Submitted:
06 November 2024
Posted:
06 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Retrieval
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison Between Vaccinated and Unvaccinated Patients
3.2. Descriptive Analysis of Non-Survivors
3.3. Analysis of Heart Transplant Recipients Based on Time from Vaccination to Hospital Admission
3.4. Analysis of Heart Transplant Recipients Based on Time from Heart Transplant
3.5. Comparison of Patients with Symptomatic and Asymptomatic COVID Disease
3.6. Bivariate Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed F, Abid M, et al. Incidence and prognosis of COVID-19 amongst heart transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2022, 29, e224–e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos LM, Baro Vila RC, et al. COVID-19 in heart transplant recipients: Outcomes according to vaccination status. Transpl Infect Dis 2022, 24, e13817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters LL, Raymer DS, et al. Association of COVID-19 Vaccination With Risk of COVID-19 Infection, Hospitalization, and Death in Heart Transplant Recipients. JAMA Cardiol 2022, 7, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura K, Nishida S, et al. Trends in COVID-19 Mortality Among Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: Implications for Prevention. Transplantation 2022, 106, e380–e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- www.slovenija-transplant.si. Available online: https://www.slovenija-transplant.si/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/kratko-letno-porocilo-2023-koncna.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- www.slovenija-transplant.si. Available online: https://www.slovenija-transplant.si/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/20-years-of-donation-programme-2021.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Duly K, Farraye FA et al. COVID-19 vaccine use in immunocompromised patients: A commentary on evidence and recommendations. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2022, 79, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- www.ishlt.org. Available online: https://www.ishlt.org/docs/default-source/default-document-library/2023-11-15-ishlt-ast-asts-joint-statement-covid19-vaccination.pdf?sfvrsn=383b0c3e_1 (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Aslam S, Ison MG. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in heart transplantation: What we do and do not know. J Heart Lung Transplant 2022, 41, 58–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memenga F, Kueppers ST, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination-Induced Immunogenicity in Heart Transplant Recipients. Transpl Int 2023, 36, 10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chih S, Clarke BA, et al. The COVID-19 Pandemic and Adult Cardiac Transplantation: Impact, Interventions, and Implications. Can J Cardiol 2023, 39, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosano G, Jankowska EA, et al. COVID-19 vaccination in patients with heart failure: a position paper of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail 2021, 23, 1806–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamot M, Kirbiš A. Multilevel analysis of COVID-19 vaccination intention: the moderating role of economic and cultural country characteristics. Eur J Public Health 2024, 34, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu Q, Shen Y, et al. Low acceptance rate of COVID-19 vaccination and reduced quality of life among heart transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Card Surg 2022, 37, 4975–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohney KL, Link CB, et al. COVID-19 Vaccination Motivation and Hesitancy in Heart Transplant Recipients During a Global Health Crisis. J Heart Lung Transplant 2022, 41, S178–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- www.mdcalc.com. Available online: https://www.mdcalc.com/calc/3917/charlson-comorbidity-index-cci (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Di Costanzo D, Mazza M, et al. Retrospective analysis of epidemiologic features and clinical course of COVID-19 patients and comparison between vaccinated and unvaccinated patients. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2023. [CrossRef]
- Slomka S, Zieba P, et al. Comparison of Post-Vaccination Response between mRNA and Vector Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in Terms of Humoral Response after Six Months of Observation. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun J, Zheng Q, et al. Effectiveness of mRNA Booster Vaccine Against Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Severe Outcomes Among Persons With and Without Immune Dysfunction: A Retrospective Cohort Study of National Electronic Medical Record Data in the United States. Open Forum Infect Dis 2024, 11, ofae019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senefeld JW, Franchini M, et al. COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma for the Treatment of Immunocompromised Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2023, 6, e2250647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang CF, Jang TY, et al. Impact of comorbidities on the serological response to COVID-19 vaccination in a Taiwanese cohort. Virol J 2023, 20, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiter Toshkov, Explaining the gender gap in COVID-19 vaccination attitudes. European Journal of Public Health 2023, 33, 490–495. [CrossRef]
- Nassiri-Ansari T, Atuhebwe P, et al. Shifting gender barriers in immunisation in the COVID-19 pandemic response and beyond. Lancet 2022, 400, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintel S, Flock C, et al. Gender differences in the intention to get vaccinated against COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Z Gesundh Wiss, 2022, 7, 1–25. [CrossRef]
- www.nijz.si. Available online: https://nijz.si/nalezljive-bolezni/cepljenje/priporocila-za-cepljenje-proti-covidu-19-za-jesen-2024/ (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Turtle L, Thorpe M, et al. Outcome of COVID-19 in hospitalised immunocompromised patients: An analysis of the WHO ISARIC CCP-UK prospective cohort study. PLoS Med 2023, 20, e1004086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas G, Bertrand M, et al. Prognosis of critically ill immunocompromised patients with virus-detected acute respiratory failure. Ann Intensive Care 2023, 13, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller SA, Manintveld OC, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in heart transplantation recipients in the Netherlands. Neth Heart J 2022, 30, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupica D, Collinet-Adler S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Clinical Presentation of COVID-19 in Patients Hospitalized during the Delta- and Omicron-Predominant Periods. J Clin Med 2023, 12, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auld SC, Harrington KRV, et al. Trends in ICU Mortality From Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Tale of Three Surges. Crit Care Med 2022, 50, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- www.who.int. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019 (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Tartof SY, Slezak JM, et al. Analysis of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake Among Immunocompromised Individuals in a Large US Health System. JAMA Netw Open 2023, 6, e2251833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avsec L, Bilban M, et al. COVID-19 vaccination intention, confidence and hesitancy among working population in Slovenia: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Saf Health Work 2022, 13, S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster ME, Shay DK, et al. Myocarditis Cases Reported After mRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccination in the US From December 2020 to August 2021. JAMA 2022, 327, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petravić L, Arh R, et al. Factors Affecting Attitudes towards COVID-19 Vaccination: An Online Survey in Slovenia. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- www.nijz.si. Available online: https://nijz.si/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/SI-PANDA-21.-izvedba_ANG_.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2024).
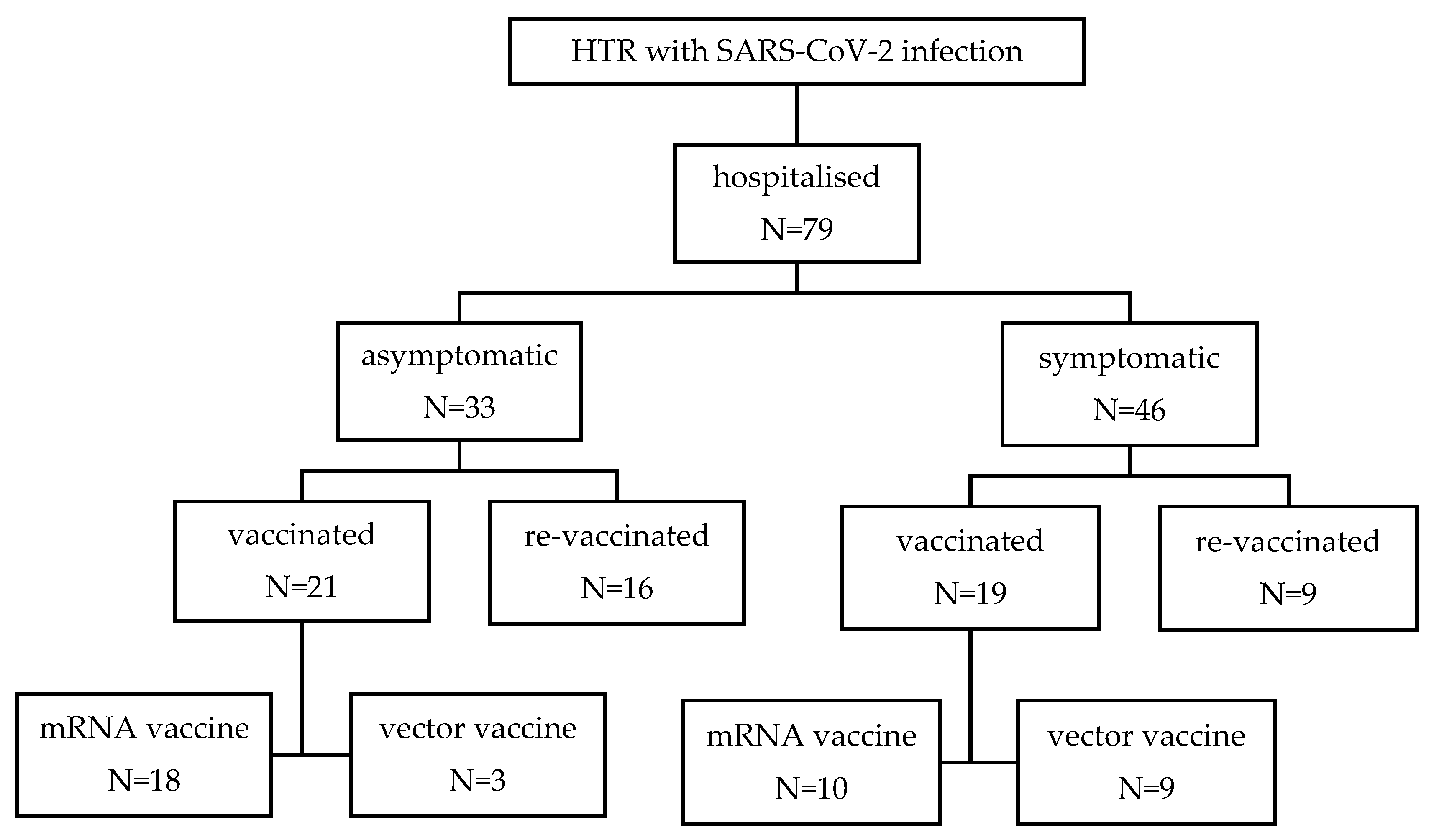
| N=79 | |
| Mean age (years) (±SD) | 62.5 (±9.8) |
| Male gender (%) | 57 (72.2) |
| CCI (±SD) | 3.3 (±1.8) |
| Time from heart transplantation (years) (±SD) | 5.66 (±5.29) |
| Time from vaccination to hospital admission (days) (±SD) | 402 ±(232) |
| Length of hospital stay in days (±SD) | 10.4 (±11.9) |
| No. of patients with symptomatic COVID disease (%) | 46 (58.2) |
| No. of patients with respiratory insufficiency (%) | 28 (35.4) |
| No. of patients admitted to ICU (%) | 6 (7.6) |
| In-hospital mortality rate (%) | 4 (5.1) |
| ICU mortality rate (%) | 4 (66.7) |
| No. of patients on corticosteroid therapy at hospital addmision (%) | 51 (64.5) |
| No. of patients treated with | |
| -hyperimmune convalescent plasma (%) | 13 (16.5) |
| -mAb (%) | 19 (24.1) |
| -remdesivir (%) | 62 (78.4) |
| -corticosteroid(%) | 19 (24.0) |
| No. of patients vaccinated (%) | 50 (63.3) |
| No of patients vaccinated before hospitalization (%) | 40 (50.6) |
| No. of patients receiving mRNA-based vaccine (%) | 28 (70.0) |
| No. of patients receiving vector-based vaccine (%) | 12 (30.0) |
| No. of patients receiving a booster dose of vaccine (%) | 34 (43.1) |
| No. of patients receiving a booster dose of vaccine before hospitalization (%) | 25 (31.6) |
|
Vaccinated N=40 |
Unvaccinated N=39 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (years) (±SD) | 65.6 (±8.9) | 59.3 (±9.8) | p=0.004* |
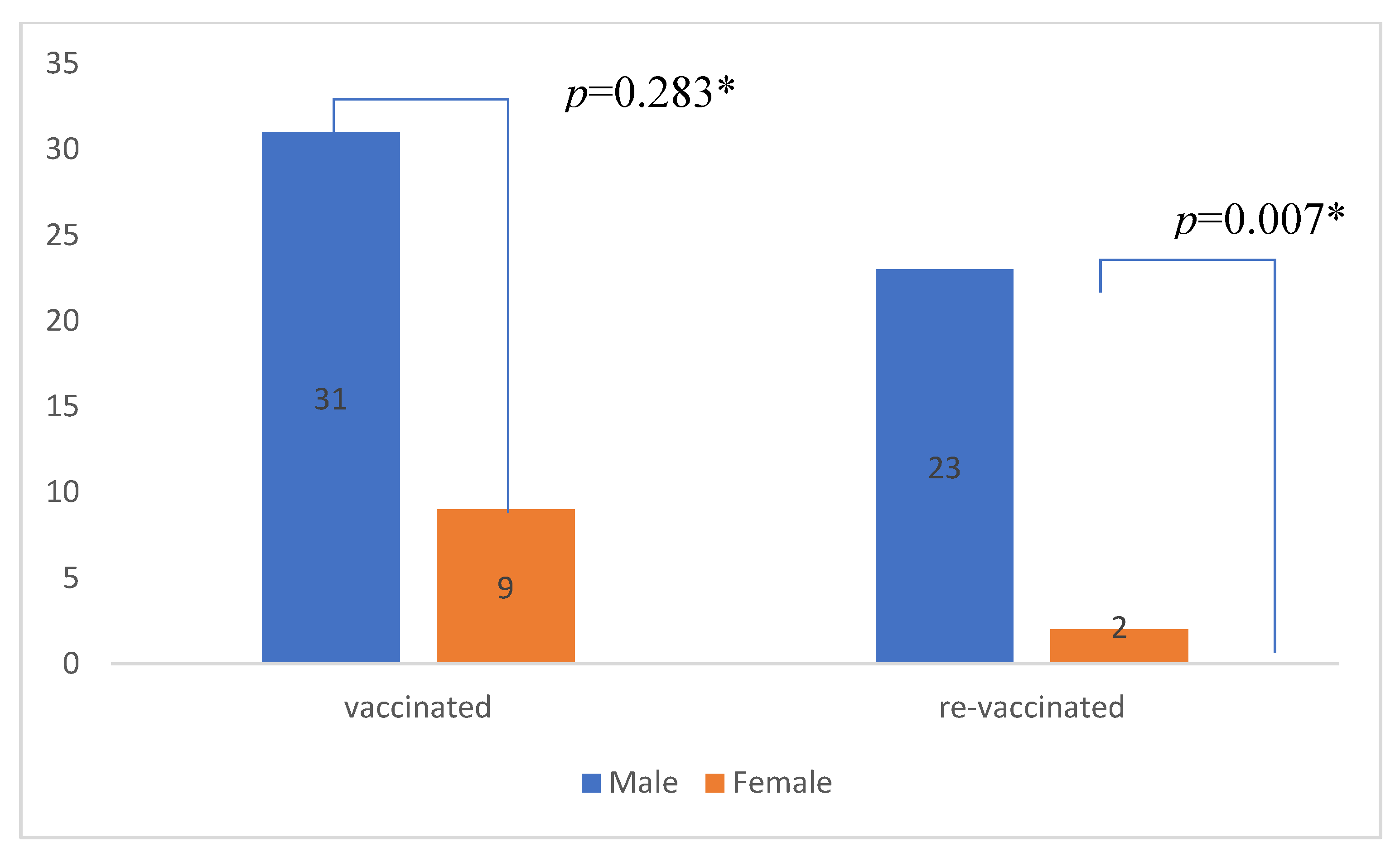
| Male gender (%) | 31 (77.5) | 26 (66.7) | p=0.283 |
| CCI (±SD) | 3.7 (±1.8) | 2.8 (±1.7) | p=0.018* |
| Time from heart transplantation (years) (±SD) | 6.4 (±4.8) | 4.9 (±5.7) | p=0.194 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) (±SD) | 9.0 (±11.8) | 12.0 (±12.0) | p=0.106 |
| No. of patients with respiratory insufficiency (%) | 11 (27.5) | 17 (43.6) | p=0.135 |
| No. of patients admitted to ICU (%) | 4 (10.0) | 2 (5.1) | p=0.414 |
| In-hospital mortality rate (%) | 3 (7.5) | 1 (2.6) | p=0.317 |
| No. of patients (%) treated with | |||
| -hyperimmune convalescent plasma | 1 (2.5) | 12 (30.8) | p=0.001* |
| -mAb | 9 (22.5) | 10 (25.6) | p=0.744 |
| -remdesivir | 34 (85.0) | 28 (71.8) | p=0.153 |
| -corticosteroid | 9 (22.5) | 10 (25.6) | p=0.744 |
| Subgroup analysis of heart transplant recipients receiving an mRNA-based vaccine or a vector-based vaccine | |||
|
mRNA vaccine N=28 |
vector vaccine N=12 |
||
| Mean age (years) (±SD) | 66.5 (±9.8) | 63.7 (±6.4) | p=0.371 |
| Male gender (%) | 22 (78.6) | 9 (75.0) | p=0.804 |
| CCI (±SD) | 3.5 (±2.0) | 4.2 (±1.3) | p=0.327 |
| Time from heart transplantation (years) (±SD) | 7.3 (±4.6) | 4.4 (±5.0) | p=0.085 |
| Time from vaccination to hospital admission (days) (±SD) | 388 (±215) | 431 (±218) | p=0.603 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) (±SD) | 6.6(±9.3) | 14.3 (±15.3) | p=0.011* |
| No. of patients with respiratory insufficiency (%) | 6 (21.4) | 5 (41.7) | p=0.189 |
| No. of patients admitted to ICU (%) | 2 (7.1) | 2 (16.7) | p=0.358 |
| In-hospital mortality rate (%) | 2 (7.1) | 1 (8.3) | p=0.896 |
| No. of patients (%) treated with | |||
| -hyperimmune convalescent plasma | 1 (3.6) | 0 | p=0.507 |
| -mAb | 6 (21.4) | 3 (25.0) | p=0.804 |
| -remdesivir | 24 (85.7) | 10 (83.3) | p=0.847 |
| -corticosteroid | 5 (17.9) | 4 (33.3) | p=0.283 |
| Subgroup analysis of vaccinated and unvaccinated heart transplant recipients with symptomatic COVID-19 | |||
|
Vaccinated N=19 |
Unvaccinated N=27 |
||
| Mean age (years) (±SD) | 66.7 (±7.2) | 61.2 (±7.7) | p=0.017* |
| Male gender (%) | 14 (73.7) | 17 (63.0) | p=0.445 |
| CCI (±SD) | 3.8 (±1.4) | 3.2 (±1.6) | p=0.154 |
| Time from heart transplantation (years) (±SD) | 5.9 (±4.7) | 4.6 (±4.7) | p=0.370 |
| No. of patients with respiratory insufficiency (%) | 11 (57.9) | 17 (63.0) | p=0.729 |
| No. of patients admitted to ICU (%) | 4 (21.1) | 2 (7.4) | p=0.176 |
| In-hospital mortality rate, % | 3 (15.8) | 1 (3.7) | p=0.152 |
| No. of patients (%) treated with | |||
| -hyperimmune convalescent plasma | 1 (5.3) | 12 (44.4) | p=0.004* |
| -mAb | 7 (36.8) | 6 (22.2) | p=0.278 |
| -remdesivir | 15 (78.9) | 18 (66.7) | p=0.362 |
| -corticosteroid | 9 (47.4) | 10 (37.0) | p=0.483 |
| Subgroup analysis of heart transplant recipients who received a booster dose of vaccine and does who did not | |||
|
Booster N=25 |
No booster N=15 |
||
| Mean age (years) (±SD) | 66.3 (±10.3) | 64.5 (±6.3) | p=0.556 |
| Male gender (%) | 23 (92.0) | 8 (53.3) | p=0.005* |
| CCI (±SD) | 4.2 (±1.9) | 3.0 (±1.5) | p=0.052 |
| Time from heart transplantation (years) (±SD) | 7.0 (±5.2) | 4.2 (±5.5) | p=0.372 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) (±SD) | 7.0 (±11.1) | 12.2 (±12.5) | p=0.030* |
| No. of patients with respiratory insufficiency (%) | 6 (24.0) | 5 (33.3) | p=0.522 |
| No. of patients admitted to ICU (%) | 3 (12.0) | 1 (6.7) | p=0.586 |
| In-hospital mortality rate, % | 3 (12.0) | 0 | p=0.163 |
| No. of patients (%) treated with | |||
| -hyperimmune convalescent plasma | 1 (4.0) | 0 | p=0.433 |
| -mAb | 4 (16.0) | 5 (33.3) | p=0.204 |
| -remdesivir | 22 (88.0) | 12 (80.0) | p=0.493 |
| -corticosteroid | 5 (20.0) | 4 (26.7) | p=0.625 |
| < 3 months N=4 |
3 – 6 months N=5 |
6 – 12 months N=9 |
> 12 months N=21 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of hospital stay (days) (±SD) | 4.5 (±1.3) | 11.8 (±7.8) | 11.6 (±16.0) | 7.4 (±11.6) | p=0.551 |
| No. of patients with respiratory insufficiency (%) | 2 (50.0) | 2 (40.0) | 2 (22.2) | 4 (19.0) | p=0.509 |
| No. of patients admitted to ICU (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (14.3) | p=0.426 |
| In-hospital mortality rate (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9.5 | p=0.613 |
| No. of patients (%) vaccinated with | |||||
| -mRNA-based vaccine | 3 (75.0) | 2 (40.0) | 8 (88.9) | 14 (66.7) | p=0.288 |
| -vector-based vaccine | 1 (25.0) | 3 (60.0) | 1 (11.1) | 7 (33.3) |
| Transplant less than one year before admission N=23 |
Transplant more than one year before admission N=56 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Length of hospital stay in days (±SD) | 11.6 (±14.3) | 10.0 (±10.9) | p=0.918 |
| No. of patients with respiratory insufficiency (%) | 6 (26.1) | 22 (39.3) | p=0.265 |
| No. of patients admitted to ICU (%) | 2 (8.7) | 4 (7.1) | p=0.813 |
| In-hospital mortality rate (%) | 0 | 4 (7.1) | p=0.188 |
| Symptomatic N=46 |
Asymptomatic N=33 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age(years) (±SD) | 63.5 (±7.9) | 61.2 (±12.0) | p=0.303 |
| Male gender (%) | 31 (67.4) | 26 (78.8) | p=0.265 |
| CCI (±SD) | 3.5 (±1.5) | 3.0 (±2.1) | p=0.141 |
| Time from heart transplantation (years) (±SD) | 5.2 (±4.7) | 6.4 (±6.1) | p=0.538 |
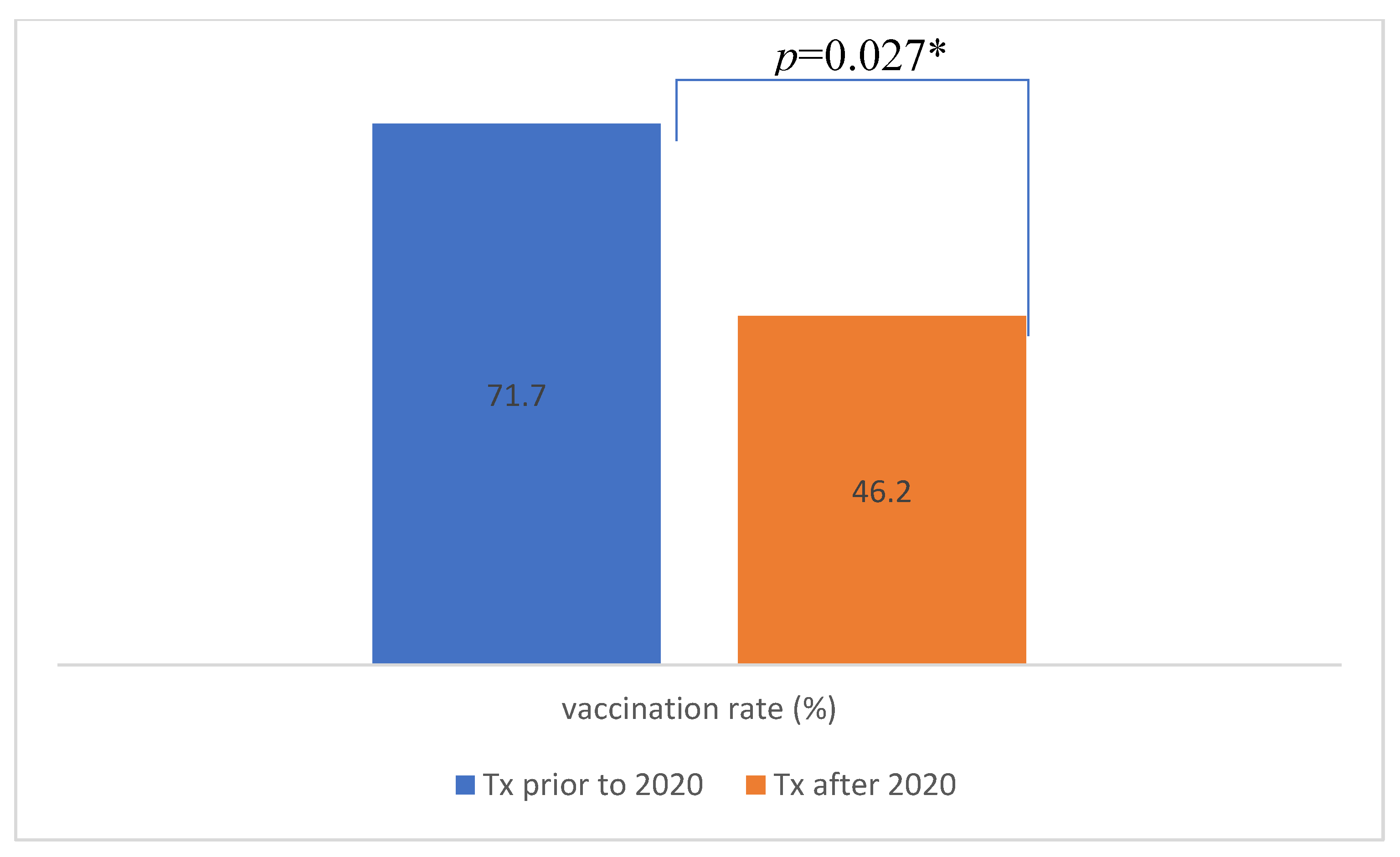
| No. of patients vaccinated (%) | 19 (41.3) | 21 (63.6) | p=0.050* |
| No. of patients receiving a booster dose of vaccine (%) | 9 (19.6) | 16 (48.5) | p=0.006* |
| No. of patients receiving a mRNA based vaccine (%) | 10 (52.6) | 18 (85.7) | p=0.023* |
| No. of patients receivig a vector based vaccine (%) | 9 (47.4) | 3 (14.3) | |
| No. of patients (%) treated with | |||
| -hyperimmune convalescent plasma | 13 (28.3) | 0 | p=0.001* |
| -mAb | 13 (28.3) | 6 (18.2) | p=0.301 |
| -remdesivir | 33 (71.7) | 29 (87.9) | p=0.085 |
| -corticosteroid | 19 (41.3) | 0 | p=0.000* |
| Measure | 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. | 7. | 8. | 9. | 10. | 11. | 12. | 13. | 14. | 15. | 16. | 17. |
| 1. Age | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2. Gender | 0.14 | 1.00 | |||||||||||||||
| 3. CCI | 0.50** | 0.23* | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||
| 4. T-TX | 0.33** | 0.17 | 0.19* | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| 5. T-VAC | -0.10 | -0.13 | -0.15 | -0.07 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
| 6. LOS | 0.09 | -0.14 | 0.18* | 0.02 | -0.11 | 1.00 | |||||||||||
| 7. SYMP | 0.04 | -0.13 | 0.15 | -0.06 | -0.19 | 0.73** | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| 8. ARI | 0.12 | -0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 | -0.20 | 0.59** | 0.63** | 1.00 | |||||||||
| 9. ICU | 0.07 | -0.04 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.32** | 0.24* | 0.39** | 1.00 | ||||||||
| 10. MORT | 0.17 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.25** | 0.20 | 0.31** | 0.81** | 1.00 | |||||||
| 11.HCP | -0.08 | 0.05 | 0.07 | -0.02 | -0.22 | 0.35** | 0.38** | 0.24* | -0.13 | -0.10 | 1.00 | ||||||
| 12. mAb | -0.05 | 0.09 | -0.02 | -0.05 | -0.33* | 0.01 | 0.12 | 0.08 | -0.05 | 0.01 | -0.25* | 1.00 | |||||
| 13. remde | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.02 | -0.06 | 0.29* | -0.11 | -0.19 | 0.00 | 0.03 | -0.02 | 0.15 | -0.43 | 1.00 | ||||
| 14. stero | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.33* | 0.44** | 0.48** | 0.76** | 0.29* | 0.41** | 0.15 | 0.10 | -0.14 | 1.00 | |||
| 15. VAC. | 0.28** | 0.12 | 0.25* | 0.18 | A | -0.16 | -0.22 | -0.17 | 0.09 | 0.11 | -0.38** | -0.04 | 0.16 | -0.04 | 1.00 | ||
| 16. mRNA | 0.19 | 0.04 | -0.21 | 0.26 | -0.09 | -0.35* | -0.36* | -0.21 | -0.15 | -0.02 | 0.11 | -0.04 | 0.03 | -0.17 | a | 1.00 | |
| 17.R-VAC. | 0.25** | 0.30** | 0.31** | 0.18 | 0.05 | -0.25** | -0.31** | -0.16 | 0.11 | 0.22 | -0.23* | -0.13 | 0.16 | -0.06 | 0.67** | 0.06 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





