Submitted:
05 November 2024
Posted:
07 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Flexible Integration of External Knowledge: We introduce a methodology that facilitates the utilization of external knowledge,such as Tencent's 8-million-word corpus and Netease's embedding corpus, as inputs for Chinese word-level semantic understanding. This methodology offers the flexibility to incorporate domain-specific word embedding libraries based on task requirements.
- Combination of Global and Local Information: By integrating external knowledge with internal attention mechanisms, the methodology effectively combines global semantic information with local contextual relationships. This addresses the limitations of previous methodologies that focused solely on global relationships.
- Task Generalizability: The proposed methodology transcends the confines of short text similarity, extending its application to enhance semantic understanding and recognition accuracy across various NLP tasks. We conduct innovative experiments on Named Entity Recognition (NER), demonstrating remarkable results.
- Extensive Experimental Validation: The proposed methodology undergoes extensive validation on datasets such as MSRA-NER. The results demonstrate not only superior performance in general tasks but also versatility across various language processing scenarios. These findings provide new insights for future NLP research.
2. Related Work
2.1. Pre-Trained Models
2.2. Integration of External Knowledge Bases
- Knowledge Graph Embeddings[23]: Converting KGs into low-dimensional vectors allows neural models to process entity relationships through vector arithmetic, enabling semantic relationship modeling.
- Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)[24]: GNNs aggregate information across graph nodes, with attention mechanisms like Graph Attention Network (GAT) enhancing node representation by focusing on the importance of connections.
- Knowledge-Enhanced Transformer Models[25]: Models like K-BERT incorporate KG embeddings directly, allowing the Transformer architecture to utilize structured external knowledge during both pre-training and fine-tuning, thereby improving tasks such as text classification.
2.3. Applications of External Knowledge in Chinese NLP
- Polysemy and Homophones: Due to frequent ambiguity, models often require additional context to accurately interpret meaning.
- Lexical Scarcity and Conciseness: Chinese language relies on idioms and phrases, making semantic analysis difficult without enhanced segmentation accuracy.
- Lexical Representations: thesaurus like the Tencent’s 8-million-word corpus and NetEase bce embedding model enrich word embeddings for Chinese, which is especially helpful in handling synonyms and reducing semantic interference.
- Knowledge Graph-Based Enhancement: Structured data from Chinese knowledge graphs provides hierarchical relationships, aiding semantic similarity by embedding this information into models for complex relationship handling.
- Contextual Computations: External knowledge supports disambiguation, particularly for polysemy, thereby improving similarity computation accuracy.
2.4. Insights for This Study
3. Methodology
3.1. Model Design
3.1.1. Pre-Trained Language Models
3.1.2. Integration of External Word Vector Databases
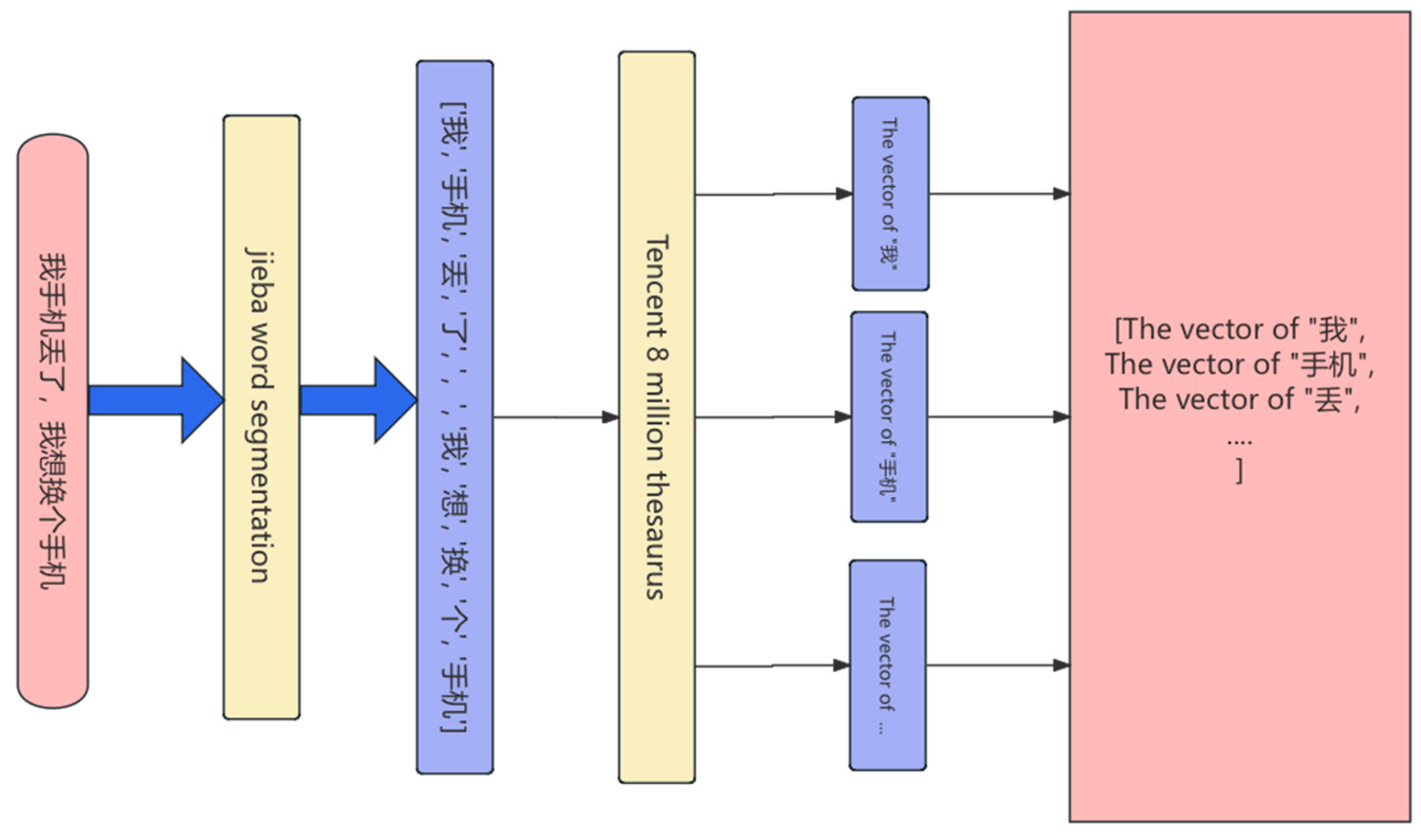
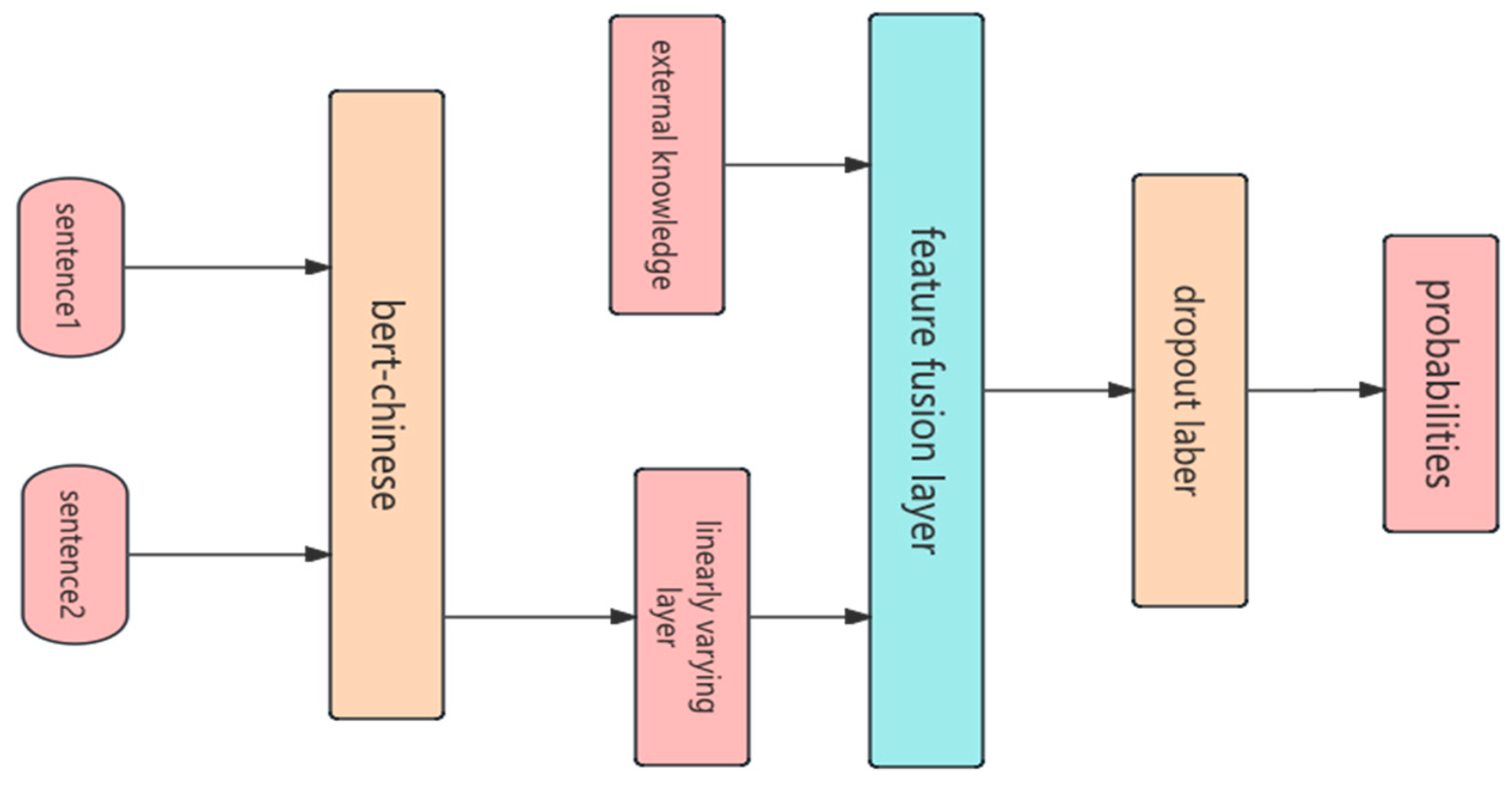
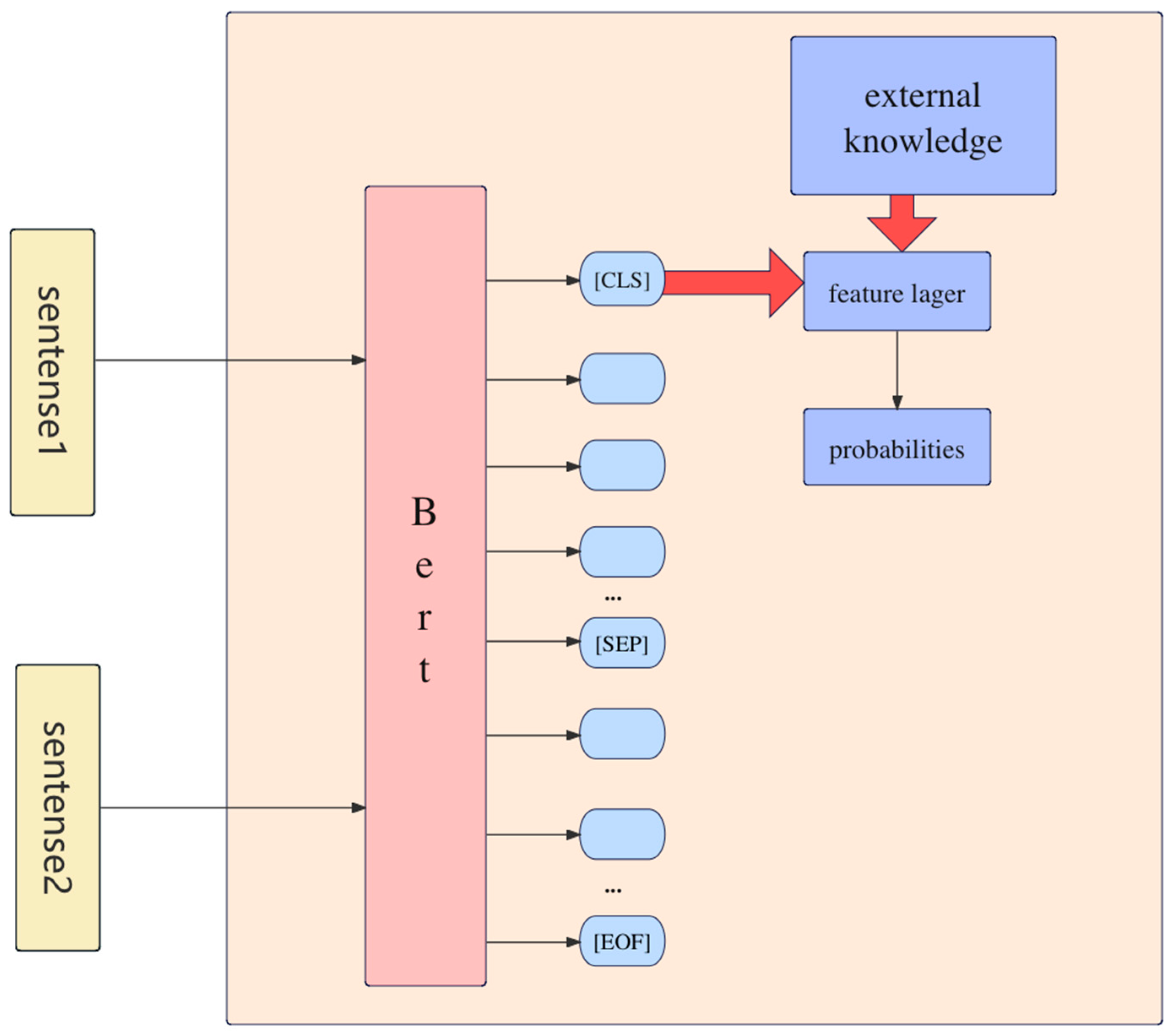
3.1.3. Feature Fusion Strategy
3.2. Similarity Computation and Optimization
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Dataset Overview
- LCQMC(the dataset can be downloaded from https://www.modelscope.cn/datasets/DAMO_NLP/LCQMC/files)[28]: This is a large-scale Chinese question matching corpus designed to assess the semantic similarity between two questions. The dataset contains diverse short-text features and covers common question-answering scenarios in daily life, making it highly suitable for short-text similarity tasks.
- BQ(the dataset can be downloaded from https://www.modelscope.cn/datasets/DAMO_NLP/BQ_Corpus)[29]: Derived from a banking question-answering system, this dataset focuses on short-text matching tasks in the financial domain. The BQ dataset has a complex structure involving financial terms and concepts, allowing it to test a model’s adaptability in specialized domains.
- OPPO-xiaobu(the dataset can be downloaded from https://github.com/CLUEbenchmark/FewCLUE/tree/main/datasets/bustm): This dataset, provided by OPPO, consists of real user queries from an intelligent assistant. It is used to evaluate short-text similarity performance in dialogue-based scenarios.
- AFQMC(the dataset can be downloaded from https://www.modelscope.cn/datasets/modelscope/afqmc_small): A financial domain short-text similarity dataset containing 80,000 samples, primarily used to assess performance in matching financial-related queries.
4.1.2. Experimental Environment
- Hardware: The experiments were conducted on a server equipped with an NVIDIA RTX 4090 GPU with 24 GB of memory and 500 GB of storage.
- Operating System: Ubuntu 20.04.
- Development Framework: Python was used for model implementation and training, with PyTorch serving as the deep learning framework.
- Dependencies: Jieba was utilized for Chinese word segmentation. External knowledge bases such as Tencent’s 8-million-word corpus and NetEase’s word vector library were integrated to enhance the model’s lexical representation capabilities.
4.1.3. Model Selection and Configuration
- BERT-Base-Chinese: A bidirectional encoder model based on the Transformer architecture, used as a baseline model without incorporating external knowledge.
- RoBERTa-Base-Chinese: An optimized version of BERT, with the next-sentence prediction task removed and trained on a larger dataset for improved performance.
- BART-Base-Chinese: A model combining features of BERT and GPT, suitable for generation and summarization tasks.
- ERNIE 2.0: A knowledge-enhanced pre-trained model that integrates knowledge such as entities and concepts.
- The proposed knowledge-enhanced model: Built upon pre-trained models, this model integrates Tencent’s 8-million corpus and NetEase bce embedding model, fusing external lexical knowledge with pre-trained models to capture both global and local semantic features of sentences.
4.1.4. Feature Fusion Strategy
4.1.5. Experimental Parameters
- Optimization Algorithm: Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of 1e-5, applying a linear decay strategy to a minimum of 1e-6.
- Batch Size: 64.
- Training Epochs: Maximum of 15 epochs, with early stopping applied if no performance improvement is observed on the validation set for 5 consecutive epochs.
- Loss Function: Binary cross-entropy loss.
- Activation Function: Sigmoid function, used to map the output similarity score to a probability between 0 and 1.
4.2. Experimental Design
4.2.1. Pre-Trained Model Comparison
4.2.2. Cross-Dataset Performance Comparison
4.2.3. Comparison of Different External Knowledge Bases
4.2.4. Comparison with Other Advanced Models
4.3. Summary
5. Extended Experiments
5.1. NER
5.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
5. Conclusion
References
- Devlin, J. (2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805.
- Vaswani, A. (2017). Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
- Petroni, F., Rocktäschel, T., Lewis, P., Bakhtin, A., Wu, Y., Miller, A. H., & Riedel, S. (2019). Language models as knowledge bases?. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.01066.
- Roberts, A., Raffel, C., & Shazeer, N. (2020). How much knowledge can you pack into the parameters of a language model?. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.08910.
- Velickovic, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Lio, P., & Bengio, Y. (2017). Graph attention networks. stat, 1050(20), 10-48550.
- Lee, K., Chang, M. W., & Toutanova, K. (2019). Latent retrieval for weakly supervised open domain question answering. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.00300.
- Petroni, F., Rocktäschel, T., Lewis, P., Bakhtin, A., Wu, Y., Miller, A. H., & Riedel, S. (2019). Language models as knowledge bases?. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.01066.
- Wang, H., Liu, Y., Zhu, C., Shou, L., Gong, M., Xu, Y., & Zeng, M. (2021, August). Retrieval Enhanced Model for Commonsense Generation. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021 (pp. 3056-3062).
- Chen, D., Fisch, A., Weston, J., & Bordes, A. (2017). Reading Wikipedia to answer open-domain questions. In 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL 2017 (pp. 1870-1879). Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL).
- Lin, Y., Han, X., Xie, R., Liu, Z., & Sun, M. (2018). Knowledge representation learning: A quantitative review. arXiv preprint arXiv:1812.10901.
- Zhou, Y., Li, C., Huang, G., Guo, Q., Li, H., & Wei, X. (2023). A short-text similarity model combining semantic and syntactic information. Electronics, 12(14), 3126. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Han, X., Liu, Z., Jiang, X., Sun, M., & Liu, Q. ERNIE: Enhanced Language Representation with Informative Entities.
- Reimers, N., & Gurevych, I. (2019). Sentence-BERT: Sentence Embeddings using Siamese BERT-Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing.
- Yang, Z., Dai, Z., Yang, Y., Carbonell, J., Salakhutdinov, R., & Le, Q. V. (2019). XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.08237.
- Liu, Y., Ott, M., Goyal, N., Du, J., Joshi, M., Chen, D., ... & Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach.
- Lan, Z., Chen, M., Goodman, S., Gimpel, K., Sharma, P., & Soricut, R. (2019, September). ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations. In International Conference on Learning Representations.
- Lewis, M., Liu, Y., Goyal, N., Ghazvininejad, M., Mohamed, A., Levy, O., ... & Zettlemoyer, L. (2020). BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (p. 7871). Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Radford, A., Narasimhan, K., Salimans, T., & Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training.
- Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., & Sutskever, I. (2019). Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI blog, 1(8), 9.
- Brown, T. B., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P., ... & Amodei, D. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners.
- Bollacker, K., Evans, C., Paritosh, P., Sturge, T., & Taylor, J. (2008, June). Freebase: a collaboratively created graph database for structuring human knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGMOD international conference on Management of data (pp. 1247-1250).
- Noy, N., Gao, Y., Jain, A., Narayanan, A., Patterson, A., & Taylor, J. (2019). Industry-scale Knowledge Graphs: Lessons and Challenges: Five diverse technology companies show how it’s done. Queue, 17(2), 48-75.
- Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garcia-Duran, A., Weston, J., & Yakhnenko, O. (2013). Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. Advances in neural information processing systems, 26.
- Kipf, T. N., & Welling, M. (2016). Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02907.
- Liu, W., Zhou, P., Zhao, Z., Wang, Z., Ju, Q., Deng, H., & Wang, P. (2020, April). K-bert: Enabling language representation with knowledge graph. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 34, No. 03, pp. 2901-2908).
- Wang, X., Gao, T., Zhu, Z., Zhang, Z., Liu, Z., Li, J., & Tang, J. (2021). KEPLER: A unified model for knowledge embedding and pre-trained language representation. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 9, 176-194. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J., Zhang, H., Xia, C., & Sun, L. (2020). Graph-bert: Only attention is needed for learning graph representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.05140.
- Liu, X., Chen, Q., Deng, C., Zeng, H., Chen, J., Li, D., & Tang, B. (2018, August). Lcqmc: A large-scale chinese question matching corpus. In Proceedings of the 27th international conference on computational linguistics (pp. 1952-1962).
- Chen, J., Chen, Q., Liu, X., Yang, H., Lu, D., & Tang, B. (2018). The bq corpus: A large-scale domain-specific chinese corpus for sentence semantic equivalence identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (pp. 4946-4951).
- Sun, Y., Wang, S., Li, Y., Feng, S., Tian, H., Wu, H., & Wang, H. (2020, April). Ernie 2.0: A continual pre-training framework for language understanding. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (Vol. 34, No. 05, pp. 8968-8975).
- Diao, S., Bai, J., Song, Y., Zhang, T., & Wang, Y. (2019). ZEN: Pre-training Chinese text encoder enhanced by n-gram representations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.00720.
- Liu, R., Zhong, Q., Cui, M., Mai, H., Zhang, Q., Xu, S., ... & Du, Y. (2024, March). External Knowledge Enhanced Contrastive Learning for Chinese Short Text Matching. In 2024 5th International Seminar on Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Information Technology (AINIT) (pp. 1436-1440). IEEE.
- Ma, H., Li, Z., & Guo, H. (2022, October). Using Noise and External Knowledge to Enhance Chinese Pre-trained Model. In 2022 IEEE 34th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI) (pp. 476-480). IEEE.
- Meng, Y., Wu, W., Wang, F., Li, X., Nie, P., Yin, F., ... & Li, J. (2019). Glyce: Glyph-vectors for chinese character representations. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 32.
| Model | Dataset | Without External Knowledge | With External Knowledge |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERT-Base-Chinese | LCQMC | 88.13% | 88.66% |
| BERT-Base-Chinese | AFQMC | 72.66% | 74.50% |
| RoBERTa-Base-Chinese | LCQMC | 88.80% | 90.16% |
| RoBERTa-Base-Chinese | AFQMC | 73.3% | 74.56% |
| BART-large-Chinese | LCQMC | 88.73% | 90.11% |
| BART-large-Chinese | AFQMC | 72.84% | 74.68% |
| Model | Dataset | Without External Knowledge | With External Knowledge |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERT-Base-Chinese | LCQMC | 88.13% | 88.66% |
| BQ | 84.43% | 85.32% | |
| OPPO-xiaobu | 86.64% | 88.03% | |
| AFQMC | 72.66% | 74.50% |
| Model | Dataset | External Knowledge | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| BERT-Base-Chinese | AFQMC | None | 72.66% |
| AFQMC | Tencent’s 8-million-word corpus | 73.4% | |
| AFQMC | NetEase bce embedding model | 73.22% |
| Model | LCQMC | BQ |
|---|---|---|
| ERNIE 2.0 Base[30] | 87.9% | 85.0% |
| ERNIE 2.0 Large[30] | 87.9% | 85.2% |
| ZEN[31] | 87.95% | - |
| KECM[32] | 88.91% | 87.62% |
| NEK[33] | 88.15% | 85.08% |
| Ours | 90.16% | 85.32% |
| Model | Dataset | F1 |
|---|---|---|
| ERNIE 2.0 Base | MSRA-NER | 93.8% |
| ERNIE 2.0 Large | MSRA-NER | 95.25% |
| ZEN | MSRA-NER | 95.25% |
| Glyce + BERT[34] | MSRA-NER | 95.54% |
| Bert | MSRA-NER | 93.56% |
| Ours | MSRA-NER | 95.74% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





