1. Introduction
The fitting of orthokeratology (OK) lenses has been growing in the clinical practice in recent years due to the rising cases of myopia. During 2023, 1% of worldwide fits were OK fits, this percentage being higher in Spain (4%) [
1]. OK offers a non-surgical alternative for vision correction, particularly for individuals with mild to moderate myopia or those seeking myopia management in children and adolescents. The main principle of OK involves reshaping the cornea by the hydraulic forces within the tear-lens pressure on the eye while sleeping [
2].
The changes in corneal curvature induced by the OK lenses wear create an optical zone or treatment zone (TZ) dependent on the magnitude of the refractive error to be corrected or the wearing time [
3,
4]. To achieve successful optical outcomes, the TZ should be centered on the cornea. The estimated displacement between the pupil center and the nominal TZ center indicates lens fitting decentration. The decentration of OK lenses is a prevalent and inevitable occurrence even when fitted optimally. The complications resulting from lens decentration lead to a reduction in contrast sensitivity, causing symptoms such as halos, glare, and blurred vision [
5,
6].
Although the mechanism behind the decentration of OK lenses remains unclear, some studies have suggested that it is a multifactorial phenomenon [
6,
7,
8]. In the literature, it has been correlated with corneal astigmatism, considering different lens designs and material permeability [
3,
6,
9]. In the study of Yang et al [
8], a significant correlation was found between the magnitude of decentration, lens diameter, and corneal toricity, where smaller lens diameters and higher corneal toricity were associated with greater lens decentration. Another study further confirmed the relationship between lens decentration and corneal toricity [
7], showing that the magnitude of lens decentration in the moderate toricity group was twice as large as that in the low toricity group.
It has also been observed that, during overnight OK lens treatment, the majority of lenses decentered to the temporal and inferior quadrant of the cornea [
6,
8]. These authors suggested that corneal asymmetry might be the primary contributing factor to this phenomenon.
According to several studies, a high prevalence of astigmatism in children with myopia [
10,
11,
12,
13] has been reported. Therefore, a high proportion of corneal astigmatism patients have relative contraindications to traditional OK lens fitting because of remarkable lens decentration and poor visual quality. In response to this issue, toric or dual-axis ortho-k lenses have been developed; they have since demonstrated improved lens centration in patients with moderate to high corneal astigmatism [
14,
15,
16,
17].
Nevertheless, despite establishing a central position initially, toric lens wearers sometimes experience gradual lens decentration during follow-up visits. Diverse designs of the posterior surface may have distinct impacts on corneal reshaping. However, there is a lack of published papers measuring the decentration of two OK lens designs. Considering the impact of the OK decentration on the effectiveness and satisfaction with OK lenses, this study aimed to assess the decentration of two different designs of Corneal Refractive Therapy (CRT) lenses over a year.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
A prospective, randomized, and longitudinal study has been performed. The study was conducted in compliance with good clinical practice guidelines and the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics committee of the Hospital Clinico San Carlos (Madrid, Spain). Before beginning the study, the risks and benefits of the treatment were explained, and informed consent was obtained from all subjects (and their parents or guardians).
The study had a duration of 12 months from the beginning of the treatment. The visits were categorized as follows: baseline measurements before initiating the treatment (PRE-OK), which provided data for assessing the feasibility of OK lens wear. Follow-up visits occurred at 1 night (1N), 1 week (1W), 1 month (1M), 3 months (3M), 6 months (6M), and 12 months (12M) from the beginning of OK lens wear.
Inclusion criteria were myopia less than or equal to − 6.00 dioptres (D), astigmatism less than or equal to −2.50 D, and best spectacle-corrected visual acuity (VA) of 0.1 logMAR or better. No previous OK lens wearers were included in this study. Exclusion criteria were history of ocular disease and diabetes mellitus. Contact lens wearers were asked to stop wearing their contact lenses 1 week before the day of examination (PRE-OK).
2.2. OK Lens Fitting
All subjects were fitted with Corneal Refractive Therapy CRT™ contact lens (Paragon Vision Sciences, USA) in HDS 100 material (paflufocon D, Dk = 100 barrer) according to manufacturer fitting guidelines. When lenses were prescribed, instructions about the wearing schedule (to wear the lenses at least 6 h during the night), insertion, removal, and care system were given to the subjects. For lens insertion, single-dose artificial tears Lacrifresh ocu-dry (AVIZOR, Madrid, Spain) with a 0.20% of hyaluronic acid were used. For daily maintenance, the lenses were cleaned with Menicare Pure (Menicon, Nagoya, Japan), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The cleaning process was completed using the weekly disinfecting system Progent (Menicon, Nagoya, Japan). Each participant was also provided with written instructions.
The design for the initial lens for the right and left eyes of the patient was selected using a random calculation system with Microsoft Excel 2000. The variable 1 was assigned to the CRT™ standard design (STD), and variable 2 was assigned to the CRT™ Dual Axis design (DA). Changes in lens parameters and even in lens design, from STD to DA, were made based on fluorogram pattern and VA, especially if there was incomplete lens landing across the cornea (360°). The CRT™ lens features a sigmoidal design that replicates the curvature of the posterior surface on the anterior surface. It is divided into three zones: the base curve or optical zone (OZ), the Return Zone Depth (RZD), and the Landing Zone Angle (LZA). Furthermore, DA design lens has two meridians with different sagittal height to get better centering of the lens on toric corneas where the STD design may not achieve proper centering and treatment. In both designs, the central optical zone was spherical, with a fixed diameter of 6 mm and a base curve radius (BOZR) determined by the desired refractive change.
To calculate both STD and DA lenses, the value of the flattest corneal meridian (Kf) from Oculus Pentacam (pentacam.com/int) and the sphere value obtained from subjective refraction (without distometry or spherical equivalent) were selected from both eyes. These data were entered into a calculation table provided by the manufacturer. In the eye to be fitted with DA, the initial difference in the tear reservoir zone (RZD) was 25 microns.
2.3. Clinical Procedure
Subjects underwent a previous examination to assess ocular health and to exclude subjects with any contraindications in the OK lenses wear. All measurements were performed by the same experienced examiner (L.B.) at the same time each day for each subject in all visits. Measurements on the 1N were conducted between 8:00 and 10:00 am in the morning, within three hours after lens removal. Follow-up measurements were performed in the evening between 7:00 and 8:00 pm.
Refraction without cycloplegia, high and low uncorrected VA and best corrected VA, and corneal topography, were performed. The topographer was calibrated before the PRE-OK measurement and at least once more during the study. Best corrected VA were determined monocularly in photopic luminance conditions (85 cd/m2) using the ETDRS test form Chart Display VX24 (eng.visionix.ru/product/display-vx24/) with high contrast (100%) and low contrast (10%) letters at 4 m. At baseline and in the follow-up, all subjects underwent monocular testing their best correction and without correction.
2.4. Lens Centration Analysis
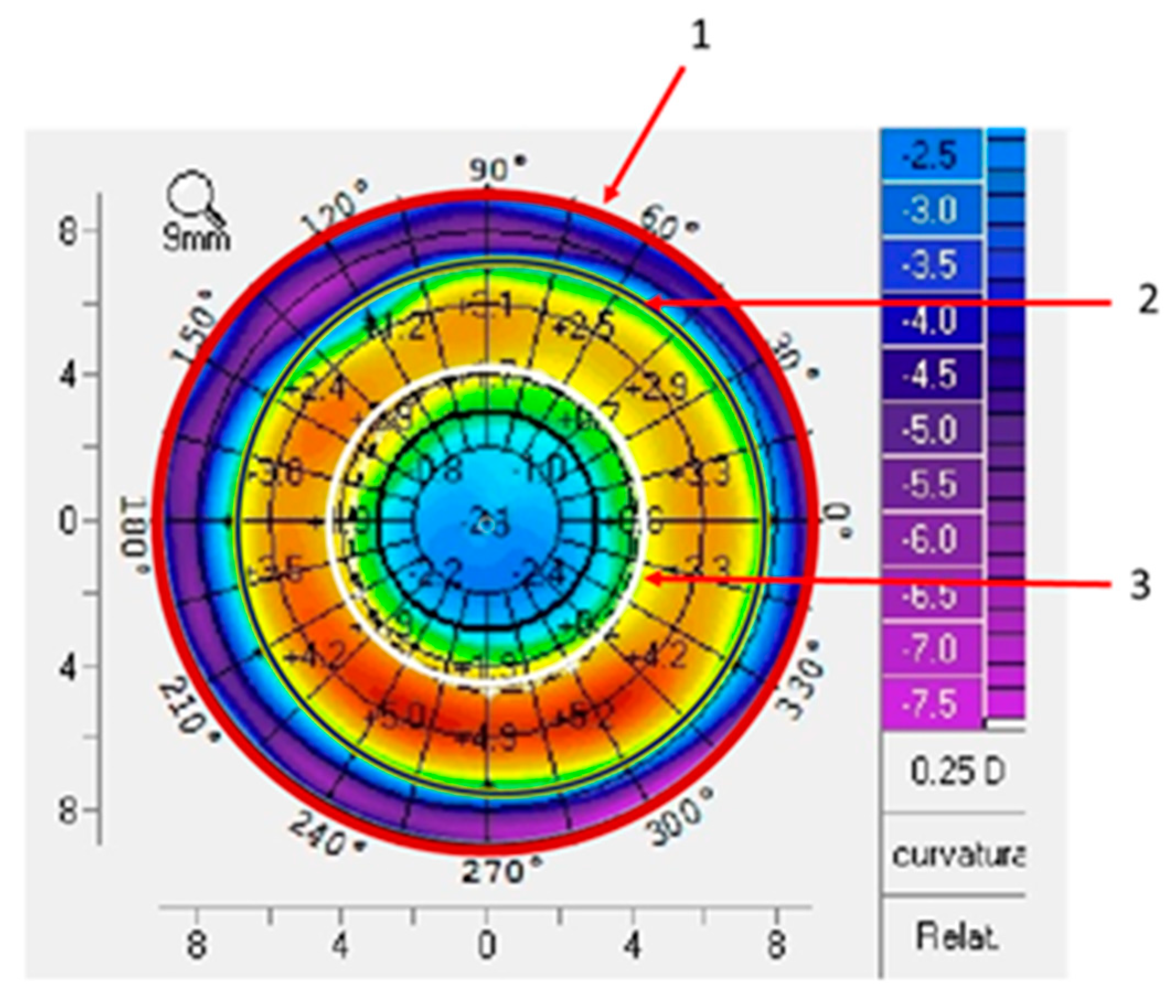
For lens centration measurement only one topography per eye was selected. A difference map was obtained by subtracting the PRE-OK lens tangential curvature map from the POST-OK lens tangential curvature map at each visit. Subjects with changes in lens parameters or lens replacement due to breakage were excluded. Three measurements were taken in each differential topography (visit - PRE-OK) for each visit and each eye, and the area to be measured was delimited by marking the four outermost Cartesian points of the topography (
Figure 1, circle 1). Then, twelve points corresponding to the reverse curve of the OK lens in the differential map were drawn around the ring (
Figure 1, circle 2); and eight points around the pupil diameter were drawn (
Figure 1, circle 3). Based on the literature [
6], the corneal optical TZ and the decentration distance of the OK lens were measured on the difference map using a MATLAB program. The TZ for each design was calculated with the comparative tangential topographic map, and it was plotted surrounding the central flattened area on which the power was zero on the difference map.
The marked points were loaded into Matlab 24 (MathWorks, Natick, MA), and analysed by using a programming code. Another blinded investigator, different from the clinician (J.B) was trained to perform the analysis. Three measurements of the horizontal and vertical decentration were calculated from the comparative tangential topographic map. The formulas used to calculate the centration were the following:
Horizontal decentration: X = mean value of the 3 measurements obtained from the distance from the center of the topography ring to the pupillary center.
Vertical decentration: Y = mean value of the 3 measurements obtained from distance from the center of the topography ring to the pupillary center.
Total decentration:
For the axis calculation it was considered:
If x and y > 0 ˚ axis was between 0 y 90˚
If x < 0 ˚, axis was + 90˚.
If x > 0 and y < 0, axis was + 180˚.
To standardize the results and maintain the coordinate system for both eyes, the transpose along the horizontal axis of the left eye was calculated.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Sample size calculations were performed with statistical software Granmo 6.0 (Institut Municipal d’Investigació Mèdica, Barcelona, Spain). The paired repeated-measures calculation tool was used, accepting an alpha risk of 0.05 and a statistical power of 80%. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS Statistics 23 software (IBM, Chicago, Illinois, USA) and Microsoft Office Excel (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA). Normal distribution of variables was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk normality test. The Wilcoxon test was used to compare changes in lens decentration across study visits. The Friedman test, followed by pairwise Wilcoxon signed-rank tests with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, evaluated changes in lens centration across visits for both lenses. Spearman’s rank correlation was employed to assess the relationship between decentration and uncorrected VA. Results are reported as means (standard deviations), and statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Study Sample and OK Lens Fitting
Sixty-four healthy subjects were recruited from the Optometry Clinic of the Faculty of Optics and Optometry (University Complutense of Madrid, Spain). However, for the study purposes, subjects who had undergone any changes in lens parameters after the 3M visit or replacement due to breakage were excluded. Changes in lens parameters were considered based on the fluorogram pattern and over-refraction, so that the patient achieved the best centration and VA with the lens. A lens was considered fitted if the patient slept with it on the first night. Thus, 30 subjects were included, of whom 3 had changes in both eyes at the 1M visit, while 3 had changes in only one eye. Additionally, at the 3M visit, one subject had changes in both lenses, and 3 subjects had changes in only one lens. Regarding the total eyes fitted with STD lens, there were not any changes in 62.30% of the lenses suggested by the calculation rule. For the DA design this percentage was 49.25%.
The number of STD lenses and DA lenses fitted according to the corneal astigmatism at the end of the study is presented in
Table 1.
Demographics, spherical equivalent and corneal parameters of the study sample during the baseline visit are presented in
Table 2.
3.2. Lens Centration Analysis
According to the total decentration formula, the value of total decentration and its orientation based on the visit and lens design is presented in
Table 3. No significant differences were found between OK designs in total decentration in each visit.
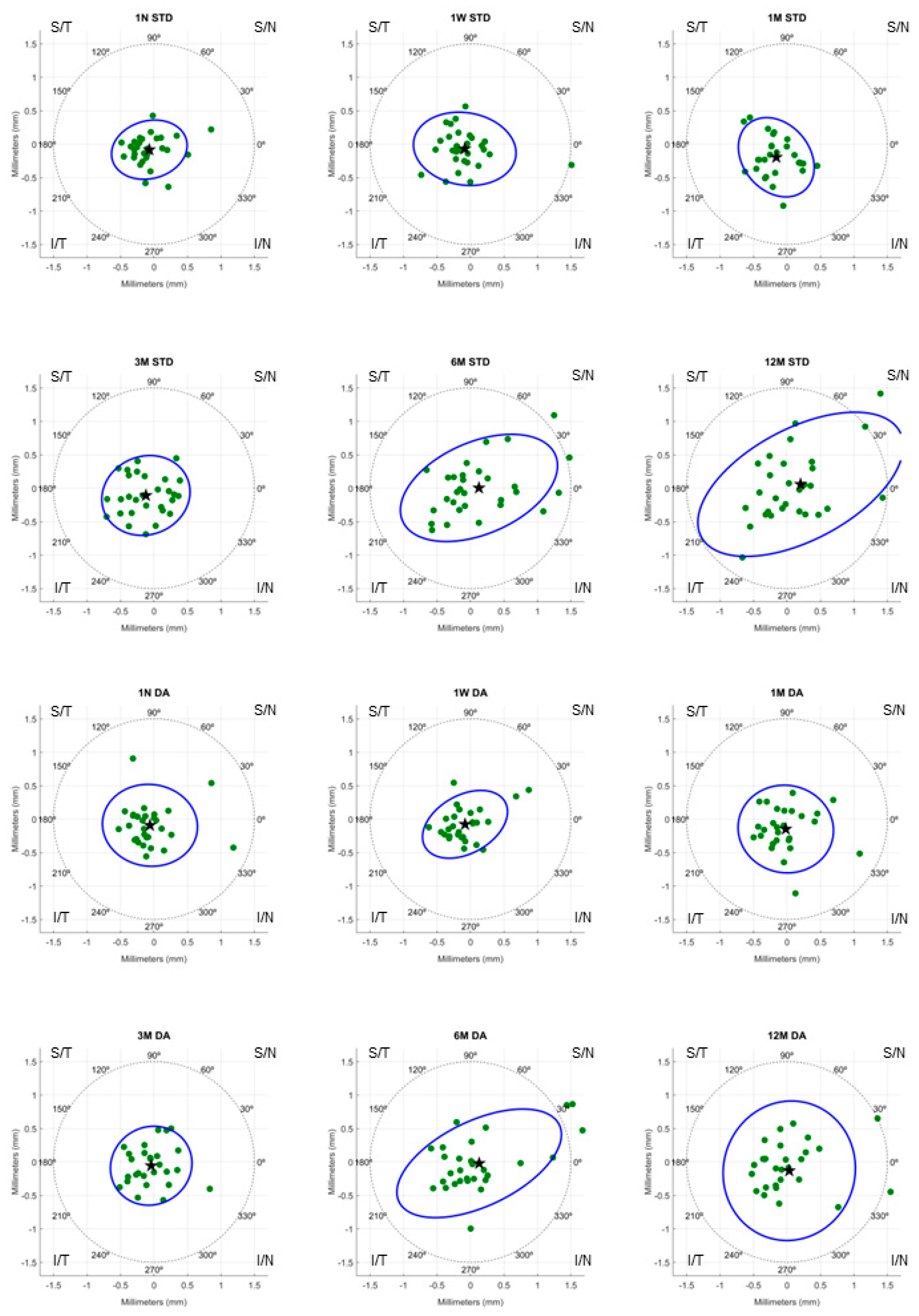
Figure 2 represents the decentration of STD and DA lenses design on a polar coordinate map. Each point represents the position of the vector (x. y) obtained from the corneal topography map. According to
Figure 2 and
Table 3, mean total decentration of both lens designs were inferotemporal.
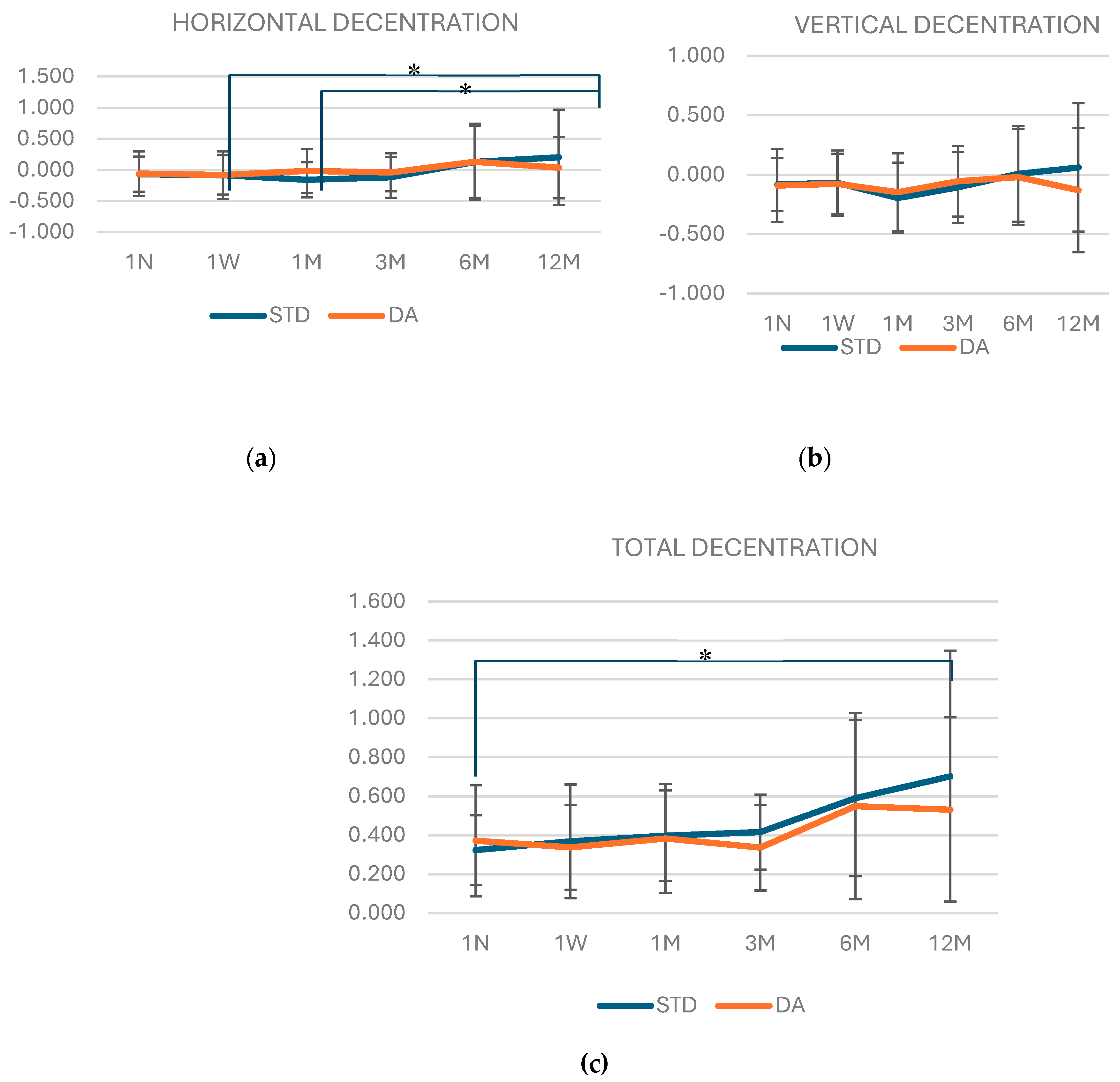
Figure 3 (A, B and C) shows the amount of horizontal, vertical and total decentration for both designs at each visit. No statistically significant differences (p>0.05) were found neither in the horizontal, vertical nor total decentration through the visits between lenses. However, in
Figure 3A, it can be observed that horizontal decentration of the STD design increased significantly in the last visit (12M) compared with the 1W and 1M visit of the study (p=0.017 and p=0.01, respectively). In addition, the total decentration (
Figure 3C) for STD design was significantly higher in 12M visit compared with 1N (p=0.014). However, no differences were found in vertical decentration for STD design. Meanwhile, decentration of DA design was constant through all the visits (p>0.05).
Uncorrected VA during the visits for both designs are presented in
Table 4. No differences were found in VA between lenses. In addition, Spearman correlation did not show any significant correlation between decentration and uncorrected VA for both designs in all visits (ρ<0.3; p>0.05).
4. Discussion
The decentration of OK lenses and their influential factors has long been a concern in clinical practice. It cannot be completely avoided, being the main cause of about 50% of the complications [
18]. It has been shown that nearly 0.5% of all the clinical OK wearers experiment OK decentration [
19]. The first month of OK treatment is critical for corneal reshaping, although achieving perfect centration may be challenging due to variations in corneal parameters and lens design [
20]. Recent studies indicate that both the size of the TZ and decentration increase significantly during this period, gradually stabilizing thereafter [
21,
22]. Then, the TZ decentration have shown smooth fluctuation up to 6M and a significant increase from 6 to 12 months [
21]. For this reason, changes in lens parameters during the first 3 months have been included in the analysis, as it is thereafter when changes in lens decentration begin to increase.
There are different methods for fitting OK lenses, ranging from empirical calculation and the use of a lens set to specific software provided by the manufacturer. For instance, in cases of high astigmatism, specific software is often used to assist the lens fitting. For this study, the success rate with the initial lens calculated by the calculation algorithm was moderate for both designs, 62.30% of subjects were fitted with the first lens suggested by the calculation rule. A similar percentage was found by Mika et al., which had about 60% success in fitting with the first empirically calculated lens [
23]. The fitting of the DA design allows adjustment in the periphery, improving molding when there are differences in corneal curvature (or elevation) of the principal meridians. Adjustment using the fluorogram allows the lens design to modify from spherical to toric design in cases where the lens does not properly land around the 360° corneal surface or remains off-center. González-Méijome and Villa-Collar [
24] analyzed the success rate of calculating the first STD lens provided by the manufacturer's nomogram. In 92% of the cases fitted, the final prescribed lens was achieved by changing two parameters or less, being the RZD value the parameter requiring the most changes.
Recently, Li et al [
25] published results evaluating the centration during OK lenses wear with a toric periphery compared to lenses with a spherical design. In that study, the magnitude of the off-centered TZ was significantly smaller when the patient was fitted with a toric design, concluding that this design improves the success of fitting, especially in cases of high elevation differences between meridians at 8 mm. Toric lens designs, with a toric optical zone but a periphery with different curvature or sagittal difference, are fitted to ensure complete lens support and centration. Additionally, several authors have demonstrated their effectiveness in reducing total refractive error, corneal astigmatism, and refractive astigmatism [
14,
26].
In 1999, Tsai and Lin [
27] established the classification for corneal refractive surgery, defining mild decentration as less than 0.5 mm, moderate decentration between 0.5 and 1.0 mm, and severe decentration as greater than 1.0 mm. This classification subsequently formed the foundation for the classification of TZ decentration in OK fitting. According to this classification, throughout the 12-month period of lens wear, both designs experienced a similar mild temporal-inferior decentration of less than 0.5 mm. The spherical design exhibited slightly greater horizontal decentration, which increased at the 12-month visit. This design also showed a progressive increase in the total decentration compared to 1 night of wear. However, the toric design was stable during all the study visits. The toric design of the midperipheral zone could make toric lenses more resistant to the gradual flattening of the central corneal curvature. Previous studies reported a similar inferotemporal decentration [
28], which was most commonly observed in patients with astigmatism wearing spherical lenses [
7,
29]. According to Chen et al, it was observed that temporal decentration, inferior decentration, and inferotemporal decentration accounted for 84.9%, 58.5% and 49.1% of all the fitted OK lenses, respectively [
19]. Temporal decentration resulted from the cornea's steeper temporal side compared to the nasal side, while vertical decentration was presumed to be a composite result of eyelid tension, lens design, and fitting technology [
6,
8]. Therefore, in ten eyes with corneal astigmatism less than 1 D, a toric design was fitted even though it is not typically indicated as the first choice. Fitting a design with low toricity in the periphery resulted in more stable centration from the beginning of treatment and consequently improved visual quality in children.
There are few studies evaluating TZ decentration over a one-year follow-up period. In the most recent study by Li et al. [
21], it was found that after 12 months of OK wear, 36.17% of participants experienced mild decentration, 53.19% had moderate decentration, and 10.64% had severe decentration. The mean decentration distance of the TZ in this study did not achieve moderate or severe decentrations and was smaller than that reported in other clinical studies [
21,
30]. This discrepancy may be attributed to the use of DA designs fitted even in low astigmatism.
Although decentration in OK lenses may be beneficial in controlling the progression of myopia, this decentration can also have a negative influence in uncorrected VA, increasing glare or ghosting [
18]. However, in this study no correlations were found between decentration and uncorrected VA. Moreover, uncorrected VA was not difference between OK lens designs along visits. This could be explained due all the decentration were considered mild.
The current study did not explore eyelid force as a potential factor affecting the alignment between the lens and the corneal surface. When fitting OK lenses, numerous factors, such as corneal parameters, lens design, and eyelid forces, should be considered. Further research is necessary to examine how the interplay of these factors could impact OK lens fitting. Another limitation of the present study is the reduced sample size, to ensure a proper measurement only subjects who had not undergone any changes in lens parameters after lens fitting or replacement due to breakage were included.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, total decentration in both lens designs, STD and DA, is similar throughout a year of follow up. Spheric design tends to decenter horizontally during the first 6 months meanwhile toric design achieves the maximum vertical decentration at the end of the year.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, L.B. and G.C.; methodology, L.B., J.B. and G.C.; software, J.B..; formal analysis, L.B. and C.A; investigation, L.B.; resources, L.B. and G.C.; data curation, L.B..; writing—original draft preparation, L.B. and C.A.; writing—review and editing, L.B., C.A. and G.C.; supervision, G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
CA-A was supported by the “European Union – Next Generation.”
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Hospital Clinico San Carlos (Madrid, Spain).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to Ana Privado for her invaluable contribution in generating the MATLAB code used in this study for calculating OK lens decentration.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Contact Lens Spectrum | PentaVision [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 24]. Available from: https://clspectrum.com/issues/2024/januaryfebruary/international-contact-lens-prescribing-in-2023/.
- Wang J, Fonn D, Simpson TL, Sorbara L, Kort R, Jones L. Topographical Thickness of the Epithelium and Total Cornea after Overnight Wear of Reverse-Geometry Rigid Contact Lenses for Myopia Reduction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:4742–6. [CrossRef]
- Lu F, Simpson T, Sorbara L, Fonn D. The relationship between the treatment zone diameter and visual, optical and subjective performance in Corneal Refractive TherapyTM lens wearers1. Ophthalmic and Physiological Optics. 2007;27:568–78. [CrossRef]
- Carracedo G, Espinosa-Vidal TM, Martínez-Alberquilla I, Batres L. The Topographical Effect of Optical Zone Diameter in Orthokeratology Contact Lenses in High Myopes. J Ophthalmol. 2019;1082472. [CrossRef]
- Liu G, Chen Z, Xue F, Li J, Tian M, Zhou X, et al. Effects of Myopic Orthokeratology on Visual Performance and Optical Quality. Eye Contact Lens. 2018;44:316–21. [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka T, Mihashi T, Okamoto C, Okamoto F, Hirohara Y, Oshika T. Influence of induced decentered orthokeratology lens on ocular higher-order wavefront aberrations and contrast sensitivity function. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35:1918–26. [CrossRef]
- Maseedupally VK, Gifford P, Lum E, Naidu R, Sidawi D, Wang B, et al. Treatment Zone Decentration During Orthokeratology on Eyes with Corneal Toricity. Optom Vis Sci. 2016;93:1101–11. [CrossRef]
- Yang X, Zhong X, Gong X, Zeng J. Topographical evaluation of the decentration of orthokeratology lenses. Yan Ke Xue Bao. 2005;21:132–5.
- Lum E, Swarbrick HA. Lens Dk/t influences the clinical response in overnight orthokeratology. Optom Vis Sci. 2011;88:469–75. [CrossRef]
- Harvey EM, Dobson V, Miller JM, Schwiegerling J, Clifford-Donaldson CE, Green TK, et al. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism in Tohono O’odham Native American children 6 months to 8 years of age. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:4350–5. [CrossRef]
- McAlinden C, Lipson M. Orthokeratology and Contact Lens Quality of Life Questionnaire (OCL-QoL). Eye Contact Lens. 2018;44:279–85. [CrossRef]
- Shih YF, Hsiao CK, Tung YL, Lin LLK, Chen CJ, Hung PT. The Prevallence of Astigmatism in Taiwan Schoolchildren. Optometry and Vision Science. 2004;81:94–8. [CrossRef]
- Harvey EM, Dobson V, Clifford-Donaldson CE, Green TK, Messer DH, Miller JM. Prevalence of astigmatism in Native American infants and children. Optom Vis Sci. 2010;87:400–5. [CrossRef]
- Pauné J, Cardona G, Quevedo L. Toric double tear reservoir contact lens in orthokeratology for astigmatism. Eye Contact Lens. 2012;38:245–51. [CrossRef]
- Chen C, Cheung SW, Cho P. Myopia control using toric orthokeratology (TO-SEE study). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54:6510–7. [CrossRef]
- Jiang J, Lian L, Wang F, Zhou L, Zhang X, Song E. Comparison of Toric and Spherical Orthokeratology Lenses in Patients with Astigmatism. J Ophthalmol. 2019;4275269. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Chen YG. Comparison of myopia control between toric and spherical periphery design orthokeratology in myopic children with moderate-to-high corneal astigmatism. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018;11:650–5. [CrossRef]
- Chu M, Zhao Y, Hu P, Chen D, Yu Y, Ni H. Is Orthokeratology Treatment Zone Decentration Effective and Safe in Controlling Myopic Progression? Eye Contact Lens. 2023;49:147–51. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Huang W, Zhu R, Jiang J, Li Y. Influence of overnight orthokeratology lens fitting decentration on corneal topography reshaping. Eye and Vision. 2018;5:5. [CrossRef]
- Alharbi A, Swarbrick HA. The Effects of Overnight Orthokeratology Lens Wear on Corneal Thickness. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:2518–23. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Hu J, Li X, Tang J, Li Y, Wang K, et al. Long-term variations and influential factors of the treatment zone of wearing orthokeratology lenses. Contact Lens and Anterior Eye. 2023; 101867. [CrossRef]
- Gifford KL, Gifford P, Hendicott PL, Schmid KL. Stability of peripheral refraction changes in orthokeratology for myopia. Contact Lens and Anterior Eye. 2020;43:44–53. [CrossRef]
- Mika R, Morgan B, Cron M, Lotoczky J, Pole J. Safety and efficacy of overnight orthokeratology in myopic children. Optometry. 2007;78:225–31. [CrossRef]
- González-Méijome JM, Villa-Collar C. Nomogram, corneal topography, and final prescription relations for corneal refractive therapy. Optometry and Vision Science. 2007;84:59–64. [CrossRef]
- Li Z, Cui D, Long W, Hu Y, He L, Yang X. Predictive Role of Paracentral Corneal Toricity Using Elevation Data for Treatment Zone Decentration During Orthokeratology. Curr Eye Res. 2018;43:1083–9. [CrossRef]
- Chen CC, Cheung SW, Cho P. Toric orthokeratology for highly astigmatic children. Optom Vis Sci. 2012;89:849–55. [CrossRef]
- Tsai YY, Lin JM. Ablation centration after active eye-tracker-assisted photorefractive keratectomy and laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:28–34. [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka T, Okamoto F, Kaji Y, Oshika T. Optical Quality of the Cornea After Overnight Orthokeratology. Cornea. 2006;25:S59–63. [CrossRef]
- Chen Z, Xue F, Zhou J, Qu X, Zhou X. Prediction of Orthokeratology Lens Decentration with Corneal Elevation. Optom Vis Sci. 2017;94:903–7. [CrossRef]
- Wu GY, Lai XQ, Dai XD. Effect of decentration in controlling the development of myopia after orthokeratology. International Eye Science. 2018;18:188–91.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).