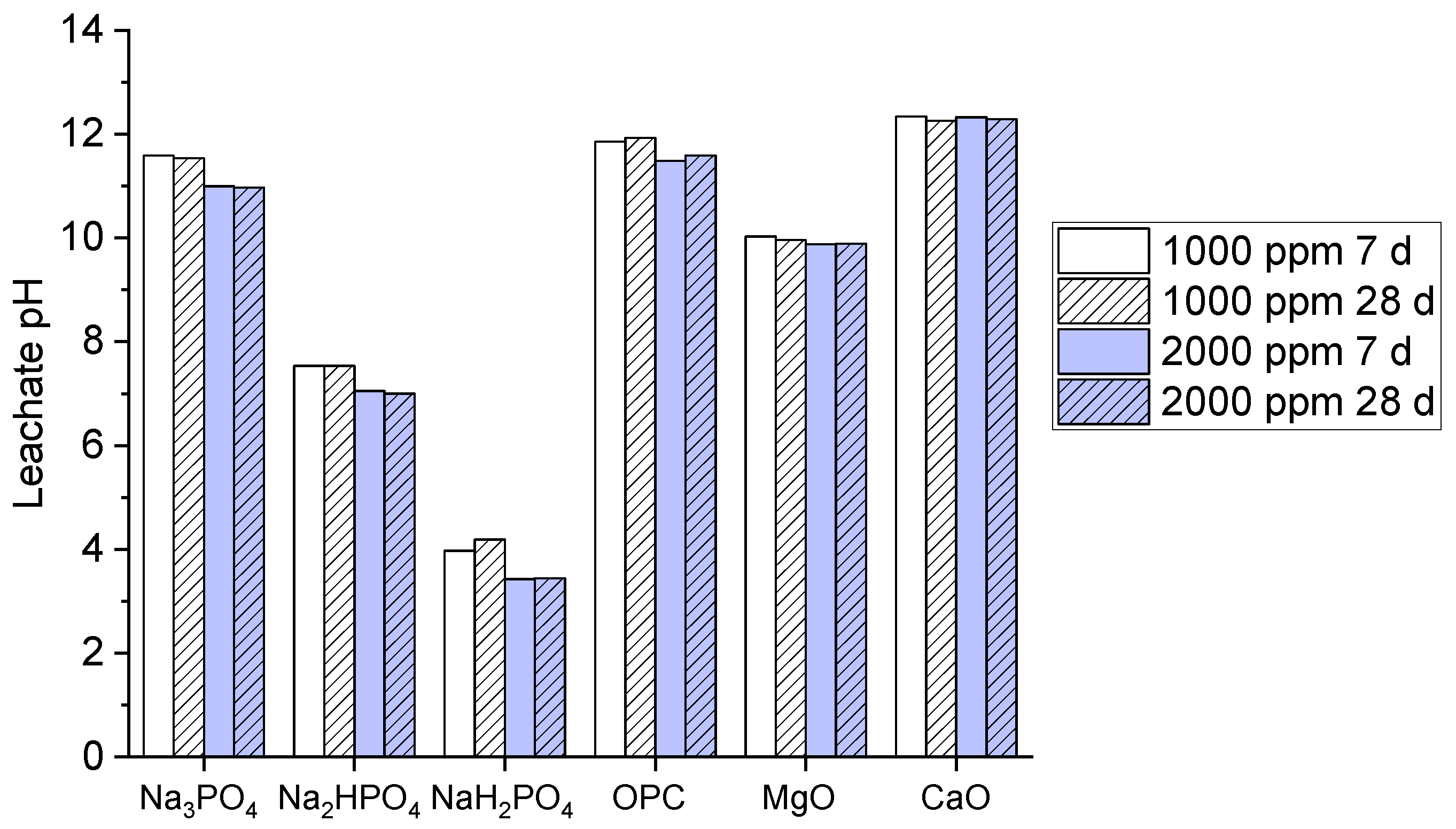Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS)
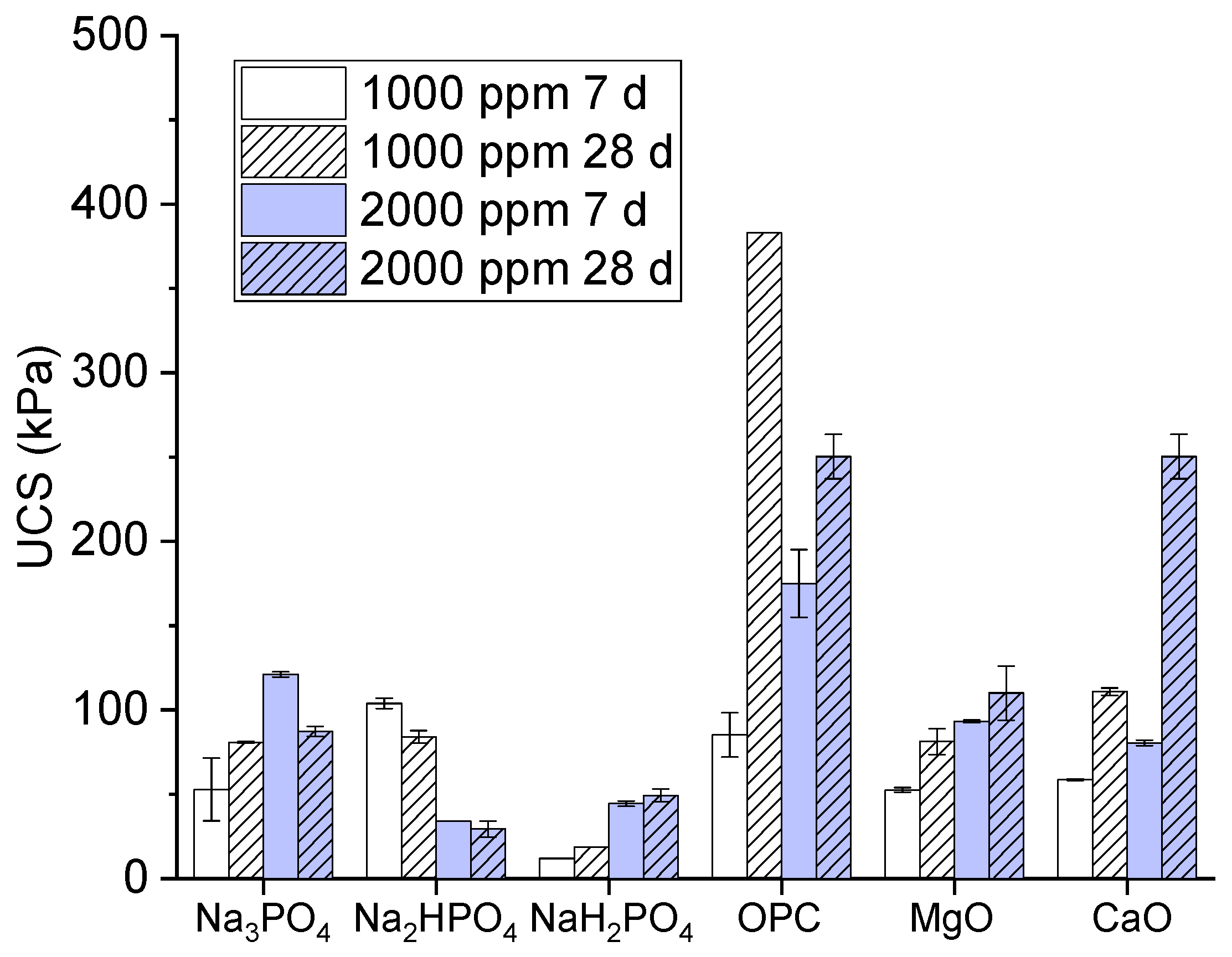
The unconfined compressive strength (UCS) values of multi-metal polluted soil treated with different phosphate-based binders and additives, including Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), magnesium oxide (MgO), and calcium oxide (CaO), are depicted in (
Figure 1). The values of UCS are expressed in kilopascals (kPa). The treatments are evaluated at two distinct concentrations (1000 parts per million and 2000 parts per million) and two different curing durations (7 days and 28 days).
The present study results and key observations of binders in comparison between monosodium phosphate, disodium phosphate, and trisodium phosphate, are explained as; monosodium phosphate (NaH₂PO₄) has the lowest Unbound Colloidal Solids (UCS) values among the polyphosphate-based binders. This value exhibits an uncertain rise with concentration and curing time, although they are notably lower than those seen for Na₃PO₄ and Na₃HPO₄. While, on the other hand, disodium phosphates Na₂HPO₄) displays lower water content saturation (UCS) values in comparison to Na₃PO₄. A clear correlation exists between higher concentration and longer curing time and an increase in UCS, albeit the values remain somewhat modest. Besides, the compound Trisodium Phosphate (Na₃PO₄) has intermediate Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) values, with greater strength recorded at 2000 ppm compared to 1000 ppm for curing periods of 7 and 28 days. Strength rises proportionally with extended cure duration.
Additionally, in comparison with OPC, MgO, and CaO our results depicted that ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) exhibits the highest Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) values as compared to all other binders that were examined. These values show a notable rise at 2000 ppm after 28 days of curing, reaching about 500 kPa. These findings suggest that Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) is very efficient in enhancing the structural integrity of the polluted soil. Moreover, magnesium Oxide (MgO) has moderate Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) values, surpassing those of Na₂HPO₄ and NaH₂PO₄ but falling short of Na₃PO₄ and OPC [
19]. However, its strength rises proportionally with both increased concentration and extended cure duration. Calcium Oxide (CaO) also exhibits moderate Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) values, as compared to MgO, whereby its strength gradually increases with time and higher concentrations. While the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) values of CaO are often lower than those obtained with OPC [
20].
Though, while discussing about the effect of concentration of UCS for all the binders rise when the concentration becomes double from 1000-2000 ppm. This trend suggests that binder’s concentration and soil strengthen capacity are directly proportional to each other, when the binder’s concentration increases it also increases soil strength [
20]. On the other hand, for all phosphates-based binders the value of UCS is greater at 28 days as compared to 7 days. This comparison significantly expresses the extended curing duration enables and increases the interactions of chemical reactions which consequences greater soil strength.
Henceforth, the logical reasoning behind the effectiveness of binders, phosphate-based binders, MgO and CaO oxides performances and their implications are of great importance for stabilizing contaminated soil. Besides, when compared to alternative binders, OPC greatly improves the UCS of soil that is polluted with several metals. Whereas, soil contamination can be efficiently stabilized by OPC due to its hydraulic properties and pozzolanic reactions. Following the findings of the current study it seems that, OPC is the best binder for making soil stronger and more robust, especially in cases when pollution is substantially higher. Following 28 days at a concentration of 2000 ppm, OPC exhibits the highest unconfined compressive strength (UCS) values, approaching 500 kPa. While, on the other hand, the pozzolanic and hydraulic properties of OPC are well-known and are responsible for its exceptional performance [
21]. Important binding strength is provided by calcium hydroxide and calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) that are formed when OPC is hydrated. Therefore, according to the high UCS values, OPC has the ability to encapsulate metal pollutants, which could make them less mobile and less likely to leach. Because of this, OPC is an excellent binder for contaminated site cleanup and other similar applications that call for soil stabilization and pollutant immobilization [
22].
Additionally, in compared to Na₂HPO₄ and NaH₂PO₄, Na₃PO₄ is the most effective phosphate-based binder containing the ability to raise UCS, Na₃PO₄ may also proposed stabilization in the form of more stable complexes or precipitates formed by chemical interactions with metal impurities. Since phosphate-based binders aren't as powerful as OPC, therefore they possibly might not be enough to drastically increase strength on their own, but they could be useful in immobilizing some contaminants because of their capacity to react with water and produce binding phases, certain oxides (such as Mg(OH)₂ and Ca(OH)₂) [
23]. Although phosphate-based binders and MgO/CaO can enhance the UCS of polluted soil, whereas the results confirms that OPC is the superior choice, particularly for uses that demand strong soil. The selection of a binder for soil stabilization should, however, take environmental factors like leachability and OPC's effect on the environment into account.
With moderate UCS values, we find MgO and CaO. These binders work as binding agents because, when combined with water, they generate Mg(OH)₂ and Ca(OH)₂. This is why they boost strength by filling voids and cementing soil particles together. These hydroxides also increase the pH, promoting the precipitation of metal hydroxides, which aids in contaminant stabilization. [
24]. Due to its sluggish hydration process, MgO is renowned for its ability to cause a modest but steady increase in strength. In contrast, calcium oxide has a faster reaction time to produce calcium hydroxide, which helps boost initial strength [
25]. Although their UCS effectiveness is lower than that of OPC, they can nevertheless contribute to soil stabilization, particularly when mixed with other binders. More binders may accelerate chemical reactions, making soil matrices denser and stronger [
26]. However, increasing binder concentration may raise treatment costs and environmental impacts, such as OPC carbon emissions.
Similarly, the strength of soil samples increases significantly with extended curing time, from 7 days to 28 days. This is expected as curing time allows for more complete hydration and pozzolanic reactions, which are critical for the development of strength in cementitious materials. Longer curing periods facilitate the formation of more stable and crystalline structures, enhancing the UCS. For OPC, extended curing allows for more C-S-H to form, while for phosphate-based binders, longer curing may allow more complete complexation reactions. This observation underscores the importance of allowing adequate time for chemical stabilization processes to occur in remediation projects.
Leachability
Leachability is the very important and key factor referring to the potential contaminates to be released in to the environment when visible to other solvents. Typically, high pH defines the reduction in leaching when used with other phosphates binders. Leachate pH values of multi-metal-contaminated soil treated with phosphate-based binders (Na₃PO₄, Na₂HPO₄, NaH₂PO₄) and other common binders (OPC, MgO, CaO) at 1000 and 2000 ppm concentrations and 7 and 28 days curing times are shown in the (
Figure 2).
However, the graph shows that both Na₃PO₄ and Na₂HPO₄ both exhibits a high pH value approximately above10, which strongly shows the alkalinity but the pH becomes high at 28 days 2000 ppm concentration. Similarly, NaH₂PO₄ demonstrate significantly lower pH ranges from 4-5 signifying its acidic conditions. Besides, OPC, MgO, and CaO binders upholds high pH values above 9 which reflects its alkaline nature in compared to OPC and CaO which represents the highest pH stability. The reason behind high pH levels for Na₃PO₄ and Na₂HPO₄ suggested their effectiveness and efficiency in immobilizing metals via precipitation method under alkaline conditions which further enhances the stabilization of multi-metal contaminants. However, the acidic nature of NaH₂PO₄ may specified the limited metal immobilization potential as compared to other binders. Besides, OPC, MgO, and CaO additionally maintains strong alkalinity [
27], typical for these binders, which supports their known capability in metal stabilization by raising pH.
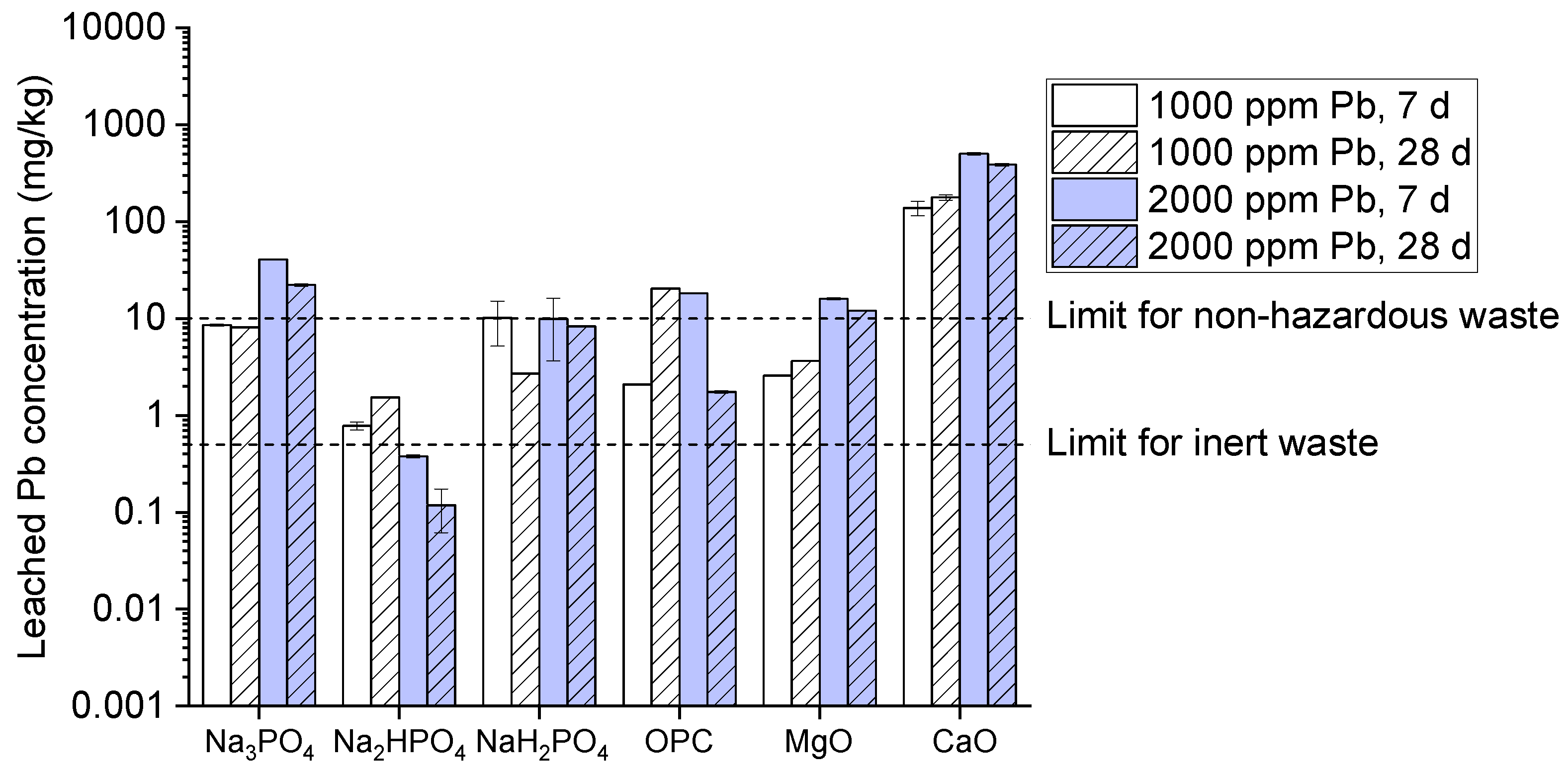
Furthermore, the leached lead (Pb) concentrations from multi-metal-contaminated soil treated with several binders (Na₃PO₄, Na₂HPO₄, NaH₂PO₄, OPC, MgO, and CaO) at 1000 and 2000 ppm concentrations and 7 and 28 days curing durations are shown in the (
Figure 3). The comparison includes non-hazardous and inert waste regulatory limits. Though, the graph explains that Na₃PO₄ somewhat reduced the leached Pb concentration drops with the passage of time within the range of 1000-2000 ppm while making in comparison between (Na₂HPO₄ + NaH₂PO₄) and OPC and MgO the strength of reduction of Pb concentration is significantly higher below the waste limit rather than OPC and MgO which further reduces Pb concentration moderately below the hazardous limits [
28]. Logical reason behind NaH₂PO₄ highest Pb immobilization potential, is due to its acidic nature promoting metal bonding or stable complexes[
29] which effectively reduced by Na₃PO₄ and Na₂HPO₄, though Pb remains above the inert waste limit. Besides, OPC and MgO temperately stabilizes owing to their pH-buffering abilities. While CaO's high leachability indicates poor Pb stabilization, which further limits Pb immobilization under these conditions.
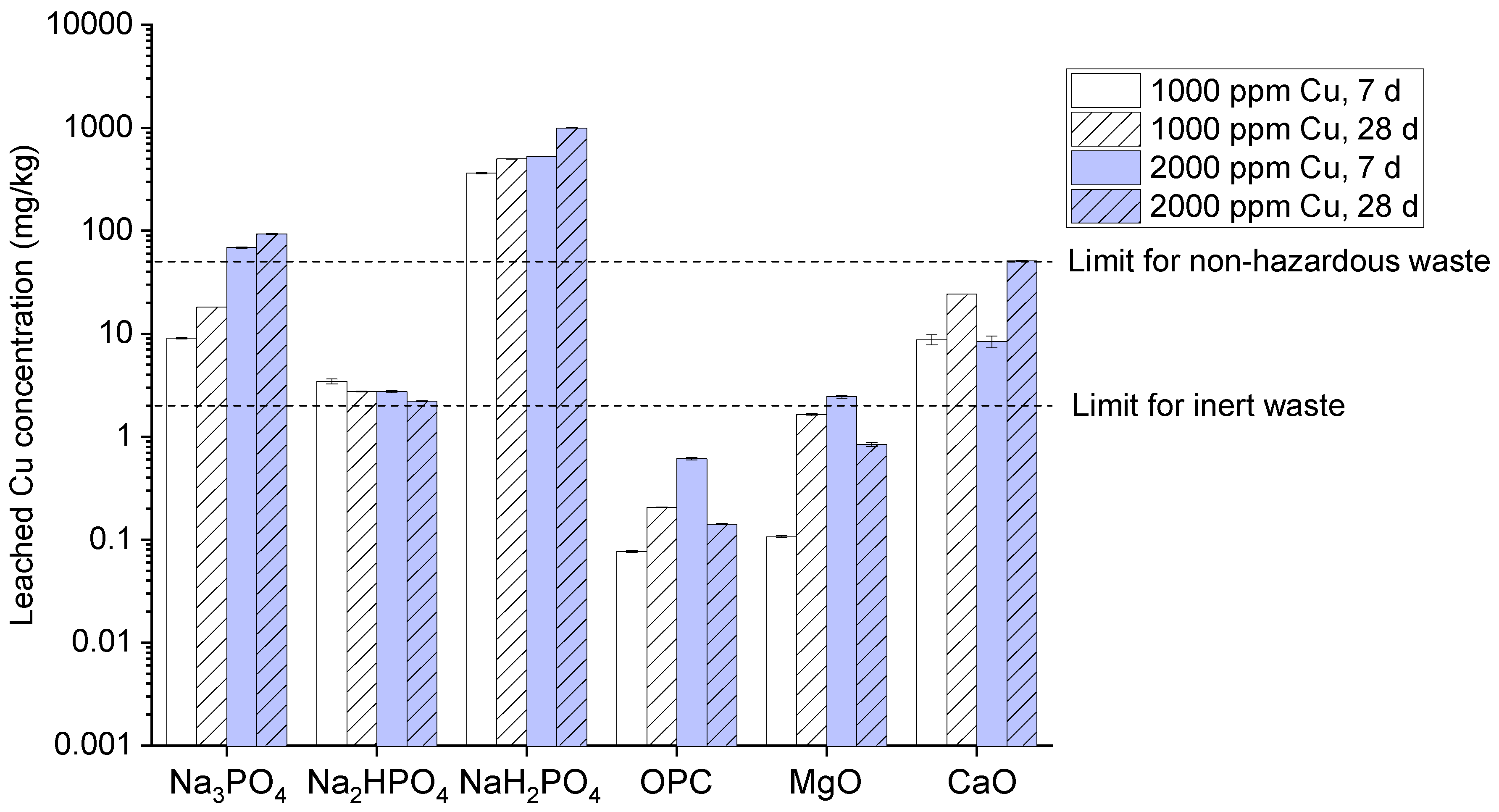
Additionally, the graph as shown in (
Figure 4) represents the leached copper concentration from various compounds like Na₃PO₄, Na₂HPO₄, NaH₂PO₄, OPC, MgO, and CaO at 1000-2000 ppm concentration for 7 and 28 days. Results revealed that among different sodium phosphate compounds Na₃PO₄ and Na₂HPO₄ confirms the high Cu leaching when it surpasses the limit for non-hazardous waste range from 100mg/kg. It’s due to the phosphate compound which make many insoluble metal-phosphate complexes which assists in stabilization [
30,
31]. According to our study results the mechanism of phosphorous is due to generation of less stable and soluble copper phosphates complexes which varies due to the significant variations in degree of dissociation in water and reduce its ability to bind with copper ions [
32]. Likewise, MgO and CaO also demonstrates the high leaching over time and concentration. Whereas, MgO shows a moderate effect on Cu leaching mostly below hazardous limit [
22]. While, Cao approaches slightly exceeds the limit for 2000 ppm at 28 days. It’s because they have the ability to increase the pH which leads to precipitation of copper hydroxide layers having the capability to bind metals like copper on its surface.
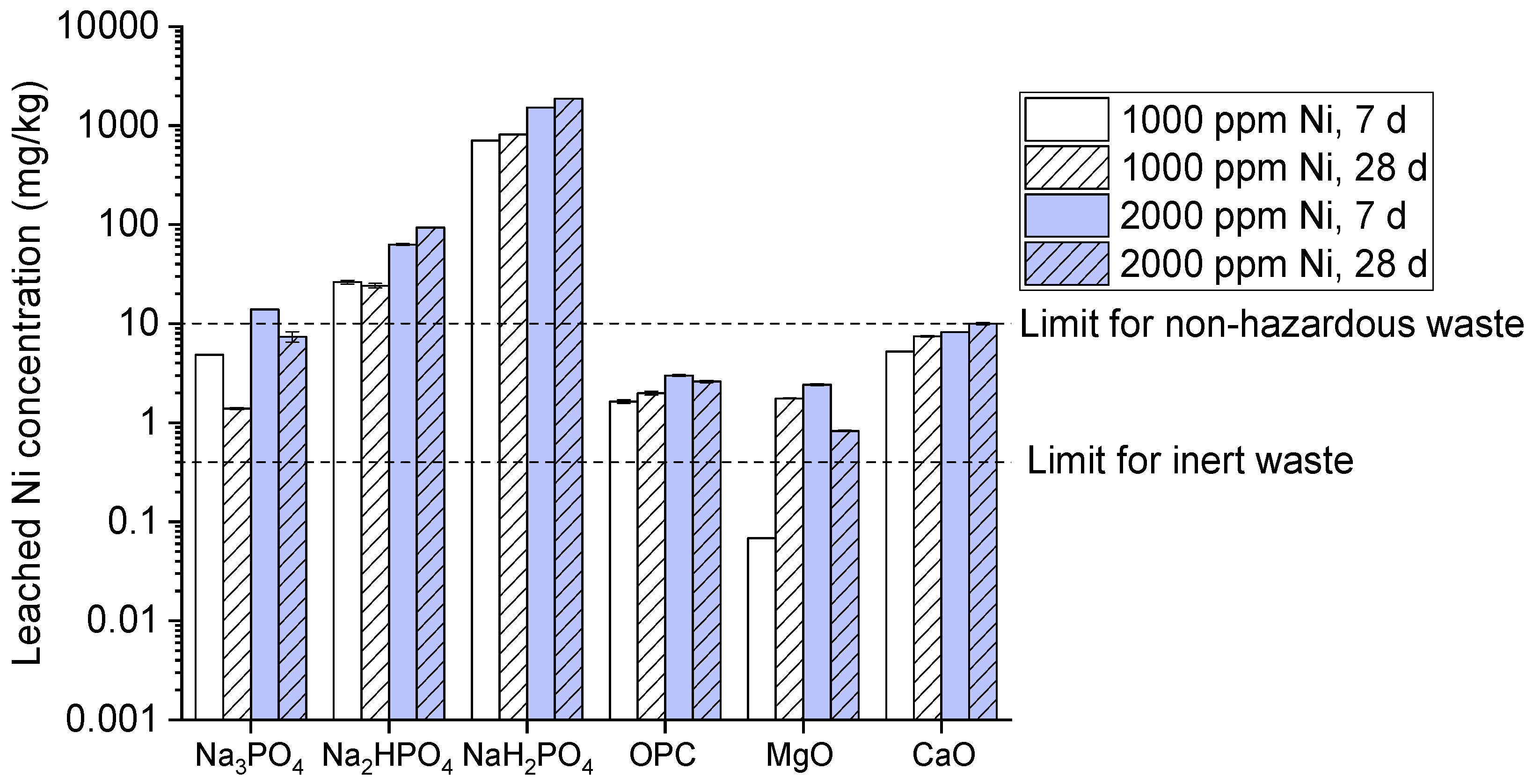
Similarly for nickel the leaching trend is relatively higher at 2000 ppm after 28 days showing highest leaching as described in (
Figure 5). OPC on the other hand represents decline trend of leaching at 2000 ppm after 28 days. But, MgO and CaO exhibits significantly moderate trend and surpasses the inert waste limit after 28 days. Th reason behind phosphate compounds results shows the same reason for cadmium with making highly insoluble complexes which leads to significant leaching [
33]. Similar behavior trend was observed for OPC which lower down the Ni concentration due to cementitious matrix creates a physical barrier around Ni ions. Furthermore, OPC’s has high pH which is less soluble and immobilize Ni. Additionally, MgO and CaO shows relative moderate Ni leaching due to its ability to make alkaline environment which aids Ni hydroxide precipitation and diminishes slightly at 28 days. It’s may be due to carbonation which reduces the pH and destabilizes Ni compounds making them more soluble [
34].
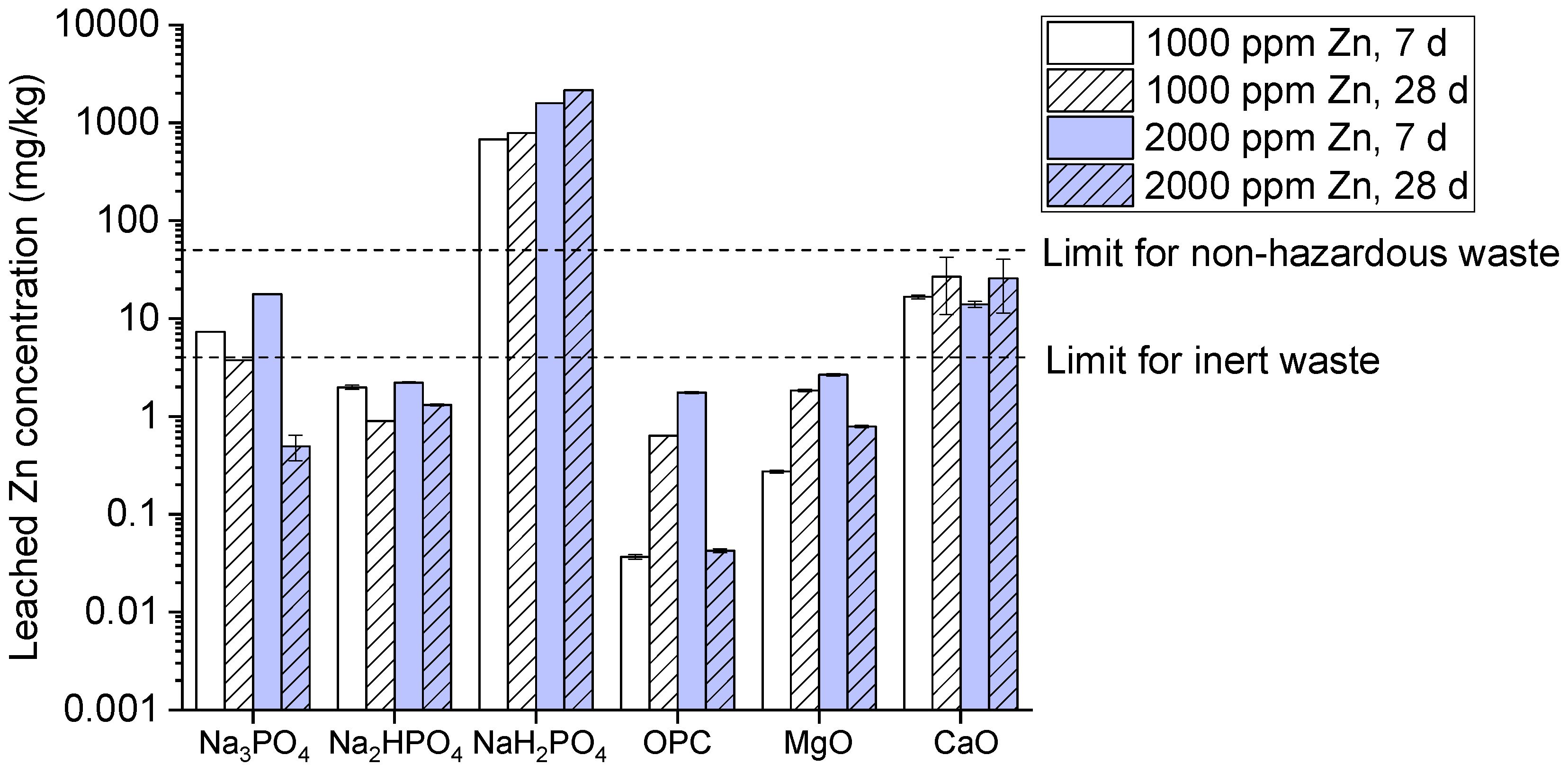
Onwards to Zinc leaching, results of the present study explain that Na₃PO₄ and NaH₂PO₄ particularly high leaching at 2000 ppm after 28 days as shown in (
Figure 6). While Na₂HPO₄ shows lower zinc leaching as compared to other phosphates compounds which still exceeds the inert waste limit of 2mg/kg at both concentrations. Besides, OPC also shows lower leaching level after 28 days which indicates strong immobilization. But, MgO and CaO exhibits relatively higher leaching value at 28 days. Reason behind phosphoric compounds leaching it’s not effectively immobilized Zn. It occurs maybe due to its intermediate dissociation. Moreover, leaching by MgO and CaO creates alkaline environment for immobilizing metals (Wang et al., 2020).
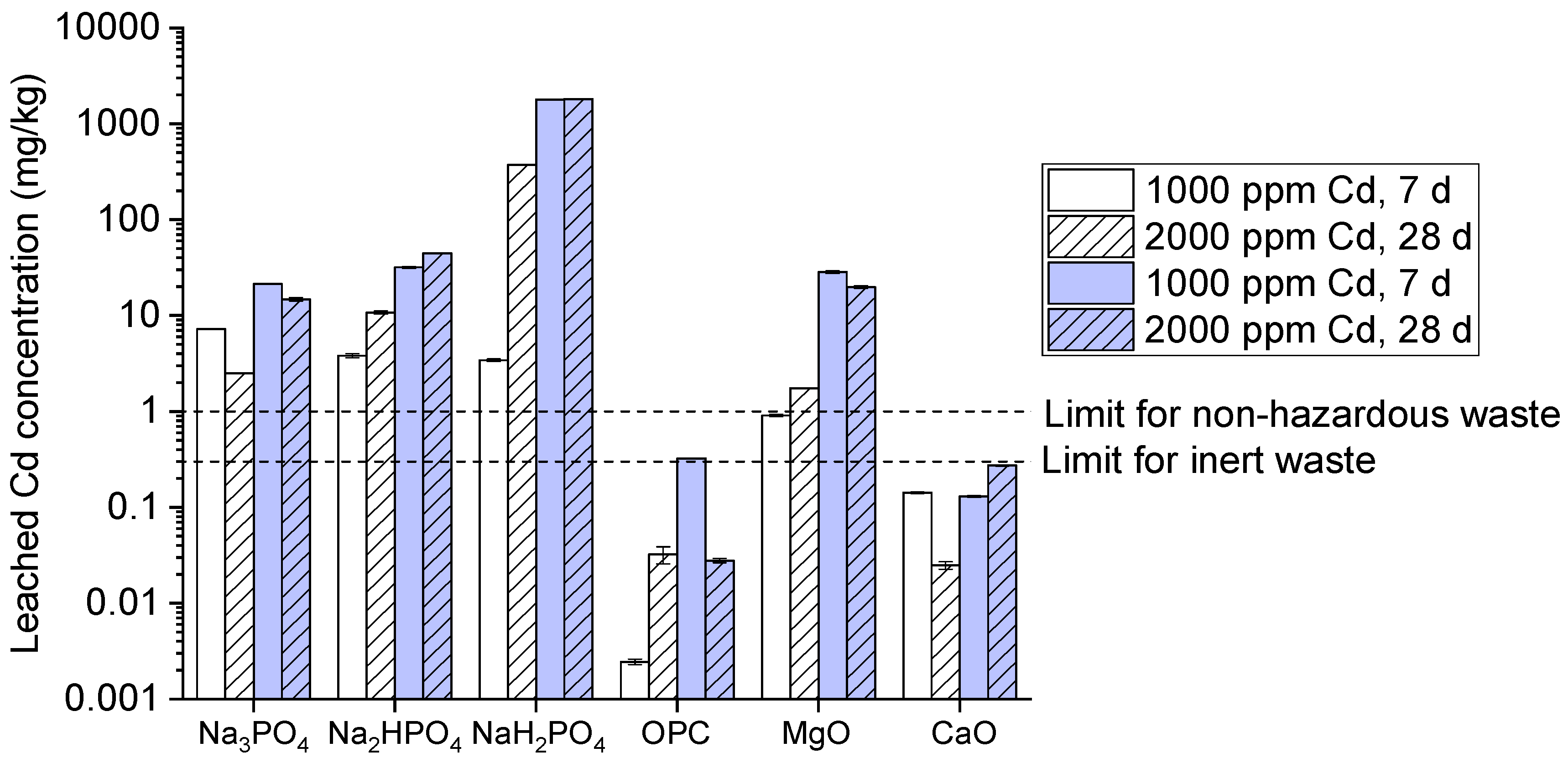
As well, the results of cadmium high leaching have been observed among all three phosphates compounds, along with slightly better performance from Na₂HPO₄ which exceeds the inert waste limit up to 2mg/kg as illustrated in (
Figure 7). OPC on the other hand gives very superb performance with cadmium leaching below the inert waste limit transversely all conditions. Likewise, MgO and CaO shows high cadmium leaching specifically at 2000 ppm after 28 days. Logical reasoning behind Na₂HPO₄ best performance is due to insoluble cadmium phosphate complexes for its immobilization. High leaching in cadmium is due to the unstable complexes or might be the soluble at present conditions. However, the variations among three phosphates groups are due to the fluctuation in pH and long exposure which shows strong immobilization for cadmium. MgO and CaO also relies on increasing the pH to immobilize cadmium through hydroxide precipitation [
36]. The reason behind it might be due to reduction in pH with the passage of time which further leads to cadmium hydroxides and increases cadmium stability [
37].
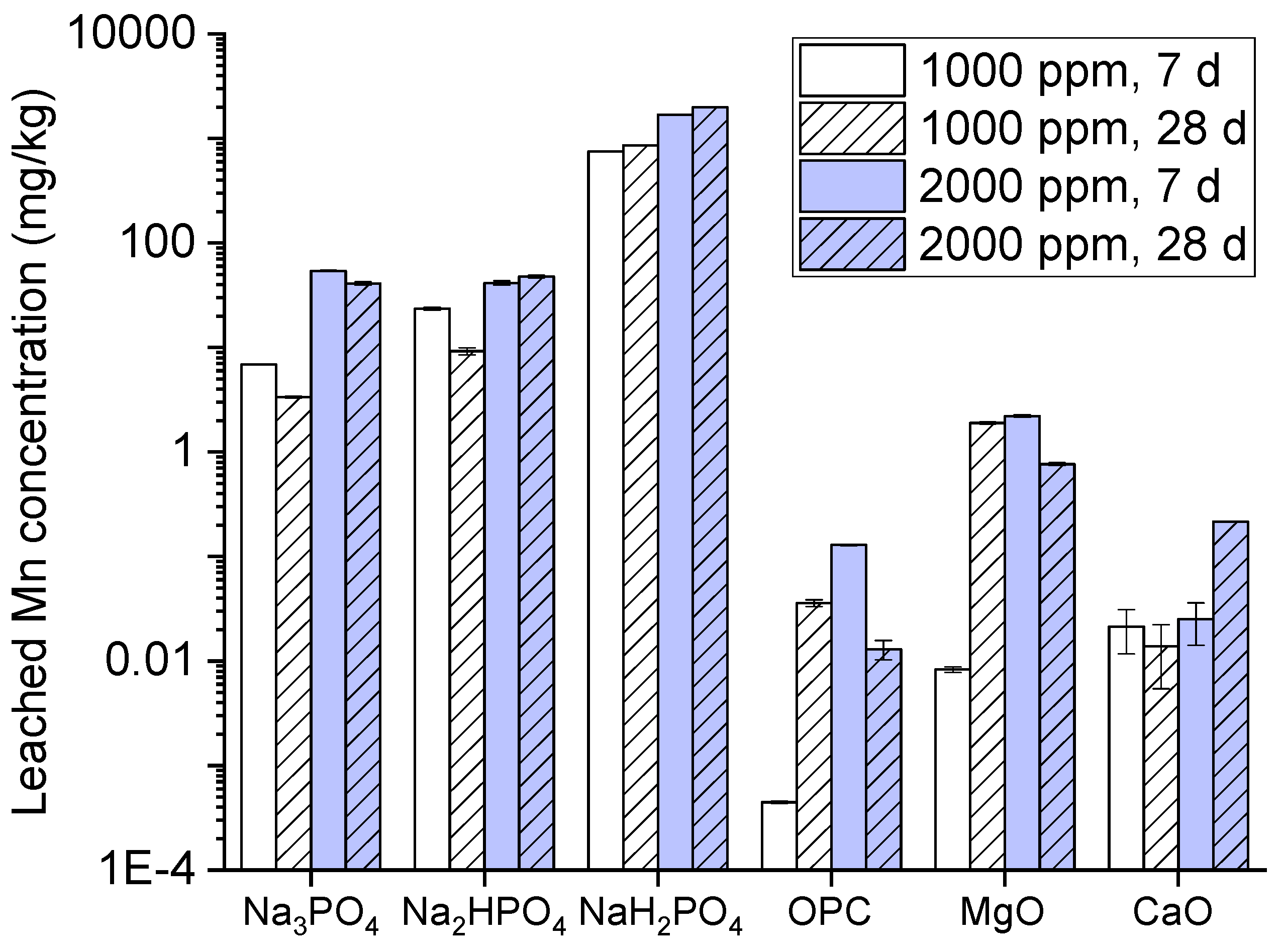
Manganese leaching become high with three phosphates compounds which suggests that manganese complexation is weak or unstable under this experimental condition. Manganese has different nature than other metals by not having strong insoluble complexes with phosphates at high pH as illustrated in (
Figure 8). OPC is low in leaching is due to its ability to generate highly alkaline environment which promotes manganese hydroxides having low solubility in this condition. Moreover, MgO and CaO on the other hand performs better but still allows manganese leaching for longer period of time Manganese helps to rise pH which further assists to precipitate Mn(OH)
2 but its immobilization capacity weakens with period of time [
38]. Though leaching increases with the passage of time especially for Na₃PO₄, NaH₂PO₄, MgO, and CaO. This recommends the initial immobilization mechanisms which may degrade or release more manganese in to the environment.
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
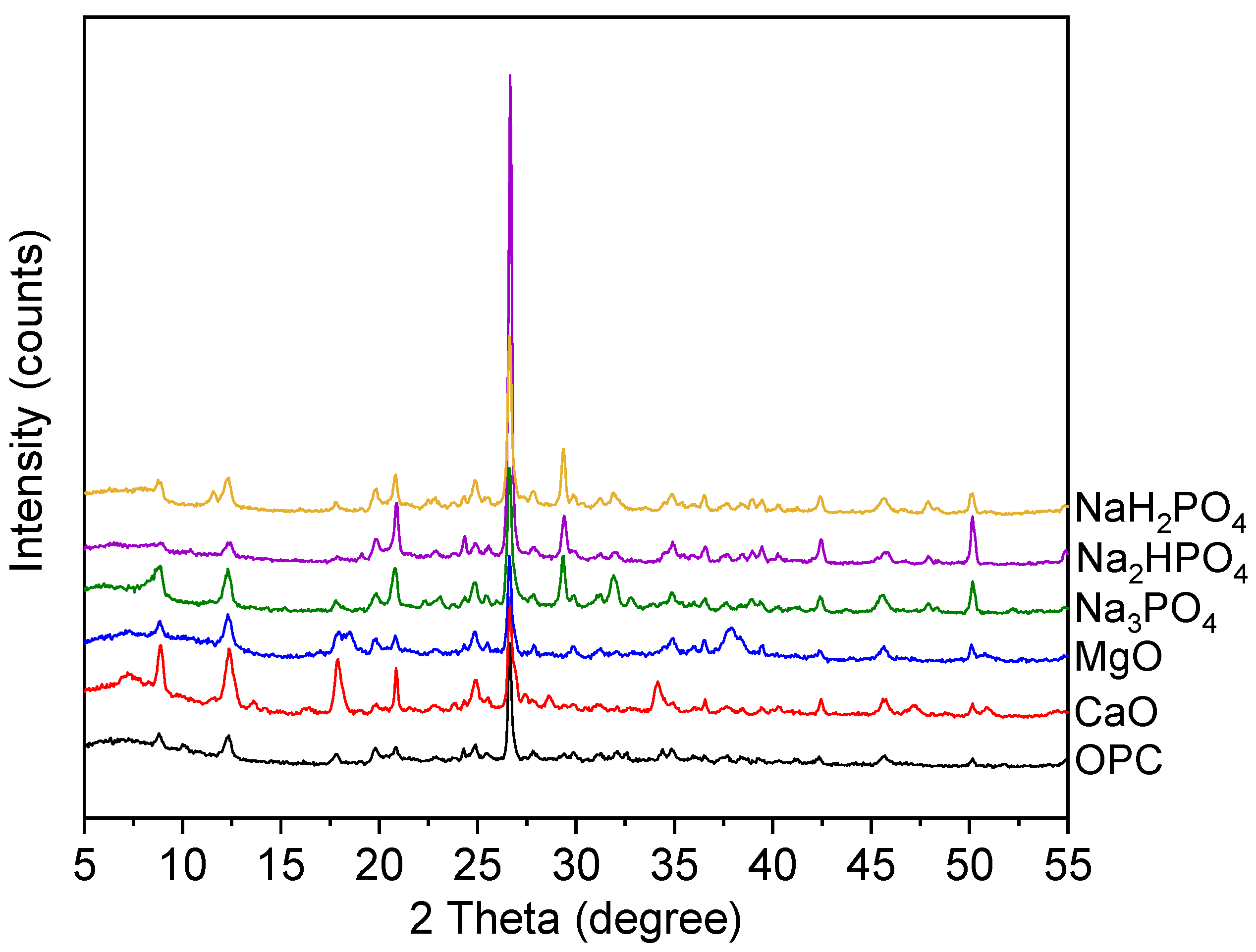
X-ray diffraction (XRD), also referred to as X-ray diffraction, is a very effective analytical method employed for investigating the crystal structure of materials. This technique enables the identification and characterization of several crystalline structures and phases within a sample by comparing the diffraction pattern with established reference patterns. Thus, in the existing study XRD pattern and the common Peaks at 2θ = Approximately 25–30° signifies the majority of the samples, irrespective of the binder employed, display a visible peak within the range of 25° to 30° as explains in the below (
Figure 9). However, this peak is most likely analogous to quartz, which is a prevalent mineral present in soil, demonstrates that the fundamental mineral composition of the soil remains intact even after treatment.
Moreover, the spectra linked with Na₃PO₄, Na₃HPO₄, and NaH₂PO₄ reveals well defined peaks that are less prominent in the treatments involving MgO, CaO, or OPC. The distinct peaks observed suggest the development of particular mineral phases predominantly composed of phosphate. These phases may be associated with the immobilization of metals by precipitation as metal-phosphate complexes [
39]. Additionally, the peaks in the OPC-treated soil are larger and less defined, indicating the production of weakly crystalline calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H), or amorphous phases, which are characteristic of OPC. The complex and less ordered nature of OPC hydration products is indicated by the absence of prominent peaks [
40]. Additionally, while comparing various phosphates-based binders (NaH₂PO₄, Na₂HPO₄, Na₃PO₄) it’s found that the specific diffraction peaks seen in these treatments indicate the development of solid mineral phases, most likely incorporating different phosphate compounds. These phases have the potential to be advantageous in stabilizing heavy metals by virtue of chemisorption or precipitation as insoluble phosphate salts [
41].
Likewise, MgO and CaO binders have more sharp and defined peaks and crystalline structures than Ordinary Portltand cement (OPC) due to their xrd patterns. However, these chemicals may aid in the creation of several crystalline phases like brucite (Mg(OH)₂) and portlandite (Ca(OH)₂) in soils treated with magnesium oxide (MgO) and calcium oxide respectively. The new peaks made by Cao and MgO or by OPC treatments reveals phosphate binders which uniquely create metal-phosphate complexes to immobilize metal like Pb, Cd, and Zn.
On the other hand, these phases additionally produce metal hydroxides containing high pH settings which facilitates metal immobilization process. Similarly, wide peaks indicate the synthesis of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₃), and calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) which are exceptional to hydrated ordinary Portland cement because the physical encapsulation and chemical binding of heavy metals depend on C-S-H phases.
Moreover, the logical reasoning behind these results includes that consistently all the samples exhibit an obvious peak between 25° and 30°, irrespective of the binder employed. Whereas, this particular peak is commonly accompanying to quartz (SiO₂), which is a widely distributed mineral present in various soil types due to its chemical stability and low treatment binder interaction (Wang et al., 2017). While, the persistence of this peak after stabilization process not only suggests that quartz remains the dominant and most visible phase in the treated soil matrix but also that the original mineral composition is kept unchanged. This study findings that quartz is a persistent mineral phase that strengthens soils even with diverse stabilizing agents [
43]. Quartz's resilience protects the soil matrix while allowing binders to interact with contaminants and other reactive soil elements.
Studies conducted by Du et al., (2014) have also documented similar results, demonstrating that phosphate treatments successfully immobilized heavy metals in polluted soil sites. Insoluble phosphate compounds, such pyromorphite (Pb(PO₄)₃Cl), have made a significant contribution to decreasing the mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals [
45]. The efficiency of phosphate-based binders can be ascribed to their capacity to create durable, slowly dissolving metal-phosphate complexes, which are less susceptible to leaching in different environmental circumstances.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
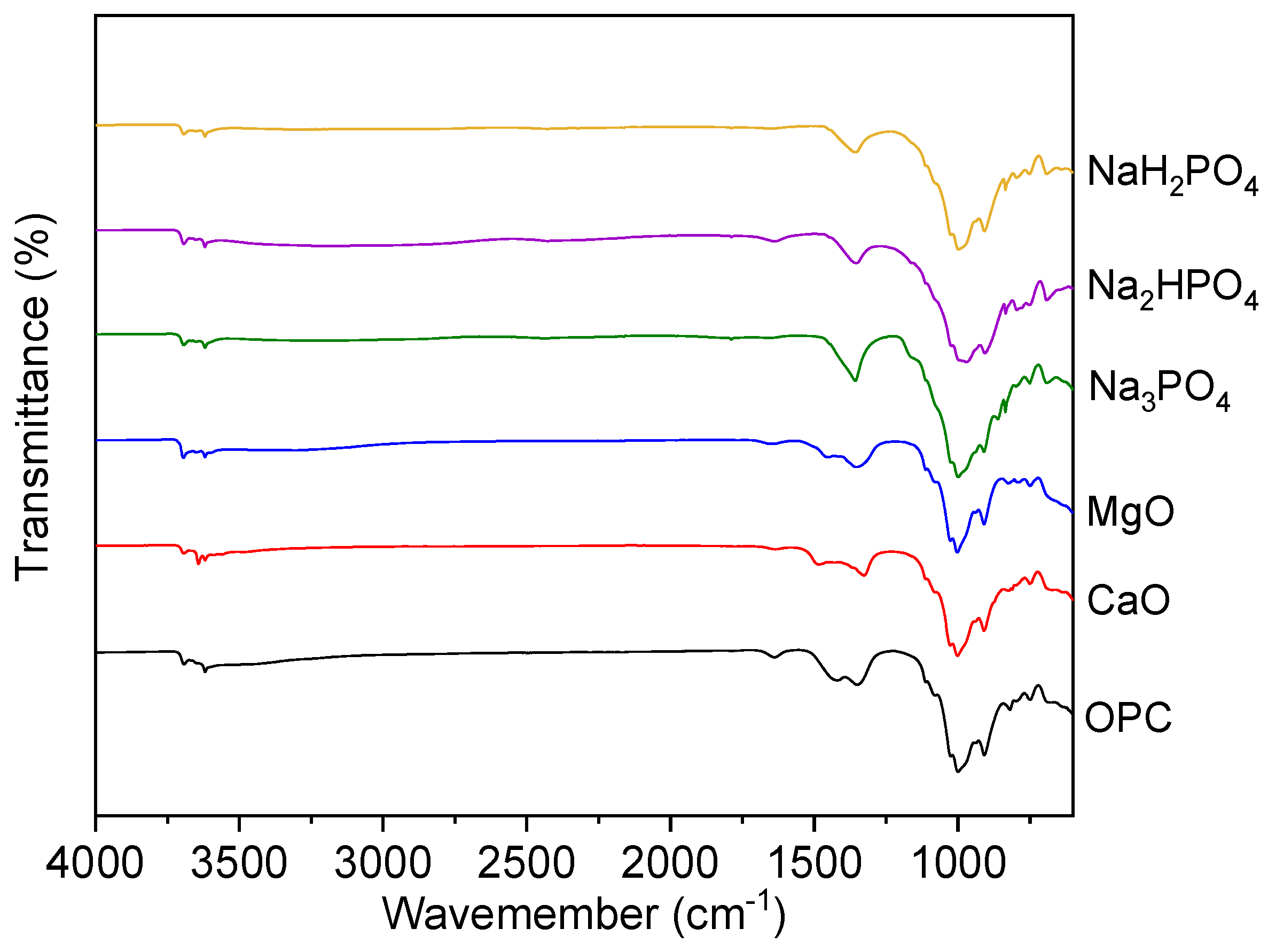
The FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) graph compares transmittance spectra for multi-metal polluted soils treated with several phosphate-based binders (NaH₂PO₄, Na₂HPO₄, Na₃PO₄) to traditional binders such as MgO, CaO, and OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement) as explains in the below (
Figure 10). These spectra provide information on the functional groups and molecular interactions in the treated soils.
In the present study, the FTIR spectra for all samples show a large absorption band about 3400 cm⁻¹ which is ascribed to O-H stretching vibrations. This indicates the existence of hydroxyl groups (-OH), which indicate hydration processes or water molecules. However, the binders like OPC, CaO, and MgO also expressed more pronounced bands, indicating the development of calcium silicate hydrates (C-S-H) and other hydrated phases including portlandite (Ca (OH)₂) and brucite (Mg(OH)₂). Analogously, absorption bands observed at around 1640 cm⁺¹ (H-O-H) and these bending peaks on this particular region are mostly caused by the bending vibrations of water molecules. The consistent existence of these peaks in all samples confirms the essential function of hydration in the remediation of polluted soils. The observed differences in phosphate-treated soils may be attributed to variances in their levels of hydration or water retention capacities.
As well, phosphatic compounds Na₃PO₄, Na₂HPO₄, and NaH₂PO₄ in phosphorus-treated soils show a distinct peak at 1000-1100 cm⁺¹, which is the sign of the synthesis of metal phosphates, which effectively bind heavy metals together. Whereas, the absence or weak peak of MgO, CaO, and OPC spectra implies reduced phosphate interaction, which reveals another unique chemical property of phosphate binders for immobilizing heavy metals. Additionally, the absorption bands made at 1400-1500 cm⁺¹ characterize C-O and O-C-O stretching pairs. The bands are more projecting in OPC, MgO, and CaO samples and are connected to carbonates. Because the carbonate peaks propose carbonation reactions, which are common in alkali base treatments. Similarly, bands at 500-700 cm⁺¹ represent M-O stretching, indicating metal ions like Fe, Mg, and Ca. Metal oxides or metal-hydroxides can be detected by metal-oxygen stretching vibrations in this range. These bands in soils treated with MgO, CaO, and OPC help form metal oxide or hydroxide layers, immobilizing metals. Due to phosphate-metal conjugates, phosphate treatments may affect metal-oxygen interactions.
Thenceforth, towards technical analysis discussion and deductive reasoning of FTIR results it has been clearly shown that FTIR analysis of contaminated soils and the other soils treated with phosphate-based binders, MgO, CaO, and OPC exposes the functional groups and molecular interactions that immobilize metals. Additionally, the wide broad absorption bands at 3400 cm⁻¹ at O-H stretching region among all samples specifies the O-H stretching vibrations, which often connected to hydroxyl groups or water molecules. This further proposes that soil treatment chemical activities produce hydroxide and hydrated mineral phases through hydration reactions. Calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) phases and portlandite (Ca(OH)₂) in OPC-treated soils cause this band. Moreover, MgO-treated soils produce brucite (Mg(OH)₂), which aids in heavy metal immobilization by raising pH and facilitating metal hydroxide precipitation [
46]. Similarly, other researchers have also found similar O-H stretching bands in cementitious materials used for heavy metal stability. Moreover, a study found by Li et al., (2023) and confirms that C-S-H and brucite phases in cement-based polluted soil treatments. These phases play a significant role for physical encapsulation and chemical binding of lead and cadmium. Similarly, H-O-H Bending absorption bands at 1640 cm⁻¹ are associated with the H-O-H twisting mode of water molecules which provides the status of water in binder hydration process[
48].
Moreover, these observed peaks further suggests that bound water in the soil treatment-generated hydrated phases. The severity of phosphate-based treatments depends on hydration and phosphate binder, which affects water retention. These investigations found that hydration condition considerably affects mechanical properties and durability of treated materials. Whereas, long-term heavy metal immobilization in polluted soils requires good water retention and hydrated phases. Whereas, the peaks at 1000-1100 cm⁻¹ for P-O stretching in phosphate groups shows the strong peaks and stretching vibrations between phosphate group and oxygen atoms. These peaks imply the production of phosphate-based chemical compound probably made due to metal-phosphate complexation. During this process heavy metals leaching reduced when they interact with phosphate groups for producing stable, insoluble metal-phosphate minerals. Moreover, phosphate stabilizes metals also as described in previous studies. In a study conducted by [
49] explains that phosphorus is a widely used remediation agent which has a high affinity for metals in soil. Analogous, absorption bands at 1400-1500 cm⁺¹: C-O and O-C-O stretching vibrations for the samples treated with OPC, MgO, and CaO which have substantial carbonate absorption bonds. These bands indicate carbonation activities that may produce carbonate minerals like calcite (CaCO₃). Therefore, a study organized by [
50] found that carbonating OPC and MgO-stabilized soils reduced lead and zinc leachability, supporting the present FTIR studies. These bands in MgO, CaO, and OPC-treated soils indicate metal hydroxides and oxides. These substances create metal precipitation sites and change soil pH to create insoluble metal alloys, immobilizing metals [
51].
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
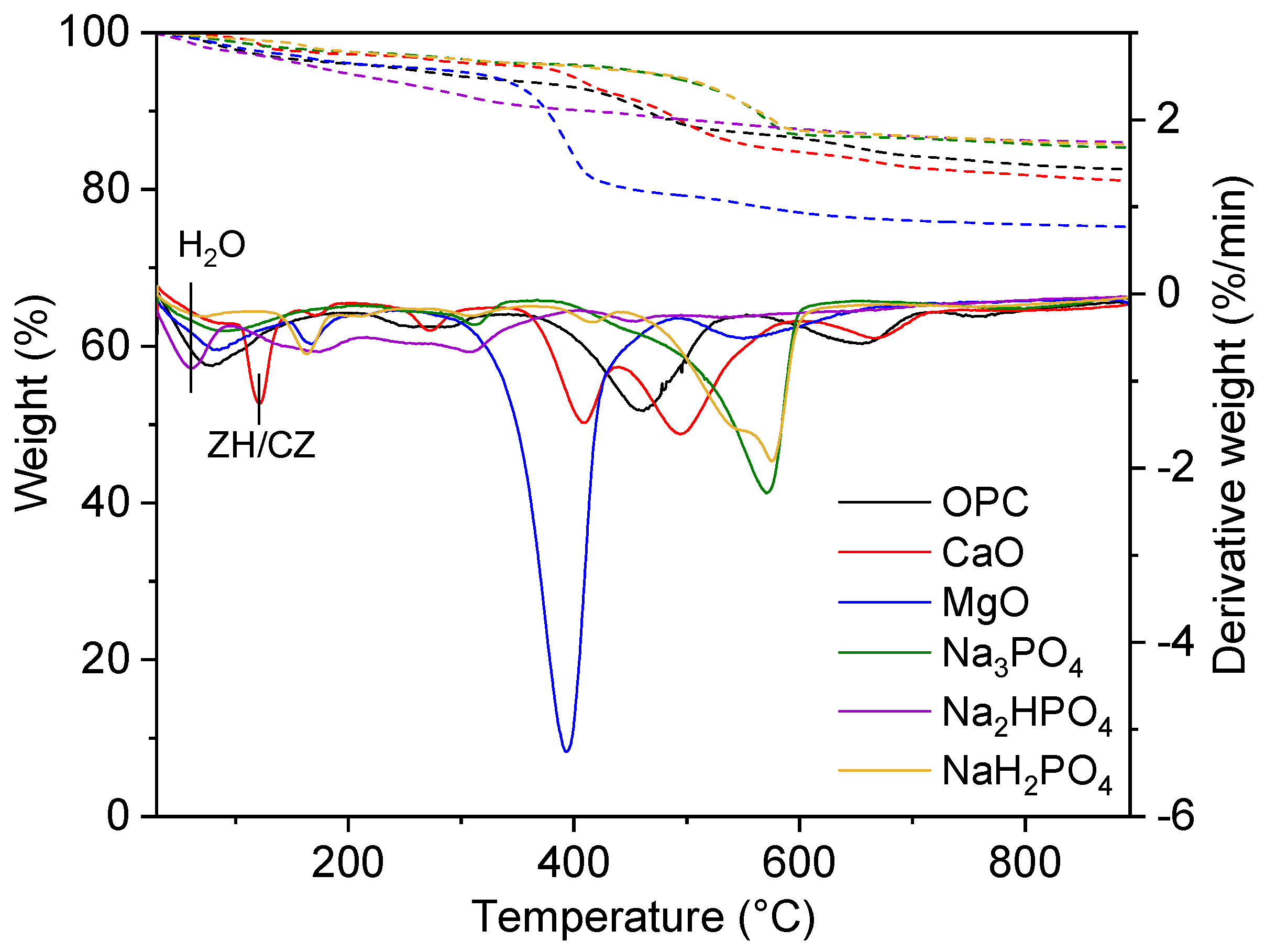
Current study reveals the analysis and interpretation of TGA and DTG curves for metal-contaminated soils treated with several binders of phosphate-based binders (NaH₂PO₄, Na₂HPO₄, Na₃PO₄) to regular binders like MgO, CaO, and OPC as shown in (
Figure 11). These graphs compare the TGA and DTG curves which explains that TGA measures the weight loss caused by temperature, while, besides this, DTG measures the weight loss pace. A detailed analysis of the results follows the main findings for Initial weight loss up to 200° is mainly due to evaporation of physically adsorbed water and also by the dehydration process between loosely bound moisture particles. However, this loss is constant across all the binders, which explains that the treated soils encompass similar amounts of free and weakly bound water. Analogously, the same treatment occurred with MgO treated soil and also signifies the weight loss of a DTG peaks at 400-500°C which assists to alter the form of magnesium hydroxide (brucite, Mg(OH)₂) into MgO and water which decomposes at this temperature.
Furthermore, numerous phosphate binders (NaH₂PO₄, NaHPO₄, and Na₃PO₄) treatment phenomenon suggests thermally stable phosphate complexes having the ability to bind metals even at reasonable temperature ranges and without any structural changes. On the other hand, weight loss at 600°C or higher indicates that the treated soils are thermally durable. This stability suggests that primary phase transitions and decomposition occur at lower absolute temperatures. Additionally, Peaks in DTG curves represents Spectral density (DTG) plots explains distinct MgO peaks and wider OPC and phosphate binder peaks. These observed peaks indicate heat processes such hydrate dehydration and carbonate or metal-phosphate complex breakdown. Likewise, the MgO-treated soil's high rise at 400–500°C shows brucite decomposition. The stable formation of metal-phosphate compounds may explain the large peaks in phosphate-treated soils, which show more constant thermal behaviour [
52]. Also, [
53] found that phosphate treatments can form lasting lead, cadmium, and arsenic compounds. These compounds resist thermal degradation well. Phosphate-treated soils have lower weight loss in TGA/DTG curves, indicating thermal stability and efficient immobilization.