Submitted:
04 November 2024
Posted:
06 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
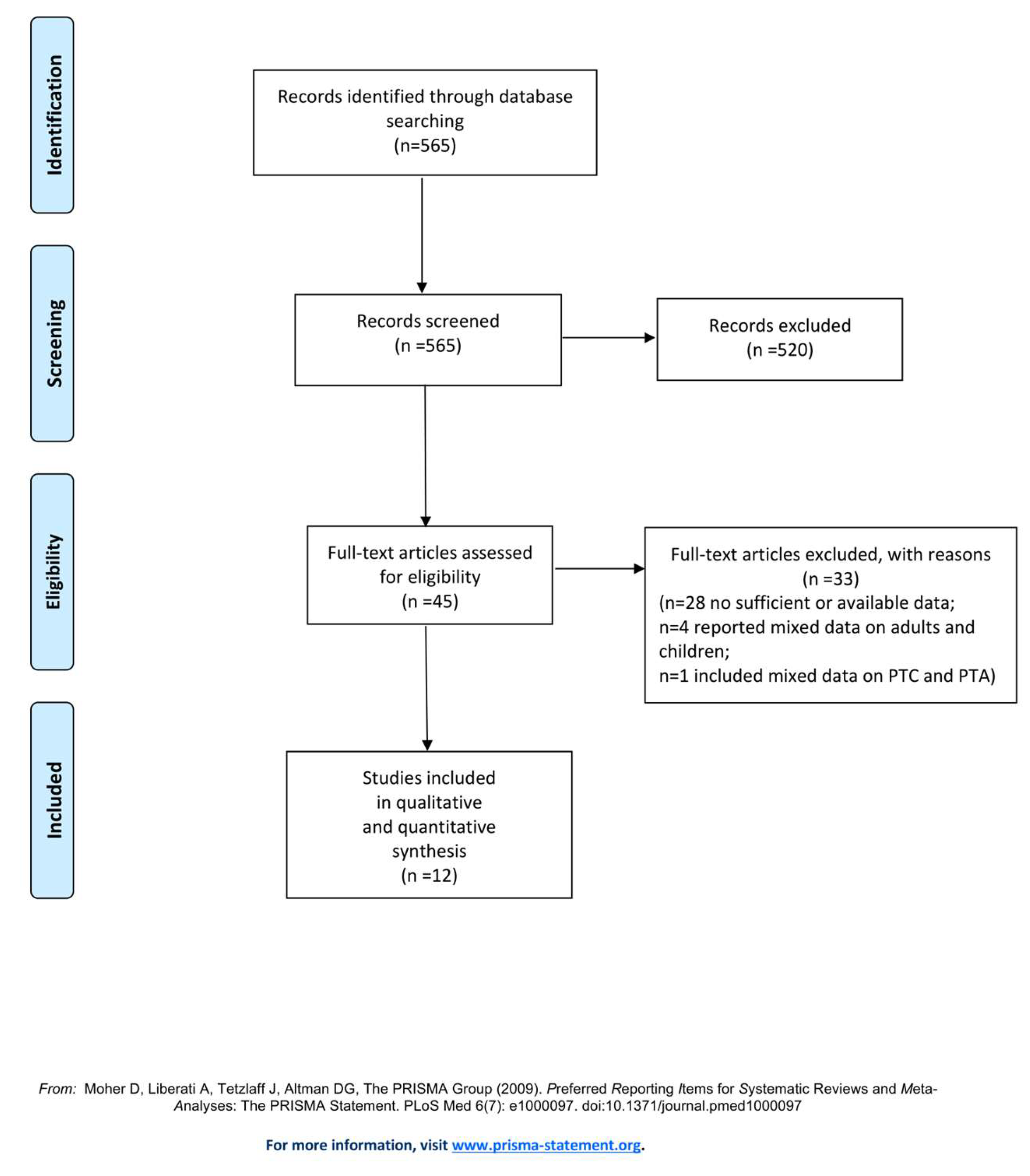
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality of Evidence Assessment
2.5. Data Synthesis
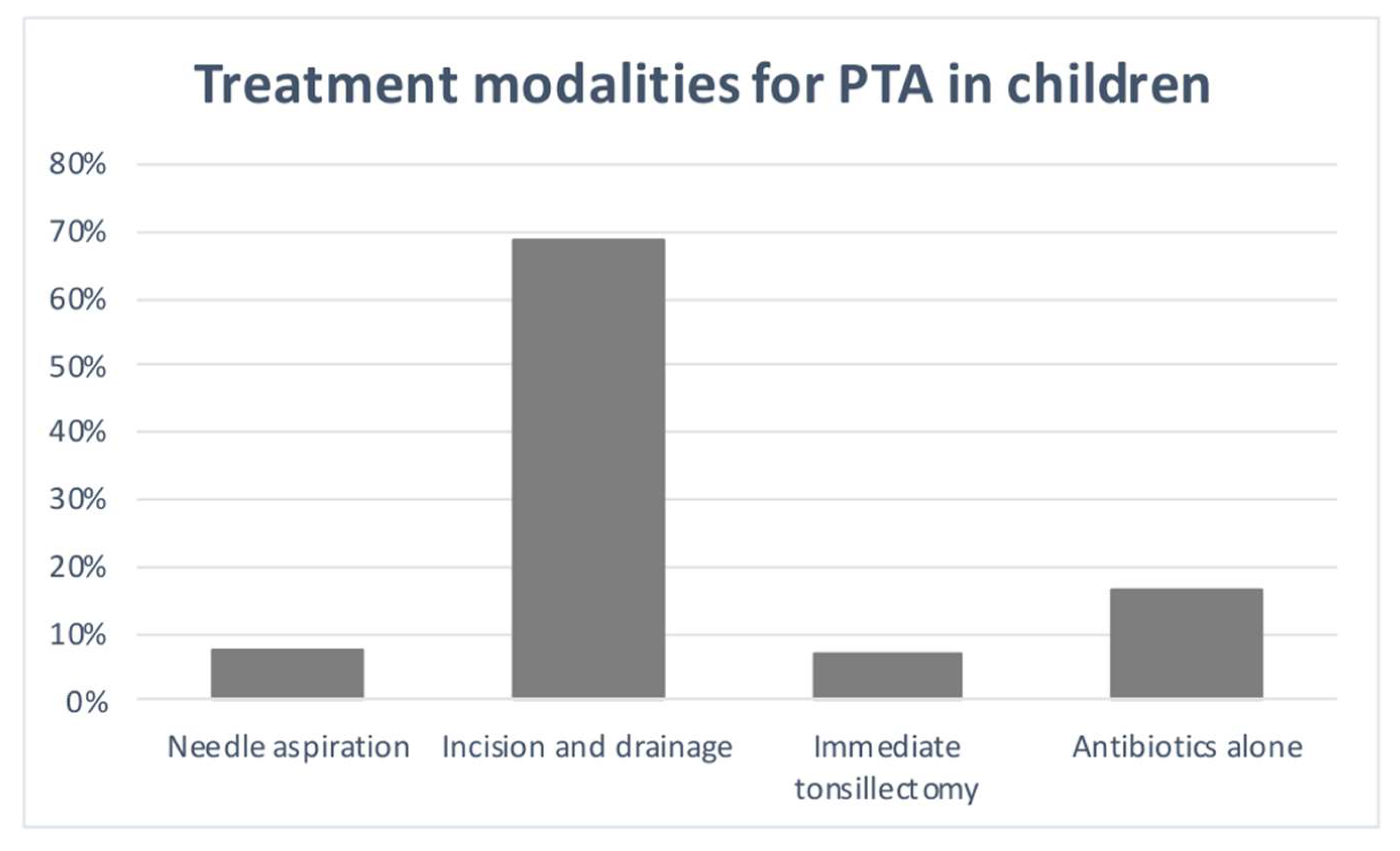
3. Results
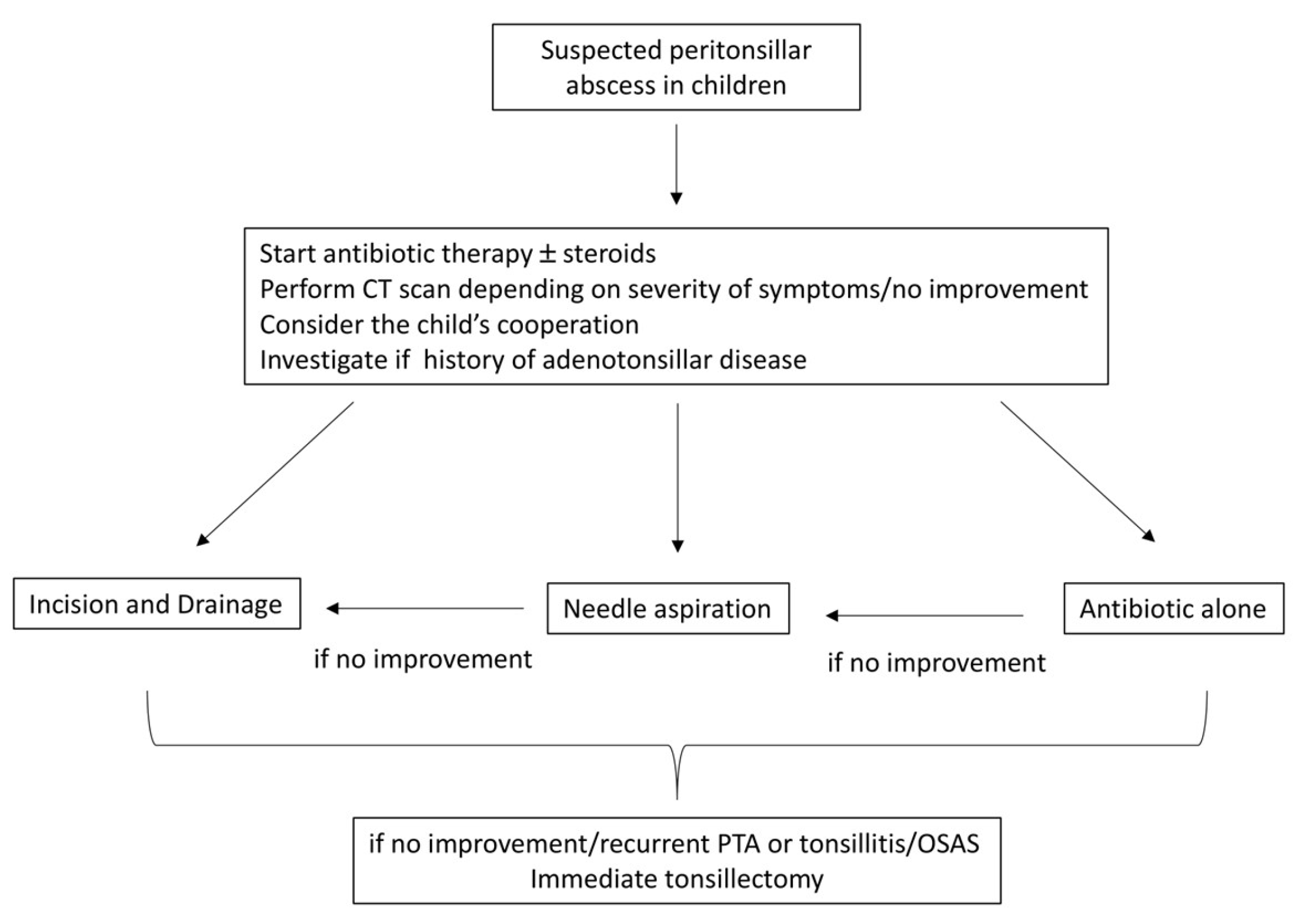
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Novis SJ, Pritchett CV, Thorne MC, et al. Pediatric deep space neck infections in U.S. children, 2000–2009. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2014, 78, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassari C, K. Shah R. Pediatric Peritonsillar Abscess: An Overview. IDDT. 2012, 12, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slouka D, Hanakova J, Kostlivy T, et al. Epidemiological and Microbiological Aspects of the Peritonsillar Abscess. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal N, El-Saied S, Puterman M. Peritonsillar abscess in children in the southern district of Israel. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2009, 73, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzon FS, Nicklaus P. Pediatric peritonsillar abscess: Management guidelines. Current Problems in Pediatrics 1996, 26, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varelas AN, LoSavio PS, Misch E, et al. Utilization of emergency department computed tomography and otolaryngology consultation in the diagnosis of pediatric peritonsillar abscess. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2019, 117, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandarkar AN, Adeyiga AO, Fordham MT, et al. Tonsil ultrasound: technical approach and spectrum of pediatric peritonsillar infections. Pediatr Radiol 2016, 46, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordham MT, Rock AN, Bandarkar A, et al. Transcervical ultrasonography in the diagnosis of pediatric peritonsillar abscess: Transcervical US in Pediatric PTA. The Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 2799–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pong AL, Bradley JS. Guidelines for the Selection of Antibacterial Therapy in Children. Pediatric Clinics of North America 2005, 52, 869–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafei K, Lichenstein R. Airway Infectious Disease Emergencies. Pediatric Clinics of North America. 2006, 53, 215–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraff S, McGinn JD, Derkay CS. Peritonsillar abscess in children: a 10-year review of diagnosis and management. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2001, 57, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al. The PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, e1000097.
- Munn Z, Barker TH, Moola S, et al. Methodological quality of case series studies: an introduction to the JBI critical appraisal tool. JBI Database of Systematic Reviews and Implementation Reports. 2019, Publish Ahead of Print.
- Wolf M, Even-Chen I, Talmi YP, et al. The indication for tonsillectomy in children following peritonsillar abscess. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 1995, 31, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosi-Schumacher M, Nagy R, Virgen C, et al. Peritonsillar abscess on NSQIP: Safety of indicated quinsy tonsillectomy. Int J Pediat Otorhinolaryngol 2023, 171, 111636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim DK, Lee JW, Na YS et al. Clinical factor for successful nonsurgical treatment of pediatric peritonsillar abscess. Laryngoscope. 2015, 125, 2608–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar KR, Johnson DW, Drummond D et al. Suspected Peritonsillar Abscess in Children: Pediatric Emergency Care. 2007, 23, 431–438.
- Apostolopoulos NJ, Nikolopoulos TP, Bairamis TN. Peritonsillar abscess in children. Is incision and drainage an effective management? Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngolol 1995, 31, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Chang L, Chi H, Chiu NC, et al. Deep Neck Infections in Different Age Groups of Children. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection 2010, 43, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao HJ, Huang YC, Hsia SH, et al. Clinical Features of Peritonsillar Abscess in Children. Pediatrics & Neonatology. 2012, 53, 366–370. [Google Scholar]
- Allen DZ, Rawlins K, Onwuka A, et al. Comparison of inpatient versus outpatient management of pediatric peritonsillar abscess outcomes. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2019, 123, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm AG, Little BD, Johnson RF. Validating peritonsillar abscess drainage rates using the Pediatric hospital information system data. Laryngoscope. 2020, 130, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg E, Brodsky L, Stanievich J, et al. Needle Aspiration of Peritonsillar Abscess in Children. Archives of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery. 1993, 119, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghantous J, Heiman E, Zelman A, Hadar A, Schwarz Y, Attal P, Sichel JY, Shaul C. Conscious sedation for the management of peritonsillar abscess in pediatric patients: A prospective case series and literature review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 183, 112032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi H, Ference E, Novis S, et al. Trends in the management of pediatric peritonsillar abscess infections in the U.S., 2000–2009. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2015, 79, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen T, Haberland CA, Hernandez-Boussard T. Pediatric Patient and Hospital Characteristics Associated With Treatment of Peritonsillar Abscess and Peritonsillar Cellulitis. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2015, 54, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, M. Ear, Nose, Throat. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 2021, 39, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon LM, Matijasec JWD, Perry AP, et al. Pediatric peritonsillar abscess: Quinsy ie versus interval tonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2013, 77, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang BA, Thamboo A, Burton MJ, et al. Needle aspiration versus incision and drainage for the treatment of peritonsillar abscess. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016, 23, CD006287. [Google Scholar]
| Authors, year | Study | N° cases PTA | Mean Age (y) |
Sex | Symptoms PTA |
Signs | Microbiology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weinberg et al.,1993 [23] | Retrospective | 43 | 13.9 | - | Shore throat 100% Drooling 34% Muffled voice 59% |
Unilateral peritonsillar bulge 100% Trismus |
GABHS, Str. Viridans Fusobacterium necrophorum H. influenzae |
| Apostolopoulos et al., 1995 [18] | Retrospective | 189 | 9 | 86M:103F | Sore throat | Peritonsillar bulge Trismus |
GABHS 35% Anaerobs 12% Others 12% Str. Viridans 10% Str. non-A 7% St. Aureus 6% Candida 6% H. Influenzae 4.5% Str. pneumoniae 4.5% Str. Sanguis 3% |
| Wolf et al., 1995 [14] |
Retrospective | 19 | 10-16y | - | Pain and dysphagia |
Trismus 50% Fever |
GABHS St. Aureus Str. Viridans Str. Non-A Pneumococci Peptostreptococci Mixed flora |
| Schraff et al., 2001 [11] |
Retrospective | 83 | 12.1 | - | Sore throat/neck pain 93% Odynophagia 83% Muffled voice 37% |
Neck adenopathy 94% Uvular deviation 52% Trismus 30% Dehydration 47% Fever 55% |
Mixed flora with Str. pyogenes the predominant organism |
| Millar et al., 2007 [17] |
Retrospective | 43 PTA 178 PTC |
15.4 PTA 3.2 PTC |
- | Sore throat 100% Painful swallowing 100 % Voice changes 86.7% Decrease oral intake 90.6% Drooling 75% |
Peritonsillar swelling 100% Cervical adenopathy 96.1% Trismus 78.9% Uvular deviation 73.3% Airway compromise 8% Fever 59.5% |
GABHS Str. non group A St. Aureus |
| Segal et al., 2009 [4] |
Retrospective | 126 | 12.8 | 55M:71F | - | - | GABHS 45.3% Anaerobes 14% Mixed w/o anaerobes 15.6% Str. C 6.2% others 17.3 |
| Chang et al., 2010 [19] |
Retrospective | 21 | 14.8 | 10M:11F | Odynophagia 21% | Fever 61.9% Trismus 4% Uvular deviation 6% Neck pain/mass1% |
Mixed flora |
| Hsiao et al., 2012 [20] |
Retrospective | 56 | 12.9 | 31M:24F | Sore throat |
Fever Asymmetric Swollen/bulging tonsil Uvular deviation |
Str.72% Fusobacterium species 44% Anaerobes 74% |
| Kim et al., 2015 [16] |
Retrospective | 88 | 8.5 | 52M:36F | - | - | - |
| Allen et al., 2019 [21] |
Retrospective | 566 | 12.9 outpt 9.9 inpt | 261M:305F | - | - | - |
| Chisholm et al., 2020 [22] | Retrospective | 200 |
12.6 |
77M:123F | - | - | - |
| Rosi-Schumacher et al., 2023 [15] |
Retrospective | 777 | 10.7 |
357M:420F | Sepsis 45.9% Systemic inflammatory response syndrome 4.8% |
- | - |
| Authors, year | Needle aspiration and/or Incision&drainage |
Tonsillectomy | Antibiotics | Recurrence (%) |
Time of recurrence | Complications | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weinberg et al.,1993 [23] |
41 needle aspiration (31 positive, 10 negative) |
5 immediate |
7 antibiotics alone | - | - | - | - |
| Apostolopoulos et al., 1995 [18] |
136 I&D (53 negative) |
- | - | 15.8% | 1 m | 12 (6.3%) torticollis, prologed fever |
1m-7y |
| Wolf et al., 1995 [14] |
7 needle aspiration (6 LA, 1 GA) 12 I&D (5 LA, 7 GA) |
2 immediate 1 elective |
17 antibiotics initiated 1-8 d prior the admission |
0 | - | 1 torticollis 1 dyspnea |
2 y |
| Schraff et al., 2001 [11] |
54 I&D | 25 immediate | 3 antibiotics alone | 0 | - | - | - |
| Millar et al., 2007 [17] |
43 needle aspiration or I&D | - | - | 4.7% | within 60 d | - | - |
| Segal et al., 2009 [4] |
95 needle aspiration 30 I&D GA |
1 immediate | 64.2% amoxicillin-clavulanate, 19% cefuroxime 13.5% cefuroxime + metronidazole 2.1% azithromycin |
- | - | - | - |
| Chang et al., 2010 [19] |
3 I&D 10 needle aspiration |
- | 8 antibiotics alone | - | - | no complications | - |
| Hsiao et al., 2012 [20] |
48 |
1 elective | 9 penic. 15 penic.+genta. 4 penic.+clyndamicina 5 penic.+clyndamicina+genta 12 amox.cl. 5 amox.cl+ genta. 1 amox.cl+ ciprofloxacina 3 ampicillina/sulbactam 1 oxacillin + genta. 1 vancomycin + ceftazidime 8 intravenous antibiotics alone |
2% | 1 IOT 2 parapharyngeal involvement |
||
| Kim et al., 2015 [16] |
55 any surgery “Poor responder “ | 0 | 33 antibiotic alone “good responder” |
- | - | - | - |
| Allen et al., 2019 [21] |
113 I&D outpt 184 I&D inpt |
immediate 12 outpt + 42 inpt elective 22 outpt + 33 inpt |
antibiotics only 181 outpt + 88 inpt |
9.1% 29 outpt 23 inpt |
within 30 d | - | - |
| Chisholm et al., 2020 [22] |
115 I&D | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Rosi-Schumacher et al., 2023 [15] |
725 I&D | 52 immediate 6 elective |
- | 2.5% | - |
357 sepsis 37 systemic inflammatory response syndrom |
1m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





