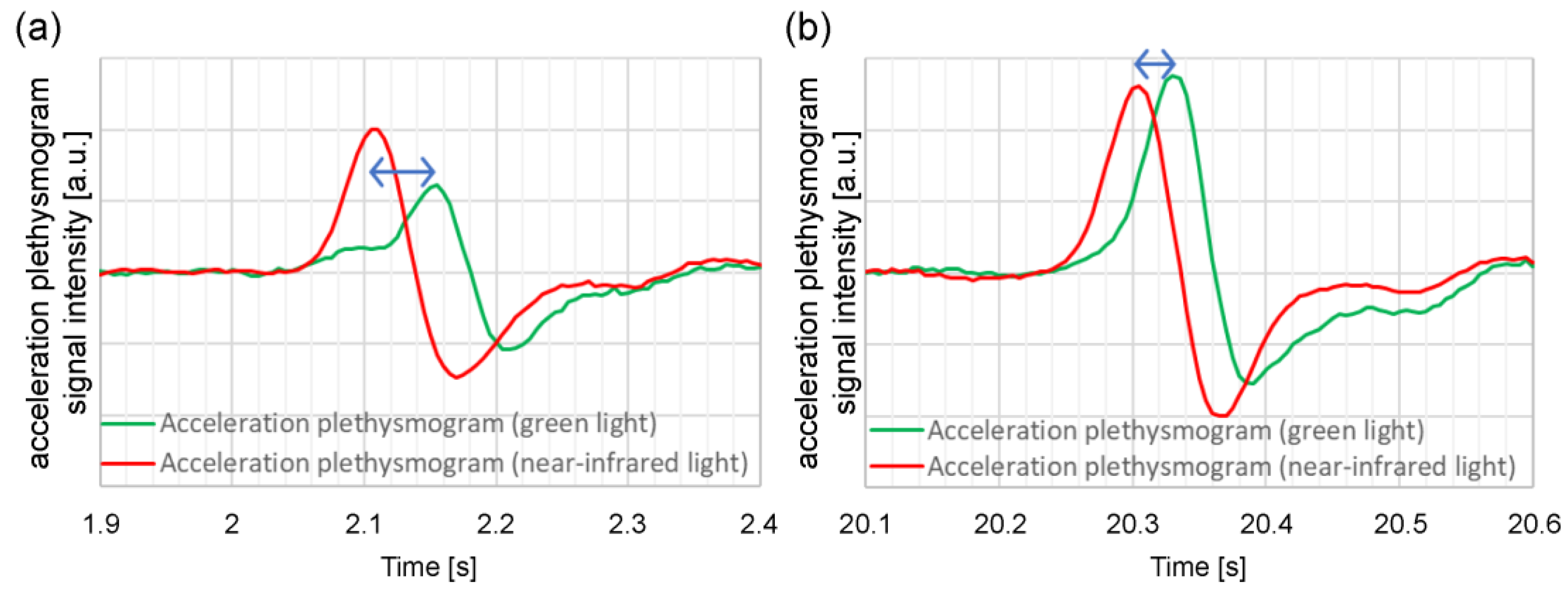
Figure 6 shows an example of an acceleration plethysmogram obtained by calculating the time delay between the green light
a-wave peak and the near-infrared light
a-wave peak. The peak of the acceleration plethysmogram’s maximum value is the
a-wave peak, and the length of the arrow in
Figure 6 represents the time delay between the green light
a-wave peak and the near-infrared light
a-wave peak. As shown in
Figure 6, the time delay between the green light
a-wave peak and the near-infrared light
a-wave peak varies considerably during the measurement process;
Figure 6(a) and 6(b) shows the waveforms when the time delays between the green light
a-wave peak and the near-infrared light
a-wave peak are large and small, respectively. When the time delay between the green light
a-wave peak and the near-infrared light
a-wave peak in (a) is long, the amplitude of the green light acceleration pulse is smaller than that of (b), and the waveform shape differs considerably.
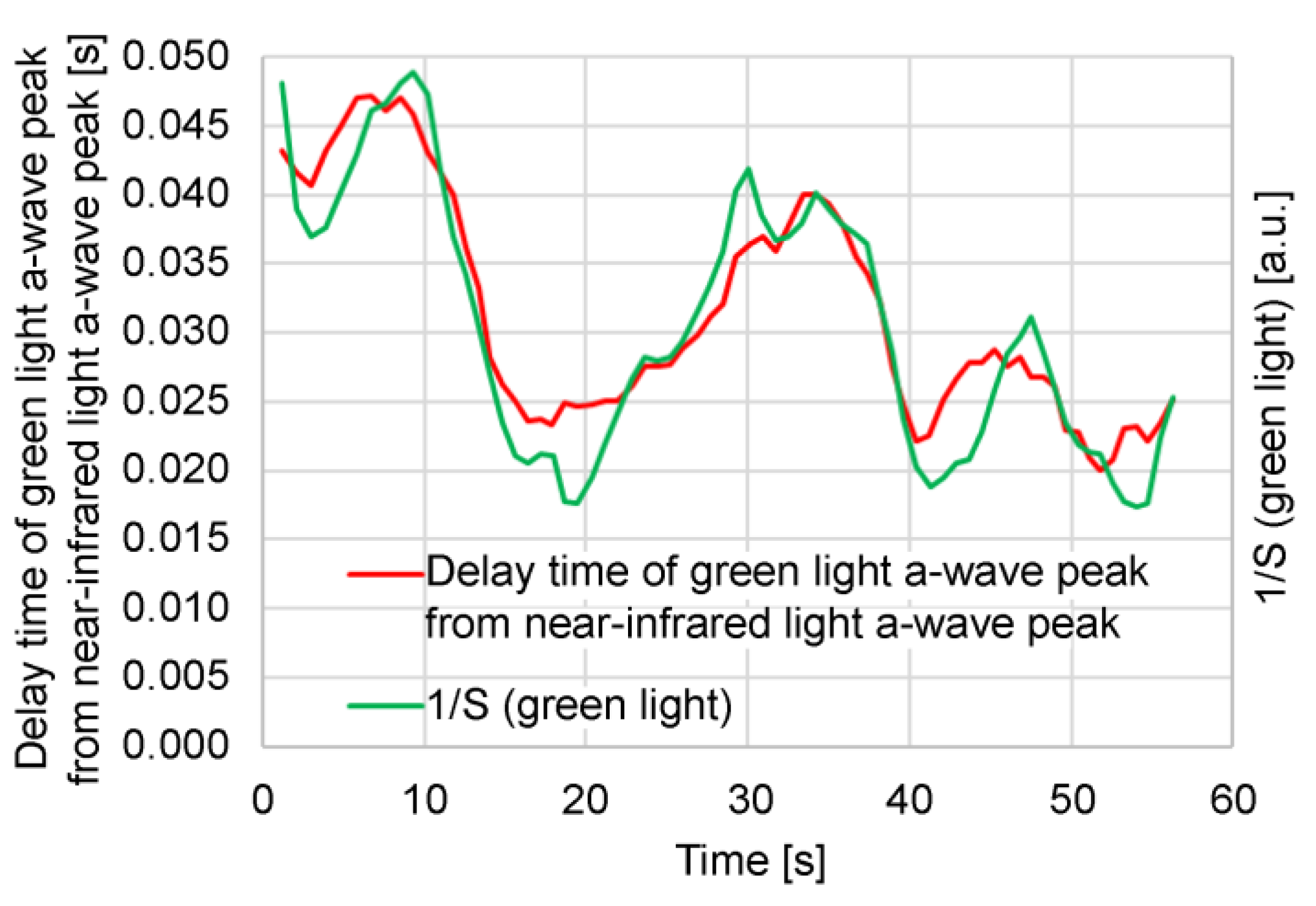
Figure 7 compares the time delay between the green light
a-wave peak and the near-infrared light
a-wave peak and the reciprocal (1/
S) of the green light photoplethysmogram amplitude (
S) in this measurement. It is evident that the time delay between the green light
a-wave peak and the near-infrared light
a-wave peak correlates with 1/
S. A large 1/
S value (i.e., a small
S) signifies low blood flow. In this example, it is speculated that 1/
S increases because of a decrease in capillary blood flow owing to a temporary decrease in the stroke volume. From this example, it can be speculated that the pulse wave transit time increases as the blood flow in the capillaries decreases. Additionally, the photoplethysmogram amplitude (
S) varies depending on the contact state and pressure between the sensor and the skin; consequently, it can be difficult to use the absolute value of 1/
S to estimate the hemodynamics of capillaries because of the variations in each measurement.
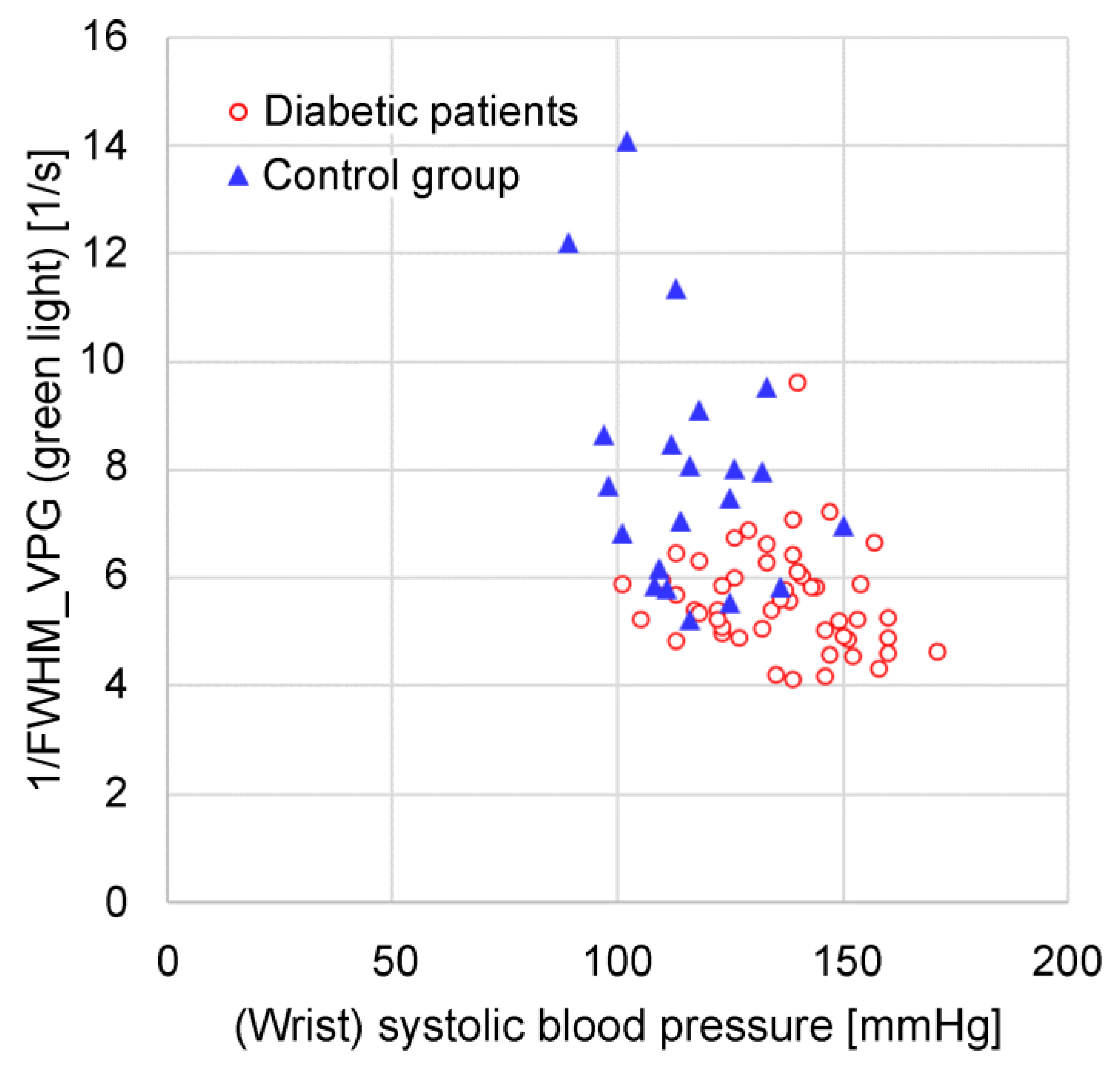
2.2./FWHMVPG
Blood pressure in large arteries is generally measured using a cuff-type sphygmomanometer; the blood pressure in blood vessels decreases as blood progresses from arteries to arterioles to capillaries [
17], and the blood flow velocity decreases as it progresses from the aorta to the capillaries. The extent of the decrease in blood pressure and blood flow velocity varies depending on the measurement site, individual vascular condition (arteriosclerosis, etc.), mental condition (autonomic nerve condition, etc.), environment (temperature, noise, etc.), and clothing. Moreover, we found 1/FWHM
VPG to be a feature related to hemodynamics in the arterioles and capillaries, particularly in the latter, the following two aspects being confirmed as features of 1/FWHM
VPG:
Measurements in adult males and females who had not been diagnosed or treated for diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease showed an almost proportional relationship with wrist blood pressure under conditions where the vascular resistance did not change.
The value decreased when the blood vessels contracted owing to cooling in the vicinity of the measurement site. Brachial and wrist blood pressure increased in some cases.
In addition to the feature values of features (1) and (2), the following three feature values were found:
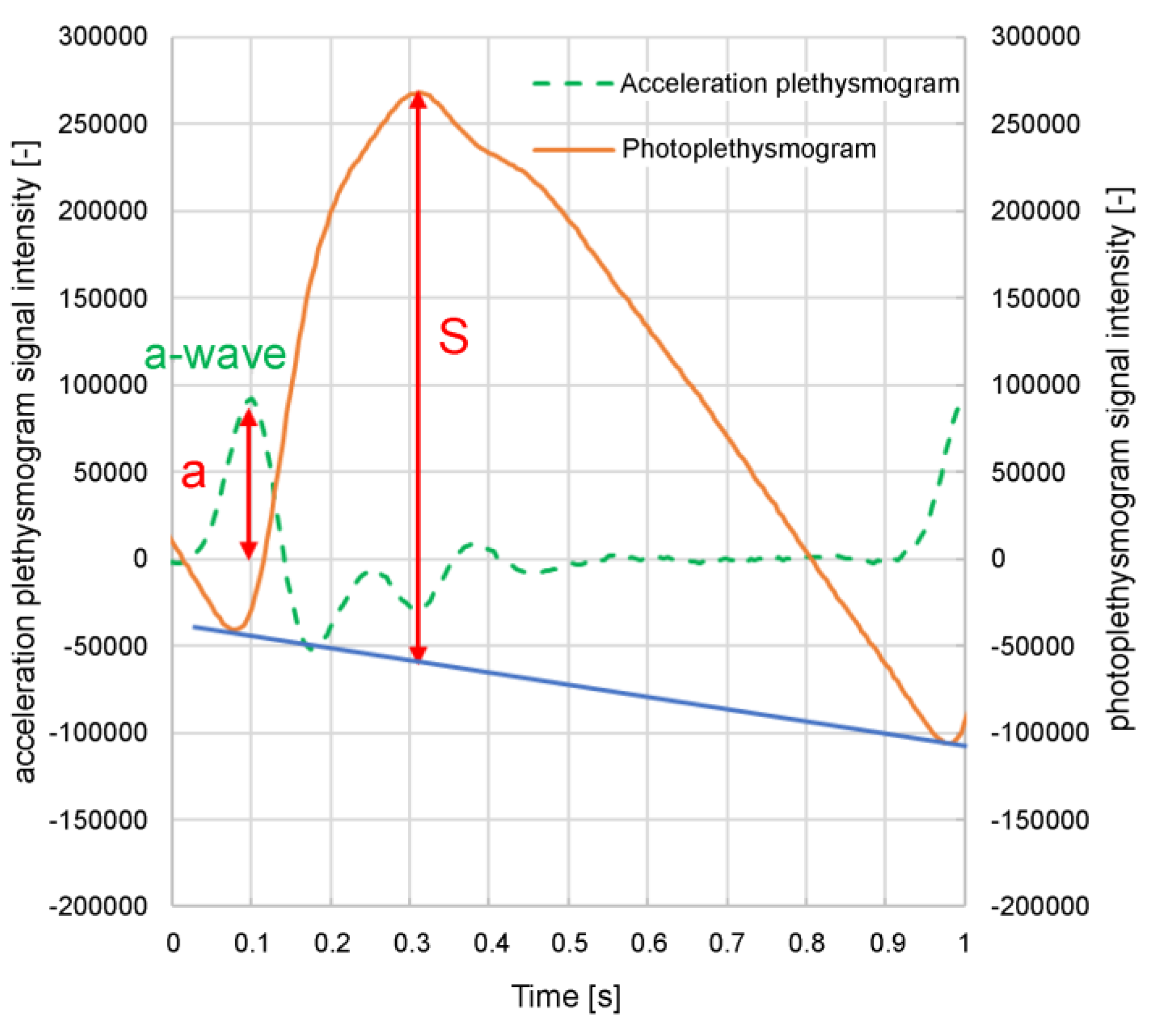
a/S;
(a-b)/(a-d);
1/ab time.
Here,
a/S is the acceleration plethysmogram
a-wave peak height (
a) divided by the photoplethysmogram height (
S) (
Figure 3); (
a-b)/(
a-d) are the normalized
a-b divided by the normalized
a-d (
Figure 4); and 1/
ab time is the difference between the
a- and
b-wave peak times (
Figure 4). These feature values, including 1/FWHM
VPG, are related to the sharpness of the increase in the photoplethysmogram waveform.
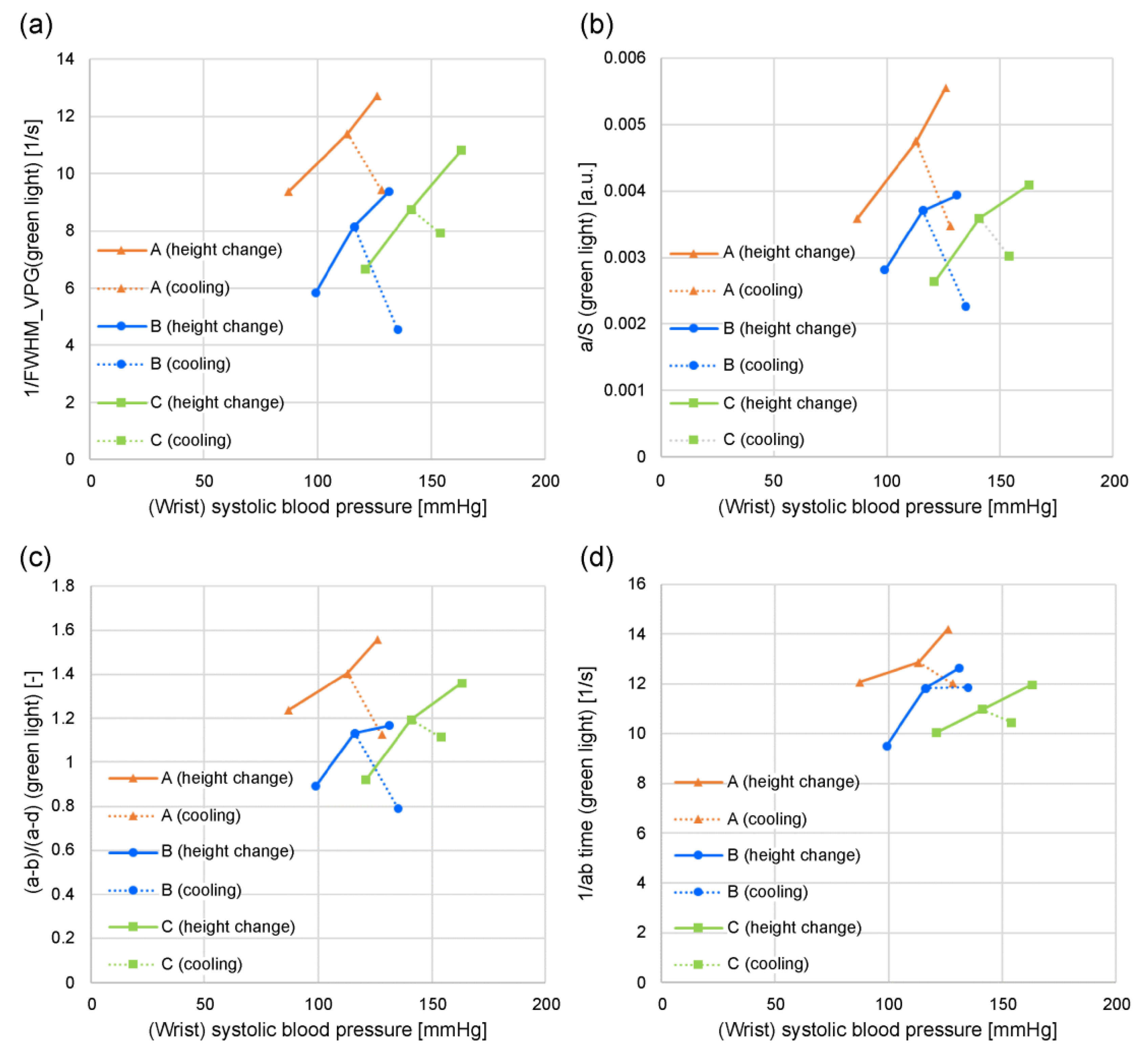
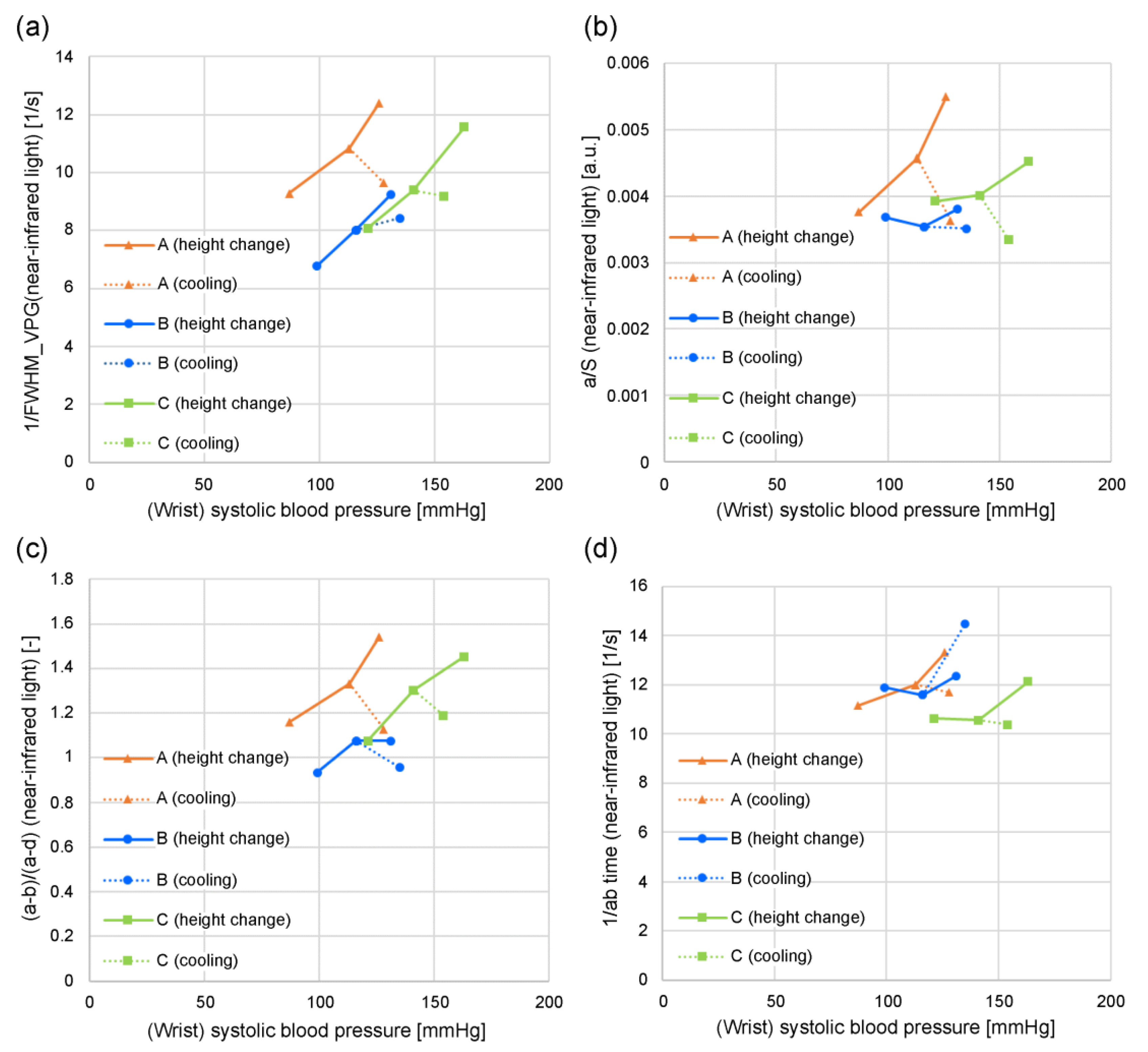
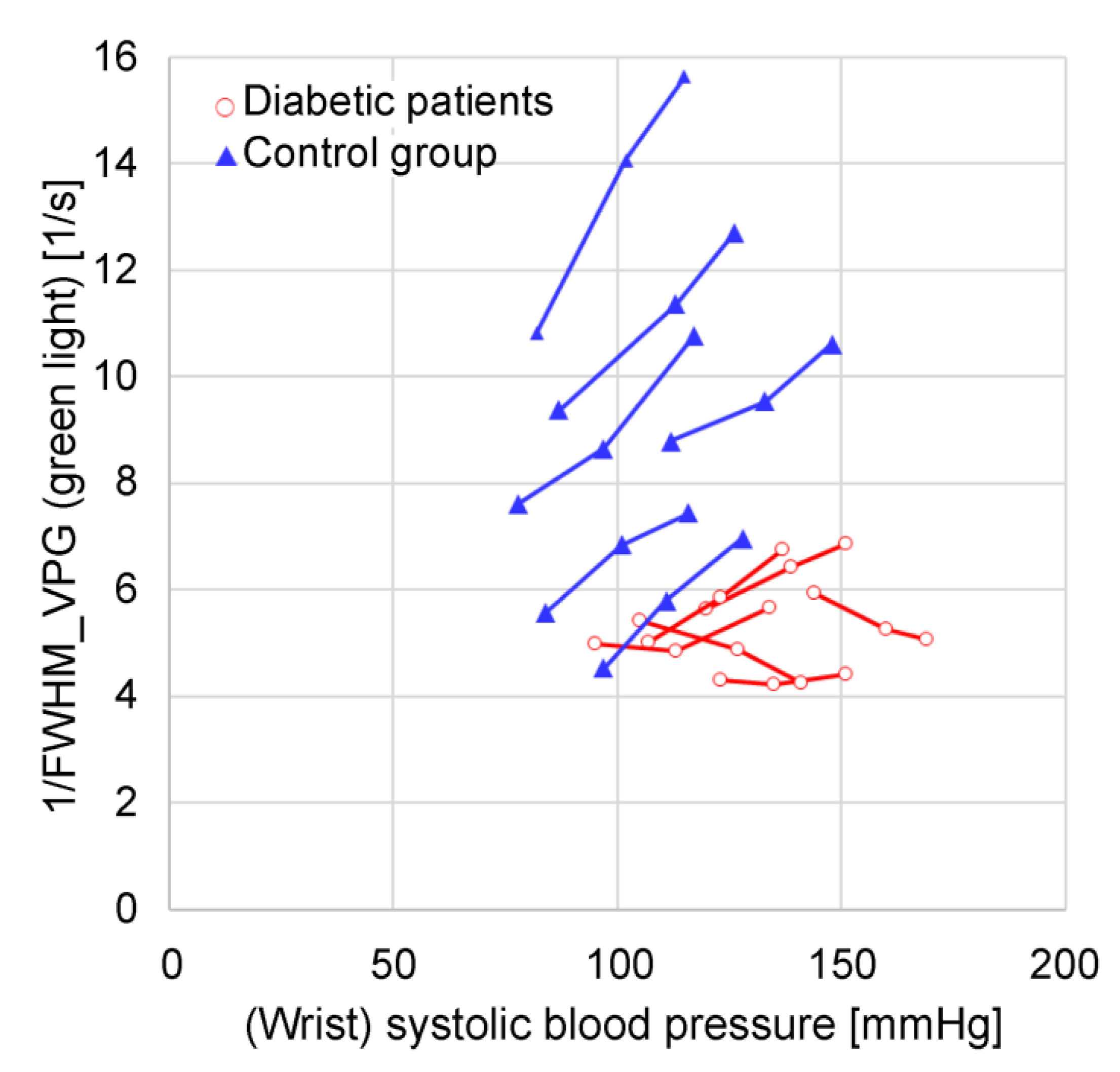
Figure 8 and
Figure 9 show the relationship between the wrist systolic blood pressure and each feature value in adult men and women who have not been diagnosed and treated for diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease when changing the height of the measurement site (finger) from the heart, when the area near the elbow of the arm on the side where the finger is located (that is, the measurement site at chest height) is cooled (plotted for subjects
A, B, and
C). The orange line denotes subject
A, the blue line denotes subject
B, and the green line denotes subject
C.
Figure 8(a) shows 1/FWHM
VPG (green light),
Figure 8(b) shows
a/S (green light),
Figure 8(c) shows (
a-b)/(
a-d) (green light),
Figure 8(d) shows 1/
ab time (green light),
Figure 9(a) shows 1/FWHM
VPG (near-infrared light),
Figure 9(b) shows
a/S (near-infrared light),
Figure 9(c) shows (
a-b)/(
a-d) (near-infrared light), and
Figure 9(d) shows 1/
ab time (near-infrared light).
As shown in
Figure 8(a)–8(c), the wrist systolic blood pressure and each feature value tend to be proportional when the height changes (solid line). It is also evident that cooling reduces each feature value and increases the systolic blood pressure of the wrist (dashed line).
Compared with
Figure 8(a)-8(c),
Figure 8(d) 1/
ab time exhibits less dependence on the wrist systolic blood pressure.
Figure 8(a)–8(d) shows the feature values calculated from the photoplethysmogram measured by the green light LED, and the results of the feature values calculated from the photoplethysmogram measured by the near-infrared light LED are shown in
Figure 9(a)–9(d). The aforementioned trends are unclear, especially in subject
B in
Figure 9(b)–9(d), when compared to those for the green light.
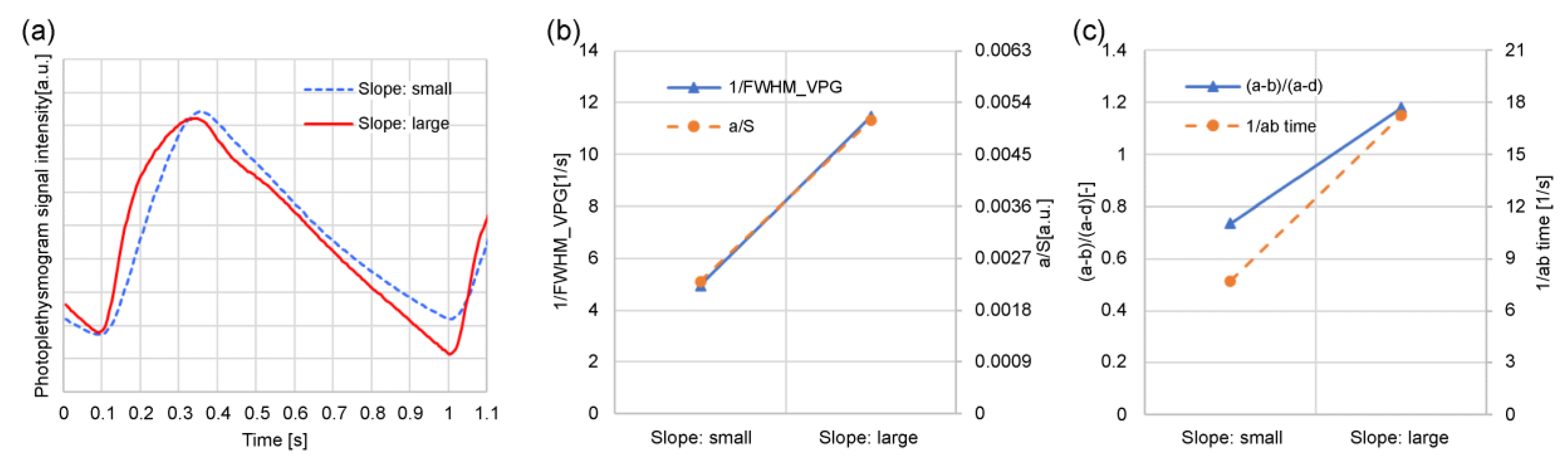
Figure 10 shows that the above feature values are related to the steep increase in the photoplethysmogram waveform.
Figure 10 shows examples of waveforms with different rising slopes in the photoplethysmograms. Of the two photoplethysmogram waveforms shown in
Figure 10(a), the solid line increases sharply (slope: large). As shown in
Figure 10(b), 1/FWHM
VPG and
a/S change, and
Figure 10(c) (
a-b)/(
a-d) and 1/
ab time change, it being evident that in both cases the waveforms with large slopes have considerably larger feature values related to the sharp rise of the photoplethysmogram waveform. However, for (
a-b)/(
a-d), the ratio of “slope: small” to “slope: large” is slightly different compared to other feature values. This is because (
a-b)/(
a-d) includes the features of the
d-wave; consequently, it is a feature value that includes information other than the steepness of the rising slope.
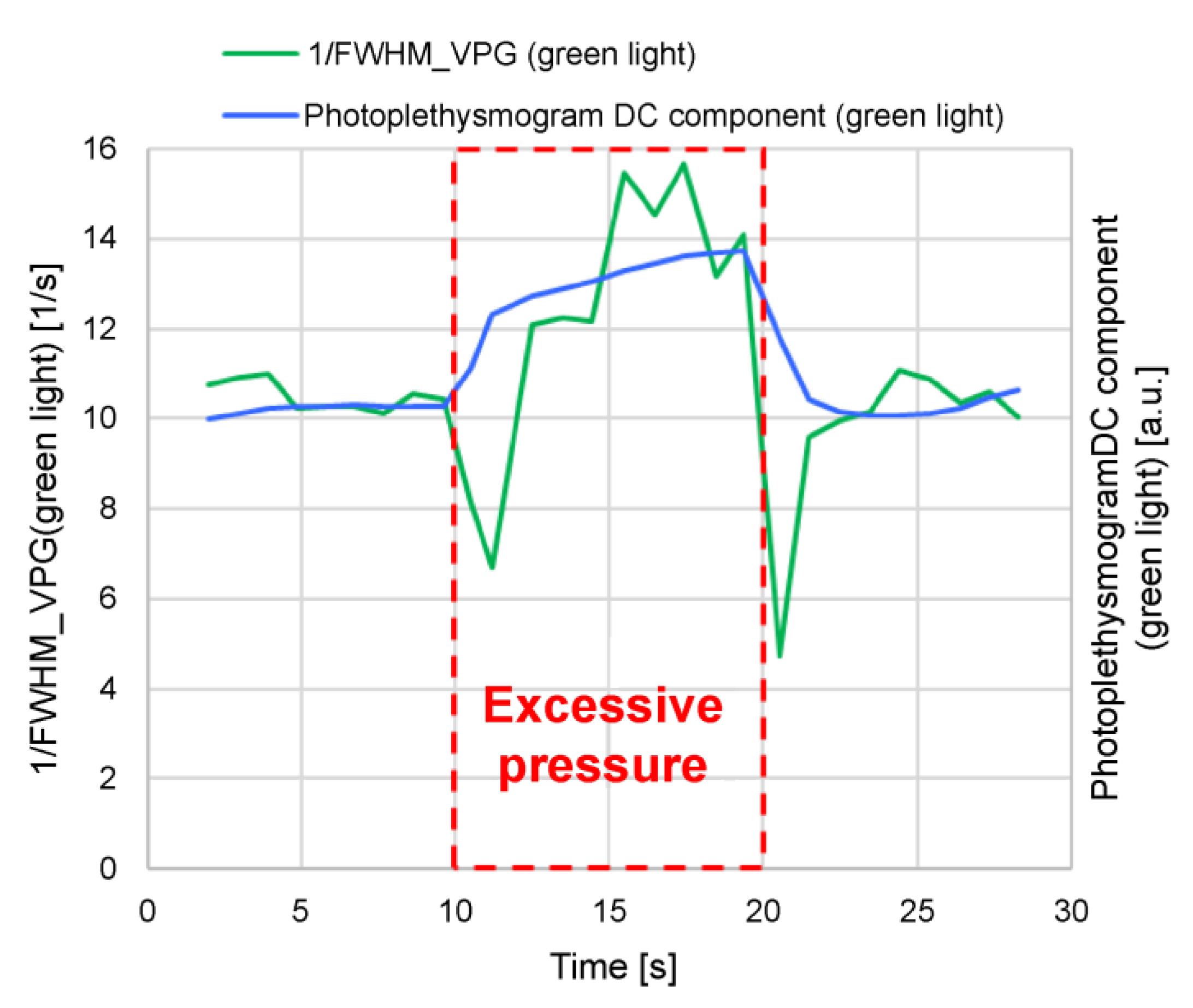
The 1/FWHMVPG value acquired with the green light is more applicable to features (1) and (2). It can be speculated that this is because green light has a high bio-absorption rate and is absorbed before reaching the deep skin regions, resulting in only superficial region information being included (i.e., only capillary information). Similarly, near-infrared light includes not only information on capillaries but also information on arterioles; therefore, it can be speculated that it is susceptible to measurement conditions and individual differences.
Of the four feature values, a/S and (a-b)/(a-d) are susceptible to pressure and body motion noise because the values b, d, and S are more susceptible to them. Furthermore, (a-b)/(a-d) contains d-wave information other than the rising slope. Additionally, the 1/ab time value tends to be less dependent on the wrist systolic blood pressure. Consequently, it can be speculated that the extent of matching with features (1) and (2) is lower for other feature values than for 1/FWHMVPG (green light).
The following section presents the experimental results, with a focus on two feature values—that is, the time delay between the green light a-wave peak and the near-infrared light a-wave peak, and 1/FWHMVPG (green light).
The use of LEDs or lasers with wavelengths in the vicinity of blue to yellowish-green light (in the vicinity of 500–550 nm)—which are highly absorbed by the body—is suitable for acquiring information on shallow skin regions. Furthermore, the distance between the light source and light receiver should be as short as possible, specifically 1–3 mm.
The measurement sites of the photoplethysmogram included the wrist, neck, face, and ear, although the fingers are preferable, as the epidermis of the finger is relatively thin, making it easier to measure photoplethysmograms, the paths from the arterioles to the capillaries are less complicated than those of the face, and the values of each feature tend to be stable.
A ring-shaped wearable device equipped with an optical sensor worn on a finger is suitable for measuring photoplethysmograms, as there is little discomfort during continuous and intermittent measurements, even when worn for long periods.