1. Introduction
The use of cannabis by pregnant people in the United States is increasing [
1,
2], raising concerns about potential fetal and neurodevelopmental toxicity [
3,
4] of (-)-Δ
9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive constituent of cannabis. To inform such toxicity, it is important to determine the mechanism and extent of placental transfer of THC and its psychoactive circulating metabolite 11-OH-THC.
In both humans and non-human primates, THC is effluxed in the fetal-to-maternal direction, resulting in fetal circulatory concentrations that are less than the corresponding maternal concentrations [
5,
6]. These data suggest the involvement of efflux transporters at the blood-placenta barrier, particularly P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and/or breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), which are highly expressed in the apical membrane of the syncytiotrophoblast [
7]. This hypothesis is supported by some studies in the P-gp knock-out (KO) mice [
8], but not by those conducted in our laboratory [
9,
10]. Using both, P-gp or BCRP overexpressing cells, vesicles or pregnant P-gp or BCRP KO mice, we found that THC is not a substrate or inhibitor of P-gp or BCRP at pharmacologically relevant concentrations [
9,
10]. Moreover, in our perfused human placenta studies, the THC unbound clearance (CL) in the fetal to maternal direction (normalized to the unbound CL of the passive diffusion marker, antipyrine) was significantly greater than its corresponding maternal-fetal direction indicating active efflux of THC in the maternal to fetal direction. In addition, this active efflux was not inhibitable by a pan-P-gp/BCRP inhibitor, valspodar [
6]. In these perfused placental studies, 11-OH-THC and THC-COOH were found to cross the placenta passively [
6].
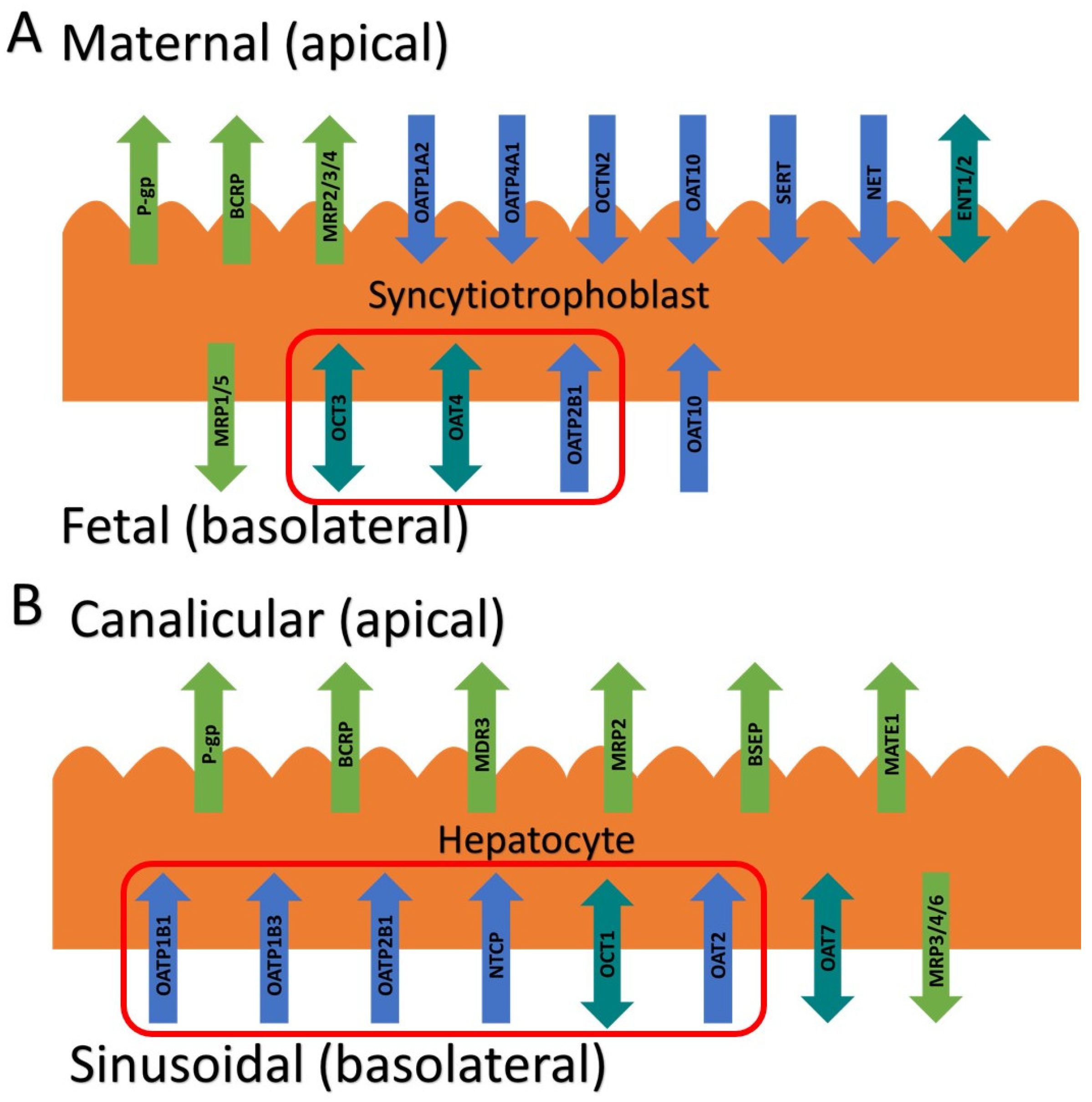
The above findings raise an interesting question: which transporter(s) is responsible for the fetal to maternal efflux of THC? Studies to predict and verify the observed fetal umbilical vein concentrations in our human studies through physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling suggest that the transporter(s) is more likely to be localized in the basal membrane of the syncytiotrophoblast. We hypothesized that this transporter could be one of the solute carrier (SLC) uptake transporter, such as the organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP2B1), the organic cation transporter (OCT3), or the organic anion transporter (OAT4) (
Figure 1A) [
11,
12]. That is, THC could be actively transported from the fetal circulation into the syncytiotrophoblast by one of these transporters and then THC could reach the maternal circulation by diffusion across the apical membrane of the syncytiotrophoblast. Therefore, here we investigated if THC or its major circulatory metabolites are substrates or inhibitors of these basolateral placental transporters at their pharmacologically relevant concentrations.
In humans THC is primarily metabolized in the liver [via cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C9] to its psychoactive circulatory metabolite, 11-OH-THC, which is further metabolized (via CYP2C9 and 3A) to the non-psychoactive circulatory metabolite,11-
nor-9-carboxy-THC (THC-COOH) [
13,
14]. After intravenous dosing of THC (0.5 mg), 41-45% of dose is excreted in the feces 72 hours after administration [
15]. It is possible that hepatic transporters may be important in the hepatic uptake of THC or its metabolites and subsequent excretion in the bile or urine. If they are, this has potential implications for drug-drug interactions, either as object drugs or as perpetrators when present in the circulation at their upper range of their pharmacological concentrations (5 μM THC, 0.3 μM 11-OH-THC, or 2.5 μM THC-COOH, as justified by our previous publication [
9]). Therefore, we also investigated if THC and its major circulatory metabolites are substrates or inhibitors of hepatic SLC transporters such as OATP1B1/1B3/2B1, OCT1, and sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide (NTCP) (
Figure 1B) [
16].
3. Discussion
In this study, we systemically evaluated whether THC and its major metabolites, 11-OH-THC and THC-COOH, at their pharmacologically relevant concentrations, are substrates or inhibitors of numerous placental and hepatic SLC transporters. The impetus for this study arose from our previous findings that THC (but not 11-OH-THC or THC-COOH) is transported in the fetal- maternal direction in the term perfused human placenta [
6]. An obvious explanation is that THC is transported by either P-gp and/or BCRP, two efflux transporters highly expressed in the apical membrane of the syncytiotrophoblast (
Figure 1). However, in our perfused human placenta studies, the fetal-maternal THC transport was not inhibitable by valspodar, an inhibitor of P-gp, BCRP and multidrug resistance associated proteins 4 (MRP4). In addition, studies in cells overexpressing human P-gp or BCRP or in mice where P-gp and/or Bcrp was knocked-out, THC was not transported by either P-gp or Bcrp [
9,
10]. An alternative explanation is that THC is effluxed in the perfused human placenta by MRP2/3 expressed in the apical membrane of the syncytiotrophoblast. However, through PBPK modeling and simulations together with observed THC concentrations in the fetal circulation and tissues, we concluded that THC is most likely effluxed in the fetal-maternal direction via an uptake transporter(s) in the basal membrane of the syncytiotrophoblast [
17]. Thus, based on our previous quantitative targeted proteomics data, we chose to investigate OATP2B1, OCT3, and OAT4 as potential candidates as they are highly expressed in the basal membrane of the syncytiotrophoblast [
12] (
Figure 1). Though OAT10 is also expressed there [
18] (not quantified in our proteomics study), we did not have access to a cell line overexpressing this transporter. We deliberately utilized cells that overexpress human SLCs (such as HEK293 cells) to allow maximum sensitivity to identify the transporter(s) involved in the placental efflux of THC. Endogenous transporters in our HEK cell lines were not a confounding factor as uptake of cannabinoids or the transporter prototypic substrates in the presence and absence of selective inhibitors of the transporters in the non-transfected HEK cells was found not to be significantly different (data not shown).
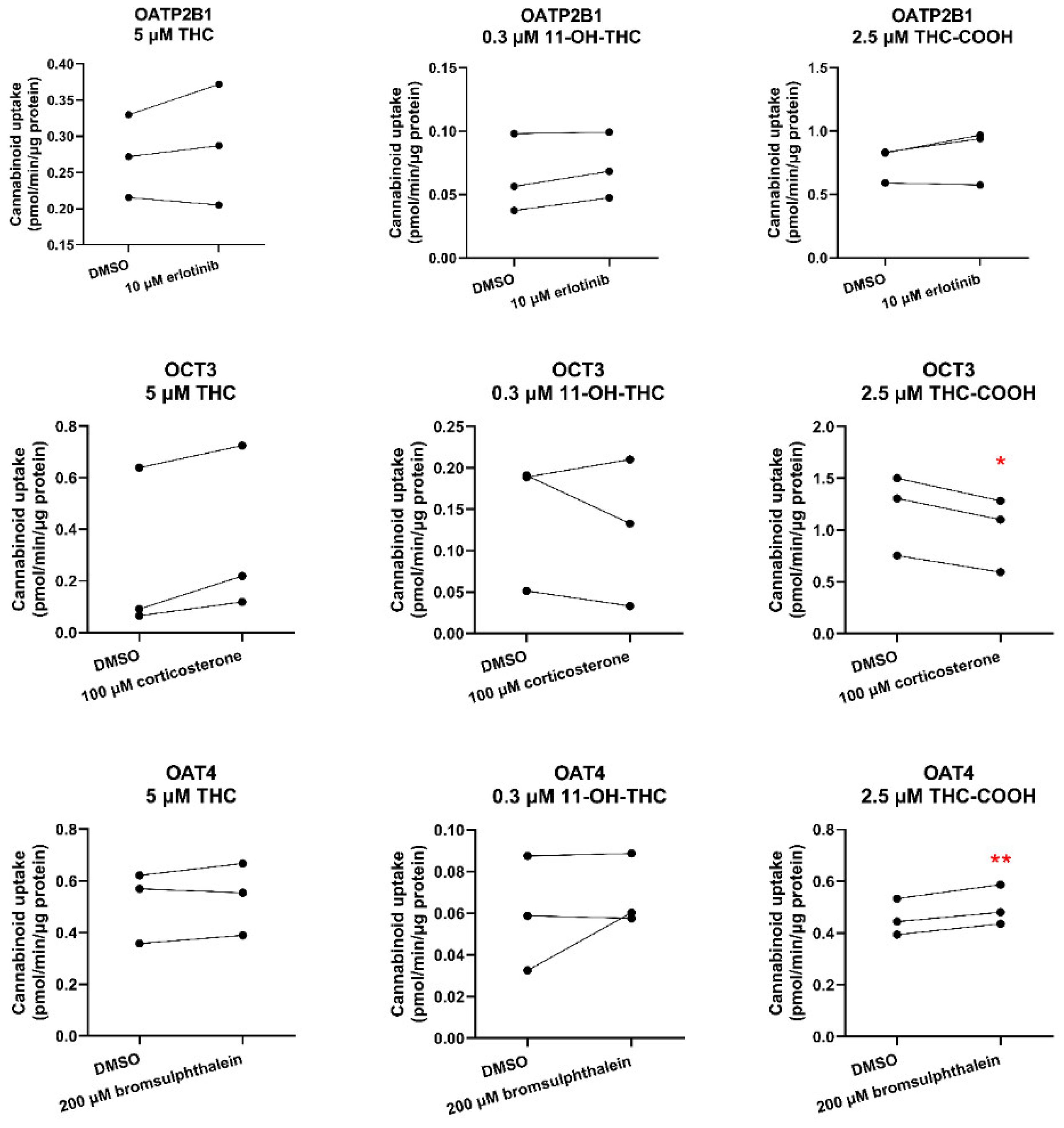
We found that THC or 11-OH-THC are not substrates of OATP2B1, OCT3 or OAT4 (
Figure 2,
Table S3). Therefore, the identity of the transporter(s) mediating fetal-maternal efflux of THC remains unknown. At the same time, we cannot completely discount efflux transporters in the apical membrane of the syncytiotrophoblast other than P-gp, BCRP or MRP4. Possible candidates are MRP2 and MRP3 based on immunohistochemistry, colocalization, and proteomics data [
11,
12,
19]. We were unable to investigate these transporters as cell lines expressing these transporters to conduct efflux studies in Transwells were not available to us. Experiments using Transwells (rather than using membrane vesicles) is best suited to identify transport of highly lipophilic compounds such as THC (pK
a = 10.6, Log P = 6.97) which binds avidly to labware. Moreover, the majority of the reported substrates of MRP2/3 are hydrophilic compounds [
20].
Surprisingly, THC-COOH (an anion, pK
a = 4.2, Log P = 5.24) was found to be a weak substrate of OCT3 and therefore OCT3 could potentially limit fetal exposure to THC-COOH provided OCT3 transports drugs in the fetal to maternal direction. There is evidence to suggest that OCT3 transport can be bidirectional [
21]. In
Oct3-/- pregnant mice, the fetal-to-maternal area under the curve (AUC
0-∞) ratio exposure to metformin, an OCT3 substrate, is decreased by 44% [
21]. Irrespective of the directionality of OCT3 transport, our perfused human placenta studies indicate that THC-COOH passively crosses the placenta [
6]. These data indicate that any in vivo (or
ex-vivo) transport of THC-COOH by placental OCT3 is likely negligible.
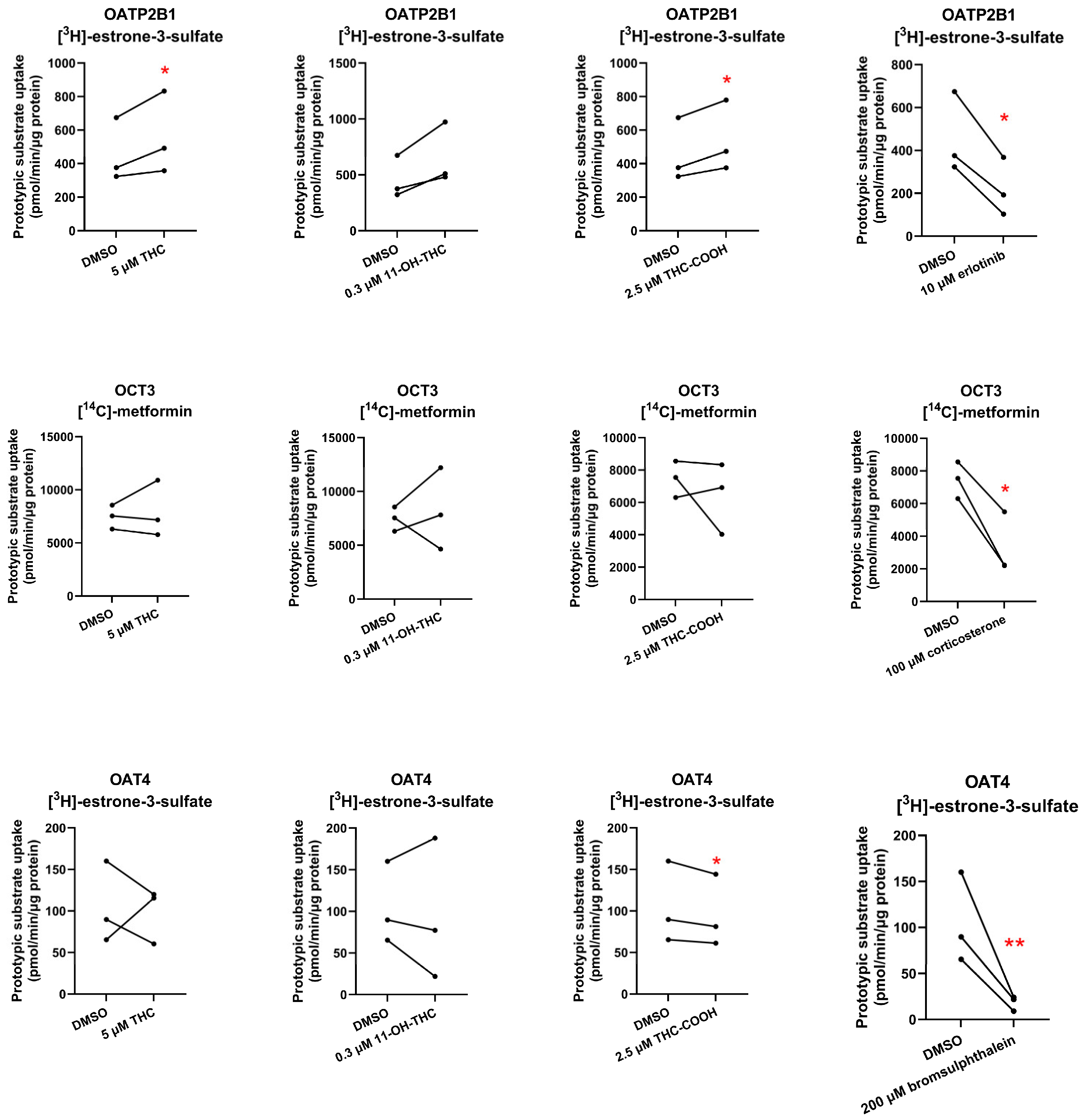
None of the cannabinoids were found to be inhibitors of the investigated placental SLC transporters except for THC-COOH which weakly inhibited OAT4 (
Figure 3,
Table S3). Given the high plasma protein binding of THC-COOH (96.35% in mice) [
10] and its estimated in vivo maximal fetal plasma concentrations (~125 nM after maternal oral administration of 14.8 mg THC [
22,
23], assuming it crosses the placenta by passive diffusion, it is unlikely to result in any in vivo inhibition of placental OAT4. Interestingly, 11-OH-THC, and THC-COOH slightly stimulated OATP2B1-mediated uptake of estrone-3-sulfate, suggesting that they allosterically modulate OATP2B1 activity.
THC’s blood CL in humans after intravenous or inhalation administration is blood-flow limited [
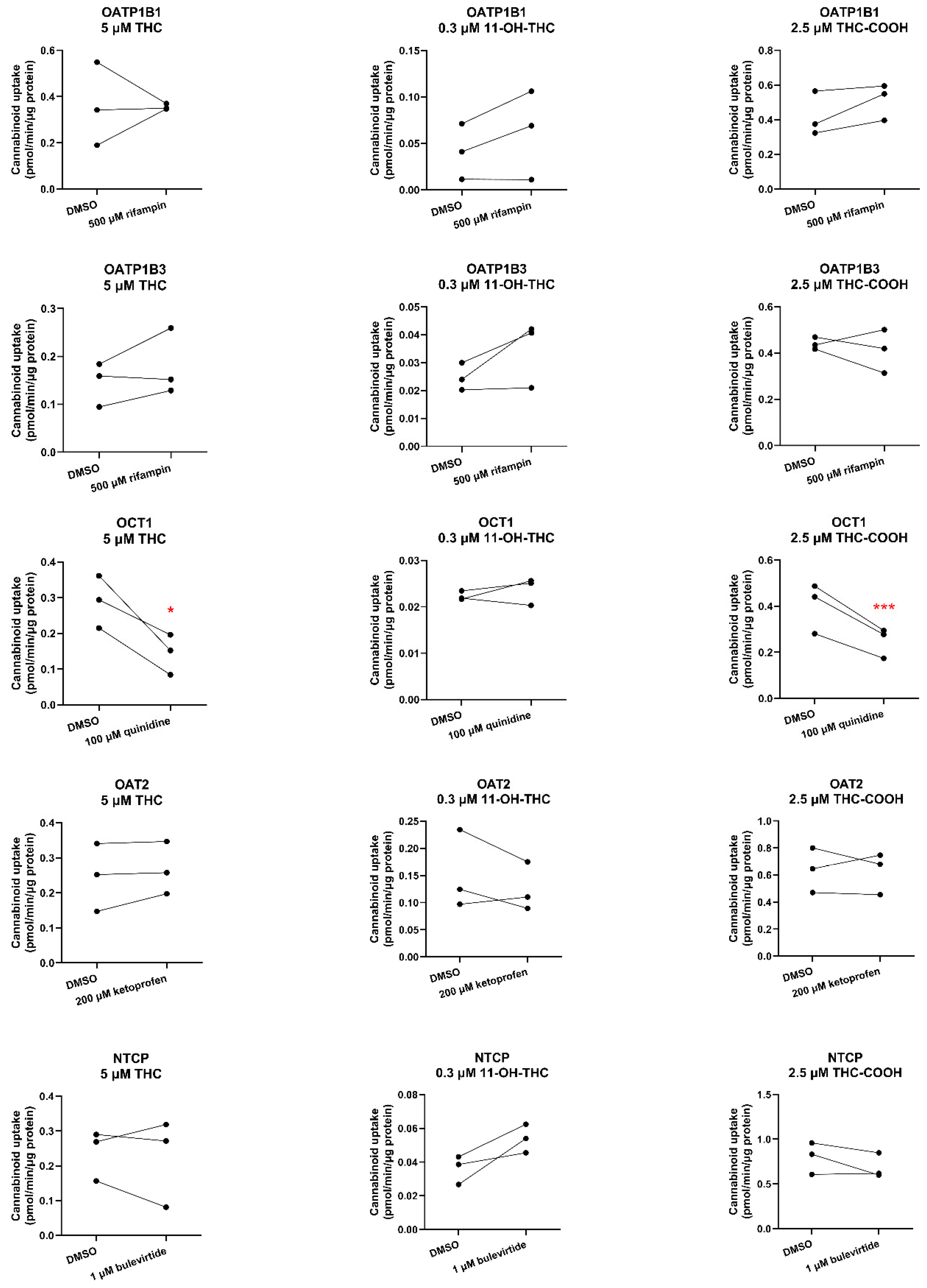
24] while its oral CL is dependent on its intrinsic hepatic CL. However, it is unknown whether THC utilizes transporters to gain entry into the hepatocytes. If it does, drug-drug interactions or genetic polymorphism of the transporters may affect its blood CL (especially after oral administration). Therefore, we investigated whether THC and its major metabolites are substrates or inhibitors of sinusoidal transporters namely, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OATP2B1, OCT1, OAT2, and NTCP.
Except for OCT1, none of the cannabinoids were substrates or inhibitors of the investigated transporters. We found THC and THC-COOH are OCT1 substrates (
Figure 4,
Table S4) but not OCT1 inhibitors at their pharmacologically relevant concentrations (
Figure 5,
Table S4). That OCT1 can transport THC was surprising because THC is an anion at physiological pH (pK
a = 10.6; [
25]). Anions transported by OCTs are usually zwitterions like creatinine, cimetidine [
26,
27]. Based on these data, THC and THC-COOH are unlikely to be perpetrators of OCT1 drug interactions but could be objects of OCT1-related cannabinoid-drug interactions provided their fraction transported in vivo by OCT1 is significant.
Our data has some limitations. First, there was a moderate degree of inter-day variability in transporter activity. However, this does not detract from the conclusions drawn. We were not able to evaluate all the major drug transporters expressed in the placenta (e.g. MRPs) due to lack of availability of cells that express these transporters and can form tight junctions (e.g. Madin-Darby canine kidney cells). It is also possible that THC is a substrate of one of the many transporters that transport endogenous compounds (e.g. nutrients) and are distinct from transporters investigated here.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
(-)-Δ9-THC (50 mg/mL) was purchased from Cayman Chemicals (Ann Arbor, MI). (±)11-OH-THC (1 mg/mL), (±)-11-nor-9-carboxy-THC (THC-COOH) (1 mg/mL), (-)-Δ9-THC-D3 (1 mg/mL), (±)11-OH-THC-D3 (1 mg/mL), and (±)-11-nor-9-carboxy-Δ9-THC-D3 (1 mg/mL) in methanol were from Cerilliant Corporation (Round Rock, TX). Bromsulphthalein, bulevirtide trifluoroacetate, corticosterone, erlotinib, ketoprofen, quinidine, and rifampin were from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). For radiolabeled compounds, 1 mCi/mL (25 Ci/mmol) [3H]-rosuvastatin, 1 mCi/mL (40 Ci/mmol) [3H]-estrone-3-sulfate, 1 mCi/mL (25 Ci/mmol) [3H]-cGMP, and 1 mCi/mL (20 Ci/mmol) [3H]-taurocholic acid were from American Radiolabeled Chemicals (St. Louis, MO), while 0.1 mCi/mL (110 mCi/mmol) [14C]-metformin was from Moravek Biochemicals, Inc (Brea, CA). Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS), 0.25% trypsin-EDTA, GlutaMAX, fetal bovine serum (FBS), Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium (DMEM) (4.5 g/L glucose and 1.0 g/L glucose), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), acetonitrile (liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry grade), acetic acid (liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry grade), SureSTART™ polypropylene insert (Catalog #6EME03CPPSP) were from ThermoFisher Scientific (Hampton, NH). Poly-D-lysine-coated 48-well cell culture plate were from Corning (Corning, NY). Low-binding microcentrifuge tubes were from Genesee Scientific (San Diego, CA). Milli-Q water was used in all preparations. High Density Polyethylene MiniVial (7 mL, catalog #125500) was from RPI Research Products International (Mount Prospect, IL). All other chemicals and reagents were obtained commercially at the highest quality available.
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Cell Culture
HEK-OATP2B1, HEK-OCT1, HEK-OCT3, HEK-OAT4, and HEK-NTCP cells were generously provided by SOLVO Biotechnology (Szeged, Hungary). HEK-OATP1B1 and HEK-OATP1B3 cells were generously provided by Gilead Sciences Inc (Foster City, CA). HEK-OAT2 cells were generously provided by Pfizer Inc (Cambridge, MA). All cells were preserved in liquid nitrogen. The passage number of all cells used was no greater than 10. Except for HEK-OATP1B1 and HEK-OATP1B3 cells, all cells were cultured in high glucose (4.5 g/L) DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% GlutaMAX, 1% penicillin-streptomycin. HEK-OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 cells were cultured in high glucose (4.5 g/L) DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin-streptomycin, 25 mM HEPES, 0.1 mM MEM non-essential amino acid solution, 600 μg/mL geneticin, and 10 μg/mL blasticidin. All cells were maintained in a humidified incubator at 37°C in 5% CO2 with 95% humidity. When cells reached ~90% confluency, after washing with HBSS and trypsinization, they were passaged into a new flask, and then seeded into 48-well plates at a density of 20,000 cells per well for transport assays.
4.2.2. Cannabinoid Uptake by SLC Transporters
When confluent in the 48-well plate, cells were rinsed twice with 0.5 mL 37°C HBSS and preincubated with 0.5 mL HBSS at 37°C for 15 min. In order to ensure that the contents of the transport assays were at 37°C, pilot studies showed that the setting of the water bath or hot plate needed to be at 42°C. After aspiration of HBSS, cells were incubated with 5 μM THC, 0.3 μM 11-OH-THC, or 2.5 μM THC-COOH with or without the transporter inhibitor (or inhibitory condition) in HBSS (0.2 mL) containing DMSO (final concentration <0.2% v/v) at 37°C for 15 s (preliminary studies showed that this time was within the linear uptake range, data not shown). After aspirating HBSS, cells were immediately washed three times with 0.5 mL ice-cold HBSS. Then, cells were lysed with 200 μL 80% acetonitrile containing 100 nM THC-D3, 100 nM 11-OH-THC-D3, or 100 nM THC-COOH-D3. All cell lysates were vortexed for 15 s and centrifuged at 19083g for 15 min at 4°C. The supernatant (100 μL) was transferred to a disposable clean SureSTART™ polypropylene insert and stored at -20°C until analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
4.2.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
On the day of analysis, 10 μL sample was injected onto LC-MS/MS for analysis using a Xevo TQ-XS Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer (Waters, Milford, MA) coupled with the Acquity ultra-performance liquid chromatography system (Waters, Milford, MA). The samples were eluted on an Acquity ultra-performance liquid chromatography BEH C
18 column (130Å, 1.7 µm, 2.1 mm × 50 mm) attached to the AccQ Tag Ultra C
18 VanGuard Pre-column (100Å, 1.7 µm, 2.1 mm × 5 mm). For other analytical conditions, please see
Tables S1 and S2. All sample was quantified and analyzed by MassLynx™ V4.2. Given that the corresponding deuterated cannabinoid was employed as an internal standard, a single-point calibration method was utilized to quantify the molar concentration of the analytes, assuming that the analyte and the internal standard produce equivalent signal intensity.
4.2.4. Inhibition of SLC Transporters by the Cannabinoids
When confluent in 48-well plate, cells were processed as described above. After aspirating HBSS, the cells were incubated with the radiolabeled transporter substrate, transport inhibitor (see
Table 1 for concentrations), 5 μM THC, 0.3 μM 11-OH-THC, or 2.5 μM THC-COOH in 0.2 mL of HBSS containing DMSO (final concentrations <0.2% v/v) at 37°C for 2 min for substrates labeled with [
3H] or for 10 min for substrates labeled with [
14C] (preliminary studies showed that these times were within the linear uptake range). Uptake was quenched by aspirating the buffer and immediately washing the cells three times with ice-cold HBSS. Then, cells were lysed with 80% acetonitrile and 100 μL of the cell lysate were added to 5 mL Ecoscint™ (National Diagnostics, Atlanta, GA) in High Density Polyethylene MiniVial and capped. After 15s of mixing on a vortex, the radioactivity (corrected for background radioactivity) was quantified using a scintillation counter (PerkinElmer Tri-Carb 3110TK).
4.2.5. Statistical Analysis
Three independent experiments were performed, each in triplicate, for all the uptake and inhibition assays. Data are reported as means of each experiment and were analyzed using the paired t-test. P-values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 10 (La Jolla, CA).