1. Introduction
Pregnancy is a critical period requiring careful monitoring to prevent complications affecting both the mother and the fetus. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 295,000 women died during and following pregnancy and childbirth in 2017, with the majority of these deaths being preventable through timely medical interventions [
1]. Early and accurate prediction of pregnancy risk levels enables healthcare providers to allocate resources effectively, implement preventive measures, and provide timely interventions, thereby reducing maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality.
Traditional statistical methods often struggle with the complex, nonlinear relationships and class imbalances present in medical data, limiting their predictive capabilities [
2]. Machine learning techniques offer advanced modeling capabilities to handle such complexities, making them well-suited for medical data analysis. Recent studies have applied machine learning to predict specific pregnancy complications, such as gestational diabetes [
3], preterm birth [
4], preeclampsia [
5], and maternal mortality [
6]. While these studies have shown promising results in predicting individual complications, there remains a gap in developing models that can assess overall pregnancy risk levels.
Accurately predicting overall pregnancy risk is crucial because it encompasses a broader range of potential complications, allowing for more comprehensive prenatal care. Moreover, datasets in this domain often suffer from class imbalance, where high-risk cases are underrepresented compared to low-risk cases. This imbalance poses challenges for traditional modeling approaches, potentially leading to biased predictions and reduced sensitivity to minority classes [
7]. Therefore, there is a pressing need for robust machine learning models that can effectively handle imbalanced data and accurately predict overall pregnancy risk levels.
In this study, we aim to address this need by developing ensemble machine learning models combined with advanced oversampling techniques to predict pregnancy risk levels. By utilizing ensemble methods, we leverage the strengths of multiple algorithms to improve predictive performance and robustness. We also employ the Adaptive Synthetic Sampling (ADASYN) method to address class imbalance, enhancing the model’s ability to detect high-risk cases. Our approach includes extensive feature engineering, introducing new features such as Mean Arterial Pressure and Pulse Pressure to capture critical physiological information. Through this research, we contribute to the field by enhancing prediction accuracy, providing insights into important features influencing pregnancy risk, and addressing ethical considerations in deploying machine learning models in healthcare.
1.1. Recent Advances in Pregnancy Risk Prediction
Recent years have witnessed significant advancements in the application of machine learning techniques for predicting pregnancy-related complications. Sakr and et al. [
8] developed a deep learning model to predict preeclampsia using electronic health records, achieving high accuracy in their predictions. Their study demonstrated that deep learning models can effectively handle complex medical data, but they also highlighted the necessity of large datasets to train such models adequately. The requirement for extensive data poses a challenge, especially in medical fields where data privacy and the rarity of certain conditions can limit data availability.
Similarly, Sufriyana et al. [
9] utilized machine learning algorithms to predict anemia during pregnancy, emphasizing the importance of feature selection in enhancing model performance. By carefully selecting relevant clinical features, they improved the predictive accuracy of their models. This study underscores the critical role that feature engineering plays in medical predictive modeling, where irrelevant or redundant features can adversely affect model outcomes.
Furthermore, Zhang and et al. [
10] proposed a hybrid model combining convolutional neural networks (CNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks for predicting gestational diabetes mellitus. Their hybrid approach leveraged the strengths of CNNs in extracting spatial features and LSTMs in capturing temporal dependencies within the data. This combination led to improved prediction performance, demonstrating the potential of integrating different deep learning architectures to address complex medical prediction tasks.
In addition, Calwin [
11] conducted a study on predicting pregnancy risk levels using machine learning algorithms, employing the Maternal Health Risk Data Set from the UCI Machine Learning Repository. The research explored various classifiers, including Random Forest and XGBoost, and addressed issues related to class imbalance and feature importance. By implementing ensemble methods and focusing on significant predictors, the study highlighted the effectiveness of these approaches in improving predictive accuracy. It also emphasized the challenges posed by imbalanced datasets, a common issue in medical data that can lead to biased models if not properly managed.
These studies collectively demonstrate the substantial potential of machine learning in pregnancy risk prediction. They also indicate persistent challenges, such as data imbalance, the need for large and high-quality datasets, and the importance of model interpretability. Addressing these challenges is essential for the successful integration of machine learning models into clinical practice, ensuring that predictions are both accurate and trustworthy for healthcare providers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Description
We utilized the Maternal Health Risk Data Set from the UCI Machine Learning Repository [
12]. This dataset contains medical records of pregnant women and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license, allowing for sharing and adaptation with appropriate credit.
Features Included
The dataset includes several key features relevant to pregnancy risk prediction. These features are:
Age (years), representing the age of the pregnant woman, which provides insights into age-related risk factors associated with pregnancy complications. Blood pressure measurements are captured through Systolic Blood Pressure (SystolicBP) and Diastolic Blood Pressure (DiastolicBP), both measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). These measurements are critical indicators of cardiovascular health and are essential for assessing the risk of hypertension-related complications during pregnancy. Blood Sugar (BS), measured in millimoles per liter (mmol/L), reflects the glucose concentration in the blood. Body Temperature (BodyTemp), recorded in degrees Celsius (C), indicates the body’s thermoregulatory status and can signal infections or other physiological changes. Heart Rate, measured in beats per minute, provides information about the cardiovascular activity and can indicate stress levels or potential cardiac issues. The target variable, Risk Level, categorizes each instance into ’low risk’, ’mid risk’, or ’high risk’, serving as the outcome variable that the machine learning models aim to predict.
These features collectively provide a comprehensive overview of the physiological state of pregnant women, enabling the development of predictive models for assessing pregnancy risk levels.
Class Distribution Before Resampling
Prior to applying any resampling techniques, the dataset exhibited a notable class imbalance across the three pregnancy risk levels. The Low Risk category comprised the majority of the data, containing a total of 406 samples. This significant proportion indicates that most instances in the dataset were classified as low risk, which is a common scenario in medical datasets where adverse outcomes are less frequent than normal cases. The prevalence of low-risk cases can lead to a model that is biased towards predicting the majority class if not properly addressed.
In contrast, the Mid Risk category was underrepresented, with only 192 samples. This underrepresentation poses challenges for machine learning models, as they may not have sufficient data to learn the patterns and features associated with medium-risk pregnancies effectively. Models trained on such imbalanced data tend to have lower sensitivity for minority classes, potentially leading to higher misclassification rates for mid-risk cases.
The High Risk category consisted of 202 samples, which, while slightly more than the mid-risk class, was still substantially fewer than the low-risk class. The imbalance between the high-risk and low-risk classes can result in the model being less attentive to high-risk cases, which are critical to identify accurately in a healthcare setting.
This imbalance necessitated the use of resampling techniques to ensure that the machine learning models could learn effectively from all risk levels and not be biased towards the majority class. Addressing class imbalance is crucial for developing a predictive model with high sensitivity and specificity across all categories, thereby improving its clinical utility in accurately identifying patients at varying levels of risk.
Data Ethics and Permissions
The dataset utilized in this study is publicly available and has been fully anonymized, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations and ethical standards. All personal identifiers have been removed, and the data cannot be traced back to individual subjects, thus protecting the confidentiality and privacy of the participants. The use of this dataset complies with the terms specified by the data provider under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. As such, our use of the dataset aligns with the licensing agreement, and appropriate acknowledgments have been made.
No ethical approval was required for this study due to the dataset’s public availability and anonymized nature. According to institutional guidelines and international research ethics standards, studies utilizing publicly available, anonymized data are exempt from ethical review processes. This exemption is based on the principle that the use of such data does not infringe upon the privacy or rights of individuals. Nonetheless, we have adhered to all relevant ethical considerations to ensure that our research is conducted responsibly and with integrity. By utilizing an anonymized dataset and complying with the licensing terms, we uphold the ethical standards expected in scientific research while contributing valuable insights to the field of pregnancy risk prediction.
2.2. Data Preprocessing
Effective data preprocessing is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of machine learning models. In this study, several preprocessing steps were undertaken to prepare the dataset for analysis:
2.2.1. Missing Values
The dataset was thoroughly examined for missing values using exploratory data analysis techniques. This process involved checking each feature for null or undefined entries. The analysis confirmed the absence of missing values across all features, indicating that the dataset was complete and did not require imputation strategies. The completeness of the data facilitates more accurate modeling, as missing values can introduce bias or reduce the statistical power of the analysis.
2.2.2. Outlier Detection and Removal
Outliers can significantly affect the performance of machine learning models by skewing the results and introducing anomalies that are not representative of the general population. An outlier with a heart rate of 7 beats per minute (bpm) was identified during the data exploration phase. Given that such a low heart rate is physiologically implausible for a pregnant woman and could be the result of a recording error or data entry mistake, this data point was considered erroneous. To maintain data integrity and ensure the accuracy of the model, this outlier was removed from the dataset. The decision to remove this outlier is supported by clinical research indicating normal heart rate ranges during pregnancy [
13].
2.2.3. Label Encoding
The target variable,
Risk Level, consists of categorical values: ’low risk’, ’mid risk’, and ’high risk’. To enable the machine learning algorithms to process this categorical data, label encoding was applied using the
LabelEncoder from the
scikit-learn library [
14]. The encoding mapped the categories to numerical values, assigning ’Low Risk’ to 0, ’Mid Risk’ to 1, and ’High Risk’ to 2. This transformation allows the models to interpret the risk levels quantitatively while preserving the ordinal relationship between the categories.
2.2.4. Feature Scaling
Feature scaling is essential for algorithms that are sensitive to the scale of data, such as distance-based models and those using gradient descent optimization [
15]. In this study, numerical features were standardized using the
StandardScaler from the
scikit-learn library. Standardization transforms the data so that each feature has a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one. This process ensures that all features contribute equally to the model’s performance and prevents features with larger scales from dominating those with smaller scales. The standardized features improve the convergence of optimization algorithms and enhance the overall accuracy of the models.
2.3. Feature Engineering and Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
2.3.1. Incorporation of Cardiovascular Features
The relationship between blood pressure parameters and maternal health risks has been highlighted in recent studies. Calwin [
11] observed a strong positive correlation between SystolicBP and DiastolicBP. To capture this relationship more effectively, our study introduces
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) as a new feature, calculated as:
Mean Arterial Pressure provides a better indicator of perfusion to vital organs than systolic or diastolic blood pressure alone. This formula is widely accepted because the heart spends approximately two-thirds of the cardiac cycle in diastole and one-third in systole [
16]. By weighting the diastolic pressure twice as much as the systolic pressure, the formula accounts for the longer duration of diastole, providing a more accurate estimation of the average arterial pressure over time.
2.3.2. Additional Engineered Features
Pulse Pressure (
PP) is an important hemodynamic parameter calculated as the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. It is defined by the formula:
Pulse Pressure reflects the force that the heart generates each time it contracts. It is a measure of the stiffness of the arteries and is associated with cardiovascular health. In the context of pregnancy, elevated PP values have been linked to complications such as preeclampsia and increased cardiovascular risk [
17]. By incorporating PP as an engineered feature, the model can capture additional physiological information that may improve the prediction of pregnancy risk levels. Including PP allows the model to account for arterial compliance and vascular resistance, which are not fully represented by systolic or diastolic blood pressure alone.
After creating MAP and PP, the original ’SystolicBP’ and ’DiastolicBP’ features were dropped to reduce multicollinearity.
2.3.3. Correlation Analysis
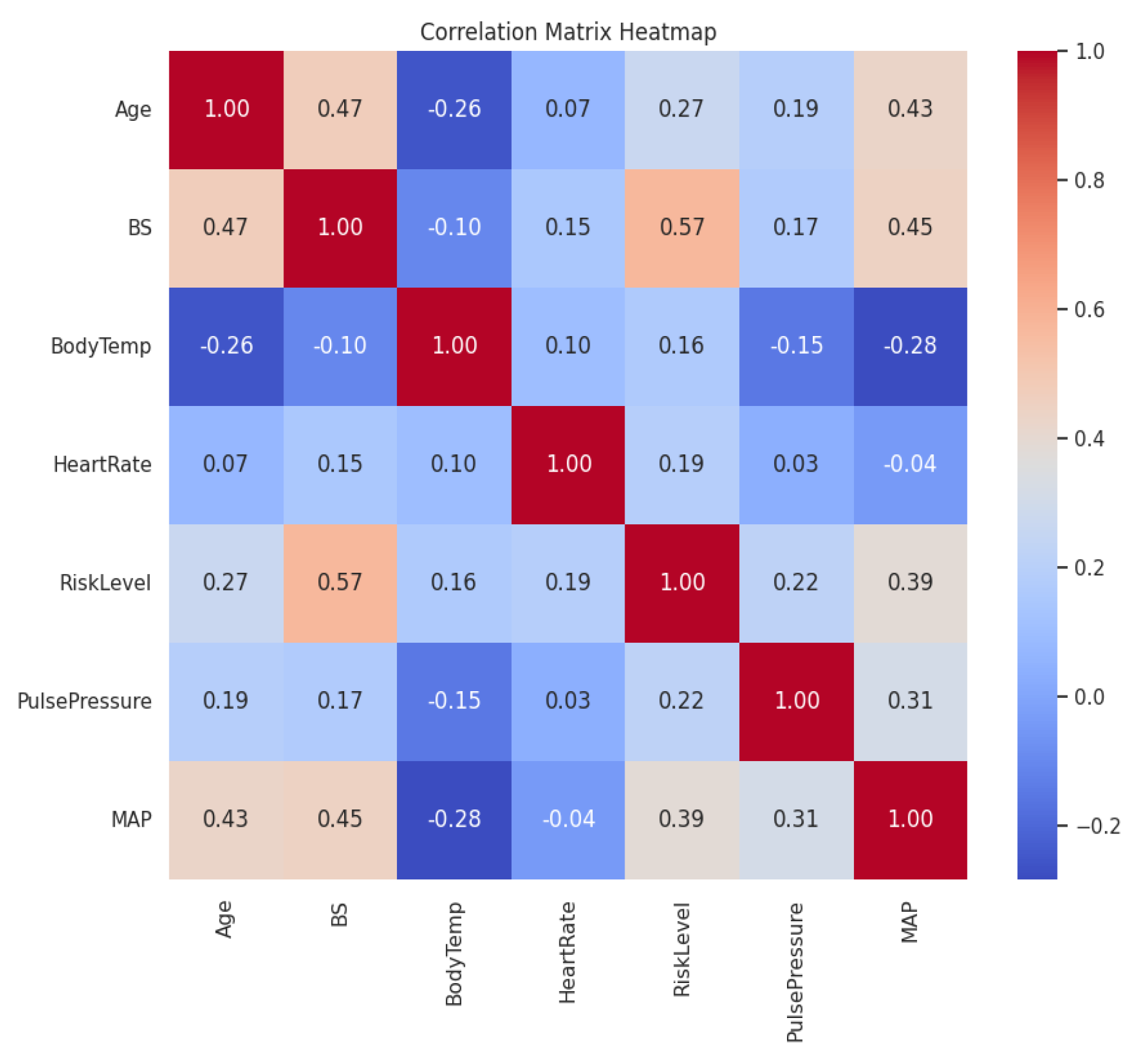
We performed a correlation analysis to understand the relationships between features and the target variable.
Key Observations
The correlation analysis revealed several important relationships between the features and the target variable, Risk Level. Blood Sugar (BS) exhibited the highest positive correlation with Risk Level, with a correlation coefficient of 0.570. This indicates a strong linear relationship, suggesting that higher blood sugar levels are associated with higher pregnancy risk. This finding aligns with medical knowledge that elevated glucose levels can lead to complications such as gestational diabetes mellitus.
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) showed a moderate positive correlation with Risk Level, with a correlation coefficient of 0.387. This suggests that higher MAP values are associated with increased pregnancy risk. Since MAP reflects the overall blood pressure status, elevated MAP may indicate hypertension, which is a known risk factor for conditions like preeclampsia.
Age demonstrated a weaker positive correlation with Risk Level, with a correlation coefficient of 0.266. This implies that as maternal age increases, there is a slight tendency for the pregnancy risk to increase. While advanced maternal age is associated with higher risks of complications, the weaker correlation suggests that age alone is not as strong a predictor compared to other factors like blood sugar or blood pressure.
Figure 1.
Correlation Matrix Heatmap
Figure 1.
Correlation Matrix Heatmap
Pulse Pressure (PP) had a low positive correlation with Risk Level (0.220), indicating that while there is some relationship, it is not as strong as that of BS or MAP. PP reflects arterial stiffness and cardiovascular health, which can contribute to pregnancy risk but may be influenced by other factors.
Body Temperature and Heart Rate had weak correlations with Risk Level (0.163 and 0.190, respectively), suggesting they are less significant predictors when considered in isolation.
Implications for Machine Learning Algorithms
The findings from the correlation analysis have several implications for the development of machine learning models. Features with higher absolute correlation coefficients with the target variable are likely to be more important predictors. In this case, Blood Sugar (BS) and Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) are expected to have significant contributions to the predictive performance of the models.
Some features exhibit significant correlations with each other—for example, Age and BS have a correlation of 0.473, and BS and MAP have a correlation of 0.448. This multicollinearity can affect certain algorithms that assume feature independence, such as linear regression. However, ensemble methods like Random Forest and XGBoost are robust to multicollinearity due to their ability to handle correlated features through feature bagging and regularization.
Features with low correlation to the target variable may still contribute to the model, especially in capturing nonlinear relationships or interactions between features. Machine learning algorithms can exploit these complex patterns beyond linear correlations, so it is important not to disregard features solely based on their low correlation coefficients.
The presence of both strong and weak correlations suggests that algorithms capable of capturing both linear and nonlinear relationships are suitable for this problem. Ensemble methods like Random Forest and XGBoost are effective in handling such complexities due to their tree-based structures and ability to model interactions between features.
2.3.4. Visualization of Feature Distributions
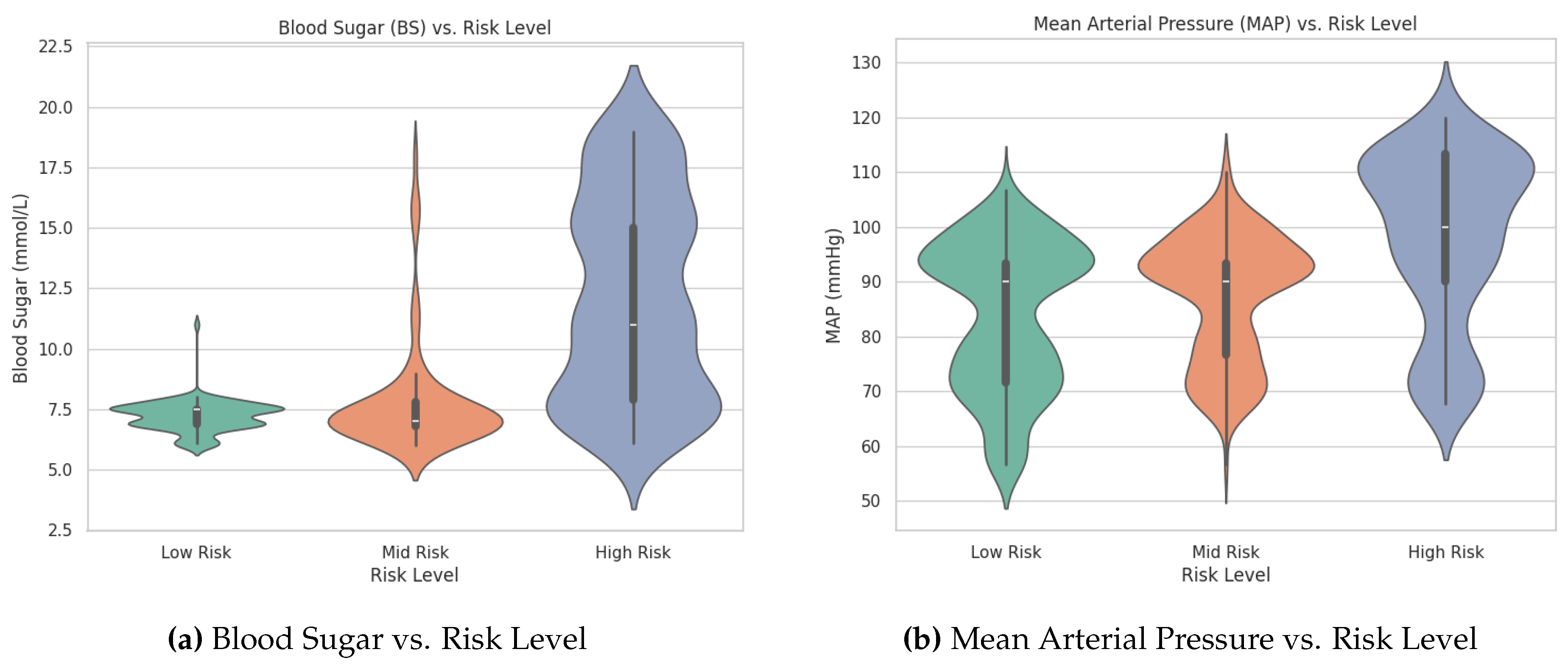
An analysis of the violin plots for Blood Sugar (BS) and Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) reveals clear distinctions among the pregnancy risk levels. The High Risk group exhibits wider distributions and higher median values for both BS and MAP compared to the Mid Risk and Low Risk groups. This indicates that individuals in the High Risk category tend to have elevated blood sugar levels and arterial pressure. These visual observations underscore the importance of BS and MAP as key predictive features in distinguishing between different risk levels. The patterns suggest that incorporating these variables into machine learning models can enhance the early identification of high-risk pregnancies, enabling timely medical interventions.
Figure 2.
Comparison of Blood Sugar and Mean Arterial Pressure vs. Risk Level
Figure 2.
Comparison of Blood Sugar and Mean Arterial Pressure vs. Risk Level
2.3.5. One-Way ANOVA Tests
To determine whether the means of certain features differ significantly across the pregnancy risk levels (
Low Risk,
Mid Risk, and
High Risk), we conducted one-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) tests. The one-way ANOVA is a statistical method used to compare the means of three or more independent groups to ascertain if at least one group mean is statistically different from the others [
18].
In the context of ANOVA, the
F-statistic is a ratio of the variance between the group means to the variance within the groups. A higher F-statistic value indicates a greater degree of difference between group means relative to the variability within the groups. The
p-value corresponds to the probability of observing an F-statistic as extreme as, or more extreme than, the one calculated from the data, assuming that the null hypothesis (no difference between group means) is true. A low p-value (typically less than 0.05) suggests that the differences between group means are statistically significant [
19].
The results of the one-way ANOVA tests for
Blood Sugar (BS),
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP), and
Pulse Pressure (PP) are summarized in
Table 1.
The ANOVA results indicate that the F-statistics for BS, MAP, and PP are substantially high, and the corresponding p-values are less than 0.0001. This implies that there are statistically significant differences in the means of these features across the different risk levels.
These statistical tests confirm that BS, MAP, and PP are significant variables that differ across the pregnancy risk categories. The findings justify the inclusion of these features in our predictive models and support the hypothesis that physiological measurements related to blood pressure and glucose levels are critical in assessing pregnancy risk.
2.4. Handling Class Imbalance
Given the class imbalance, we employed an oversampling technique to balance the dataset.
2.4.1. Oversampling Method Used
To address class imbalance in our dataset, we utilized the Adaptive Synthetic Sampling (
ADASYN) method. ADASYN is an oversampling technique that generates synthetic samples for minority classes by focusing more on difficult-to-learn examples [
20]. It adaptively creates synthetic data points in regions where the minority class is underrepresented, effectively balancing the dataset and improving the model’s ability to learn complex patterns associated with minority classes. By prioritizing samples that are harder to classify, ADASYN enhances the classifier’s performance, particularly in detecting minority class instances. Significant increase of performance have also been observed in using similar oversampling techniques as in for e.g., [
21,
22].
2.4.2. Class Distribution After ADASYN
After applying ADASYN, the class distribution was adjusted to have 332 samples for the Low Risk class, 325 samples for the Mid Risk class, and 276 samples for the High Risk class. This resulted in a more balanced dataset, improving the model’s ability to learn from all classes and enhancing the potential for accurate predictions across all risk levels.
2.4.3. Model Development
We developed several machine learning models to predict pregnancy risk levels, focusing on ensemble methods that can leverage the strengths of multiple algorithms.
2.4.4. Machine Learning Algorithms
In this study, we employed several machine learning algorithms to build predictive models for pregnancy risk classification. The algorithms used include the Random Forest Classifier, XGBoost Classifier, and Voting Classifier. Each of these algorithms offers unique advantages in handling classification tasks, particularly in dealing with complex and imbalanced datasets.
Random Forest Classifier is an ensemble learning method that constructs multiple decision trees during training and outputs the class that is the mode of the classes predicted by individual trees [
23]. It reduces overfitting by averaging the results of many decision trees, which individually may have high variance. The randomness introduced in selecting features and data subsets for each tree helps improve generalization and robustness to noise. Random Forests are effective in handling large datasets with higher dimensionality and can manage missing values and maintain accuracy for a large proportion of data.
XGBoost Classifier stands for Extreme Gradient Boosting and is an optimized implementation of the gradient boosting algorithm [
24]. XGBoost builds an ensemble of weak learners, typically decision trees, in a sequential manner, where each subsequent tree aims to correct the errors of its predecessor by focusing on the residuals. The algorithm employs second-order gradient information, regularization techniques, and parallel processing to improve performance and prevent overfitting. XGBoost is renowned for its speed and efficiency, especially with large datasets, and often achieves state-of-the-art results in machine learning competitions.
Voting Classifier is an ensemble learning technique that combines the predictions from multiple different models to improve overall predictive performance [
25]. In a soft voting classifier, the predicted class probabilities from each model are averaged, and the class with the highest average probability is selected as the final prediction. This approach leverages the strengths of each individual model and can lead to better generalization by mitigating the biases inherent in any single model. In our study, we combined the predictions from the Random Forest and XGBoost classifiers to create a Voting Classifier, aiming to enhance the robustness and accuracy of the pregnancy risk predictions.
2.4.5. Hyperparameter Tuning
We performed hyperparameter tuning using cross-validation to optimize the performance of our models. For the Random Forest classifier, we tuned several parameters including n_estimators, max_depth, min_samples_split, min_samples_leaf, max_features, and bootstrap. The tuning process was carried out using RandomizedSearchCV with 5-fold cross-validation to efficiently search through the parameter space.
Similarly, for the XGBoost classifier, we tuned parameters such as n_estimators, max_depth, learning_rate, subsample, colsample_bytree, and gamma. The RandomizedSearchCV method with 5-fold cross-validation was also employed for XGBoost to identify the optimal combination of hyperparameters that would enhance the model’s predictive performance.
2.4.6. Evaluation Metrics
To evaluate the performance of the machine learning models, we used several metrics: Accuracy Score, Precision, Recall, F1 Score, Macro F1 Score, Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC-ROC), and Precision-Recall Curves. These metrics provide a comprehensive assessment of the models’ predictive capabilities, especially in the context of class imbalance.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
We conducted statistical tests to determine the significance of performance differences between models. Specifically, we used the paired t-test to compare the macro F1 scores of the models. This test assumes that the differences between paired observations are normally distributed. We calculated confidence intervals at a 95% confidence level to estimate the range within which the true mean difference lies. The p-values were determined to assess statistical significance, with a threshold of 0.05 indicating whether the observed differences were statistically significant.
2.6. Cross-Validation
We employed Stratified K-Fold cross-validation with 5 folds to ensure robustness and mitigate overfitting.
3. Results
Three models were evaluated on the dataset: Random Forest (RF), XGBoost (XGB), and a Voting Classifier combining both.
3.1. Random Forest
The Random Forest model achieved an
accuracy of 85.22% and a
macro F1 score of 85.83% on the test set. The detailed classification report is presented in
Table 2.
3.1.1. Evaluation Metrics Explained
To provide a comprehensive evaluation of the model’s performance, we used several metrics, including Precision, Recall, F1-score, and Support. Additionally, we considered both the Macro Average and Weighted Average of these metrics to assess overall model effectiveness across all classes.
Precision
Precision for a particular class is the ratio of true positive predictions to the total predicted positives for that class. It measures the model’s accuracy in predicting a specific class.
A high precision indicates that the model has a low false positive rate for that class.
Recall
Recall, also known as sensitivity or true positive rate, is the ratio of true positive predictions to the actual total positives for that class. It measures the model’s ability to correctly identify all positive instances.
A high recall indicates that the model has a low false negative rate for that class.
F1-score
The F1-score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, providing a balance between the two metrics.
An F1-score considers both false positives and false negatives, offering a single metric that balances precision and recall.
Support
Support is the number of actual occurrences of the class in the dataset. It indicates how many instances there are to be predicted for each class.
Macro Average vs. Weighted Average
Macro Average computes the metric independently for each class and then takes the unweighted mean. This treats all classes equally, regardless of their support (number of instances).
where
N is the number of classes and
is the metric (e.g., precision, recall, F1-score) for class
i.
Weighted Average computes the metric for each class, weights it by the number of instances (support) in that class, and then takes the mean.
where
is the support for class
i.
3.1.2. Interpretation and Considerations
In the context of our imbalanced dataset, where some classes have fewer instances than others, the Macro Average is particularly informative because it treats all classes equally, without considering the support. This means that each class contributes equally to the final average, making it a useful metric for evaluating the model’s performance across all classes, especially the minority classes.
The Weighted Average, on the other hand, accounts for the support of each class, giving more weight to classes with more instances. While this provides an overall performance measure that reflects the class distribution, it may mask poor performance in minority classes due to the influence of the majority class.
Given our goal of accurately predicting all risk levels, including the minority classes, we focus on the Macro Average metrics. The Random Forest model’s macro F1-score of 86% indicates a balanced performance across all classes.
3.1.3. Summary of Results
The Random Forest classifier demonstrated strong performance, particularly in predicting the High Risk class, with a precision of 0.91, recall of 0.96, and F1-score of 0.94. The Low Risk and Mid Risk classes also showed good results, though with slightly lower precision and recall values. The overall macro averages reflect a consistent performance across all classes, supporting the effectiveness of the Random Forest model in predicting pregnancy risk levels.
3.2. XGBoost
The XGBoost model achieved an
accuracy of 85.71% and a
macro F1 score of 86.21% on the test set, indicating strong overall performance. The detailed classification report is presented in
Table 3.
3.2.1. Interpretation of Results
The XGBoost classifier demonstrated high performance across all classes. For the High Risk class, the model achieved a precision of 0.91, recall of 0.93, and F1-score of 0.92, indicating that it effectively identifies high-risk pregnancies with few false positives and negatives.
For the Low Risk class, the precision was 0.90, and the recall was 0.79, resulting in an F1-score of 0.84. This suggests that while the model is good at predicting low-risk cases (high precision), there is room for improvement in capturing all actual low-risk instances (lower recall).
The Mid Risk class had a precision of 0.78 and a recall of 0.88, yielding an F1-score of 0.83. This indicates that the model is effective at identifying most mid-risk cases (high recall) but has a higher rate of false positives for this class (lower precision).
The Macro Average F1-score of 86% reflects balanced performance across all classes, treating each class equally. The Weighted Average also shows consistent results, accounting for the class distribution in the dataset.
Overall, the XGBoost model performed comparably to the Random Forest model, with slight variations in precision and recall for the different classes. Its strong performance, particularly in predicting high-risk cases, makes it a valuable tool for pregnancy risk classification.
3.3. Voting Classifier
The Voting Classifier outperformed both individual models, achieving an
accuracy of 87.19% and a
macro F1 score of 87.66%. See
Table 4.
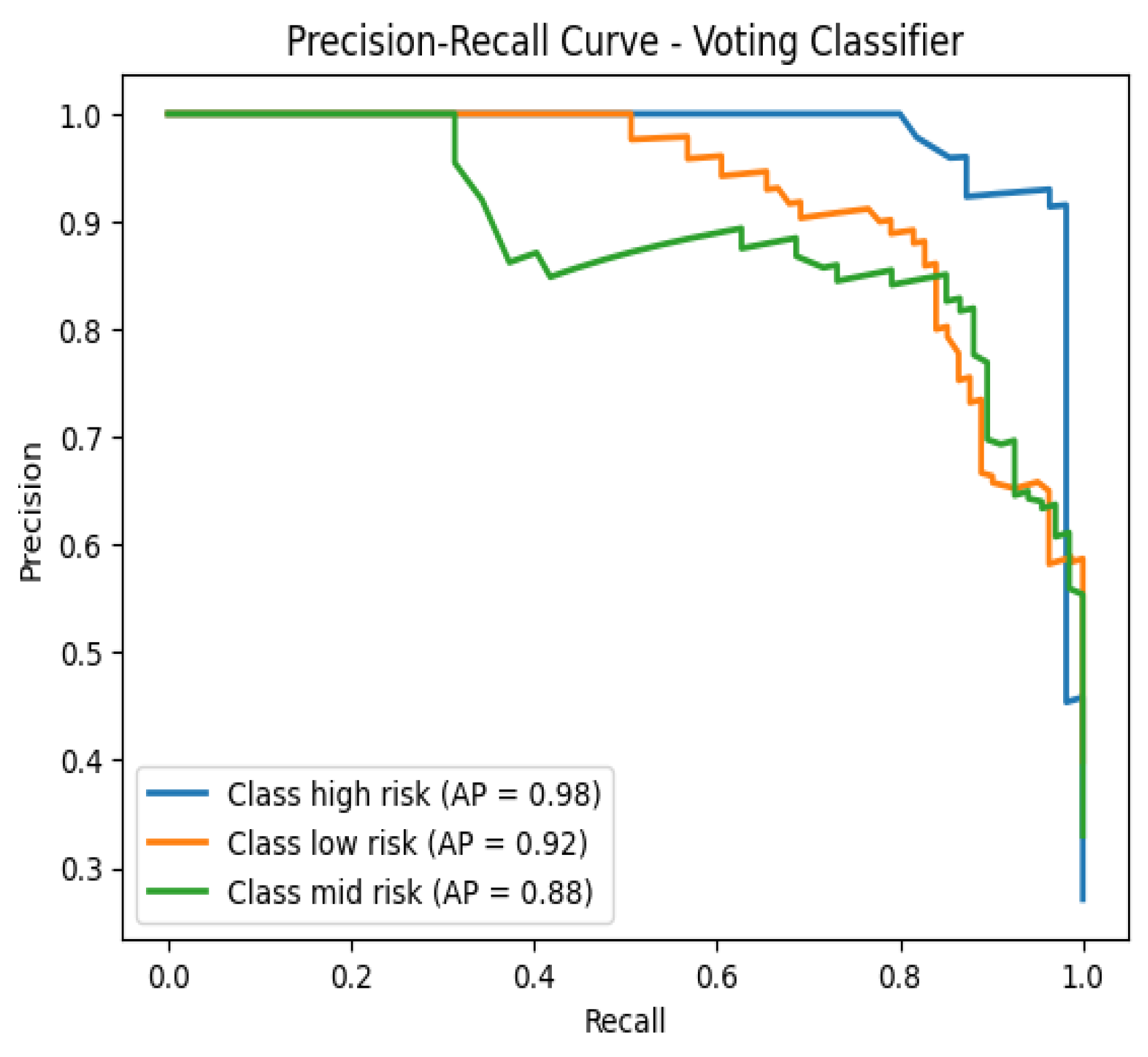
Figure 3.
Precision-Recall Curve - Voting Classifier
Figure 3.
Precision-Recall Curve - Voting Classifier
3.4. Cross-Validation Results
We conducted stratified 5-fold cross-validation using the Voting Classifier with ADASYN resampling (with n_neighbors set to 3). The F1 Macro scores across the folds were 0.7781 for Fold 1, 0.8198 for Fold 2, 0.8065 for Fold 3, 0.8501 for Fold 4, and 0.8201 for Fold 5. The mean cross-validation F1 Macro score was 81.49%, indicating consistent performance across the folds.
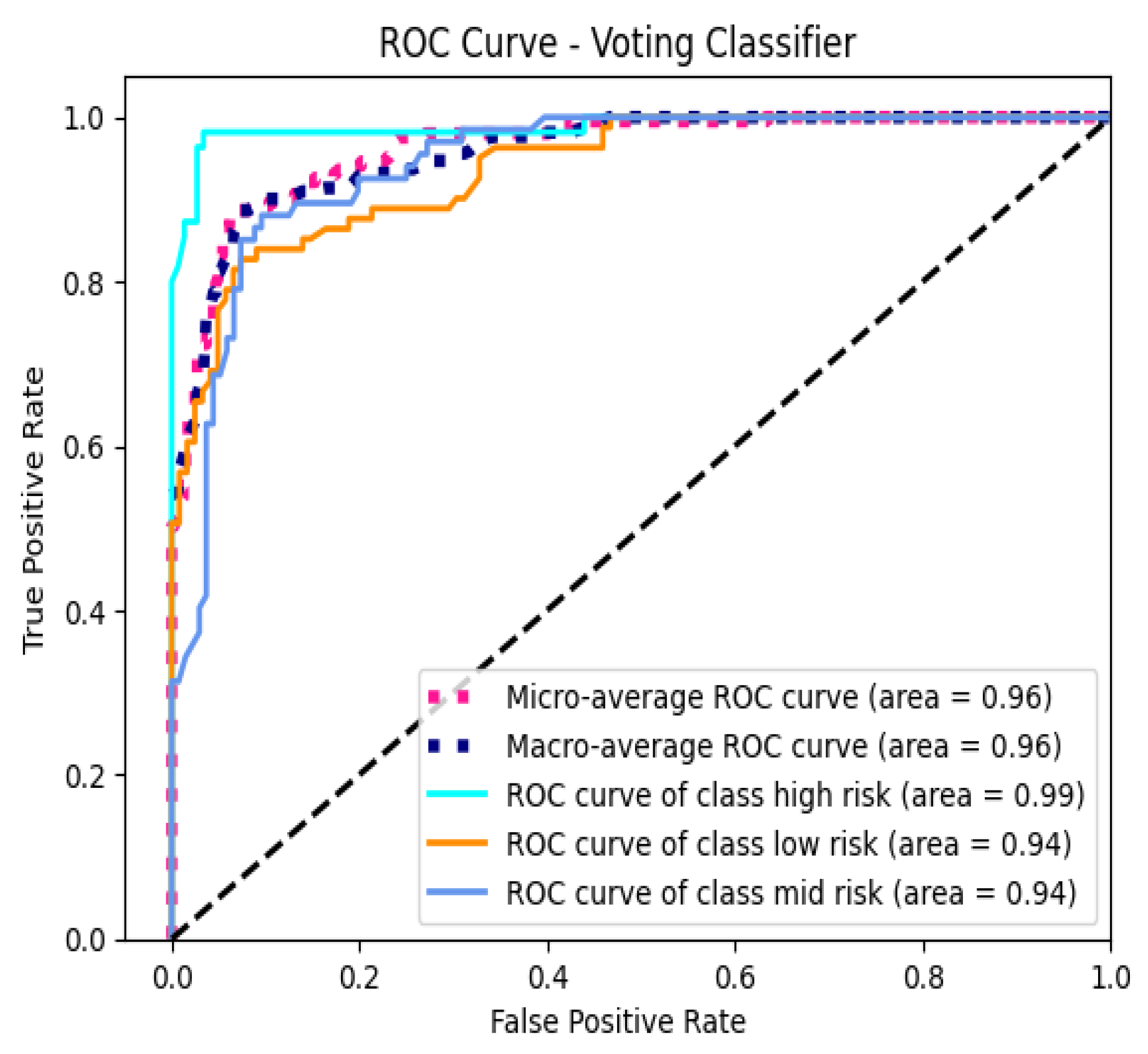
3.5. AUC-ROC Analysis
Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted for each class to evaluate the model’s discriminative performance. The macro-average AUC-ROC score was 95.67%, and the micro-average AUC-ROC score was 96.19%, indicating that the model exhibits excellent ability to distinguish between the different pregnancy risk levels across all classes.
Figure 4.
ROC Curve - Voting Classifier
Figure 4.
ROC Curve - Voting Classifier
3.6. Feature Importance Analysis
Both the Random Forest and XGBoost models identified Blood Sugar (BS) as the most significant feature in predicting pregnancy risk levels. In the Random Forest model, Blood Sugar (BS) contributed 35.99% to the model’s decisions, followed by Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) at 19.24%, Age at 15.19%, Pulse Pressure (PP) at 11.06%, Heart Rate at 10.48%, and Body Temperature at 8.05%.
In the XGBoost model, Blood Sugar (BS) remained the most influential feature, accounting for 25.37% of the model’s predictive power. This was followed by Body Temperature at 23.42%, Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) at 17.41%, Pulse Pressure (PP) at 13.88%, Age at 10.08%, and Heart Rate at 9.85%.
These results highlight the critical role of blood sugar levels in assessing pregnancy risk, as consistently identified by both models. While the importance of other features varies slightly between the models, factors such as Mean Arterial Pressure, Body Temperature, Pulse Pressure, Age, and Heart Rate also contribute significantly to the predictive capabilities of the models.
3.7. Misclassification Analysis
An analysis of misclassified samples from the Voting Classifier revealed a total of 26 instances. The distribution of true labels among these misclassifications included 14 instances of Low Risk, 10 instances of Mid Risk, and 2 instances of High Risk. This indicates that the majority of misclassifications occurred in the Low Risk and Mid Risk categories.
Sample Misclassifications
Table 5.
Sample Misclassified Instances
Table 5.
Sample Misclassified Instances
| No. |
Age |
BS |
BodyTemp |
HeartRate |
PP |
MAP |
True → Predicted |
| 1 |
-1.0297 |
-0.5562 |
-0.4927 |
0.6814 |
-0.5782 |
-0.5851 |
Low Risk → Mid Risk |
| 2 |
0.9005 |
2.8084 |
-0.4927 |
-0.5276 |
1.1532 |
0.5478 |
High Risk → Mid Risk |
| 3 |
2.2368 |
-0.2834 |
-0.4927 |
0.0769 |
0.2875 |
0.3212 |
High Risk → Low Risk |
| 4 |
-1.1040 |
-0.8290 |
-0.4927 |
-0.5276 |
-1.4439 |
-2.1711 |
Mid Risk → Low Risk |
| 5 |
-0.5843 |
-0.5865 |
-0.4927 |
0.3187 |
-0.5782 |
-1.2648 |
Mid Risk → Low Risk |
3.8. Statistical Analysis
We conducted a paired t-test to compare the cross-validation F1 Macro scores of the Random Forest and XGBoost models. The Random Forest model achieved F1 Macro scores of 0.8014, 0.7932, 0.7852, 0.8245, and 0.8126 across the five folds. The XGBoost model obtained F1 Macro scores of 0.7774, 0.8268, 0.7948, 0.8251, and 0.8312. The paired t-test resulted in a t-statistic of -0.7969 and a p-value of 0.4701. Since the p-value is greater than 0.05, we conclude that there is no statistically significant difference between the performances of the Random Forest and XGBoost models.
3.9. Overall Findings
The Voting Classifier demonstrated the best performance among all models, achieving high predictive accuracy across all risk levels. Blood Sugar (BS) was consistently identified as the most important feature in predicting pregnancy risk. The model also achieved high AUC-ROC scores, indicating strong discriminative ability. Misclassifications were more common between the Low Risk and Mid Risk classes, suggesting some overlap in feature patterns between these groups.
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Performance and Ensemble Advantage
The Voting Classifier, which combines the strengths of both the Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost (XGB) classifiers, demonstrated superior performance compared to the individual models. This enhancement underscores the inherent advantage of ensemble methods in machine learning, particularly in capturing diverse patterns within complex datasets that single models might overlook.
Ensemble methods leverage the concept of
model diversity, where different algorithms or models make varying errors. By aggregating their predictions, ensemble classifiers can mitigate individual weaknesses, leading to improved overall performance. In this study, the Voting Classifier benefited from the robustness of RF, which excels in handling high-dimensional data and mitigating overfitting through averaging, and the efficiency of XGB, known for its gradient boosting capabilities and superior handling of structured data [
23,
24].
Moreover, the ensemble approach enhances model stability. While RF introduces randomness by selecting different subsets of features and data samples for each tree, XGB focuses on correcting the errors of its predecessors, thereby refining the decision boundaries. The combination of these methodologies in the Voting Classifier likely contributed to its higher accuracy and macro F1 score, as evidenced by the results.
Comparing these findings to previous studies, [
8] also observed that ensemble methods outperform individual classifiers in predicting preeclampsia, highlighting a consistent trend across different pregnancy-related risk predictions. This alignment reinforces the reliability of ensemble techniques in medical predictive modeling.
4.2. Importance of Feature Selection
Feature importance analysis revealed that
Blood Sugar (BS) was the most significant predictor in both RF and XGB models. This finding aligns with clinical understanding, as elevated blood sugar levels are closely associated with conditions like gestational diabetes mellitus, which can lead to significant maternal and fetal complications [
3].
The prominence of BS underscores the critical role of metabolic indicators in assessing pregnancy risks. Additionally, the analysis highlighted
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) and
Pulse Pressure (PP) as influential features, indicating that cardiovascular health metrics are equally vital in risk stratification. This is consistent with literature suggesting that hypertension and related blood pressure abnormalities are significant predictors of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preeclampsia and preterm birth [
13].
Interestingly, while Age and Heart Rate also contributed to the models, their lower importance scores suggest that, within the context of this dataset, metabolic and cardiovascular factors are more directly indicative of pregnancy risk levels. This insight prompts a reevaluation of feature selection strategies in similar studies, emphasizing the need to prioritize physiological markers over demographic variables when appropriate.
Furthermore, the correlation analysis revealed multicollinearity between certain features, such as Age and BS, and BS and MAP. While multicollinearity can pose challenges for some algorithms, ensemble methods like RF and XGB are inherently capable of managing correlated features through their tree-based structures and regularization techniques. This capability ensures that the models do not overly rely on any single correlated feature, maintaining overall predictive performance.
4.3. Addressing Class Imbalance with ADASYN
Class imbalance is a pervasive issue in medical datasets, where minority classes (e.g., high-risk pregnancies) are underrepresented compared to majority classes (e.g., low-risk pregnancies). Such imbalance can lead to biased models that perform well on majority classes while neglecting minority classes, which are often of greater clinical importance [
7].
In this study, the Adaptive Synthetic Sampling (ADASYN) method was employed to address class imbalance. ADASYN enhances the minority class by generating synthetic samples, particularly focusing on those instances that are harder to learn, thereby improving the decision boundaries around these classes. By setting n_neighbors to 3, ADASYN effectively generated synthetic instances in regions with sparse minority class data, facilitating better model learning and reducing bias.
The application of ADASYN resulted in a more balanced class distribution, with the low, mid, and high-risk classes having 332, 325, and 276 samples, respectively. This balance is crucial for training models that are sensitive to all classes, ensuring that high-risk pregnancies are accurately identified. The improved macro F1 scores across models corroborate the effectiveness of ADASYN in enhancing minority class detection.
Comparatively, traditional oversampling methods like Random Over Sampling (ROS) might introduce redundancy by replicating existing minority samples, potentially leading to overfitting [
20]. In contrast, ADASYN’s synthetic sample generation introduces variability, offering a more robust augmentation strategy that enhances the model’s generalization capabilities.
However, it is important to acknowledge that synthetic data generation methods like ADASYN may not fully capture the intricate variability inherent in real-world data. While ADASYN improves model performance on the training set, external validation with independent datasets is essential to ensure that the models maintain their predictive power in diverse clinical settings.
4.4. Model Discrimination and AUC-ROC Analysis
The high Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC-ROC) scores for the Voting Classifier—95.67% (macro-average) and 96.19% (micro-average)—demonstrate the model’s exceptional discriminative ability. These scores indicate that the model can effectively distinguish between different pregnancy risk levels across all classes, a critical requirement for clinical decision-making.
AUC-ROC is a robust metric that evaluates a model’s performance across all classification thresholds, providing a comprehensive assessment of its ability to rank positive instances higher than negative ones. The high AUC-ROC scores suggest that the Voting Classifier maintains a strong true positive rate while minimizing false positives, which is essential for identifying high-risk pregnancies without overwhelming healthcare providers with false alarms.
Comparing these results to existing literature, similar studies have reported varying AUC-ROC scores based on the specific models and datasets used. For instance, Sakr and et al. [
8] achieved AUC-ROC scores above 90% using ensemble methods for preeclampsia prediction, reinforcing the efficacy of ensemble techniques in medical risk assessments.
Furthermore, the precision-recall curves (
Figure 3) complement the AUC-ROC analysis by highlighting the trade-offs between precision and recall for each class. The Voting Classifier’s performance in these curves aligns with its high AUC-ROC scores, underscoring its balanced capability to correctly identify high-risk pregnancies while maintaining a low rate of false positives.
4.5. Misclassification Insights
An in-depth analysis of misclassified samples from the Voting Classifier revealed 26 instances where the model’s predictions did not align with the true risk levels. Notably, the majority of misclassifications occurred between the Low Risk and Mid Risk classes, with 14 and 10 instances, respectively. Only 2 misclassifications involved the High Risk class.
This pattern suggests that the model struggles to distinguish between low and mid-risk pregnancies, possibly due to overlapping feature distributions between these categories. Such overlaps can stem from the subtle variations in physiological measurements that do not strongly differentiate mid-risk from low-risk cases. For instance, slight elevations in blood sugar or blood pressure might not be sufficient to categorically classify a pregnancy as mid-risk, leading to ambiguity.
These misclassifications highlight the need for enhanced feature representation or the incorporation of additional distinguishing features. Potential avenues for improvement include the inclusion of temporal data, such as changes in blood sugar and blood pressure over the course of pregnancy, which could provide a more dynamic view of risk progression. Additionally, integrating more comprehensive clinical indicators, such as body mass index (BMI), history of previous pregnancies, genetic markers, and socio-economic factors, might offer more granular insights into risk levels.
Advanced feature engineering techniques, such as creating composite features or leveraging dimensionality reduction methods like Principal Component Analysis (PCA), could also help in capturing the underlying patterns more effectively. Moreover, employing cost-sensitive learning strategies that assign higher penalties to misclassifications of higher-risk classes could further enhance the model’s focus on accurately identifying high-risk pregnancies.
4.6. Statistical Significance and Model Comparison
The paired t-test conducted to compare the cross-validation F1 Macro scores of the Random Forest and XGBoost models yielded a t-statistic of -0.7969 and a p-value of 0.4701. Given that the p-value exceeds the conventional significance threshold of 0.05, we conclude that there is no statistically significant difference between the performances of the RF and XGB models.
This finding suggests that both models perform comparably in predicting pregnancy risk levels, with neither exhibiting a distinct advantage over the other in this specific application. This equivalence reinforces the rationale for utilizing an ensemble approach, as combining the two models can harness their individual strengths to achieve superior overall performance, as observed with the Voting Classifier.
The lack of significant difference also implies that model selection can be flexible, allowing practitioners to choose either RF or XGB based on other considerations such as computational efficiency, interpretability, or ease of integration into clinical workflows.
However, it is important to note that statistical tests like the paired t-test assume normality of the differences between paired observations. Given the relatively small number of folds (5-fold cross-validation), the normality assumption may not hold robustly. Future studies with larger cross-validation splits or employing non-parametric tests like the Wilcoxon signed-rank test could provide more reliable comparisons.
4.7. Clinical Implications
The high accuracy and discriminative ability of the developed models, particularly the Voting Classifier, have significant clinical implications. Early and accurate identification of pregnancy risk levels enables healthcare professionals to implement preventive measures, allocate resources efficiently, and develop personalized care plans for expectant mothers.
Accurate risk stratification can lead to timely interventions for high-risk pregnancies, reducing the likelihood of complications such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and preterm birth. Moreover, the models’ ability to maintain high performance across all risk levels ensures that they are reliable tools in diverse clinical settings. Integrating such predictive models into electronic health record (EHR) systems can facilitate real-time risk assessments, supporting clinicians in making informed decisions.
The identification of Blood Sugar (BS) as the most significant predictor also emphasizes the importance of metabolic monitoring during pregnancy. Clinicians can focus more on managing blood sugar levels to mitigate associated risks effectively. Additionally, the inclusion of cardiovascular metrics like MAP and PP highlights the need for comprehensive cardiovascular assessments as part of prenatal care.
However, the successful clinical application of these models requires further validation through prospective studies and integration with clinical workflows. Ensuring model interpretability is crucial for gaining the trust of healthcare professionals. Techniques such as SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) values or LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) can be employed to elucidate model predictions, enhancing transparency and facilitating clinical adoption.
4.8. Limitations
Despite the promising results, this study has several limitations that must be acknowledged:
Sample Size: The dataset’s relatively small size may limit the generalizability of the findings. Larger datasets encompassing diverse populations are necessary to ensure that the models perform consistently across different demographic and clinical groups.
Class Imbalance: Although ADASYN effectively addressed class imbalance, synthetic data generation methods may not fully capture the inherent variability of real-world data. This limitation could affect the model’s performance when deployed in varied clinical settings where data distributions may differ.
Feature Scope: The study was restricted to a specific set of physiological measurements, excluding potentially relevant features such as genetic information, detailed medical histories, lifestyle factors, and socio-economic indicators. Incorporating a broader range of features could enhance the models’ predictive capabilities and provide a more comprehensive risk assessment.
Risk of Overfitting: Training and testing the models on the same dataset, even with cross-validation, poses a risk of overfitting. Overfitted models may perform well on the training data but fail to generalize to unseen data. External validation using independent datasets is essential to evaluate the models’ robustness and real-world applicability.
Model Interpretability: While ensemble methods offer superior performance, they are often perceived as "black-box" models, making it challenging to interpret the underlying decision-making processes. Enhancing model interpretability is crucial for clinical acceptance and trust.
Temporal Dynamics: The dataset did not account for temporal changes in physiological measurements throughout pregnancy. Incorporating time-series data could provide insights into the progression of risk levels and improve predictive accuracy.
Ethical Considerations: The study utilized anonymized, publicly available data. However, ethical considerations regarding data privacy, informed consent, and potential biases in model predictions need continuous attention, especially when deploying models in sensitive healthcare settings.
Addressing these limitations in future research will be pivotal in enhancing the models’ effectiveness and ensuring their practical utility in clinical environments.
5. Future Work
Future research could focus on expanding the dataset to include a larger and more diverse population, which would enhance the generalizability of the models. Incorporating additional features, such as genetic markers or detailed medical histories, may improve predictive accuracy. Enhancing model interpretability through techniques like explainable AI could provide deeper insights into how the models make predictions, increasing trust among clinicians. Real-world validation is essential; implementing the models in clinical settings would assess their practical utility and effectiveness in supporting pregnancy risk assessment. Additionally, exploring adaptive modeling approaches could allow the models to update and improve over time as new data becomes available, ensuring they remain relevant and accurate in changing environments.
6. Conclusion
This study demonstrates the effectiveness of ensemble methods, particularly the Voting Classifier combining Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost (XGB), in predicting pregnancy risk levels within an imbalanced medical dataset. The implementation of ADASYN for oversampling successfully addressed the class imbalance issue, enhancing the models’ ability to learn from minority class examples and improving overall predictive performance.
The individual models, Random Forest and XGBoost, exhibited strong classification capabilities, achieving high accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-scores. Feature importance analysis consistently identified Blood Sugar (BS) as the most significant predictor, underscoring its critical role in assessing pregnancy risk. Other vital features included Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP), Body Temperature, and Pulse Pressure (PP), which also contributed substantially to the models’ predictions.
The Voting Classifier outperformed the individual models by leveraging the strengths of both RF and XGB. It achieved a higher macro F1-score and demonstrated superior performance across all risk levels, particularly in correctly identifying high-risk pregnancies. The high AUC-ROC scores further indicate the model’s excellent discriminative ability, confirming its effectiveness in distinguishing between different pregnancy risk categories.
Misclassification analysis revealed that most errors occurred between the Low Risk and Mid Risk classes, suggesting some overlap in their feature patterns. This insight highlights the need for additional features or more sophisticated modeling techniques to better distinguish between these classes.
Despite the promising results, the study has several limitations. The relatively small sample size may limit the generalizability of the findings to a broader population. While ADASYN helped mitigate class imbalance, synthetic data may not capture all real-world variability, potentially affecting model performance on unseen data. The models relied on a limited set of features; incorporating additional relevant features could enhance predictive accuracy. Moreover, there is a risk of overfitting since the models were trained and tested on the same dataset. External validation with independent datasets is necessary to confirm the models’ robustness and applicability in real-world settings.
In conclusion, this study underscores the potential of ensemble machine learning methods in predicting pregnancy risk levels. The successful application of the Voting Classifier and the identification of key predictive features contribute to advancing risk assessment in prenatal care. By addressing the identified limitations—such as expanding the dataset, incorporating more features, and validating the models externally—future research can build upon these findings to develop more robust, accurate, and generalizable models. Ultimately, such advancements have the potential to improve early detection of high-risk pregnancies, allowing for timely interventions and better health outcomes for both mothers and infants.
Acknowledgments
We thank the UCI Machine Learning Repository and the dataset contributors for providing access to the Maternal Health Risk Data Set.
References
- World Health Organization. Maternal mortality: key facts. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/maternal-mortality, 2019. Accessed: [Your Access Date].
- Johnson, J.M.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. Survey on deep learning with class imbalance. Journal of Big Data 2019, 6, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavakiotis, I.; Tsave, O.; Salifoglou, A.; Maglaveras, N.; Vlahavas, I.; Chouvarda, I. Machine learning and data mining methods in diabetes research. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2017, 15, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, Q.; Ma, L. Machine learning in prediction of preterm birth. Journal of Translational Medicine 2019, 17, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, K.A.; et al. Deep learning as a tool for prediction of preeclampsia in pregnant women. npj Digital Medicine 2019, 2, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Say, L.; Chou, D.; Gemmill, A.; Tuncalp, O.; Moller, A.B.; Daniels, J.; Gülmezoglu, A.M.; Temmerman, M.; Alkema, L. Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. The Lancet Global Health 2014, 2, e323–e333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Garcia, E.A. Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2009, 21, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, S.; et al. Predicting preeclampsia: A comparison of machine learning techniques. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufriyana, H.; Wu, Y.W.; Su, E.C.Y.; et al. Comparison of machine learning approaches to classify maternal anemia levels. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making 2020, 20, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; et al. Hybrid deep learning model for predicting gestational diabetes mellitus. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 13303–13312. [Google Scholar]
- Calwin, C. Predicting Pregnancy Risk Levels with Machine Learning. https://www.kaggle.com/code/calwin9/predicting-pregnancy-risk-levels-with-machine-lear, 2021. Accessed: [Your Access Date].
- Dua, D.; Graff, C. UCI Machine Learning Repository. https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Maternal+Health+Risk+Data+Set, 2020. Accessed: [Your Access Date].
- Loerup, L.; Pullon, R.M.C.; Birks, J.; Fleming, S.; Mackillop, L.; Tarassenko, L. Trends of blood pressure and heart rate in normal pregnancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Medicine 2019, 17, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; Vanderplas, J.; Passos, A.; Cournapeau, D.; Brucher, M.; Perrot, M.; Duchesnay, E. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning: With Applications in R; Springer Texts in Statistics, Springer, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.E. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 13th ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences, 2016.
- Mayet, J.; Hughes, A. Cardiac and vascular pathophysiology in hypertension. Heart 2003, 89, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 9th ed.; Wiley, 2017.
- Moore, D.S.; McCabe, G.P.; Craig, B.A. Introduction to the Practice of Statistics, 9th ed.; W. H. Freeman, 2017.
- He, H.; Bai, Y.; Garcia, E.A.; Li, S. ADASYN: Adaptive Synthetic Sampling Approach for Imbalanced Learning. IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2008, pp. 1322–1328. [CrossRef]
- Gaso, M.S.; Mekuria, R.R.; Khan, A.; Gulbarga, M.I.; Tologonov, I.; Sadriddin, Z. Utilizing Machine and Deep Learning Techniques for Predicting Re-admission Cases in Diabetes Patients. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies 2024; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; CompSysTech ’24, p. 76–81. [CrossRef]
- Tologonov, I.; Mekuria, R.R.; Istamov, K.; Gaso, M.S. Detection of Tuberculosis Using Convolutional Neural Network. EasyChair Preprint 1 3500, EasyChair, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Machine Learning 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 2016, pp. 785–794. [CrossRef]
- Kuncheva, L.I. Combining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and Algorithms; Wiley-Interscience, 2004.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).