Submitted:
04 November 2024
Posted:
05 November 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
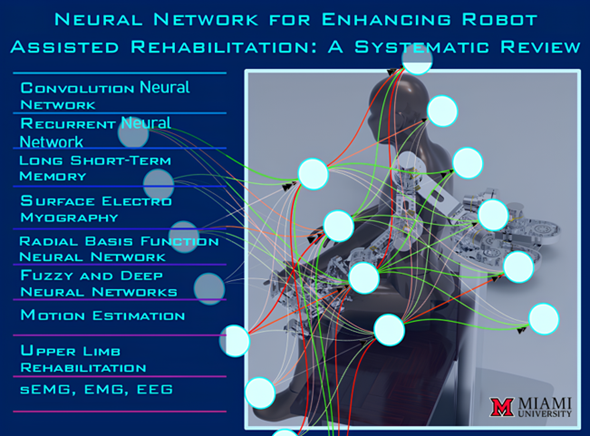
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Current State of Art
1.2. Article Selection Methodology
2. Research Question Formulation
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
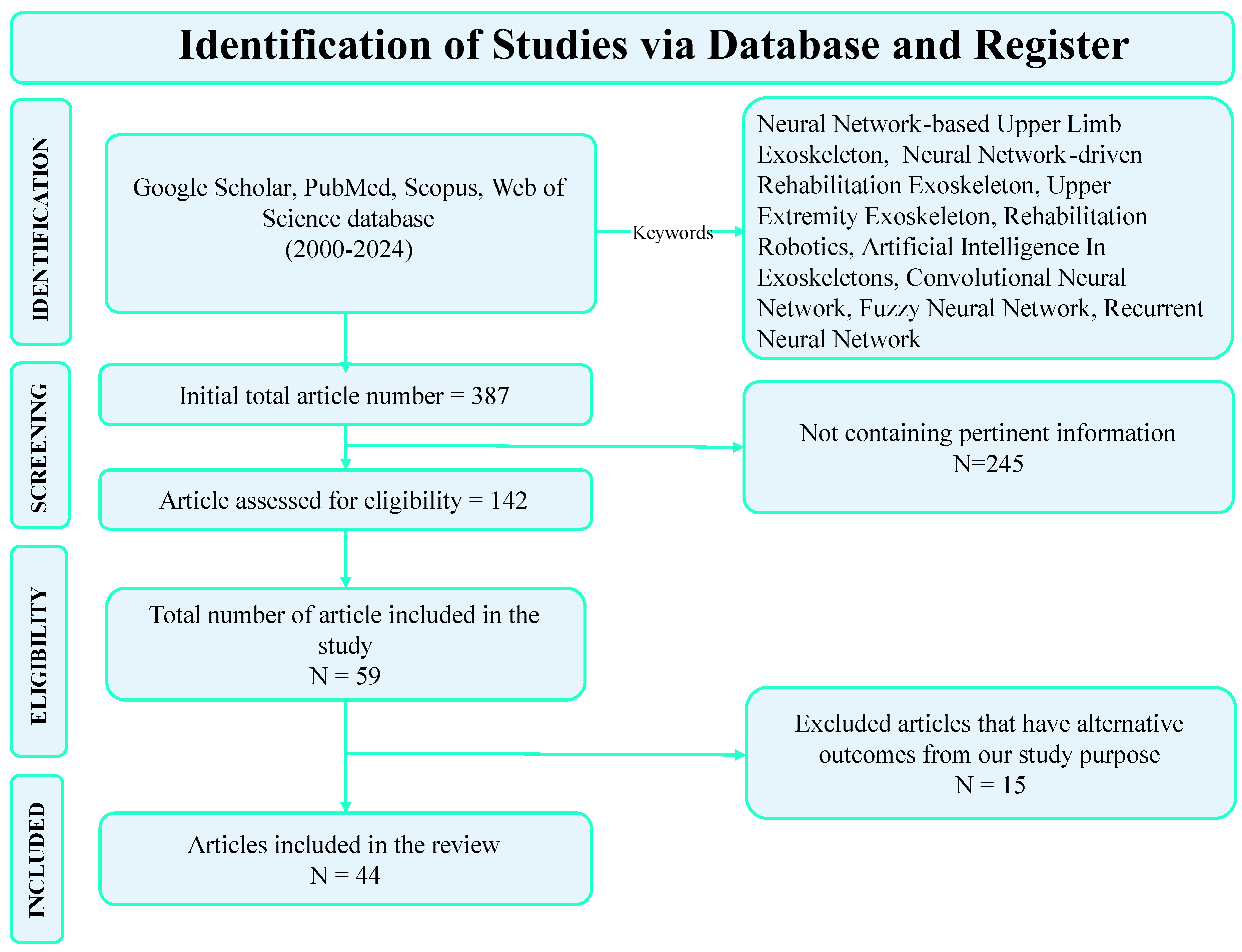
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction and Synthesis
2.5. Quality Assessment
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Exploring Neural Network Applications in Robot Assisted Rehabilitation
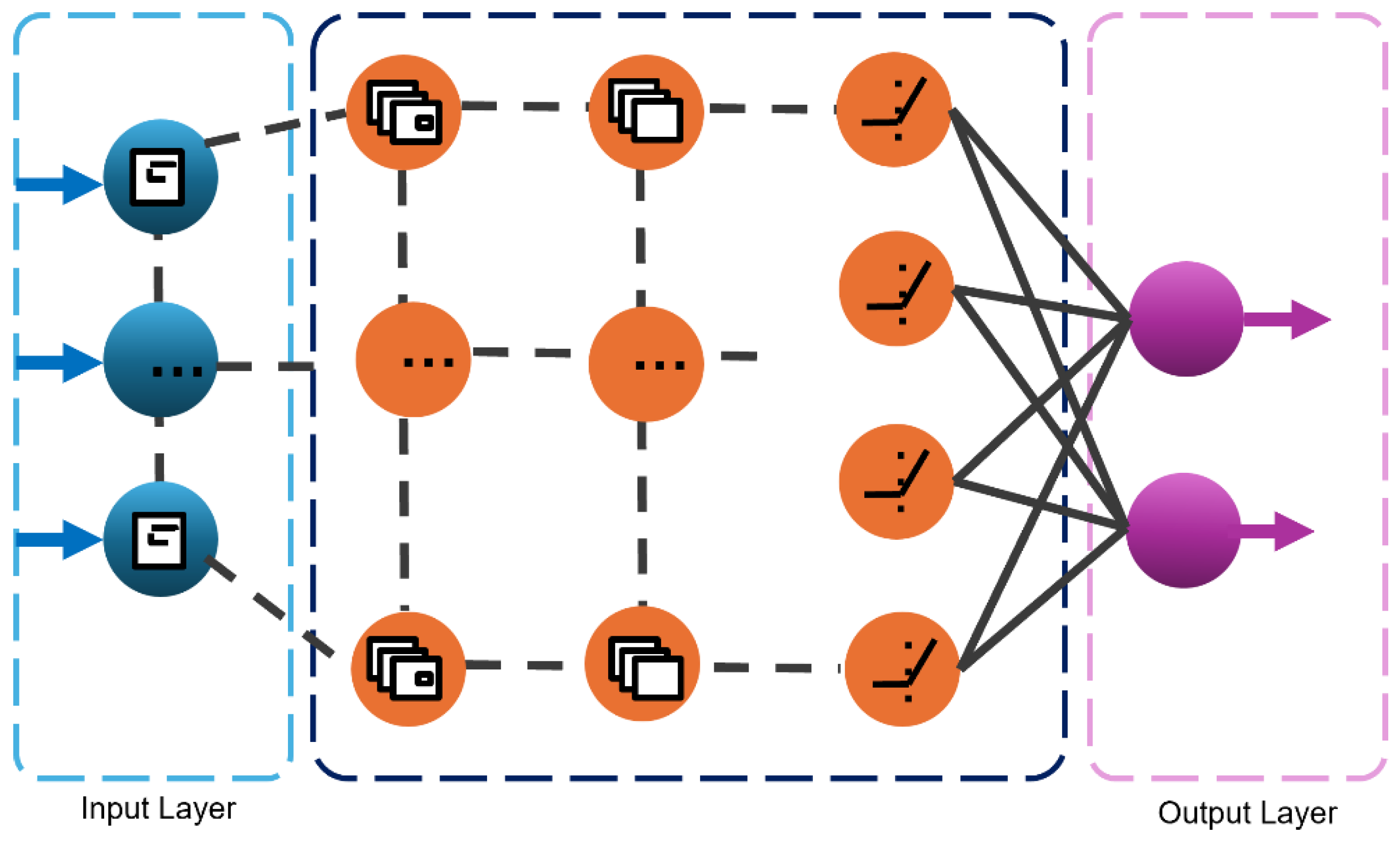
3.1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
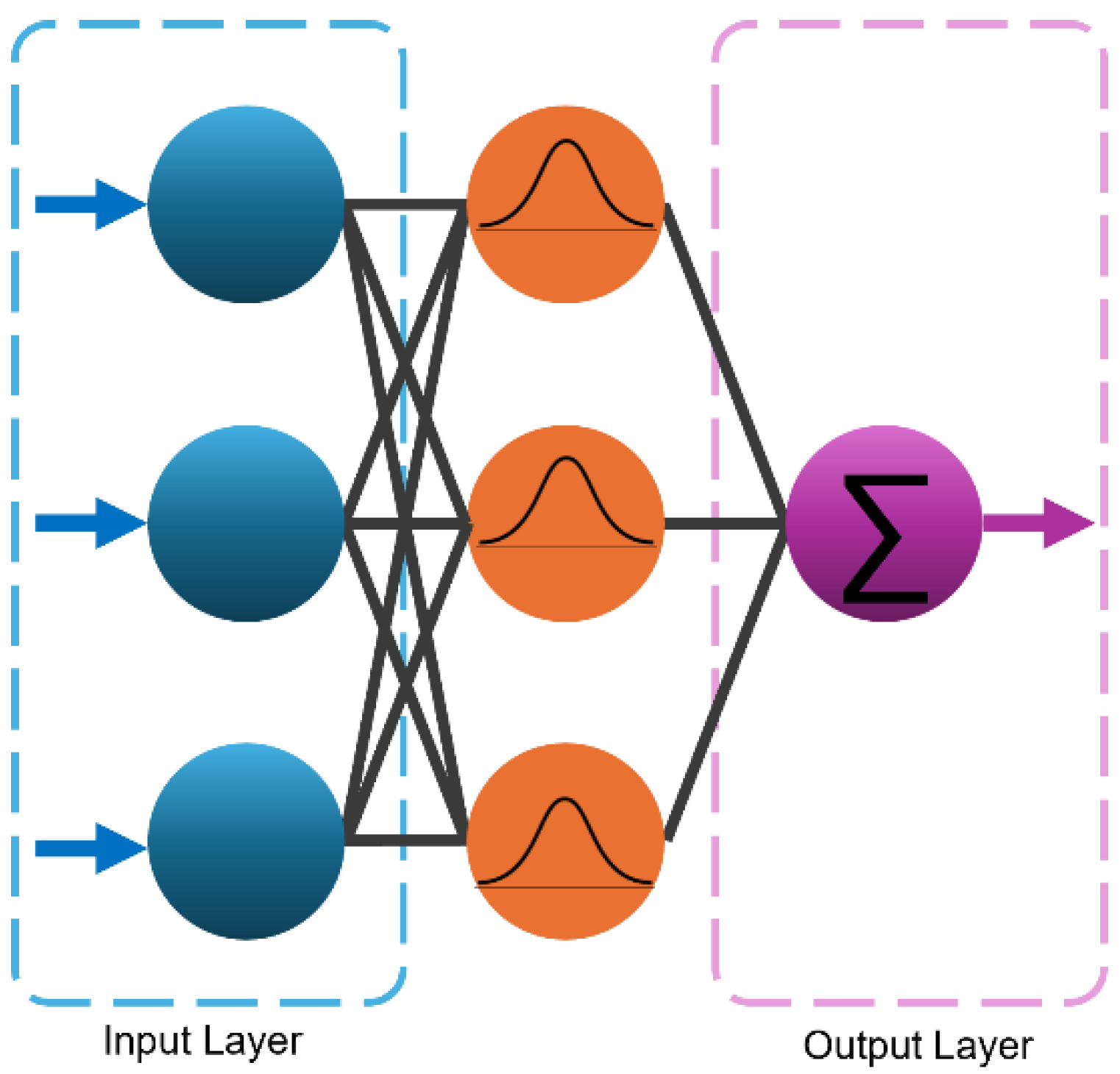
3.2. Radial Basis Function Neural Networks (RBFNN)
3.3. Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN)
3.4. Fuzzy Neural Network (FNN)
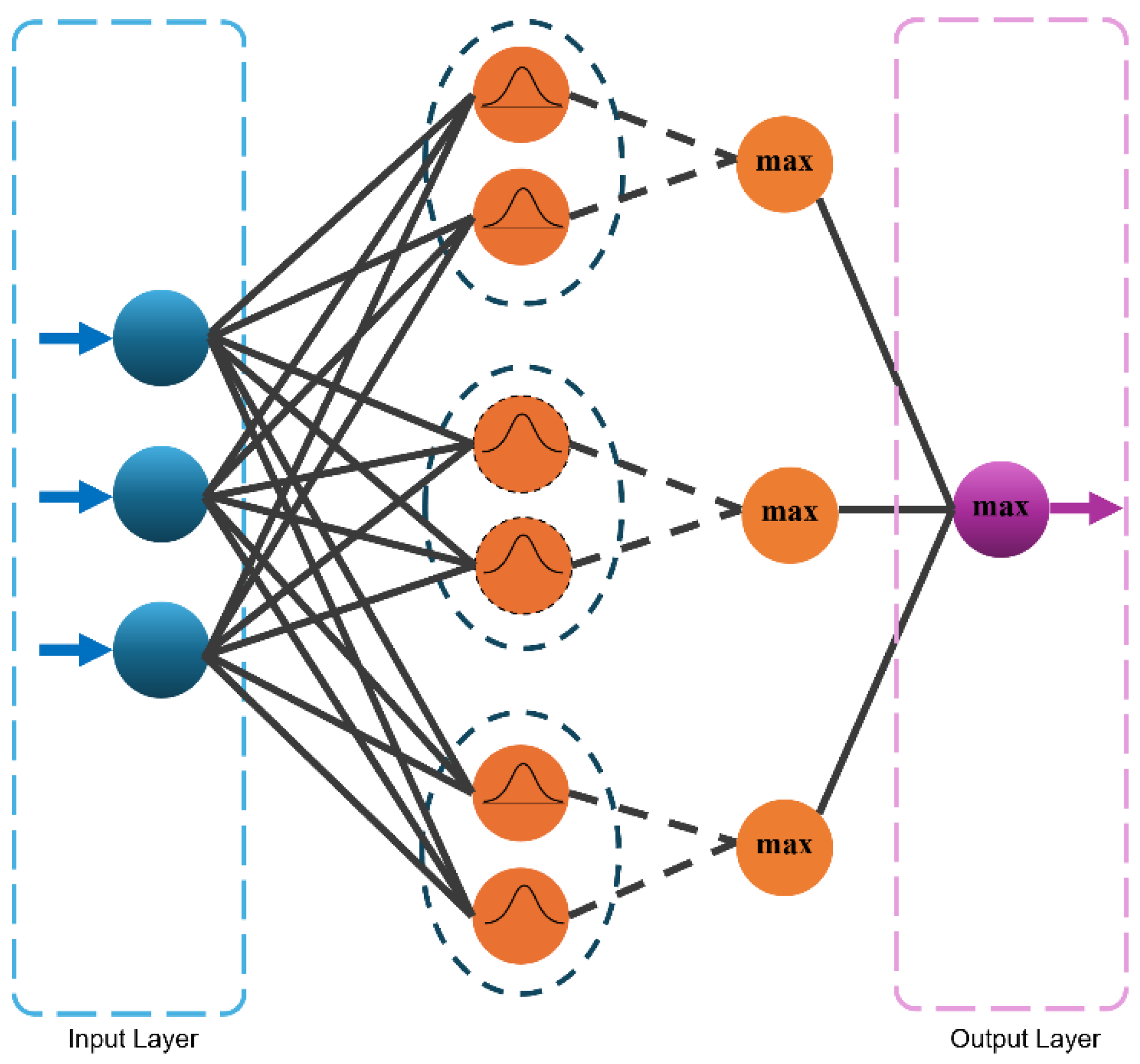
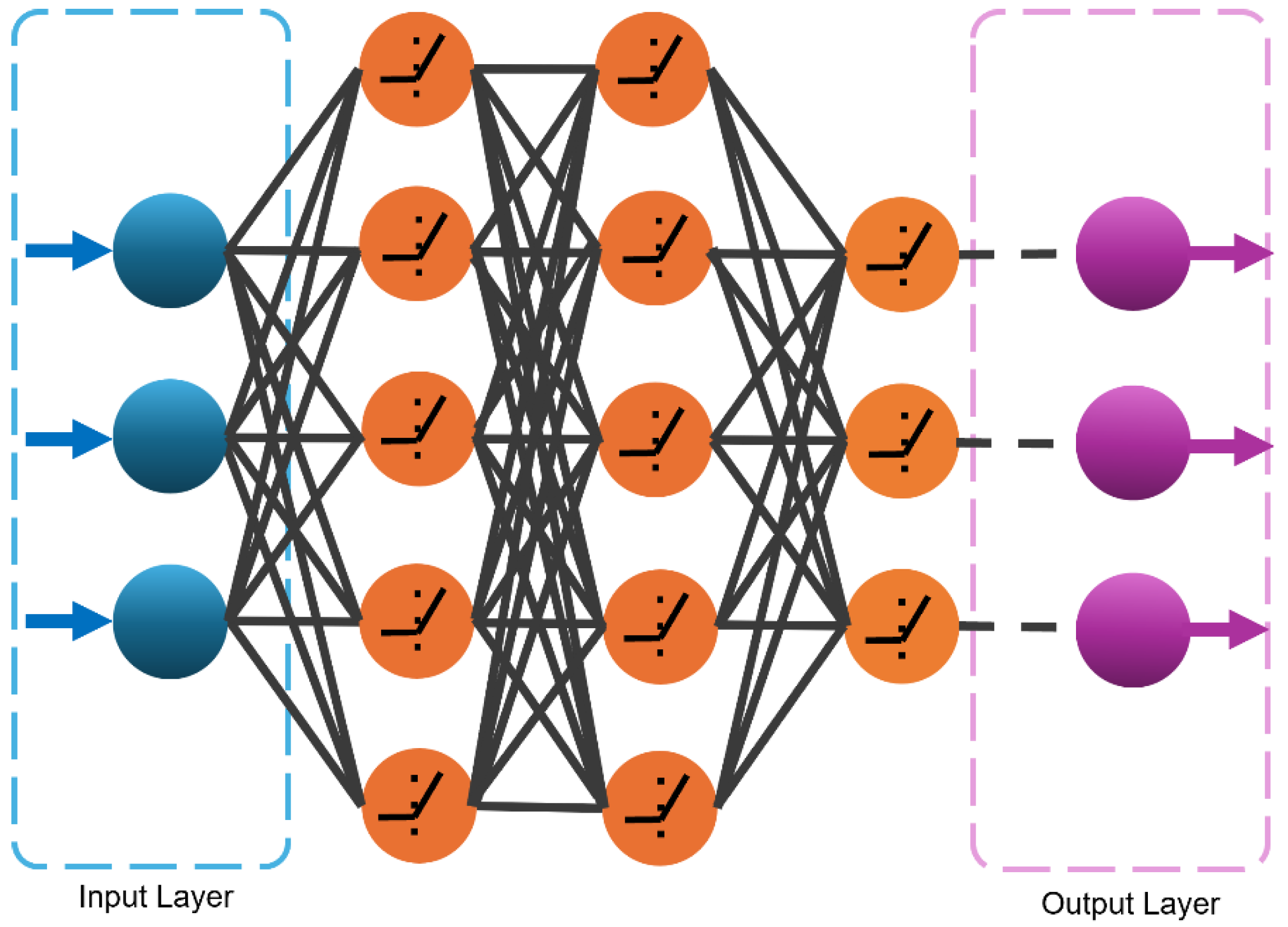
3.5. Deep Neural Network (DNN)
3.6. Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTM)
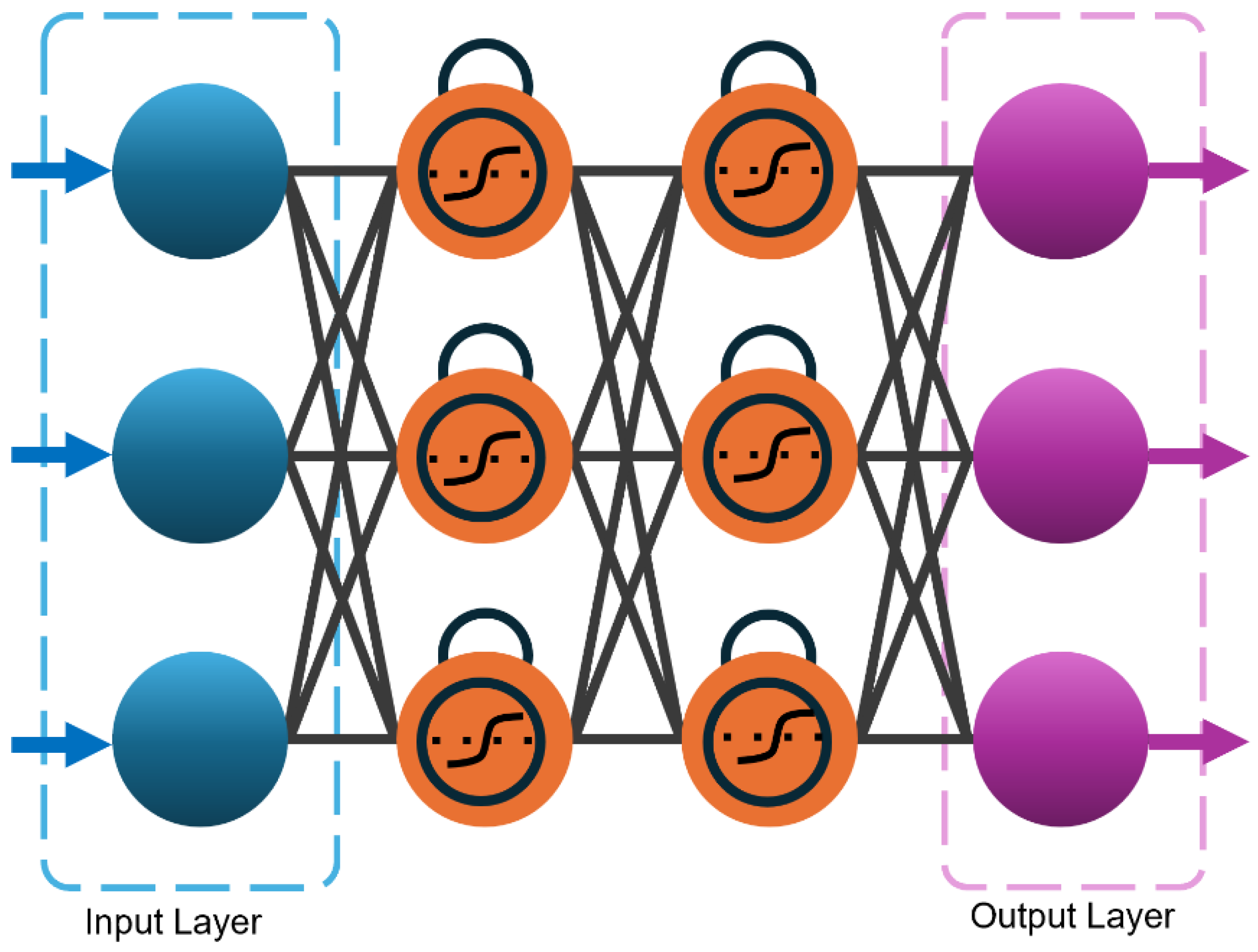
3.7. Adaptive Neural Network (ANN)
3.8. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
3.9. Support Vector Machines Neural Networks (SVNN)
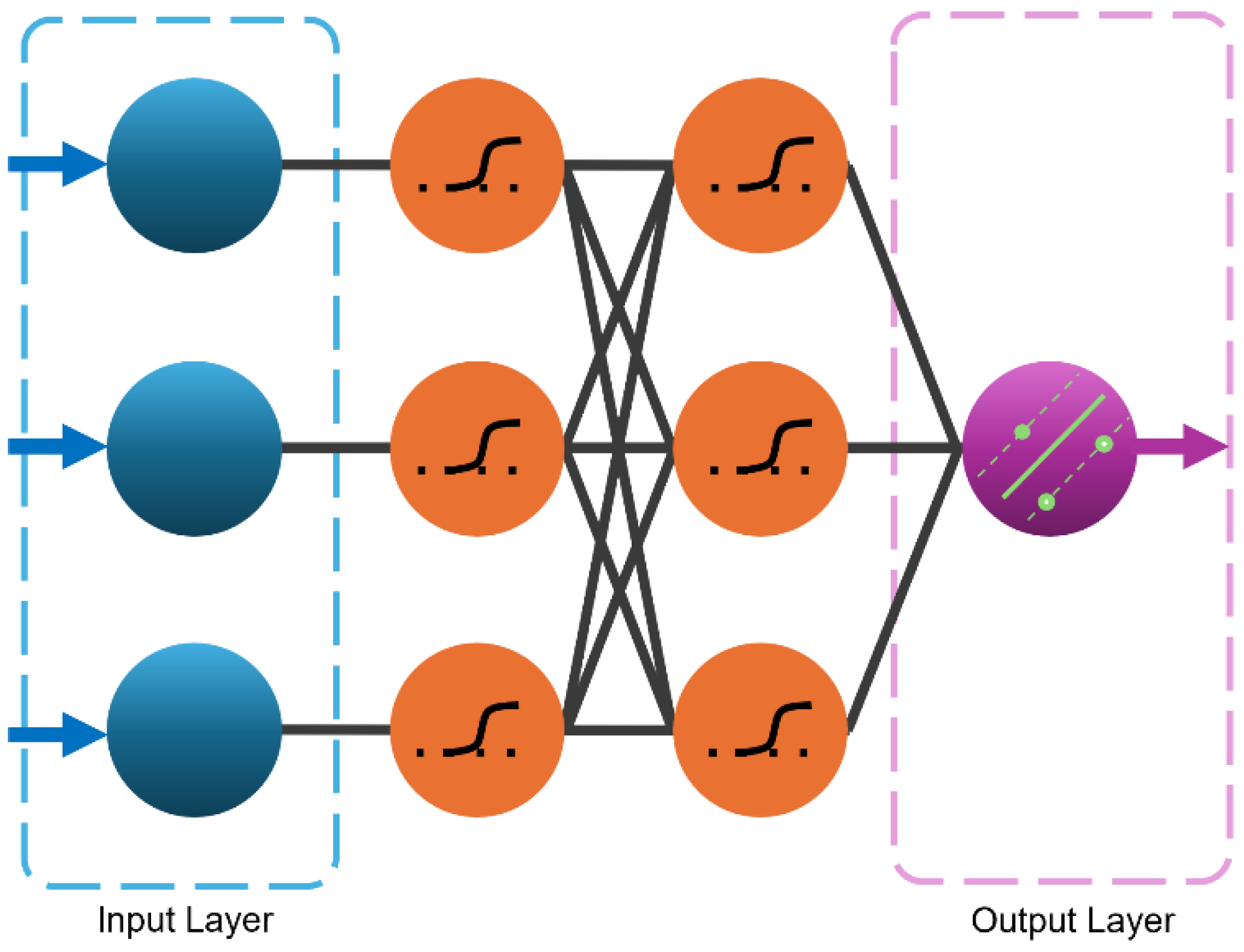
3.10. Multi-Layer Neural Network (MLNN)
4. Discussion
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusion
References
- A. Houtenville and S. Bach, “Annual Report on People with Disabilities in America: 2024,” University of New Hampshire, Institute on Disability, Durham, NH, 2024.
- S. Bhujel and · Sk Hasan, “A comparative study of end-effector and exoskeleton type rehabilitation robots in human upper extremity rehabilitation,” Human-Intelligent Systems Integration 2023 5:1, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 11–42, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Gull, S. Bai, and T. Bak, “A Review on Design of Upper Limb Exoskeletons,” Robotics 2020, Vol. 9, Page 16, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 16, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. J. Hasson, J. Manczurowsky, E. C. Collins, and M. Yarossi, “Neurorehabilitation robotics: how much control should therapists have?,” Front Hum Neurosci, vol. 17, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Alzubaidi et al., “Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions,” Journal of Big Data 2021 8:1, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 1–74, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. D. Banyai and C. Brișan, “Robotics in Physical Rehabilitation: Systematic Review,” Healthcare 2024, Vol. 12, Page 1720, vol. 12, no. 17, p. 1720, Aug. 2024. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Al-Selwi et al., “RNN-LSTM: From applications to modeling techniques and beyond—Systematic review,” Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, vol. 36, no. 5, p. 102068, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- B. Ren, Z. Zhang, C. Zhang, and S. Chen, “Motion Trajectories Prediction of Lower Limb Exoskeleton Based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Networks,” Actuators 2022, Vol. 11, Page 73, vol. 11, no. 3, p. 73, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Fareh, A. Elsabe, M. Baziyad, T. Kawser, B. Brahmi, and M. H. Rahman, “Will Your Next Therapist Be a Robot?—A Review of the Advancements in Robotic Upper Extremity Rehabilitation,” Sensors 2023, Vol. 23, Page 5054, vol. 23, no. 11, p. 5054, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- Q. Ai, Z. Liu, W. Meng, Q. Liu, and S. Q. Xie, “Machine Learning in Robot-Assisted Upper Limb Rehabilitation: A Focused Review,” IEEE Trans Cogn Dev Syst, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 2053–2063, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. Bardi, M. Gandolla, F. Braghin, F. Resta, A. L. G. Pedrocchi, and E. Ambrosini, “Upper limb soft robotic wearable devices: a systematic review,” J Neuroeng Rehabil, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 1–17, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Fu, R. Choudhury, S. M. Hosseini, R. Simpson, and J. H. Park, “Myoelectric Control Systems for Upper Limb Wearable Robotic Exoskeletons and Exosuits—A Systematic Review,” Sensors 2022, Vol. 22, Page 8134, vol. 22, no. 21, p. 8134, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Dalla Gasperina, L. Roveda, A. Pedrocchi, F. Braghin, and M. Gandolla, “Review on Patient-Cooperative Control Strategies for Upper-Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeletons,” Front Robot AI, vol. 8, p. 745018, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Gaudet, M. Raison, and S. Achiche, “Current Trends and Challenges in Pediatric Access to Sensorless and Sensor-Based Upper Limb Exoskeletons,” Sensors 2021, Vol. 21, Page 3561, vol. 21, no. 10, p. 3561, May 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Dežman et al., “Wearable upper limb robotics for pervasive health: a review,” Progress in Biomedical Engineering, vol. 5, no. 3, p. 032003, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Sarhan, M. Z. Al-Faiz, and A. M. Takhakh, “A review on EMG/EEG based control scheme of upper limb rehabilitation robots for stroke patients,” Heliyon, vol. 9, no. 8, p. e18308, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. Xu, D. Xia, J. Li, J. Zhou, and L. Xie, “Execution and perception of upper limb exoskeleton for stroke patients: a systematic review,” Intelligent Service Robotics 2022 15:4, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 557–578, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Robinson, S. Pawar, A. Rasheed, and O. San, “Physics guided neural networks for modelling of non-linear dynamics,” Neural Networks, vol. 154, pp. 333–345, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Kotyrba et al., “Proposal of neural network model for neurocognitive rehabilitation and its comparison with fuzzy expert system model,” BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, vol. 23, no. 1, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Szczȩsna, M. Błaszczyszyn, and A. Kawala-Sterniuk, “Convolutional neural network in upper limb functional motion analysis after stroke,” PeerJ, vol. 8, Oct. 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Ben Haj Amor, O. El Ghoul, and M. Jemni, “Sign Language Recognition Using the Electromyographic Signal: A Systematic Literature Review,” Sensors (Basel), vol. 23, no. 19, Oct. 2023. [CrossRef]
- O. A. M. López, A. M. López, and Dr. J. Crossa, “Convolutional Neural Networks,” Multivariate Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Genomic Prediction, pp. 533–577, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Taye, “Theoretical Understanding of Convolutional Neural Network: Concepts, Architectures, Applications, Future Directions,” Computation 2023, Vol. 11, Page 52, vol. 11, no. 3, p. 52, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Li, S. Guo, D. Bu, H. Wang, and M. Kawanishi, “Subject-Independent Estimation of Continuous Movements Using CNN-LSTM for a Home-Based Upper Limb Rehabilitation System,” IEEE Robot Autom Lett, vol. 8, no. 10, pp. 6403–6410, Oct. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Tryon and A. L. Trejos, “Evaluating Convolutional Neural Networks as a Method of EEG–EMG Fusion,” Front Neurorobot, vol. 15, p. 692183, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Q. Liu et al., “Path Planning and Impedance Control of a Soft Modular Exoskeleton for Coordinated Upper Limb Rehabilitation,” Front Neurorobot, vol. 15, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Jiang et al., “Shoulder muscle activation pattern recognition based on sEMG and machine learning algorithms,” Comput Methods Programs Biomed, vol. 197, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Z. Tang et al., “An Upper-Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton System Controlled by MI Recognition Model With Deep Emphasized Informative Features in a VR Scene,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 31, pp. 4390–4401, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Bu, S. Guo, and H. Li, “sEMG-Based Motion Recognition of Upper Limb Rehabilitation Using the Improved Yolo-v4 Algorithm,” Life, vol. 12, no. 1, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Al Bakri, M. Y. Lezzar, M. Alzinati, K. Mortazavi, W. Shehieb, and T. Sharif, “Intelligent Exoskeleton for Patients with Paralysis,” 2018 IEEE 9th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference, IEMCON 2018, pp. 189–193, Jul. 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. Sedighi, X. Li, and M. Tavakoli, “EMG-Based Intention Detection Using Deep Learning for Shared Control in Upper-Limb Assistive Exoskeletons,” IEEE Robot Autom Lett, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 41–48, Jan. 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. Lee et al., “Intelligent upper-limb exoskeleton integrated with soft bioelectronics and deep learning for intention-driven augmentation,” npj Flexible Electronics 2024 8:1, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 1–13, Feb. 2024. [CrossRef]
- T. Zhong, D. Li, J. Wang, J. Xu, Z. An, and Y. Zhu, “Fusion Learning for sEMG Recognition of Multiple Upper-Limb Rehabilitation Movements,” Sensors 2021, Vol. 21, Page 5385, vol. 21, no. 16, p. 5385, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. Kong, W. Wang, Y. Shi, and L. Kong, “Flexible Control Strategy for Upper-Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton Based on Virtual Spring Damper Hypothesis,” Actuators, vol. 11, no. 5, May 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. Zhang, J. Wang, P. Yang, and S. Guo, “A learning control scheme for upper-limb exoskeleton via adaptive sliding mode technique,” Mechatronics, vol. 86, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. K. Hasan, “Radial basis function-based exoskeleton robot controller development,” IET Cyber-Systems and Robotics, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 228–250, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Guo, W. Gao, and D. Bu, “Radial Basis Function Neural Network-based Control Method for a Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot,” Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, ICMA 2019, pp. 1327–1332, Aug. 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. Xu, Q. Wu, and Y. Zhu, “Development of a sEMG-Based Joint Torque Estimation Strategy Using Hill-Type Muscle Model and Neural Network,” J Med Biol Eng, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 34–44, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wu, B. Chen, and H. Wu, “RBFN-Based Adaptive Backstepping Sliding Mode Control of an Upper-Limb Exoskeleton with Dynamic Uncertainties,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 134635–134646, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wu, B. Chen, and H. Wu, “Adaptive admittance control of an upper extremity rehabilitation robot with neural-network-based disturbance observer,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 123807–123819, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Wang, L. Peng, and Z. G. Hou, “A Control Framework for Adaptation of Training Task and Robotic Assistance for Promoting Motor Learning With an Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot,” IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, vol. 52, no. 12, pp. 7737–7747, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Guo, H. Wang, Y. Tian, and D. G. Caldwell, “Task performance-based adaptive velocity assist-as-needed control for an upper limb exoskeleton,” Biomed Signal Process Control, vol. 73, p. 103474, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wu and Y. Chen, “Adaptive cooperative control of a soft elbow rehabilitation exoskeleton based on improved joint torque estimation,” Mech Syst Signal Process, vol. 184, p. 109748, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Li, “Comprehensive Review of Backpropagation Neural Networks,” Academic Journal of Science and Technology, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 150–154, Jan. 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. Liang et al., “A Real-Time Control Method for Upper Limb Exoskeleton Based on Active Torque Prediction Model,” Bioengineering 2023, Vol. 10, Page 1441, vol. 10, no. 12, p. 1441, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. Tang et al., “Glenohumeral joint trajectory tracking for improving the shoulder compliance of the upper limb rehabilitation robot,” Med Eng Phys, vol. 113, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Tang, K. Zhang, S. Sun, Z. Gao, L. Zhang, and Z. Yang, “An Upper-Limb Power-Assist Exoskeleton Using Proportional Myoelectric Control,” Sensors 2014, Vol. 14, Pages 6677-6694, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 6677–6694, Apr. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yang, S. Guo, Y. Liu, H. Hirata, and T. Tamiya, “An intention-based online bilateral training system for upper limb motor rehabilitation,” Microsystem Technologies, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 211–222, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Wai and R. Muthusamy, “Design of fuzzy-neural-network-inherited backstepping control for robot manipulator including actuator dynamics,” IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 709–722, 2014. [CrossRef]
- P. V. de Campos Souza, “Fuzzy neural networks and neuro-fuzzy networks: A review the main techniques and applications used in the literature,” Appl Soft Comput, vol. 92, p. 106275, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Xu, A. Song, and H. Li, “Adaptive impedance control for upper-limb rehabilitation robot using evolutionary dynamic recurrent fuzzy neural network,” Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems: Theory and Applications, vol. 62, no. 3–4, pp. 501–525, Jun. 2011. [CrossRef]
- B. O. Mushage, J. C. Chedjou, and K. Kyamakya, “Fuzzy neural network and observer-based fault-tolerant adaptive nonlinear control of uncertain 5-DOF upper-limb exoskeleton robot for passive rehabilitation,” Nonlinear Dyn, vol. 87, no. 3, pp. 2021–2037, Feb. 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Razzaghian, “A fuzzy neural network-based fractional-order Lyapunov-based robust control strategy for exoskeleton robots: Application in upper-limb rehabilitation,” Math Comput Simul, vol. 193, pp. 567–583, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Liu, Z. Wang, X. Liu, N. Zeng, Y. Liu, and F. E. Alsaadi, “A survey of deep neural network architectures and their applications,” Neurocomputing, vol. 234, pp. 11–26, Apr. 2017. [CrossRef]
- D. Mikołajewski, I. Rojek, P. Kotlarz, J. Dorożyński, and J. Kopowski, “Personalization of the 3D-Printed Upper Limb Exoskeleton Design—Mechanical and IT Aspects,” Applied Sciences 2023, Vol. 13, Page 7236, vol. 13, no. 12, p. 7236, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- W. D. Wang, J. B. Zhang, X. Wang, X. Q. Yuan, and P. Zhang, “Motion intensity modeling and trajectory control of upper limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot based on multi-modal information,” Complex and Intelligent Systems, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 2091–2103, Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. S. Hasan, “Deep Learning Technology-Based Exoskeleton Robot Controller Development,” Sep. 2022, Accessed: Oct. 09, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.12133v2.
- W. Wendong et al., “Design and verification of a human–robot interaction system for upper limb exoskeleton rehabilitation,” Med Eng Phys, vol. 79, pp. 19–25, May 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Ghislieri, G. L. Cerone, M. Knaflitz, and V. Agostini, “Long short-term memory (LSTM) recurrent neural network for muscle activity detection,” J Neuroeng Rehabil, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 153, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Van Houdt, C. Mosquera, and G. Nápoles, “A review on the long short-term memory model,” Artif Intell Rev, vol. 53, no. 8, pp. 5929–5955, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Ren, Y. H. Chien, E. Y. Chia, L. C. Fu, and J. S. Lai, “Deep learning based motion prediction for exoskeleton robot control in upper limb rehabilitation,” Proc IEEE Int Conf Robot Autom, vol. 2019-May, pp. 5076–5082, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Kansal, D. Garg, A. Upadhyay, S. Mittal, and G. S. Talwar, “DL-AMPUT-EEG: Design and development of the low-cost prosthesis for rehabilitation of upper limb amputees using deep-learning-based techniques,” Eng Appl Artif Intell, vol. 126, p. 106990, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Ding, S. Li, Y. J. Liu, H. Gao, C. Chen, and Z. Deng, “Adaptive neural network-based tracking control for full-state constrained wheeled mobile robotic system,” IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, vol. 47, no. 8, pp. 2410–2419, Aug. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. S. Ge, J. Zhang, and T. H. Lee, “Adaptive neural network control for a class of MIMO nonlinear systems with disturbances in discrete-time,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 1630–1645, Aug. 2004. [CrossRef]
- J. B. Aldrich and C. A. Cousin, “Saturated Adaptive Control of Antagonistic Muscles on an Upper-Limb Hybrid Exoskeleton,” Proceedings of the American Control Conference, vol. 2022-June, pp. 4397–4402, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Rahmani and M. H. Rahman, “Adaptive Neural Network Fast Fractional Sliding Mode Control of a 7-DOF Exoskeleton Robot,” Int J Control Autom Syst, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 124–133, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- D. He, H. P. Wang, Y. Tian, and Y. Guo, “A Fractional-Order Ultra-Local Model-Based Adaptive Neural Network Sliding Mode Control of n-DOF Upper-Limb Exoskeleton With Input Deadzone,” IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 760–781, Mar. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Z. C. Lipton, J. Berkowitz, and C. Elkan, “A Critical Review of Recurrent Neural Networks for Sequence Learning,” May 2015, Accessed: Oct. 09, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.00019v4.
- Y. ; Gu et al., “A Review of Hand Function Rehabilitation Systems Based on Hand Motion Recognition Devices and Artificial Intelligence,” Brain Sciences 2022, Vol. 12, Page 1079, vol. 12, no. 8, p. 1079, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Guido, S. Ferrisi, D. Lofaro, and D. Conforti, “An Overview on the Advancements of Support Vector Machine Models in Healthcare Applications: A Review,” Information 2024, Vol. 15, Page 235, vol. 15, no. 4, p. 235, Apr. 2024. [CrossRef]
- R. Joshua Samuel Raj, J. Prince Antony Joel, S. Alelyani, M. S. Alsaqer, and C. Anand Deva Durai, “Design of Human Adaptive Mechatronics Controller for Upper Limb Motion Intention Prediction,” Computers, Materials & Continua, vol. 71, no. 1, pp. 1171–1188, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Maler, “Neural Networks: How a Multi-Layer Network Learns to Disentangle Exogenous from Self-Generated Signals,” Curr Biol, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. R224–R226, Mar. 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. Wang, L. Peng, Z. G. Hou, L. Luo, S. Chen, and W. Wang, “SEMG-Based Torque Estimation Using Time-Delay ANN for Control of an Upper-Limb Rehabilitation Robot,” 2018 IEEE International Conference on Cyborg and Bionic Systems, CBS 2018, pp. 585–591, Jul. 2018. [CrossRef]
- F. Resquín et al., “Adaptive hybrid robotic system for rehabilitation of reaching movement after a brain injury: A usability study,” J Neuroeng Rehabil, vol. 14, no. 1, Oct. 2017. [CrossRef]
- F. Medina, K. Perez, D. Cruz-Ortiz, M. Ballesteros, and I. Chairez, “Control of a hybrid upper-limb orthosis device based on a data-driven artificial neural network classifier of electromyography signals,” Biomed Signal Process Control, vol. 68, p. 102624, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Risteiu, M. Leba, O. Stoicuta, and A. Ionica, “Study on ANN based Upper Limb Exoskeleton,” 20th IEEE Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference, MELECON 2020 - Proceedings, pp. 402–405, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. E. Aktan and E. Akdoğan, “Development of an intelligent controller for robot-aided assessment andtreatment guidance in physical medicine and rehabilitation,” Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 403–420, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Jebri, T. Madani, and K. Djouani, “Neural adaptive integral-sliding-mode controller with a SSVEP-based BCI for exoskeletons,” 2019 19th International Conference on Advanced Robotics, ICAR 2019, pp. 87–92, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wu, B. Chen, and H. Wu, “Neural-network-enhanced torque estimation control of a soft wearable exoskeleton for elbow assistance,” Mechatronics, vol. 63, p. 102279, Nov. 2019. [CrossRef]

| Reference | NN Tool | Motion | Body segment | DOF | Actuator | Control Mode | Hybrid Control | Sensor Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [30] | CNN | Grasping Motion | Arm, Hand | 3 | DC Motor | Sliding mode control | yes | IMU, EEG, IR Depth |
| [78] | Multi-Layer | Flexion of Shoulder and Elbow Joints | Shoulder, Elbow | 2 | DC Motor | Sliding mode control | yes | EEG (Electroencephalogram) |
| [41] | RBFNN | Horizontal Plane | Hand, Elbow | 2 | DC Motor | Impedance control | yes | Six Axis Force/Torque |
| [73] | Multi-Layer NN | Horizontal Plane | Wrist, Shoulder, Elbow | 3 | DC Motor | Torque Control | yes | Rotary Encoders |
| [55] | DNN | Stair Climbing | Hand | Variable | Shape memory wire | multi-mode grasping assistance control | yes | FSR, EMG |
| [34] | RBFNN | Flexion | Shoulder | 1 | Servo Motors | RBF sliding mode | Yes | sEMG |
| [74] | Multi-Layer NN | Reaching Movement in 3D space | Elbow | 2 | Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES). | Feedback Error Learning (FEL) | Yes | Angular position transducer |
| [75] | Multi-Layer NN | Wrist & horizontal flexion | Hand | 5 | DC Motors | Decentralized | Yes | EMG |
| [24] | CNN | Elbow Flexion | Elbow | 2 | Servo Motors | Real-time low-level control | yes | Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) |
| [65] | ANN | Rotational | Biceps, Triceps | 1 | DC Motors | Adaptive Control | yes | encoder |
| [61] | LSTM | synchronization of movement | Arm | 8 | PID controlar | Bilateral Mode | yes | sEMG |
| [32] | CNN | Flexion | Elbow, Shoulder | 2 | oft pneumatic artificial muscles (PAMs) | intent-driven control mode | yes | Thin film sensors |
| [76] | Multi-Layer | Abduction/Adduction | Arm | 3 | N/A | Adaptive Control | yes | EMG, IMU |
| [31] | CNN | Trajectory Tracking | Elbow | 3 | Pneumatic cable | Proportional-Derivative (PD) | yes | Optical Encoders, sEMG |
| [39] | RBFNN | flexion of elbow | Elbow | 1 | compliant tendon-sheath | Adaptive Cooperative Control strategy | yes | sEMG |
| [79] | Multi-Layer | flexion of elbow | Elbow | 1 | compliant tendon-sheath | Active control | yes | sEMG, IMU |
| [26] | CNN | coordinated | Elbow, Wrists | 2 | PAM | Impedance control | Yes | sEMG, PAM |
| [62] | LSTM | Grab/Release | Hand, Elbow, Shoulder | 3 | Servo Motor | Real time control | yes | EEG |
| [45] | BPNN | flexion of elbow | Elbow | 0-120 | Servo Motor | Real time active torque prediction | no | EMG, Angle Sensors |
| [33] | CNN, | Flexion, Feeding return | Shoulder, Elbow | 12 | N/A | myoelectric control | yes | sEMG |
| [58] | (DNN) | Flexible | Hand, Elbow | 6 | Stepper | trajectory control | yes | motion signal |
| [46] | BPNN | Trajectory Tracking | Shoulder | 3 | N/A | N/A | N/A | BP Neural Network Input Sensors |
| [42] | (RBFNN) | Adaptive Assistance | Forearm | 7 | DC Motor | Task Performance-based Adaptive Velocity control | yes | Motion Capture, Velocity Sensor |
| [27] | CNN | Abduction, Resting | Shoulder | Multiple | Linear actuator | Closed Loop Control | no | EMG |
| [69] | LSTM | Flexion of Hand | Hand | 15 | Soft actuator embedded with optical fibre | Sliding mode control | yes | optical fiber curvature sensors |
| [47] | BPNN | Elbow flexion | Elbow | 7 | Pnematic Muscle | proportional myoelectric control | yes | Myoscan |
| [28] | CNN | Unilateral Hand Movement | Hand | 5 | servo moto gear | online hybrid control | yes | EEG |
| [48] | BPNN | Bilateral arm training | Elbow | 2 | cable-driven powered variable-stiffness device | real-time bilateral control processing | yes | sEMG |
| [37] | RBFNN | Rotation, Telescopic joint | Elbow | 3 | EC-max motor | RBF Neural network control system | no | potentiometer |
| Gaowei Zhang [35] | RBFNN | Sagittal Flexion, Rotation | Forearm | 3 | Brushless Servo motor | Sliding Mode Control | yes | VICON Motion capture system |
| [77] | Multi-Layer NN | Ulnar and Radial Deviation | Wrist, Forearm | N/A | N/A | Impedance Control, PID Control | yes | Torque, Encoder |
| [57] | DNN | Flexion/extension | Elbow | 2 | Electromechanical actuators | Adaptive control | Yes | Position sensors and force sensors |
| [52] | Fuzzy NN | abduction/adduction, flexion/extension, internal/external rotation | Elbow, Wrists, shoulder | 5 | N/A | sliding mode control | yes | Position sensors |
| [53] | Fuzzy NN | Flexion and extension | Shoulder, elbow, and wrist | 5 | N/A | Sliding mode control | yes | position sensors |
| [66] | ANN | flexion/extension, radial/ulnar deviation | Shoulder, elbow, and wrist | 7 | N/A | sliding mode control | yes | Position and force sensors |
| [29] | CNN | flexion/extension, pronation/supination | Elbow, Wrists | 3 | N/A | sEMG-based control | no | Surface electromyography (sEMG) sensors |
| [71] | (SVNN) | Flexion and extension | Elbow, wrist, and hand | 6 | Servo motors | EMG-based control | yes | Surface electromyography (sEMG) sensors |
| [67] | ANN | Flexion/extension | shoulder, elbow, and wrist | 7 | Electromechanical actuators | neural network sliding mode control | yes | Position and force sensors |
| [38] | RBFNN | Flexion and extension | Elbow | 1 | N/A | Torque control | yes | Angle, sEMG, Encoder |
| [40] | RBFNN | Flexion/extension and rotation | Hand, Elbow, Shoulder | 7 | Servo Motor | Adaptive backstepping sliding mode control | yes | Rotary potentiometers |
| [79] | RBFNN | Flexion/extension | Hand, Elbow, Shoulder | 3 | Servo AC motors | Adaptive Admittance Control | yes | Laser displacement sensors, angular potentiometer |
| [25] | CNN | internal/external rotation, flexion/extension | shoulder, elbow, and forearm | 7 | Servo motor | Torque control mode and position control mode | yes | Position sensors, force/torque sensors, and rotary potentiometers |
| [36] | RBFNN | Flexion/extension | Elbow | 1 | Servo motors | Sliding mode control | no | Torque sensors and position sensors |
| [51] | Fuzzy NN | Flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, flexion/extensions | Hand, Shoulder, elbow | 3 | N/A | Impedance Control | yes | force and displacement sensors |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




