1. Introduction
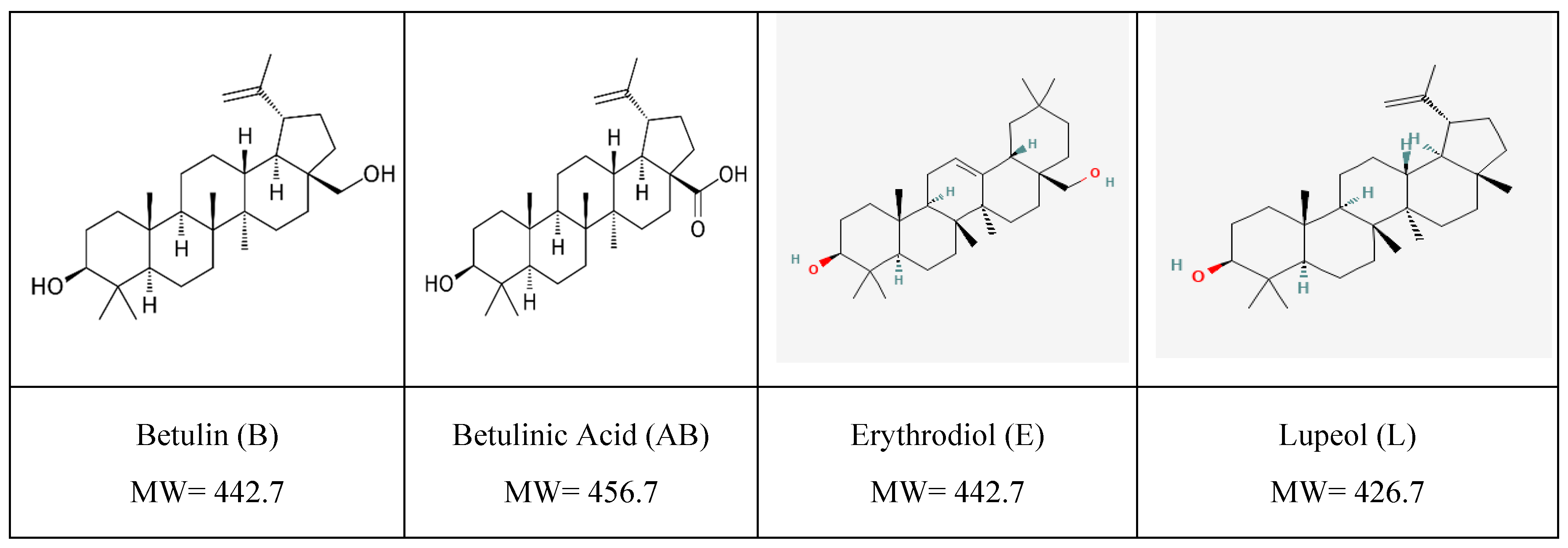
Pentacyclic triterpenoids [TTs] represent a unique family of phytochemicals having a 30-carbon skeleton with five interconnected rings. It includes hydrocarbons (terpenes), hydroxylated or carboxylated derivatives. Depending on their molecular structure, TTs are divided into 5 classes, the most known being of lupane-type (lupeol, betulin, and betulinic acid) (
Figure 1), oleanane type (oleanolic acid, erythrodiol) and ursane type (ursolic acid, uvaol).
One of the richest sources of TTs is represented by birch (Betula species). In Central and Eastern Europe, the silver birch (Betula Pendula Roth) is dominant, its outer bark contains betulin (B) as a major component (5-22%) and lupeol (aprox.1,3%) along with minor amounts of betulinic acid (AB), and traces of other pentacyclic triterpenes, their identification and isolation, bioavailability, self-assembly behavior, applications being well documented [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. Their major disadvantage is the low solubility, and bioavailability, mainly due to their self-assemblies with 3D nanosized structures, as demonstrated for ursolic acid [
6]. In some cases, organic solvents such structures may form vesicles or tubes, tested as possible delivery vehicles for different chemicals with anti-cancer effect at physiological pH [
6].
The scientific interest in these molecules significantly increased after 1995 when B and AB demonstrated cytotoxicity against human Melanoma in vitro and in vivo [
7,
8,
9]. Lupeol, also proved to have cytotoxicity, affecting the cellular viability [
10]. Therefore, TTs as natural sources of medication, have a powerful biological potential including antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, antiviral and hypoglycemic, and especially as potent anticancer molecules, assuming their action as pharmacological agents [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. Many publications were related to their isolation, cytotoxic effects, including patents and patent applications [
4,
8,
16,
17]. Non-malignant cells and tissues are not affected by AB, since it exerts its effects directly on the mitochondrion and triggers death selectively against cancerous cells, and circumvent drug resistance in human cancers [
18,
19]. AB was initially considered a Melanoma-specific cytotoxic compound inducing surface blebbing and cytoplasmic shrinking, DNA fragmentation as indicative of the induction of apoptosis [
7] but further evidence indicated to possesses a broader spectrum of activity against other cancer cell types, e.g. human neuroblastoma cell lines acting through induction of apoptosis independent of the p53 status [
20], activation of caspases, production of reactive oxygen species, and permeability transition pore openings [
21,
22]. Betulin was tested in vitro on A431, HeLa and MCF7 cell lines, acting as an angiogenic inhibitor in vivo [
23].
However, their hydrophobicity, poor permeability and absorption, lower their bioavailability, and hinder their efficacy. Therefore, to enhance their efficacy by parenteral or skin administration, different non-toxic carriers were tested in the last decades. Nanoparticles and nanocolloids are increasingly used for terpenoid derivatives’ delivery in experimental in vitro and in vivo systems due to their multiple advantages, as reviewed [
16,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31].
Compared to conventional drugs, lipid-based nanoparticles which incorporate anticancer drugs have specific advantages, such as improved stability, permeability and retention, biocompatibility, and more precise targeting. These include liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs), nanoemulsions, phytosomes, or nano-lipoproteins, whose preparation, characterization, and application in different drug delivery systems is continuously updated [
32,
33,
34,
35]. The most known nano-delivery vehicles are liposomes, especially used to incorporate hydrophilic drugs in the aqueous nucleus but also lipophilic drugs to be inserted in the membrane bilayer [
36,
37]. A better alternative for improved stability is the Polyethylene Glycol modified (PEGylated) stealth liposomes applied on lipophilic anticancer agents. A drug release study showed that PEGylated AB liposomes of 142 nm had a better drug release effect than AB liposomes and better tumor inhibition compared to free AB or AB liposomes by in vitro and in vivo experiments [
38].
Dxorubicin (DOXO) is a well-known anthracycline antibiotic currently used in clinics, as a hydro chlorinated formula, one of the most effective anticancer drugs, acting by topoisomerase I and II inhibition, mitochondrial apoptosis and anti-angiogenesis in cancer cells, activation of caspases, production of reactive oxygen species [
11,
39]. Liposomal DOXO proved high efficiency after encapsulation, with significant anticancer activity and reduced cardiotoxicity comparative to free DOXO [
36,
40]. New versions of PEGylated liposomal DOXO were produced and improved its molecular targeting and tumor recognition [
41,
42,
43], commercially known as Doxil® or Caelyx®.
Development of lipid nanoparticles is one of emerging applications in drug delivery, due to their unique composition- and size-dependent properties, physiologically like body lipids, bioavailable and well tolerated. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) represents a second generation of SLNs [
44,
45,
46], with many advantages over SLNs, by an enhanced drug loading capacity, improved stability and different applications in both pharmaceutical and cosmetic industry [
34,
47]. Different procedures were elaborated to obtain NLCs, but the most applied is the melt-emulsification & ultrasonication method as recently reviewed [
47,
48]. The development of B-loaded NLCs (of around 200 nm) using the emulsification was recently reported, showing their efficacy on Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis with an entrapment efficiency of 47 to 88% [
49].
Our group has previous experience in preparing and characterizing birch extracts rich in TTs [
2,
16] as well to build liposomes and NLCs which may incorporate different bioactive molecules [
48,
49,
50,
51]. The incorporation of TTs (B, AB and L) in such carriers is still a challenge, as shown above. Their use for improved cell delivery and study of apoptotic effects comparatively represents not only scientific bottlenecks and starting points for innovative ways to deliver parenterally such anticancer molecules.
In this context, this study aims to apply cheap and easy procedures to obtain a bioactive extract rich in TTs, with a well-defined composition, and to incorporate it into PEGylated stealth liposomes (Lipo) and into NLCs, comparative with pure AB and Doxorubicin (as positive control) in similar nanoformulations. Their size and structure as well as their effects on two cancer cell lines (Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 carcinoma cells) were tested at different exposure times, as well their impact on cell cycle and apoptosis, according to Flow cytometry measurements.
2. Results
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of the TTs Extract
The TTs extract was obtained in three steps by successive extractions different solvents, as described in
Materials and methods. The structure and solubility of TTs comparative to pure AB in three different organic solvents was first checked and visualized by fluorescence microscopy, as shown in
Figure S1 (supplementary file). Comparative to iso-propanol and ethanol: water mix, the mix of ethanol and DMSO (3:1) showed the best solubilization of TTs, resulting in a stable suspension.
The TTs extract was characterized first by UHPLC-QTOF-ESI
+-MS analysis and four major pentacyclic terpenoids were identified and quantified, namely Erythrodiol (E), Betulin(B), Betulinic acid (AB) and Lupeol (L). Their identification was made by Mass spectrometry, based on specific precursor ions and specific fragmentation, as shown in
Figure S2 (supplementary file). The concentration of each component was expressed in AB equivalents (mg/ml) as described in Materials and methods. The total concentration of TTs in ethanol: DMSO (3:1) was 10.8 mg/ml AB eq. and the percentage of each component was found to be E: B: AB: L, 15.2: 44.4: 23.9:16.5 (w: w: w: w). This standardized extract (TTs) was used to build all nanoformulations and compared with similar formulations containing pure AB and Doxorubicin (as positive control for anti-cancer effects).
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of the Nanoformulations with Entrapped TTs, AB and Doxo
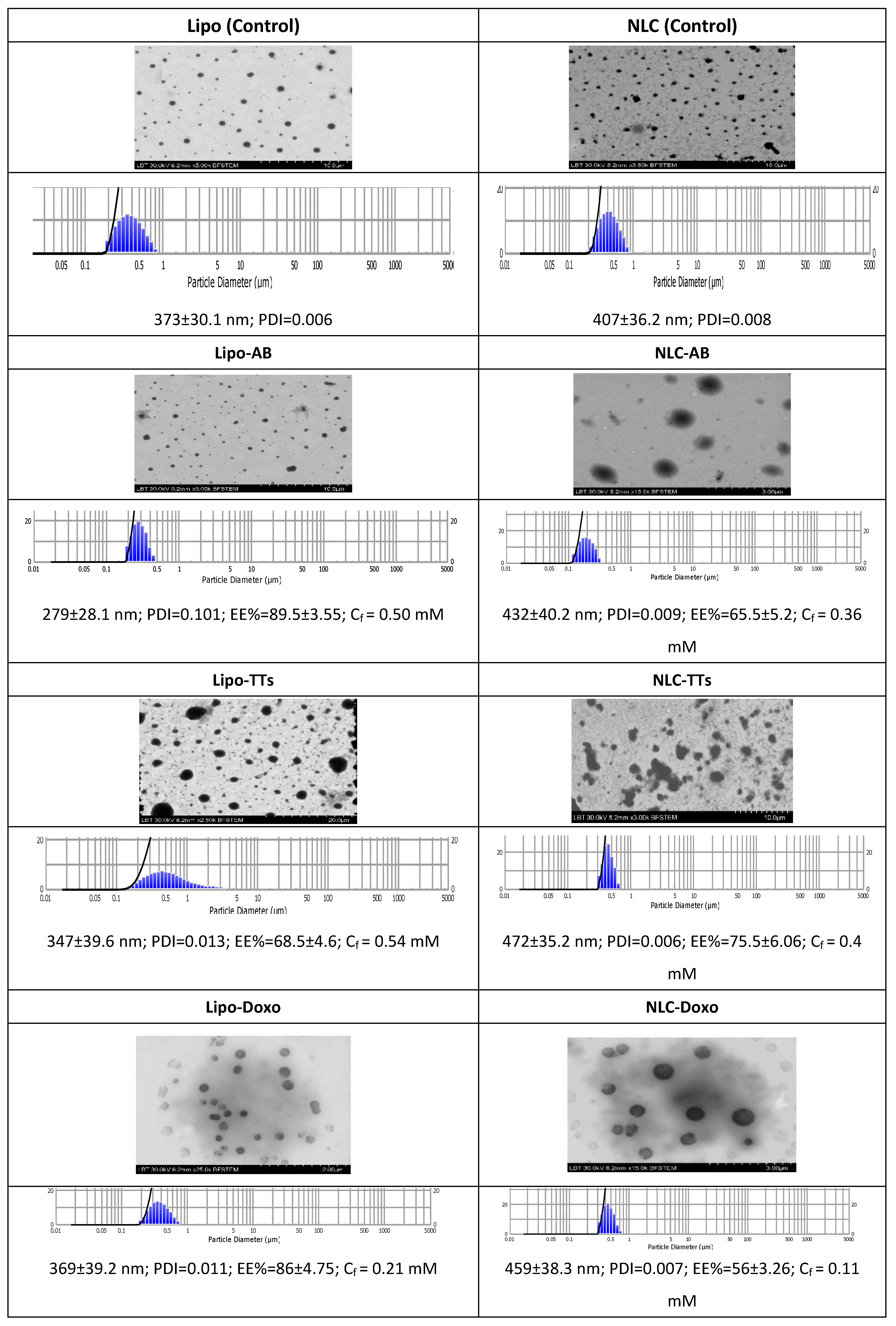
The aspect of the different variants of Lipo- and NLC- nanoformulations are presented in
Figure S3 (supplementary file). The morphology of Lipo- and NLC- nanoformulations containing AB, TTs and Doxo, comparative to controls, as determined by TEM is presented in
Figure 2. The figure includes also the size distribution and diameters (mean± SD (nm) of all formulations, the encapsulation efficiency (EE% ± SD) and the PDI values. The final concentrations (Cf) of AB, TTs and Doxo after entrapment were calculated according to the EE values, as described in
Materials and methods.
As shown, the population of nanoparticles had spheric shapes, and sizes between 279-472 nm, the NLCs being bigger, but not significantly, and showed to be inserted in a cloudy network, with increased tendency for aggregation comparative to Lipo- structures. The polydispersibility index (PDI) showed a good distribution of nanoparticles in all cases. The stability of both types of formulations was high, with constant sizes, as checked for one month storage at 4°C. Significant correlations were found between microscopic evaluation and the DLS measurements, as shown above. The encapsulation efficiency was higher in Lipo-formulations for AB and Doxo, while TTs (including more unpolar molecules) showed a higher encapsulation efficiency in NLC formulations.
2.3. Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity
The viability of both cell lines indicated in general dose-dependent and time-dependent decreases of viability. In general, the cytotoxic effects were more pronounced in the range 4-24 h and were more pronounced in Walker cell line.
Figure S4 (supplementary fle) includes the graphs representing the viability of Walker 256 cancer cells after the incubation (4, 24, 48h) with successive concentrations (0.2-30 µM) of Lipo-AB, Lipo-TT, NLC-AB, NLC-TT comparative to controls (Lipo and NLC). The graphs for Doxo, Lipo-Doxo and NLC-Doxo are available from our previous publication [
51].
Table 1 includes the comparative IC50 values (µM) of Doxo, AB and TT delivered from Lipo- and NLC-formulations vs free Doxo, AB, TT and controls (Lipo- or NLC) in Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 cell cultures, after 24h of incubation.
In all cases, a more significant decrease of viability was noticed from 4 to 24 hrs.
Table 1 presents the IC50 values (µM) of Doxo, AB and TTs, delivered from Lipo- and NLC versus free forms (DOXO, AB, TTs) in Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 cell cultures, after 24h of incubation. The statistical significance of differences between Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 cell as well between the different formulations was mentioned also.
The controls (Lipo- and NLC) did not show a significant cytotoxic effect, nevertheless NLC affected the cell viability of around 10% in both cell lines. Free Doxo showed higher cytotoxicity in Melanoma
vs Walker cell lines, the mean IC
50 values ranging from 0.18 to 0.87 µM, while after entrapment these values increased to 1.03 to 1.66 µM in Lipo- and 2.14-1.35 µM in NLC. According to statistical significance (
Table 1B), the Doxo-nanoformulations were less toxic compared to free Doxo. Lipo-AB and NLC-AB showed higher IC
50 values, especially in Melanoma cells. Comparatively, Lipo-TTs at similar concentrations proved to be less toxic in both cell lines while NLC-TTs affected more Walker cell viability comparatively to free TTs (p<0.01).
To conclude, the viability/cytotoxicity data according to IC50 values showed that Melanoma cells were more affected than Walker cells when free molecules were delivered to cells and a gradual decrease of toxicity was observed in most cases when molecules were inserted in nanoformulations. When compared AB and TTs nanoformulations, Lipo-AB were more toxic than NLC-AB, while NLC formulations of TTs were more toxic than Lipo-TTs. This data can be explained by a higher solubility and bioavailability of AB in liposomal formulations versus a higher solubility and bioavailability of TTs in NLC formulations.
2.4. Cell Cycle Distribution
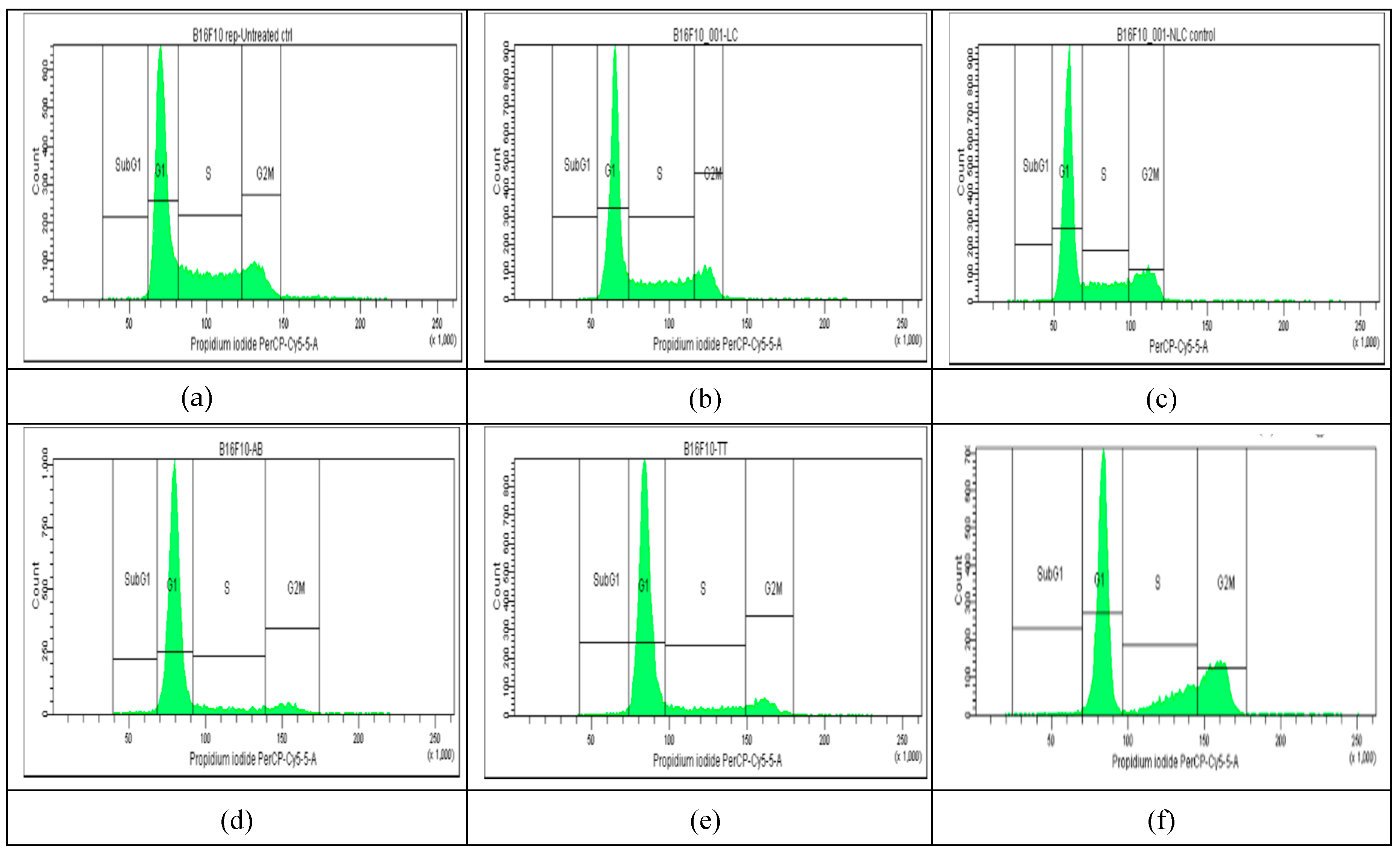
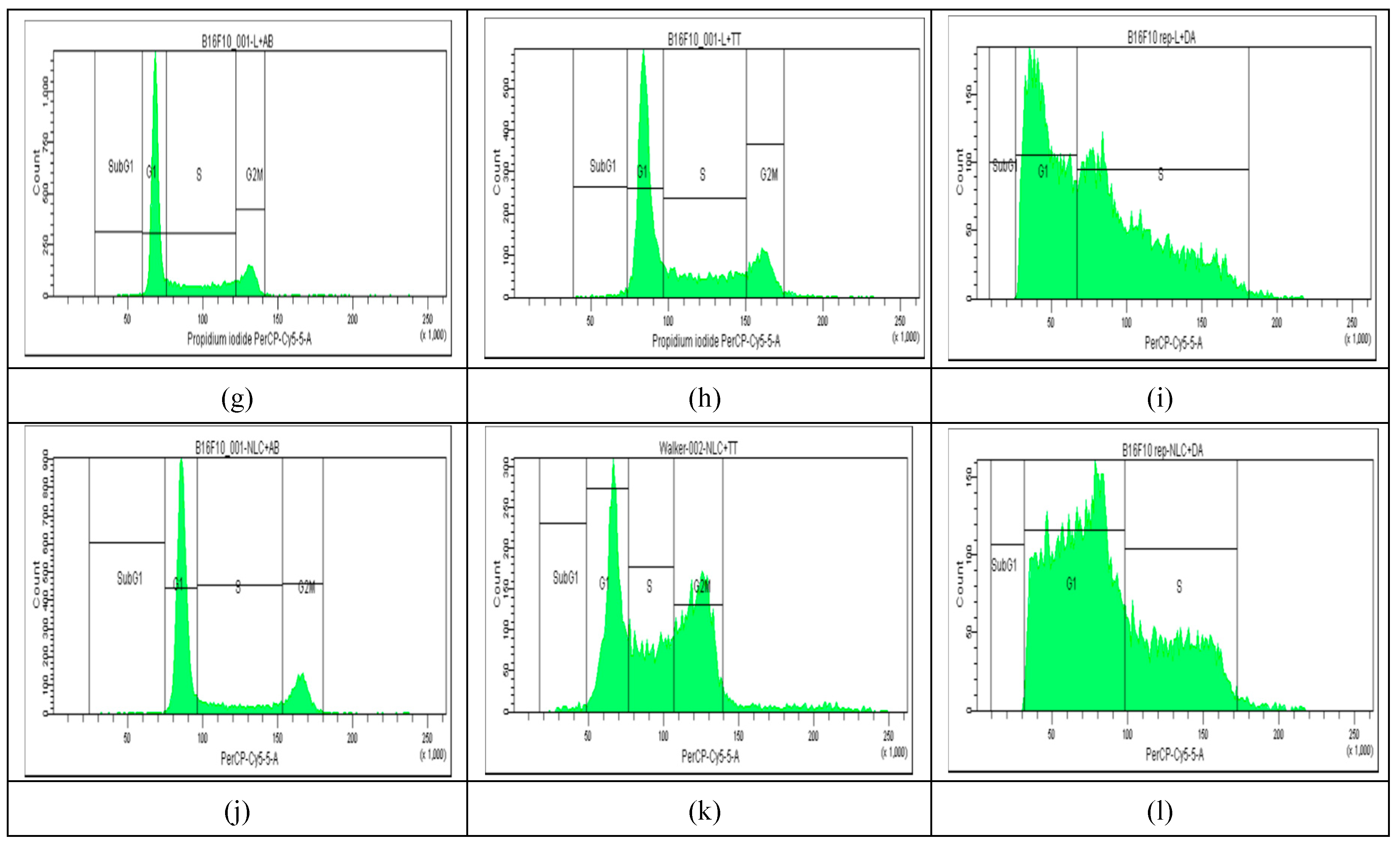
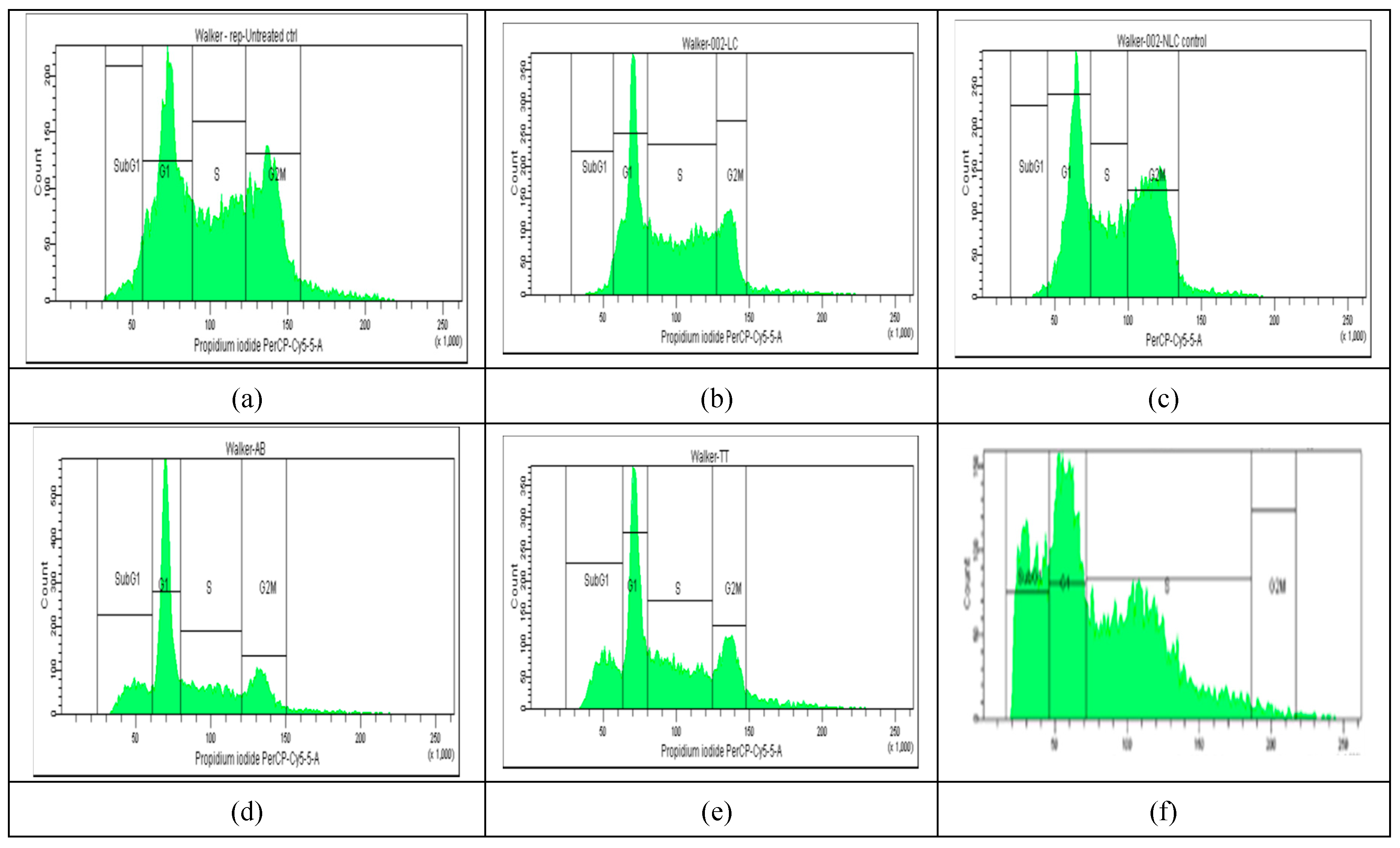
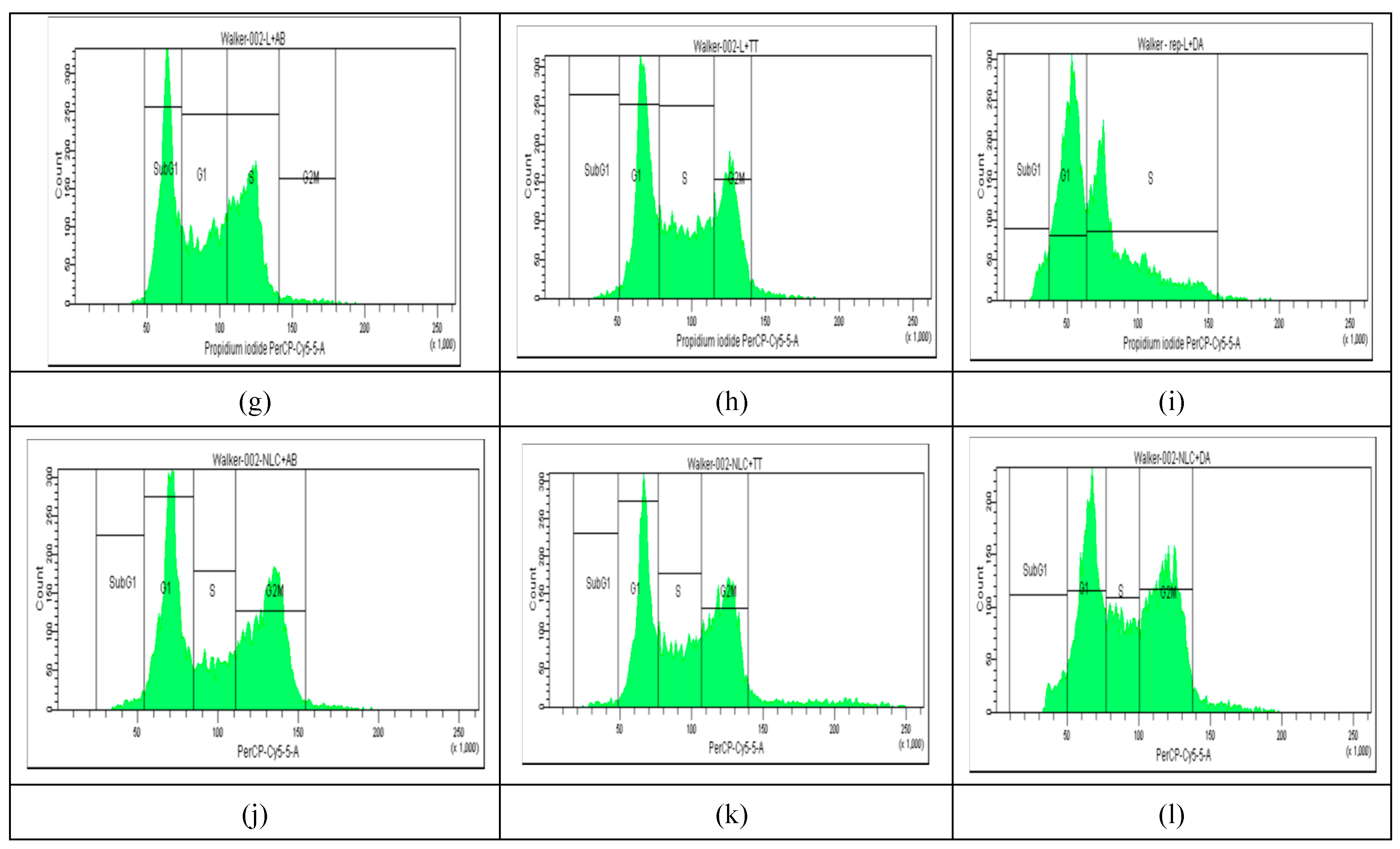
The results of cell cycle analysis done for the two cell cultures (Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 cells) using flow cytometry, are shown in
Figure 3 and
Figure 4. The concentrations of Doxo, AB, TTs as free or in nano formulations corresponded in each case to the IC
50 registered at 24 h cultivation for viability test (as presented in
Table 1A). The percentage of Melanoma cell population affected (by counting and distribution) and inhibition of specific cell cycle stage (subG1, G1, G2, and S phases) were recorded and presented below for AB, TTs, Doxo and each Lipo- and NLC-formulation (
Figure 3 d-l), comparative to control cell culture and free Lipo- and NLC- (
Figure 3 a-c).
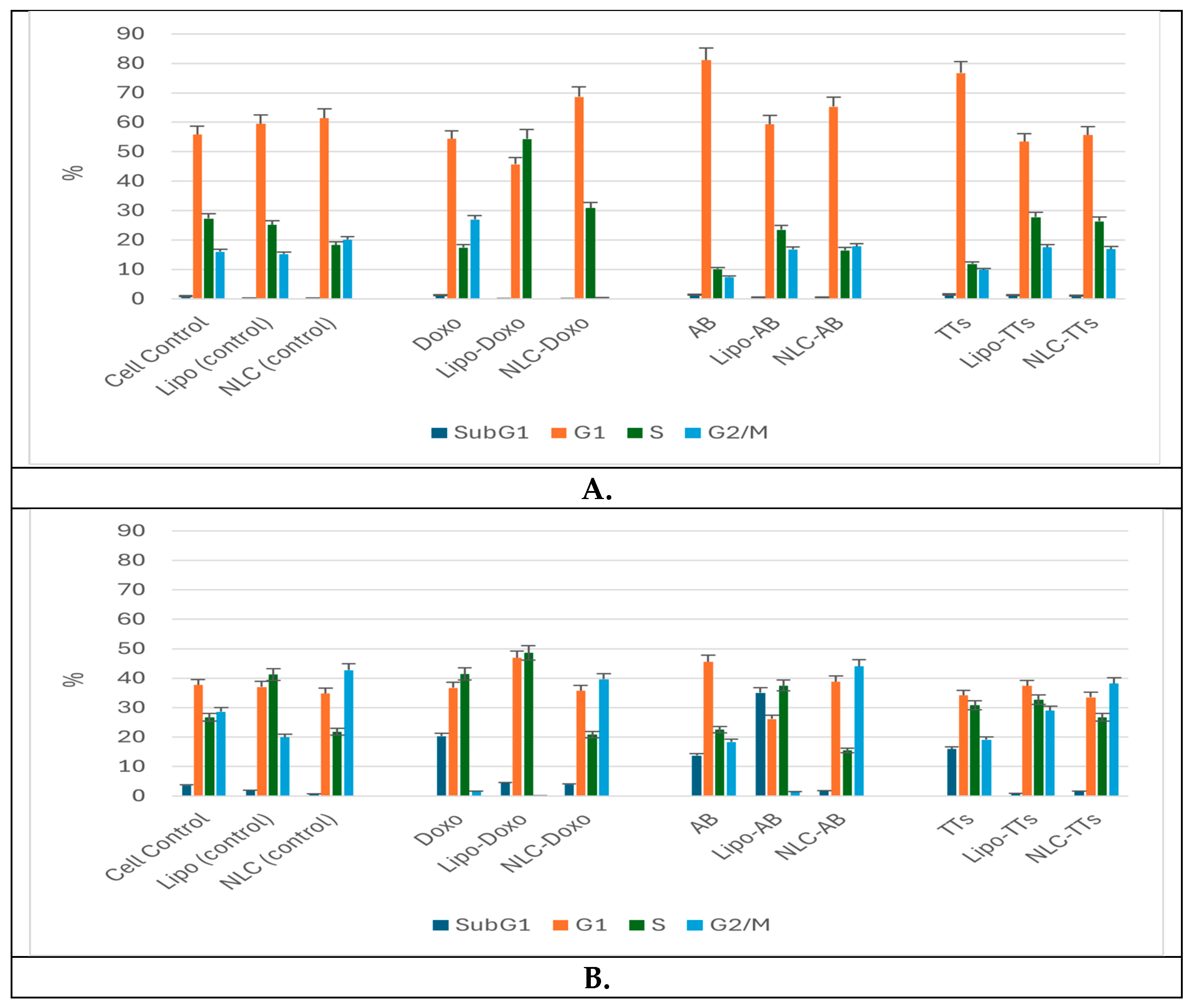
The percentages of cell populations arrested in subG1, G1, G2, and S phases are shown as mean ± SD in
Figure 5A and B.
No significant modifications were observed between the distribution of Melanoma cell population (%) in non-treated controls comparative ti Lipo- and NLc-controls (
Figure 3 a-c and
Figure 5 A). The free AB and TTs showed similar effects with highest counts in G1 while Doxo showed increased counts in S and especially G2M. The nanoformulas including AB or TTs showed similar effects, with significant arrests in S and G2M phases. Lipo-AB and NLC-AB showed similar distribution profiles while Lipo-TTs and especially NLC-TTs showed significant arrests in S and G2M phases. Different effects
On a similar scale, the percentage of Walker cell population was differently distributed comparative to Melanoma cells, with lower distribution in G1 phase, due to a high rate of proliferation (in S and G2M phases). In this case Lipo- and NLC- controls affected differently the cell cycle, Lipo- increasing the cell arrest in S phase while NLC in G2M phase. The free Doxo, AB and TTs induced cell arrests especially in subG1 phase comparative to controls. Significant differences were noticed also between the nanoformulations with entrapped Doxo, AB and TTs: Lipo-Doxo showed an increased cycle arrest in S phase while NLC-Doxo in G2M phase. Lipo-TTs induced more significant arrests in G2M while Lipo-AB, more on subG1 phase. NLC-TTs and NLC-AB showed similar effects, with a higher percentage of arrested cells in G2M phase. These data confirm the apoptotic effect of TTs, as well AB, like Doxo, by shifting the cell cycle arrest to S and G2Mphases, either as Lipo- or in NLC-formulations. For Doxo it was yet documented its inhibitory effect on cell proliferation through cell cycle arrest at the G(2)/M phase as well as by cell death, via enhanced caspase activation which promote intracellular apoptotic signaling for cell death. To confirm and detail the apoptotic mechanisms complementary evaluation was made, as presented below.
2.5. Apoptosis
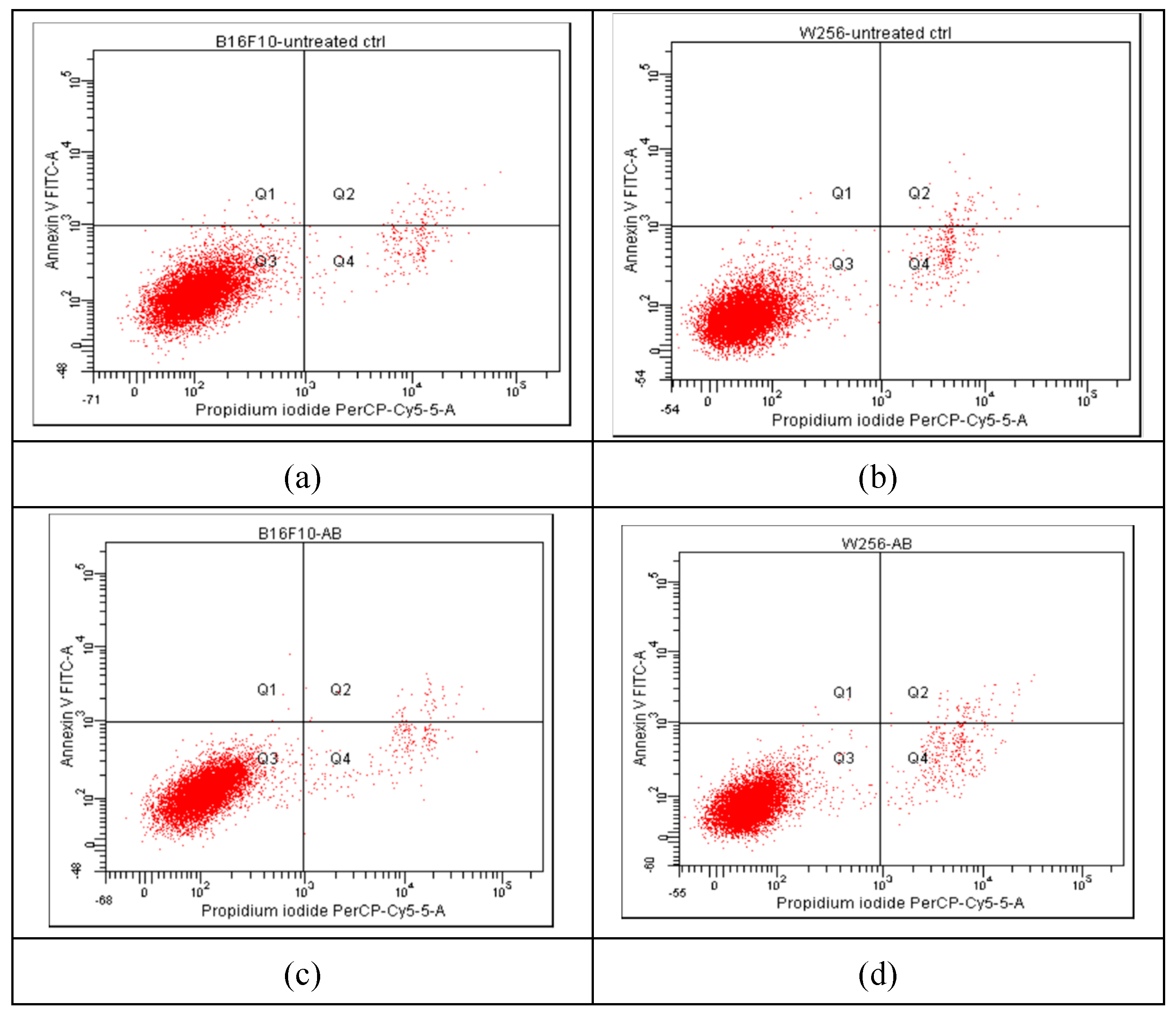
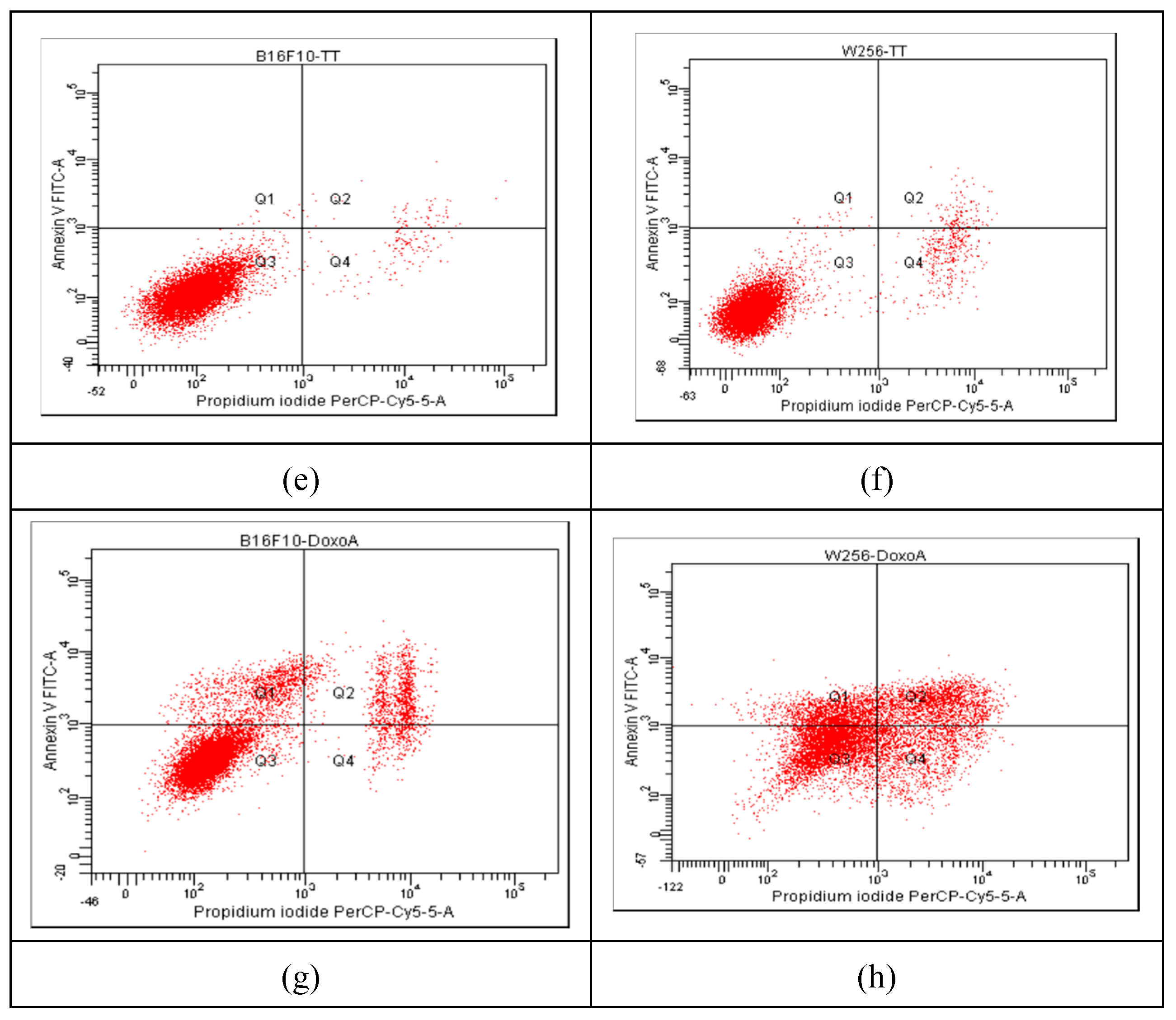
The progression of apoptosis was monitored also by flow cytometry, using the standard procedure with propidium iodide (PI) and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated Annexin V (Annexin V-FITC). The results are presented in
Figure 6, showing comparatively the results for Melanoma B16F10 (a, c, e, g) and Walker 256 cells (b, d, f, h), as untreated cells (a, b) and after incubation for 24 hrs with Ab, TTs and Doxo.
According to the plots in quadrant Q1 (Annexin V-FITC+/PI−) the early apoptotic cells are marked, whereas in quadrant Q2 (Annexin V-FITC+/PI+) the late apoptotic cells (end-stage, due to a loss of plasma membrane integrity) are distributed. The necrotic cells are in quadrant Q4, while viable cells (Annexin V-FITC−/PI−) in quadrant Q3. The non-treated cells (
Figure 6 a, b) showed a non-significant percentage of cells in apoptosis, while the strongest apoptotic and necrotic effects were noticed after the treatment with 0.87 µM Doxo, especially in Walker 256 cells (
Figure 6g and h). The same cells treated with AB (10.22 µM in Melanoma and 13.53 µM in Walker cells) and TTs (19.25 µM in Melanoma and 28.53 µM in Walker cells) showed similar behavior, and a lower impact on apoptosis comparative to Doxo. The nano-formulations, at the same range of concentrations, showed significantly different impact, as presented in
Figure 7.
While Lipo-Doxo and NLC-Doxo at around 1 µM decreased the apoptotic effect comparative to free Doxo, for the nano-formulations with entrapped triterpenoids (AB and TTs) at similar concentration ranges, from 14.42 to 27.33 µM and 19.48 to 27.25 µM, respectively, enhanced apoptotic effects were observed. Lipo-formulations of TTs showed similar apoptotic effects in both cancer cells, while NLC formulations were more active on Melanoma cells. Meanwhile, the necrotic effects were predominant in Doxo-entrapped nanoformulations, and superior to terpenoid nanoformulations. In Walker cells, the NLC-formulations containing AB or TTs induced more necrosis than Lipo-formulations, in correlation with a stronger cytotoxicity ( see
Table 1).
These data were positively correlated with the cell cycle measurements, as presented in
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 and confirmed by complementary measurements on caspase 3/7 activation (data not shown).
3. Discussion
In the current study, an extract rich in pentacyclic terpenoids (TTs including Betulin, AB, lupeol and erythritol) from outer bark of silver, was characterized and entrapped in two types of nanoformulations (liposomes and nanolipid complexes), to increase their bioavailability and activity as anticancer agents in two types of cancer cells, Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 carcinoma cells. Different morphology parameters, sizes, entrapment efficiencies were determined and compared with pure betulinic acid, the confirmed anticancer terpenoid and Doxorubicin, the studied terpenoid which proved to parameters, from including pure betulinic acid and Doxorubicin, considered the most effective anticancer drugs used in clinics.
The viability/cytotoxicity data according to IC50 values showed that Melanoma cells were more affected than Walker cells when free molecules were delivered to cells and a gradual decrease of toxicity was observed in most cases when molecules were inserted in nanoformulations. When compared TTs and AB nanoformulations, Lipo-AB were more toxic than NLC-AB, while NLC formulations of TTs were more toxic than Lipo-TTs. This data can be explained by a higher solubility and bioavailability of AB in liposomal formulations versus a higher solubility and bioavailability of TTs in NLC formulations. Both types of nanoformulations enhanced active loading into both cancer cells with dose and time related cytotoxicity and improved bioavailability, enhancing the intracellular accumulation and their apoptotic and or necrotic effects.
We applied an improved version of PEGylated liposomes, to entrap AB and TTs or Doxo, according to previous findings [
53], new recipes for NLCs, as well updated protocols for delivery systems recently documented [
54,
55,
56]. These results confirm the complexity of cytotoxicity studies involving nanoparticles, where the cell cycle arrest varies significantly depending on composition, size, size distribution of formulations. In addition, the results vary depending on cellular types and experimental conditions, including the measurement protocols (e.g., flow cytometry, laser scanning cytometry) [
57].
According to our experimental data, TTs extract showed good entrapment in both Liposomal and NLC nanoformulations, these delivery systems having the advantage to include natural and biodegradable ingredients that can be found in the vascular system too and to enhance bioavailability. The apoptosis and necrosis effect were more pronounced for Liposomal formulations in both types of cancer cells and can be correlated with their increased bioavailability.
Complementary findings were obtained from in vivo experiments on Walker 256 rat carcinoma, where similar formulations were studied, and confirmed the apoptotic and necrotic effects of these terpenoid nanoformulations.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Extraction of TTs from Birch Bark
The bark of Silver birch (
Betula pendula) was collected in Transylvania region in September, 2023. The detached outer layer was dried for 24 hours at 45°C and stored in a dark desiccator. After grinding, 5 g of powder was washed 2x with petroleum ether to eliminate resins and then extracted successively with 2x100 ml mixture of iso-propanol: ethyl acetate,1:1 (v/v), during 48 hrs at 40°C. The extract was then evaporated under vacuum and re-extracted in iso-propanol, ethanol:water (1:1) or ethanol:dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) 3:1. To evaluate the structural conformation, fluorescence microscopy was applied, using a trinocular digital Microscope IM-3LD4D (Optika, Italy) with green (emission/excitation 575/550 nm) and blue filters (emission/excitation 700/650 nm). Since the extract in ethanol: DMSO showed a stable colloid suspension, this type of extract was used in further experiments. By high performance liquid chromatography coupled with MS spectrometry (UHPLC-ESI+MS), the qualitative and quantitative composition of TTs extract was determined as described in
Figure S2 (supplementary file) using a calibration curve with pure AB, in the range 2-10 mg/ml. The composition of TTs included Erythrodiol E (Rt=9.38 min), betulin B (Rt=9.9 min), Betulinic aid AB (RT=10.1 min) and Lupeol L (10.6 min) in a total concentration of 10.8 mg/ml expressed in equivalents AB and the weight percentages of the four components were E: B: AB: L, 15.2: 44.4: 23.9:16.5 This standardized extract was used in all experiments.
4.2. Preparation of PEGylated Liposomes Using the Ethanol Injection Method
The procedure applied was adapted from the Fan et all, 2008 [
53]. The lipid phase (LP) included 16 ml soybean lecithin (Sigma) 6.25% and 25 mg cholesterol dissolved in pure Ethanol (HPLC grade). The aqueous phase (AqP) included 40 ml phosphate buffer 0.01M pH 6.5, 40 µl Tween-80 and 20 mg PEG2000. The AqP was heated on water bath and under magnetic stirring at 60°C, the LP heated at 65°C was added dropwise for about 15 min, with a ratio AqP/LP 2:1 (v:v). After a further mix for another 15 min, to evaporate ethanol, the liposomal suspension was ultrasonicated at high amplitude, using an UP50H Compact Lab Homogenizer (Hielscher). Empty, control liposomes and liposomes containing Doxorubicin (Doxo), AB and TTs extracts were prepared using this procedure.
Preparation for Lipo-Doxo. Doxorubicin hydrochloride (Doxo) 2 mg/ml (3.45 mM) saline solution was purchased as a commercial perfusion solution (Accord Healthcare Ltd, UK). This solution was diluted up to a final concentration of 2 mM, using a mix of ethanol: DMSO 3:1.A volume of 5 ml Doxo(2 mM) was mixed with 32 ml AqP and, following the procedure mentioned before, 16 ml LP was added, and after ethanol evaporation, a volume of 40 ml liposomal suspension was obtained with an theoretical concentration of 0.25 mM Doxo. The entrapment rate, as described below.
Preparation for Lipo-AB and Lipo-TTs. Following the same procedure, 1 ml solution of ethanol: DMSO containing 10 mg/ml AB and 10.8 mg/ml TTs, respectively was mixed with 15 ml FL. Then the liposomes were built similarly using a volume of 32 ml AqP. The final suspension had 40 ml. The theoretical concentration of AB and TTs was (considering the MW of AB = 456.7 and mean MW for TTs = 443.5) was 0.25 mg/ml and 0.27 mg/ml in each case, corresponding to 0.55 mM for AB and 0.6 mM TTs. For all formulations, obtained in triplicate, the entrapment efficiency was determined as presented below.
4.3. Preparation of NLC Formulations
To obtain the NLC formulations, Compritol 888ATO, a standardized glycerol dibehenate ( Gattefosse France) previously used in similar formulations [
45,
46] was mixed with stearic acid, oleic acid, Tween 80 and Triethanolamine, in a ratio 10:5:2.5:2.5 (w/w). By hot emulsification procedure, a dropwise addition of 50 ml hot ultrapure water phase (pH 7.2) to 2 g melted lipid mix (at 80°C) was applied using an ultraturax at 20000 rpm speed, for 15 min. The hot emulsion was ultrasonicated for 5 min with high amplitude using the UP50H Compact Lab Homogenizer (Hielscher). The resulting suspension (50 ml) suspension was kept on ice for 15 min. To obtain NLC-Doxo formulations, 5 ml of Doxo (2 mM ) were included in 50 ml hot water phase, their theoretical concentration being 0.2 mM in the final suspension Similarly, 1 ml solutions including 10 mg AB and 15 mg TTs in ethanol:DMSO (3:1), were introduced in 50 ml hot water, their theoretical concentrations being considered to be 0.44 mM and respectively 0.68mM. For all formulations, obtained in triplicate, the entrapment efficiency was determined as presented below.
4.4. Entrapment Efficiency, Size Determination and Morphology of Liposomes vs NLCs
To evaluate the percentage of Doxo, AB and TTs entrapment in both systems (Lipo- and NLC-), Amicon® Ultra 15 mL Centrifugal Filter devices (Millipore) with 100K cut-off were used. The liposome or NLC suspensions were filtered by centrifugation at 4600 rpm for 30 min at 25°C in a Hettich Rotofix 46 Centrifuge and the retentate was collected. The procedure was repeated two times. After restoration of the initial volume, the concentrations of Doxo, AB and TTs in the retentate were determined in each case, and compared to the theoretical concentration. The evaluation of entrapment efficiency (EE%) was made by UV-VIS spectrometry (Perkin Elmer Lambda 25), recording the specific absorptions for Doxo (480 nm) and Ab or TT ( 210 nm) after dissolving the liposomal or NLC suspensions in a solution of 0.1% Triton X-100 in ethanol. The formula used to calculate was EE% = (At-Aret/At) x 100, where At- absorption of initial suspension; Aret - absorption of retentate suspension. The sizes of all formulations were determined by laser diffraction technique using the Shimadzu SALD 2300 DLS instrument (Shimadzu, Japan) with the software Wing SALDII version 3.4.10. The Polydispersibility Index (PDI) was also calculated in each case. The morphology and size were visualized in parallel by Transmission Electronic Microscopy (TEM-Hitachi SU8320 FEGSTEM instrument) with a calibrated size range between 50 nm and 50 mm to obtain TEM images.
4.5. Cell Cultures
The Melanoma B16-F10 cell line, isolated from mouse skin tissue was purchased from ATCC (Manassas, VA, USA) and cultured in growth media containing Dulbeco’s modified Minimum Essential Medium (DMEM) supplemented with foetal bovine serum (10%), L-glutamine (1%), and a mixture of penicillin-streptomycin (1%). Cells were maintained under standard conditions in a humidified atmosphere (95%) at 37 °C and 5% CO2. The Walker 256 cell line (synonym LLC-WRC 256) from a rat breast carcinoma, originally obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) and adapted with an aggressive metastatic behaviour in suspension (kindly donated by Prof. Oliver Thews, Martin Luther University, Halle-Wittenberg, Germany) was used as an appropriate model. This line was cultured in Sigma RPMI-1640 growth medium containing 10% sterile foetal bovine serum, 20 mM HEPES, 10 mM L-glutamine, 10 mL 7.5% NaHCO3, and 1 mL penicillin and streptomycin (Sigma 10,000 units penicillin and 10 mg of streptomycin/mL) for each 100 mL volume. Both types of cell cultures were incubated in parallel with Doxo (0.5-3.5 µM), AB (0.5-30 µM), TTs (0.5-30 µM), after dilution in Ethanol: DMSO, 3:1 and addition to the cell cultures. The same concentrations were applied for the Lipo-and NLC-formulations.
4.6. Viability Assays
The cytotoxic impact of free molecules ( Doxo, AB, TTs) and Lipo- and NLC- formulations comparative ti Lipo- and NLC-controls was measured using similar concentrations, in the range 0-3.6 µM for Doxo, 0-30 µM for AB and 0-25 µM for TTs. The viability was evaluated by the MTT assay applied on B16-F10 Melanoma cells and Walker 256 cells. Shortly, in a 96-well plate, 8x103 B16-F10 cells and 1x104 of Walker 256 cells were seeded. On the next day, cells were subjected to the successive concentrations of free molecules and their formulations. At 4, 24 and 48 h after treatments, 10 µL of the 12 mM MTT solution in PBS were added in each well, followed by incubation at 37°C for 4h. Afterwards, 150 µL of a mixture of DMSO: SDS 30% (90:60) were added in each well, the plate was shaken for 5 minutes at room temperature, in the dark, and then incubated for more 10 minutes, at 37°C. Using a microplate reader (Biotek, SynergyHT, CA, USA) the absorbance of the formazan was determined at 550 nm. Half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values, utilizing sigmoidal fitting equation, were calculated (GraphPad Prism program).
4.7. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry
For each cell line, 1x106 cells were seeded in 6-well plates, and left to adapt for 24h (B16-F10 adherent cell line), and for 2h (Walker 256 cell line in suspension) respectively, prior to treatment. Separate sets of treatments were prepared for the two cell lines using the concentrations of all formulations corresponding to IC50 registered at 24 h cultivation for viability test (see Table 2). The cells were incubated for 24h, at 37°C and after the media removal (collected in a 15 ml tube), the adherent B16-F10 cells are detached with trypsin, their growth medium being also collected, and together were centrifuged for 3 min at 1500 rpm. The cellular pellet was washed 2x with cold PBS and fixed with 2-5 mL dropwise of 70% ethanol on ice. For fixation procedure, both cell lines were kept at 4°C for 30 min, then, the ethanol was removed by centrifugation (5 min, 2000 rpm) and a washing procedure with 2x PBS was done. A volume of 50 μL RNAse (100 μg/mL) was added to all cell pellets, and followed by an incubation at 37°C for 15 min. Finally, 200 μL of propidium iodide (50 μg/mL), a nuclear staining dye was added for 10 min at 4°C to measure the cell cycle. All data were collected, stored, and analysed using a BD FACS Canto II flux cytometer (Becton Dickinson, NJ, USA).
4.8. Apoptosis and Necrosis Assays by Flow Cytometry
The percentage of cells that undergo apoptosis and/or necrosis was measured by using the Annexin V - FITC and propidium iodide staining kit, provided from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), and analysed using the same BD FACS. The analysis was performed on the same cell lines, for each cell line, 1 x 106 cells being seeded in 6-well plates, and left to adapt to the medium for 24h (B16-F10), and 2h (Walker 256) respectively, prior to treatment. Separate sets of treatments were prepared for each formulation. Next, the cells were incubated for 24h, at 37°. After the completion of the treatment time, the media was removed, the cells were prepared for staining by washing twice with PBS (3 min, 1500 rpm centrifugation), submersed in 500µL binding Buffer, provided by the kit, and transferred intro flow cytometry testing tubes. Finally, 5 µL Annexin V FITC and 10 µL Propidium Iodide solution were added in each sample tube. After 10 min of incubation at room temperature, protected from light, the cells were diluted 2x with cell wash solution. All data were collected, stored, and analyzed also by BD FACS Canto II flux cytometer (Becton Dickinson, NJ, USA).
4.9. Statistics
The estimation of the statistical differences in this study used one-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey’s test provided by GraphPad prism package software (CA, USA). The viability data presented as mean ± SD. Values of p ˂ 0.1, p<0.01 and p<0.001 counted as thresholds for significant differences.
5. Conclusions
The pentacyclic triterpenoid extract showed good stability, synergistic effects of main components and superior comparative to pure betulinic acid. According to experimental data, this extract showed good entrapment in liposomal and NLC nanoformulations, both delivery systems including natural, biodegradable ingredients and enhanced bioavailability. The apoptosis and necrosis effects were more pronounced for its liposomal formulations in both types of cancer cells, with lower cytotoxicity comparative to Doxorubicin, and can be correlated with their bioavailability. The added value of the four terpenoid components (Betulin, Betulinic acid, Erythrodiol and Lupeol) in this extract was demonstrated by amplified effects of the TTs extract, comparative to pure betulinic acid, either free or entrapped in bioavailable nanoformulations. These data may fill the existing literature which confirms the potential of pentacyclic triterpenoids as natural anticancer agents, and the potential of nanoformulations to improve their cellular uptake, to influence cytotoxicity, to induce apoptosis or necrosis, as main mechanisms involved in the modulation of tumor cell inhibition.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1. Comparative structures of the betulinic acid (A-C) and the TTs extract (D-F) in different solvents: iso-propanol (A and D), ethanol: water 1:1 (B and E) and ethanol: DMSO, 3:1 (C and F), as determined by fluorescence microscopy. Green filters were used for images B, C, D, while blue filters were used for images A, E, F. The fluorescent Sudan III was added for an optimized image of the structures in iso-propanol (A and D). Figure S2. Birch bark extract (TTs) composition, according to UHPLC-ESI+-MS analysis. Figure S3. Liposomal (Lipo-) and NLC formulations containing Doxorubicin (Doxo), Betulinic acid (AB) and triterpene extract (TTs Figure S4. Viability of Walker 256 cancer cells after the incubation (4, 24, 48h) with successive concentrations (0.2-30 µM) of Lipo-AB, Lipo-TT, NLC-AB, NLC-TT comparative to controls (Lipo and NLC).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization S.M.A., R.D. and S.C.; Methodology R.D., N.M., D.Z., C.M., T.F.; validation R.D, and S.M.A.; formal analysis S.C.; resources S.M.A., D.Z., S.C.; data curation R.D., S.C. and S.M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, R.D. and S.M.A.; writing—review and editing, R.D., S.M.A. and S.C.; visualization, S.C.; supervision S.M.A., R.D. and S.C.; project administration S.C.; funding acquisition, S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Romanian National Executive Authority for Scientific Research (UEFISCDI), grant nr. PN-III-P4-PCE-2021-0378.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author’s contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Kovač-Bešović EE, Durić K, Kalođera Z, Sofić E: Identification and isolation of pharmacologically active triterpenes in Betulae Cortex, Betula pendula Roth., Betulaceae. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 2009, 9, 31–38.
- Holonec, L.; Ranga, F.; Crainic, D.; Truţa, A.; Socaciu, C*. Evaluation of Betulin and Betulinic Acid Content in Birch Bark from Different Forestry Areas of Western Carpathians. Not Bot Horti Agrobo 2012, 40, 99-105.
- Šiman, P.; Filipová, A.; Tichá, A.; Niang, M.; Bezrouk, A.; Havelek, R. Effective Method of Purification of Betulin from Birch Bark: The Importance of Its Purity for Scientific and Medicinal Use. Plos One 2016, 11, e0154933.
- Demets, O.V.; Takibayeva, A.T.; Kassenov, R.Z.; Aliyeva, M.R. Methods of Betulin Extraction from Birch Bark. Molecules 2022, 27, 3621.
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ma, C.; Abd El-Aty, A. M. Edible pentacyclic triterpenes: A review of their sources, bioactivities, bioavailability, self-assembly behavior, and emerging applications as functional delivery vehicles. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022, 1-17.
- Bag, B. G.; Majumdar, R. Self-assembly of Renewable Nano-sized Triterpenoids. Chem Record 2017, 17, 841–873.
- Pisha, E.; Chai, H.; Lee, I.S.; Chagwedera, T.E.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Cordell, A.C.; Beecher, C.W.W.; Fong, H.H.S.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Brown, D.M.; Wani, M.C.; Wall, M.E.; Hieken, T.J.; Das Gupta, T.K.; Pezzuto, J.M. Discovery of betulinic acid as a selective inhibitor of human Melanoma that functions by induction of apoptosis. Nat Med 1995, 1, 1046–1051.
- Cichewicz, R.H.; Kouzi, S.A. Chemistry, biological activity, and chemotherapeutic potential of betulinic acid for the prevention and treatment of cancer and HIV infection. Med Res Rev 2004, 24, 90–114.
- Furtado, N.A.J.C.; Pirson, L.; Edelberg, H.; Miranda, L.M.; Loira-Pastoriza, C.; Preat V.; Larondelle, Y.; André, C.M. Pentacyclic Triterpene Bioavailability: An Overview of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2017, 22, 400.
- Sohag, A.A.; Hossain, T.; Rahaman, A.; Rahman, P.; Hasan, M.S.; Das, R.C.; Khan, K., Sikder, M.H.; Alam, M.; Uddin, J.; Rahman, H.; Islam, T.; Moon, I.S.; Hannan, A. Molecular pharmacology and therapeutic advances of the pentacyclic triterpene lupeol. Phytomedicine: Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol 2022, 99, 154012.
- Ghante MH, Jamkhande P.G, Role of Pentacyclic Triterpenoids in Chemoprevention and Anticancer Treatment: An Overview on Targets and Underling Mechanisms. J Pharmacopuncture 2019, 22, 55–67.
- Patlolla,J.M.R.; Rao,C.V.Triterpenoids for cancer prevention and treatment: current status and future prospects. Curr Pharmaceut Biotechnol 2012, 13, 147–155.
- Hordyjewska, A.; Ostapiuk, A.; Horecka, A. Betulin and betulinic acid: triterpenoids derivatives with a powerful biological potential. Phytochem Rev 2019, 18, 929-951.
- Hordyjewska, A.; Prendecka-Wróbel, M.; Kurach, Ł.; Horecka, A.; Olszewska, A.; Pigo ´n-Zaj ˛ac, D.; Małecka-Massalska, T.; Kurzepa, J. Antiproliferative Properties of Triterpenoids by ECIS Method—A New Promising Approach in Anticancer Studies? Molecules 2022, 27, 3150.
- Król, S.K.; Kiełbus, M.; Rivero-Muller, A.; Stepulak, A. Comprehensive review on betulin as a potent anticancer agent. BioMed Res Intl 2015, Article ID 584189.
- Nistor, M.; Rugina, D.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Socaciu, C.; Socaciu, M.A. Pentacyclic Triterpenoid Phytochemicals with Anticancer Activity: Updated Studies on Mechanisms and Targeted Delivery. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 12923.
- Moghaddam, M.G.; Ahmad, F.B.H.; Kermani, A.S. Biological activity of betulinic acid: A review. Pharmacol Pharm 2012, 3, 119–123.
- Zuco, V.; Supino, R.; Righetti, SC.; Cleris, K.; Marchesi, E.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Formelli, F. Selective cytotoxicity of betulinic acid on tumor cell lines, but not normal cells. Cancer Lett 2002, 175, 17–25.
- Ali-Seyed, M.; Jantan, I.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Bukhari, S. N. A. Betulinic Acid: Recent Advances in Chemical Modifications, Effective Delivery, and Molecular Mechanisms of a Promising Anticancer Therapy. Chemical Biol & Drug Design 2015, 87, 517–536.
- Schmidt, M.L.; Kuzmanoff, K.L.; Ling-Indeck, L.; Pezzuto, J.M. Betulinic acid induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Eur J Cancer 1997, 33, 2007–2010.
- Kwon, H.J.; Shim, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, H.Y.; Yum, Y.N.; Kim, S.H.; Yu, J. Betulinic acid inhibits growth factor-induced in vitro angiogenesis via the modulation of mitochondrial function in endothelial cells. Jpn J Cancer Res 2002, 93, 417–425.
- Fulda, S.; Scaffidi, C.; Susin, SA.; Krammer, PH.; Kroemer, G.; Peter, ME.; Debatin, K-M. Activation of mitochondria and release of mitochondrial apoptogenic factors by betulinic acid. J Biol Chem 1998, 273, 33942–33948.
- Dehelean, C.A.; Feflea, S.; Molnár, J.; Zupko, I.; Soica, C. Betulin as an antitumor agent tested in vitro on A431, HeLa and MCF7, and as an angiogenic inhibitor in vivo in the CAM assay. Nat Prod Commun 2012, 7, 981–985.
- Pinzaru, I.; Sarau, C.; Coricovac, D.; Marcovici, I.; Utescu, C.; Tofan, S.; Popovici, RA.; Manea, HC.; Pavel, IE.; Soica, C.; Dehelean, C. Silver Nanocolloids Loaded with Betulinic Acid with Enhanced Antitumor Potential: Physicochemical Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2021, 11, 152.
- Gómez-Favela Mario Armando, David Ulises Santos-Ballardo, Magdalena Elizabeth Bergés-Tiznado, Dulce Libna Ambriz-Pérez, Chapter 6 - Nanoformulations applied to the delivery of terpenes, Editor(s): J. Basilio Heredia, Erick P. Gutiérrez-Grijalva, Angel Licea-Claverie, Janet Alejandra Gutierrez-Uribe, Jayanta Kumar Patra, In: Nanotechnology in Biomedicine, Phytochemical Nanodelivery Systems as Potential Biopharmaceuticals, Elsevier, 2023, 221-256, ISBN 9780323903905.
- Mierina, I.; Vilskersts, R.; Turks M. Delivery Systems for Birch-bark Triterpenoids and their Derivatives in Anticancer Research. Curr Med Chem 2020, 27, 1308 – 1336.
- Kaps, A.; Gwiazdo´n, P.; Chodurek, E. Nanoformulations for Delivery of Pentacyclic Triterpenoids in Anticancer Therapies. Molecules 2021, 26, 1764.
- Kuznetsova, S.A.; Shakhtshneider, T.; Mikhailenko, M.A.; Malyar, Y. Preparation and antitumor activity of betulin dipropionate and its composites. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 2021,12, 6873-6894.
- Chen, X.; Lu, S.; Gong, F.; Sui, X.; Liu,T.; Wang,T. Research on the synthesis of nanoparticles of betulinic acid and their targeting antitumor activity. J Biomed Mater Res 2022,110, 1789-1795.
- Saneja, A.; Arora, D.; Kumar, R.; Dubey, R.D.; Panda, A.K.; Gupta, P.N. Therapeutic applications of betulinic acid nanoformulations. Ann NY Acad Sci 2018, 1421, 5–18.
- Zhang, D.-M.; Xu, H.-G.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.-J.; Sun, P.-H.; Wu, X.-M.; Wang, G.J.; Chen, W.M.; Ye, W.-C. Betulinic Acid and its Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents. Med Res Rev 2015, 35, 1127–1155.
- Sharma, N.; Deepak.; C., Sandeep, K. Nanoparticles: Fundamental and Prospectives. Res J Pharmaceut Biol Chem Sci 2018, 9, 152–164.
- Li, Q.; Cai, T.G.; Huang, Y.H.; Xia, X.; Cole, S.P.C.; Cai, Y. A Review of the Structure, Preparation, and Application of NLCs, PNPs, and PLNs. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 122–135.
- Khan S, Sharma A, Jain V. An Overview of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers and its Application in Drug Delivery through Different Routes. Adv Pharm Bull 2023, 13, 446-460.
- Mahmoud, K.; Swidan, S.; El-Nabarawi, M.; Teaima, M. Lipid based nanoparticles as a novel treatment modality for hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive review on targeting and recent advances. J Nanobiotechnol 2022, 20, 109.
- Tran, M.A.; Watts, R.J.; Robertson, G.P. Use of liposomes as drug delivery vehicles for treatment of melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 2009, 22, 388-399.
- Taléns-Visconti, R.; Díez-Sales, O.; de Julián-Ortiz, J.V.; Nácher, A. Nanoliposomes in Cancer Therapy: Marketed Products and Current Clinical Trials. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 23084249.
- Liu, W.-K.; Ho, J.C.K.; Cheung, F.W.K.; Liu, B.P.L.; Ye, W.-C.; Che, C.-T. Apoptotic activity of betulinic acid derivatives on murine melanoma B16 cell line. Eur J Pharmacol 2004, 498, 71–78.
- Abraham, S.A.; Waterhouse, D.N.; Mayer, L.D.; Cullis, P.R.; Madden, T.D.; Bally, M.B. The liposomal formulation of Doxorubicin. Methods Enzymol 2005, 391, 71-97.
- Kciuk, M.; Gielecińska, A.; Mujwar, S.; Kołat, D.; Kałuzińska-Kołat, Ż.; Celik, I.; Kontek, R. Doxorubicin-An Agent with Multiple Mechanisms of Anticancer Activity. Cells 2023, 12, 659.
- Arshad, R.; Arshad, M. S.; Rahdar, A.; Hassan, D.; Behzadmehr, R.; Ghotekar, S.; Medina, D.I.; Sadanand Pandey, S. Nanomaterials as an advanced nano-tool for the Doxorubicin delivery/ Co-Delivery-A Comprehensive Review. J Drug Deliv Technol 2023, 83,104432.
- Sesarman, A.; Tefas, L.; Sylvester, B.; Licarete, E.; Rauca, V.; Luput, L.; Patras, L.; Banciu, M.; Porfire, A. Anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory effects of long-circulating liposomes coencapsulating curcumin and Doxorubicin on C26 murine colon cancer cells. Pharm Rep 2010, 70, 331–339.
- Bisht, A., Avinash, D., Sahu, K. K., Patel, P., Das Gupta, G., & Kurmi, B. D. A comprehensive review on doxorubicin: mechanisms, toxicity, clinical trials, combination therapies and nanoformulations in breast cancer. Drug Deliv Transl Res, 2024, 1-32.
- Dhiman N.; Awasthi R.; Sharma B.; Kharkwal H.; Kulkarni G.T. Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers for Bioactive Delivery. Frontiers in Chemistry 2021, 9, nr. 580118.
- Mishra, V.; Bansal, K.K.; Verma, A.; Yadav, N.; Thakur, S.; Sudhakar, K.; Rosenholm, J.M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Emerging Colloidal Nano Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 191.
- Müller, R.H.; Alexiev, U.; Sinambela, P.; Keck, C.M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): The Second Generation of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. In: Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Chemical Methods in Penetration Enhancement; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 161–185.
- Khosa, A.; Reddi, S.; Saha, R.N. Nanostructured lipid carriers for site-specific drug delivery, Biomed & Pharmacother 2018, 103, 598-613.
- Muntean, P.; Socaciu, C.; Socaciu, M. Lipid nanostructured particles as emerging carriers for targeted delivery of bioactive molecules: Applications in food and biomedical sciences (an overview). Bull UASVM Food Sci Technol 2020, 77, 37–46.
- Biswasroy, P.; Pradhan, D.; Pradhan, DK.; Ghosh, G.; Rath, G. Development of Betulin-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for the Management of Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis. AAPS Pharm SciTech 2024, 25, 57.
- Socaciu, M.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Socaciu, C. Simple and fast procedure to incorporate Doxorubicine in small unilamellar liposomes: Effects on liposome size and zeta potential. Studia UBB Chemia LXIV 2019, 3, 181–192.
- Rugină, D.; Pop R.; Nistor, M.; Cenariu, M.; Tăbăran F.; Socaciu,C.; Socaciu, M.A. Distinct in vitro effects of liposomal and nanostructured lipid nanoformulations with entrapped acidic and neutral doxorubicin on B16-F10 melanoma and Walker 256 carcinoma cells. Discover Oncology 2024 (submitted, under revision).
- Fan, M. ; Xu, S. ; Xia, S. Zhang, X. Preparation of salidroside nano-liposomes by ethanol injection method and in vitro release study. Eur Food Res Technol 2008, 227, 167–174.
- Liu Y.; Gao, D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Dai, K.; Ji,B.; Wang, Q.; Luo, L. Antitumor drug effect of betulinic acid mediated by polyethylene glycol modified liposomes. Materials Sci Engineering C 2016, 64, 124–132.
- Ibrahim, M.; Abuwatfa, W.H.; Awad, N.S.; Sabouni, R.; Husseini, G.A. Encapsulation, Release, and Cytotoxicity of Doxorubicin Loaded in Liposomes, Micelles, and Metal-Organic Frameworks: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 254.
- Rus, I.; Tertiș, M.; Paşcalău, V.; Pavel C.; Melean B.; Suciu M.; Moldovan C.; Topală T.; Popa C.; Săndulescu R.; Cristea C. Simple And Fast Analytical Method For The Evaluation Of The Encapsulation and Release Profile Of Doxorubicin From Drug Delivery Systems, Farmacia 2021, 69, 670-681.
- Zhu, L.; Lin, M. The Synthesis of Nano-Doxorubicin and its Anticancer Effect. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2021, 21, 2466-2477.
- Mahmoudi, M.; Azadmanesh, K.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Journeay, W.S.; Laurent S. Effect of Nanoparticles on the Cell Life Cycle. Chem Rev 2011, 111, 3407-3432. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Most representative pentacyclic triterpenoids in birch bark extracts: structure and molecular weight [MW].
Figure 1.
Most representative pentacyclic triterpenoids in birch bark extracts: structure and molecular weight [MW].
Figure 2.
Morphology of Lipo- and NLC- nanoformulations containing AB, TTs and Doxo, comparative to controls, as determined by TEM. Size distribution diameters (mean± SD) (nm) of the formulations, the encapsulation efficiency (EE% ± SD) and the PDI values are included. The final concentrations (Cf) for each nanoformulation including AB, TT and Doxo were mentioned. .
Figure 2.
Morphology of Lipo- and NLC- nanoformulations containing AB, TTs and Doxo, comparative to controls, as determined by TEM. Size distribution diameters (mean± SD) (nm) of the formulations, the encapsulation efficiency (EE% ± SD) and the PDI values are included. The final concentrations (Cf) for each nanoformulation including AB, TT and Doxo were mentioned. .
Figure 3.
a-l. The flow cytometry distribution of cell cycle affected in Melanoma B16-F10 cell population. (a): non-treated cells. (b and c): after incubation with Lipo- and NLC-controls. (d, e, f): after incubation with AB, TTs, Doxo. (g, h, i): after incubation with Lipo-AB, Lipo-TTs and Lipo-Doxo. (j, k, l): after incubation with NLC-AB, NLC-TTs, NLC-Doxo.
Figure 3.
a-l. The flow cytometry distribution of cell cycle affected in Melanoma B16-F10 cell population. (a): non-treated cells. (b and c): after incubation with Lipo- and NLC-controls. (d, e, f): after incubation with AB, TTs, Doxo. (g, h, i): after incubation with Lipo-AB, Lipo-TTs and Lipo-Doxo. (j, k, l): after incubation with NLC-AB, NLC-TTs, NLC-Doxo.
Figure 4.
a-l. The flow cytometry distribution of cell cycle affected Walker 256 cacinoma cell population. (a): non-treated cells. (b and c): after incubation with Lipo- and NLC-controls. (d, e, f): after incubation with AB, TTs, Doxo. (g, h, i): after incubation with Lipo-AB, Lipo-TTs and Lipo-Doxo. (j, k, l): after incubation with NLC-AB, NLC-TTs, NLC-Doxo.
Figure 4.
a-l. The flow cytometry distribution of cell cycle affected Walker 256 cacinoma cell population. (a): non-treated cells. (b and c): after incubation with Lipo- and NLC-controls. (d, e, f): after incubation with AB, TTs, Doxo. (g, h, i): after incubation with Lipo-AB, Lipo-TTs and Lipo-Doxo. (j, k, l): after incubation with NLC-AB, NLC-TTs, NLC-Doxo.
Figure 5.
Comparative effects of Lipo- and NLC- nanoformulations and free extracts (TTs, AB and Doxo) on Melanoma B16-F10 (A) and Walker 256 (B) cell cycle.
Figure 5.
Comparative effects of Lipo- and NLC- nanoformulations and free extracts (TTs, AB and Doxo) on Melanoma B16-F10 (A) and Walker 256 (B) cell cycle.
Figure 6.
Comparative results of Annexin V/Propidium iodide-stained Flow cytometry for Melanoma B16F10 (a, c, e, g) and Walker 256 cells (b, d, f, h) after 24h of incubation. (a) Melanoma B16F10 untreated cells; (b) Walker 256 untreated cells; (c, e, g) Melanoma B16F10 incubated with AB, TTs and Doxo; (d, f, h) Walker 256 cells incubated with AB, TTs and Doxo. Q1+Q2 = A (early and late apoptosis) ; Q3 – viable cells; Q4 – Necrosis.
Figure 6.
Comparative results of Annexin V/Propidium iodide-stained Flow cytometry for Melanoma B16F10 (a, c, e, g) and Walker 256 cells (b, d, f, h) after 24h of incubation. (a) Melanoma B16F10 untreated cells; (b) Walker 256 untreated cells; (c, e, g) Melanoma B16F10 incubated with AB, TTs and Doxo; (d, f, h) Walker 256 cells incubated with AB, TTs and Doxo. Q1+Q2 = A (early and late apoptosis) ; Q3 – viable cells; Q4 – Necrosis.
Figure 7.
Comparative apototic (A) and necrotic (N) effects of different Lipo- and NLC- formulations comparative to free molecules Doxo, AB and TTs controls in Melanoma B16-F10 (M) and Walker 256 cells (W). A=Q1+Q2 (early and late apoptosis) ; Q4 – Necrosis.
Figure 7.
Comparative apototic (A) and necrotic (N) effects of different Lipo- and NLC- formulations comparative to free molecules Doxo, AB and TTs controls in Melanoma B16-F10 (M) and Walker 256 cells (W). A=Q1+Q2 (early and late apoptosis) ; Q4 – Necrosis.
Table 1.
The IC50 (mean ± SD) values (µM) of Doxo, AB and TTs, free or after entrapment in Lipo and NLC in Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 cell cultures, after 24h of incubation. The statistical significance of differences between Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 cell (A) as well between the different formulations (B) was mentioned also, by t and p values (* p<0.1; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001). NS- nonsignificant.
Table 1.
The IC50 (mean ± SD) values (µM) of Doxo, AB and TTs, free or after entrapment in Lipo and NLC in Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 cell cultures, after 24h of incubation. The statistical significance of differences between Melanoma B16-F10 and Walker 256 cell (A) as well between the different formulations (B) was mentioned also, by t and p values (* p<0.1; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001). NS- nonsignificant.
| A. |
Melanoma B16-F10 |
Walker 256 |
t (M vs W256) |
significance |
| Doxo |
0.18±0.5 |
0.87±0.14 |
-2.555 |
NS |
| Lipo-Doxo |
1.03±0.11 |
1.66±0.18 |
-10.203 |
** |
| NLC-Doxo |
2.14±0.12 |
1.35±0.12 |
11.401 |
** |
| AB |
10.22±4.03 |
13.53±1.65 |
-3.087 |
* |
| Lipo-AB |
15.52±1.1 |
14.42±1.13 |
0.62 |
NS |
| NLC-AB |
22.58±0.03 |
27.33±2.8 |
-279.883 |
*** |
| TTs |
19.25±2.33 |
28.55±3.2 |
-8.074 |
* |
| Lipo-TTs |
23.58±0.03 |
27.25±1.8 |
-215.883 |
*** |
| NLC-TTs |
20.22±0.9 |
19.48±1.55 |
-0.111 |
NS |
| B. |
Melanoma B16-F10 |
Walker 256 |
| |
t |
significance |
t |
significance |
| NLC-Doxo/Doxo |
28.083 |
** |
6.86 |
* |
| Lipo-Doxo/Doxo |
13.023 |
** |
7.540556 |
* |
| NLC-Doxo/Lipo Doxo |
16.078 |
** |
-4.70083 |
NS |
| NLC-AB/AB |
716.97 |
*** |
6.975 |
* |
| Lipo-AB/AB |
4.402 |
* |
-0.27168 |
NS |
| NLC-AB/Lipo-AB |
410.733 |
*** |
6.93875 |
* |
| NLC-TTs/TTs |
-0.444 |
NS |
-11.8774 |
** |
| Lipo-TTs/TTs |
250.253 |
*** |
-2.67361 |
NS |
| NLC-TTs/Lipo-TTs |
-6.563 |
* |
-10.5726 |
** |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).