Introduction: Neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Barth Syndrome have shown strong associations with mitochondrial dysfunction, particularly involving lipid metabolism within the mitochondrial inner membrane. Cardiolipin (CL), a critical phospholipid unique to mitochondria, plays a pivotal role in maintaining mitochondrial structure and function. This review examines the relevance of CL in these diseases, exploring how CL variations serve both as diagnostic biomarkers and as potential therapeutic targets. Emphasis is placed on recent lipidomic studies, which highlight the alterations in CL composition, particularly in NDDs where oxidative stress and mitochondrial failure are common.
Materials and Methods: This comprehensive review includes a synarticle of data from peer-reviewed publications over the last decade, with specific focus on lipidomics, mitochondrial dynamics, and neurodegeneration-related protein-lipid interactions. Studies were selected based on their contributions to understanding cardiolipin’s molecular role in disease contexts. The methodology includes a critical analysis of research articles, focusing on CL’s quantitative and qualitative alterations in Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Barth Syndrome. Key lipidomic findings were extracted, and data on CL-to-monolysocardiolipin ratios were included as biomarkers of disease state and progression.
Repeated Abbreviations:
Aβ: Amyloid-β
AβPP: Amyloid-β precursor protein
Ac-DHAP: 1-acyl-dihydroxyacetone-phosphate
AD: Alzheimer’s Disease
ADP: Adenosine diphosphate
AGP: 1-acyl-glycerol-3-phosphate
ALCAT1: Acyl-CoA-lysocardiolipin acyl transferase
ANOVA: Analysis of variance
ApoE: Apolipoprotein E
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate
BN-PAGE: Blue native-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
BTHS: Barth Syndrome
cDNA: complementary DNA
CDP-DAG: Cytidine-diphosphate-diacyl-glycerol
CLi: immature cardiolipin
CLm: mature cardiolipin
CLS1: Cardiolipin synthase 1
Complex 1: NADH Dehydrogenase
Complex 3: Ubiquinol-ferricytochrome-c oxidoreductas
Complex 4: Cytochrome-c oxidase
Complex 5: ATP Synthase
CTP: Cytidine Triphosphate
DHAP: dihydroxyacetone phosphate
DHAPAT: DHAP acyltransferase
DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid
DPI: dual polarization interferometry
ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
ESI-MS: Electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry
ETC: Electron Transport Chain
FS: Fluorescence Spectroscopy
FTD: Frontotemporal dementia
GC-MS: Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
HPLC: High performance liquid chromatography
HPLC-MS: High performance liquid chromatography
IMM: Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
LC-MS: Liquid chromatography-mass spectrophotometry
LC3: Microtubule-associated protein -light chain 3
LPS: Lipopolysaccharide
LUV(s): Large unilamellar vesicle(s)
LOOH: Lipid hydroperoxide
MALDI-TOF/MS: Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight/ mass spectrophotometry
MLCL: Monolysocardiolipin
MMP: Mitochondrial membrane potential
MPTP: 1- methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,4,6-tetrahydropyridine
mtDNA: mitochondrial DNA
NDD: Neurodegenerative Disease
NDDs: Neurodegenerative Diseases
nDNA: nuclear DNA
NMR: Nuclear magnetic resonance
OMM: Outer mitochondrial membrane
OXPHOS: Oxidative Phosphorylation
PA: phosphatidic acid
PCR: Polymerase chain reaction
PG: Phosphatidyl-glycerol
PGP: Phosphatidyl-glycerol-phosphate
PUFA(s): Polyunsaturated fatty acids(s)
ROS: Reactive oxygen species
RNA: Ribonucleic acid
RSC: Respirasome Supercomplex
SDS-PAGE: Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
SNCA: α-synuclein
SS: Szeto-Schiller
SS-31: Elampretide
TAZ: Tafazzin
TLC: Thin Layer Chromatography
Tg: Transgenic
TUNEL: Terminal Transferase biotinylated-deoxyuridine triphosphate nick end labeling
WT: Wild-Type
1. Introduction
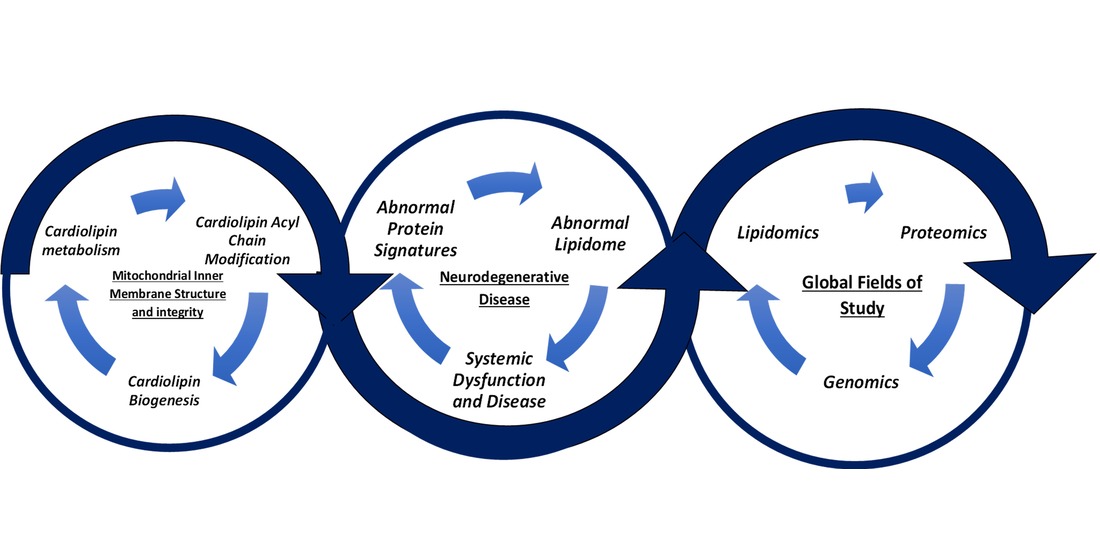
Understanding the significance of CL in NDDs requires knowledge of two main areas, which include the role of IMM structure in NDDs and the significance of NDD biomarkers and protein signatures.1,2 These two areas can be better understood by applying lipidomics, which is a field of study in which lipid profiles are identified, quantified, and characterized to understand their role in biological systems.2-8 Recently, NDD research has had a focal point around the mitochondria’s role in disease development and diagnosis.9-10
Broadly, mitochondria have been at the forefront of biochemical research, being a focal point for numerous Nobel prizes in Chemistry, including in 1978 and 1997, owing to its crucial role in cellular respiration, cardiovascular disease, and NDDs.11-12 In terms of function, mitochondria perform oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), an oxidative process in the IMM that synthesizes ATP.9 The exergonic flow of electrons in the IMM fuels the endergonic pumping of protons across the proteins in the respirasome super-complex (RSC), which drives the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP via ATP synthase.13 OXPHOS is a process that involves five protein complexes that constitute the electron transport chain (ETC).3 The ETC specifically has three complexes - Complex 1 (NADH Dehydrogenase), Complex 3 (Ubiquinol-ferricytochrome- c oxidoreductase) and Complex 4 (Cytochrome-c oxidase) - which form the RSC. Also, in the IMM is ATP synthase, otherwise known as Complex V, which functions to synthesize ATP.3
OXPHOS is important within the context of CL’s role because CL is involved in maintaining the structure of the RSC.
6 CL has a conical shape due to its four acyl chains. Also, CL operates as an anchorage and docking component for the RSC in the IMM.
3-5 Being situated in the IMM, an understanding of CL and mapping out its relevance to NDDs necessitates the use of different analytical fields of study such as lipidomics.
3 This article is centered around supporting lipidomics as a field of study to provide an understanding of CL in the context of NDD progression, which is seen in
Figure 1.
Lipidomics is a field of study that includes analyzing the biosynthetic, degradative, and regulatory pathways of all lipids.3 It aids in the systematic analysis and quantification of the overall lipid profile in an organism, organ, or cell.14 The lipid profile consists of different types of lipids such as prenols, sphingolipids, phospholipids (e.g., CL), fatty acids, and sterols.5,15 In addition to lipid profiling, analyses of lipid structures such as the acyl chains of CL can enhance mapping out the role lipids have in the development or diagnoses of generally idiopathic NDDs.11,16
With NDDs, the classic paradigm of “form follows function” is evident.10 Likewise, the loss of function and abnormalities with it can be understood in terms of lipid structure via lipidomics.3 The loss of function can pinpoint a disease’s genetic and metabolic origins. In the same vein, the loss of function with knockout cell lines in mice and the subsequent analyses of those cell lines via lipidomics have served as models for specific aspects of a NDDs’ phenotypes in NDD research.1-4,6
The knockout cell lines for specific genes expressing typical proteins in NDD progression such as α-synuclein (SNCA) and amyloid-β (Aβ) with lipidomics allows for relationships between key protein signatures and CL to be established.7,9 Typically, loss of function analyses compare wild-type (WT) cell lines and transgenic cell lines.17,19 From these types of analyses via lipidomics, how CL and its aberrations relate to characteristic protein signatures in NDDs (e.g., SNCA in Parkinson’s Disease (PD) and Aβ in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)) can be elucidated.9 However, it is important to note that transgenic knockout cell lines are useful in simulating a specific aspect of a NDD’s phenotype such as cognitive impairment or motor deficits, but not sufficient to replicate the entire suite of complex abnormalities and co-morbidities associated with a NDD.3,9
2. Importance of Cardiolipin in the Mitochondria and Cell
The lipid profile of the central nervous system (CNS) plays a crucial role in nerve cell functioning, particularly in the OXPHOS process in the mitochondria. The entire lipid profile of a cell is called the lipidome. Since the CNS comprises 50% lipids by dry weight and any aberrations in its lipid content can affect its physiology, knowing the lipidome is of utmost significance.
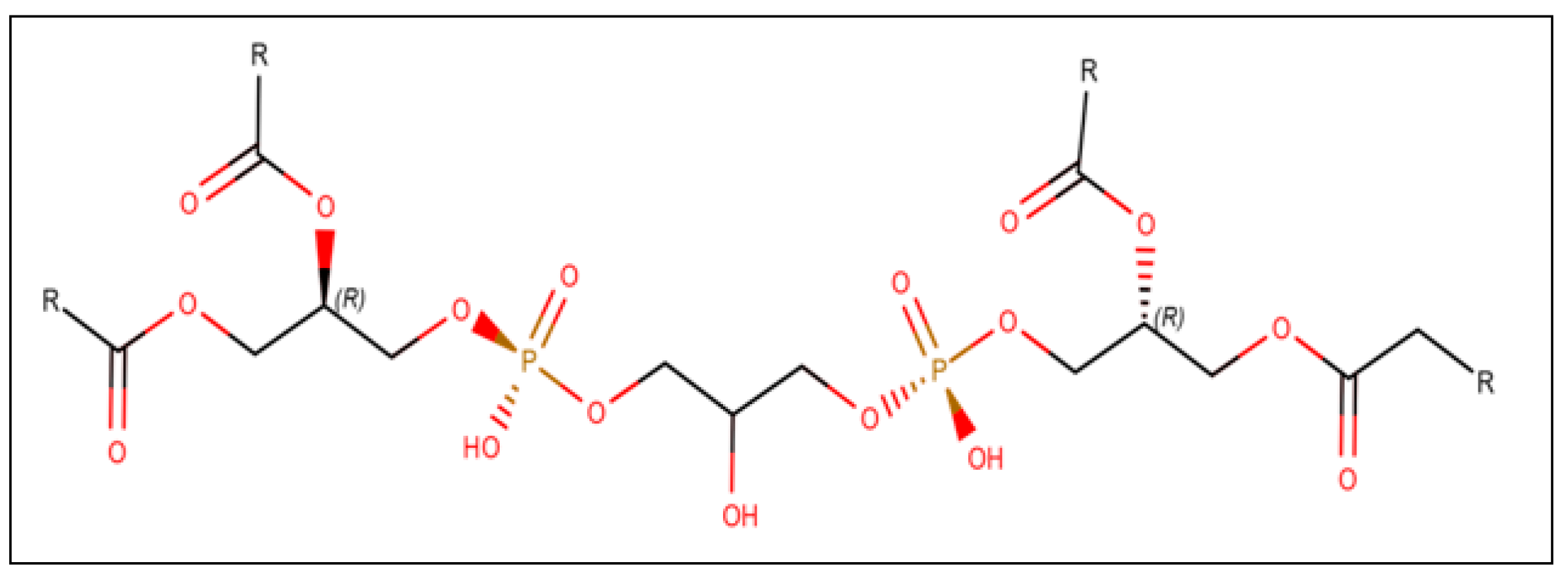
3 CL, also known as diphosphatidylglycerol as shown in
Figure 2, is an unusual member of the lipidome because it is localized in the mitochondria during the entire lifetime of the cell, unlike other members of the lipidome. In a cellular context, decreased levels of CL contribute to abnormalities in cellular respiration and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS).13,16,20
CL can also serve as a mitophagic and apoptotic signaling factor when oxidized.3 Mitophagy and apoptosis are defined as the breakdown and destruction of the mitochondria and cell, respectively. In general, CL plays a role in the docking and anchoring of the ribosomes of the IMM and protein complexes of the ETC.1
The ETC is situated in the IMM, and CL biogenesis occurs in the IMM. Further research into CL biogenesis, described fully herein and shown in
Figure 3, is warranted because of its importance in the understanding of the function of abnormal proteins in NDDs such as BTHS. Interestingly, when the enzymes that biosynthesize CL are aberrant, they can contribute to NDD progression as has been seen in BTHS.
21-23
The first step in CL synarticle is the synarticle of phosphatidate, a common intermediate for the synarticle of phospholipids and triacylglycerols. Many of these reactions with phosphatidate, which synthesize CL are driven forward by the hydrolysis of pyrophosphate.
Phosphatidate, in mammalian cells, is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and the OMM. In the beginning of this anabolic pathway, glycerol-3-phosphate either from glycolysis or the phosphorylation of glycerol is used. Then, glycerol-3-phosphate, with the addition of the fatty acid, results in phosphatidate.
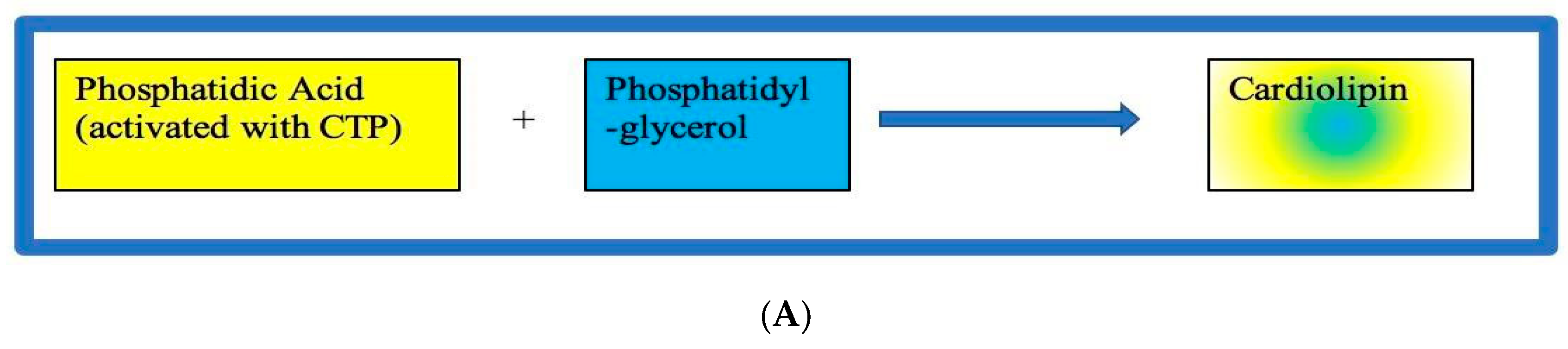
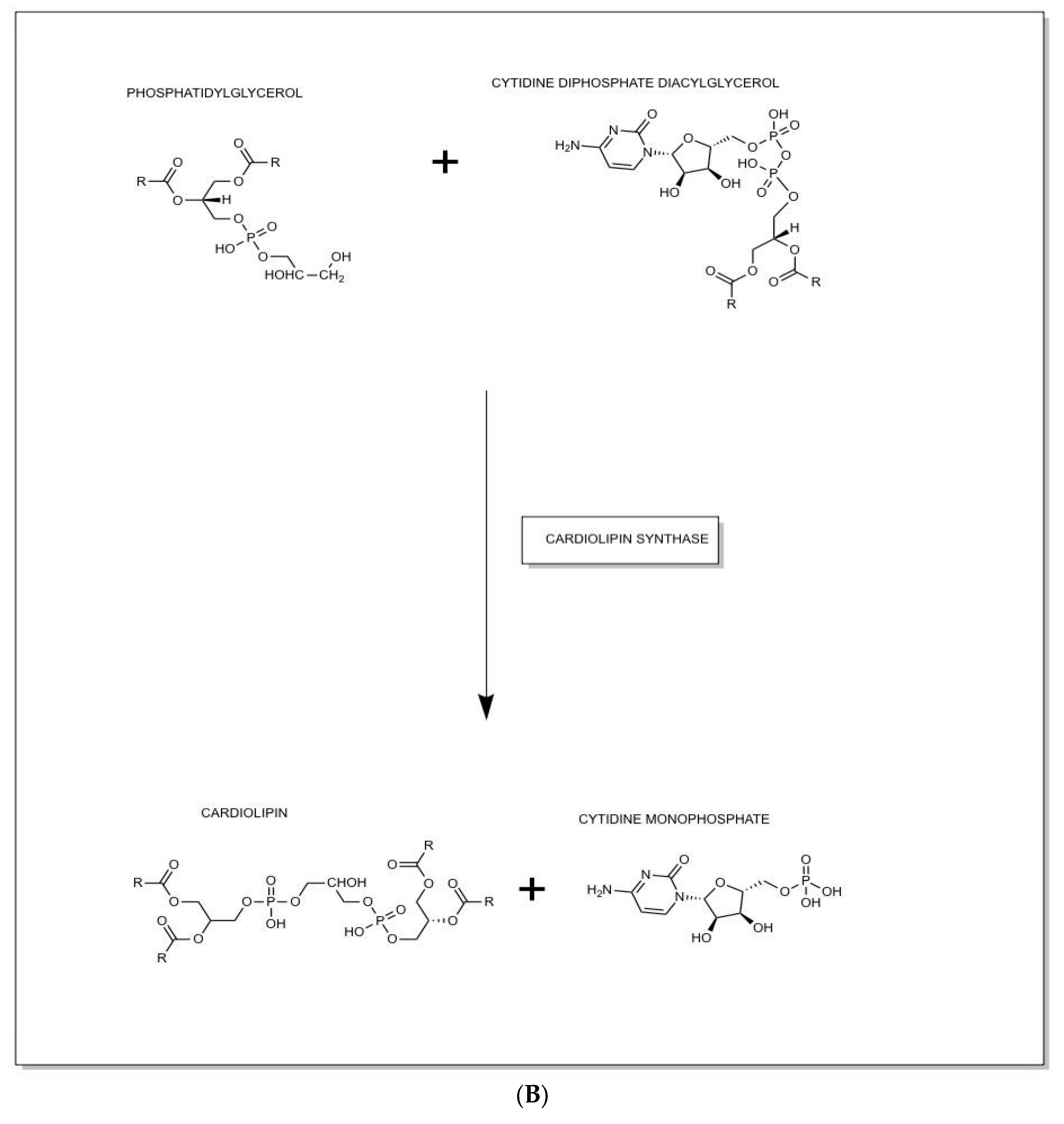
Within this anabolic pathway, there are numerous acylations with the common intermediate, phosphatidate. In these acylation reactions, the fatty acid chain is attached to the C- 1 atom and is typically saturated. However, the acyl chains attached to the C-2 atom are typically unsaturated. Second, it is important to note that pathways diverge at phosphatidate, with some membrane-lipid synarticle occurring in the endoplasmic reticulum or in the OMM. Third, in this anabolic pathway, one of the reactants – either phosphatidic acid (PA) or the alcohol as shown in
Figure 3A – has to be activated and is substrate dependent.
Specifically, for the activated reactant PA, the pathway starts with the reaction of phosphatidate with cytidine-triphosphate (CTP) that forms an activated CDP-DAG, which is known as cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-DAG). Then, the activated phosphatidyl unit in CDP-DAG reacts with a hydroxyl group of phosphatidylglycerol (PG), via CL synthase, as seen in
Figure 3B, to form a phosphodiester linkage, and the resulting product is CL.
3,14,29
3. CL and Lipidomics
Lipidomics examines the total lipid profile of a given sample, which is also known as the lipidome. The lipidome is a subset of the metabolome comprising of subclasses of lipids, including fatty acids, prenols, sphingolipids, sterols, and glycerophospholipids. Lipidomic analysis provides information regarding the variation of lipids, which facilitates the study of different disease classes, such as NDDs as reviewed in
Section 4.
24 For example, PD has been associated with aberrations in a spectrum of lipid pathways in the nervous system, some of which may be related to CL dysfunction.
24 Hence, the study of CL dysfunction
via lipidomics improves the ability of researchers to further understand the future outcomes of specific phenotypes in NDD diagnosis and development.
3,9
4. Disease Overviews
In the NDDs that are reviewed in
Section 4 - namely AD, PD, and BTHS - structural or concentration changes in CL are associated with specific simulated NDD phenotypes. Whether through chemical inhibition (
e.g., rotenone inhibiting ETC’s Complex 1, resulting in PD phenotypes) or gene knockout experiments,
21,28,34,37 the NDD phenotypes are simulated in murine models in many of the studies. These simulated NDD phenotypes provide an empirical basis to relate CL changes to NDDs as potential risk factors for NDD development and diagnosis.
4.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
AD is a NDD that progresses gradually with worsening states of cognitive function (e.g., memory loss) over time. There are three features of AD that are relevant within the context of this article. First, AD is a primary form of dementia with the World Health Organization stating that 60-70% of dementia cases are contributed to by AD.30 Dementia is a syndrome, which presents with deteriorations in cognitive functions such as memory decline, poor judgement and confusion, which is atypical when compared to the normal consequences of aging.30
Second, AD is associated with bilateral parietal hypometabolism in posterior cingulate neurons.9 In terms of AD subtypes, there are two subtypes of AD based on age of onset. The two types of AD are early-onset AD and late-onset AD. Both early onset-AD and late-onset AD are associated with A.3,9,68 A is a characteristic protein hallmark that is derived from the proteolysis of amyloid- precursor protein (APP), which is a type-1 integral membrane protein.3,9,68
Third, AD has specific mutations and symptoms associated with its subtypes: early-onset AD and late-onset AD. Early-onset AD is characterized by six different missense mutations in APP, while five missense mutations are associated with APP in familial AD.3,9 However, late- onset AD accounts for 90% of AD cases. It is noted that the susceptibility to late-onset AD is associated with genes for ApoE and APP.3,9 In terms of symptoms, AD presents with a variety of symptoms such as age-related memory impairment, episodic memory loss, and disproportionate episodic memory decline. This episodic memory decline begins in the medial and temporal regions of the brain, and then as the disease progresses it affects the visuospatial, language and executive functions of the brain.3,9 In terms of diagnosis and patient sample analysis for AD, the cerebrospinal fluid measures the total A protein and tau protein concentrations, which provides insights into AD progression in patients.9
Keller et al.25 and Maganelli et al.26 reported AD to be characterized by specific protein signatures, including Aβ plaques, which accumulate in the brain during late-onset AD. Another hallmark of AD is the formation of neurofibrillary tangles from hyperphosphorylated tau protein. Although there is not a direct mechanism known at this time, Keller et al.25 notes that there are indirect pathomechanisms that trigger lipid aberrations. Further, in this article I suggest that CL and ApoE are significant within the context of A pathology. First, CL when externalized by microtubule-associated protein -light chain 3 (LC3), functions as a mitophagic signal and mitophagy inhibits A and tau pathology.3,9 Second, ApoE affects A by binding to it and promoting its clearance from the neuronal cell.3,9,62-64 Given the significance of CL and ApoE in A pathology and processing either indirectly (CL) or directly (ApoE), I suggest that more research is warranted on pathways associated with A pathology. Specifically, more research is warranted on ApoE-mediated A clearance, and on A pathology inhibited by mitophagy that is induced by CL externalization via LC3.10,57,62-64
Furthermore, Keller
et al.25 shows the importance of interpreting the lipid profiles in mitochondrial diseases, and with this understanding, concentration changes in CL in the brain are suggested to act as a diagnostic risk factor in NDDs such as AD. This functioning as a diagnostic risk factor, as outlined in the BTHS (
Section 4.3), currently is known for BTHS since CL acyl chain abnormalities serve as a standard diagnostic risk factor for BTHS.
Association of Alzheimer’s Disease with Changes in Cardiolipin Concentrations
Monteiro-Cardoso et al.4 investigated the role of CL in mitochondria with an experimental model of AD, using lipidomics. The methods Monteiro-Cardoso et al.4 used involved HPLC, western blot, spectrophotometry, lipid extraction, and quantification using a phosphorus assay. Finally, the separation of the phospholipid classes and quantification was done using HPLC-MS. Specifically, Monteiro-Cardoso et al.4 used the lipid profiles of 3-month-old non-transgenic mice and compared those with SNCA gene knockout mice. Monteiro-Cardoso et al.4 reported the separation and quantification of phospholipid classes using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). Also, Monteiro-Cardoso et al.4 reported a decrease in CL concentration in AD mouse models. The key finding these scientists reported was that synaptic mitochondrial defects along with aberrations in CL profile represent key indicators for the development of AD.4 Furthermore, Monteiro-Cardoso et al.4 reported that the dysfunction of synaptic mitochondria and energy depletion associated with a loss of lipid asymmetry contribute Aβ accumulation and cellular dysfunction.
Guan et al.26 reported the use of brain samples from human cadavers that were diagnosed with AD. The patients had histopathological features such as neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in each cadaver’s neocortex. The methods reported involved brain regions being chosen for lipid analysis and dissected 36 hours after death. After death, the samples were homogenized and stored at -20⁰C until the analysis was done. Moreover, Guan et al.26 used HPLC and ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy to extract and quantify the lipid profiles from the brains of human cadavers with AD via the Folch method. The Folch method is a type of lipid-extraction technique based on the distribution of lipids in a two-phase mixture of methanol and chloroform, which breaks the hydrogen bonds between the lipids and proteins.20 The data obtained using HPLC was monitored at 205 nm and each peak was collected and checked for purity. Likewise, the CL content was reported to be independent of the postmortem time of the cadavers with AD. For the cadavers with AD, the regions of the brain were chosen based on the regions that were severely affected morphologically by AD.
The overall experiment design was centered around analyzing the CL content based on the region of the brain in the cadavers with AD and the type of acyl chain within the CL molecule. The data obtained was primarily based on human cadaver cases. The significant conclusions of Guan et al.26 supported the idea that abnormalities in mitochondrial enzymes and significant changes in CL concentrations in patients’ brains can potentially serve as risk factors for specific phenotypes in AD development and diagnosis.
Guan et al.26 also measured the level of CL specifically in the frontal and temporal cortices of the brains of human cadavers primarily with AD. Additionally, the major finding was reported as a statistically significant decrease (9%) of CL that contained polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), which was in the temporal cortex of human cadavers with AD.
Subsequently, research by Karmi et al.28 involved examining the consequences of a deficiency in Tafazzin (TAZ), which is a gene that expresses a protein involved in the remodeling and deacylation of CL. First, Karmi et al.28 used the TAZ gene knockout model to investigate the relationship between CL molecular species content in the brain, mitochondrial functions, and cognitive decline. Second, Karmi et al.28 reported that the TAZ deficiency alters the CL molecular species content in the brain. Then, the scientists reported quantifying that CL molecular species content by mass spectrometry in the analysis. The analysis involved the use of Western blot, RNA isolation and PCR analysis, TLC, immunohistochemical analysis, extracting lipids from the whole mouse brain using the Folch method and then quantitation using mass spectrometry.
Further, Karmi et al.28 reported using transmission electron microscopy, behavioral tests and statistical analysis in the analysis of CL content and TAZ deficiency in the murine models.
Using the reported murine models, the scientists supported the claim that abnormal CL metabolism is associated with the specific phenotypes of cognitive dysfunction, which was “memory deficiency” for the mice, and hippocampal alteration which was the “derangement of the neuronal CA1 layer” in TAZ gene knockdown mice.28 This phenotype resultant from this TAZ gene knockdown model is relevant to AD since episodic memory loss or deficiency is a characteristic condition of AD.3,9,28 Moreover, the TAZ gene knockdown in the murine models used by Karmi et al.,28 was effective in simulating the specific phenotypes of “memory deficiency” and hippocampal alteration, however the use of TAZ gene knockdown as a complete model for AD is not presented here in this article or by Karmi et al..28
Although TAZ in this article is not presented as a complete model for AD, it is however known that TAZ is a major initiator of mitophagy.3,65 First, mitophagy can be mediated by ubiquitin or receptor-mediated pathways, which include lipid-mediated mitophagy.3,65-67 Second, mitophagy is stated to inhibit A and tau pathology.3,65-66 Third, it is known that A pathology is characteristic of AD.3,9 Hence I suggest that the aforementioned findings,3,65-67 further support the use of a TAZ gene knockdown model in mice, as seen in Karmi et al.,28 as beneficial in understanding the relationship between A pathology and AD. Also, I suggest that more research is warranted on the relationship of AD diagnosis and development with TAZ, and the relevance of CL remodeling via TAZ in the diagnosis and development of AD.
The association between the specific phenotype of memory decline and abnormal CL metabolism mentioned earlier, was deduced from murine models with TAZ gene knockdown. Additionally, Karmi et al.28 reported structural abnormalities as well. Karmi et al.28 reported that CL with PUFA chains decreased, but CL with shorter fatty acyl chains (approximately 18 carbons) increased in the murine models that were studied. The TAZ gene expresses an enzyme that reacylates monolysocardiolipin (MLCL) to produce CL. This reacylation is significant as CL, when appropriately acylated, contributes to the normal structure of the IMM which has implications for cell respiration and normal mitochondrial functioning.3
Karmi et al.28 reported that TAZ-deficiency in the brain significantly decreased the total CL level and increases MLCL levels. These scientists also reported observing that TAZ deficiency in the brain resulted in altered mitochondrial respiration, elevated ROS products and deficiencies in memory. The association of TAZ deficiency and phospholipid (e.g., CL) content in the brain provided Karmi et al.28 an empirical basis of understanding CL content and specific phenotypes in NDDs’ diagnoses and development.
However, it is important to note that phenotypes such as pathological cognitive dysfunction (e.g., memory decline) as discussed by Karmi et al.28 is implicated in several NDDs namely AD. The evidenced relationship between the pathological development of cognitive dysfunction and abnormal CL metabolism was presented in the TAZ knockdown mice, which was related to a difference in the concentration of CL. This observation of abnormal CL metabolism resulting in a significant decrease in CL amount and the specific phenotype of cognitive dysfunction provided further evidence regarding the association between CL and AD risk factors in AD diagnosis and development.
Analysis of Studies
These studies, as listed in
Table 1, have significant overlap in approach, results, and conclusions. First, all three studies had hypotheses that focused on mapping out the relationship between components in the lipid profile (phospholipids,
e.g., CL) and specific phenotypes in AD. Secondly, the studies reported the use of HPLC-MS as the separation technique to distinguish, characterize, and identify the lipid classes. Third, the studies primarily used eukaryotic models to study specific phenotypes in AD, in which Karmi
et al.,28 and Monteiro-Cardosso
et al.4 reported the use of murine models, and Guan
et al.26 reported using human cadavers’ brain samples.
In terms of results, the CL content in each study was reported to have changed in amount, with decreases reported by Monteiro-Cardosso et al.4 and Guan et al.,26 and both increases for CL with short acyl chains and decreases in CL with polyunsaturated fatty acyl (PUFA) chains reported by Karmi et al..28 With those key findings about CL content, the studies outlined the changes in the lipid profile and demonstrated the potential implications for AD incidence. The extent to which these findings have therapeutic implications or the possibility of replicating a complete disease model for AD in animals was not presented here. However, these findings provide insights for further investigations on the role of CL in NDD research.
Conclusions about Alzheimer’s Disease
All three studies26-28 supported that there is a relationship between the alteration of CL concentration and specific AD phenotypes in the mammalian brain. These studies show that the alteration in CL content is specific to the CL type in terms of acyl chains. These studies also support how changes in key members of the lipidome, namely CL, can potentially serve as diagnostic co-indicators of specific phenotypes in NDD diagnosis and development. These diagnostic co-indicators I suggest can potentially serve to identify pre-symptomatic individuals with AD who are persons at risk of decline or to support accuracy with AD diagnosis. The need for more research using lipidomics also emerges from these studies, particularly with regards to the role of specific members of the lipidome, such as CL, and their functions as potential diagnostic risk factors for AD diagnosis and development.
4.2. Parkinson’s Disease
PD is a progressive disease characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, a basal ganglia structure in the midbrain31 which affects cognitive function and gait.31-32 In 2021, Bloem et al.19 reported that PD develops in patients due to the accumulation of SNCA protein-forming inclusion bodies known as Lewy bodies. SNCA is a 140 amino acid (14.5 kilodaltons) protein and considered as the major causative gene involved in the early onset of familial PD characterized by five missense mutations identified so far. It is also considered to be involved in various others NDDs such as AD, Lewy bodies’ disease and Muscular System Atrophy.27
PD is also characterized by the development of abnormal projections from the cell body of neurons, known as Lewy neurites. The development of these pathological Lewy traits is characterized by a cellular milieu that includes abnormal intracellular vesicles and abnormal mitochondria.25 Abnormal mitochondria typically have abnormal CL structures since CL is an integral part of the IMM for maintenance of IMM structure and IMM respiratory chain function.3
PD research in murine models was also reported by Ellis et al.35 They reported isolating lipids, quantifying them by lipid scintillation counting, and comparing the lipid profiles of SNCA gene knockdown and WT murine models. They reported a 23% decrease in phosphatidylglycerol (PG), a precursor to CL. Ellis et al.35 also reported a 15% decrease in the complex function of the linked ETCs of complexes 1 and 3.
In 2018, Ryan et al.36 reported a relationship between CL and PD in SNCA gene knockdown murine models using transmission electron microscopy images of mitochondria and by observing changes in IMM morphology. Using isogenic controls for SNCA-transgenic mice, they reported that the neurons display abnormal mitochondria with SNCA deposits clustered to mitochondrial membranes as a result of exposure of CL on the mitochondrial surface. In addition to studying mitochondrial morphology, binding experiments with SNCA and CL were also performed. Several key findings were noted. First, neurons with the SNCA gene mutations demonstrated aberrations with SNCA protein structure. Second, those neurons had impaired mitochondrial dynamics. Additionally, in those neurons, CL was externalized to the OMM and bound to SNCA and refolded SNCA oligomers.
Furthermore, Ryan et al.36 reported the use of time-dependent analyses with circular dichroism spectroscopy to understand the binding of CL to SNCA and its folding behavior. These scientists reported mimicking the OMM, using the CL that was present in large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs) with SNCA. They also reported that the CL exhibited an affinity for and exhibited interactions with the WT and mutant SNCA monomers. These interactions were between CL and SNCA monomers. With that noted, these interactions between CL and SNCA monomers contributed to the refolding of SNCA. In short, the results from the murine models, supported that changes in CL structure for the PD murine models were associated with cellular oxidative stress and affected SNCA monomers.36
PD murine models were also used by Song et al.37 who reported the induction of PD murine models via 1- methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,4,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), which resulted in oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. In addition, Song et al.37 reported - using ANOVA (i.e., analysis of variance, which is a statistical method that separates observed variance data into different components to use for additional tests), immunostaining, and confocal microscopy - that an upregulation of both the acyl-CoA-lysocardiolipin acyl transferase-1 (ALCAT1) mRNA and the protein expression were observed. This finding of ALCAT1 upregulation is important as ALCAT1 is a protein involved in CL acylation and remodeling.
Added to that finding, Song et al.37 also reported using ANOVA analysis, western blot staining, and confocal imaging to determine the outcome of MPTP in murine mitochondria, which was induced neurotoxicity and aberrations in SNCA oligomerization.
Analysis of Studies
The PD studies are summarized in
Table 2. They all studied the role of CL in nervous system physiology or SNCA stability regulation. The regulation of SNCA was reported in studies, which used models that either had gene-knockouts for key CL biogenesis enzymes (CL Synthase 1 (CLS1) as seen in Chicco
et al.,
34 or ALCAT1 which remodels CL in Song
et al.37). The hypotheses were based on the premise that chemical inhibitors as seen in Song
et al.37 with MPTP or rotenone (an inhibitor for Complex 1 in the ETC) as seen in other studies (
e.g., Tyurina
et al.32) were effective for inducing and simulating PD conditions (parkinsonian phenotype) in murine models.
Along with inducing PD conditions in murine models, gene mutations were reported to result in PD phenotypes or dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the organisms being studied.34,37 These results provide a model for the empirical investigation of the role of CL and specific phenotypes in PD diagnoses and development using lipidomics. Specifically, these studies support the role of CL’s structure in indicating changes in nervous system physiology, observed in membrane potential changes as seen in Chicco et al.34 CL’s structure as an indicator of specific phenotypes in nervous system physiology was also observed with SNCA stability regulation as seen in Song et al.,37 both of which are implicated in PD progression.
These studies outlined the possibilities and need for further investigations with coupling gene deletion and chemical inhibition to study NDDs.34,37 These reported findings indicate the role of potential therapeutics that affect not only the enzymes in the RSC but also molecules that may complement to improving IMM integrity and the stability of proteins, such as SNCA, which is a hallmark protein signature in PD.
Conclusions Regarding Cardiolipin and Parkinson’s Disease
The findings by Chicco et al.,34 Ryan et al.,36 and Song et al.37 using lipidomics supported the role of CL as a significant phospholipid in the IMM. Also the findings indicated that structural changes in CL acylation can potentially be biomarkers of NDDs or co-indicators of specific NDD phenotypes such as cognitive impairment, motor deficits, or pathological issues associated with senescence.3,9,34,36,37
4.3. Barth Syndrome
BTHS is a cardiomyopathic disease and is described as one of the first human diseases that has implicated CL remodeling issues as causal in BTHS progression.21 BTHS is a chromosome X-linked disease with myopathy and neutropenia. Typically, this disease is fatal in juvenile years due to cardiac failure and bacterial infection complications. In some instances,
BTHS is defined as a mitochondrial disorder and is isogenically mapped to the TAZ gene. The etiology in some cases has been tied to aberrations in the TAZ enzyme, which is a transacylase that is essential for the biosynarticle of CL.38 Vreken et al.21 reported the incidence of defective remodeling of CL and PG in BTHS patients. Using a patient sample size (n=5) and noting the ETC complex deficiencies on a patient-by-patient basis, these scientists used fibroblast cell culture, lipid extraction using the Folch method, lipid scintillation counting and thin layer chromatography (TLC) to separate the phospholipids. The key finding of this study was that fibroblasts from BTHS patients had reduced levels of CL and the PG and CL biosynarticle pathways were abnormal. Specifically, the incorporation of a specific acyl chain (linoleic acid) into PG and CL is significantly decreased.
This decrease in inclusion of linoleic acid was quantified using lipid scintillation counting with the analyte. The analyte was radioactive labeled fatty acids, which were incubated with fibroblasts. The study clearly revealed structural abnormalities associated with PG and CL metabolism in BTHS fibroblasts when compared to normal control cells and other cells from patients with other mitochondrial disorders.
In 2015, Angelini
et al.22 reported a unique screening method for BTHS using lipid profiles from leukocytes with BTHS that are compared with healthy donor cells. Specifically, these scientists reported obtaining hematological samples from 24 healthy donors and 8 BTHS patients. The blood cells were isolated using dextran sedimentation techniques. Following the dextran sedimentation, a lipid extraction protocol was modified to extract the lipids from the leukocytes. After the extraction, there were two analyses one of the intact leukocytes’ membranes using MALDI-TOF/MS and then the analysis of miniature lipid extracts. After which, the scientists reported using a ratio that included MLCL, mature CL (CLm) and immature CL (CLi) as a diagnostic parameter. The ratio that was used as a diagnostic parameter equation is listed below as Equation 1:
Additionally, the compositional changes as a result of TAZ mutations of MLCL and CL were determined using data from MALDI-TOF-MS and statistical analyses. Furthermore, those compositional changes as a result of TAZ mutations of MLCL and CL were also used as a diagnostic parameter for BTHS.
The key findings were that the method requires minimal (1ml) of blood sample, can be easily integrated into the routine work of a clinical laboratory, and methods such as those reported using MALDI-TOF/MS can potentially increase the laboratory’s capability of diagnosing BTHS.
In 2013, Gonzalvez et al.38 reported changes in CL concentration due to TAZ enzyme dysfunction. They used HPLC-MS, transmission electron microscopy, flow cytometry analysis, respiratory analysis, BN-PAGE, and sodium dodecyl sulfate-PAGE in white blood cells from two unrelated patients with BTHS. They reported the use of cell culture with lymphoblastoid cell lines from two unrelated BTHS patients. The reported results from these BTHS patients using the methods by Gonzalvez et al.38 led to the understanding of abnormal CL being associated with mitochondrial alterations. Along with the mitochondrial alterations, there was the lack of normal CL, which led to aberrations in ETC stability. These scientists also reported decreased levels of Complex V, which suggested CL significance for other complexes beyond those in the RSC (Complex 1, 3, and 4).3,38 Additionally, the alterations showed a subsequent increase in mitochondrial mass, which were observed using HPLC-MS. Then, electron microscopy was reportedly used as a visualization technique for lymphoblast’s mitochondria. On the basis of multiple images of the surface of the cristae in the mitochondria, which were averaged into a three-dimensional image of the IMM in the lymphoblasts. In conclusion, Gonzalvez et al.38 provided new insights into the pathogenesis of BTHS. These scientists emphasized the effects of TAZ gene mutations on CL structure, which is contained in the microdomains in mitochondria and mitochondrial junctions affecting the cell’s apoptotic signaling.38
Analysis of Studies and Conclusions
The studies by Vreken
et al.,
21 Angelini
et al.,
22 and Gonzalvez
et al.38 are summarized in
Table 3 and all support the idea that CL/MLCL ratio is significant, with diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for BTHS. For BTHS diagnoses, CL-based ratios are already used in the clinical determination of BTHS.
21 Also, the BTHS research reported by these scientists involved the use of TAZ gene knockouts as a “loss-of-function” type analyses which could be originated from the changes in CL structure. The changes in CL structure provided an empirical basis for monogenic studies on the TAZ gene, CL and BTHS. Specifically, gene knockouts compared with the WT murine models as well as studies with fibroblast and lymphoblastoid cell lines provided a basis for understanding how CL’s structure is affected by TAZ gene mutations. Along with reporting the effects of TAZ gene mutations, it was also reported how TAZ gene mutations lead to downstream effects, which are present in BTHS affected organisms. Overall, these studies supported the fact that the technique used in BTHS diagnoses involves the use of the MLCL:CL ratio to provide diagnostic information.
21,22,38
5. Analytical Techniques Used in Lipidomics
Lipidomics involves the use of analytical techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR), fluorescence spectroscopy (FS), dual-polarization interferometry (DPI), and in certain cases MS. In the cases where NMR, FS, DPI or MS are used, these analytical techniques are coupled often with computational techniques. The role of these analytical techniques in lipidomics is discussed herein, with a goal of answering the following question:
Can the analytical techniques discussed present an alternative snapshot of the metabolic profile of patients, specifically the CL profile of patients with NDDs?
Analytical Techniques in Lipidomics
Methods to assess the Chemical Constituents of the NDD patient’s brain.
5.1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
Utility
NMR-based lipidomics has numerous advantages compared to degradative MS-lipidomic techniques, including negligible effects on the sample being studied and high reproducibility of the analyses and results. Furthermore, NMR, allows the facile identification of the different acyl species and molecular functionalities of lipids based on the characteristic patterns in the NMR spectra. The high degree of precision of NMR spectrometers in determining molecular dynamics and providing quantitative information on the number of atoms present are also advantageous.
Hence, this method is useful for molecular characterization and can be used as a complementary method to MS.39
Technique/ Method of Use
NMR spectroscopy provides information regarding the chemical environment wherein atomic nuclei are found. This type of spectroscopy is commonly used for structure elucidation. One of the most widely used NMR techniques is 1H NMR spectroscopy. With this type of spectroscopy, as with others such as 13C and 31P, it can be assumed that only two spin states are likely. Since the distribution of electrons around chemically dissimilar hydrogen atoms is not equal, the induced fields and magnetic fields are different for different atoms, even in the same external field. Metabolites such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids can be studied using NMR spectroscopy techniques. NMR spectroscopy, particularly liquid-state NMR spectroscopy, when used as a technique in lipidomics, may introduce a better alternative for studying lipids, especially in disease states when compared to the degradative methods of most MS techniques.
Significance for Lipidomics
NMR lipidomics has opened new opportunities because of its high selectivity and nondegenerative approach to sample analysis as opposed to that of MS. In addition, NMR lipidomics can provide further insights into potential biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets.41 The nuance and finesse of NMR lipidomics is due to NMR spectroscopy’s accuracy in detecting variations for different nuclei.42 Additionally, the capacity of NMR to be multi- dimensional and coupled to imaging provides another layer of prowess for understanding brain chemical constituents and changes during the progression of NDDs.
Significance for NDDs
The importance of NMR in NDD research has increased its influence, both as an imaging tool and in providing structural information. NDDs can be examined via multivariate analyses on a wide range of biomolecules. Unlike the other forms of spectroscopy, high-resolution NMR spectroscopy is not hindered by poor spectroscopic resolution and can provide systematic information about metabolites. In a study by Pettegrew et al.,40 NMR was used to quantify the lipid composition of extracts obtained using the Folch method. The comparison of age-matched and non-demented autopsy samples via NMR showed a significant decrease in phospholipid content. Furthermore, a study by Pizarro et al.,43 analyzed 94 plasma samples to distinguish patients with PD from those with AD and classify them according to PD severity. The technique used was considered optimal for differential diagnoses.43
Table 4.
- Analytical Techniques used in Lipidomics.
Table 4.
- Analytical Techniques used in Lipidomics.
| Analytical Techniques Used |
Author |
Method |
Model |
Results |
| NMR |
Pettegrew et al.40
|
NMR spectroscopy was used to quantify the lipid composition of the extracts obtained using the Folch Methods |
AD |
Compared with the age-matched, non- demented control brain samples (n=46), the AD brain samples (n =193) showed significant reductions in levels
of phospholipids. |
| NMR |
Pizarro et al.43
|
NMR spectroscopy and data pre- processing were used for 94 plasma samples to first separate those from patients with PD. PD patients (regardless of the disease stage) and those from the patients with AD and the controls, and then the samples from the patients with PD were differentiated based on
disease severity. |
AD/PD |
The analytical technique offered an ideal discrimination strategy for the differential diagnosis of PD and AD, as well as for the purpose of staging PD patients |
5.2. Mass Spectrometry
Utility
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a quantitative analytical technique that can be used for integrated analyses of biological samples based off of the specific mass to charge ratios of biological molecules and the specific mass values of their functional groups. MS as noted in the BTHS studies (
Section 4.3) mentioned previously can be used to further separated lipid classes and groups within the lipid class. MS can also be used to elucidate changes in lipid molecular structure or lipid content by providing insights using mass to charge ratios for the different acyl chains in terms of areas of saturation, unsaturation (
i.e., double bonds). This was observed in several BTHS studies (
Section 4.3) where the differences in CL structure were determined using MS.
There are three main MS approaches used in lipidomics, which include direct infusion MS analysis (shotgun lipidomics) in which a crude lipid extract is infused to the MS instrument, and direct MS scans are typically used in high-resolution MS. Another main MS approach used is chromatography coupled with and MS (either LC-MS and GC-MS) in which information of fatty acid composition is gained and for LC-MS it provides a wide range of separation modes, even more so with reverse-phase LC. The third main MS approach is the desorption ionization techniques (e.g., MALDI), which allow for the analysis of biological tissues and cells and provide information on the spatial distribution of individual molecules including lipids, metabolites and peptides. These techniques have a high degree of analytical sensitivity and specificity.45 MS is useful since the fragmentation of lipid molecules, such as glycerophospholipids, results in selective separation (shotgun MS) and spatial distribution (desorption ionization techniques) between lipid classes due to commonalities between fragments, which are common for lipid species belonging to the same class since they frequently differ only in a mass difference of two (2) Daltons.45
Technique/Method of Use
MS is an analytical technique that involves ionizing a chemical species into distinct ions of different masses and sorting those ions into a spectrum based on their mass-to-charge ratio. The purpose of this ionization period is to maximize the signal while minimizing space charge effects. A unique aspect of the ion trap is its ability to perform multiple stages of mass spectrometry (MSn), which increases the amount of information on mass and comparative loss of mass that can be obtained from the analysis a molecule. Specifically, it provides information within considerable mass ranges and variable mass resolutions, and also as a capture site for ions. 33
Significance for Lipidomics
MS is one of the early quantitative tools that was used in the global profiling of genes, proteins, and lipid metabolites for lipidomics.46,41 Lipidomics has also been extensively performed to identify changes and abnormalities in the global lipid profile or within a specific subclass of lipids. Lipidomics, whether performed in a clinical setting or to compare pre-disease and post-disease states, provides a quantitative snapshot and profile of the analyte being studied. Hence the coupling of MS with modern analytical techniques such as NMR, FS, or other techniques can provide a more holistic profile analysis, especially in lipidomics.38,47 Shotgun lipidomics provides the framework for quantifying lipid species using an internal standard in the lipid extraction, given that all analytes and internal standards are present in the same sample matrix.45
A few factors to include are the concentration of the lipid classes, solvent, addition composition of the infusate, the biochemistry of the subclass, and the degree of unsaturation in the acyl chain of the lipid group. Likewise, the type of chromatographic technique used could result in either destruction of the sample (e.g., in gas chromatography) or non-destructive sampling (e.g., in liquid chromatography).
Significance for NDDs
Lee et al.1 reported the use of MS to analyze CL levels and their effect on the mitochondrial shape, transcription rates, and impairment of RSCs. Furthermore, they reported observing downstream effects on protein synarticle and the stress response of the endoplasmic reticulum. They also reported the effects of CL loss on mitochondrial protein synarticle by using three mutant cell lines of Crls1 (the CL biosynthetic gene) knockout. Additionally, Tyurina et al.32 used LC-MS to perform oxidative lipidomic analyses to determine the extent to which one of CL’s acyl chains had been oxidized. The oxidative lipidomic analyses provided information regarding the stage of PD in murine models induced by an inhibitor (rotenone) of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase (NADH dehydrogenase or Complex 1). Phan et al.48 supported the use of lipidomics in understanding the role of lipid changes in neurodegeneration with frontotemporal dementia (FTD).
Table 5.
- Analytical Techniques.
Table 5.
- Analytical Techniques.
| Analytical technique used |
Author |
Method |
Model |
Results |
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) /
Fluorescence Spectroscopy (FS) |
Lee et al.1
|
Three mutant knockout cell lines of the CL biosynarticle gene Crls1, were investigated for the effects of CL loss on mitochondrial protein synarticle. |
CL Synthase |
The CL levels were decreased affecting the mitochondrial shape, and transcription rates, and impairing the respirasome super-complex (RSC) formation. Moreover, there were downstream effects on protein synarticle and the stress response of the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| Liquid Chromatogra phy-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) |
Tyurina
et al.32
|
Rotenone was used to inhibit complex 1, and simulate PD- like conditions, and the analysis was performed using oxidative lipidomics
via LC-MS. |
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase Or
Complex 1 of the ETC |
PD murine models were designed using the inhibitor rotenone on complex 1, and a significant reduction of oxidizable polyunsaturated fatty acid -containing CL molecular species in the plasma of the rats
was observed. |
| MS |
Phan,
K. et al.48
|
MS was used to study the changes in the lipids in brains with frontotemporal dementia(FTD). |
FTD |
Lipid changes have been associated with neurodegeneration, and this evidence supports the notion that lipidomic analyses can be utilized to investigate pathological changes in the nervous system |
5.3. Other Informative Techniques
Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Fluorescence spectroscopy (FS) is an established tool in molecular biology and biochemistry that analyzes the fluorescence from a sample. Using a beam of electromagnetic radiation, the electrons in the light-sensitive molecules (chromophores) are excited and the resulting fluorescence is measured. It involves analysis using light-sensitive chromophores to track, target, or monitor the presence of metabolites. However, the role of FS in real-time clinical settings has continued to expand. The growing understanding and tools of FS could create a sizeable potential for clinical applications such as diagnoses potentially for NDDs. FS coupled with MS can potentially serve as a diagnostic technique, which can provide insight into the lipidome and other components of mitochondrial membranes. Hence, it can be a powerful tool when coupled with other diagnostic techniques, such as NMR technology.41,49
Dual Polarization Interferometry
Dual polarization interferometry (DPI) enables the real-time analysis and determination of the physical properties of biological layers. This optical sensing technique allows for the probing of structural layers using physical structures that guide the electromagnetic waves from the interferometer. This technique has also been used to study the protein conformational structures as well as the interaction between metabolites and membrane dynamics, the latter of which has a direct bearing on CL given its role in imparting structural integrity and the architecture of the IMM. DPI can be used to determine small molecule interactions, which could lead to the identification of potential therapeutic targets and potential biomarkers.50-51 Therefore, the use of DPI in lipidomic studies is recommended owing to its precision for real-time analysis of biological samples.
Conclusions about Analytical Techniques
Briefly, lipidomics demonstrates the progress that is occurring in systems biology with the identification and measurement of various lipid species. Lipidomics especially in NDD research contexts, and with CL allows for empirical conclusions to be deduced on the role of CL for potential diagnoses and even therapeutics. Additionally, lipidomics reveals the complex interactions of CL with other components of the lipidome and proteome in NDDs. Numerous scientists mentioned earlier (
Section 4.1-4.3) reported the role of lipidomic techniques in providing an empirical basis for comparing and studying the role of gene mutations (
e.g., TAZ gene) on CL structures. Moreover, lipidomic techniques as described (
Section 5) provided insights on how gene mutations and subsequent changes in CL structure have implications for mitochondrial function and even NDD (
e.g., AD, PD and BTHS) incidence and progression.
Also, there is comparative lipidomics which is a process wherein lipidomic data are compared between different disease states in an organism, to elucidate several findings such as disease origins and important organelle changes, as well as metabolite signatures. In the clinical field, the technique of comparative lipidomics can also be applied for identifying more precise and personalized medicine. Specifically, in terms of CL, as implied by Gaudioso et al.,16 identifying specific lipid signatures in mitochondria could offer brain-specific lipid-modifying pathways as potential therapeutic targets for NDDs.
6. Cardiolipin-Based therapeutics
NDD therapies could potentially use CL as a therapeutic target, as studies in
Section 2,
Section 3,
Section 4 and
Section 5 of this article have presented the importance of CL and its relationship with several of the hallmarks exhibited by NDDs. It has been reported and observed that NDDs exhibit similar underlying hallmarks such as harmful protein accumulation, inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
52 Szeto
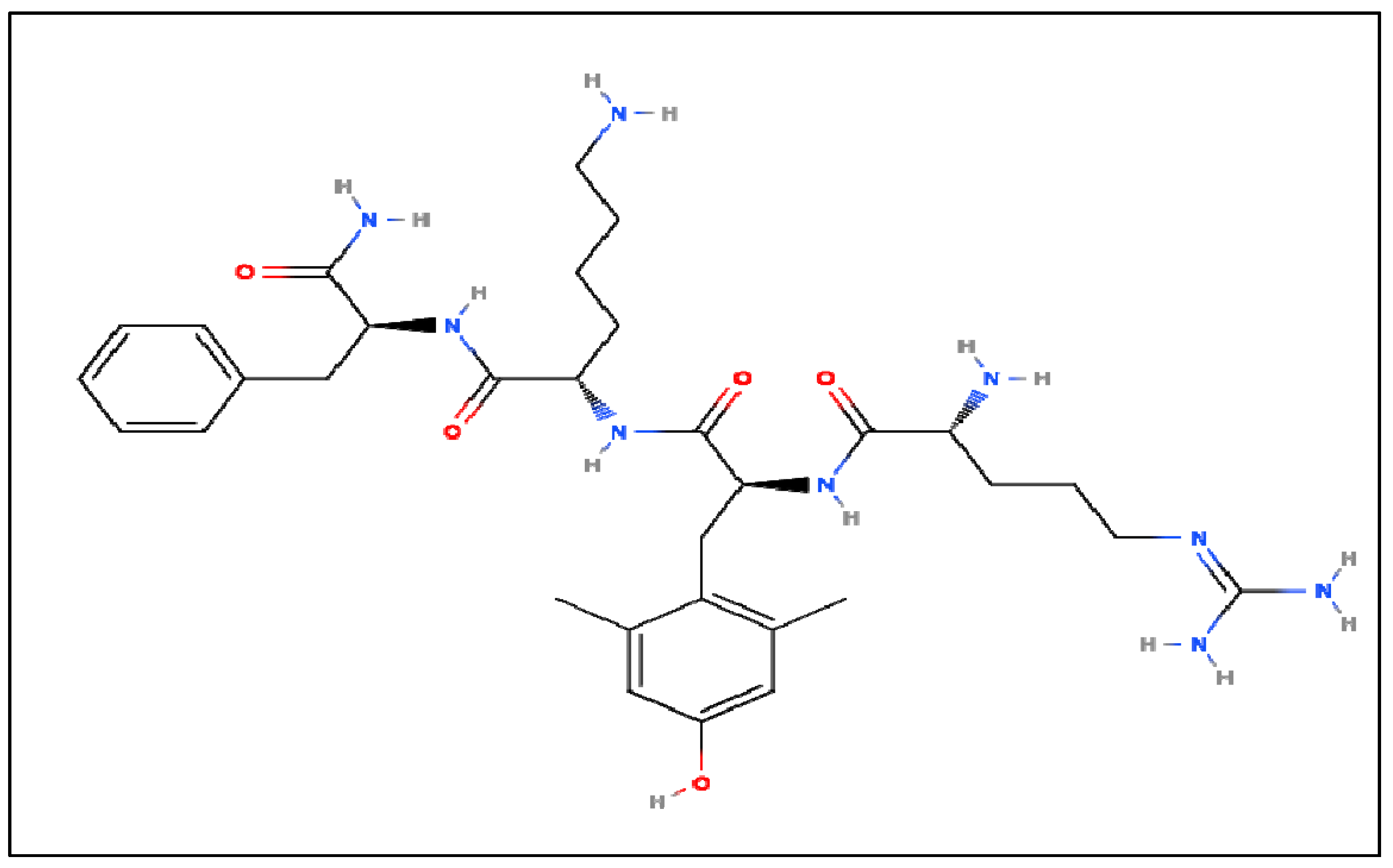
et al.46 reported that there is a unique class of small mitochondria-directed molecules known as Szeto-Schiller (SS) peptides. SS peptides are synthetic tetrapeptides, which include SS-31 shown in
Figure 8. These cell-permeable tetrapeptides can capture electrons and selectively interact with CL to stabilize cristae bends. Once bound to CL, these peptides enter the heme environments of cytochrome-c oxidase (Complex 4) to promote the transfer of electrons and prevent the conversion of cytochrome-c to a peroxidase. This transfer of electrons in turn promotes ATP synarticle, reduces ROS production, and inhibits CL peroxidation. Additionally, the inhibition of CL oxidation affects apoptotic activity as well as the structure and function of the mitochondrial RSC.
39
In the RSC, CL serves as an anchorage component and, when oxidized, as a signaling molecule.3 CL peroxidation is an intricate process that can occur based on neuronal injury or cellular dysfunction. CL peroxidation can serve as a protective mechanism since it functions as a pro-apoptotic signal which can potentially serve on the systemic scale to auto-eliminate cells that can potentially proliferate, cause necroses or neurological diseases.58,59 With that said, as alluded to by Bavir et al.,59 CL peroxidation can potentially serve as a biomarker for neuronal injury, and in this article I postulate that it may serve as a biomarker for neurological diseases, including NDDs.
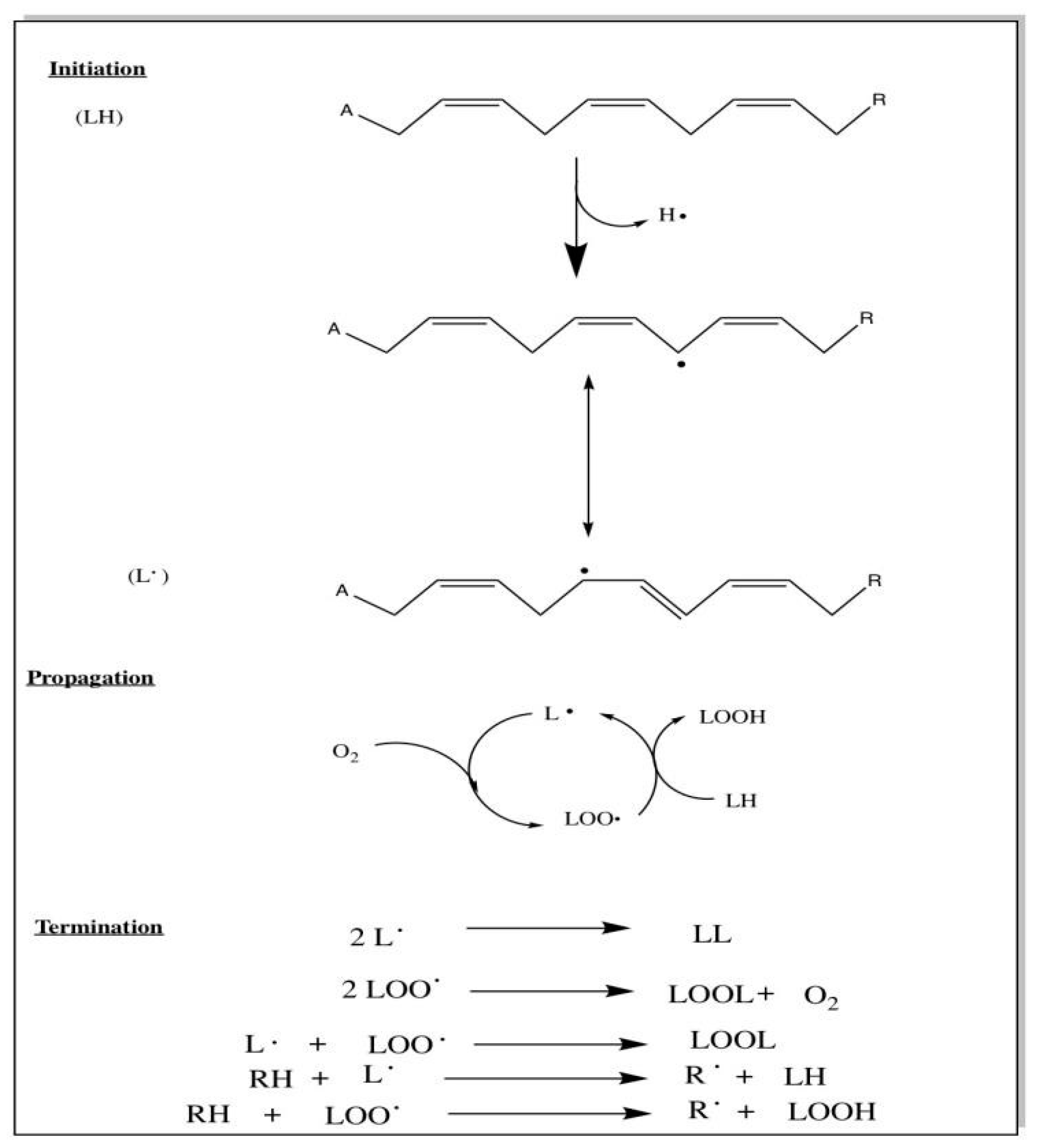
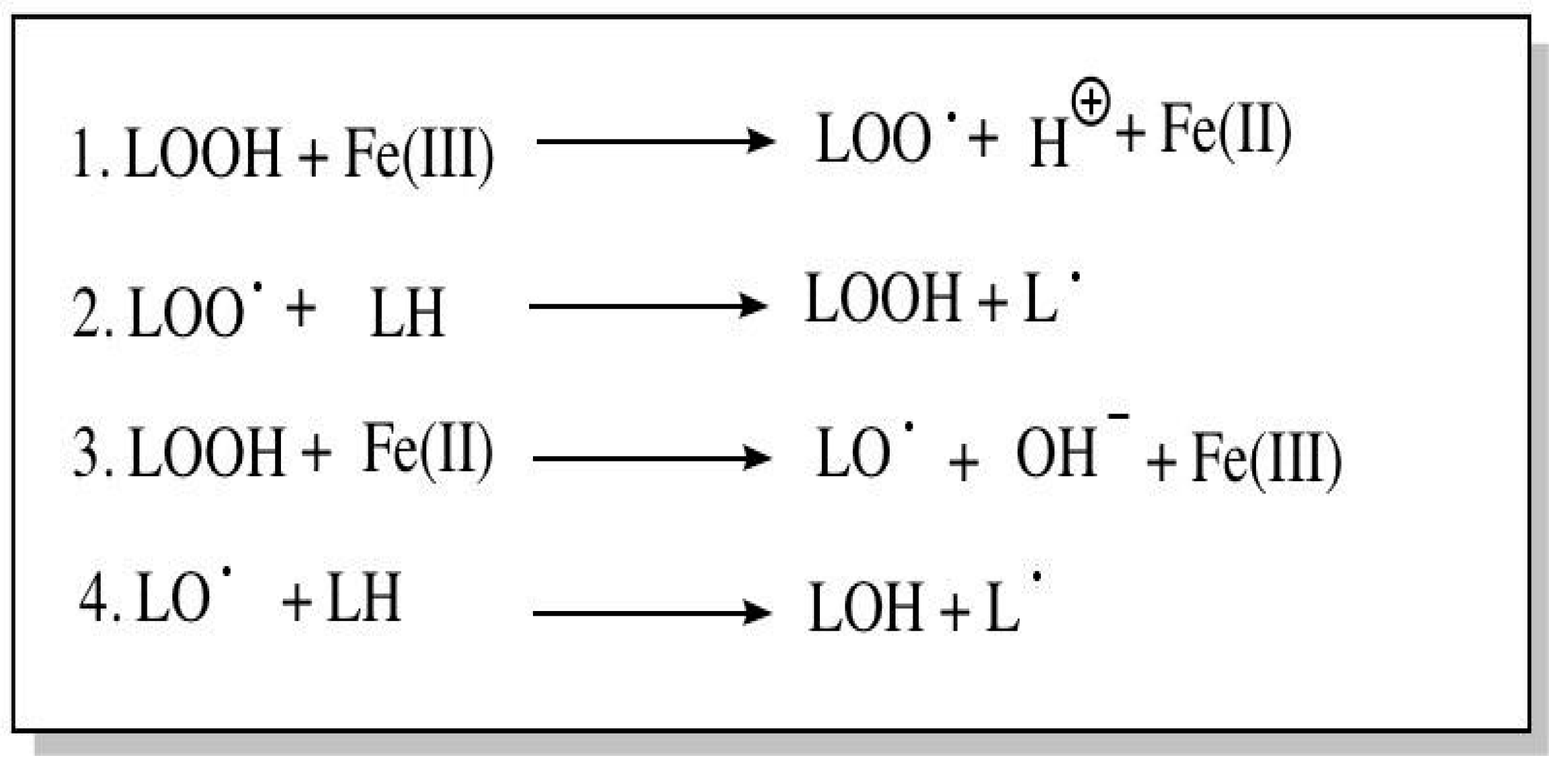
Additionally, CL peroxidation can occur via different mechanisms including free radical mediated peroxidation, metal-mediated peroxidation (including both lipid hydroperoxide independent and lipid hydroperoxide dependent), and initiation by singlet oxygen from the peroxidizing lipid. However,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7, which were adapted from Girotti
et al.,
58 show the peroxidation reactions that Girotti
et al.58 considered priority and “most biologically relevant”.
58
Figure 6.
Free-radical mediated peroxidation of linolenic acid: A = -CH2 and R = -(CH2)6COOH.58
Figure 6.
Free-radical mediated peroxidation of linolenic acid: A = -CH2 and R = -(CH2)6COOH.58
Figure 7.
The reactions for metal- mediated peroxidation. (LOOH- dependent initiation: LOOH = Lipid hydroperoxide and L = Lipid)58.
Figure 7.
The reactions for metal- mediated peroxidation. (LOOH- dependent initiation: LOOH = Lipid hydroperoxide and L = Lipid)58.
Figure 8.
Structure of SS-31, which is also known as Elampretide.
Figure 8.
Structure of SS-31, which is also known as Elampretide.
However, SS-31 peptides are promising since they are amphipathic tetrapeptide antioxidants that target the IMM, specifically CL.53,56 First, SS-peptides target mitochondria and improve mitochondrial function due to their affinity for anionic lipids such as CL.53 Second, Mitchell et al.53 further notes that SS-31 has affinity for “aqueous dispersions of anionic lipids”, especially membranes containing CL. Third, Zhao et al.56 reported that SS-31 is capable of successfully targeting the IMM and passing through the blood brain barrier. Also, these scientists also described SS-31 as a “mitochondrial-targeted protectant” with a “wide array of neuroprotective benefits”.56
With the knowledge of the neuroprotective benefits of SS-31, scientists54 report SS- peptides as molecular structures that could be further functionalized at their aromatic centers. This further functionalization would be done to potentially understand their impact on ROS, which are generated at the IMM. In a previous study, Yang et al.54 reported that including tyrosine in SS-31 or modified tyrosine residues on aromatic benzene provided additional free radical scavenging properties to the complex. The analogs of the specifically modified tyrosine residues were also reported to be very effective in enhancing ROS-induced apoptosis.
Reddy et al.55 tested the hypoarticle that the use of mitochondrial division inhibitors and SS-31 in AD neurons may have synergistic protective effects. These scientists tested this hypoarticle using mutant Aβ precursor protein (AβPP) complementary DNA constructs, tissue culture, immunoblotting analysis, immunofluorescence analysis and quantification. First, these methods used by Reddy et al.55 were reported to have revealed that “cell permeable mitochondria-targeted antioxidant SS-31 is protective against amyloid-beta induced synaptic and mitochondrial toxicities in both cell and mouse models of AD”.55
Also, Reddy et al.55 reported using apoptosis assays, comparisons of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) to nuclear DNA (nDNA), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), enzymatic assays and statistical analysis. Second, these experiments were reported to have uncovered that the combination of SS-31 and mitochondrial division inhibitors increased cell survival rates relative to untreated mutant AβPP cells. Third, the key findings were that: AβPP is toxic to cells and the use of SS-31, mitochondrial division inhibitors, and the combined use of SS-31 and mitochondrial division inhibitors are “protective against mutant AβPP and Aβ to cells”.55 They also reported using SS-31 with mitochondrial division inhibitors as a therapeutic approach for AD. Since it is established,4,26,28,55 that Aβ is a protein hallmark for AD, I postulate that this strengthens the rationale for further research into the therapeutic use of SS-31 for NDDs such as AD.
In addition, using murine models and cognitive tests such as the Morris water maze test, which is a contextual fear conditioning test to evaluate hippocampus-related learning and memory activity, Zhao et al.56 reported that treatment with SS-31 improved learning and memory status when memory impairment is induced by lipopolysaccharide (which was reported to be an endotoxin and a Toll-like receptor 4 ligand). This study56 is significant within the scope of NDDs because cognitive decline and memory challenges are common conditions associated with NDDs.21,22,26-28,34-38 Moreover, these scientists56 reported using ELISA, western blot, Terminal Transferase biotinylated-deoxy uridine triphosphate nick end labeling (TUNEL).
TUNEL is a technique that detects apoptosis by using a fluorescent label which attaches to the hydroxyl terminus of DNA breaks through the use of the terminal deoxynucleotide transferase enzyme.60 Additionally, using techniques previously mentioned, Zhao et al.56 reported understanding learning and memory performance in the murine models, mitochondrial function, oxidative stress and detecting neural cell apoptosis and inflammatory response.
Furthermore, Zhao et al.56 reported using Golgi staining to detect the dendritic spins of the hippocampal neurons and mitochondrial membrane as potential assays to detect mitochondrial membrane potential. One of Zhao et al.56 findings was that there is a relationship between memory impairment and SS-31 use because SS-31 was reported to have attenuated memory impairment in the murine models. Second, was that SS-31 prevented hippocampus- dependent learning and memory impairment induced by lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin). In that same vein, SS-31 protected the hippocampus against LPS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and ATP levels.
Additional findings were that SS-31 attenuated oxidative stress in the murine hippocampus decreased neural cell apoptosis in the hippocampus of LPS-treated mice and enhanced the hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor pathway, which plays a role in the development of normal synaptic structural complexity. Moreover, SS-31 prevented the decrease in dendritic spines on hippocampal neurons after LPS treatment. Additionally, Zhao et al.56 concluded that SS-31 may attenuate the lipopolysaccharide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and offer therapeutic benefits by improving mitochondrial function in neurons.
In line with understanding mitochondrial dysfunction and potential causes, Calkins et al.61 tested the hypoarticle that there is a relationship between the accumulation of Aβ in synapses, and synaptic degeneration in AD. The reported findings of Calkins et al.,61 along with other AD findings26-28 in this article have implications for understanding the etiology of AD within the scope of Aβ accumulation. Calkins et al.61 also tested the effects of Aβ in mitochondrial activity and the synaptic alterations of neurons in a murine model of AD. Calkins et al.61 reported using transgenic and WT murine models of AD and immunocytochemical analysis, western blot, and ELISA, reported that the mitochondria in the neurites of neurons expressing Aβ precursor protein were abnormal. Third, Calkins et al.61 reported that SS-31 restored mitochondrial transport, synaptic viability, and decreased the percentage of defective mitochondria, which according to Calkins et al.61 indicates that “SS-31 protects mitochondria and synapses from Aβ toxicity”.61
Moreover, the findings reported by Calkins et al.61 were that oligomeric Aβ were observed to localize in mitochondria. First, Calkins et al.61 reported that Aβ precursor protein cultures exhibited increased apoptosis, decreased synaptic gene expression and decreased mitochondrial dynamic gene expression. These findings further implicate Aβ as a key protein hallmark in neurodegeneration in NDDs such as AD. Second, Calkins et al. 61 reported that mitochondrial anterograde transport in Aβ precursor protein neurons was impaired but improved significantly using SS-31, stating that “SS-31 can rescue Aβ-induced deficiencies in mitochondrial transport”.61
Analysis of Studies and Conclusions
The studies by Reddy
et al.,
55 Calkins
et al.,
61 and Zhao
et al.,
56 all reported testing hypotheses on the relationship between SS-31 and mitochondria, and the implications for cognitive improvements
61 and NDDs.
55,61 As seen in
Table 6, all of the studies
55,56,61 support that SS-31 is a CL-targeting tetrapeptide, which is localized in the mitochondria. First, SS-31 functions as an antioxidant which is supported by all three studies,
55,56,61 which report the counteraction of SS-31 for oxidative stress in the IMM. Second, these scientists
55,56,61 reported that SS-31 contributed to cell survival,
55 restoration of mitochondrial anterograde transport,
61 and improved learning and memory status,
56 which was a consequence of SS-31 reducing the effects of LPS(endotoxin)-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Third, the reported
55,56,61 effects of SS-31 suggest that more research should be done on the relationship between SS-31, the IMM, and NDDs. I postulate that there could be therapeutic potential when SS-31 is further functionalized and used in tandem with established therapies that address the histopathological NDD proteins (
e.g., A, SNCA, and mutated TAZ). Overall these studies support the significance of CL in mitochondria especially in the context of NDDs as seen with SS-31’s effect on Aβ precursor protein (AβPP) cells,
55,61 and with resultant cognitive improvements.
56
Overall, SS-31 presents as a CL-based peptide that has therapeutic potential. First, this article supports the idea that CL has an integral role in the mitochondria including in the functioning of the mitochondria’s RSC, maintenance of mitochondrial structural integrity and when oxidized can serve as an pro-apoptotic signal.1-4,55 Second, this article presents the idea that each NDD has a typical array of histopathological proteomic hallmarks namely: AD (Aβ), PD (SNCA), and BTHS (mutated TAZ), and all of these relate CL aberrations to disease progression,21-2226-28,32,34-35,38 where CL is either aberrant in structure,26,32,38 or interacting in vitro with the hallmark proteins (Aβ; SNCA) and affecting the protein’s morphology.36,61 In conclusion, this article thus presents a strong rationale for further research to be done using lipidomics for relating CL to NDDs and potentially determining the therapeutic potential of SS- 31 (a CL-based therapeutic) in NDDs.
Table 6.
– Cardiolipin Based Therapeutics.
Table 6.
– Cardiolipin Based Therapeutics.
| Author |
Study Method |
Results |
Conclusion |
| Reddy et al.55 |
Cell culture using murine models with cDNA to express Aβ precursor protein; immunoblotting; immunofluorescence analysis; apoptosis assay; lipid peroxidation assay;
other bioassays |
The combined use of
SS-31 and mitochondrial division inhibitor 1, enhanced cell survival and reduced apoptotic cell death in mutant Aβ precursor protein (AβPP) cells |
There were relatively positive effects of using mitochondria-targeted antioxidants such as SS-31, and mitochondrial division inhibitors as a combined approach for AD and other neurological diseases. |
| Calkins et al.61 |
Transgenic (Tg2576 gene) and WT murine models of AD as well as immunocytochemical analysis, western blotting and enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). |
Mitochondria in the neurites of AβPP neurons were abnormal. In addition, mitochondrial anterograde transport was impaired in AβPP neurons but improved by SS-31. Synaptic proteins are decreased in Aβ precursor protein
cultures. |
Several conclusions were made, and the conclusions relevant to this review were noted. Both the number and length of mitochondria decreased in the AβPP neurons, leading to abnormal mitochondria, which was improved by treatment with SS-31. |
| Zhao et al.56 |
Murine models were used with different variables including lipopolysaccharide and SS-31 as well as the Morris water maze test, open field tests, enzyme assays, western blot, tissue isolation, ELISA, TUNEL, and Golgi staining and mitochondrial membrane potential
assay. |
Treatment with SS-31 improved learning and memory status, and the improvement involved the facilitated regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) which aids in the development of normal synaptic structural complexity. |
SS-31 may attenuate the lipopolysaccharide induced mitochondrial dysfunction, thereby presenting the therapeutic benefits in terms of mitochondrial function improvement and preventing damage from oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. |
Glossary of Terms
Amyloid-β (Aβ): Histopathological hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease
Bligh and Dyer method: A lipid extraction method
BN-PAGE : Blue native- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
BUME method: A lipid extraction method
Cardiolipin (CL): An important structural glycerophospholipid, otherwise known as diphosphatidylglycerol.
cDNA: complementary DNA
Fluorescence Spectroscopy: An analytical technique that uses chromophores to measure signals
Folch Method: A lipid extraction metho
Genome: All the nucleic acid components that encode information in the cell.
Glycosidic Regulation: The influence of substrates and enzymes on the process of glycolysis.
Heteroplasmic mtDNA : mtDNA is non-identical.
Homoplasmic mtDNA: mtDNA is identica
Lipid Homeostasis: The reactions that influence and affect the biogenesis and maintenance of the lipidome.
Lipidome: The global profile of lipids.
MALDI-TOF- MS – Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization- time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Metabolotranscriptomics: A multiomics technique that involves the metabolome and transcriptome.
Monolysoscardiolipin (MLCL): An important deacylated glycerophospholipid. Motor Neuron Disease: A type of neurological disease that affects motor muscles. mPTP: mitochondrial permeability transition pore
MTBE method: A lipid extraction method
NADH - Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced)
NMR Spectroscopy: An analytical technique
Proteome: All the biological proteins that exist in a cell, or organelle
Proteostasis: The balance and regulation of the proteome.
Tau protein: Histopathological hallmark of Huntington’s disease
Toponogenomics: A multiomics technique that involves the toponome and genome.
SDS-PAGE: Sodium dodecyl sulfate- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
α-synuclein (SNCA): Histopathological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease
References
- Lee, R.G.; Gao, J.; Siira, S.J.; Shearwood, A.M.; Ermer, J.A.; Hofferek, V.; Mathews, J.C.; Zheng, M.; Reid, G.E.; Rackham, O.; et al. Cardiolipin Is Required for Membrane Docking of Mitochondrial Ribosomes and Protein Synarticle. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadpour, S.T.; Mahéo, K.; Servais, S.; Brisson, L.; Dumas, J.F. Cardiolipin, the Mitochondrial Signature Lipid: Implication in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falabella, M.; Vernon, H.J.; Hanna, M.G.; Claypool, S.M.; Pitceathly, R.D.S. Cardiolipin, Mitochondria, and Neurological Disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2021, 32, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro-Cardoso, V.F.; Oliveira, M.M.; Melo, T.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Moreira, P.I.; Ferreiro, E.; Peixoto, F.; Videira, R.A. Cardiolipin Profile Changes Are Associated to the Early Synaptic Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 43, 1375–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudeau, P. NMR-Based Metabolomics and Fluxomics: Developments and Future Prospects. Analyst 2020, 145, 2457–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlame, M.; Greenberg, M.L. Biosynarticle, Remodeling and Turnover of Mitochondrial Cardiolipin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hafidi, M.; Correa, F.; Zazueta, C. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases Associated with Cardiolipin Remodeling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, K.; Calingasan, N.Y.; Luo, G.; Szeto, H.H.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondria Targeted Peptides Protect Against. Control 2009, 11, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Loeffler, J.P.; De Aguilar, J.L.G. Neurodegenerative Diseases: Unifying Principles. Neurodegener. Dis. 2016, 2, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffler, I.E.M. Mitochondria; 2008.
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1978. NobelPrize.org.
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1997. NobelPrize.org.
- Durand, M.; Coué, M.; Croyal, M.; Moyon, T.; Tesse, A.; Atger, F.; Ouguerram, K.; Jacobi, D. Changes in Key Mitochondrial Lipids Accompany Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in NAFLD. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9986299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganelli, V.; Capozzi, A.; Recalchi, S.; Riitano, G.; Mattei, V.; Longo, A.; Misasi, R.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M. The Role of Cardiolipin as a Scaffold Mitochondrial Phospholipid in Autophagosome Formation: In Vitro Evidence. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthonymuthu, T.S.; Kenny, E.M.; Amoscato, A.A.; Lewis, J.; Kochanek, P.M.; Kagan, V.E.; Bayır, H. Global Assessment of Oxidized Free Fatty Acids in Brain Reveals an Enzymatic Predominance to Oxidative Signaling after Trauma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudioso, A.; Garcia-Rozas, P.; Casarejos, M.J.; Pastor, O.; Rodriguez-Navarro, J.A. Lipidomic Alterations in the Mitochondria of Aged Parkin Null Mice Relevant to Autophagy. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Sabermarouf, B.; Majdi, A.; Talebi, M.; Farhoudi, M.; Mahmoudi, J. Amyloid-Beta: A Crucial Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease. Medical Principles and Practice. 2015, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; Strooper, B.M.K. Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, T.H.; Dencher, N.A. Cardiolipin: A Proton Trap for Oxidative Phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2002, 528, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreken, P.; Valianpour, F.; Nijtmans, L.G.; Grivell, L.A.; Plecko, B.; Wanders, R.J.A.; Barth, P.G. Defective Remodeling of Cardiolipin and Phosphatidylglycerol in Barth Syndrome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 279, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, R.; Lobasso, S.; Gorgoglione, R.; Bowron, A.; Steward, C.G.; Corcelli, A. Cardiolipin Fingerprinting of Leukocytes by MALDI-TOF/MS as a Screening Tool for Barth Syndrome. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalvez, F.; D’Aurelio, M.; Boutant, M.; Moustapha, A.; Puech, J.P.; Landes, T.; Arnauné-Pelloquin, L.; Vial, G.; Taleux, N.; Slomianny, C.; et al. Barth Syndrome: Cellular Compensation of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Apoptosis Inhibition Due to Changes in Cardiolipin Remodeling Linked to Tafazzin (TAZ) Gene Mutation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Nisticò, R.; Seyfried, N.T.; Levey, A.I.; Modeste, E.; Lemercier, P.; Baldacci, F.; Toschi, N.; Garaci, F.; Perry, G.; et al. Omics Sciences for Systems Biology in Alzheimer’s Disease: State-of-the-Art of the Evidence. Ageing Research Reviews. 2021, 69, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.A. Interpreting Phospholipid and Cardiolipin Profiles in Rare Mitochondrial Diseases. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 2021, 28, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.Z.; Söderberg, M.; Sindelar, P.; Edlund, C. Content and Fatty Acid Composition of Cardiolipin in the Brain of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem. Int. 1994, 25, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, I.J.; Pervaiz, N.; Abbasi, A.A. The Parkinson Disease Gene SNCA: Evolutionary and Structural Insights with Pathological Implication. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.K.; Kim, J.H.; Amoscato, A.A.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Bayır, H.; Karimi, B.; Siddiqui, T.J.; Kagan, V.E.; Hatch, G.M.; Kauppinen, T.M. Aberrant Cardiolipin Metabolism Is Associated with Cognitive Deficiency and Hippocampal Alteration in Tafazzin Knockdown Mice. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Molecular Basis of Disease. 2018, 1864, 3353–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Gatto, G. Biochemistry, 5th ed.; W.H. Freeman, 2002.
- WHO. World Health Organization. World Health Organization. Who.
- Hebb, D.O. Neural Transmission. A Textbook.; Vol. 2013.
- Tyurina, Y.Y.; Polimova, A.M.; Maciel, E.; Tyurin, V.A.; Kapralova, V.I.; Winnica, D.E.; Vikulina, A.S.; Domingues, M.R.M.; McCoy, J.; Sanders, L.H.; et al. LC/MS Analysis of Cardiolipins in Substantia Nigra and Plasma of Rotenone-Treated Rats: Implication for Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindon, J.C.; Tranter, G.E.; Koppenaal, D.W. Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry. Encycl. Spectrosc. Spectrom. 2016, 1, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, A.J.; Sparagna, G.C. Role of Cardiolipin Alterations in Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, C.E.; Murphy, E.J.; Mitchell, D.C.; Golovko, M.Y.; Scaglia, F.; Barceló-Coblijn, G.C.; Nussbaum, R.L. Mitochondrial Lipid Abnormality and Electron Transport Chain Impairment in Mice Lacking α-Synuclein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 10190–10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, T.; Bamm, V.V.; Stykel, M.G.; Coackley, C.L.; Humphries, K.M.; Jamieson- Williams, R.; Ambasudhan, R.; Mosser, D.D.; Lipton, S.A.; Harauz, G.; et al. Cardiolipin Exposure on the Outer Mitochondrial Membrane Modulates α-Synuclein. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, J.; Qi, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Andersen, J.P.; Zhang, W.; Strong, R.; Martinez, P.A.; et al. Cardiolipin Remodeling by ALCAT1 Links Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Parkinson’s Diseases. Aging Cell 2019, 18, 12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalvez, F.; D’Aurelio, M.; Boutant, M.; Moustapha, A.; Puech, J.P.; Landes, T.; Arnauné-Pelloquin, L.; Vial, G.; Taleux, N.; Slomianny, C.; et al. Barth Syndrome: Cellular Compensation of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Apoptosis Inhibition Due to Changes in Cardiolipin Remodeling Linked to Tafazzin (TAZ) Gene Mutation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Vosegaard, T.; Guo, Z. Applications of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in Lipid Analyses: An Emerging Powerful Tool for Lipidomics Studies. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 68, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettegrew, J.W.; Panchalingam, K.; Hamilton, R.L.; Mcclure, R.J. Brain Membrane Phospholipid Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2001, 26, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudeau, P. NMR-Based Metabolomics and Fluxomics: Developments and Future Prospects. Analyst 2020, 145, 2457–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiev, U.; Farrens, D.L. Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Rhodopsins: Insights and Approaches. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2014, 1837, 694–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizarro, C.; Esteban-Díez, I.; Espinosa, M.; Rodríguez-Royo, F.; González-Sáiz, J.M. An NMR-Based Lipidomic Approach to Identify Parkinson’s Disease-Stage Specific Lipoprotein- Lipid Signatures in Plasma. Analyst 2019, 144, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.; Tsang, T.M.; Tabrizi, S.J. The Application of NMR-Based Metabonomics in Neurological Disorders. NeuroRx 2006, 3, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holčapek, M.; Liebisch, G.; Ekroos, K. Lipidomic Analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2187–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, H.H. Cell-Permeable, Mitochondrial-Targeted, Peptide Antioxidants. Drug Addict. From Basic Res. to Ther. 2008, 8, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayasaka, T.; Fuda, H.; Hui, S.P.; Chiba, H. Imaging Mass Spectrometry Reveals a Decrease of Cardiolipin in the Kidney of NASH Model Mice. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, K.; He, Y.; Pickford, R.; Bhatia, S.; Katzeff, J.S.; Hodges, J.R.; Piguet, O.; Halliday, G.M.; Kim, W.S. Uncovering Pathophysiological Changes in Frontotemporal Dementia Using Serum Lipids. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Han, X. Lipidomics: Techniques, Applications, and Outcomes Related to Biomedical Sciences. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swann, M.J.; Peel, L.L.; Carrington, S.; Freeman, N.J. Dual-Polarization Interferometry: An Analytical Technique to Measure Changes in Protein Structure in Real Time, to Determine the Stoichiometry of Binding Events, and to Differentiate between Specific and Nonspecific Interactions. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 329, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolamo, F.; Lante, I.; Muraca, M.; Putignani, L. The Role of Mass Spectrometry in the “Omics” Era. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 2891–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhu, N.T.; Xiao, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Kumar, V.B.; Cui, Z.Y.; Lee, S. Da. Neuroprotective Effects of a Small Mitochondrially-Targeted Tetrapeptide Elamipretide in Neurodegeneration. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 747901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, W.; Ng, E.A.; Tamucci, J.D.; Boyd, K.J.; Sathappa, M.; Coscia, A.; Pan, M.; Han, X.; Eddy, N.A.; May, E.R.; et al. The Mitochondria-Targeted Peptide SS-31 Binds Lipid Bilayers and Modulates Surface Electrostatics as a Key Component of Its Mechanism of Action. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7452–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, K.; Calingasan, N.Y.; Luo, G.; Szeto, H.H.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondria Targeted Peptides Protect Against. Control 2009, 11, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.H.; Manczak, M.; Yin, X.L.; Reddy, A.P. Synergistic Protective Effects of Mitochondrial Division Inhibitor 1 and Mitochondria-Targeted Small Peptide SS31 in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 1549–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Sabermarouf, B.; Majdi, A.; Talebi, M.; Farhoudi, M.; Mahmoudi, J. Amyloid-Beta: A Crucial Factor in Alzheimer’s Disease. Medical Principles and Practice 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Cao, J.; Fu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Long, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Elamipretide (SS-31) Improves Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Synaptic and Memory Impairment Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in Mice. J. Neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotti, A.W. Mechanisms of Lipid Peroxidation. J. Free Radicals Biol. Med. 1985, 1, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayir, H.; Tyurin, V.A.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Viner, R.; Ritov, V.; Amoscato, A.A.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.J.; Janesko-Feldman, K.L.; Alexander, H.; et al. Selective Early Cardiolipin Peroxidation after Traumatic Brain Injury: An Oxidative Lipidomics Analysis. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S. What is TUNEL Staining? https://www.news-medical.net/life- sciences/What-is-TUNEL-Staining.aspx.
- Calkins, M.J.; Manczak, M.; Mao, P.; Shirendeb, U.; Reddy, P.H. Impaired Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Defective Axonal Transport of Mitochondria, Abnormal Mitochondrial Dynamics and Synaptic Degeneration in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 4515–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhong, M.; Elder, G.A.; Sano, M.; Holtzman, D.M.; Gandy, S.; Cardozo, C.; Haroutunian, V.; Robakis, N.K.; Cai, D. Phospholipid Dysregulation Contributes to Apoe4- Associated Cognitive Deficits in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11965–11970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambini, M.D.; Pera, M.; Kanter, E.; Yang, H.; Guardia-Laguarta, C.; Holtzman, D.; Sulzer, D.; Area-Gomez, E.; Schon, E.A. ApoE4 Upregulates the Activity of Mitochondria- associated ER Membranes. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulin, A.C.; Doss, S.V.; Trottier, Z.A.; Ikezu, T.C.; Bu, G.; Liu, C.C. ApoE in Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Strategies. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, P.X.; Ardilla-Osorio, H.; Penalvia, L.; Rainey Nathan, E. Tafazzin Mutation Affecting Cardiolipin Leads to Increased Mitochondrial Superoxide Anions and Mitophagy Inhibition in Barth Syndrome. Cells 2020, 9, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, E.F.; Hou, Y.; Palikaras, K.; Adriaanse, B.A.; Kerr, J.S.; Yang, B.; Lautrup, S.; Hasan-Olive, M.M.; Caponio, D.; Dan, X.; et al. Mitophagy Inhibits Amyloid-β and Tau Pathology and Reverses Cognitive Deficits in Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Gao, M.; Liu, B.; Qin, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Gong, G. Mitochondrial Autophagy: Molecular Mechanisms and Implications for Cardiovascular Disease. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, S.; Lu, D.C.; Chandra, S.; Pietrzik, C.U.; Koo, E.H. The Amyloidogenic Pathway of Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) Is Independent of Its Cleavage by Caspases. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 29045–29050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).