Submitted:
01 November 2024
Posted:
05 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Strain Collection
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
DNA Preparation
Statistical Analysis
Results
Drug Susceptibility Test Results
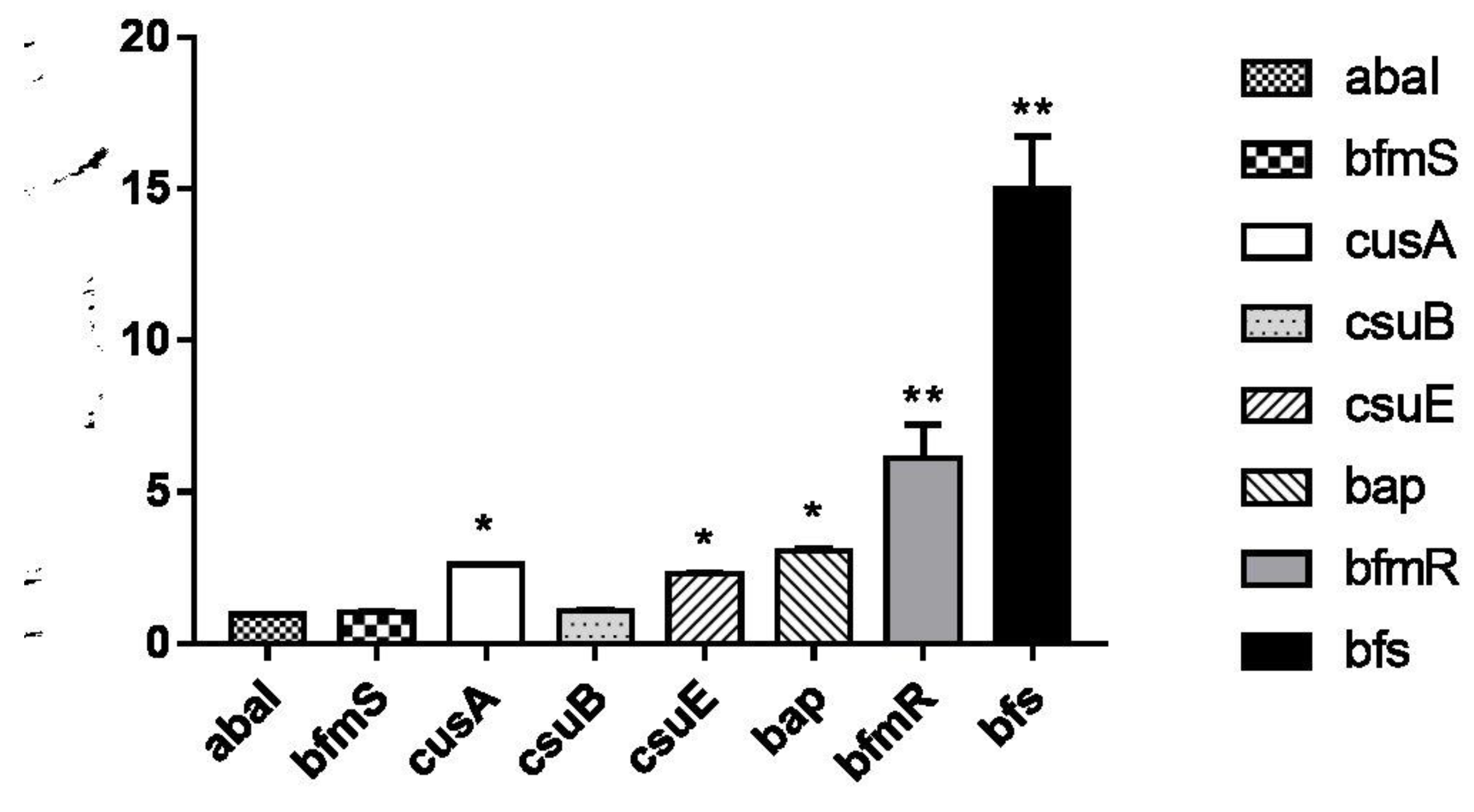
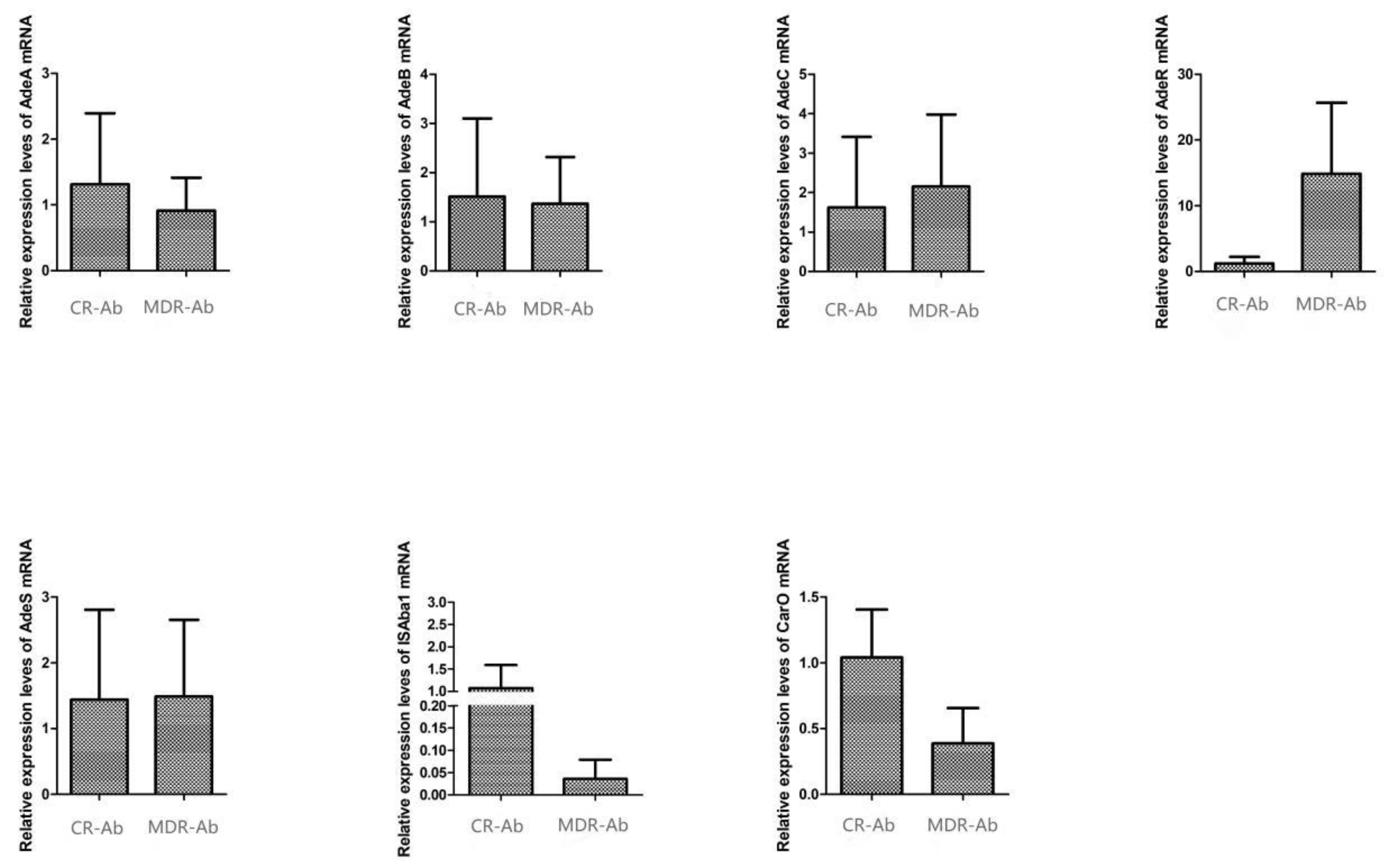
Biofilm-Related Gene Analysis
Homology Analysis
Discussion
Funding
References
- Shakibaie, M.R.; Modaresi, F.; Ghaemi, T.M.M. Amphiphilic peptide mastoparan-b induces conformational changes within the adeb efflux pump, down-regulates adeb gene expression, and restores antibiotic susceptibility in an mdr strain of acinetobacter baumannii. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Genetics 2023, 91, 1205–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F., Wei, Y., Sun, C., Yuan, M., Zeng, W., & Liu, C., et al. (2022). Pinoxaden degradation characteristics of acinetobacter pittobacter and prediction of related genes. Microbiology. [CrossRef]
- 3. Mendoza Cedeno, L. G. M. , Pincay Cantos, M. F. P. , & Giler-Molina, Jose MiguelZambrano Cedeno, Ider Josue Zambrano. (2022). Influence of bacterial microbiota on the organic matter content of shrimp pond soil. journal of ecological engineering, 23(12), 21-28. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C., Huang, P. Y., Cui, C. Y., He, Q., Sun, J., & Liu, Y., et al. (2022). Classification and molecular characteristics of tet(x)-carrying plasmids in acinetobacter species. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13. [CrossRef]
- Melike, G.; Ayegül, S.S. Combined in silico approach and whole genome sequencing: acinetobacter baumannii st218 isolate harboring adc-73 β-lactamase which has a similar c-loop with adc-56 and adc-68 β-lactamase. Journal of molecular graphics & modelling 2022, 114, 108195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, L. K., Sharma, P., & Capalash, N.. (2022). Structural insight into substrate binding of acinetobacter baumannii polyphosphate-amp phosphotransferase (ppk2), a novel drug target. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. [CrossRef]
- Castro-Jaimes, S.; Guerrero, G.; Bello-López, E.; Cevallos, M.A. Replication initiator proteins of acinetobacter baumannii plasmids: an update note. Plasmid 2022, 119–120, 102616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q. , Zhou, W. , Cheng, Y. , Wang, G. , San, Z. , & Guo, L. , et al. (2024). Four novelacinetobacter lwoffiistrains isolated from the milk of cows in china with subclinical mastitis. BMC Veterinary Research, 20(1). [CrossRef]
- Gautam, L.K.; Sharma, P.; Capalash, N. Structural insight into substrate binding of acinetobacter baumannii polyphosphate-amp phosphotransferase (ppk2), a novel drug target. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2022, 626, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N. , Singh, A. , Gupta, A. , Pant, P. , Singh, T. P. , & Sharma, S. , et al. (2022). Discovery of the lead molecules targeting the first step of the histidine biosynthesis pathway of acinetobacter baumannii. Journal of chemical information and modeling(7), 62. [CrossRef]
- Vered, S., Adi, C., & Yehuda, C.. (2024). Tailoring interventions for control of endemic carbapenem-resistant acinetobacter baumannii: an interrupted time series analysis. Open Forum Infectious Diseases(6), 6. [CrossRef]
- 12. Sabry, M. M. , El-Halawany, A. M. , Fahmy, W. G. , Eltanany, B. M. , Pont, L. , & Benavente, F. , et al. (2024). Evidence on the inhibitory effect ofbrassicaplants againstacinetobacter baumanniilipases: phytochemical analysis, in vitro, and molecular docking studies. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, 24(1). [CrossRef]
- María Pérez-Varela, Singh, R., Colquhoun, J. M., Starich, O. G., Tierney, A. R. P., & Tipton, K. A., et al. (2024). Evidence for rho-dependent control of a virulence switch in acinetobacter baumannii. mBio, 15(1). [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.G.; Lim, S.; Hyun, H.J.; Seong, H.; Noh, J.Y.; Song, J.Y.; et al. Respiratory microbiome and clinical course of carbapenem-resistantacinetobacter baumanniipneumonia in critically ill patients. Medicine 2024, 103, e38988-63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Genes | 5’-3' | product length |
| blaOXA-23 -F | GATCGGATTGGAGAACCAGA | 501 |
| blaOXA-23 -R | ATT TCTGACCGCATT TCCAT | |
| blaOXA- 51 -F | TAATGCTTTGATCGGCCTTG | 353 |
| blaOXA- 51 -R | TGGATTGCACTTCATCTTGG | |
| blaOXA- 58 -F | AAGTATTGGGGCTTGTGCTG | 599 |
| blaOXA- 58 -R | CCCCTCTGCGCTCTACATAC | |
| adeB(16)-F | ATTCGTCGTCCTGTTTTTGC | 271 |
| adeB(126)-R | CGGAGCTACACTTGGAAAGC | |
| adeA(118)-F | ATTCAACCGCAATCGGTAAA | 280 |
| adeA(260) -R | GCTTGCCCTGCTCTAACTTC | |
| AdeC 2F(AN) | TGTCGAAATCGGCAACTGTA | 310 |
| AdeC 159R(AN) | TTGTTCAGCAATCGTTTTTCC | |
| adeRS_1F(an) | ATGTTCGATCATTCTTTTTCTTTTG | 272 |
| adeRS_1849R(an) | TTACTAATCCATAGAAATTTTTATG | |
| abaI-F | GTACAGTCGACGTATTTGTTGAATATTTGGG | 382 |
| abaI-R | CGTACGTCTAGAGTAATGAGTTGTTTTGCGCC | |
| bap-F | CGTTTCCTGGGTCTGATGTATT | 942 |
| bap-R | GTTATTGAAGGCTTCTTTAGTG | |
| bfmS-F | F:CGTATGCATCAGGTCGAC | 355 |
| bfmS-R | R: ACAGACAAAAGCCTGCC | |
| bfmR-F | CACCATGAGCCAAGAAGAAAAG | 750 |
| bfmR-R | GACCAACCTTATAGGAAG | |
| bfs-F | GCGCATATGAAAAATGATGCAAATATC | 490 |
| bfs-R | GCGCTCGAGTCATTTCAAATCATATCGAG | |
| csuAB-F | ATGAATATGAAAAACATTCA | 530 |
| csuAB-R | TTAGAAATTTACAGTGACTA | |
| csuE -F | CATCTTCTATTTCGGTCCC | 372 |
| csuE -R | CGGTCTGAGCATTGGTAA | |
| DNA-N-F | TTTGGCTTCCTCTACTTC | 500 |
| DNA-N-R | CATCTTGTTCAGGGTTAT |
| Antimicrobial agent | Acinetobacter baumannii (n=72) | |
| R | S | |
| Cefoperazone-sulbactam | 95.8 | 4.2 |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 100 | 0 |
| Trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole | 40.3 | 59.7 |
| Ceftazidime | 100 | 0 |
| Cefepime | 100 | 0 |
| Amikacin | 100 | 0 |
| Gentamicin | 100 | 0 |
| Imipenem | 100 | 0 |
| Meropenem | 100 | 0 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 100 | 0 |
| Minocycline | 20.8 | 79.2 |
| Tigecycline | 2.7 | 97.3 |
| Polymixin B | 1.4 | 98.6 |
| Bacterial clone (No. of strains) | City | n | Sickroom | n | Specimen | n | Diagnosis | Number of patients |
| 1 (43) | Urumqi | 20 | SICU | 12 | Blood | 4 | Burns | 4 |
| Secretions | 6 | Burns | 1 | |||||
| Burns | 4 | |||||||
| Electric injury | 1 | |||||||
| Catheter tip | 2 | Burns | 2 | |||||
| RICU | 5 | Sputum | 2 | Severe pneumonia | 2 | |||
| Pulmonary infection | 1 | |||||||
| Blood | 2 | Severe pneumonia | 2 | |||||
| NSICU | 1 | Blood | 1 | Cerebralinfarction | 1 | |||
| Burns | 2 | Secretions | 2 | Burns | 1 | |||
| Electric injury | 1 | |||||||
| Aksu | 5 | ICU | 5 | Sputum | 5 | Severe pneumonia | 2 | |
| Pulmonary infection | 2 | |||||||
| Community pneumonia | 1 | |||||||
| Turpan | 4 | ICU | 4 | Sputum | 4 | Severe pneumonia | 2 | |
| Tuberculous meningitis | 1 | |||||||
| Cerebrel hemorrhage | 1 | |||||||
| Korla | 4 | ICU | 4 | Sputum | 4 | Tuberculous meningitis | 1 | |
| Severe pneumonia | 1 | |||||||
| Pulmonary infection | 2 | |||||||
| 3 (12) | Kashi | 3 | ICU | 3 | Sputum | 3 | Pulmonary infection | 3 |
| Ili | 3 | ICU | 3 | Sputum | 3 | Pulmonary infection | 2 | |
| Cerebrel hemorrhage | 1 | |||||||
| Shihezi | 2 | ICU | 2 | Alveolar lavage | 1 | Pulmonary infection Severe pneumonia | 1 | |
| Sputum | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Changji | 1 | ICU | 1 | Sputum | 1 | Severe pneumonia | 1 | |
| Hotan | 1 | Respiratory | 1 | Sputum | 1 | Emphysema | 1 | |
| Urumqi | 12 | Burns | 7 | Catheter tip | 4 | Burns | 3 | |
| Scald | 1 | |||||||
| Sputum | 2 | Burns | 2 | |||||
| Secretions | 1 | Electric injury | 1 | |||||
| Blood | 3 | Burns | 3 | |||||
| SICU | 4 | Drain fluid | 1 | Spinal stenosis | 1 | |||
| ICU | 1 | Sputum | 1 | Pulmonary infection | 1 | |||
| 4 (9) | Changji | 6 | ICU | 6 | Sputum | 6 | Severe pneumonia | 4 |
| Pulmonary infection | 2 | |||||||
| Hotan | 3 | Respiratory | 2 | Sputum | 2 | Pulmonary infection | 1 | |
| Emphysema | 1 | |||||||
| ICU | 1 | Sputum | 1 | AECB | 1 | |||
| 2 (8) | Urumqi | 6 | SICU | 2 | Alveolar lavage | 2 | Radius fracture | 1 |
| Thoracic vertebral fracture | 1 | |||||||
| RICU | 3 | Sputum | 1 | Severe pneumonia | 1 | |||
| Secretions | 2 | Severe pneumonia | 1 | |||||
| Acute pancreatitis | 1 | |||||||
| NSICU | 1 | Blood | 1 | Cerebrel hemorrhage | 1 | |||
| Hotan | 2 | Respiratory | 2 | Sputum | 2 | Severe pneumonia Pulmonary infection | 1 | |
| 1 |
| Antimicrobial agent | Clone 1 A. baumannii (n=43) | Clone 3 A. baumannii (n=12) | ||
| R | S | R | S | |
| Cefoperazone-sulbactam | 76.6 | 23.4 | 83.3 | 16.7 |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole | 34.9 | 65.1 | 41.7 | 58.3 |
| Ceftazidime | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Cefepime | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Amikacin | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Gentamicin | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Imipenem | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Meropenem | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Minocycline | 20.9 | 79.1 | 25 | 75 |
| Tigecycline | 0 | 100 | 16.7 | 83.3 |
| Polymixin B | 0 | 100 | 8.3 | 91.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





