1. Introduction
Cirrhosis is increasing worldwide and stands as a significant contributor to mortality, primarily due to the increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in affected patients [
1]. Indeed, HCC is the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide and the fifth in Europe [
2,
3]. MRI is considered the gold standard for HCC diagnosis [
4]. The Liver Imaging Reporting & Data System (LI-RADS) algorithm permits definitive diagnosis of HCC without pathologic confirmation when applied in patients with cirrhosis [
5]; however, it remains subject to interpretation bias. This has sparked interest in developing AI based computer-assisted analysis for imaging examinations [
6]. Two prominent approaches, radiomics and deep learning (DL), are currently the most actively investigated techniques [
7,
8,
9]. These two techniques have demonstrated their utility in applications such as characterizing focal hepatic lesions, staging liver fibrosis, and identifying portal hypertension [
10]. They both have an exceptional potential in assisting radiologists by enabling earlier disease detection, more precise disease classification, and providing additional prognostic information to guide clinical management [
11].
Robust and reliable application of these techniques rely on automated image processing pipelines, where one of the early steps is to locate the liver an isolate it from surrounding organs, a process known as segmentation. More broadly, high-quality annotated datasets represent a critical bottleneck for radiomics features extraction and DL algorithms performance [
12,
13]. Annotation-related problems may be particularly relevant in the field of biomedical image analysis, where data are typically sparse, inter-reader variability is naturally high, labeling ambiguities occur and medical experts have their individual style of annotations [
14]. Segmentation of the regions of interest can be performed using three different approaches: manual, semi-automatic, and automatic. Manual segmentation is most reliable and has the advantage of higher accuracy, although it is time-consuming and subject to inter-reader variability [
15]. Automatic segmentation aims to automatically identify the regions of interest using computer algorithms and semi-automatic segmentation combines automated processes with manual corrections as needed [
16]. These last two methods offer the benefit of faster processing times. However, most proposed automated liver segmentation techniques have been developed using small datasets, limiting their ability to deliver consistent and generalizable performance on external datasets [
17,
18].
While numerous automated liver segmentation algorithms have been developed on CT [
19,
20,
21], fewer studies have focused on MRI liver segmentation. Several automatic MRI liver segmentation methods based on convolutional neural network have been proposed [
22,
23], but manual tracing is still regarded as the gold standard and remains essential for the advancement of automatic MRI liver segmentation algorithms [
24,
25]. Liver MRI segmentation presents significant challenge due to variation in size, respiratory motion, relative organ position and phase acquisition at different points in the respiratory cycle, which complicate the segmentation process [
26]. Additionally, fibrosis processes in liver cirrhosis can significantly alter the organ's morphology [
27]. Currently, there is no consensus on the method of liver segmentation for computer-assisted analysis, especially with MRI. However, labeling instructions and exemplary images have proved to be crucial to improve the quality of annotated datasets [
14]. Despite their apparent importance, earlier research revealed that labeling instructions are typically not provided [
28].
The purpose of this study is to establish an illustrative liver MRI segmentation protocol and evaluate its potential to enhance the quality of annotated datasets through assessment by two professional annotators.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
This retrospective single-center study included 20 patients (M/F: 15/5, mean age: 54 y.o.), selected from a pre-existing database of liver MRIs collected in a cohort of patients with chronic liver disease, who underwent extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media liver MRI, as previously published [
29]. Patient selection criteria were as follows: random selection of 10 patients with cirrhosis and 10 patients without cirrhosis, all of whom were part of the previously mentioned publication. In cases where liver MRI scans were affected by significant motion artifacts, another patient was randomly selected. The study was approved by the local Institutional Review Board (ID CER-VD 2020-00680), which waived the need for signed informed consent.
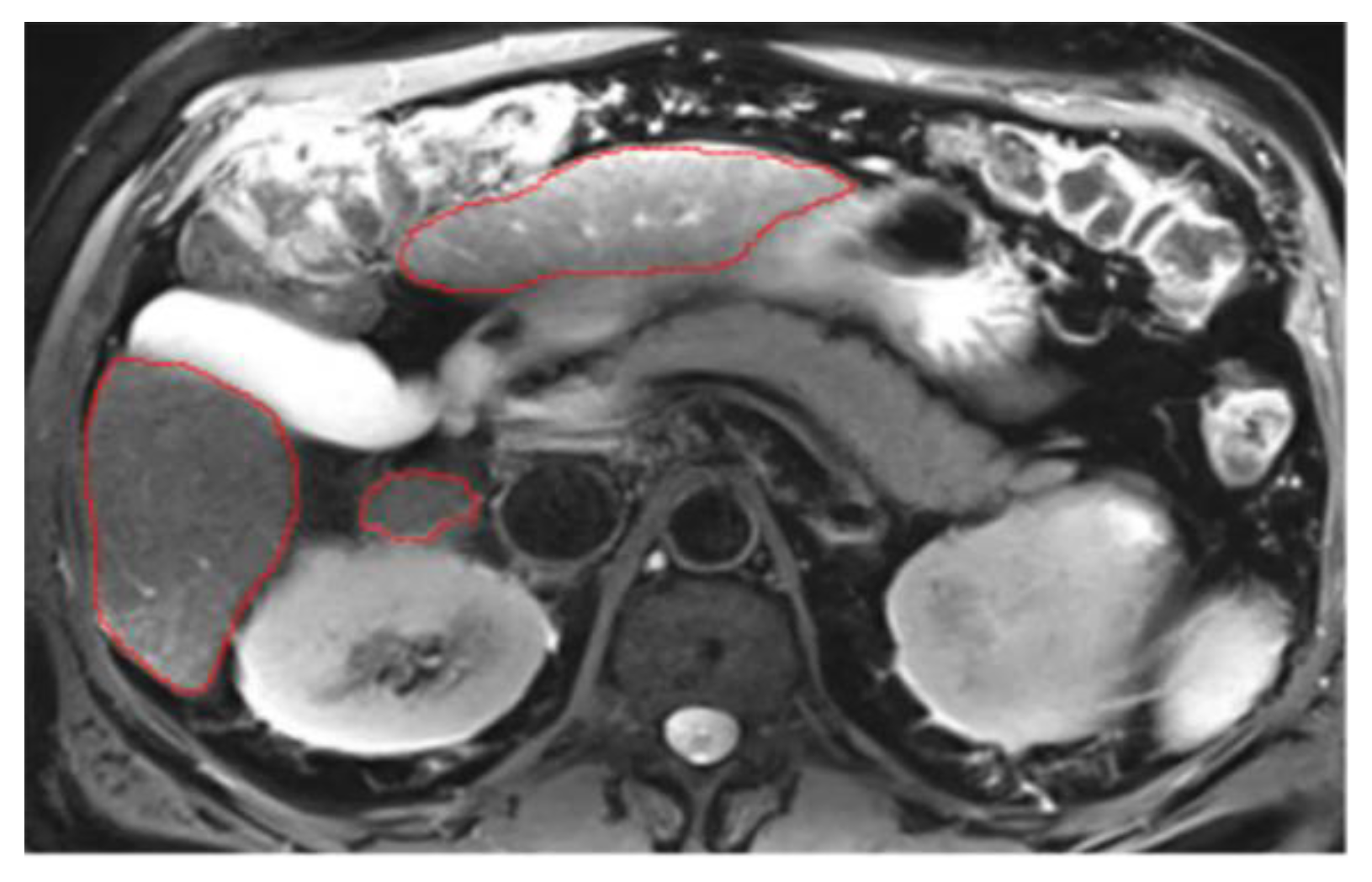
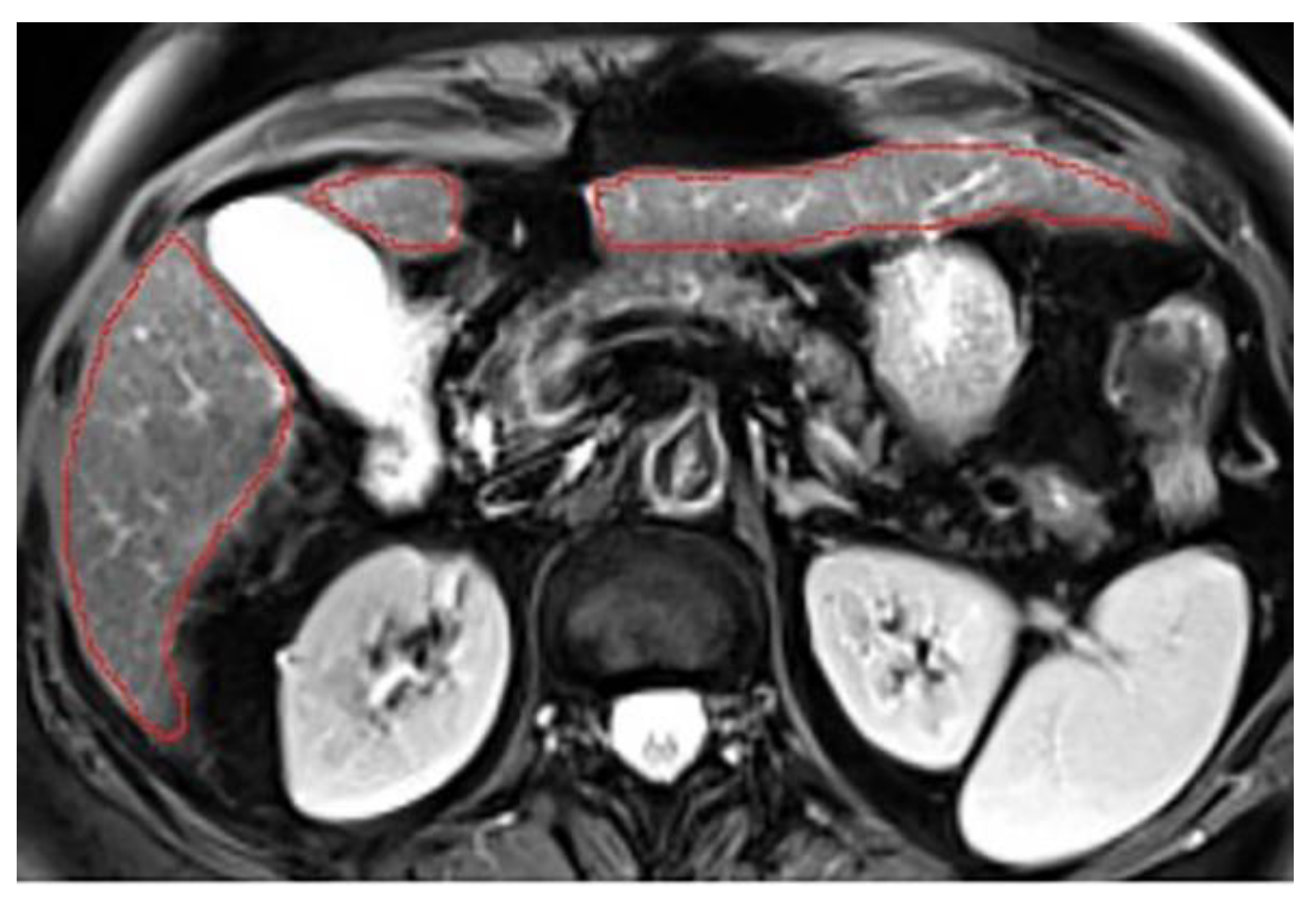
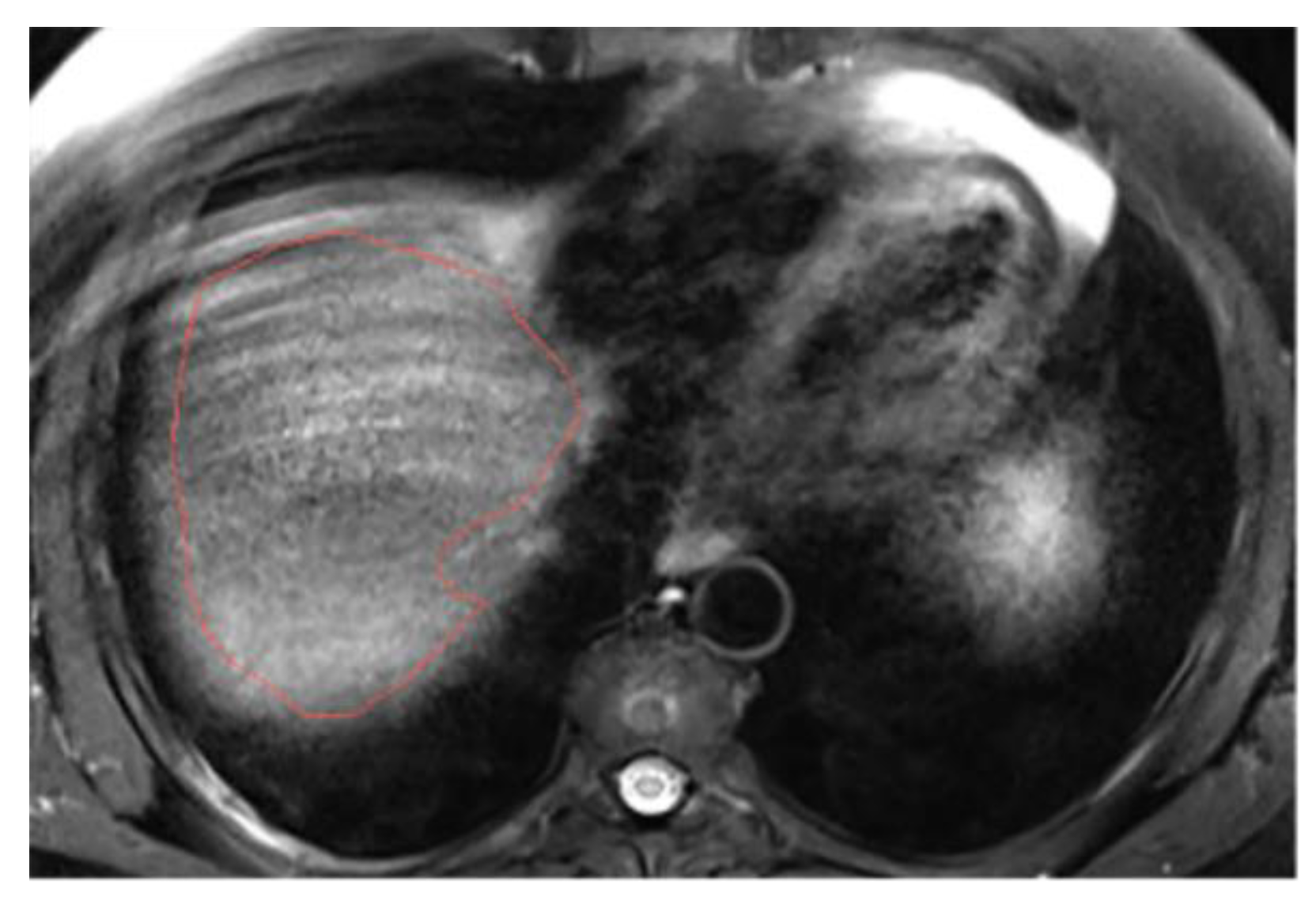
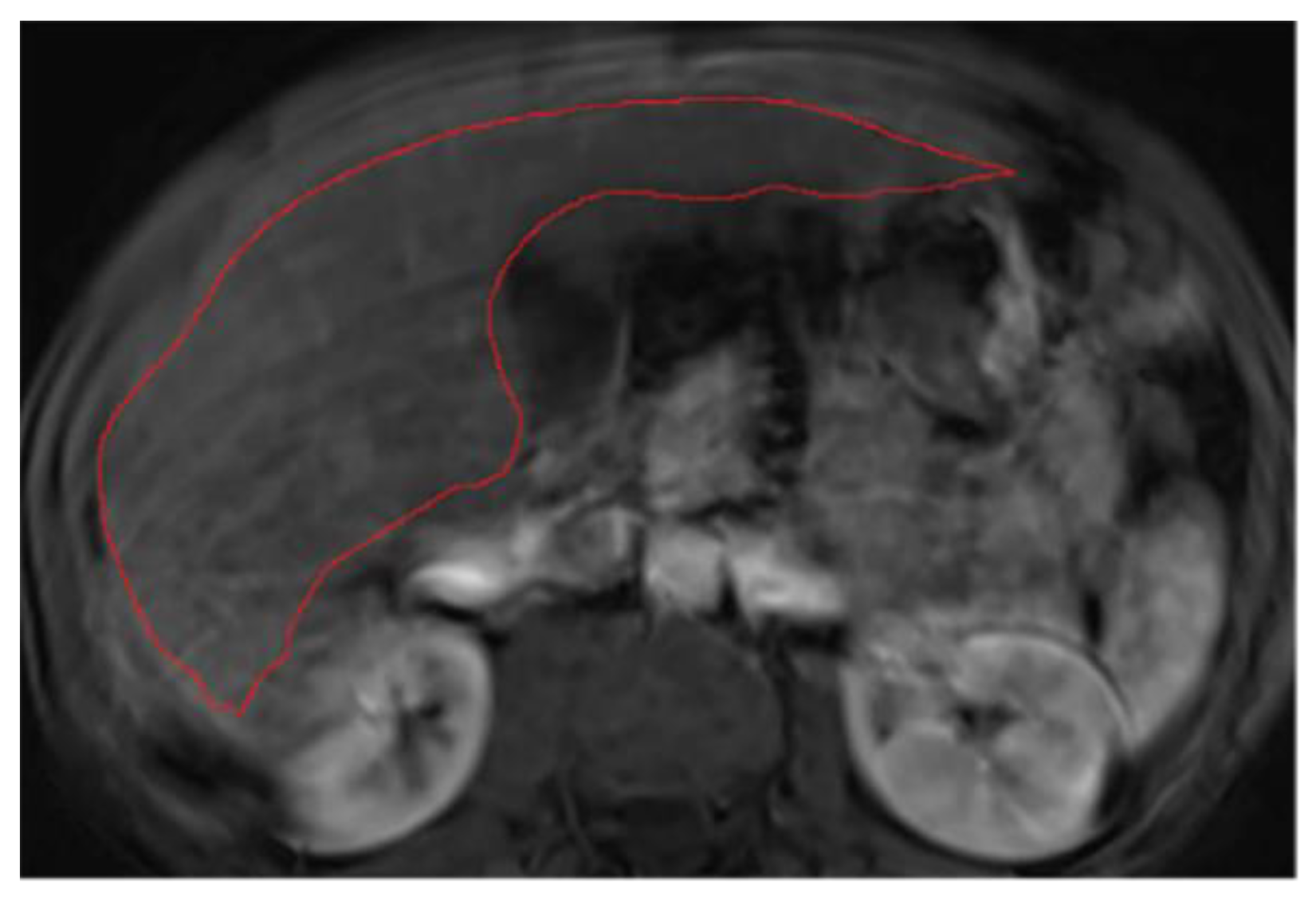
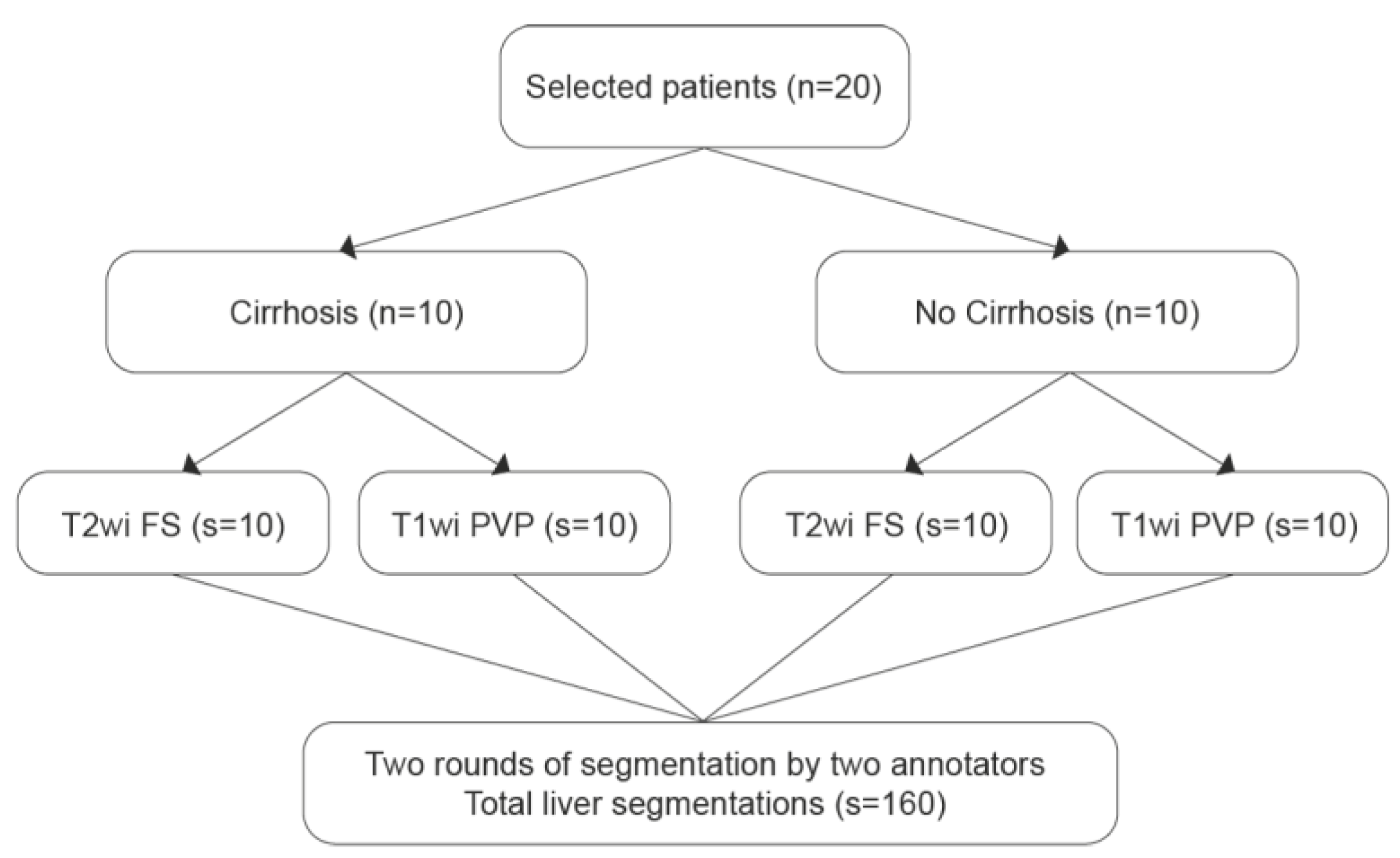
2.2. Liver Segmentations and Protocol
All liver MRIs were conducted using a 3-T MRI system (Magnetom Skyra, Siemens Healthineers) with a standard liver-dedicated protocol. Segmentations were performed on T2wi Fat Saturated (FS) and T1wi at the portal venous phase. Liver segmentations were done manually using the medical software Mint Lesion™ (version 3.9.1), by two annotators: a radiologist in training (P.J.) and a radiology technician (L.F.M.). Two rounds of segmentation were conducted. On the first round, minimal instructions were provided to the annotators. After reviewing the inter-reader discrepancies observed in this round, the team, which included two radiologists expert in abdominal imaging (C.D. and N.V.V.) and a radiologist specialized in radiomics data extraction process (M.J.), established a segmentation protocol to standardize the process and enhance consistency between annotators. The second round was performed on the same liver MRIs dataset, adhering to the protocol. In order to avoid recall bias, the second round was performed at least six weeks after the first round. The segmentation process is illustrated in
Figure 1.
The segmentation protocol provides clear guidance for accurately segmenting the liver parenchyma, including the importance of appropriate windowing and magnification. It also details how to exclude extra-hepatic structures, such as the hepatic hilum, vessels, and ligaments. Finally, it provides recommendations in cases of multi-part liver, respiratory motion artifacts, and ascites. A detailed description of the liver segmentation protocol is provided in
Appendix A.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and the Hausdorff Distance (HD) were used to evaluate the inter-reader agreement pre- and post-protocol implementation on a per-volume (whole liver) and per-slice basis. Statistical significance was assessed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test to determine if median metrics were significantly improved with the protocol. Per-slice analysis was performed treating each slice as independent. A subgroup analysis was conducted to assess liver segmentation correlation for patients with and without cirrhosis. Additionally, inter-reader agreement in selecting slices at the extreme cranial or caudal positions of the liver was evaluated pre- and post-protocol and assessed with the McNemar test. The level of significance for these statistical tests was set to 0.05. The metrics were calculated using the Python package seg-metrics v1.1.3 [
30]. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was performed with SciPy v1.10.1 [
31] and the McNemar test utilized the library Statsmodels v0.13.5 [
32].
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
The majority of patients were Caucasian. The most frequent causes of liver disease were alcohol for patients with cirrhosis, and hepatitis B virus for patients without cirrhosis. Patient demographics and clinical characteristics are summarized in
Table 1.
3.2. Liver Segmentation Correlation
The per-volume inter-reader agreement evaluation exhibited a DSC improvement after protocol implementation from 0.944 ±0.013 to 0.957 ±0.008 on T2wi and from 0.953 ±0.011 to 0.957 ±0.009 on T1wi, both with a statistically significant difference (p<0.001 and p=0.03 on T2wi and T1wi, respectively). The HD reduced after protocol implementation from 24.47 ±13.01 to 19.94 ±5.38 on T2wi and from 21.85 ±11.15 to 16.40 ±5.68 on T1wi, with a statistically significant difference on T1wi (p=0.048) but not on T2wi (p=0.216).
On average, there were 38.9 ±2.8 slices per patient on T2wi and 78.8 ±8.5 slices on T1wi. The per-slice inter-reader agreement evaluation exhibited a DSC enhancement after protocol implementation from 0.885 ±0.208 to 0.924 ±0.134 on T2wi and from 0.918 ±0.145 to 0.925 ±0.125 on T1wi, both with a statistically significant difference (p<0.001 on T2wi and T1wi). The HD reduced after protocol implementation from 8.73 ±15.81 to 7.22 ±13.45 on T2wi and from 6.26 ±11.48 to 5.70 ±9.80 on T1wi, both with a statistically significant difference (p<0.001 and p=0.035 on T2wi and T1wi, respectively).
Liver segmentation correlation results are presented in
Table 2.
Additionally, the protocol implementation resulted in a reduction of the number of liver segmentations with a non-annotated slice by at least one annotator at the extreme cranial or caudal slice of the liver, reducing from 17/20 to 11/20 segmentations on T2wi and from 20/20 to 12/20 on T1wi, with a statistically significant difference on T1wi (p=0.036) but not on T2wi (p=0.168).
In the subgroup analysis (
Table 3), conducted to assess liver segmentation correlation for patients with and without cirrhosis, the protocol implementation showed equal improvement of the DSC for the metrics measured on T2wi for patients with and without cirrhosis, both with a statistically significant difference (p=0.002 for per-volume analysis and p<0.001 for per-slice analysis). The protocol implementation resulted in a DSC enhancement for the metrics measured on T1wi for patients with cirrhosis, with a statistically significant difference (p=0.012 for per-volume analysis and p<0.001 for per-slice analysis), but not for patients without cirrhosis (p=0.556 for per-volume analysis and p=0.82 for per-slice analysis).
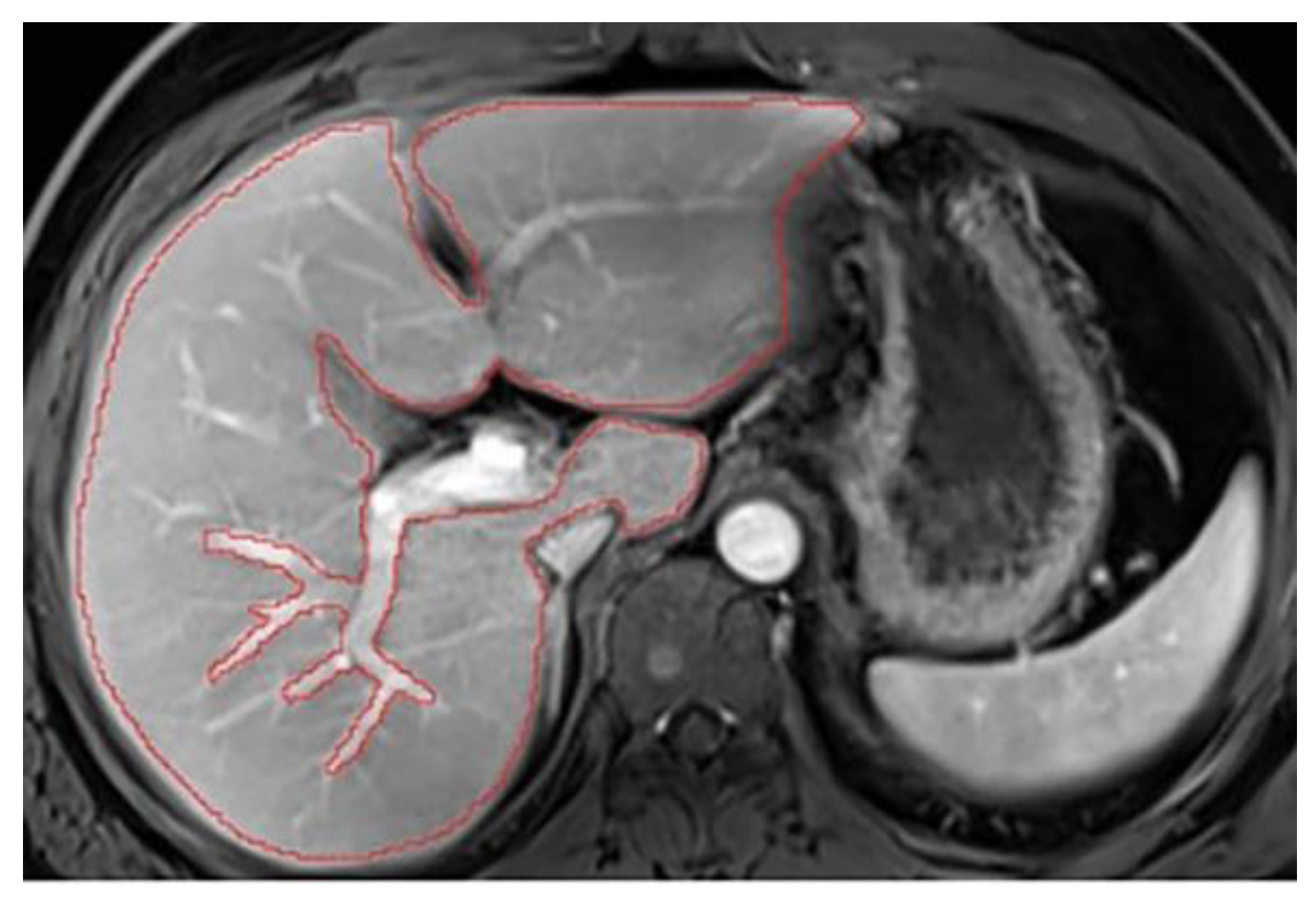
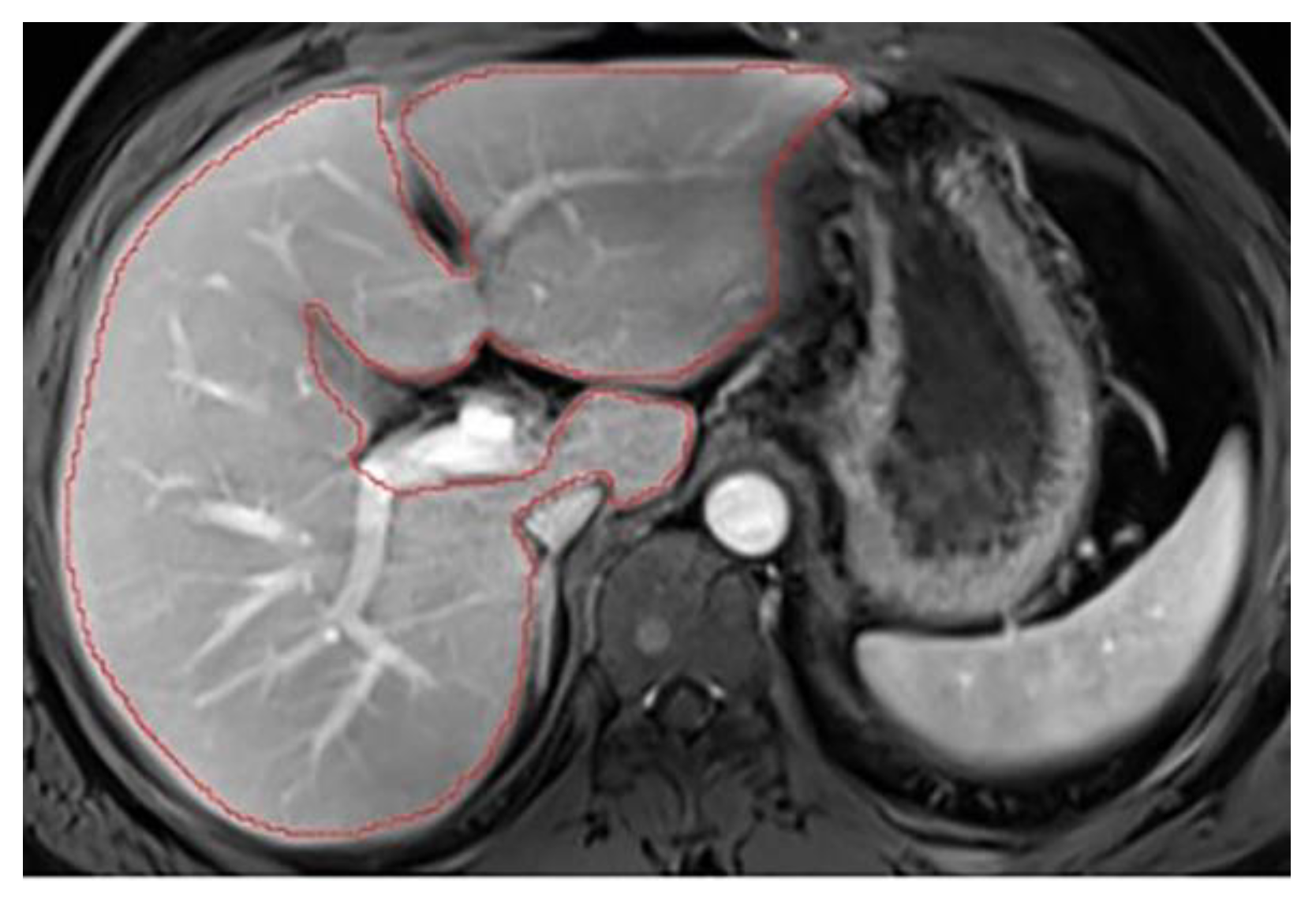
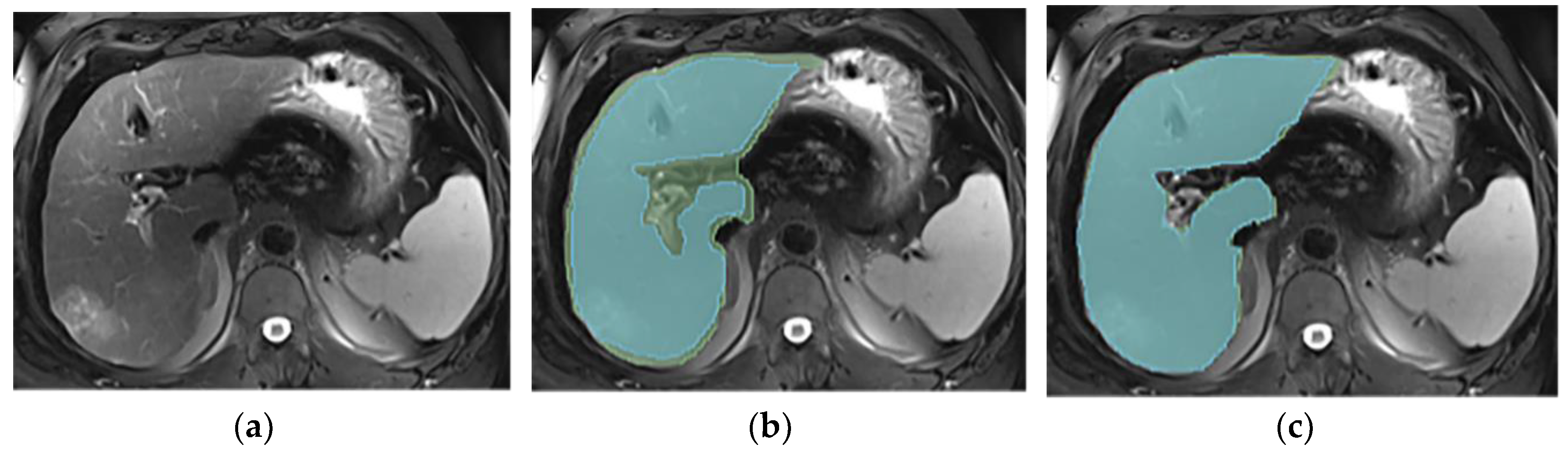
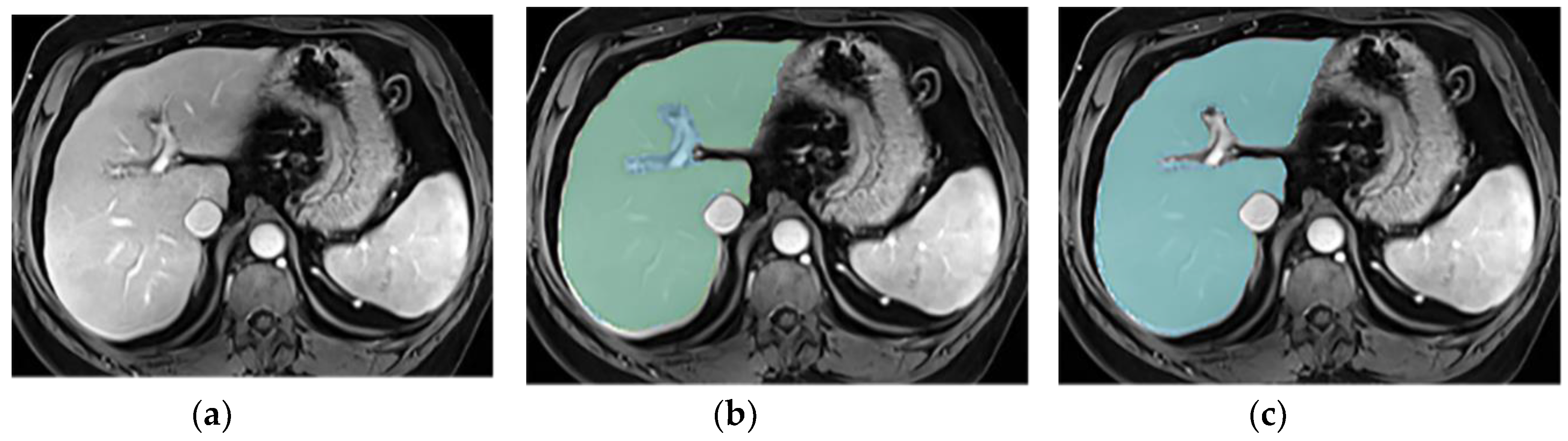
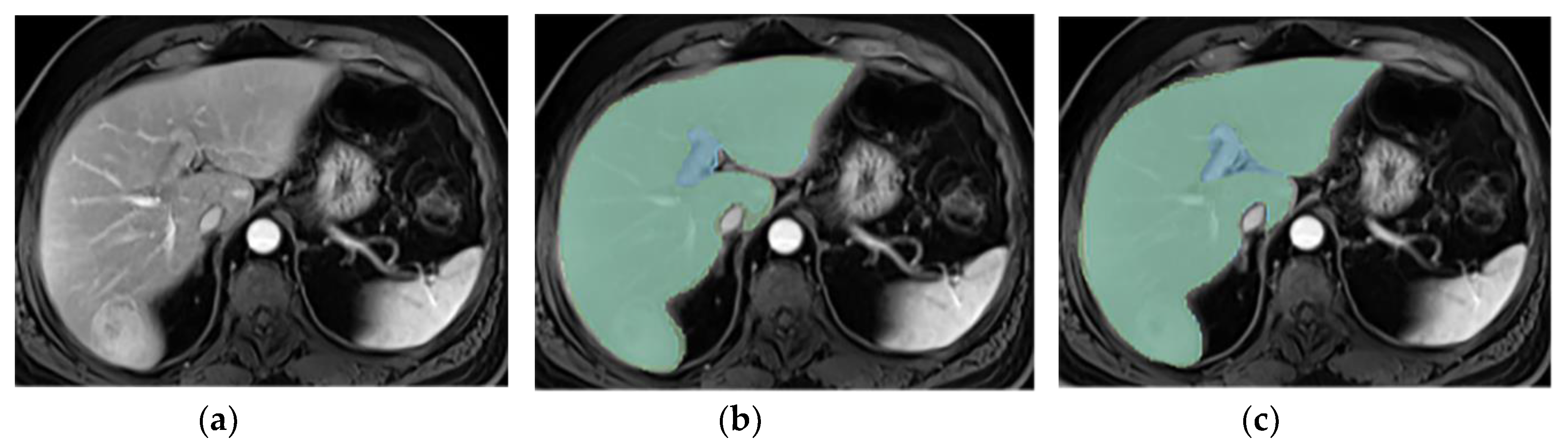
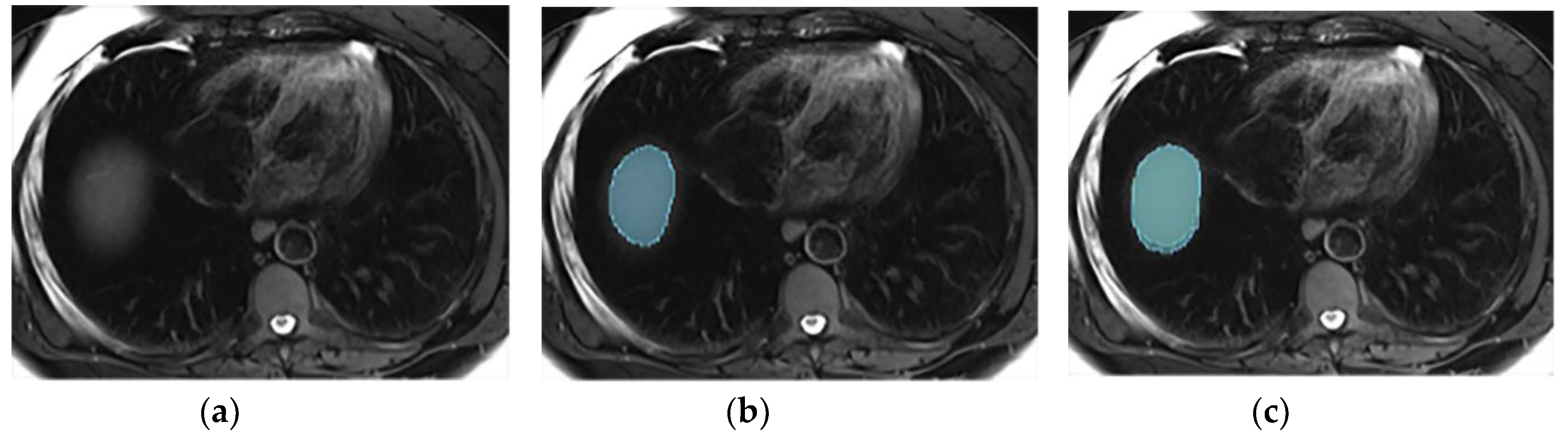
3.3. Annotations Comparison
This section illustrates the segmentation process, presenting MRI liver segmentation slices created by the annotators. Examples are provided in
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we established an illustrative liver MRI segmentation protocol that reduces inter-annotator variability and enhances the quality of annotated datasets. Annotation-related problems are particularly relevant in the field of biomedical image analysis, where labeling ambiguities occur, and medical experts have their individual style of annotations [
14]. During the creation of this segmentation protocol, we identified labeling ambiguities and pinpointed liver regions that are particularly challenging to label. Consequently, clear labeling instructions were provided to annotators, specifying actions such as excluding the hepatic hilum and identifying the vessels or ligaments to be segmented. Specifically regarding MRI, factors such as respiratory motion and phase acquisition at different points in the respiratory cycle significantly complicate the segmentation process. As detailed in the protocol, we elected to leave a larger margin at the edge of the hepatic contour to minimize the impact of these artifacts. Furthermore, chronic liver disease can markedly alter liver morphology and, in some cases, lead to the development of ascites. The protocol emphasizes the importance of windowing to delineate the hepatic contour and provides guidance for cases with ascites.
In the context of liver segmentation for pre-operative volumetry assessment, extreme precision is not warranted. Several semi-automatic and automatic liver segmentation models have been shown to yield acceptable measurements when compared to manual segmentation, as the total liver volume presents limited variation according to the technique used [
33,
34,
35]. Conversely, in the domain of radiomics and DL, high quality segmentation is critical, and manual tracing is still regarded as the gold standard [
24]. Indeed, as evidenced by Poirot
et al. in brain imaging, subtle variations in volume segmentation have a high impact on radiomics model robustness [
36]. Consequently, segmentation is one of the early steps that require improvement at the beginning of the radiomics and deep learning algorithm pipelines. When considering whole liver volume segmentation, precise segmentation of the liver parenchyma is essential to avoid incorporating adjacent tissue that might distort the extracted features. While the variation in radiomics features for HCC segmentation has been studied [
37,
38], to our knowledge, the impact of whole liver MRI segmentations on computer-assisted analysis has not yet been investigated. However, high-quality segmentation is a prior step that could reduce variation in advanced computer analysis, making this protocol a potential first solution.
The implementation of the protocol significantly enhanced the metrics measured on a per-volume basis, leading to an increase of the DSC on both T2wi and T1wi phases. This improvement indicates more consistent and robust annotations, reducing inter-reader variability. Similarly, the significant decrease of the HD suggests tighter delineations of the liver. The more pronounced reduction of the HD on T1wi compared to T2wi may be attributed to the T2wi slice thickness (6 mm), which was double the T1wi slice thickness (3 mm), thereby reducing discrepancies. The evaluation of these metrics on a per-slice basis revealed a significant improvement in both DSC and HD, confirming the enhanced consistency of the annotators in contouring the liver. The use of a protocol also significantly improved the consistency of the annotators in selecting the extreme cranial and caudal slices of the liver in T1wi. These metrics improvements are particularly relevant for advanced computer-assisted analysis. Finally, in the subgroup analysis, the implementation of the protocol showed higher correlation improvement in patients with cirrhosis compared with patients without cirrhosis. These findings highlight the importance of using a segmentation protocol in case of cirrhosis, where anatomical alterations due to fibrosis increase annotation variations.
In comparison to another study evaluating the inter-annotator agreement in liver segmentation on T1wi, the DSC we obtained before protocol implementation (0.953 ±0.013) was close to the reported DSC (0.95 ±0.01) [
39]. This study compared two board-certified abdominal radiologists while we compared a radiologist in training and a radiology technician. The initial inter-reader agreement in our study was further improved by the use of a segmentation protocol. This suggests that adopting such a protocol has the potential to reduce tasks requiring the expertise of specialized radiologist that could be replaced by junior radiologists or radiology technicians. This could facilitate the segmentation process, reducing the need for specialized radiologists for this task. The same was evidenced by Suman
et al., who evaluated the performance of trained radiology technicians in volumetric pancreas segmentation on CT using a standard operating procedure that included video and images materials, and demonstrated that trained radiology technician could achieve reasonable accuracy in pancreas [
40]. To our knowledge, the use of a liver segmentation protocol to train radiologists and radiology technicians in producing high-quality annotated datasets has not yet been explored. This approach could potentially accelerate the generation of datasets available.
As emerging noninvasive tools, radiomics and DL have shown promising performance in assisting radiologists [
41]. Despite the rapid growth of AI, its impact on daily clinical practice remains limited due to a lack of reproducibility across studies [
42]. To overcome this challenge, guidelines, standardization, and open access datasets are essential for improving robustness in radiomics features extraction and addressing the reproducibility issues in DL. Stanzione
et al. have proposed a CheckList for EvaluAtion of Radiomics research (CLEAR) as a standardization tool to facilitate the repeatability and reproducibility of radiomics studies [
43]. To our knowledge, no study has proposed a standardized protocol for accurate manual segmentation. Although Macdonald
et al. mentioned the use of a standard written protocol for their publicly available dataset of liver MRI segmentation, this protocol is only briefly mentioned and not provided in detail [
44].
The present study has limitations. The main limitation is the small size of the patient cohort, although 160 segmentations were performed. However, the cohort was intentionally designed to consider different liver morphotypes by including patients with and without cirrhosis. Despite the limited number of patients, we observed a positive impact attributed to the segmentation protocol. Additionally, not all MRI sequences have been segmented but only the most commonly used sequences for radiomics and DL analysis, including T2wi and T1wi at the portal venous phase. Finally, as the study was conducted in a single center on a European population, the findings may not generalize to other populations or to those imaged using different devices. Further studies are needed to evaluate the effect of the protocol on a larger-scale cohort and to assess its impact on advanced computer-assisted analysis, including radiomics features extraction.
5. Conclusions
Our study demonstrates the added value of implementing a standardized and illustrative protocol to enhance the robustness and reproducibility of liver segmentation. Moreover, this protocol could reduce the need of specialized radiologist in the annotation process, potentially accelerating the creation of annotated databases. Moving forward, segmentation protocols should be extended to other organs and lesions and incorporated into guidelines for radiomics and DL pipelines, thereby expanding the potential applications of AI in daily clinical practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.J.; methodology, P.J. and K.M.; software, K.M., M.J. and J.R.; validation, C.D., J.R. and N.V.V.; formal analysis, K.M, M.J. and J.R..; investigation, P.J. and K.M.; resources, P.J. and N.V.V.; data curation, P.J, K.M, M.J., L.F.M., R.G.; writing—original draft preparation, P.J. and K.M.; writing—review and editing, C.D., J.R. and N.V.V.; visualization, P.J. and K.M.; supervision, C.D.; project administration, P.J and N.V.V.; funding acquisition, N.V.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Swiss National Science Foundation, grant number: 320030_207944.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of CER-CD (ID CER-VD 2020-00680, date of approval: 20.04.2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to Institutional Review Board approval.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. MRI Liver Segmentation Protocol
The aim of liver segmentation is to accurately follow the contour of the liver parenchyma, excluding bulky ancillary structures such as the vena cava, gallbladder, hepatic hilum, and ligaments. The first step is to adjust the image display for optimal liver visualization. Two parameters are essential: windowing and magnification level. Before starting segmentation, it is necessary to scroll through the entire liver to define its boundaries and its relationships with adjacent organs (e.g. kidneys). Segmentation should then start from the upper section, at the level of the hepatic dome, and proceed towards the tip of the liver. To ensure uniformity, it is ideal to manually segment at least every other slice, staying as close to the periphery as possible, to avoid including structures that may move with the patient's breathing from one slice to the next. Additionally, each automatically segmented slice should be reviewed and corrected if necessary. Once the segmentation process is complete, it is necessary to scroll through the entire segmentation to ensure the contours are smooth and consistent. The final step is to display the volume on the coronal plane and verify its accuracy by following the contours. Key points to remember during segmentation are as follows:
1. Select appropriate windowing and magnification
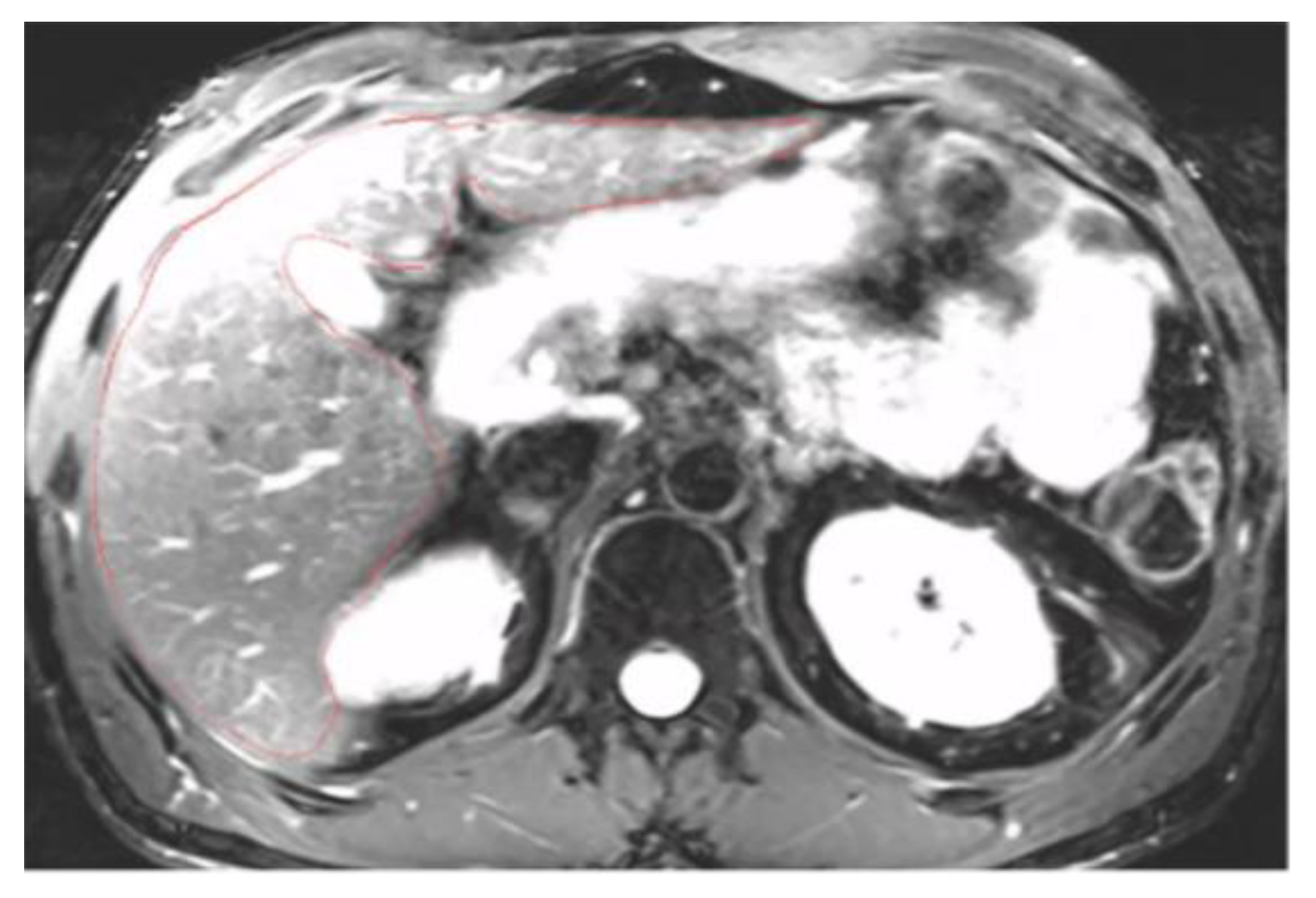
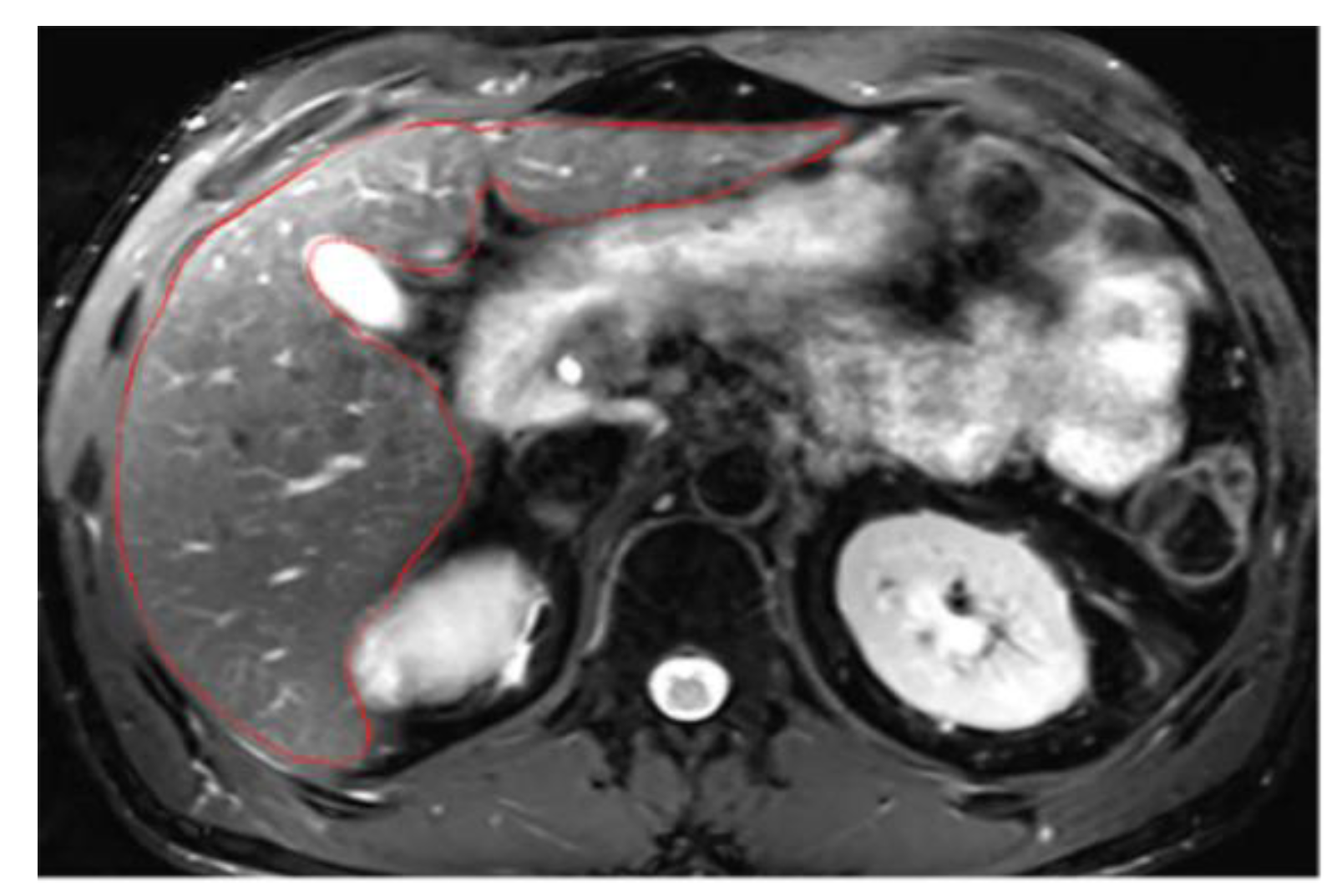
To accurately segment structures, the image display must be optimized for correct structure differentiation. Windowing may vary between patients depending on screen brightness and the examination itself. Over-saturated windows can obscure structures or reduce visibility at the liver’s periphery (
Figure A1). In this case, adjustments should be made to ensure the entire organ contour is clearly visible (
Figure A2). Windowing can also be modified during segmentation, but it is crucial to check the entire hepatic contour using the same windowing at the end of the segmentation. This helps to better highlight any irregular areas. In addition, the magnification must allow clear visualization of the liver contours.
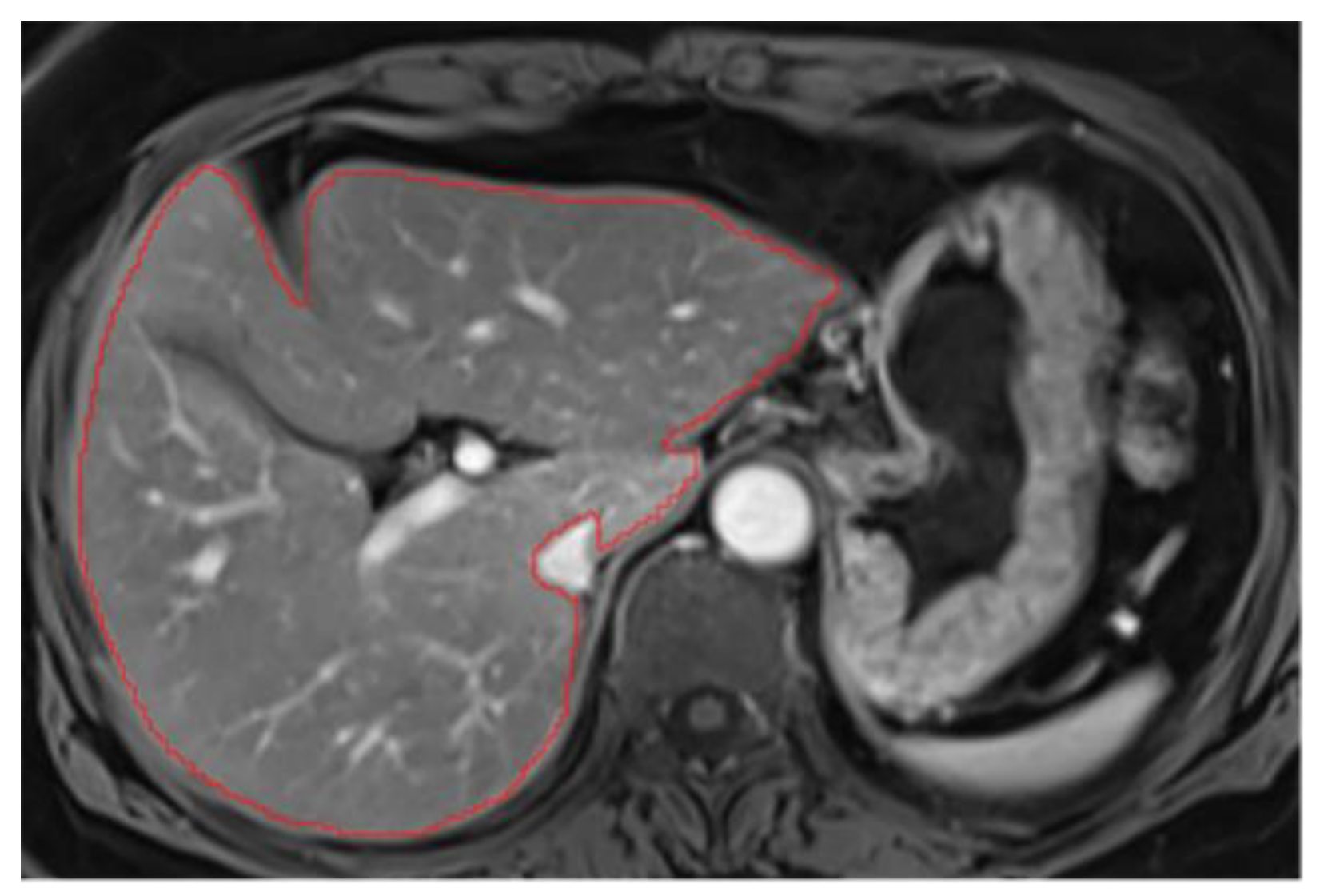
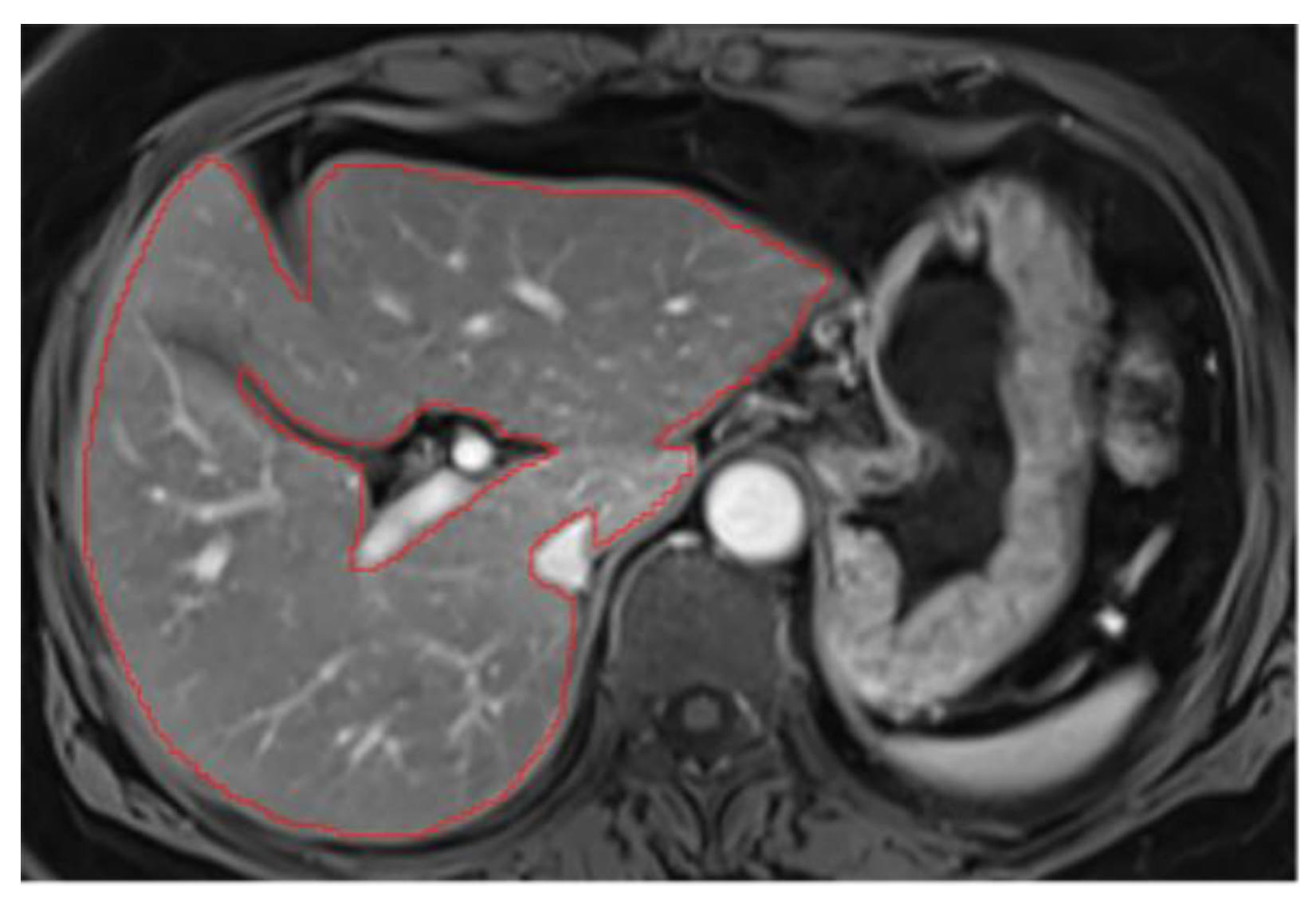
2. Hepatic hilum segmentation
Hepatic hilum can be excluded by carefully following the liver's contour, segmenting from the periphery. However, excluding the hilum often requires creating a "niche" (a small cavity in the liver parenchyma), since its inclusion could distort parenchymal measurements (
Figure A3). Therefore, even when the hilum is not directly connected to the liver's periphery, we recommend excluding it (
Figure A4).
3. Vascular segmentation
It would be too tedious to segment all the small vessels (
Figure A5). Instead, we prefer to segment only the vessels of the hepatic hilum and the inferior vena cava (
Figure A6). The goal is to maintain consistency in the results across all cases.
4. Ligaments segmentation
Two structures are systematically present and must be excluded from the segmented volume: the ligamentum venosum (
Figure A7) and the falciform ligament (
Figure A8). Since these structures differ in nature from the liver parenchyma, their inclusion could distort the analysis. It is crucial to ensure that both ligaments are excluded from the liver volume.
5. Multi-part liver parenchyma
When necessary, treat each part of the liver separately to avoid phantom connections that could integrate non-hepatic tissues. For such areas, it is preferable to perform segmentation on each slice manually, rather than using the extrapolation function (
Figure A9 and
Figure A10).
6. Presence of respiratory artifacts
Images often display artifacts related to the patient's breathing. To minimize the impact of these artifacts, it is preferable to leave a larger margin at the edges of the structure. For instance, in an image free of artifacts, we segment as close to the liver's periphery as possible. However, with respiratory motion artifact, there's a significant risk of including non-hepatic tissue in the segmented volume. Therefore, it is preferable to segment a few millimeters inside the periphery to ensure accuracy (
Figure A11 and
Figure A12).
However, in some cases, respiratory artifacts can be so severe that accurate segmentation becomes impossible (
Figure A13 and
Figure A14).
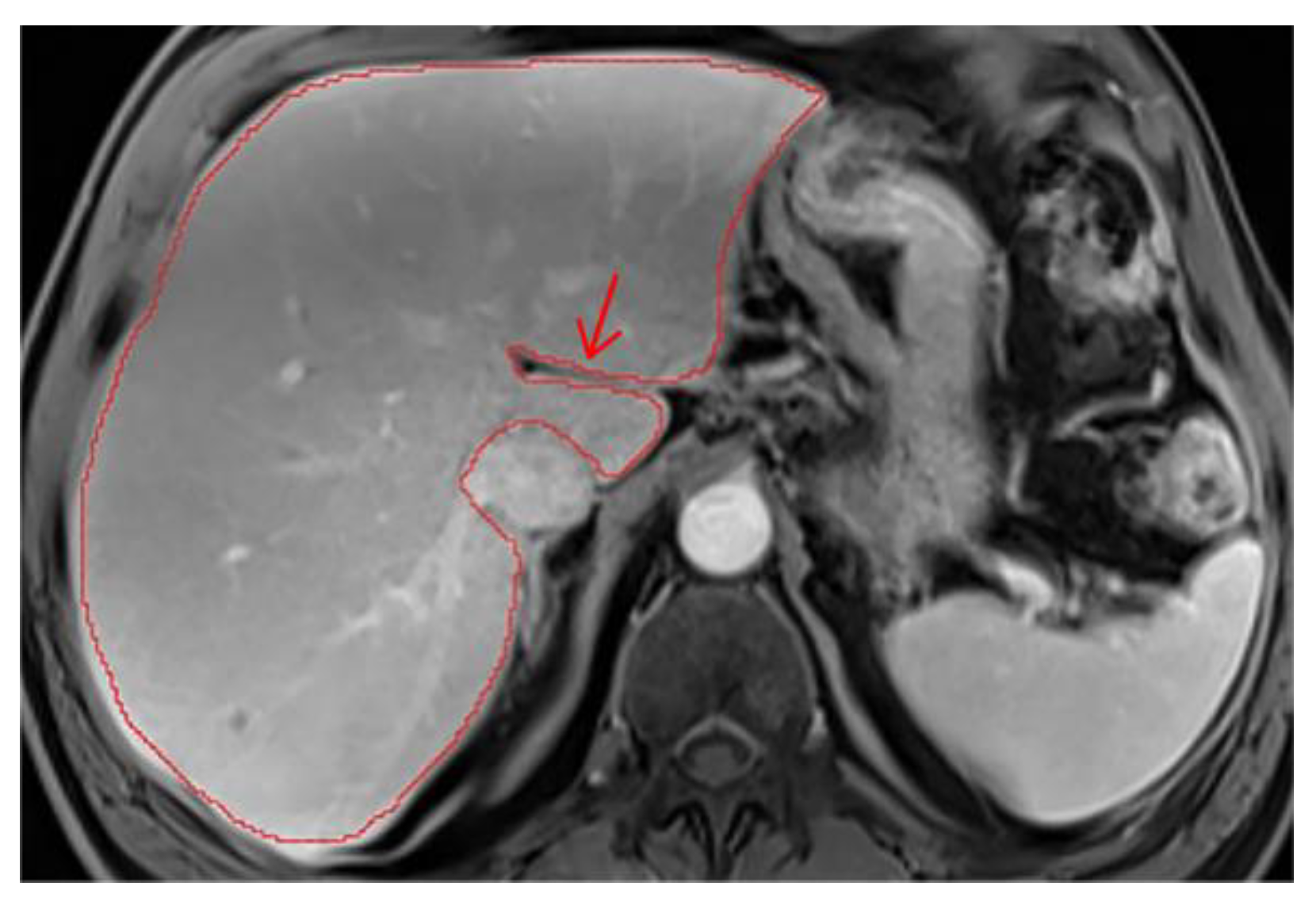
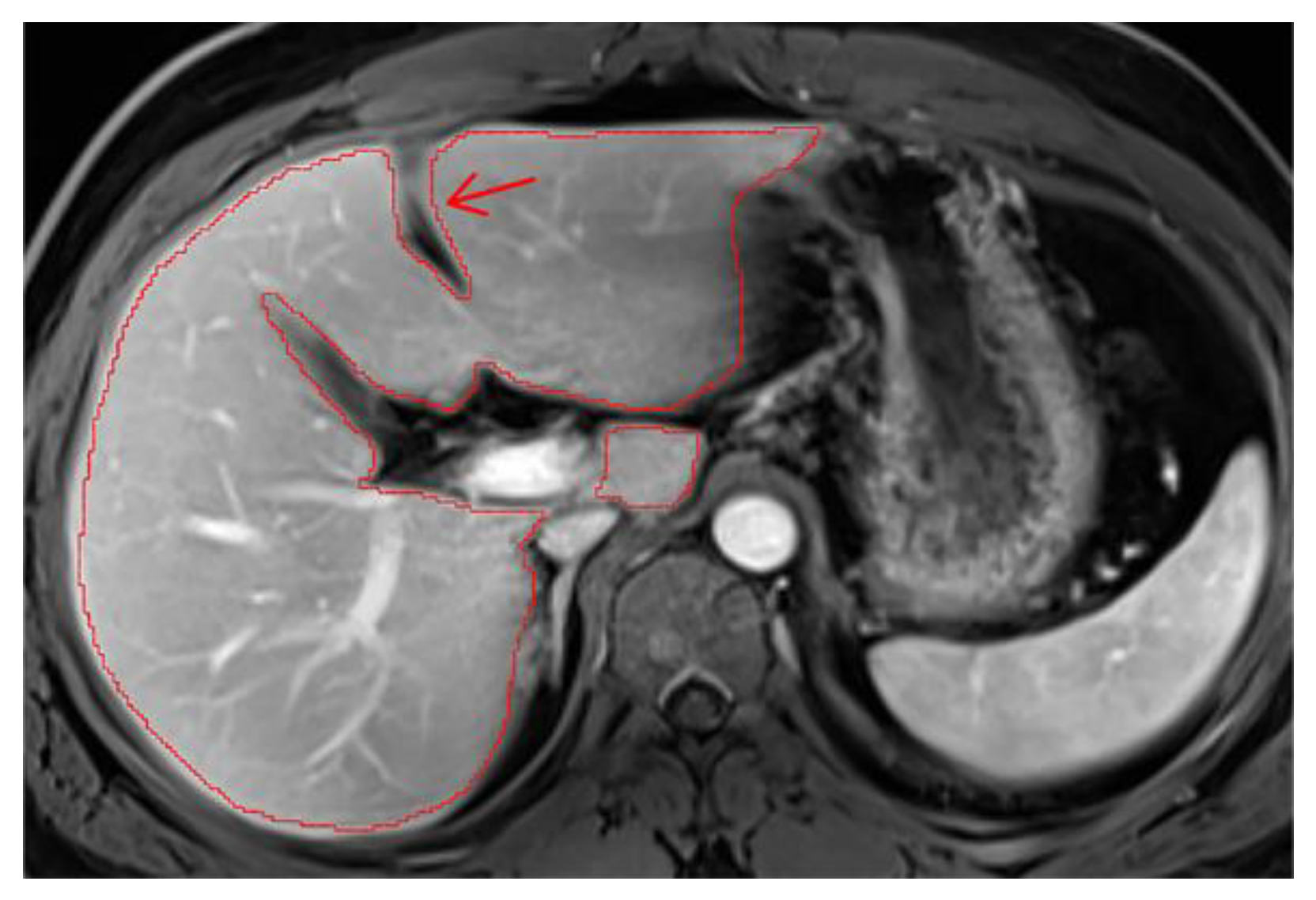
7. Ascites
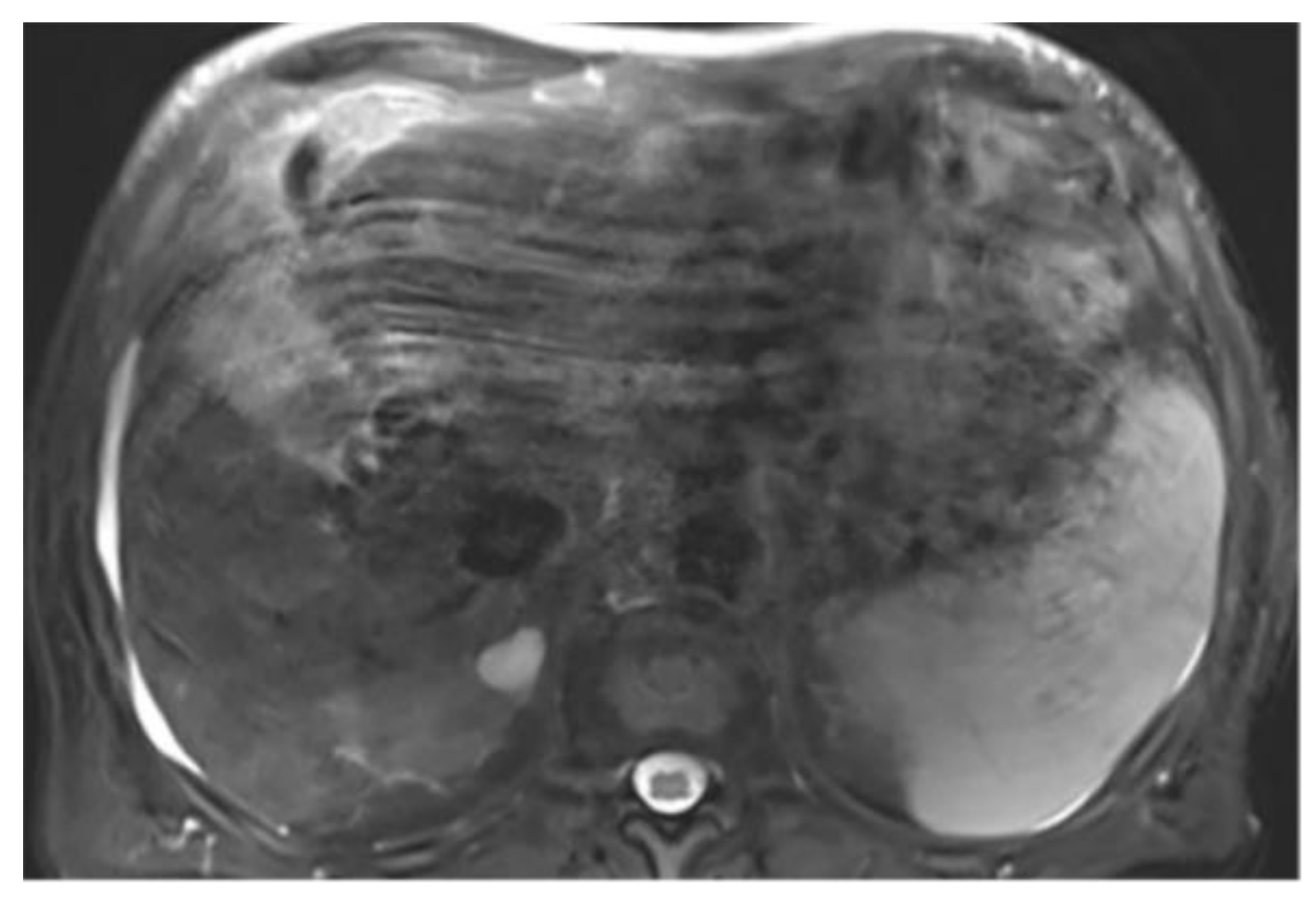
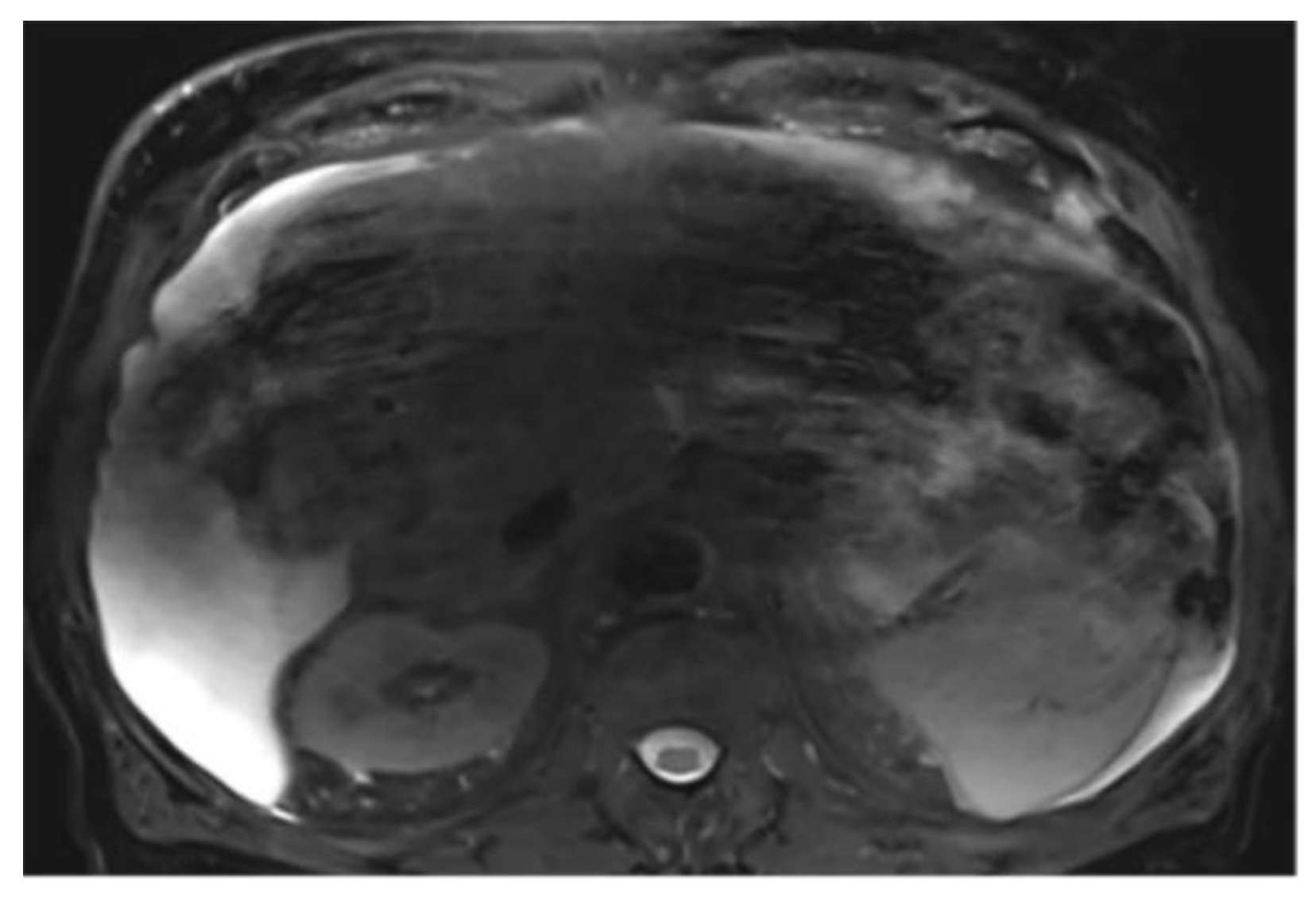
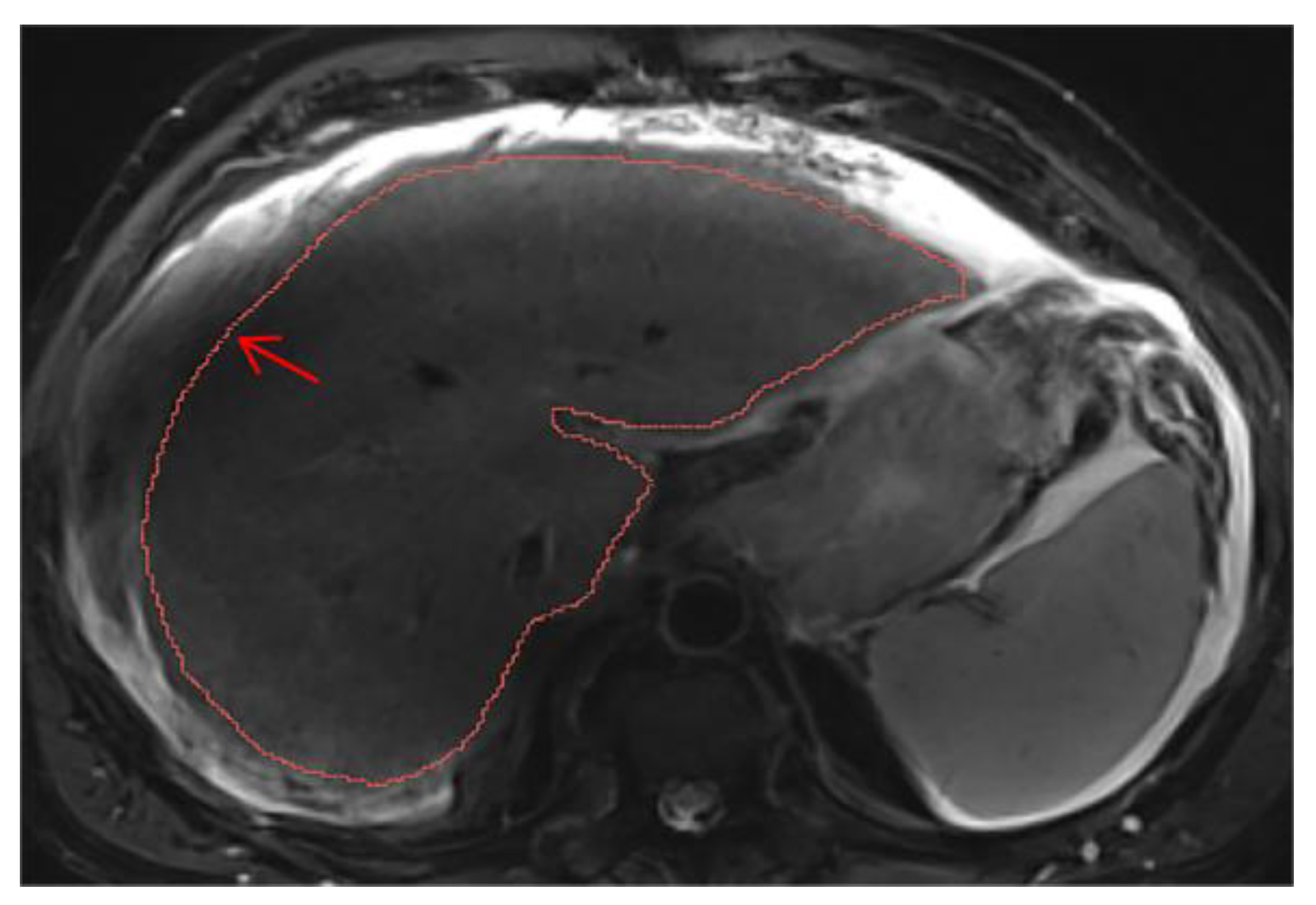
Cases with ascites require special attention, as liver contours can become difficult to delineate depending on contrast, magnification, and image type. It may be necessary to compare volumes across different phases for accurate segmentation. On T2wi imaging (
Figure A15), the anterior margins are sufficiently visible to initiate hepatic segmentation. However, ascites may appear heterogeneous, and in certain areas (red arrow), it could be mistakenly interpreted as liver parenchyma. On T1wi imaging at portal venous phase (
Figure A16), contrast provides clearer differentiation of hepatic contours, making it easier to discern the volume to be segmented. Comparing both image weights enables to confirm that the ascites surrounds the liver, allowing us to exclude unclear areas from the segmentation.
References
- B. Ryerson et al., « Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975-2012, featuring the increasing inci-dence of liver cancer: Report on Status of Cancer, 1975-2012 », Cancer, vol. 122, no 9, p. 1312-1337, mai 2016. [CrossRef]
- L. A. Torre, F. Bray, R. L. Siegel, J. Ferlay, J. Lortet-Tieulent, et A. Jemal, « Global cancer statistics, 2012: Global Can-cer Statistics, 2012 », CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, vol. 65, no 2, p. 87-108, mars 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. Ferlay et al., « Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers in 2018 », European Journal of Cancer, vol. 103, p. 356-387, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. S. Parra et al., « Advancements in the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma », IJTM, vol. 3, no 1, p. 51-65, janv. 2023. [CrossRef]
- V. Chernyak et al., « Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) Version 2018: Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in At-Risk Patients », Radiology, vol. 289, no 3, p. 816-830, déc. 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. A. Bluemke et al., « Assessing Radiology Research on Artificial Intelligence: A Brief Guide for Authors, Review-ers, and Readers—From the Radiology Editorial Board », Radiology, vol. 294, no 3, p. 487-489, mars 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. J. Park, B. Park, et S. S. Lee, « Radiomics and Deep Learning: Hepatic Applications », Korean J Radiol, vol. 21, no 4, p. 387, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Yao, Z. Ye, Y. Wei, H.-Y. Jiang, et B. Song, « Radiomics in hepatocellular carcinoma: A state-of-the-art review », WJGO, vol. 13, no 11, p. 1599-1615, nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, et G. Hinton, « Deep learning », Nature, vol. 521, no 7553, p. 436-444, mai 2015. [CrossRef]
- M. Gross et al., « Automated MRI liver segmentation for anatomical segmentation, liver volumetry, and the extrac-tion of radiomics », Eur Radiol, vol. 34, no 8, p. 5056-5065, janv. 2024. [CrossRef]
- L. C. Chu, S. Park, S. Kawamoto, A. L. Yuille, R. H. Hruban, et E. K. Fishman, « Current Status of Radiomics and Deep Learning in Liver Imaging », J Comput Assist Tomogr, vol. 45, no 3, p. 343-351, mai 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim et al., « Radiomics for precision medicine: Current challenges, future prospects, and the proposal of a new framework », Methods, vol. 188, p. 20-29, avr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Pavic et al., « Influence of inter-observer delineation variability on radiomics stability in different tumor sites », Acta Oncologica, vol. 57, no 8, p. 1070-1074, août 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. Rädsch et al., « Labelling instructions matter in biomedical image analysis », Nat Mach Intell, vol. 5, no 3, p. 273-283, mars 2023. [CrossRef]
- Gotra et al., « Liver segmentation: indications, techniques and future directions », Insights Imaging, vol. 8, no 4, p. 377-392, août 2017. [CrossRef]
- X.-Q. Gong et al., « Progress of MRI Radiomics in Hepatocellular Carcinoma », Front. Oncol., vol. 11, p. 698373, sept. 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Dockès, G. Varoquaux, et J.-B. Poline, « Preventing dataset shift from breaking machine-learning biomarkers », GigaScience, vol. 10, no 9, p. giab055, sept. 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Yu, B. Mohajer, et J. Eng, « External Validation of Deep Learning Algorithms for Radiologic Diagnosis: A Sys-tematic Review », Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, vol. 4, no 3, p. e210064, mai 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. Xu et al., « Efficient knowledge distillation for liver CT segmentation using growing assistant network », Phys. Med. Biol., vol. 66, no 23, p. 235005, déc. 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Jin, M. Wang, L. Xu, J. Lu, E. Song, et G. Ma, « Automatic 3D CT liver segmentation based on fast global minimi-zation of probabilistic active contour », Medical Physics, vol. 50, no 4, p. 2100-2120, avr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Senthilvelan et N. Jamshidi, « A pipeline for automated deep learning liver segmentation (PADLLS) from contrast enhanced CT exams », Sci Rep, vol. 12, no 1, p. 15794, sept. 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Wang et al., « Automated CT and MRI Liver Segmentation and Biometry Using a Generalized Convolutional Neural Network », Radiology: Artificial Intelligence, vol. 1, no 2, p. 180022, mars 2019. [CrossRef]
- F. López-Mir, V. Naranjo, J. Angulo, M. Alcañiz, et L. Luna, « Liver segmentation in MRI: A fully automatic method based on stochastic partitions », Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, vol. 114, no 1, p. 11-28, avr. 2014. [CrossRef]
- F. Quinton et al., « A Tumour and Liver Automatic Segmentation (ATLAS) Dataset on Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Hepatocellular Carcinoma », Data, vol. 8, no 5, p. 79, avr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Stanzione et al., « Oncologic Imaging and Radiomics: A Walkthrough Review of Methodological Challenges », Cancers, vol. 14, no 19, p. 4871, oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Y. Ansari et al., « Practical utility of liver segmentation methods in clinical surgeries and interventions », BMC Med Imaging, vol. 22, no 1, p. 97, mai 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Zuñiga-Aguilar et O. Ramírez-Fernández, « Fibrosis and hepatic regeneration mechanism », Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol, vol. 7, p. 9-9, janv. 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Maier-Hein et al., « Why rankings of biomedical image analysis competitions should be interpreted with care », Nat Commun, vol. 9, no 1, p. 5217, déc. 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. Girardet et al., « The combination of non-contrast abbreviated MRI and alpha foetoprotein has high performance for hepatocellular carcinoma screening », Eur Radiol, juill. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Jia, Jingnan-Jia/segmentation_metrics: v1.1.3. (30 octobre 2022). Zenodo. [CrossRef]
- P. Virtanen et al., « SciPy 1.0: fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python », Nat Methods, vol. 17, no 3, p. 261-272, mars 2020. [CrossRef]
- « Introduction — statsmodels ». Consulté le: 1 avril 2024. [En ligne]. Disponible sur: https://www.statsmodels.org/v0.13.5/.
- M. C. Lim, C. H. Tan, J. Cai, J. Zheng, et A. W. C. Kow, « CT volumetry of the liver: Where does it stand in clinical practice? », Clinical Radiology, vol. 69, no 9, p. 887-895, sept. 2014. [CrossRef]
- M. D’Onofrio, « Liver volumetry: Is imaging reliable? Personal experience and review of the literature », WJR, vol. 6, no 4, p. 62, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Y. Nakayama et al., « Automated Hepatic Volumetry for Living Related Liver Transplantation At Multisection CT », Radiology, vol. 240, no 3, p. 743-748, sept. 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. G. Poirot et al., « Robustness of radiomics to variations in segmentation methods in multimodal brain MRI », Sci Rep, vol. 12, no 1, p. 16712, oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Q. Qiu et al., « Reproducibility and non-redundancy of radiomic features extracted from arterial phase CT scans in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: impact of tumor segmentation variability », Quant. Imaging Med. Surg, vol. 9, no 3, p. 453-464, mars 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Duan et al., « Reproducibility for Hepatocellular Carcinoma CT Radiomic Features: Influence of Delineation Var-iability Based on 3D-CT, 4D-CT and Multiple-Parameter MR Images », Front. Oncol., vol. 12, p. 881931, avr. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Gross, S. Arora, S. Huber, A. S. Kücükkaya, et J. A. Onofrey, « LiverHccSeg: A publicly available multiphasic MRI dataset with liver and HCC tumor segmentations and inter-rater agreement analysis », Data in Brief, vol. 51, p. 109662, déc. 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. Suman et al., « Development of a volumetric pancreas segmentation CT dataset for AI applications through trained technologists: a study during the COVID 19 containment phase », Abdom Radiol, vol. 45, no 12, p. 4302-4310, déc. 2020. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhang et al., « The effects of volume of interest delineation on MRI-based radiomics analysis: evaluation with two disease groups », Cancer Imaging, vol. 19, no 1, p. 89, déc. 2019. [CrossRef]
- E. Gundersen et S. Kjensmo, « State of the Art: Reproducibility in Artificial Intelligence », AAAI, vol. 32, no 1, avr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Kocak et al., « CheckList for EvaluAtion of Radiomics research (CLEAR): a step-by-step reporting guideline for authors and reviewers endorsed by ESR and EuSoMII », Insights Imaging, vol. 14, no 1, p. 75, mai 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Macdonald, Z. Zhu, B. Konkel, M. A. Mazurowski, W. F. Wiggins, et M. R. Bashir, « Duke Liver Dataset: A Pub-licly Available Liver MRI Dataset with Liver Segmentation Masks and Series Labels », Radiology: Artificial Intelli-gence, vol. 5, no 5, p. e220275, sept. 2023. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).