Submitted:
01 November 2024
Posted:
04 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Samples
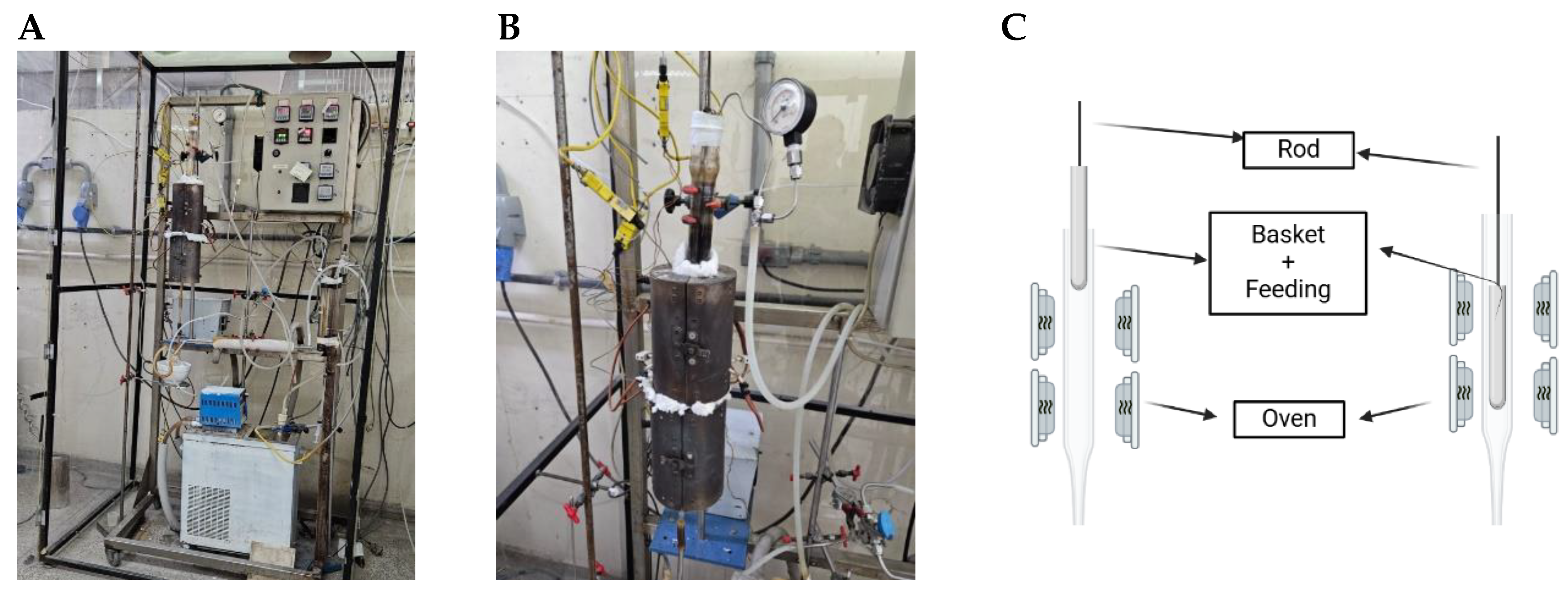
2.2. Pyrolysis and Co-Pyrolysis Experiments:
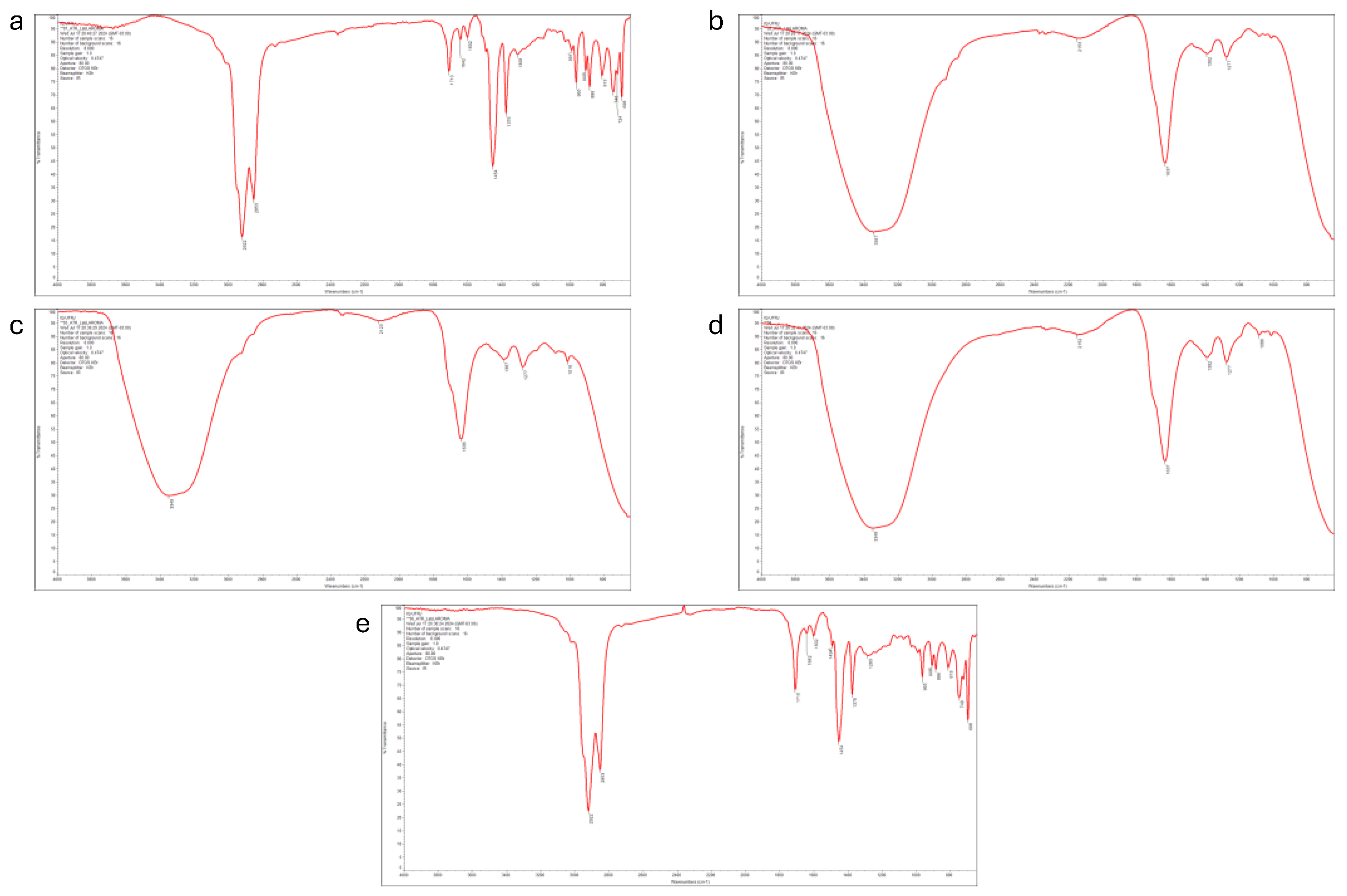
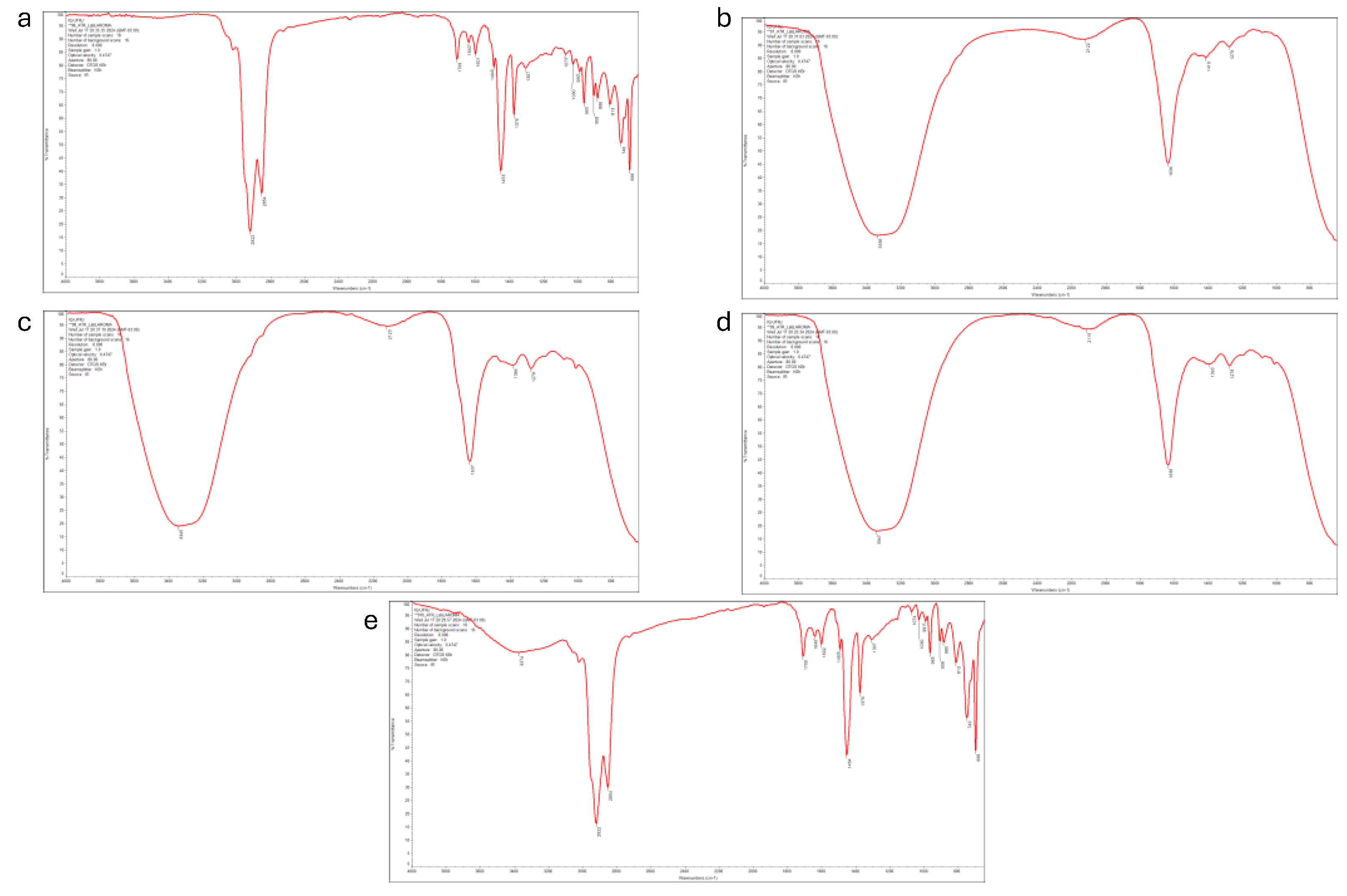
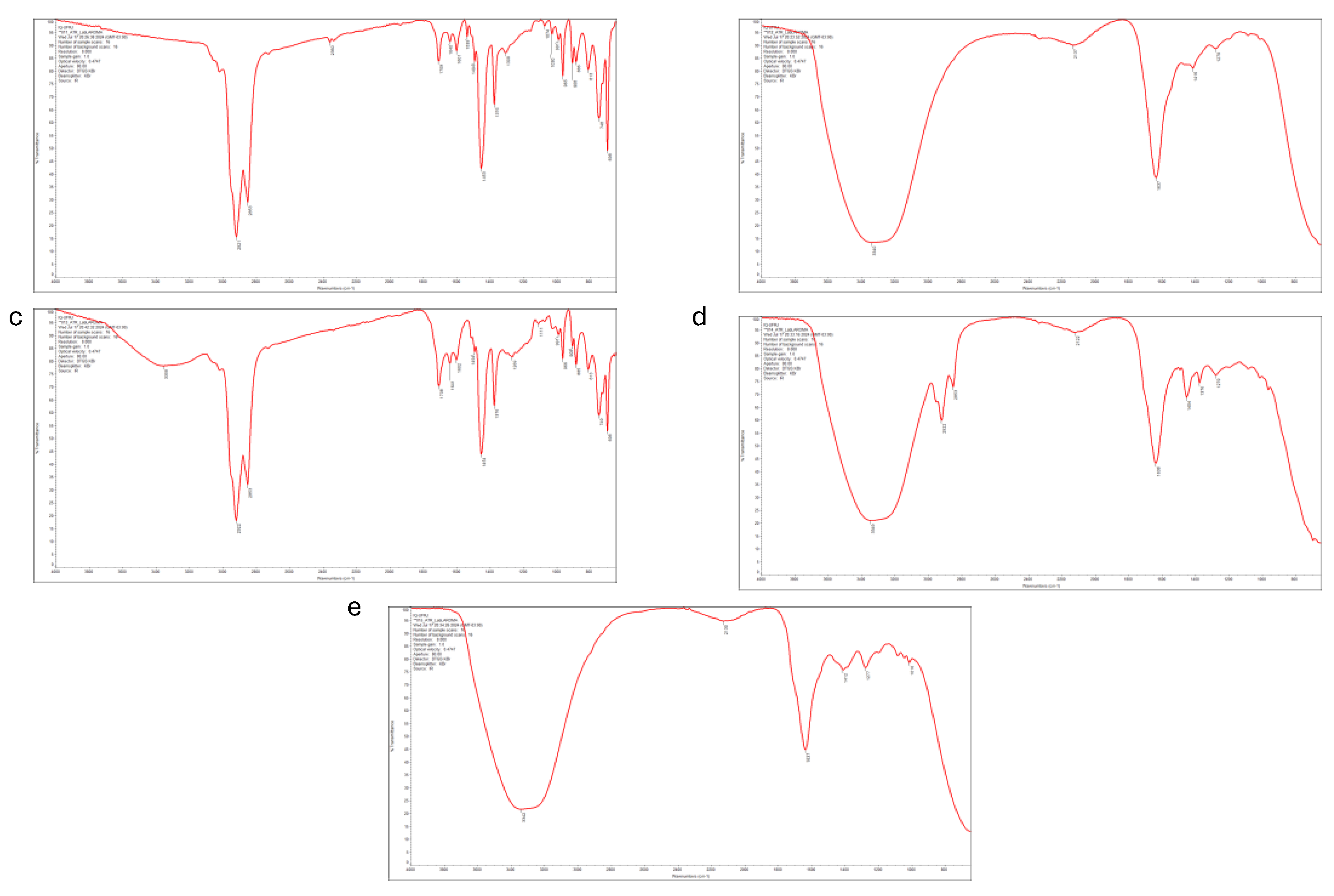
2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
2.4. Elemental Analysis
2.5. Regression Model with Decision Tree for Predicting CHN Content in Pyrolytic Oil
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Temperature and Starting Material Composition on the Yield and Chemical Compounds of Pyrolytic Oil
3.2. Regression Model with Decision Tree for Predicting CHN Content in Pyrolytic Oil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Ruschel, C.F.C.; Huang, C.T.; Samios, D.; Ferrão, M.F. EXPLORATORY ANALYSIS APPLIED TO ATTENUATED TOTAL REFLECTANCE FOURIER TRANSFORM INFRARED (ATR-FTIR) OF BIODIESEL/DIESEL BLENDS. Quím. Nova. [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M.; Ponnusamy, V.K.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Nižetić, S.; Praveenkumar, T.R. Production and Utilization of Pyrolysis Oil from Solidplastic Wastes: A Review on Pyrolysis Process and Influence of Reactors Design. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 302, 114046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Cao, L.; Gao, J.; Xu, C. Properties and Utilization of Waste Tire Pyrolysis Oil: A Mini Review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 211, 106582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Wang, F.; Quan, C.; Santamaria, L.; Lopez, G.; Williams, P.T. Tire Pyrolysis Char: Processes, Properties, Upgrading and Applications. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2022, 93, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollakota, A.R.K.; Reddy, M.; Subramanyam, M.D.; Kishore, N. A Review on the Upgradation Techniques of Pyrolysis Oil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1543–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, H.; Teoh, Y.H.; Jamil, M.A.; Gulzar, M. Potential of Tire Pyrolysis Oil as an Alternate Fuel for Diesel Engines: A Review. J. Energy Inst. 2021, 96, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Parveen, M.; Haniu, H.; Sarker, M.R.I. Innovation in Pyrolysis Technology for Management of Scrap Tire: A Solution of Energyand Environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2010, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Pan, P.; Liu, T.; Wu, L.; Xu, G. Thermodynamic and Economic Analysis of a Novel Design Combining Waste Tire Pyrolysis with Silicon Production Waste Heat Recovery and Organic Rankine Cycle. Energy 2023, 283, 128500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, B.; Yakoob, M.; Shah, M.P. Agricultural Waste Management Strategies for Environmental Sustainability. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Pandey, D.; Patil, T.; Sawarkar, A.N. Pyrolysis of Banana Leaves Biomass: Physico-Chemical Characterization, Thermal Decomposition Behavior, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analyses. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Roa Hernan, D.; Ayala Ruiz Nathaly; Malagon-Romero Dionisio H. Evaluation of the Production of Bio-Oil Obtained Through Pyrolysis of Banana Peel Waste. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 89, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taib, R.M.; Abdullah, N.; Aziz, N.S.M. Bio-Oil Derived from Banana Pseudo-Stem via Fast Pyrolysis Process. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 148, 106034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniyi, A.G.; Ighalo, J.O.; Amosa, M.K. Modelling and Simulation of Banana (Musa Spp.) Waste Pyrolysis for Bio-Oil Production. Biofuels 2021, 12, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, N.; Yargic, A.S.; Yarbay Sahin, R.Z.; Yaman, E. Valorization of Banana Peel Waste via In-Situ Catalytic Pyrolysis Using Al-Modified SBA-15. Renew. Energy 2019, 140, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moasas, A.M.; Amin, M.N.; Khan, K.; Ahmad, W.; Al-Hashem, M.N.A.; Deifalla, A.F.; Ahmad, A. A Worldwide Development in the Accumulation of Waste Tires and Its Utilization in Concrete as a Sustainable Construction Material: A Review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relatório de pneumáticos: Resolução Conama no 416/09 - 2020 (ano-base 2019); Sousa, L. F. de, Ed.; Instituto Brasileiro Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis - IBAMA: Brasília, DF, 2021; ISBN 9786557990162. [Google Scholar]
- Kandpal, S.; Tagade, A.; Sawarkar, A.N. Critical Insights into Ensemble Learning with Decision Trees for the Prediction of Biochar Yield and Higher Heating Value from Pyrolysis of Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 411, 131321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.H.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification And Regression Trees; 1st, *!!! REPLACE !!!* (Eds.) ; Routledge, 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-13947-0.
- Miranda, D.M.V. de Degradação térmica e catalítica dos polímeros poli(acrilonitrila-co-butadieno-co-estireno) (ABS) e poliestireno de alto impacto (HIPS) oriundos de resíduos eletroeletrônicos. 217.
- Daimary, N.; Boruah, P.; Eldiehy, K.S.H.; Pegu, T.; Bardhan, P.; Bora, U.; Mandal, M.; Deka, D. Musa Acuminata Peel: A Bioresource for Bio-Oil and by-Product Utilization as a Sustainable Source of Renewable Green Catalyst for Biodiesel Production. Renew. Energy 2022, 187, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyari, M.; Cunliffe, A.; Williams, P.T. Characterization of Oils, Gases, and Char in Relation to the Pyrolysis of Different Brands of Scrap Automotive Tires. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čepić, Z.; Mihajlović, V.; Đurić, S.; Milotić, M.; Stošić, M.; Stepanov, B.; Ilić Mićunović, M. Experimental Analysis of Temperature Influence on Waste Tire Pyrolysis. Energies 2021, 14, 5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunliffe, A.M.; Williams, P.T. Composition of Oils Derived from the Batch Pyrolysis of Tyres. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1998, 44, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banar, M.; Akyıldız, V.; Özkan, A.; Çokaygil, Z.; Onay, Ö. Characterization of Pyrolytic Oil Obtained from Pyrolysis of TDF (Tire Derived Fuel). Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 62, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, C.W.; Wilby, R. An Artificial Neural Network Approach to Rainfall-Runoff Modelling. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1998, 43, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.W.; Mourshed, M.; Rezgui, Y. Trees vs Neurons: Comparison between Random Forest and ANN for High-Resolution Prediction of Building Energy Consumption. Energy Build. 2017, 147, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
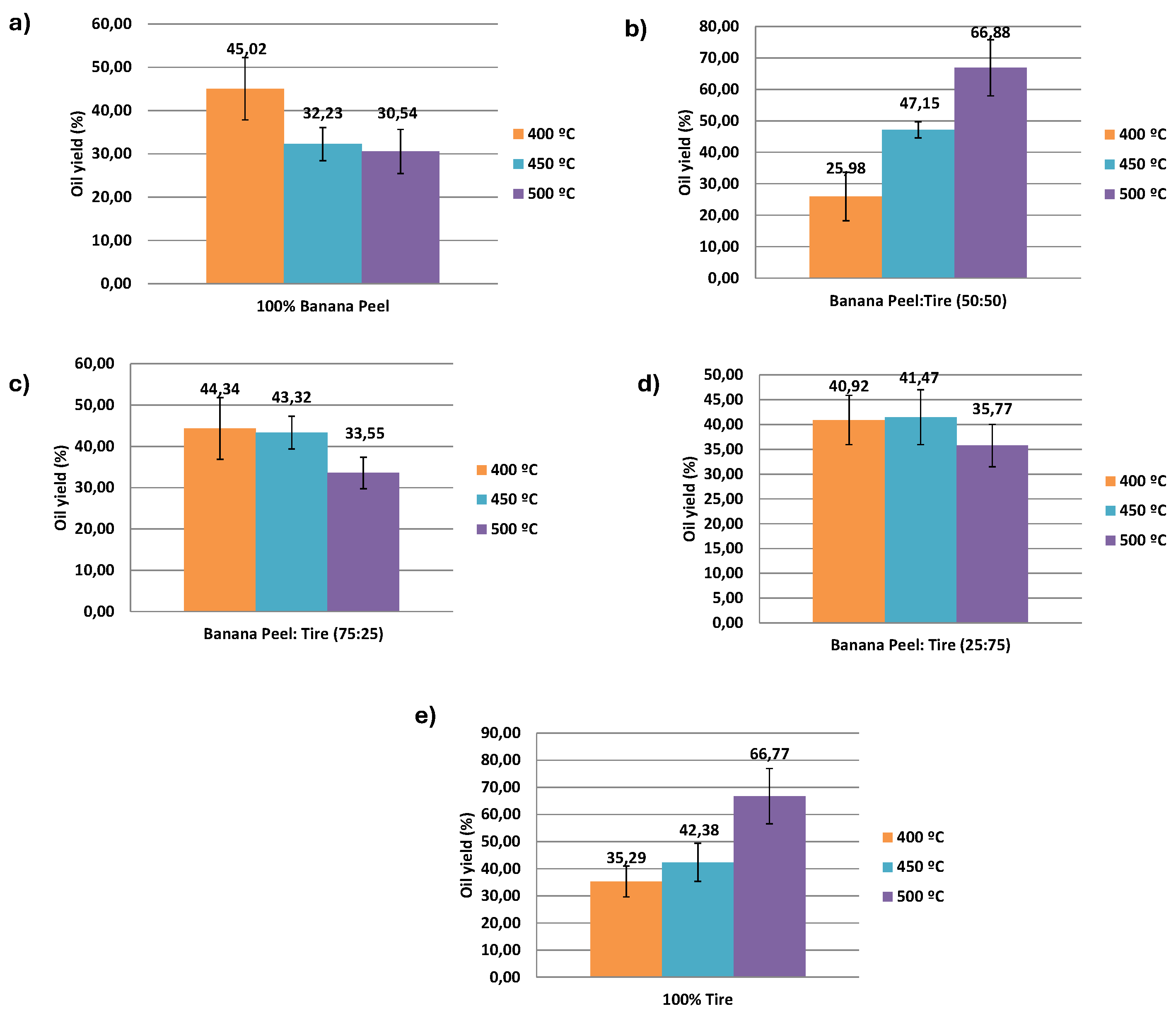
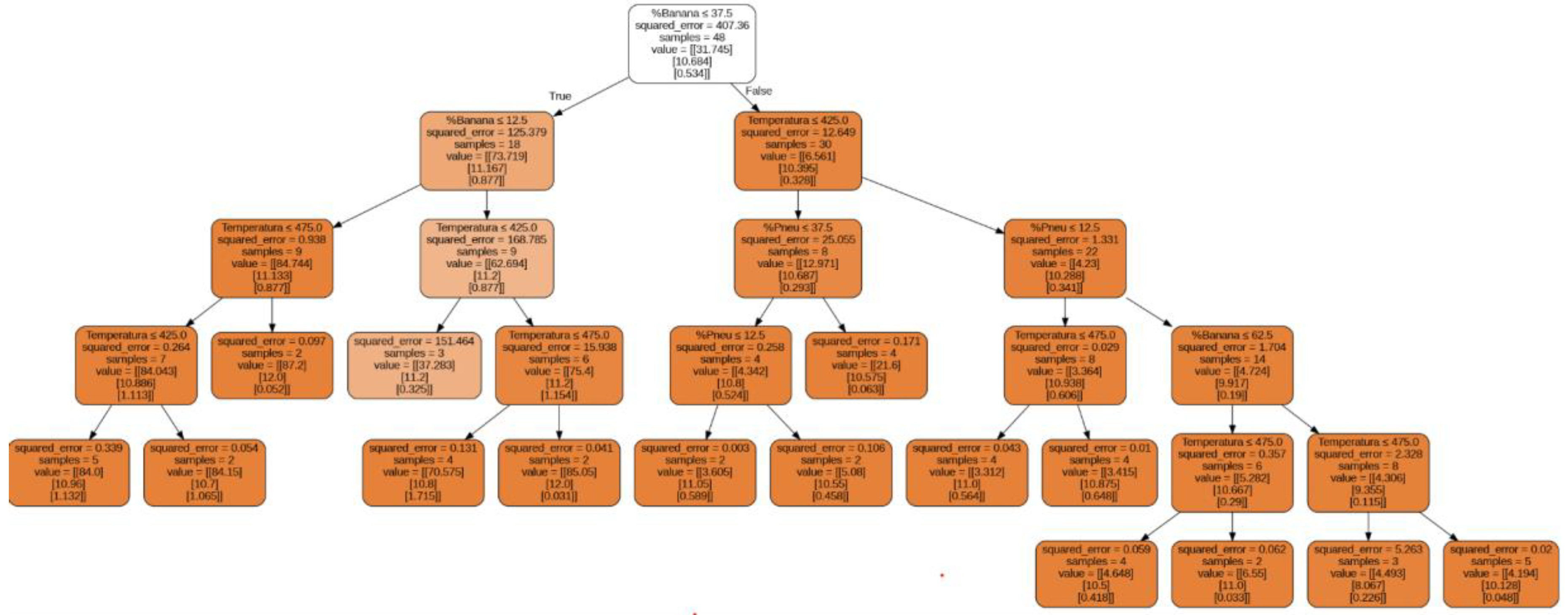
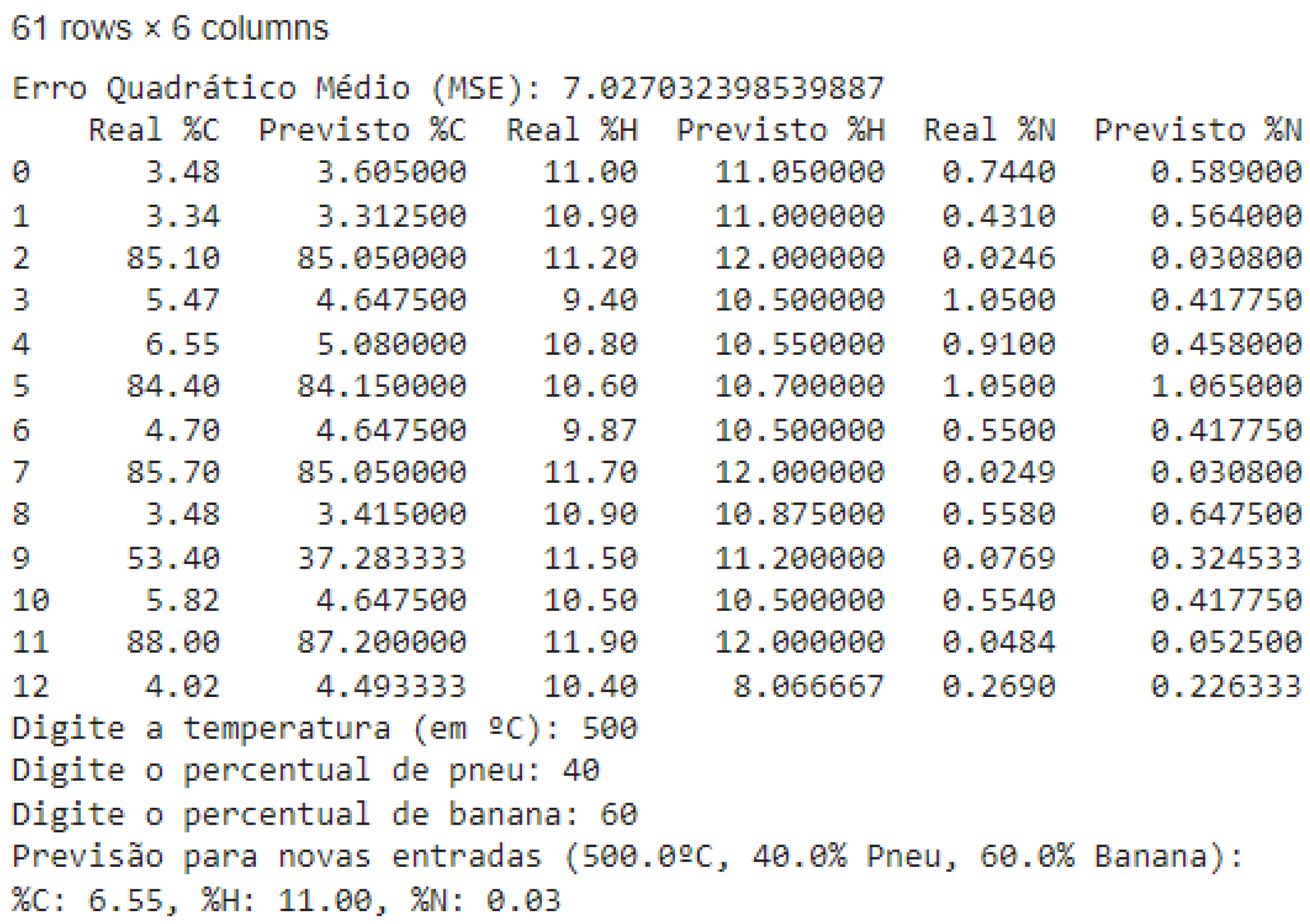
| Starting material | Temperature |
|---|---|
| Banana peel (100%) | 400, 450 and 500 ºC |
| Waste tire (100%) | |
| Banana peel: waste tire (75:25) | |
| Banana peel: waste tire (50:50) | |
| Banana peel: waste tire (25:75) |
| Wavelength (cm-1) |
Functional Groups | Components | Pyrolysis temperature | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 ºC | 450 ºC | 500 ºC | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| 3500-3200 | O-H bonded | Alcohol and phenols | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + |
| 3500-3200 | O-H stretching | Water, O-H polymeric | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + |
| 3050-2800 | C-H stretching | Alkanes | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| 1750-1650 | C=O stretching | Aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, quinines | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| 1645-1500 | C=C stretching | Alkenes | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1475-1350 | C-H bending | Alkanes | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| 1266-1342 | C-N bending | Aromatic amines | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - |
| 1300-1150 | C-O stretching | Alcohols | - | + | + | - | + | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + |
| 1300-1150 | O=H bending | Phenols, esters, ethers | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + |
| 1150-1000 | C-H bending | Alkenes | - | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | - | + |
| 650-1000 | C=C stretching | Alkenes | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | - | - |
| 900-675 | O-H bending | Aromatics | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | - | - |
| Temperature (ºC) | Type of oil | C%* | H%* | N%* | H/C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 | T* (100%) | 82,74±1,03 | 11,01±2,31 | 1,23±14,95 | 0,13 |
| BP* (100 %) | 3,54±0,20 | 11,43±0,62 | 0,07±10,88 | 3,22 | |
| T/ BP (50/50) | 5,47±12,27 | 9,37±10,80 | 1,05±10,77 | 1,71 | |
| T/ BP (25/75) | 7,15±1,09 | 10,69±3,97 | 0,79±4,50 | 1,49 | |
| T/ BP (75/25) | 6,55±3,02 | 10,77±7,09 | 0,91±3,91 | 1,64 | |
| 450 | T (100%) | 83,20±1,79 | 10,81±0,12 | 1,02±2,20 | 2,20 |
| BP (100 %) | 3,30±1,43 | 10,72±0,84 | 0,46±2,02 | 3,25 | |
| T/ BP (50/50) | 4,30±2,59 | 10,78±2,19 | 0,34±2,31 | 2,51 | |
| T/ BP (25/75) | 3,75±1,06 | 10,75±2,47 | 0,15±7,28 | 2,87 | |
| T/ BP (75/25) | 71,50±4,33 | 10,63±1,89 | 1,64±11,65 | 0,15 | |
| 500 | T (100%) | 87,47±0,50 | 11,97±0,50 | 0,05±0,01 | 0,14 |
| BP (100 %) | 3,43±0,14 | 10,88±0,08 | 0,63±0,07 | 3,18 | |
| T/ BP (50/50) | 6,55±0,61 | 11,00±0,01 | 0,03±0,01 | 1,69 | |
| T/ BP (25/75) | 4,29±0,17 | 10,23±0,21 | 0,05±0,01 | 2,38 | |
| T/ BP (75/25) | 85,27±0,51 | 11,90±0,17 | 0,03±0,01 | 0,14 |
| Temperature | Proportion of the base material | Elementary Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tire (%) | Banana Peel(%) | %C | %H | %N | |
| 400 ºC | 70 | 30 | 37,28 | 11,20 | 0,32 |
| 80 | 20 | 37,28 | 11,20 | 0,32 | |
| 60 | 40 | 21,60 | 10,57 | 0,06 | |
| 40 | 60 | 21,60 | 10,57 | 0,06 | |
| 20 | 80 | 5,08 | 10,55 | 0,46 | |
| 425 ºC | 70 | 30 | 37,28 | 11,20 | 0,32 |
| 80 | 20 | 37,28 | 11,20 | 0,32 | |
| 60 | 40 | 21,60 | 10,57 | 0,06 | |
| 40 | 60 | 21,60 | 10,57 | 0,06 | |
| 30 | 70 | 5,08 | 10,80 | 0,46 | |
| 20 | 80 | 5,08 | 10,80 | 0,46 | |
| 75 | 25 | 37,28 | 11,20 | 0,32 | |
| 25 | 75 | 5,08 | 10,55 | 0,46 | |
| 50 | 50 | 21,60 | 10,57 | 0,06 | |
| 450 ºC | 70 | 30 | 70,58 | 10,80 | 1,71 |
| 80 | 20 | 70,58 | 10,80 | 1,71 | |
| 60 | 40 | 4,65 | 10,50 | 0,42 | |
| 40 | 60 | 4,65 | 10,50 | 0,42 | |
| 30 | 70 | 4,49 | 8,07 | 0,23 | |
| 20 | 80 | 4,49 | 8,07 | 0,23 | |
| 475 ºC | 70 | 30 | 70,58 | 10,80 | 1,71 |
| 80 | 20 | 70,58 | 10,80 | 1,71 | |
| 60 | 40 | 4,65 | 10,50 | 0,42 | |
| 40 | 60 | 4,65 | 10,50 | 0,42 | |
| 20 | 80 | 4,49 | 8,07 | 0,23 | |
| 30 | 70 | 4,49 | 8,07 | 0,23 | |
| 75 | 25 | 70,58 | 10,80 | 1,71 | |
| 25 | 75 | 4,49 | 8,07 | 0,23 | |
| 50 | 50 | 4,65 | 10,50 | 0,42 | |
| 500 ºC | 70 | 30 | 85,05 | 12,00 | 0,03 |
| 80 | 20 | 85,05 | 12,00 | 0,03 | |
| 60 | 40 | 6,55 | 11,00 | 0,03 | |
| 40 | 60 | 6,55 | 11,00 | 0,03 | |
| 30 | 70 | 4,19 | 10,13 | 0,05 | |
| 20 | 80 | 4,19 | 10,13 | 0,05 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





