Introduction
All women with primary breast cancer (PBC) who are carriers of germline pathogenic variant (PV) of the
BRCA1 (NM_007294.4;
Homo sapiens BRCA1 ) gene, face high lifetime risk of contralateral breast cancer (CBC) as well as ovarian cancer (OC). According to published data, in
BRCA1 carriers, the 10-year cumulative risk of CBC ranges from 10.4% to 41.5% and lifetime risk for OC ranges from 34% to 59%. [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10] The broad risk ranges reported in literature may be due to differences in study designs, ascertainment process, number and age distribution of enrolled subjects, miscellaneous genetic modifying factors, as well as specific spectra of PV in various populations, especially ones with founder effect where only few PV types may dominate. Little was known about the role of PV location in the
BRCA1 gene before recent largest to date observational study led by
Consortium of Investigators of Modifiers of BRCA (CIMBA) [
11]. This study reported significant variations of PBC to OC risk ratio between pre-defined regions (
bins) of mutation locations in the
BRCA1 gene - breast cancer cluster regions (BCCR1 c.179 - c.505, BCCR2 c.4328 - c.4945, and BCCR2’, c.5261 - c.5563) and ovarian cancer cluster region (OCCR, c.1380 – c.4062). Moreover, another large group of investigators from Cambridge recently have shown that PVs of
BRCA1 located outside the region bounded by positions c.2282 to c.4071 (also defined as OCCR) were associated with a significantly higher PBC risk compared to mutations within the region (hazard ratio 1.46, 95% CI 1.11-1.93,
p = 0.007)[
1]. Above mentioned studies used breast/ovarian risk ratio, to compare different PV’s without revealing if this is due to variations of only breast cancer risks, only ovarian cancer risks or both variables coexist. Moreover, these studies have compared risks of PBC and OC depending on the location of PV within
BRCA1/2 genes.
We propose a hypothesis that the risk of CBC is related to the risk of PBC and therefore should be higher for PV’s located inside BCCR cluster regions. The risk of OC after PBC could still be related to lifetime risk of OC (higher for PVs located in OCCR), with most OC’s diagnosed at later age than PBC. In this study we analyze BRCA1 carriers with PBC and aim to test this hypothesis, as they still constitute the majority of newly diagnosed BRCA1 carriers in our clinical practice. To our knowledge, no previous study has focused on the risk of CBC and OC following PBC in a similar PV location-related context The precise assessment of individual CBC and OC risk after PBC is important for making further surveillance and risk-reduction recommendations.
According to previous research, the population of Latvia is dominated by two founder PV’s of the
BRCA1, with c.5266dup being the most prevalent and c.4035del being second most prevalent, which combined together contribute up to 84% of all local
BRCA1 PV cases in Latvia (PV c.5266dup constituting up to 50% and PV c.4035del up to 34% of all
BRCA1 PV carriers) [
12,
13,
14].
BRCA1 PV c.5266dup is a frameshift variant leading to a slightly truncated protein, located in the BCCR2 and therefore could be associated with relatively higher BC risks. It is also the most frequent PV in neighbor country Estonia and second frequent in neighbor country Lithuania (33%)[
15,
16] It is thought to have originated around 1800 years ago in either Scandinavia or what is now northern Russia and subsequently spread to various populations, including Ashkenazi Jewish population, central and eastern Europe, Russia (90% - 96% of all
BRCA1 PV) and Poland (51% of all
BRCA1 PV )[
17,
18,
19]
BRCA1 PV c.4035del is a frameshift variant leading to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) and is located in the OCCR, therefore potentially could be associated with relatively higher OC risk. It is the most frequent PV in Lithuania (53%) and second most frequent PV in Estonia (27%). This PV is also generally frequent in populations of central and eastern Europe [
20]
In previous smaller study from Latvia, authors found that the prevalence of PBC and OC cases (breast: ovarian cancer ratio) differs significantly among the carriers of the
BRCA1 PV c.5266dup and c.4035del (OR = 2.98, 95%CI = 1.58 to 5.62, P < 0.001)[
21]. Therefore, to test our hypothesis, we aim to compare the risks of CBC between these two above mentioned PVs. Additionally, we aim to test if there is any difference in future OC risks between those two PVs, once the diagnosis of PBC has been established. To achieve higher statistical power, we had to maximize the volume of cases, especially PV c.4035del, therefore we combined data from the registry of Riga Stradins University, Institute of Oncology and Molecular Genetics, Latvia and International Hereditary Cancer Center, Department of Genetics and Pathology, Pomeranian Medical University, Szczecin, Poland.
Young age at the diagnosis of PBC has been previously documented as independent risk factor for future CBC, therefore we decided to check if this holds true for our founder
BRCA1 population [
24].
Subjects and Methods
In the analysis we included cohort of unselected non-metastatic (Stage I – III) BRCA1 gene PV carriers with diagnosis of PBC. “time to event” calculation was performed. The follow-up started at the time of PBC diagnosis and continued till the event of CBC or OC had occurred. Censored cases were considered those, which did not score the event by the time of last follow-up, death or risk reducing procedure (contralateral risk-reducing mastectomy (RRM) for CBC risk/risk-reducing bilateral salpingo-ophorectomy (RRBSO) for OC risk), whichever occurred first. The ipsilateral breast cancer and other tumors were not considered as events in this study. All cases with OC diagnosis prior to PBC were excluded. All subjects underwent genetic counselling and BRCA1 founder PV testing. The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Riga Stradins University.
In the analysis of CBC risk, we included a total of 1408 cases. The cohort consisted of 239 unselected cases from Latvia (diagnosed between years 1980 and 2023) and 1169 unselected cases from Poland (diagnosed between year 1978 and 2022), We only included cases with metachronous CBC, which was defined as CBC not earlier than 6 months from the PBC. Consequently 47 synchronous PBC cases were excluded. The remaining 1363 cases were included in the study.
In the analysis of OC risk, we included only 239 cases from Latvia, as only for this cohort we had all essential data including RRBSO data available.
The control group consisted of 11,350 consequent unselected cases from Latvian Cancer Registry, diagnosed with PBC in 10 years period (between year 2009 and 2019), followed up till 10/2022. The genetic testing data was not available for this cohort. Total of 9554 cases were enrolled in control group after exclusion of stage IV at the time of PBC, those who died from oncologic disorder within less than 6 months of PBC diagnosis, cases with OC diagnosed prior to PBC, as well as 165 cases of synchronous PBC.
Statistical Analysis
The cumulative risks of CBC and OC were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier type analysis, including “cumulative events” function. The log-rank test was used to test the differences between groups. Age younger than 40 years at the time of PBC was used as binary variable (risk factor) and calculated using cox proportional hazards model. All statistical analysis was carried out using “R” (R Core Team. (2024). R:A language and environment for statistical computing) and “Jamovi” (The jamovi project (2024). jamovi (Version 2.5) software.
Results
Risk of CBC
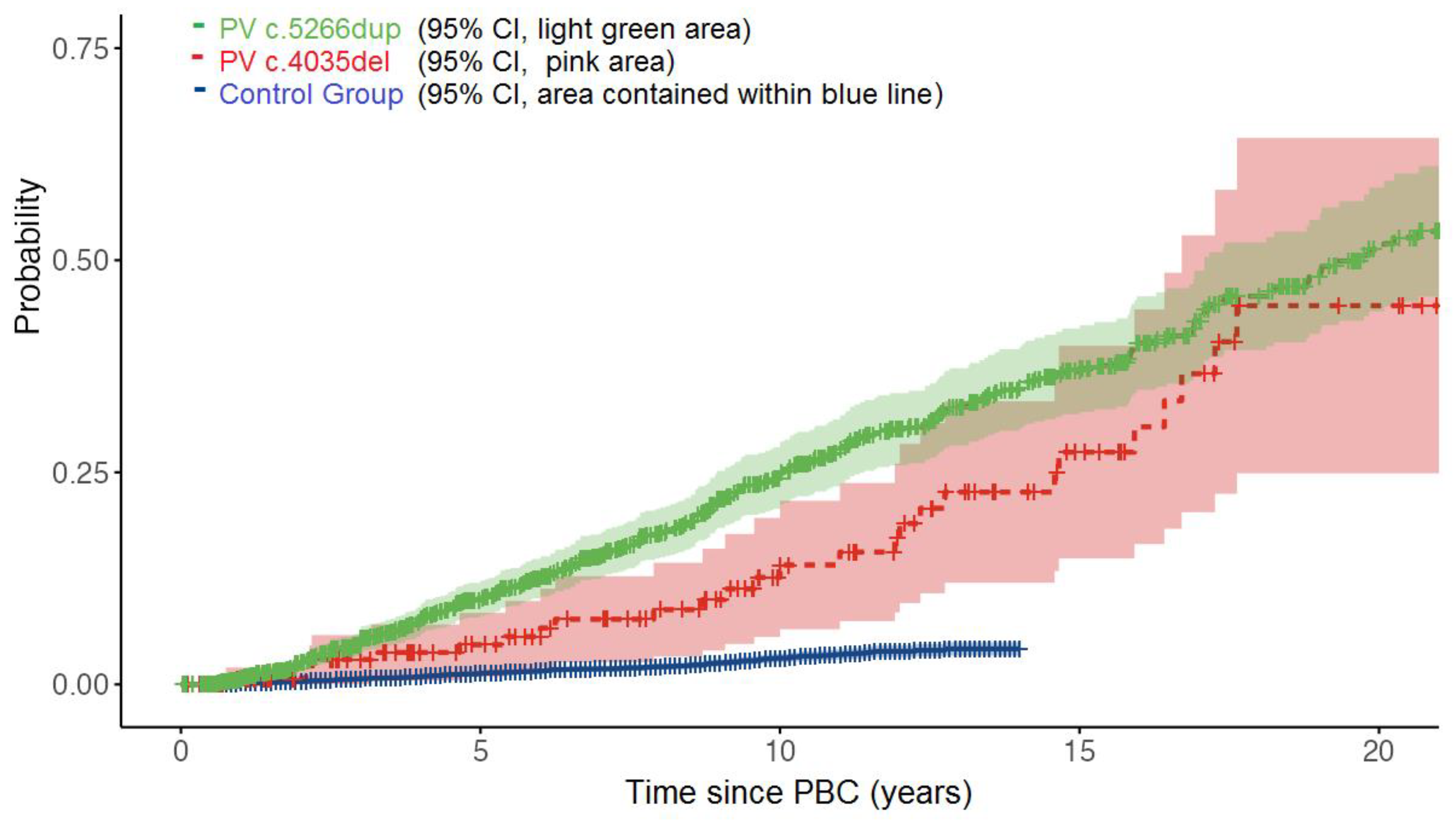
In the CBC study group (n = 1363) we had 1187 cases with PV c.5266dup and 176 cases with PV c.4035del. Median follow-up time was 9.8 (0.6 - 32.0) years. Mean age at diagnosis of PBC in BRCA1 carriers was 45.5 (range 23.4-81.5) years, 45.2 years for PV c.5266dup and 47.5 years for PV c.4035del. In follow-up time, there were 305 events of CBC, constituting 22.4% of all cases.
In PV c.5266dup subgroup, there were 279/1187 (23.5%) events and in PV c.4035del subgroup, there were 26/176 (14.7%) events,
Table 1.
Over one third of cases, 478/1363 (35.1%) were younger than 40 years at the time of PBC and these cases had higher risk of future CBC (hazard ratio 2.06, 95% CI 1.83-2.29, p<0.001)
In control group (N = 9554), mean follow-up was 7.2 (0.6-13) years in which we observed 186/9554 (1.9%) events of CBC.
Cumulative 10 years risk of developing CBC was 3.0% in control group, and 20.1% in study group of BRCA1 carriers (log-rank p< 0.001).
Cumulative risk of CBC at 10,15 and 20 years was 25.0%, 37.0% and 51.4% in PV c.5266dup subgroup, as opposed to 14.1%, 27.2% and 44.5% in PV c.4035del subgroup (log-rank p = 0.045),
Figure 1.
Risk of OC
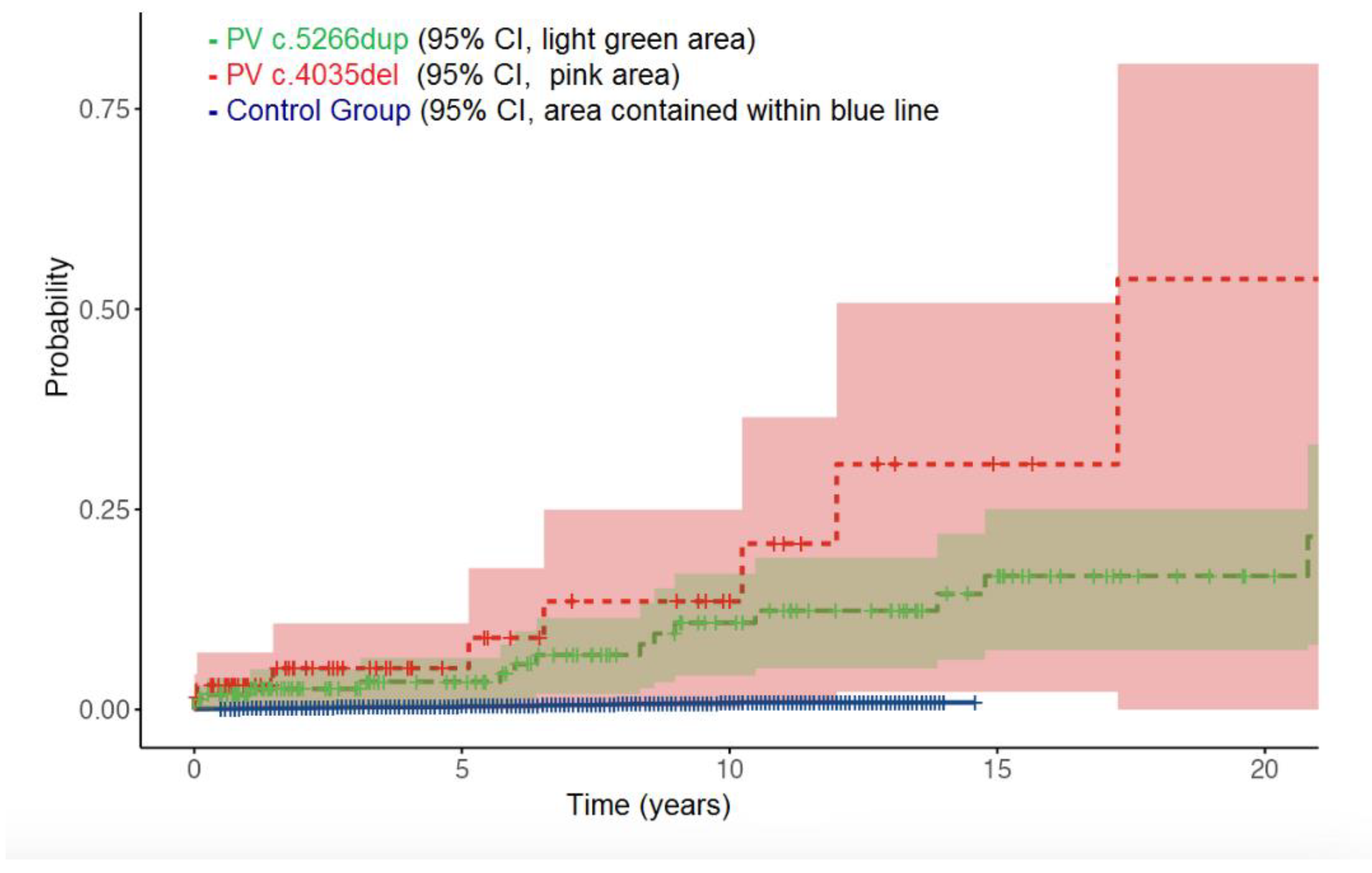
In OC study group we included 228 BRCA1 PV carriers with PBC. In 58 cases RRBSO was done at some time after PBC diagnosis. Median follow-up time for OC study group was 7.8 (0.8-34) years, during which 27 (11.8%) events of OC were observed. Mean age at diagnosis of OC was 56.2 (range 36-79) years, 55.3 for PV c.5266dup and 58.1 for PV c.4035del.
In control group (N = 9554), during median follow-up time of 7.2 (0.6-13) years, 52/9554 (0.53%) events of OC were observed.
Cumulative risk of developing OC at 10 and 15 years was 1.0% and 1.2% in control group, 10.8% and 16.8% for PV c.5266dup, 13.5% and 30.8% for PV c.4035del. There was clear difference in OC risks between control group and
BRCA1 carriers (log-rank p< 0.001). PV c.4035del showed higher risk of OC, compared to PV c.5266dup, however, this was of borderline statistical significance (log-rank p = 0.057),
Table 2 and
Figure 2. Age younger than 40 years at the time of PBC was not associated with any difference in future OC risks (hazard ratio 1.03, 95% CI 0.77-1.29, p = 0.23)
Discussion
The data of this study confirms previously established evidence, that in cases of PBC the risk of future CBC and OC is increased significantly in
BRCA1 carriers as opposed to general unscreened population, and we have demonstrated this now with two locally and regionally prevalent PVs of
BRCA1. Our data of CBC in
BRCA1 carriers and control group are generally in line with other larger European studies. In a meta-analysis done by Swedish group , which included 807
BRCA1/2 mutation carriers and 3163 non-carrier controls from eleven studies (7 cohort and 4 case–control studies), patients with
BRCA mutations had a higher risk for CBC compared with non-mutation carriers (RR 3.56, 95% CI 2.50–5.08, p < 0.001). [
4] In Dutch multicenter study of 6294 invasive breast cancer patients ≤50 years, the risk of CBC for
BRCA1 carriers at a median follow-up of 12.5 years was shown to be more than 4 times higher compared to non-carriers (10-year cumulative CBC risks of 21.1% for
BRCA1 mutation carriers versus 5.1% for non-carriers) [
22]. The findings were similar in a recent German multicenter study (total of 1,345 BRCA1 carriers and 4,195 BRCA1/2 noncarriers), where the 10-year cumulative CBC risk was 25.1% (95% CI 19.6–31.9) for
BRCA1 carriers and 3.6% (95% CI 2.2–5.7) for non-carriers [
23]. In this study we showed 10-year cumulative risks of CBC of 20.1% in
BRCA1 PV carriers and 3.0% in PBC population for whom
BRCA status was unknown, but definetely contained some high risk cases.
Moreover, in our study we managed to show significant differences in CBC risks between two types of PVs, PV c.5266dup being associated with higher CBC risk in comparison with PV 4035del. Our larger number cohort of PV c.5266dup improved accuracy for calculation of CBC risks, allowing to outline differences between both PVs with higher statistical power and confirmed our hypothesis. The two risk curves (PV c.5266dup, c.4035del) clearly diverge from the time of PBC and have tendency to converge again after 15+ years, however, much more cases in PV 4035del group are needed to see if this holds true.
Our data from OC study subgroup suggests that PV c.5266dup could be associated with lower OC risk, as opposed to PV c.4035del. However, still rather small number of cases and events were included in this study subgroup, which leads to lower statistical power and harder to prove any significant differences between two groups. Although two curves seem to diverge from the beginning of time, the statistical power was not enough to conclude the real difference between them. Therefore, in future, studies with larger data sets are necessary to support the concept of OC risk modified by PV location, in the context of PBC affected BRCA1 carriers.
We can conclude, that once PBC diagnosis is established, BRCA1 PV c.5266dup is associated with higher CBC risk and possibly lower OC risk in comparison to BRCA1 PV c.4035del. Recommendations about risk reducing surgeries could be adjusted basing on this fact.
According to our study, age younger than 40 years at diagnosis of PBC holds as independent risk factor for CBC in
BRCA1 founder variant carriers, but does not seem to alter the risk of OC. Young age at the time of PBC has previously been reported as risk factor for developing CBC in
BRCA1/2 carriers [
24].
Author Contributions
PL, AI, and ZD were major contributors in writing and reviewing the manuscript. SS, JM, PL,AI, and GT contributed in selection of individuals for BRCA1 screening in Latvia. JG, JL provided data from Poland. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported (not financially) by the European Reference Network on Genetic Tumour Risk Syndromes (ERN GENTURIS)—Project ID No. 739547. ERN GENTURIS is partly co-funded by the European Union within the framework of the Third Health Program “ERN-2016—Framework Partnership Agreement 2017–2021. This work was supported by Riga Stradins University grant “The Identification of Clinical, Pathologic and Genomic Factors for Escalation and De-escalation of Breast Cancer Treatment”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by a Central Medical Ethics Committee of Latvia (03.6.2019. Nr.3/19–06-03) and Genome Research Council of Latvia (04.07.2019. Nr.A-12/19–07-04).
Informed Consent Statement
All individuals provided written informed consent, including for publication.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Hopper, J.L.; Barnes, D.R.; Phillips, K.A.; Mooij, T.M.; Roos-Blom, M.J.; Jervis, S.; van Leeuwen, F.E.; Milne, R.L.; Andrieu, N.; Goldgar, D.E.; Terry, M.B.; Rookus, M.A.; Easton, D.F.; Antoniou, A.C.; McGuffog, L.; Evans, D.G.; Barrowdale, D.; Frost, D.; Adlard, J.; Ong, K.R.; Izatt, L.; Tischkowitz, M.; Eeles, R.; Davidson, R.; Hodgson, S.; Ellis, S.; Nogues, C.; Lasset, C.; Stoppa-Lyonnet, D.; Fricker, J.P.; Faivre, L.; Berthet, P.; Hooning, M.J.; van der Kolk, L.E.; Kets, C.M.; Adank, M.A.; John, E.M.; Chung, W.K.; Andrulis, I.L.; Southey, M.; Daly, M.B.; Buys, S.S.; Osorio, A.; Engel, C.; Kast, K.; Schmutzler, R.K.; Caldes, T.; Jakubowska, A.; Simard, J.; Friedlander, M.L.; McLachlan, S.A.; Machackova, E.; Foretova, L.; Tan, Y.Y.; Singer, C.F.; Olah, E.; Gerdes, A.M.; Arver, B.; Olsson, H. Risks of Breast, Ovarian, and Contralateral Breast Cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers. Jama 2017, 317, 2402–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavaddat, N.; Peock, S.; Frost, D.; Ellis, S.; Platte, R.; Fineberg, E.; Evans, D.G.; Izatt, L.; Eeles, R.A.; Adlard, J.; Davidson, R.; Eccles, D.; Cole, T.; Cook, J.; Brewer, C.; Tischkowitz, M.; Douglas, F.; Hodgson, S.; Walker, L.; Porteous, M.E.; Morrison, P.J.; Side, L.E.; Kennedy, M.J.; Houghton, C.; Donaldson, A.; Rogers, M.T.; Dorkins, H.; Miedzybrodzka, Z.; Gregory, H.; Eason, J.; Barwell, J.; McCann, E.; Murray, A.; Antoniou, A.C.; Easton, D.F. Cancer risks for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers: results from prospective analysis of EMBRACE. J Natl Cancer Inst 2013, 105, 812–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, K.; Gershman, S.; Lynch, H.T.; Ghadirian, P.; Tung, N.; Kim-Sing, C.; Olopade, O.I.; Domchek, S.; McLennan, J.; Eisen, A.; Foulkes, W.D.; Rosen, B.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Predictors of contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. Br J Cancer 2011, 104, 1384–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valachis, A.; Nearchou, A.D.; Lind, P. Surgical management of breast cancer in BRCA-mutation carriers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014, 144, 443–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, N.N.; Ingham, S.; Hodson, J.; Lalloo, F.; Bulman, M.; Howell, A.; Evans, D.G. Risk of contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers: a 30-year semi-prospective analysis. Fam Cancer 2015, 14, 531–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Broek, A.J.; van 't Veer, L.J.; Hooning, M.J.; Cornelissen, S.; Broeks, A.; Rutgers, E.J.; Smit, V.T.; Cornelisse, C.J.; van Beek, M.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.L.; Seynaeve, C.; Westenend, P.J.; Jobsen, J.J.; Siesling, S.; Tollenaar, R.A.; van Leeuwen, F.E.; Schmidt, M.K. Impact of Age at Primary Breast Cancer on Contralateral Breast Cancer Risk in BRCA1/2 Mutation Carriers. J Clin Oncol 2016, 34, 409–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubinski, J.; Huzarski, T.; Gronwald, J.; Cybulski, C.; Debniak, T.; Sun, P.; Kim, S.J.; Kotsopoulos, J.; Narod, S.A. Age-specific risks of incident, contralateral and ipsilateral breast cancer among 1776 Polish BRCA1 mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2019, 174, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagan, E.; Gershoni-Baruch, R.; Kurolap, A.; Fried, G. Early onset breast cancer in Ashkenazi women carriers of founder BRCA1/2 mutations: beyond 10 years of follow-up. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 2017, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Malone, K.E.; Begg, C.B.; Haile, R.W.; Borg, A.; Concannon, P.; Tellhed, L.; Xue, S.; Teraoka, S.; Bernstein, L.; Capanu, M.; Reiner, A.S.; Riedel, E.R.; Thomas, D.C.; Mellemkjaer, L.; Lynch, C.F.; Boice, J.D., Jr.; Anton-Culver, H.; Bernstein, J.L. Population-based study of the risk of second primary contralateral breast cancer associated with carrying a mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2. J Clin Oncol 2010, 28, 2404–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.G.; Ingham, S.L.; Baildam, A.; Ross, G.L.; Lalloo, F.; Buchan, I.; Howell, A. Contralateral mastectomy improves survival in women with BRCA1/2-associated breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2013, 140, 135–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timothy, R. Rebbeck, Associatyion of Type and Location of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations with risk of breast and ovarioan cancer. JAMA. 2015 Apr 7;313(13):1347-61. [CrossRef]
- Laima Tikhomirova, Olga Sinicka, Dagnija Smite, Janis Eglitis, High prevalence of two BRCA1 mutations, 4154delA and 5382insC, in Latvia, Familial Cancer (2005) 4: 77–84, Springer 2005. [CrossRef]
- Gardovskis, A.; Irmejs, A.; Miklasevics, E.; et al. Clinical, Molecular and Geographical Features of Hereditary Breast/Ovarian Cancer in Latvia. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2005, 3, 71–76 101186/1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loza, P.; et al. A novel frequent BRCA1 recurrent variant c.5117G > A (p.Gly1206Glu) identified after 20 years of BRCA1/2 research in the Baltic region: cohort study and literature review.
- Kristiina Tamboom, Krista Kaasik, Jelena Aršavskaja, Mare Tekkel, Aili Lilleorg, Peeter Padrik, Andres Metspalu, Toomas Veidebau, BRCA1 mutations in women with familial or early-onset breast cancer and BRCA2 mutations in familial cancer in Estonia, Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2010, 8, 4. [CrossRef]
- Elsakov, P.; et al. The contribution of founder mutations in BRCA1 to breast and ovarian cancer in Lithuania. Clin Genet. 2010. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolenko, A.P.; Rozanov, M.E.; Mitiushkina, N.V.; Sherina, N.Y.; Iyevleva, A.G.; Chekmariova, E.V.; Buslov, K.G.; Shilov, E.S.; Togo, A.V.; Bit-Sava, E.M.; Voskresenskiy, D.A.; Chagunava, O.L.; Devilee, P.; Cornelisse, C.; Semiglazov, V.F.; Imyanitov, E.N. Founder mutations in early-onset, familial and bilateral breast cancer patients from Russia. Fam Cancer 2007, 6, 281–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanvy Hamel; et al. On the origin and diffusion of BRCA1 c.5266dupC (5382insC) in European populations. Eur J Hum Genet 2011, 19, 300–306.
- Gorski, B.; Byrski, T.; Huzarski, T.; Jakubowska, A.; Menkiszak, J.; Gronwald, J.; Pluzańska, A.; Bebenek, M.; Fischer-Maliszewska, L.; Grzybowska, E.; Narod, S.A.; Lubiński, J. Founder mutations in the BRCA1 gene in Polish families with breast-ovarian cancer. Am J Hum Genet 2000, 66, 1963–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasinska, A.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Prevalence of BRCA1 founder mutations in western Poland. Hum Mutat 2001, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigorijs Plakhins 1, Arvids Irmejs, Andris Gardovskis, Signe Subatniece, Santa Rozite, Marianna Bitina, Guntars Keire, Gunta Purkalne, Uldis Teibe, Genadijs Trofimovics, Edvins Miklasevics, Janis Gardovskis, Genotype-phenotype correlations among BRCA1 4153delA and 5382insC mutation carriers from Latvia. [CrossRef]
- Van den Broek, A.J.; van’t Veer, L.J.; Hooning, M.J.; Cornelissen, S.; Broeks, A.; Rutgers, E.J.; Smit, V.T.; Cornelisse, C.J.; van Beek, M.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.L.; et al. Impact of Age at Primary Breast Cancer on Contralateral Breast Cancer Risk in BRCA1/2 Mutation Carriers. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, C.; Fischer, C.; Zachariae, S.; Bucksch, K.; Rhiem, K.; Giesecke, J.; Herold, N.; Wappenschmidt, B.; Hubbel, V.; Maringa, M.; et al. Breast cancer risk in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers and noncarriers under prospective intensified surveillance. Int. J. Cancer 2019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K Metcalfe, S Gershman, HT Lynch, P Ghadirian, N Tung, C Kim-Sin “Predictors of contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers”.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).