1. Introduction
1.1. Background
The attainable moment set (AMS), initially proposed in Ref. [
1,
2], is an important concept for an aircraft’s control authority. Given limits of the actuators, the AMS is a moment set producible by the effectors’ joint effort [
3]. Consider an LTI system, its AMS is a convex set described by [
4]:
where
is the vector of
k-dimensional generalized moments;
is the vector of
m-dimensional inputs;
is the effectiveness matrix;
and
are the inputs’ lower and upper limits. The term “generalized moment” refers to all quantities which have an arithmetic relationship with the inputs, such as moments, forces, rotational and translational accelerations, or load factors [
5].
For conventional airplanes, usually
, with a one-to-one mapping between 3 moments and 3 inputs. However, modern designs such as electrical Vertical Take-Off and Landing vehicles (eVTOLs) pose a difference due to utilization of distributed electric propulsion (DEP) to provide VTOL ability [
6,
7,
8,
9]. During VTOL flight, the powered-lift DEP provides both rotational and vertical translational trim and maneuver. As a result, the maximum rotational and vertical translational maneuverability is also coupled due to limits of the rotors. To fully understand the control authority of eVTOLs, the conventional AMS in
described in [
2] should be naturally extended to
, adding the vertical force on top of the three moments. Accordingly, the term “Attainable Moment Set” should be generalized to “Attainable Generalized Moment Set” to differentiate from conventional definition.
For ease of description, the term “AMS” is kept in this article but used to indicate the generalized concept.
The AMS has a substantial significance for an eVTOL’s control performance since it directly confines the maximum amplitude of achievable states’ time derivatives, e.g., angular/translational accelerations, consequentially constraining its agility, disturbance rejection capability, flight envelope, and eventually the mission profile. An inadequate generalized AMS indicates hazard in off-nominal circumstances such as input failures. Consequently, a larger margin of AMS with respect to the operation boundary means better safety margin against critical situations.
The AMS is a system’s inherent attribute given its control effectors’ parameters, such as their size, position, orientation, and available power. For conventional aircraft, the design freedom for AMS is rather restricted under the constraint of preliminary parameters such as stability and endurance; while for novel configurations like eVTOLs, the situation is opposite given their high input redundancy: number of inputs onboard an eVTOL ranges from a dozen to as much as 30 plus [
6,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15], e.g., the Lilium Jet as described in [
6]. The level of redundancy allows for designers to exploit optimized control authority given limits in available design resources such as mass and power penalty, without violating preliminary design parameters, meanwhile increasing the system’s safety according to certification standards, such as the single failure requirement for enhanced category eVTOLs prescribed in EASA SC-VTOL [
16,
17]. For example, orientations of powered lift rotors could have a minor influence on the overall weight and stability of the airplane, while it exhibits a major impact on the moments’ production capability during VTOL flight. Owing to the large design space, the only viable means to find the most advantageous combination of all the design parameters is to calculate via optimization.
1.2. Literature Review
Several studies have already adopted optimization to design the effectors related parameters for optimal AMS. In Ref. [
18], a trim analysis is performed for a conventional aircraft enhanced with DEP over its wingspan, showing that the size of the vertical tail can be reduced by 45% by exploiting differential thrust without adversely affecting directional stability. The idea is further explored in Ref. [
19] together with a
control methodology in a sequential optimization process, resulting in reduction of the vertical tail area by 60% and lowering the required actuator bandwidth, while maintaining the overall control loop bandwidth. In Ref. [
20], propeller optimization is applied to a DEP enhanced airplane configuration to decide for the optimal propeller diameter, which shows up to 80% of take-off distance reduction compared to the two-propeller conventional counterpart. As for AMS optimization, a generic AMS framework is proposed in Ref. [
21] to aid visualize AMSs of complex systems during design phase, which is then conceptually applied to the Max Launch Abort System escape vehicle to help decide the optimal orientation of the thrust nozzles. In Ref. [
22], a trim routine is developed for an unconventional box-wing configuration to maximize local AMS at operation point. Although it does not directly relate to effector configuration of the system, it implements an optimization framework to exploit best control capability given the system redundancy.
1.3. Motivation and Objective
AMS Optimization from design perspective has been extensively discussed, however, seldom link the goal of such optimizations directly with design requirements. In Ref. [
23], a concept named “required moment set” (RMS) is developed to relate flight performance requirements with the moments that shall be generated to fulfill these requirements. As the name suggests, the RMS is the set of generalized moments that are defined according to aircraft requirements, specifying generalized moments that are required, to achieve, e.g., required bandwidth of transient maneuvers, required ability to reject disturbances, or flying according to a required mission profile. Like AMS, RMS is an inherent property of the system. The goal of optimizing the AMS is therefore to ensure its enclosing of the RMS to a maximum degree. In Ref. [
24], a framework is proposed to optimize coverage of the AMS over a given RMS. However, the work only considers 3D AMS during failure-free operation, meaning for eVTOLs one dimension in the control space is compromised and the results do not hold under failure situations, which involve more critical situations compared to normal operations, especially for certifiable applications.
In this paper, we extend the framework developed in Ref. [
24] to optimize AMS in
space, and additionally account for the critical situation of one engine inoperative (OEI). In other words, the optimization maximizes coverage of the AMS over the RMS in
under a critical engine failure. The problem essentially transforms into maximal coverage between two polytopes in 4D space. The approach is implemented for an eight-rotor eVTOL to optimize for their installation orientations, and the result is verified in a model-in-the-loop (MIL) closed-loop simulation by comparing tracking performance of initial design and the optimized configuration under failure.
2. Preliminaries and Definitions
The concepts of AMS and RMS are elaborated in Ref. [
1,
2,
23]. We briefly recall them here and extend the definitions to the generalized moment space.
Admissible Control Set (): A set in the control space, which is a Cartesian system in with as the number of effectors. consists of all possible combinations of effector positions constrained by their respective limits. Since each effector is independently actuated, it is a convex set resembling a cuboid or hyper-cuboid in the control space.
Attainable (generalized) Moment Set (
): A set in the generalized moment space, which is a Cartesian system in
with
as number of generalized moments. For traditional aircrafts,
equals 3 with roll, pitch and yaw moments. For eVTOLs,
equals 4 by adding the vertical acceleration as another “generalized” moment.
consists of all possible combinations of generalized moments that can be produced by elements in
. In this paper, we consider a linear mapping
, also known as the effectiveness matrix. Given convexity of
,
is also convex due to linear mapping of
[
5]. As a result,
is a convex polytope in
.
is principally determined by the effector configuration.
Required (generalized) Moment Set (): A set in the generalized moment space, which contains all generalized moments the system must produce to fulfill its requirements. is determined by the requirements such as disturbance rejection capability, as well as preliminary parameters of the system such as mass and moment of inertia. is considered fixed after preliminary design phase once concepts of operations and requirements are frozen.
3. Optimization Setup
3.1. Problem Definition
The problem is defined as below:
given a fixed RMS , search for an optimal set of effector related parameters within their constraint limits, to maximize the margin between and .
Geometrically, the polytope of the generalized AMS is shaped and sized such that it maximally encloses the polytope of the RMS. Note that the RMS is fixed once the system’s requirements are validated and hence will not change according to p. To reduce dimension and complexity of the optimization, it is assumed that parameters must be chosen to make a major impact on the size and shape of the AMS, while only affecting other design requirements with negligible consequences.
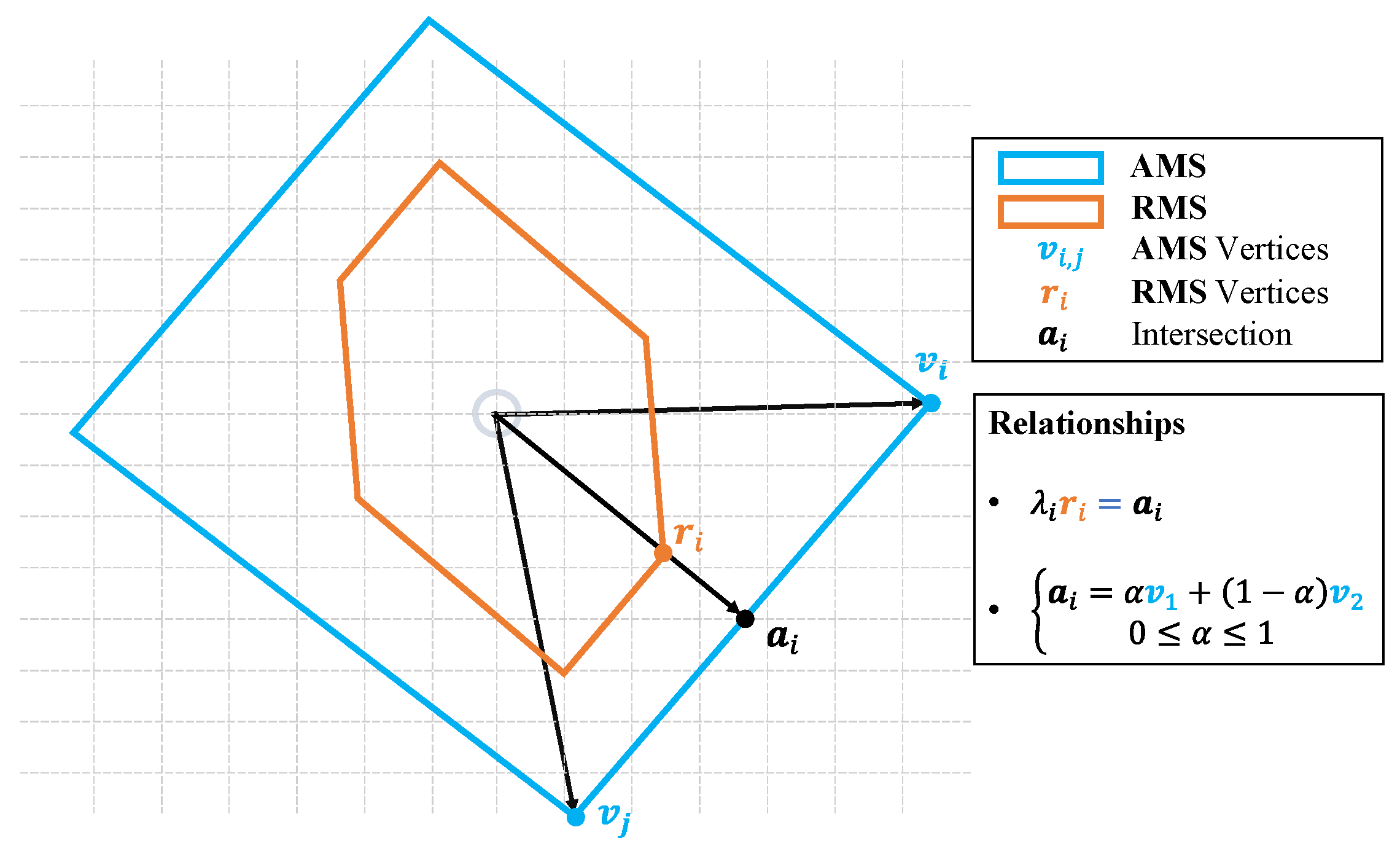
Since the AMS and the RMS are convex polytopes, the margin from the RMS to the AMS can be checked by the distance of the RMS vertices towards the AMS boundary. The concept can be illustrated by a 2D example in
Figure 1 below:
If a certain RMS vertex draws too near to the AMS boundary or in a worse case exceeds it, then the system would be limited or unable to fulfill the requirements in this direction. Given this intuition, the task could be summarized as: search for an optimal set of effector related parameters , such that the resultant has its boundary farthest away from the vertices. As mentioned earlier should be chosen and constrained in a way to mainly affect the system’s control authority instead of other preliminary design parameters. For eVTOLs, one such parameter could be orientation of the powered-lift rotors, which presents inconsequential effect on mass and CG but can largely change the moment generation due to forces, i.e., the AMS.
3.2. Optimization Formulation
The distance between AMS and RMS can be represented by a positive margin factor,
, as shown in
Figure 1. To punish RMS vertices that are close to, or even exceeds the AMS boundary, that is,
is close to 1 or smaller than 1, the optimization is formulated as [
24]:
where,
is total number of vertices on RMS,
is margin factor of the RMS vertex,
is the vector of variables to optimize, with and its lower and upper limits,
is the vector of additional constraints, e.g., structural or spatial restriction; is the upper limits of .
3.3. Optimization to Account for Critical Engine Failure
Equation (2) describes in general the coverage problem between two polytopes. For a system operating under nominal conditions, it is straightforward to simply apply Equation (2) for the optimization. However, failure cases would drastically degrade the AMS, and each single failure or combination of different failures would result in a different AMS. According to Ref. [
16,
17], a manned eVTOL in the enhanced category shall be able to continue safety flight and landing after any single failure, with minor influence on the handling quality. This means the control authority shall still present enough margin for the prescribed performance after loss of an effector. To account for this requirement, the cost function shall include failure conditions and aim to optimize the case of the most critical single failure.
To achieve the goal of critical failure optimization, Equation (2) is extended for all single failure cases in each optimization step, and then among all failure cases, take the worst-case cost function value (i.e., the highest one) among all as the critical case to optimize with, leading to the following argument as:
where,
3.4. Solving for
Key to the problem in Equation (3) is to calculate
for each RMS vertex
. Consider the 2D example in
Figure 1, the relationship between
and
is:
Equation (4) is a linear system with two equations and two unknows. Since the AMS is convex, there is only one intersection between the direction of and the AMS boundary, which occurs on one boundary cell of the AMS among others. For a 2D AMS, its boundary cell is a line segment, while the counterpart for a 3D AMS is a facet and for 4D is a tetrahedron. Given the cell of intersection, the solution will automatically guarantee that .
The concept could be generalized to 4D. The smallest boundary cell of a 4D polyhedron is a tetrahedron with 4 vertices. Assume the query direction
intersects with a cell of vertices
, then the relationship between
and
is:
With 5 equations and 5 variables to solve for. To find the right for , one way is to solve this equation for all the boundary tetrahedral of the AMS, and the only valid solution is found when is satisfied.
3.5. Solving the Optimization
The formulation in Equation (3) is highly nonlinear and might be subject to multiple local minimums. To robustly solve the optimization, a global optimization tool should be considered. For our application in this paper, we used “
surrogateopt” provided by the MATLAB global optimization toolbox [
25].
4. Test Implementation
4.1. Airframe Under Consideration
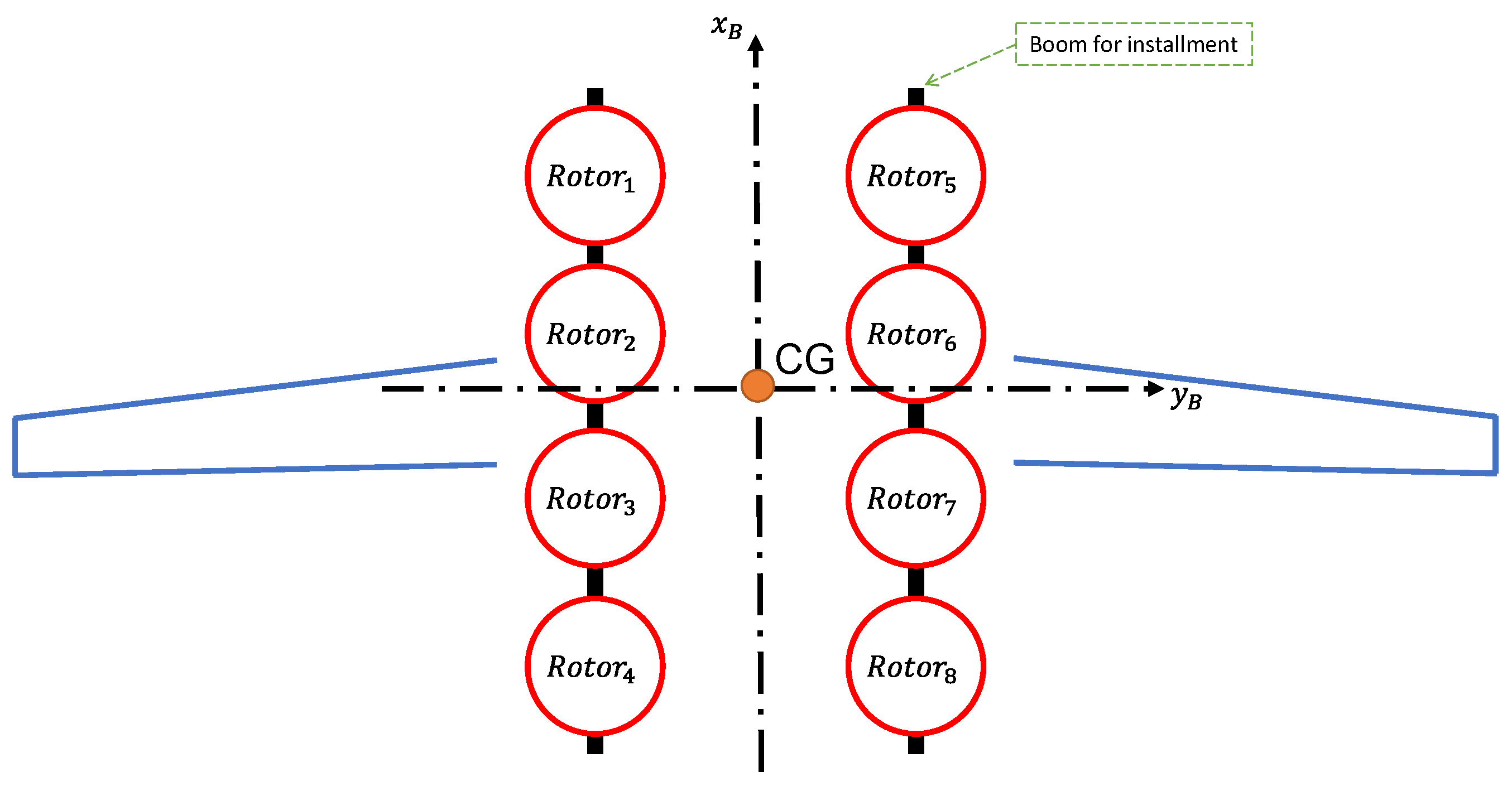
The airframe considered in this paper is a hybrid-type eVTOL with 8 similar, non-tiltable, fixed-pitch rotors for hover lift and control, and a wing to provide aerodynamic lift for cruise. The layout of the rotors and the wing w.r.t the CG is outlined in
Figure 2. Note that the rotors are NOT symmetrical about the CG in the
-axis (that is, the geometric center of the rotors do NOT coincide with the center of gravity). Given the large wingspan, the aircraft exhibits a considerably large moment of inertia in the yaw direction, which is a common characteristic of eVTOLs with such a configuration compared to normal multi-copters. Owing to this property, eVTOLs of this category often show limited yaw control authority. For the system under discussion, the rotors are fixed on two booms parallel to the fuselage, leading to the design freedom of installation orientation around the
-axis. Improvement to the yaw control authority could be hence addressed by adjusting installation angles of the hover rotors, e.g., fixation orientation of the rotors around either
axis, with certain sacrifice on the lift, pitch and roll capability.
Forces and torques of rotors in steady-state hover flight can be assumed to be linearly dependent on squared rotational speed of the rotors [
26,
27]. Since the generalized moments directly show an arithmetic relationship with the rotor forces and torques [
28], therefore, the AMS of this system is defined by:
where,
are the orientations of rotors around the -axis, positive is defined by the right-hand rule;
is the generalized moments vector of rotational accelerations and vertical load factor in the body-fixed axis;
is the effectiveness matrix [
28], as a function of
;
and are the rotational speed of the propellers and their upper limit.
By this definition, we can compute, change, and optimize the AMS by changing
, detailed derivation of the AMS by this definition could be found in Ref. [
24]. Initial design of
is by engineering tinkering based on simulation and flight tests, which takes symmetrical value in degree of
.
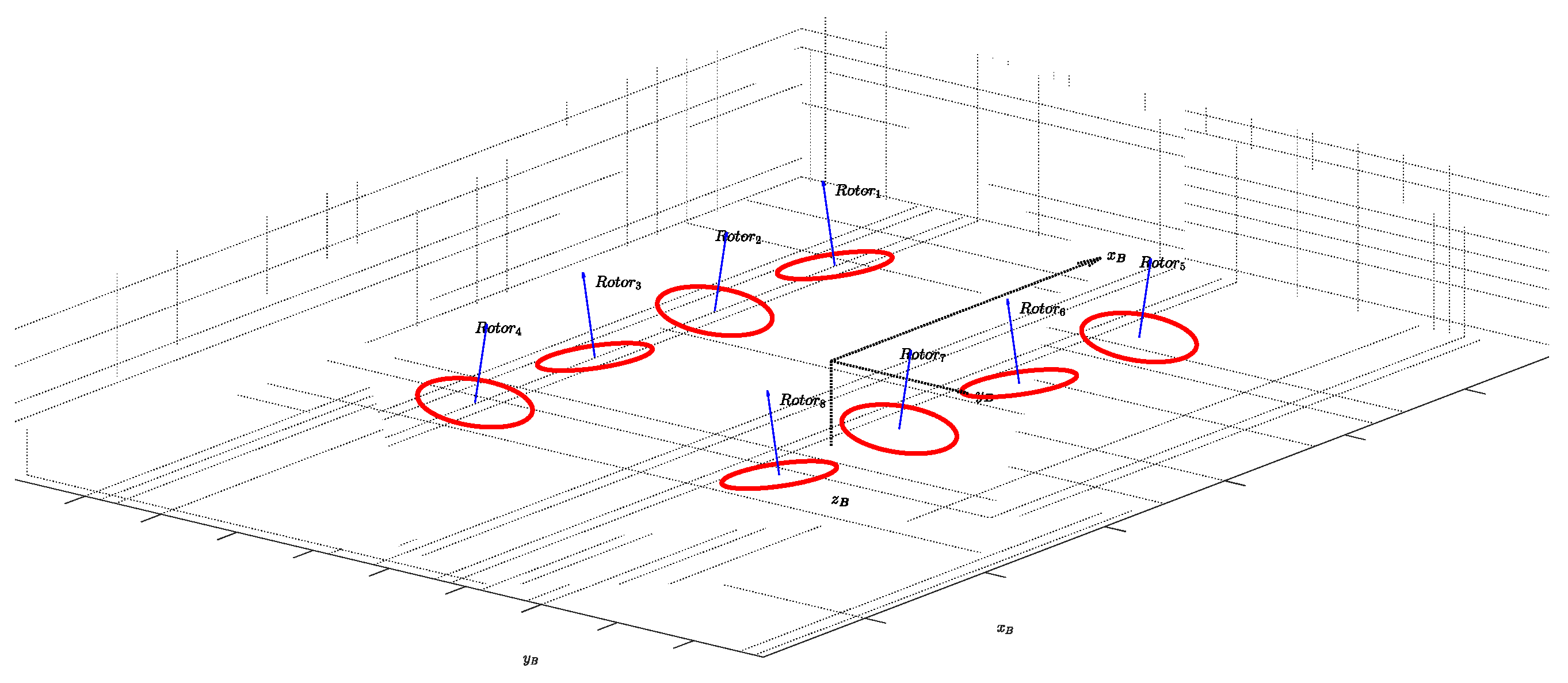
Figure 3 shows the initial design of the tilted rotors. For our test, the RMS of this A/C is derived from [
23], which considers maneuverability and wind resistance requirements. It is directly used as a priori information.
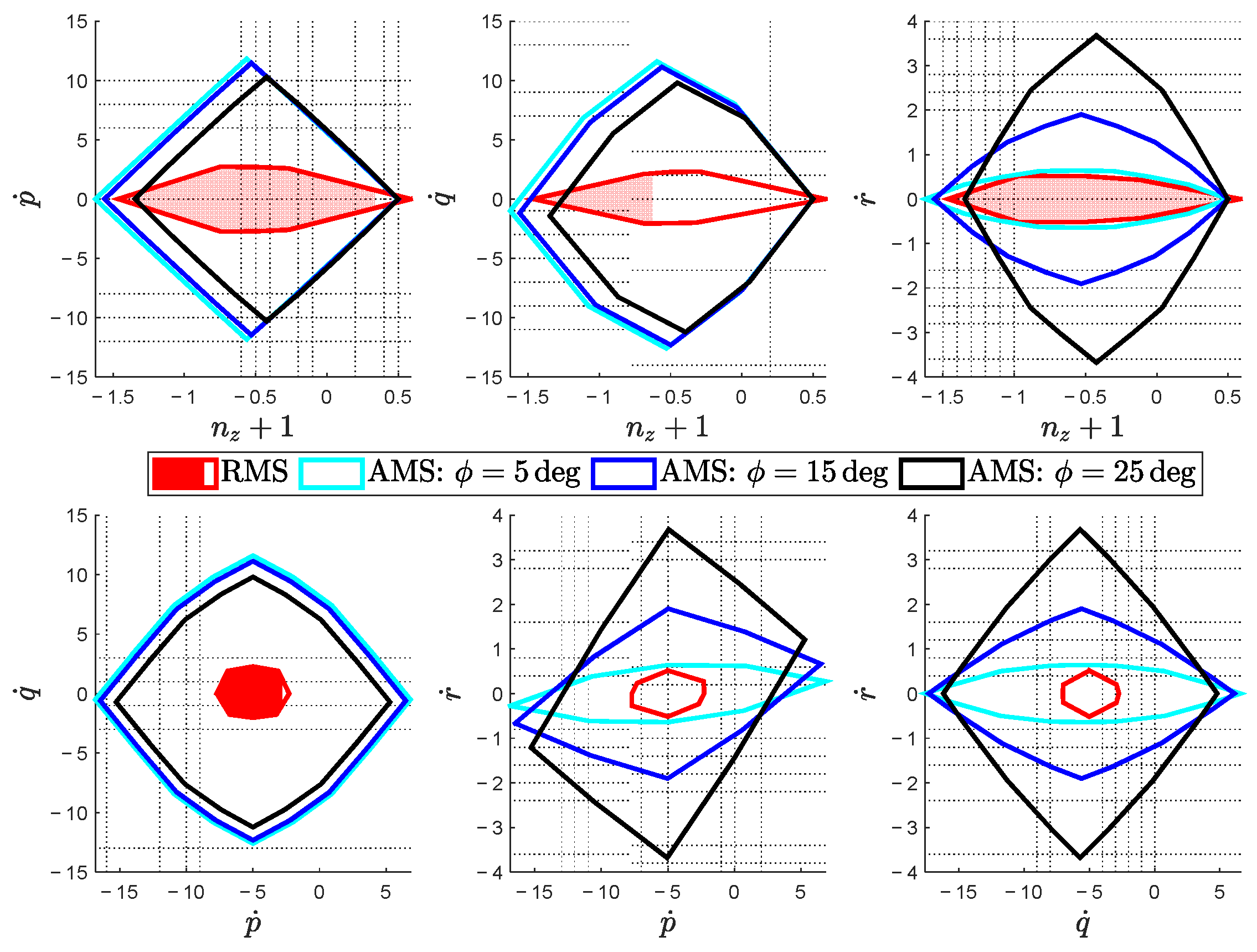
Figure 4 shows how the AMS would be changing when the value in
changes from 5
to 15
and 25
respectively, and their comparison with the a-priori RMS. Since the problem is inherently 4D, the 4D objects are projected into 2D plane for presentation, resulting in six 2D figures. It could be seen that the initial design largely fulfills the RMS requirement, however with trivial margin for the yaw control authority. Simply increasing the tilt angles to 25
already leads to well improved yaw control authority with slightly degraded pitch, roll and thrust strengths, yet leads to noticeable loss in the available vertical thrust (load factor). To exploit the optimal solution especially for the critical OEI circumstance, manual tinkering shall be replaced by rigorous optimization procedures.
4.2. Assumptions
Often in the process of aircraft design, decisions on the control authority are made along with other preliminary parameters such as MTOW, lift-to-weight ratio, power consumption required, etc. With the proposed method described in section III, we can integrate limits of other preliminary parameters in the constraints and guarantee that the changes in the controls will not violate the design decisions on other preliminary parameters. To do this, there shall be a relatively high-fidelity model which accounts for other design domains, such as structural, motor and battery models. However, in this paper, as concept proof, such constraints are not directly accounted for, and it is assumed that the change in tilt angles will not lead to major changes of preliminary design parameters such as weight and power. It is a valid assumption since the range of change in tilt angles is confined and shall lead to negligible lift and power penalty and require little structural and mass adaptation. At the end of this section, an analysis of lift and power penalty are addressed to validate this assumption. Still, it should be noted that, in a real application, considering other preliminary design parameters in the constraints could result in more realistic outcomes.
4.3. Test Setup
Due to symmetry of the system considered, the design degree of freedom is 4. Here we start with 2-variable optimization by ganging corner rotors in one group, and the central rotors as another group. This allows us to visually check if the optimizer has reached global optimum. In total, 4 sets of tests are set up and results of whom given in the next section. Recalling that we use as tunable parameters in Equation (2) and (3), and the 4 tests are defined as:
2-variable failure-free test as Equation (2), with
2-variable failure-free test as Equation (3), with
Same grouping as test 1, including critical OEI according to Equation (3);
Same grouping as test 2, including critical OEI according to Equation (3).
Limits on are chosen to be . For the assumptions elaborated in the previous part, no constraints as which appears in Equation (2) and Equation (3) are included in the optimization.
5. Optimization Results
5.1. Optimization Results—Failure-free Cases
In this part, two groups of results for the failure-free optimization according to Equation (2) are presented, one group for 2-variable and the other for 4-variable optimization.
Test 1: failure-free 2-variable optimization, as in Equation (7). The reason for this way of grouping is that the corner ones have longer lever arms hence can better produce moments, while the inner ones are relatively weak to produce moments. The intuition is therefore to use the corner ones to produce higher moments and use the inner ones as major lift producers. This 2-variable test enables us to check if the optimization finds actual global optimum by directly plotting the cost function over the two variables.
Optimization results for this test are shown in
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7 and
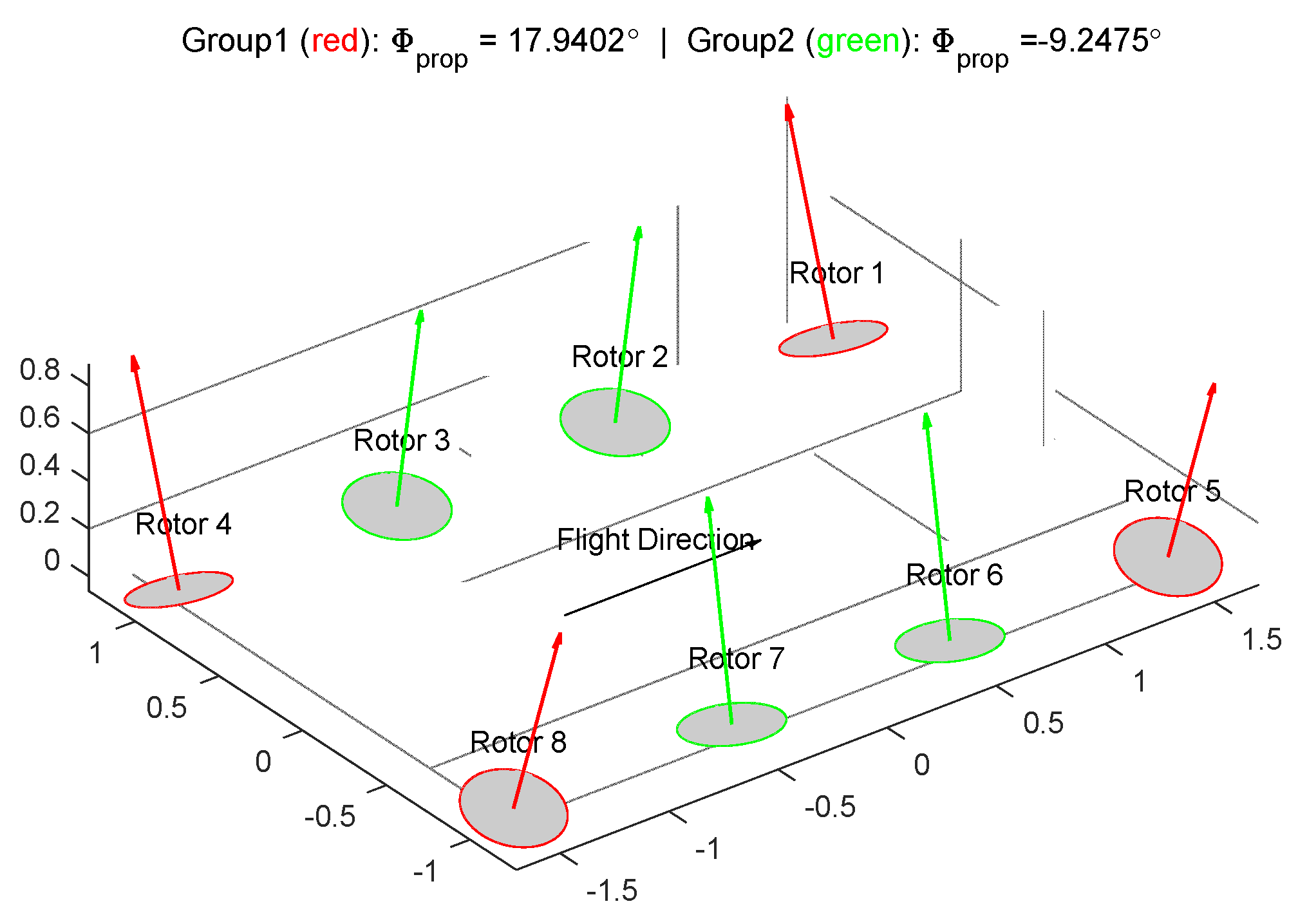
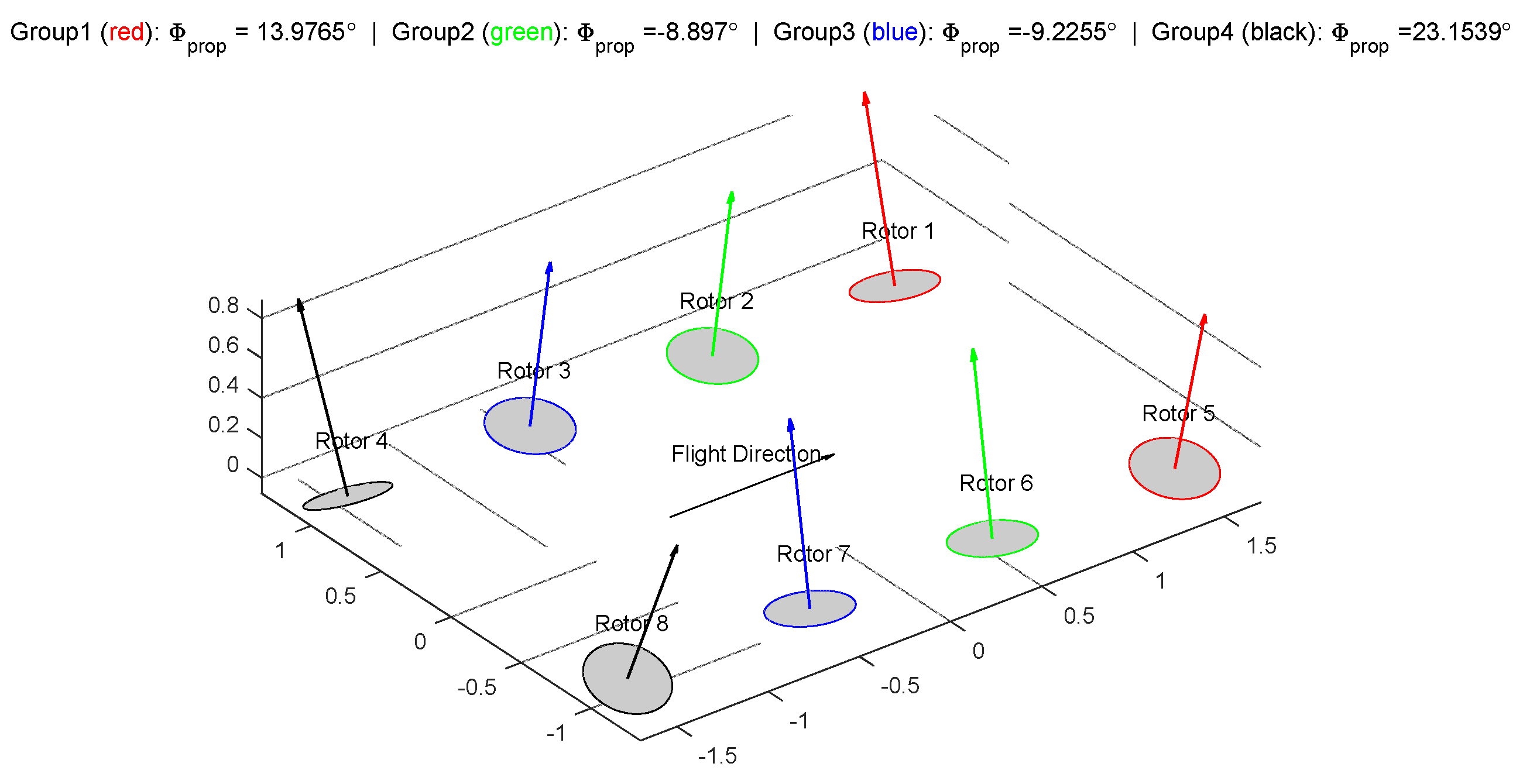
Figure 8. Firstly, the rotor arrangement of the optimal solution is shown in
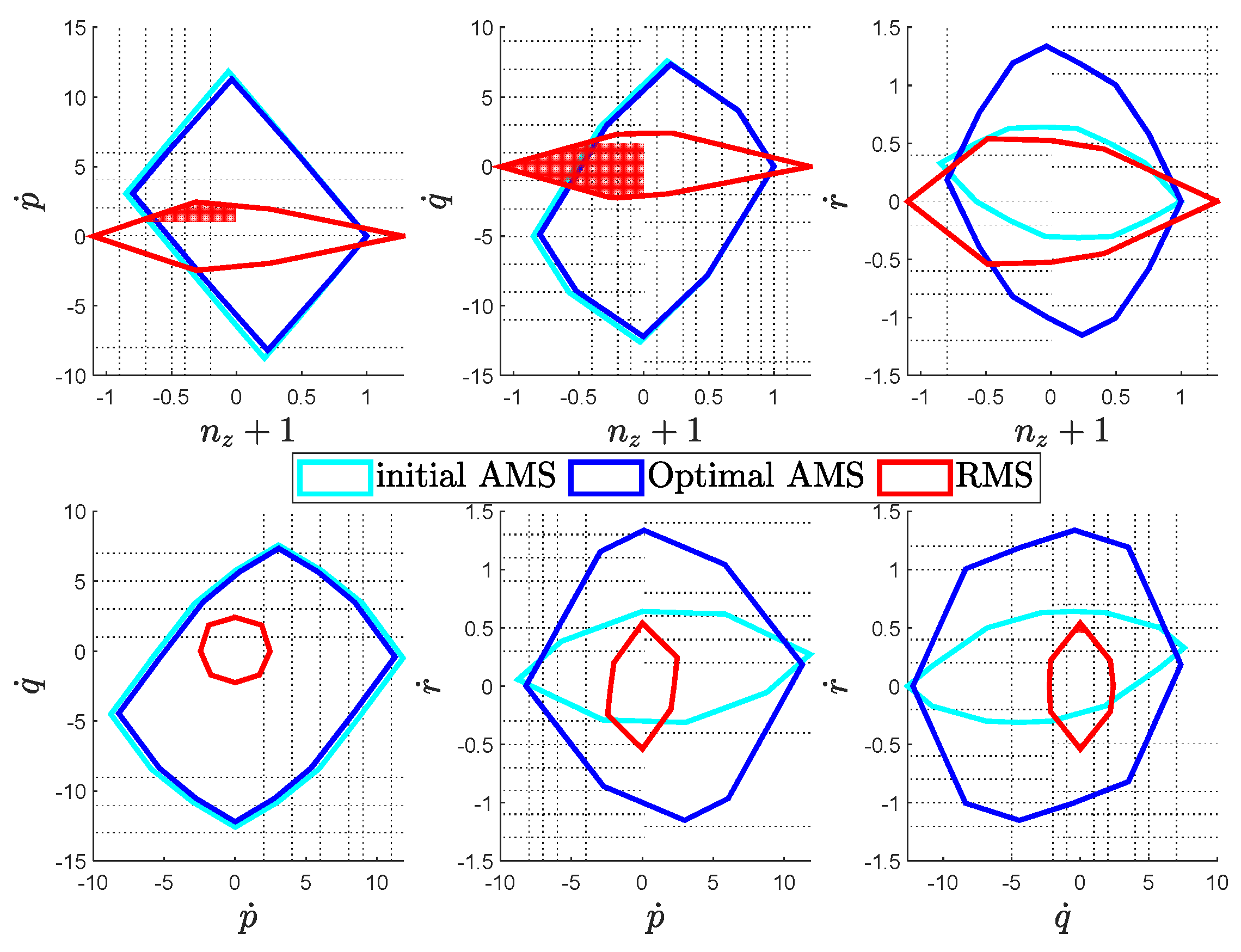
Figure 5. The optimization result aligns well with the intuition behind the way of grouping, with corner rotors more tilted for larger moments and inner ones relatively vertical as a major vertical thrust producer.
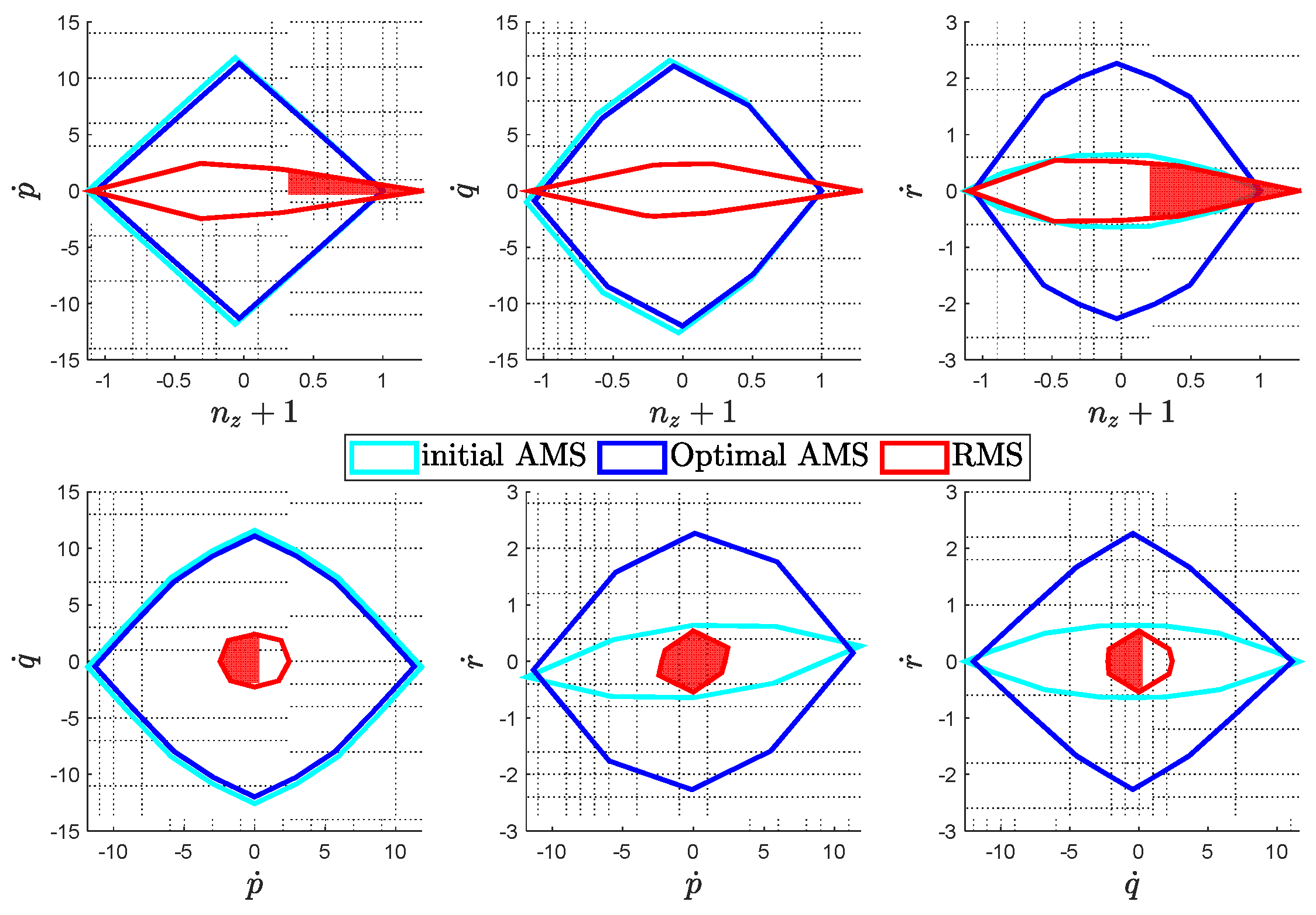
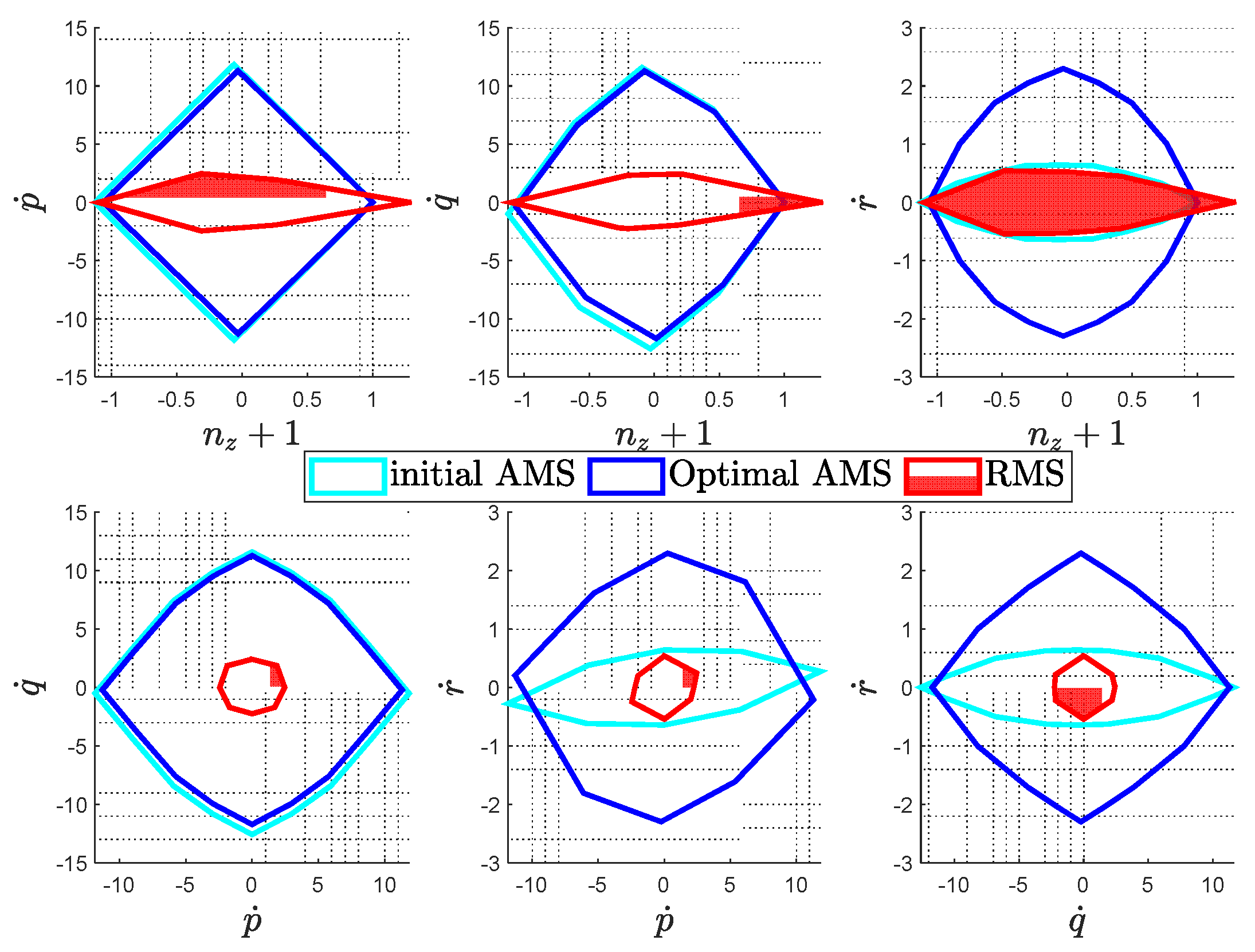
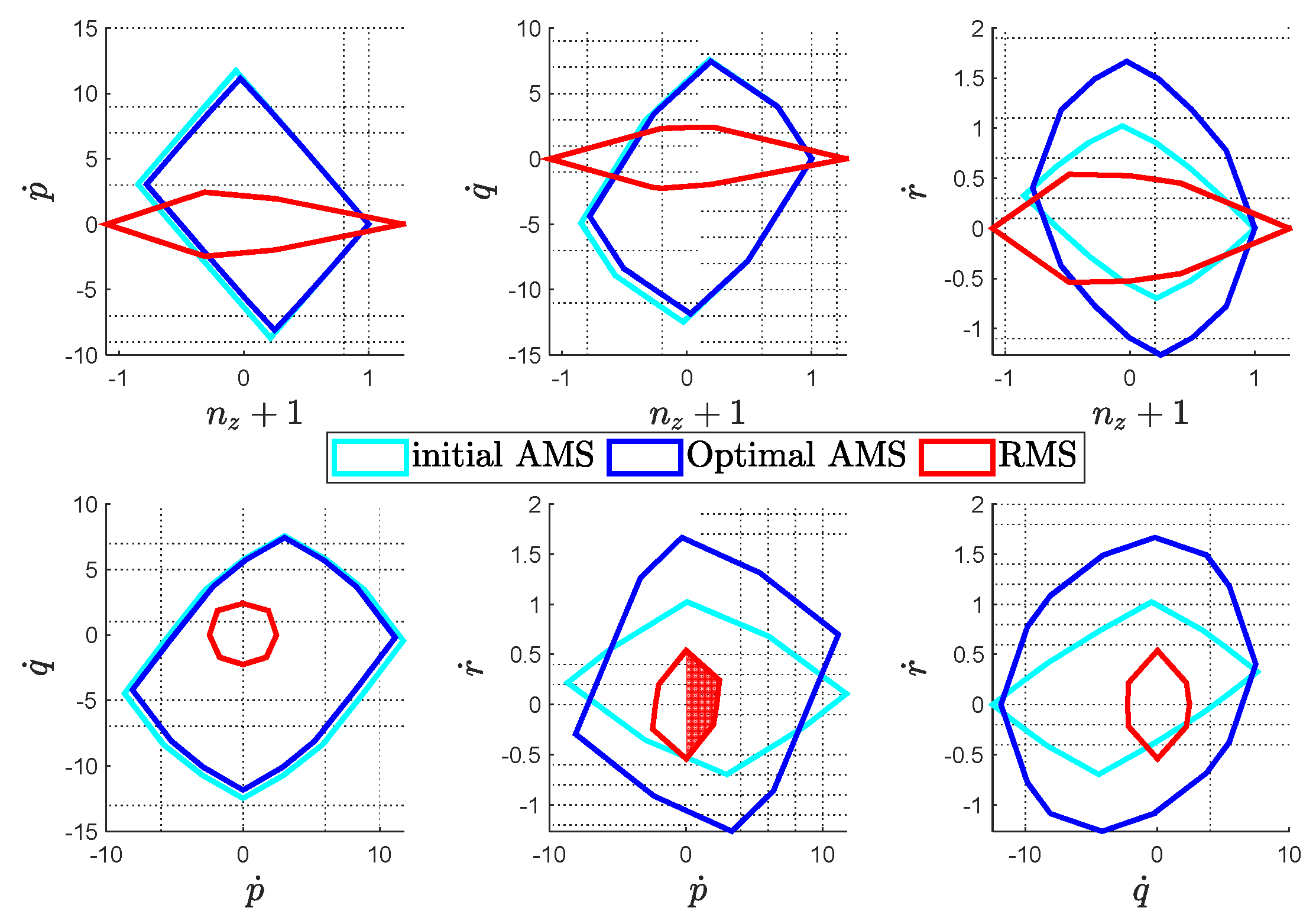
Direct comparison of the RMS, initial and optimal AMS are depicted in
Figure 6. The optimal configuration presents twice as much as the yaw authority as compared to the initial design, with minor sacrifice in the other axes.
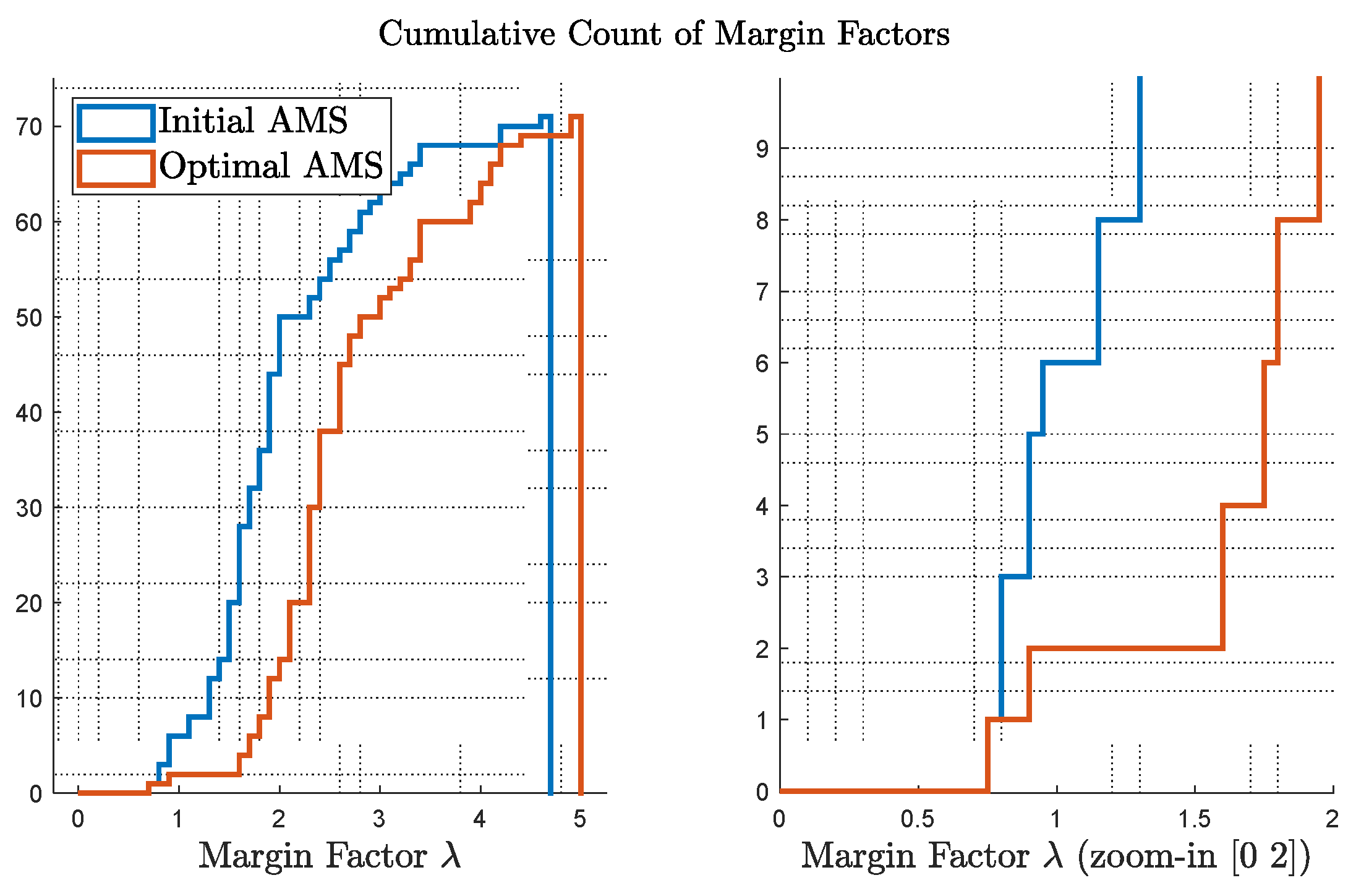
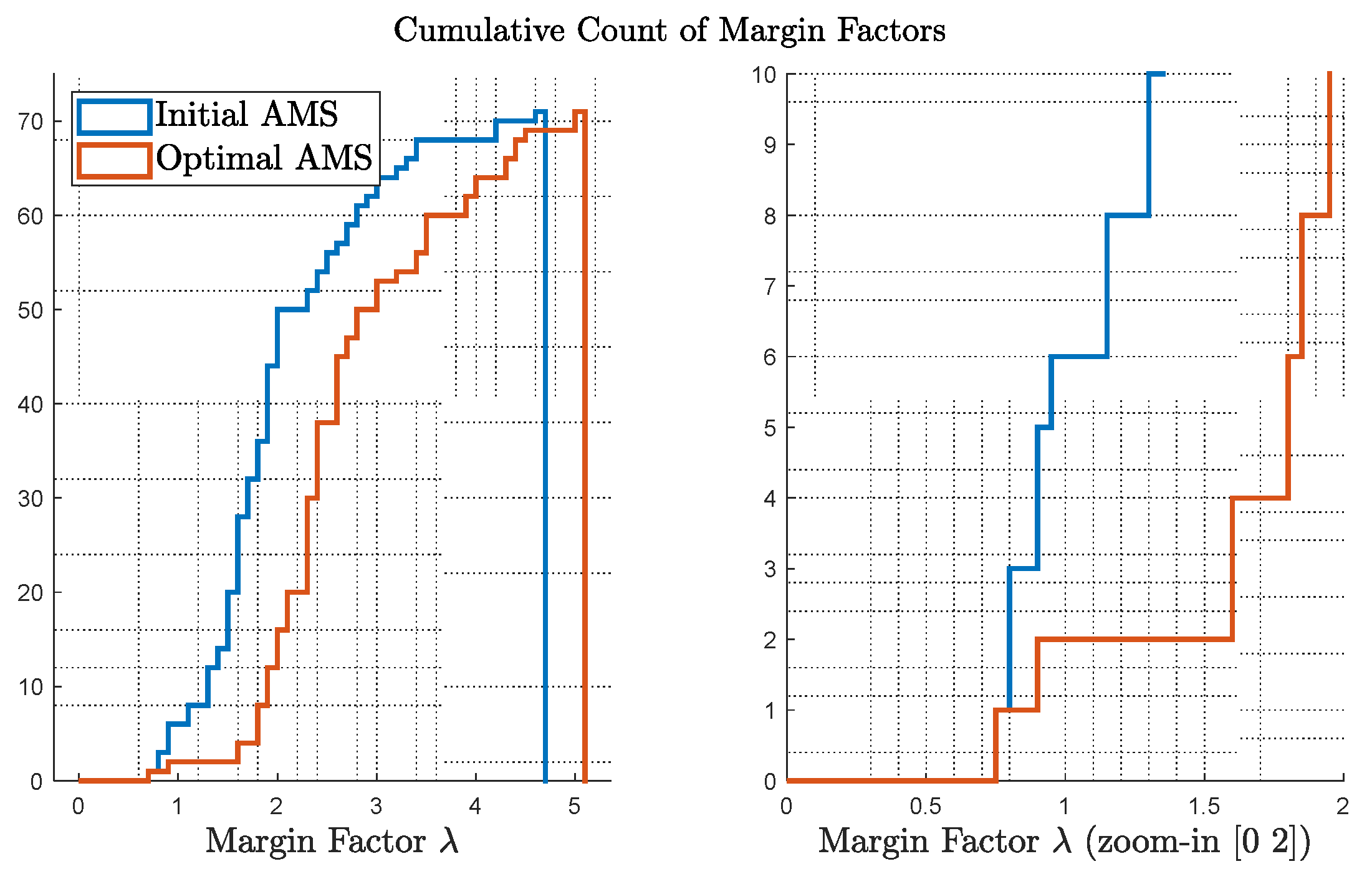
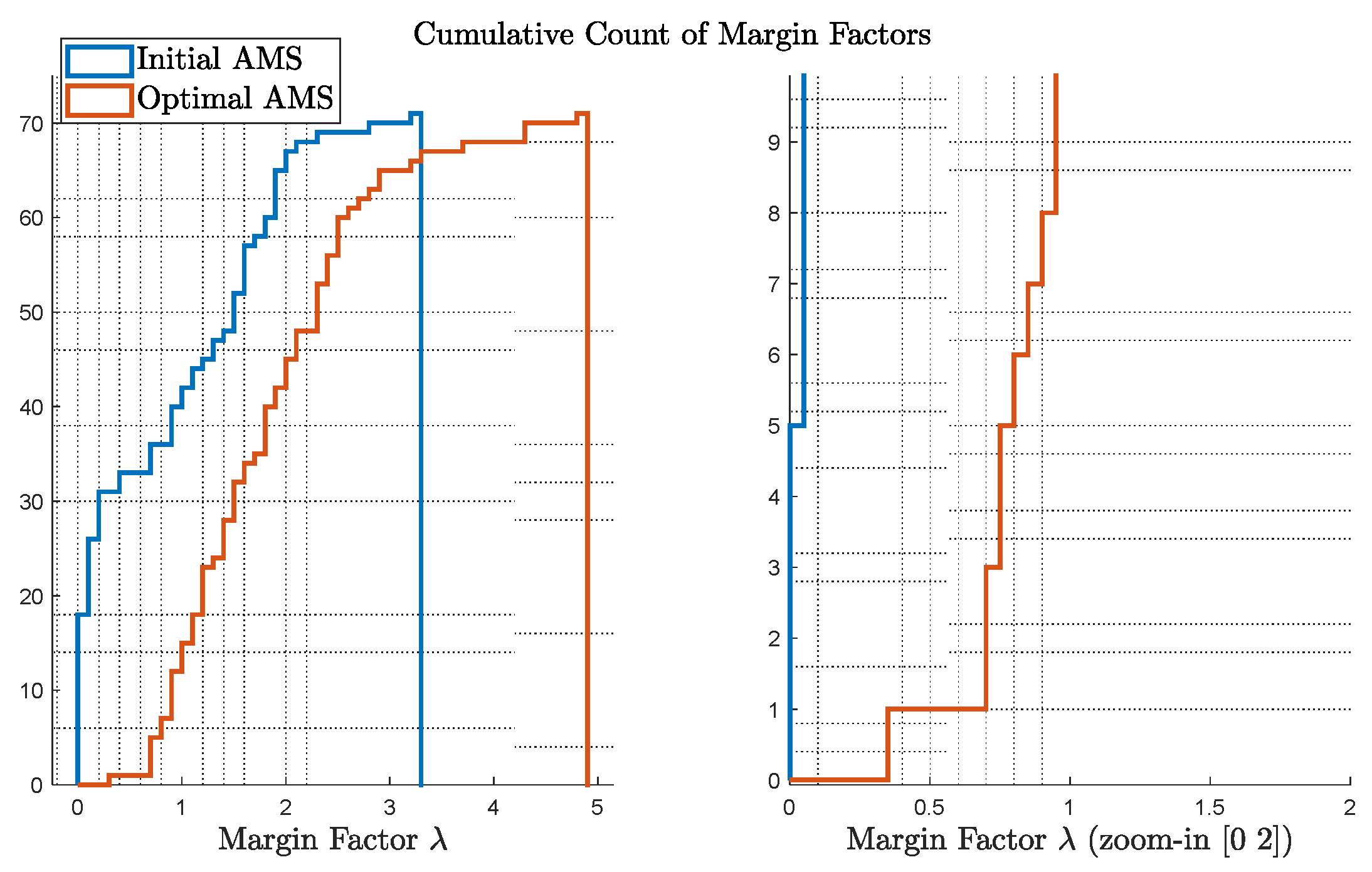
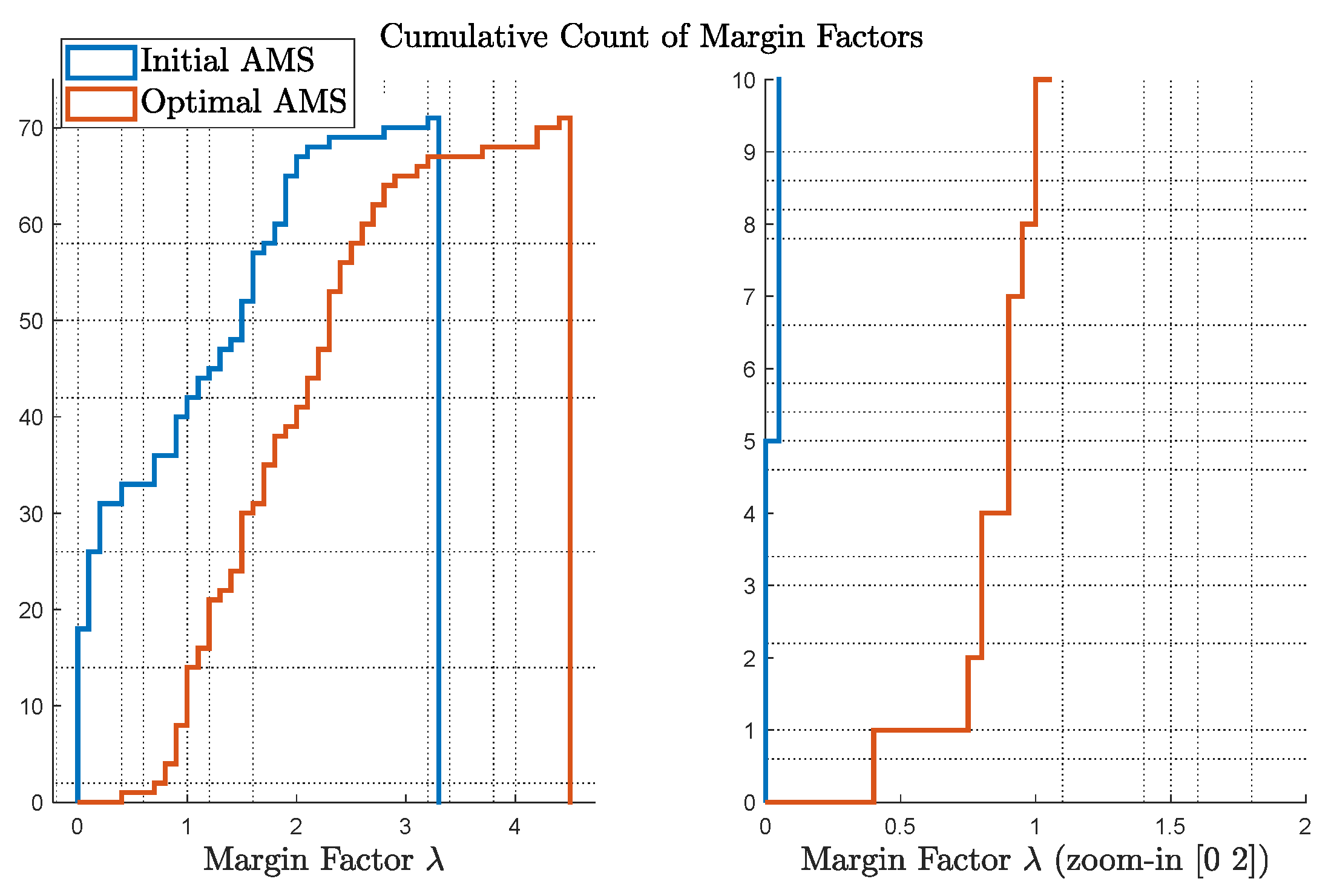
Figure 7 shows the cumulative count of the margin factors
as defined in Equation (2) and Equation (3). On the left, comparison of
for initial and optimal AMS is provided; on the right, the figure is zoomed-in to show the most critical cases, e.g., the points with small margins. Considering a margin of 1.5 is sufficient from an engineering rule of thumb, the optimal case only presents 2 points with a less than 1.5 margin, while the initial design presents more than 10 cases.
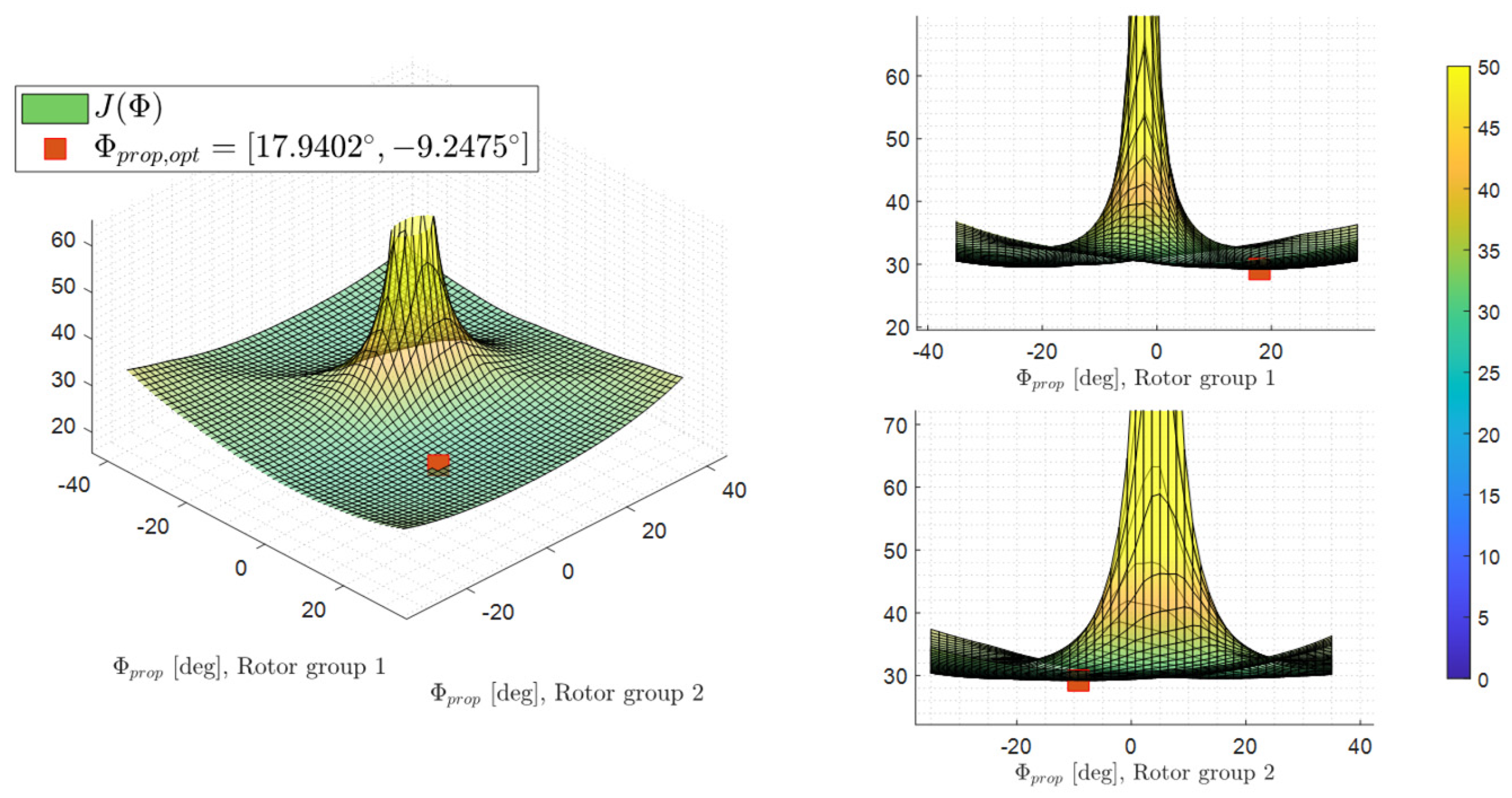
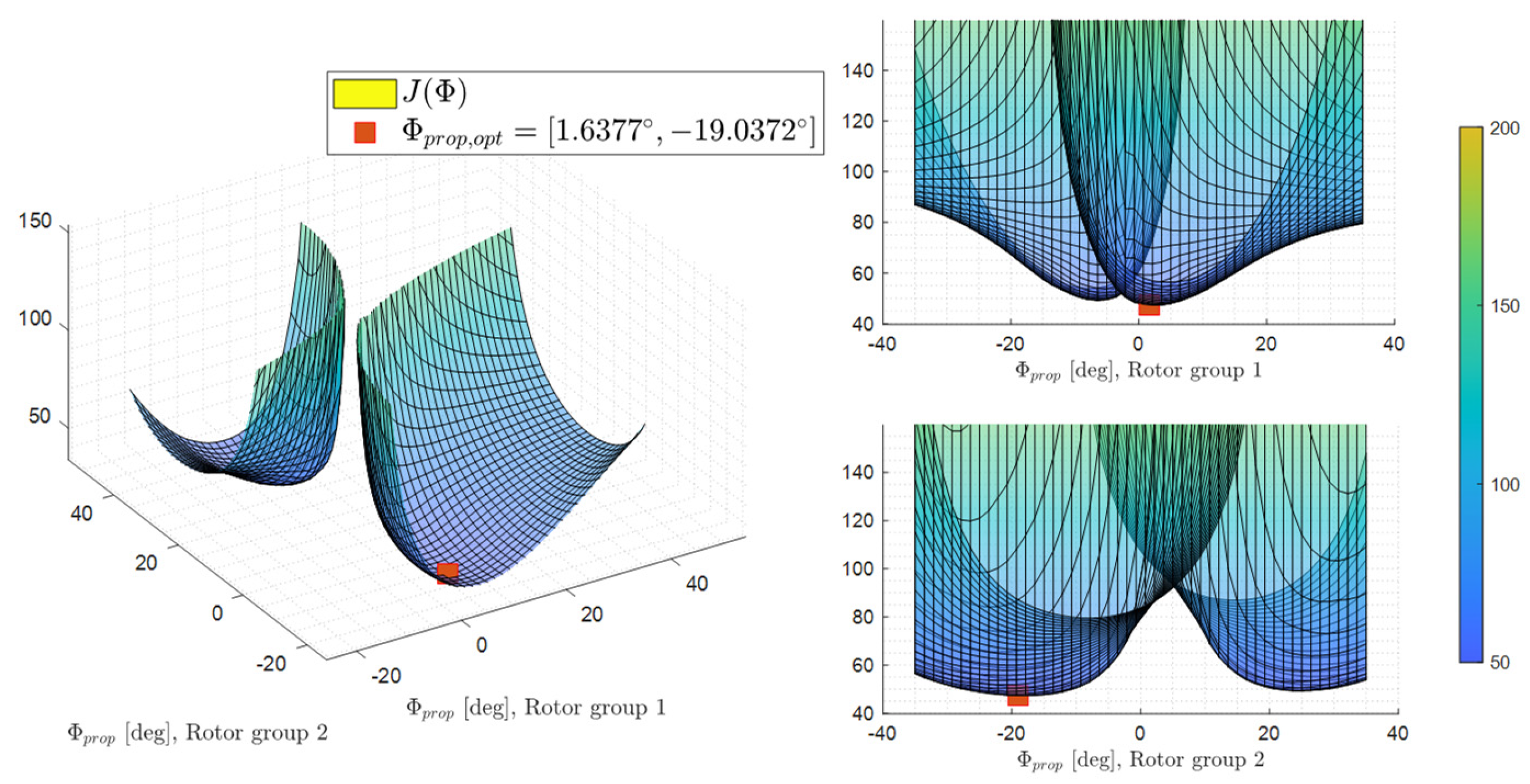
To show that the optimization converges to the global minimum,
Figure 8 shows the relationship between the cost function as a function of the optimization variables. It could be clearly seen that global optimum has been reached by optimization, as the red marker. The system is not completely symmetrical around the body x-axis, since the rotors also generate torques which act as a yaw moment to the system. Therefore,
is found as optimal instead of the
. However, from
Figure 8 it can also be concluded that this effect is relatively small compared to tilted forces, and therefore is not further addressed for the problem.
What’s also obvious in
Figure 8 is that, when both variables are 0, the system shows a singularity in the cost function, indicating a complete loss of control in at least one direction in the generalized moment space. For this failure-free case, good overall control authority could be achieved when both angles’ absolute values are between
to
.
Test 2: failure-free 4-variable optimization, as in Equation (8). The results are given from
Figure 9,
Figure 10 and
Figure 11. Similar outcomes can be drawn from the figures as of Test 1. It can be noticed that the resultant rotor configuration is not symmetric with respect to the CG (otherwise 4-variable optimization would be meaningless).
5.2. Optimization Results—Critical-failure Case
In this part, results of the critical-failure optimization according to Equation (2) are presented, one for 2-dimension and the other for 4-dimision optimization.
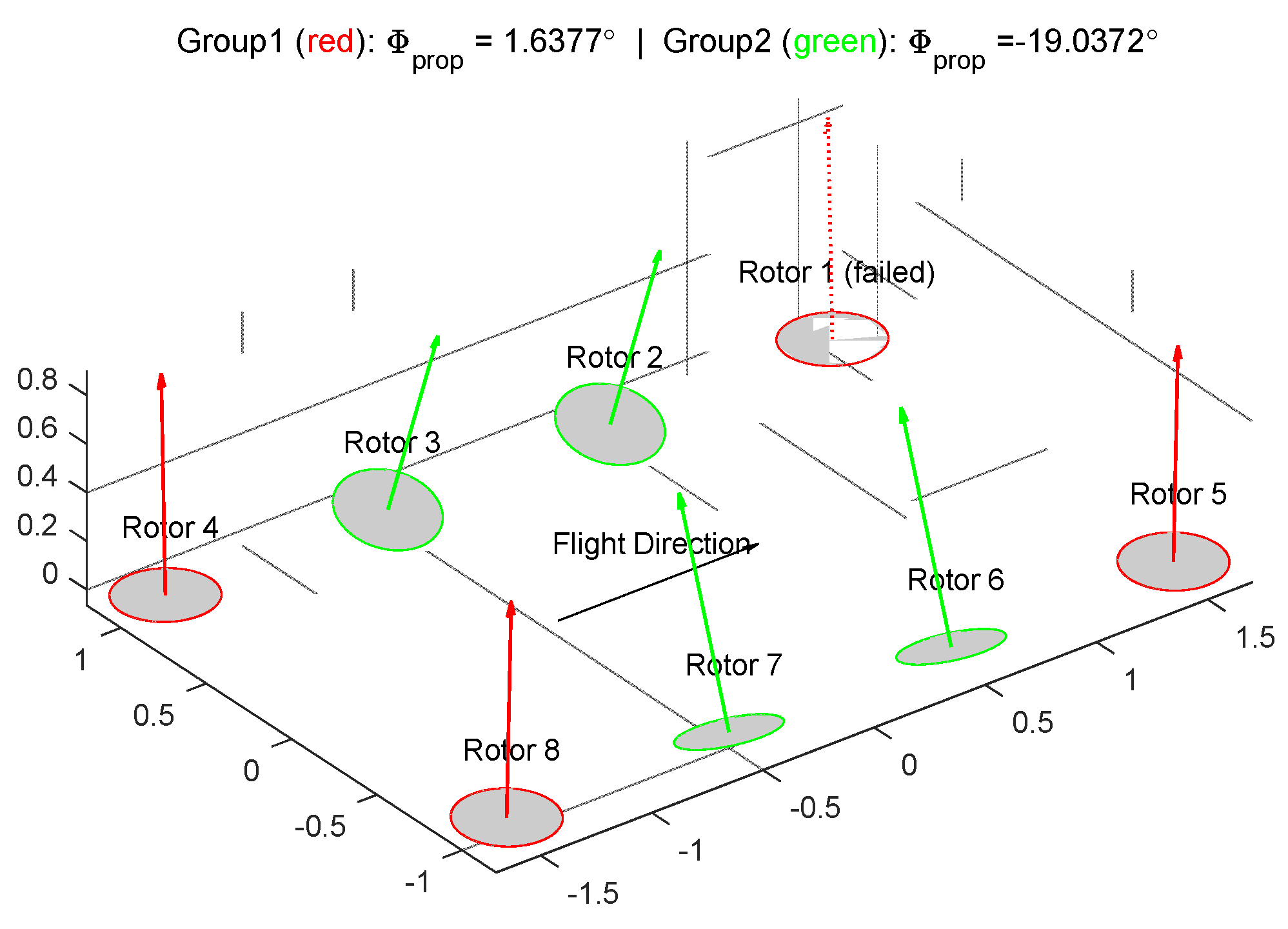
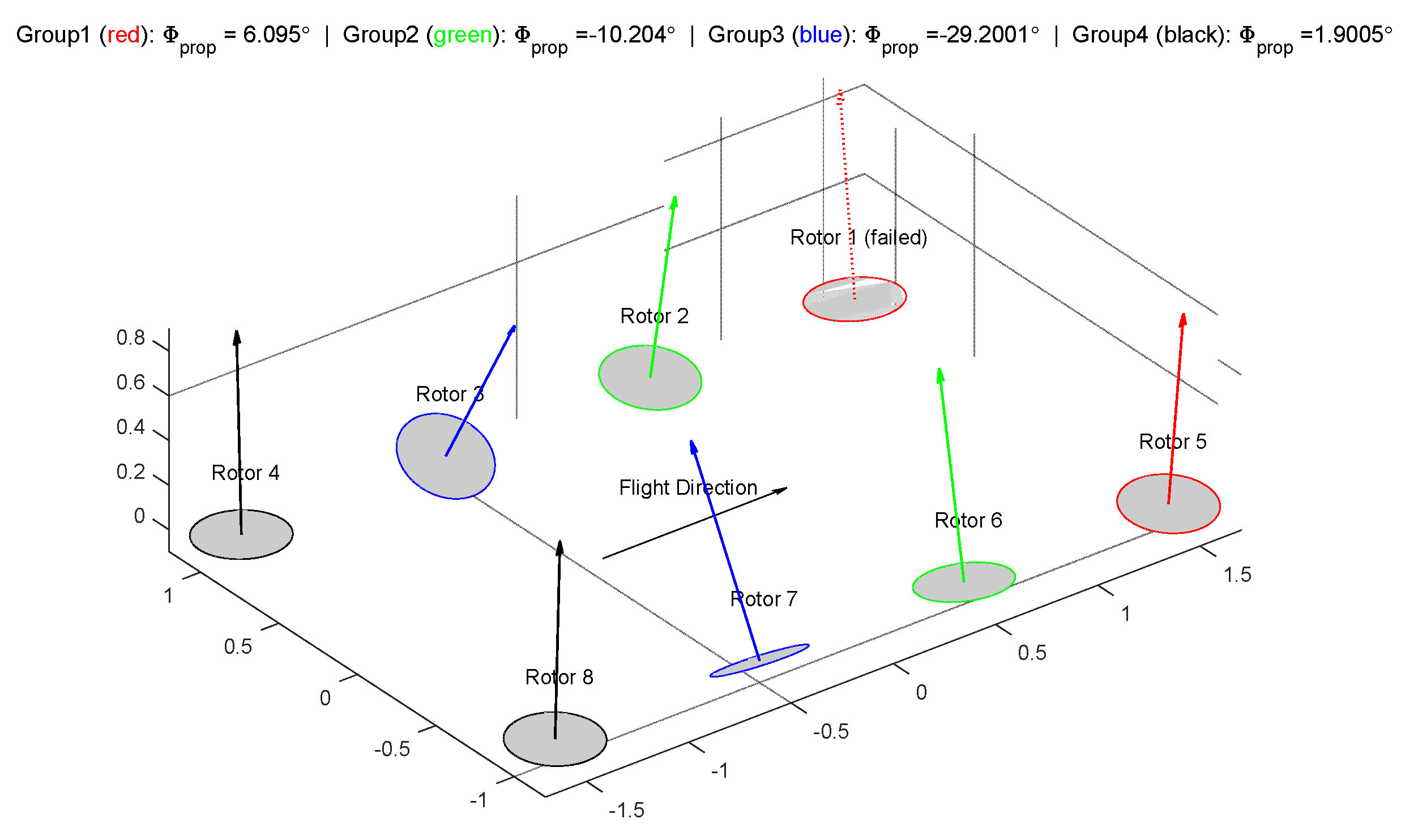
Test setup 3: Repeats grouping of Test 1 but considers a critical rotor failure according to Equation (3). Results are displayed from
Figure 12–15. Rotors 1 is found to be critical and marked “Failed” with dotted line in
Figure 12. Major differences could be noticed as compared to the failure free case of Test 1. Firstly, the corner rotors, instead of being tilted more than the centric ones, are positioned almost vertically up with just a slight angle of
. The rationale behind can be that, as a critical rotor whose failure can lead to worst case reduced control authority, it is essential to balance out the authority and avoid relying on the critical rotor in all four axes—positioning the critical rotor vertically reduced its contribution on the yaw axes, which is a relatively “weak” direction. As a result, the yaw control authorities are all allocated to the inner ones, whose pitch and roll authority are lower due to shorter lever arms. In other words, this layout averages out the criticality of the corner rotors, by allowing the center rotors to take over more yaw responsibility. Although in the failure free case the system does not present optimal authority as compared to Test 1 results, the optimized configuration in this test shows better controllability once a critical failure occurs.
Figure 13 compares the initial, optimal AMS and RMS under the condition of a complete loss of the critical rotor. While the initial condition sees a major degradation in the yaw moment with the critical failure, the optimized configuration largely compensates for this drawback, and authority in the other axes are preserved with minor differences.
Figure 14 shows the cumulative count of margin factors
for this test. Due to lack of consideration of a critical failure in the initial design, almost half of the margin factors got reduced to less than 1 after the same failure, leaving the system largely uncontrollable, while the optimized layout from Test 3 guarantees 90% of the directions still achievable.
Figure 15 shows again that global minimum is achieved. Compared to
Figure 8, singularities, e.g., cost function of very high values, occur on the diagonal of the variable plane. The actual optimal design point is also hard to achieve without using optimization techniques.
Test setup 4: Repeats grouping of test setup 2, on top of which considering critical failure. Again, the corner rotors are positioned almost vertically, while the center four rotors are tilted more. Detailed results are shown in
Figure 16,
Figure 17 and
Figure 18. Similar intuitions and explanations can be drawn as the results from Test 3.
5.3. Comparison and Discussion of Optimization Results
While optimization aims for improving control authority, the higher values in the rotor tilt angles will lead to loss of total vertical thrust and therefore higher power consumptions during hover trim conditions. In Section IV, it is assumed that optimization shall lead to a minor influence on the preliminary parameters. Given the optimal results in this section, each configuration’s performance per optimization target, their thrust and power consumption during hover trim conditions is analyzed and compared for different configurations.
Considering the tilt angles of the rotors, the total force available in the vertical axis in the NED frame, compared to total thrust available from the rotors are defined by:
is a measurement of thrust penalties due to the tilt angles. To trim the A/C during hover condition, additional forces that must be produced is consequently
. According to [
22], the force of a rotor is linearly dependent on the square of its rotational rates, and the power produced by the rotor is linearly dependent on the third power of its rotational rates. As a result, power consumption is linearly dependent on the
power of the forces produced. Consequently, additional power consumption to account for the tilt angles can be represented by
as
.
To compare the results between the initial design configuration and the resultant configurations from optimization, the rotor angles of each case, cost function values according to Equation (2) and Equation (3), as well as force and power penalties are compared in
Table 1.
Firstly, regarding the control authority optimization, while the failure-free optimizations produce the best minimum failure-free cost functions, their performance given a failure is very similar or even worse under failure condition. On the other hand, the critical-failure optimizations, although produce slightly worse results in the failure-free case, present major improvements given the failure. In this sense, the results from critical-failure optimizations win over the failure-free optimal results.
Secondly, regarding the penalties, loss in vertical force due to optimization ranges between 3%-4% and power compensation ranges between 4% to 6%. Among the four group results, Test 3, that is the 2-variable critical failure optimization, produces least lift and power compensation, that is 2.8% and 4.3% percent, respectively. For safety reasons, eVTOL designs normally present large margins in both total available lift and power to account for failures. Such penalties could therefore be considered negligible.
As a summary, Test 3 shows the best overall results, for its performance in control authority for both failure-free and critical-failure conditions, as well as minimum loss in lift and power penalties. Additionally, there might be weight penalties due to structural strengthening due to larger tilt angles. This paper, as concept proof for the proposed method, ignores such effects. Once again, towards real applications, such effects can be considered as additional constraints given proper modelling fidelity to generate more realistically meaningful results.
6. Closed-Loop Verification
6.1. Closed-Loop Simulation Framework
To further test the performance of the optimized configurations, closed-loop model-in-the-loop simulations are carried out. The airframe under consideration is modelled as a 6-DoF rigid body with each propulsion system (motor and rotor together) modelled as a first order linear system. A baseline incremental nonlinear dynamic inversion (INDI) attitude and vertical load factor controller is designed to perform the control task of the system. The performance of INDI controllers has been extensively discussed [
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. For the control allocation, redistributed pseudo inverse (RPI) method [
34] is used to handle redundancy and reallocate pseudo controls command once saturation occurs. RPI might fail to deliver the optimal input commands as compared to other optimization methods, such as weighted least square (WLS) as found in Ref. [
3,
34], however, it is still chosen due to its simplicity and advantage in predictable and low worst-case execution time (WCET), which is important towards a certifiable implementation. To handle redundancy related wind-up issues of incremental controllers, a null space technique is applied to bring the inputs always back to trim states once the system is in steady state [
35].
Both failure-free and critical-failure cases are simulated. In simulations with failures, rotor 1 is injected with a complete loss of power, whose rotational rate decays to zero over time. Failure is assumed to be known to the system one second after the failure takes place. Overall, 4 groups of simulations are carried out, and the results are elaborated in the following sections. For the controller design, the only difference between the tests is the effectiveness matrix calculation according to the used layout.
6.2. Baseline Configuration Failure Free Simulation
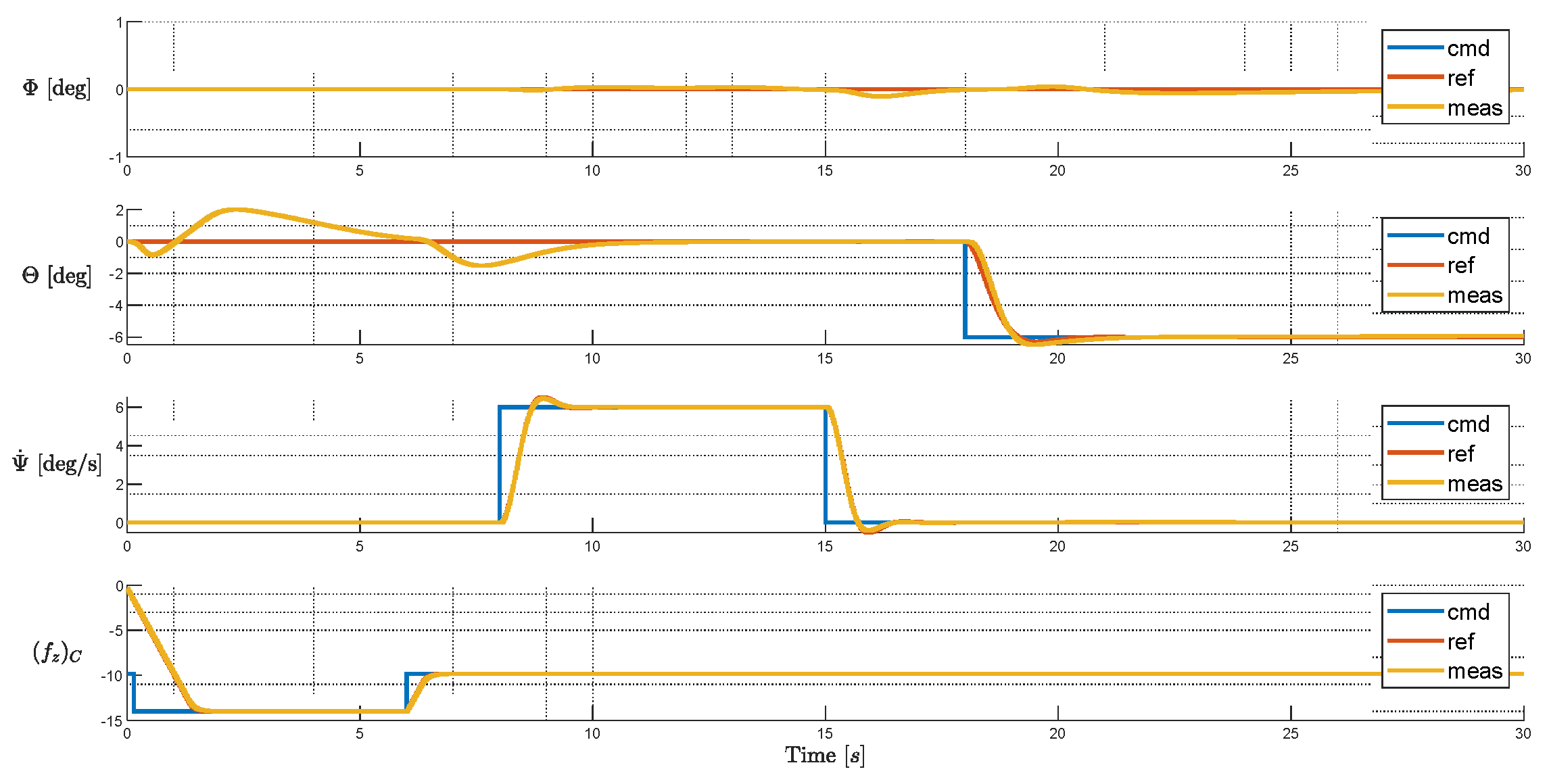
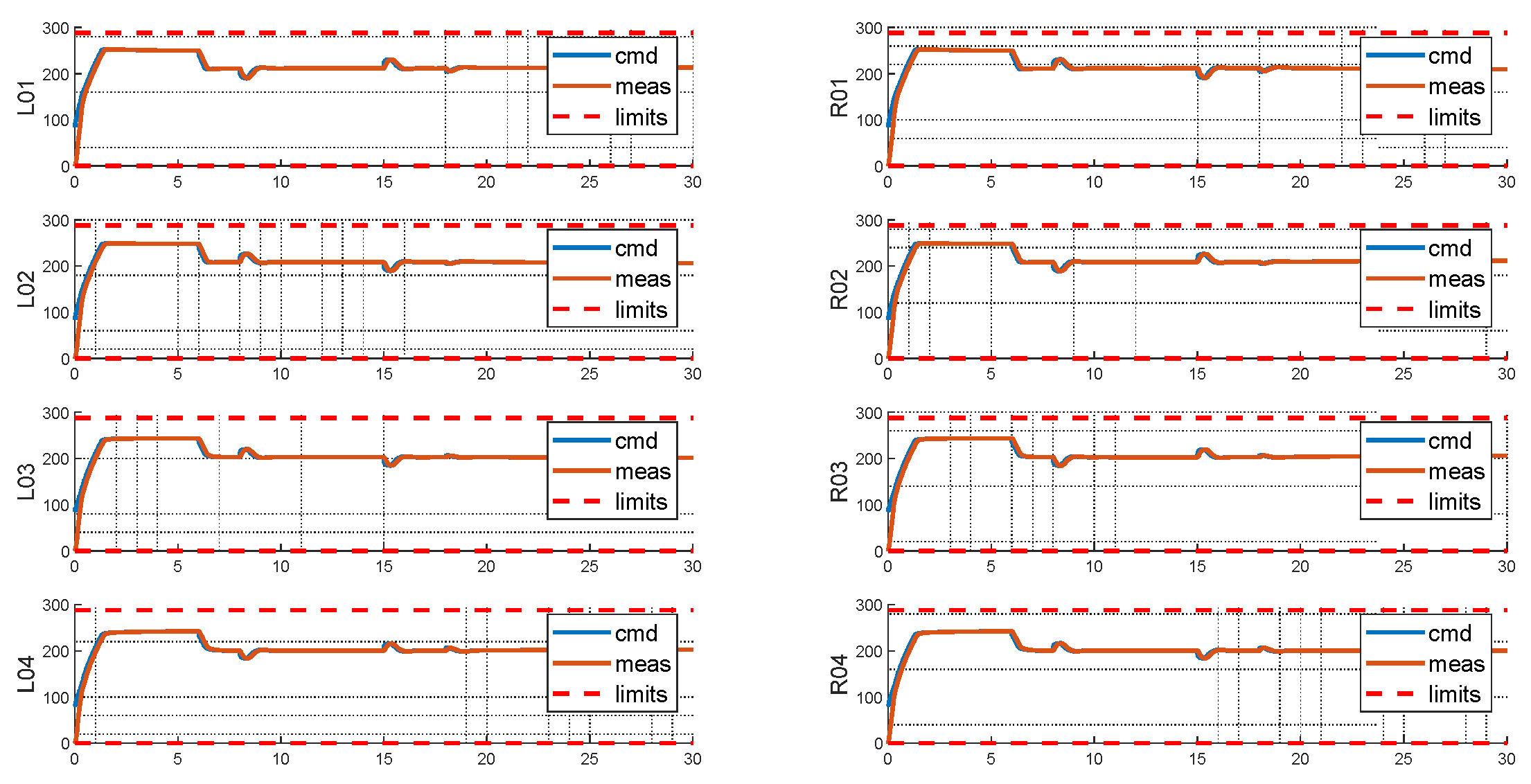
Firstly, the initial configuration is tested to produce baseline results, without failures injected. The commands are designed to simulate a typical take-off process, composed of vertical climb, yaw towards a specified direction, and then accelerate by nose down pitch. As can be seen, it reacts to commands or holds a commanded attitude in each axis properly. Small cross-axis transient errors can be noticed but steady state errors are well bounded. For this maneuver, the rotor commands stay well bounded within the saturation limits.
Figure 19.
Tracking Performance of Baseline Layout.
Figure 19.
Tracking Performance of Baseline Layout.
Figure 20.
Rotor States of Baseline Layout.
Figure 20.
Rotor States of Baseline Layout.
6.3. Baseline Layout Simulation with Injected Failure
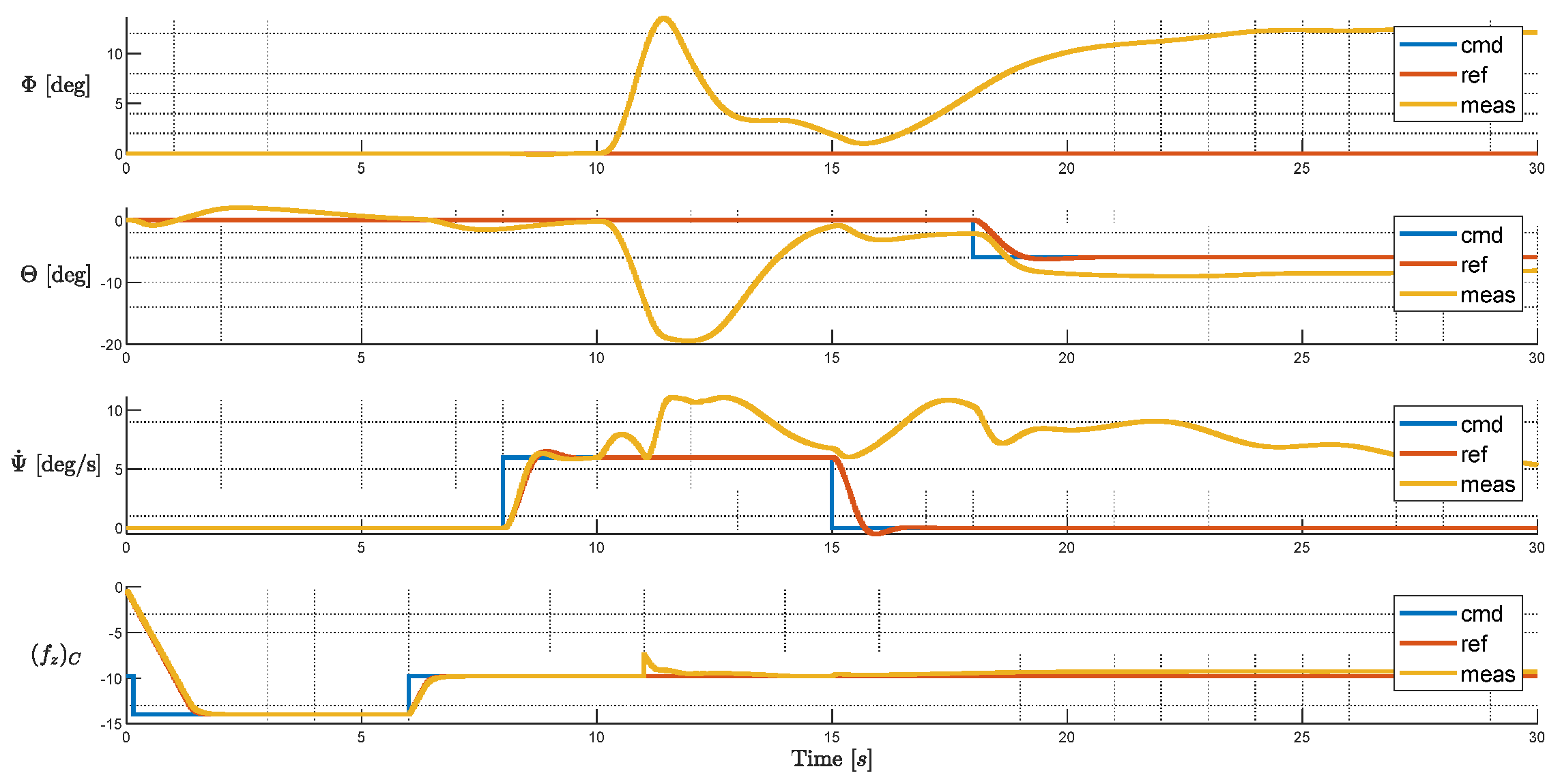
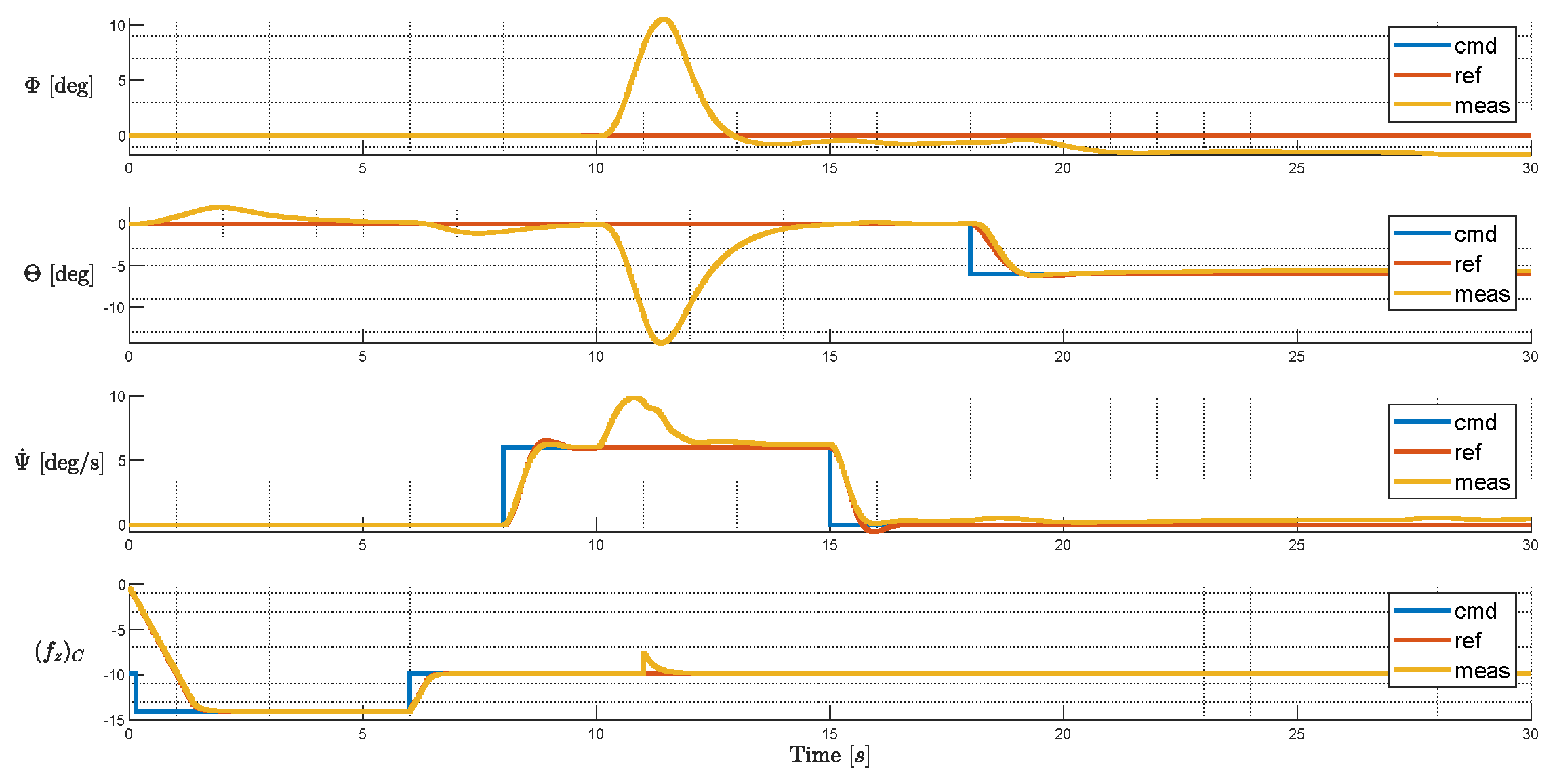
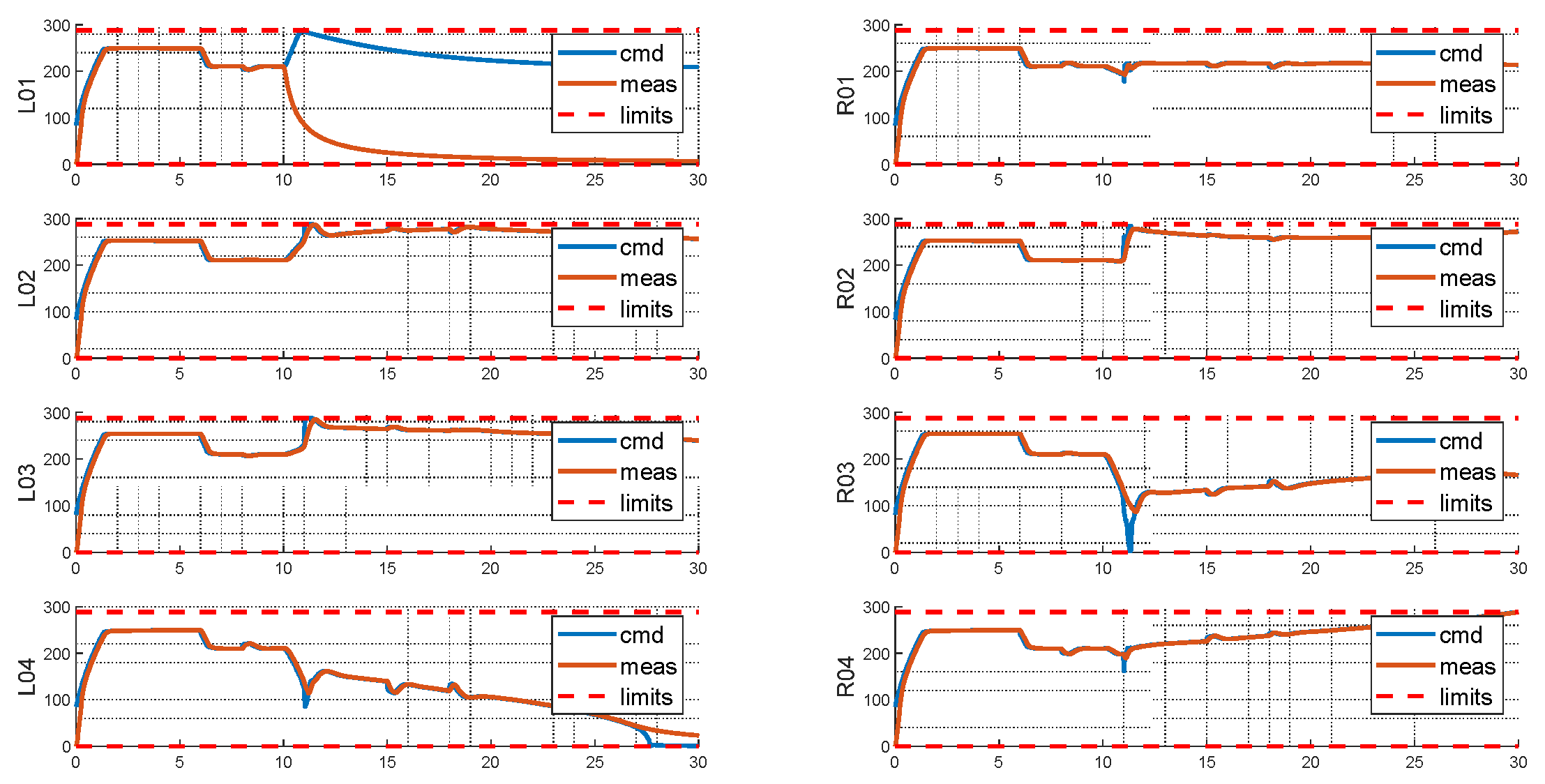
The baseline test in the previous section is repeated, and in addition the failure of rotor 1 is injected at 10s. From the moment when the failure takes place, the system diverges within all axes. Given the knowledge of failure, the system arrives at a steady state after 20 seconds. Still, at the end of the simulation, large bank angle and yaw rate steady state errors are observed. Under this situation, the system can be hardly managed safely—it is expected the system will keep diverging in its velocities and emergency landing with such an attitude can be a hazardous or even catastrophic situation.
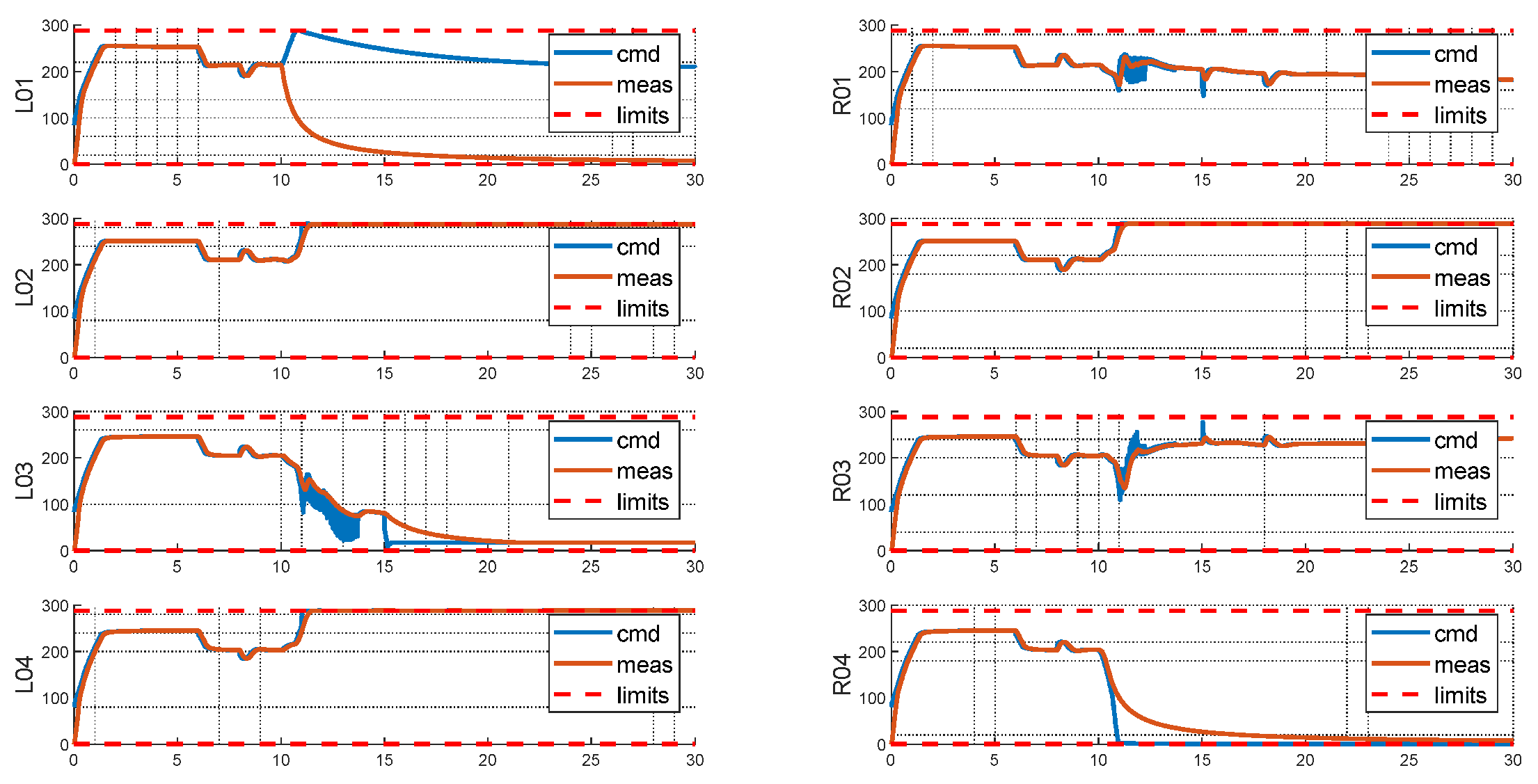
From the rotor side, the failed rotor introduced multiple saturations, with R04 saturates at its lower limit, and L02, R02 and L04 saturates at their upper limits. For the baseline configuration, since L01 and R04 would produce exactly opposite moments, the failures of L01 and R04 are coupled, with one failure leading to the other one abandoned by the allocation scheme. The burden therefore must be resolved by the remaining rotors, resulting in 6 rotors saturated either on the upper or the lower limits, and consequently a highly degraded controllability.
Figure 21.
Tracking Performance of Baseline Layout with Injected Failure.
Figure 21.
Tracking Performance of Baseline Layout with Injected Failure.
Figure 22.
Rotor States of Baseline Layout with Injected Failure.
Figure 22.
Rotor States of Baseline Layout with Injected Failure.
6.4. Failure-Free Optimized Layout Simulation with Injected Failure
In this case, the optimized configuration of Test Setup 2 in Chapter IV, namely the 4-variable failure-free optimization is simulated with injected failure. This test allows us to check whether the failure-free optimization improves overall performance compared to the baseline layout under injected failure scenario. At the beginning of the failure, a large transient error is also noticed, however, given the failure knowledge at 11s, the system recovers to a controllable state, with small steady state tracking errors in all axes compared to the failure-injected baseline simulation.
Regarding rotor states, with the failed L01’s rotational speed slowly decaying to 0, L04 and R04 respectively approach their lower and upper limit to compensate for the residual control error caused by constant change of L01’s rotational speed. Due to increase in the control authority, the overall level of saturation is relatively lower than the counterpart of the simulation of the baseline layout under failure.
Figure 23.
Tracking Performance of Failure-free Optimal Layout with Injected Failure.
Figure 23.
Tracking Performance of Failure-free Optimal Layout with Injected Failure.
Figure 24.
Rotor States of Failure-free Optimal Layout with Injected Failure.
Figure 24.
Rotor States of Failure-free Optimal Layout with Injected Failure.
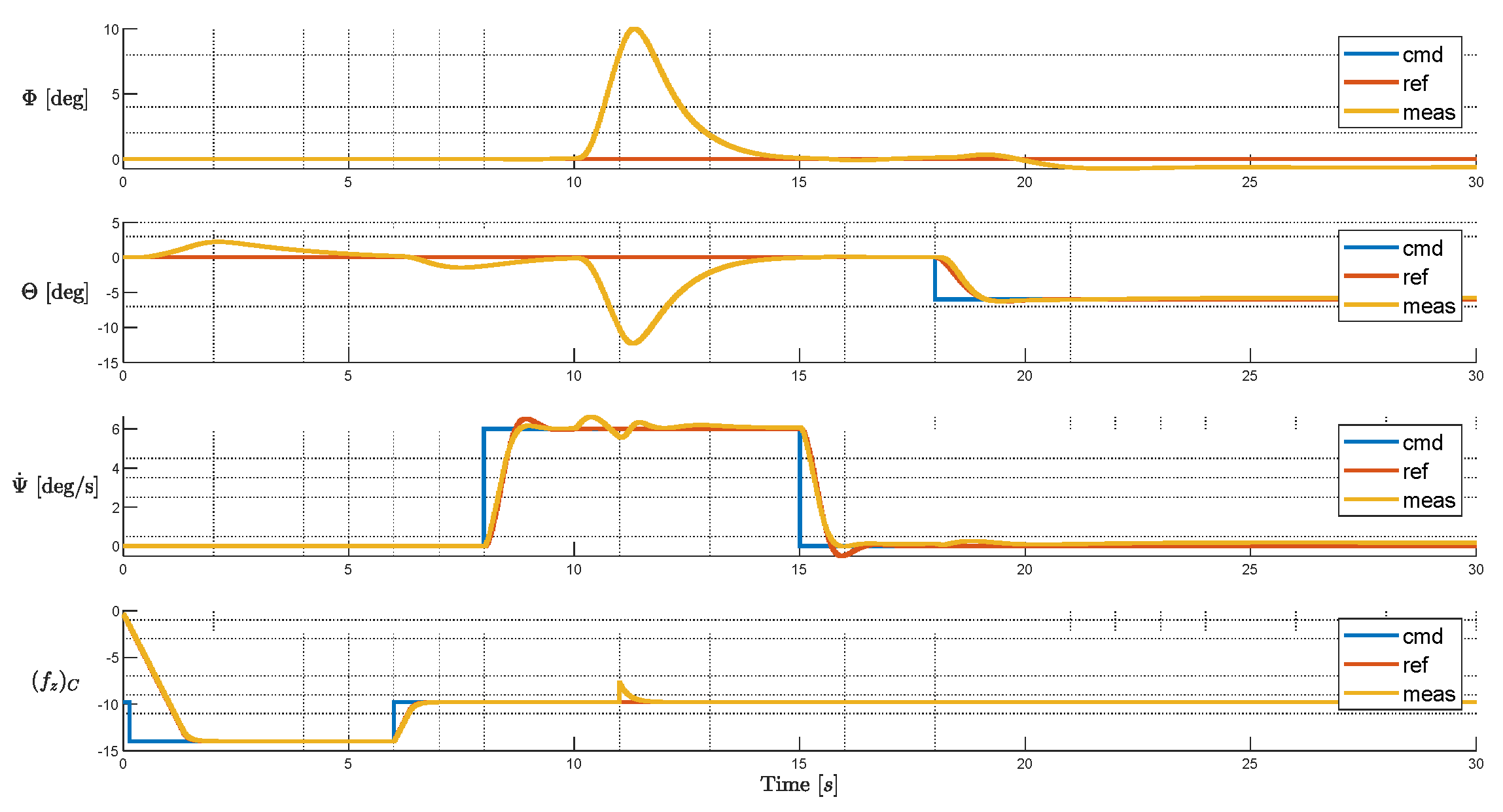
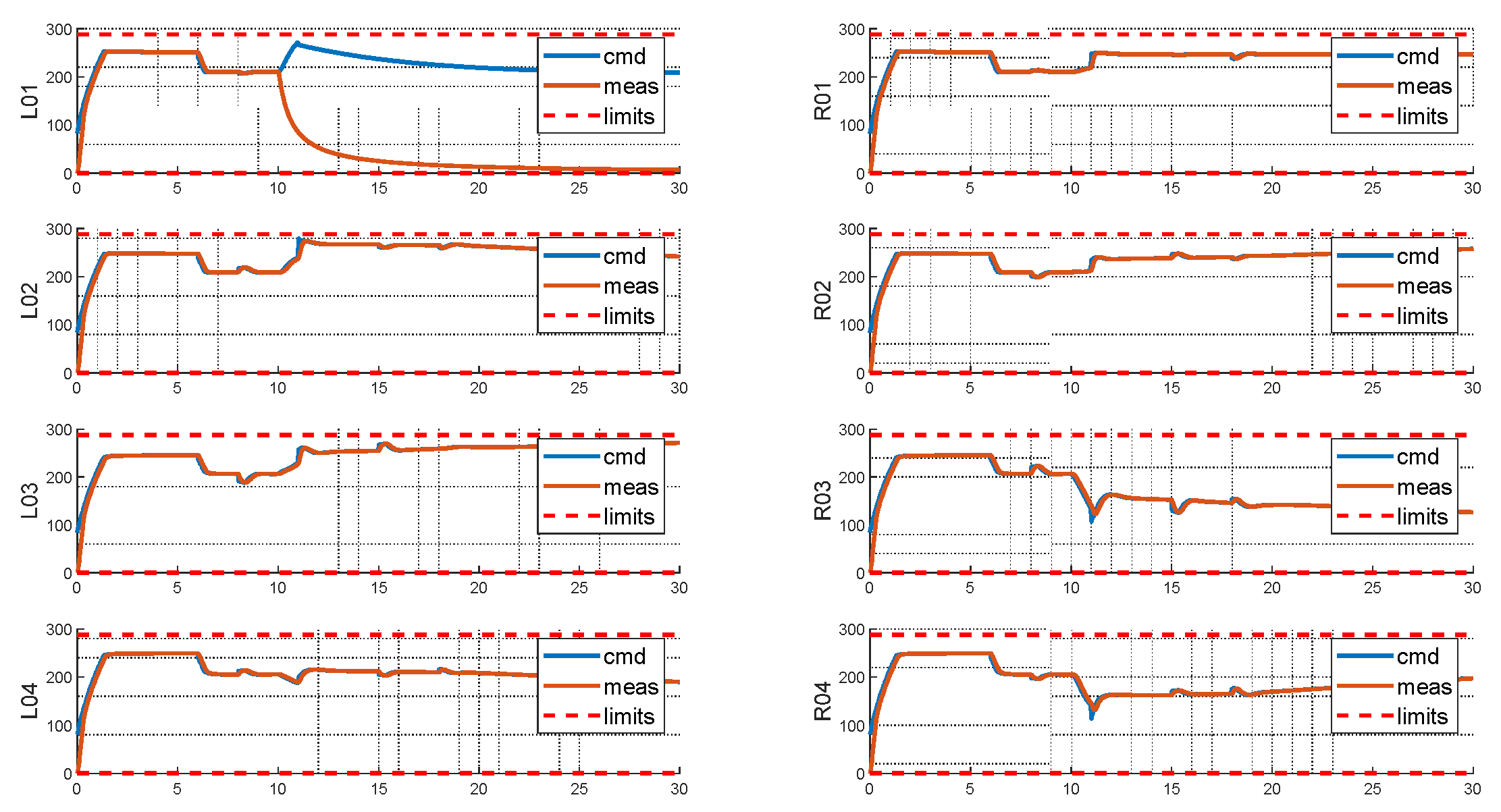
6.5. Critical-Failure Optimized Layout Simulation with Injected Failure
In this simulation case, the 4-variable critical-failure optimized layout (optimal layout from Test Setup 4) is simulated. Compared to the failure-free optimal layout, the system responds in a similar trend whereas the biggest transient errors in all axes are reduced, especially with minor yaw rate error noticed during the complete simulation. The steady state tracking error is also reduced. Apart from the transient behavior between 10-15 seconds, the system does not present any peculiar actions once failure information is known, enabling the system to perform continued safety flight even under a critical rotor failure.
Major improvements in rotor utilization can be noticed. Compared to all previous results, the variance between remaining rotors’ RPMs is much smaller, with no saturations encountered in both upper and lower limits. Especially, apart from the failed L01 rotor, no other rotors are driven down to the lower RPM, thus preserving the authority of the system to what’s physically available, instead of being limited due to trim requirements.
Figure 25.
Tracking Performance of Critical-failure Optimal Layout with Injected Failure.
Figure 25.
Tracking Performance of Critical-failure Optimal Layout with Injected Failure.
Figure 26.
Rotor States of Critical-failure Optimal Layout with Injected Failure.
Figure 26.
Rotor States of Critical-failure Optimal Layout with Injected Failure.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, a method to optimize generalized AMS in 4D space is proposed, which maximizes eVTOL’s control authority over prescribed RMS from performance requirements. Especially, the failure of a critical rotor is considered. Closed-loop model-in-the-loop simulations are designed to compare the performances of the baseline configuration and optimized configurations. Major improvements can be observed for the optimized configurations, especially the two optimized with critical-failure criteria, with respect to the margin factors as well as closed-loop tracking performance after failure. While the baseline configuration presents large attitude deviations from commands after the critical failure, the optimized configurations present the ability to perform a continued safety flight, which fulfills the single point of failure criteria according to EASA SC-VTOL. Although optimization does not directly account for loss in total lift or power consumption, a validation analysis shows that only slight penalties are found regarding these two aspects. Further work could be focused on integrating the philosophy into a multi-objective optimization framework, given sufficient modelling fidelity, to directly address constraints such as structural strengths penalties, aerodynamic properties, weight penalties and power consumption penalties. Additionally, other failure modes might be considered, such as loss of a battery pack, or cascaded rotor failures due to rotor plane intersections, which might introduce simultaneous loss of more than one propulsion system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization J.Z.; methodology J.Z.; software J.Z. and M.S.; validation J.Z. and M.S.; investigation J.Z.; writing-original draft preparation J.Z.; writing-review and editing, J.Z. and M.S.; visualization J.Z.; supervision F.H.; project administration F.H.; funding acquisition, F.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Durham, W.C. Constrained control allocation. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics 1993, 16, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, W.C. Constrained control allocation—Three-moment problem. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics 1994, 17, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, T.A.; Fossen, T.I. Control allocation—A Survey. Automatica 2013, 49, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, W.C. Attainable moments for the constrained control allocation problem. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics 1994, 17, 1371–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varriale, C.; Voskuijl, M.; Veldhuis, L.L. Trim for Maximum Control Authority using the Attainable Moment Set. In . AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum, 2020/01/05; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, ISBN 9781624105951.
- Ma, T.; Wang, X.; Qiao, N.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.; Bao, M. A Conceptual Design and Optimization Approach for Distributed Electric Propulsion eVTOL Aircraft Based on Ducted-Fan Wing Unit. Aerospace 2022, 9, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suiçmez, E.C. Full Envelope Nonlinear Controller Design for a Novel Electric VTOL(eVTOL) Air-taxi via INDI Approach Combined with CA.
- Moore, K.R.; Ning, A. Distributed Electric Propulsion Effects on Existing Aircraft Through Multidisciplinary Optimization. In 2018 AIAA/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference. 2018 AIAA/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Kissimmee, Florida; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, Virginia, 01082018, ISBN 978-1-62410-532-6.
- Fard, M.T.; He, J.; Huang, H.; Cao, Y. Aircraft Distributed Electric Propulsion Technologies—A Review. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2022, 8, 4067–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchini, A.; Cestino, E. Electric VTOL Configurations Comparison. Aerospace 2019, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, A.; Raj, V.S.J.; Sushmitha, R.; Prateek, B.; Aditya, S.; Sreehari, V.M. Design and Analysis of VTOL Operated Intercity Electrical Vehicle for Urban Air Mobility. Electronics 2022, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinini, R.; Tugnoli, M.; Zanotti, A. Numerical Investigation of the Rotor-Rotor Aerodynamic Interaction for eVTOL Aircraft Configurations. Energies 2020, 13, 5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumuluru Ramesh, N.; V. Pandurangi, P. A flight performance based optimization model for eVTOL vehicles; Engineering Archive, 2022.
- Cook, J. A Strip Theory Approach to Dynamic Modeling of eVTOL Aircraft. In AIAA Scitech 2021 Forum, Reston, Virginia; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, Virginia, 2021.
- Stokkermans, T.C.A.; Usai, D.; Sinnige, T.; Veldhuis, L.L.M. Aerodynamic Interaction Effects Between Propellers in Typical eVTOL Vehicle Configurations. Journal of Aircraft 2021, 58, 815–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASA. Special Condition for small-category VTOL-capable aircraft. Available online: https://www.easa.europa.eu/en/downloads/139946/en.
- EASA. Means of Compliance with the Special Condition VTOL—MOC SC-VTOL Issue 2. Available online: https://www.easa.europa.eu/en/downloads/127717/en.
- Eric Nguyen Van; Pierre Troillard; Joël Jézégou; Daniel Alazard; Philippe Pastor; Carsten Döll. Reduction of Vertical Tail Using Differential Thrust: Influence on Flight Control and Certification. In . Advanced Aircraft Efficiency in a Global Air Transport System (AEGATS’18), 2018; pp 1–8.
- Van, E.N.; Alazard, D.; Döll, C.; Pastor, P. Co-design of aircraft vertical tail and control laws using distributed electric propulsion. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.R.; Ning, A. Takeoff and Performance Trade-Offs of Retrofit Distributed Electric Propulsion for Urban Transport. Journal of Aircraft 2019, 56, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Bassett, G.; Grisham, J.; Finch, P.; Toniolo, M.; Miller, L.; Bandu, P. Generic Control Allocation Toolbox for Preliminary Vehicle Design. In 2018 Modeling and Simulation Technologies Conference, Reston, Virginia; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, Virginia, 2018, ISBN 9781624105517.
- Varriale, C.; Voskuijl, M. A trim problem formulation for maximum control authority using the Attainable Moment Set geometry. CEAS Aeronaut J 2022, 13, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söpper, M.; Zhang, J.; Holzapfel, F. Required Moment Sets: Enhanced Controllability Analysis for Nonlinear Aircraft Models. (submitted). applied sciences 2021.
- Zhang, J.; Söpper, M.; Holzapfel, F. Attainable Moment Set Optimization to Support Configuration Design: A Required Moment Set Based Approach. applied sciences 2021, 11, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MathWorks. MATLAB Version: 9.8.0.1451342 (R2021a); MathWorks: Natick, Massachusetts, 2021.
- Gupta, G.; Abdallah, S. Propeller Force-Constant Modeling for Multirotor UAVs from Experimental Estimation of Inflow Velocity. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIT. Performance of Propellers. Available online: https://web.mit.edu/16.unified/www/FALL/thermodynamics/notes/node86.html.
- Du, G.-X.; Quan, Q.; Yang, B.; Cai, K.-Y. Controllability Analysis for Multirotor Helicopter Rotor Degradation and Failure. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics 2015, 38, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, G.; Mattei, M. Modeling and Incremental Nonlinear Dynamic Inversion Control of a Novel Unmanned Tiltrotor. Journal of Aircraft 2016, 53, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; van Kampen, E.-J.; Chu, Q.; Lu, P. Stability Analysis for Incremental Nonlinear Dynamic Inversion Control. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics 2019, 42, 1116–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; van Kampen, E.-J.; Visser, C. de; Chu, Q. Aircraft fault-tolerant trajectory control using Incremental Nonlinear Dynamic Inversion. Control Engineering Practice 2016, 57, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeur, E.J.J.; Chu, Q.; Croon, G.C.H.E. de. Adaptive Incremental Nonlinear Dynamic Inversion for Attitude Control of Micro Air Vehicles. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics 2016, 39, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieberling, S.; Chu, Q.P.; Mulder, J.A. Robust Flight Control Using Incremental Nonlinear Dynamic Inversion and Angular Acceleration Prediction. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics 2010, 33, 1732–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodson, M. Evaluation of Optimization Methods for Control Allocation. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics 2002, 25, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bhardwaj, P.; Raab, S.A.; Saboo, S.; Holzapfel, F. Control Allocation Framework for a Tilt-rotor Vertical Take-off and Landing Transition Aircraft Configuration. In 2018 Applied Aerodynamics Conference. 2018 Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Atlanta, Georgia; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, Virginia, 06252018, ISBN 978-1-62410-559-3.
Figure 1.
2D Example of AMS, RMS and the Margin in between.
Figure 1.
2D Example of AMS, RMS and the Margin in between.
Figure 2.
Rotor Layout of Considered Airframe.
Figure 2.
Rotor Layout of Considered Airframe.
Figure 3.
Rotor Tilt Layout according to Initial Design Parameter.
Figure 3.
Rotor Tilt Layout according to Initial Design Parameter.
Figure 4.
Comparison of AMS with Different Rotor Tilt Angle and the RMS.
Figure 4.
Comparison of AMS with Different Rotor Tilt Angle and the RMS.
Figure 5.
Test 1 Optimized Rotor Layout.
Figure 5.
Test 1 Optimized Rotor Layout.
Figure 6.
Test 1 Comparison: Optimized AMS, Initial AMS and RMS.
Figure 6.
Test 1 Comparison: Optimized AMS, Initial AMS and RMS.
Figure 7.
Test 1 Comparison: Cumulative Count of Margin Factors.
Figure 7.
Test 1 Comparison: Cumulative Count of Margin Factors.
Figure 8.
Test 1 Cost Function over Optimization Variables.
Figure 8.
Test 1 Cost Function over Optimization Variables.
Figure 9.
Test 2 Optimized Rotor Layout.
Figure 9.
Test 2 Optimized Rotor Layout.
Figure 10.
Test 2 Comparison: Optimized AMS, Initial AMS and RMS.
Figure 10.
Test 2 Comparison: Optimized AMS, Initial AMS and RMS.
Figure 11.
Test 2 Comparison: Cumulative Count of Margin Factors.
Figure 11.
Test 2 Comparison: Cumulative Count of Margin Factors.
Figure 12.
Test 3 Optimized Rotor Layout.
Figure 12.
Test 3 Optimized Rotor Layout.
Figure 13.
Test 3 Comparison: Optimized AMS, Initial AMS and RMS.
Figure 13.
Test 3 Comparison: Optimized AMS, Initial AMS and RMS.
Figure 14.
Test 3 Comparison: Cumulative Count of Margin Factors.
Figure 14.
Test 3 Comparison: Cumulative Count of Margin Factors.
Figure 15.
Test 3 Cost Function over Optimization Variables.
Figure 15.
Test 3 Cost Function over Optimization Variables.
Figure 16.
Test 3 Optimized Rotor Layout.
Figure 16.
Test 3 Optimized Rotor Layout.
Figure 17.
Test 4 Comparison: Optimized AMS, Initial AMS and RMS.
Figure 17.
Test 4 Comparison: Optimized AMS, Initial AMS and RMS.
Figure 18.
Cumulative Count of Margin Factors.
Figure 18.
Cumulative Count of Margin Factors.
Table 1.
Comparison between Different Configurations.
Table 1.
Comparison between Different Configurations.
| |
Initial Value |
Test 1 |
Test 2 |
Test 3 |
Test 4 |
| P1 tilt angle () |
-5 |
-17.94 |
-13.98 |
-1.64 |
-6.09 |
| P2 tilt angle () |
5 |
9.25 |
8.90 |
19.04 |
10.20 |
| P3 tilt angle () |
-5 |
9.25 |
9.23 |
19.04 |
29.20 |
| P4 tilt angle () |
5 |
-17.94 |
-23.15 |
-1.64 |
-1.90 |
| Failure free cost function:
|
33.06 |
29.22 |
29.12 |
30.29 |
30.28 |
| Critical failure cost function:
|
61.31 |
67.85 |
59.58 |
47.39 |
45.6667 |
| Total force available in the vertical direction (%):
|
99.6% |
96.92% |
96.62% |
97.24% |
96.27% |
| additional force to trim (%):
|
0.40% |
3.18% |
3.50% |
2.84% |
3.87% |
| additional power to trim (%):
|
0.6% |
4.8% |
5.3% |
4.3% |
5.9% |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).