1. Introduction
In recent years, the global environmental context has demanded a shift towards more eco-friendly solutions to address the world’s material needs [
1]. Natural fiber polymer composites (NFPCs) stand out among these due to their low cost, biodegradability, low density, and renewability. NFPCs are polymer matrix-based composites containing natural fibers like jute, flax, hemp, kenaf, oil palm, and sisal as reinforcements. The addition of natural fiber improves the polymer’s physical and mechanical properties while also minimizing carbon dioxide emissions during the process of material production [
2]. The expanding interest in NFPCs can be recognized by several factors. First, Natural fibers are a source of renewable resources, since they can be grown with limited environmental damage, which appeals to sustainable development. Second, they have useful mechanical properties, such as high tensile strength and stiffness compared to synthetic fibers based on the proper processing of the fibers and fiber alignment. In addition, the use of compostable fibers for composite materials matches the global commitment to reducing plastic waste and sustainable circular economy principles [
3].
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a thermoplastic material, which is made of natural gas and mineral oil by a complex process. Styrene copolymer is the main constitutes of EPS, which contains a flam-retarding agent and foaming. EPS is composed of 98% of air and the remaining 2% of polystyrene [
4]. It is naturally non-toxic, inactive material compared to other thermoplastics polymers. The high insulating properties, shock absorbing properties and other qualities of EPS foam, combined with its low density, low cost, ease of processing and custom moldability (easy of casting) make it a trendy packaging material [
5]. Therefore, the formulation of NFPCs from flax fiber with recycled materials such as expanded polystyrene (EPS) waste not only enhances mechanical and other properties but also contributes to waste reduction and resource conservation.
Flax (Linum usitatissimum) is a commercially important plant within the Linaceae family, which comprises over 300 species and 13 genera [
6]. Flax, also known as linseed, is the only species cultivated for its diverse applications. Grown in moderate climates, flax seeds are a versatile crop used for food, fiber, oil production, pharmaceuticals, animal feed, and as additives in paints [
7]. Flax fibers have high strength, durability and fineness. Currently, the applications of flax fibers are increasing due to their low density, availability, low cost, degradability, biodiversity, and ease of handling as well as excellent properties [
8]. Unlike other fibers, flax fibers can operate at high temperatures, reaching up to 250°C, making them suitable for use in polymer composites. Despite their low density, flax fibers exhibit comparable specific properties (properties divided by density) to glass fibers. In the automotive and aviation sectors, flax fiber composites are being explored as a lightweight replacement for synthetic fiber-reinforced composites, contributing to weight reduction [
9]. Combining randomly oriented short flax fibers into a recycled EPS matrix forms a unique composite material that changes the strengths of both constituents. Flax fibers contribute stiffness and strength, while recycled EPS waste provides lightweight and thermal insulation properties. However, the mechanical properties of such composites are affected by various factors, including fiber content, distribution, and the interfacial bonding between the matrix and the fibers. The effects of those factors on the mechanical properties of composite materials are evaluated by experimental and micromechanics analysis.
Many researchers have used mathematical and numerical approaches to estimate the mechanical behavior of natural fiber-reinforced polymer composites (NFPCs). Such methods can derive effective properties from the microstructure directly, enabling an inexpensive and efficient alternative to transformational experimental testing, giving insight into and predictability of the behavior of a composite based on the properties of its constituents. Theoretical models that are commonly used for the prediction of mechanical properties include the rule of mixtures (ROM), inverse rule of mixtures (IROM), Halpin-Tsai model, etc. Other successful theories including Hirsch model, Cox-Krenchel model, and Einstein and Guth models are also applicable to compute the mechanical properties of composites based on the properties of the individual components. Venkateshwaran et al. [
10] have compared the experimental tensile properties of randomly oriented banana/epoxy composite with theoretical models. Theoretical models such as the Modified Rule of Mixture, Hirsch, Nielson, Halpin–Tsai, Bowyer and Bader’s were used for comparison to the experimental results. From all the models, the modified rule of mixture predicts the tensile strength of the composite very close to the experimental result next to Bowyer and Bader’s model. S. Palsule et al. [
11] studied the tensile modulus of jute fiber reinforced with chemically modified polypropylene composites using experimental and theoretical models. Compared to experimental result, rule of mixture predicts higher modulus value and inverse rule of mixture predicts lower result in all fiber loadings. On the other hand, Hirsch model predicts a close agreement to the experimental result. The other Halpin –Tsai and Nielson model predicts almost a similar result and lower modulus value compared to the experimental result in all fractions of fiber. In addition, the new proposed Palsule model has a reasonable tensile modulus value at optimum fiber fraction. Wahyu Purwo et al. [
12] studied the experimental and micromechanical modeling of short zalacca fiber reinforced with low-density polyethylene composite. The tensile strength of the composite is predicted using the Bowyer-Bader and Hirsch models while, the tensile modulus is estimated using the Manera, Tsai–Pagano, and Cox Krenchel models. The predictions of the Bowyer-Bader and Tsai–Pagano model showed a close agreement with experimental results for tensile strength and elastic modulus of the composites respectively.
This study aims to evaluate the tensile properties of randomly oriented short flax fiber-reinforced recycled EPS waste composites through both theoretical models and experimental approaches. Theoretical models such as the rule of mixture (ROM) series, Hirsch, modified Bader and Bowyer, Einstein-Guth, Cox-Krenchel, and Palsule model were compared with experimental results for tensile strength and tensile modulus of the composite. This dual approach not only enhances the reliability of the findings but also provides insights into the practical applications of these eco-friendly materials in industries such as construction, automotive, and packaging.
2. Theoretical Models for Tensile Properties
The theoretical models of natural fiber polymer composite are very essential to understanding the fiber-matrix interaction and the effect of one constitutes on the final product before doing experimental results. It also helps to sympathize with the macro and micro properties of the material by reducing cost and time for experimentation. Various micromechanics models are given to predict the composite’s tensile strength and tensile modulus based on the natural fiber’s elastic strength and the matrix in the composite [
13,
14,
15].
The ROM models are the most common type of tensile strength prediction model for natural fiber polymer composite. The ROM models, series, and parallel models were examined by Voigt and Reuses in 1889 and 1892 respectively. In this model, both assumed that the fiber and matrix act as a perfect bonding; no voids are present, there is homogenous fiber distribution and it acts as a perfectly elastic material. ROM model is best suitable and fits with the experimental value for aligned continuous fiber polymer composite. Nevertheless, for short fiber polymer composite the value of tensile stress only agrees at low fiber content and deviates at higher fiber content compared to the experimental result [
14,
15]. ROM series equation for prediction of tensile stress and modulus on natural fiber composite are given by the following relation.
where,
σ, and
E are the stress, volume fraction, and modulus respectively. The subscript C, F, M, represents the composite, fiber and matrix respectively. The above model is more suitable for aligned continuous fiber so the stress along transverse direction equals the strength of the matrix and does not fit with the experiment most of the time for random oriented short fiber composite.
- ▪
Modified Bader’s and Bowyer model
This model is a modification of the Kelly-Tyson strength model. This model is also determined based on the assumption that the fiber and matrix are perfectly bonded, and behave as a linear elastic material. According to Modified Bader and Bowyer’s model, the tensile strength of short fiber thermoplastic composite is the sum of contributions of fiber and matrix strength [
15,
16]. In this model, the tensile and elastic modulus of the composite can be given by
where
K1 is the fiber orientation factor its value changes from (0-1) and is allowed to vary best fit to experimental data and
K2 is the length factor of fiber its values are given by equation
where, LC = critical fiber length, d = is fiber average diameter, τ = shear strength of fiber/matrix bond (0.5 times matrix strength), L= is the fiber average length, σF= fiber tensile strength, σM= matrix tensile strength, VF = is the fiber volume fraction and VM = the matrix volume fraction.
- ▪
Hirsch’s model
Hirsch’s model also predicts the tensile modulus and strength by combining the parallel and series models multiplying with some parameters.
For elastic modulus
where,
σ, E and
V are stress, modulus and volume fraction respectively. The subscript F, M is fiber and matrix respectively.
X is the empirical considerations found by the Hirsch model to fit the experimental value with the theoretical model. It determines the stress transfer and good fiber-matrix bonding of the composite. It also depends on fiber length, fiber distribution and fiber orientation. The value of
X lies between 0 to 1 to optimum fit to that of the experiment result [
15].
- ▪
Einstein and Guth equations
This model is used to predict the theoretical tensile strength of very short fiber-reinforced polymer composites [
17]. The equations are given by
- ▪
Palsule model
The Palsule model as expressed in Equation (2.9), is employed to estimate the tensile modulus of short fiber-reinforced composites [
11].
In this model, represents the aspect ratio (L/d) and is the packing fraction of the fibers (assumed to be 0.5 for randomly oriented fibers); the constant and represent the longitudinal and transverse stress distribution across the composite. The value of and can vary between 1/2 and 1/8 depending on the fiber distribution within the composite. For this study, the value of and has been taken 1/6.
- ▪
Cox-Krenchel Model
The Cox-Krenchel model gives another model for predicting the tensile strength and modulus. According to Cox, the tensile strength and longitudinal modulus of the composite are given by the following equation.
where
Gm and
m are the shear modulus of the matrix and Poisson’s ratio of the matrix respectively. For square packing fibers, the value of
Xi = 4 is used for calculation. The value of
ηο = 0.375 for composites reinforced with random in-plane fiber but, allowed to vary the best fit to experimental data [
10,
15]. The values of the tensile strength and modulus of the polystyrene matrix used in this study are 26MPa and 1.93GPa respectively [
18].
3. Material
3.1. Fiber Characterization
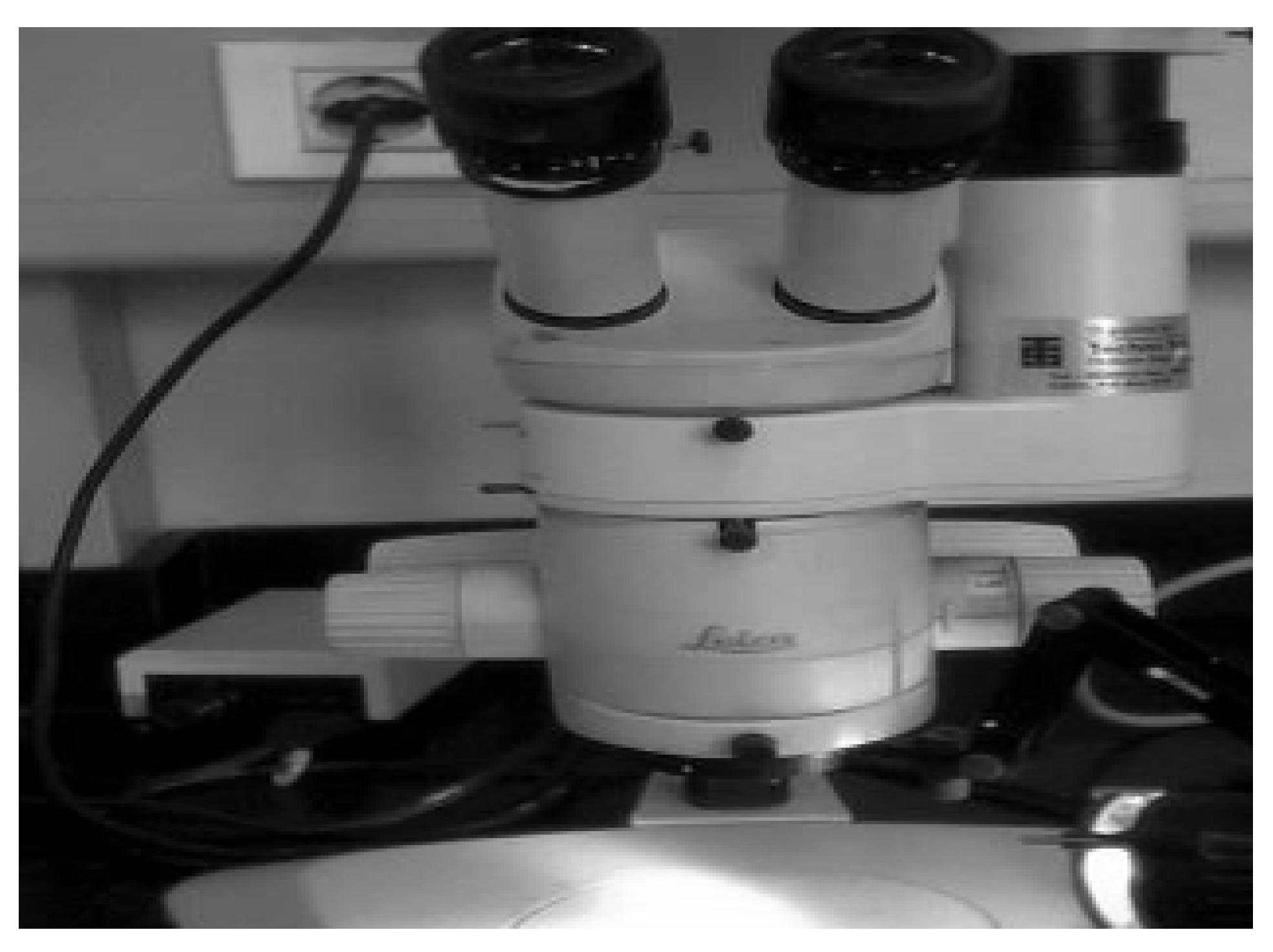
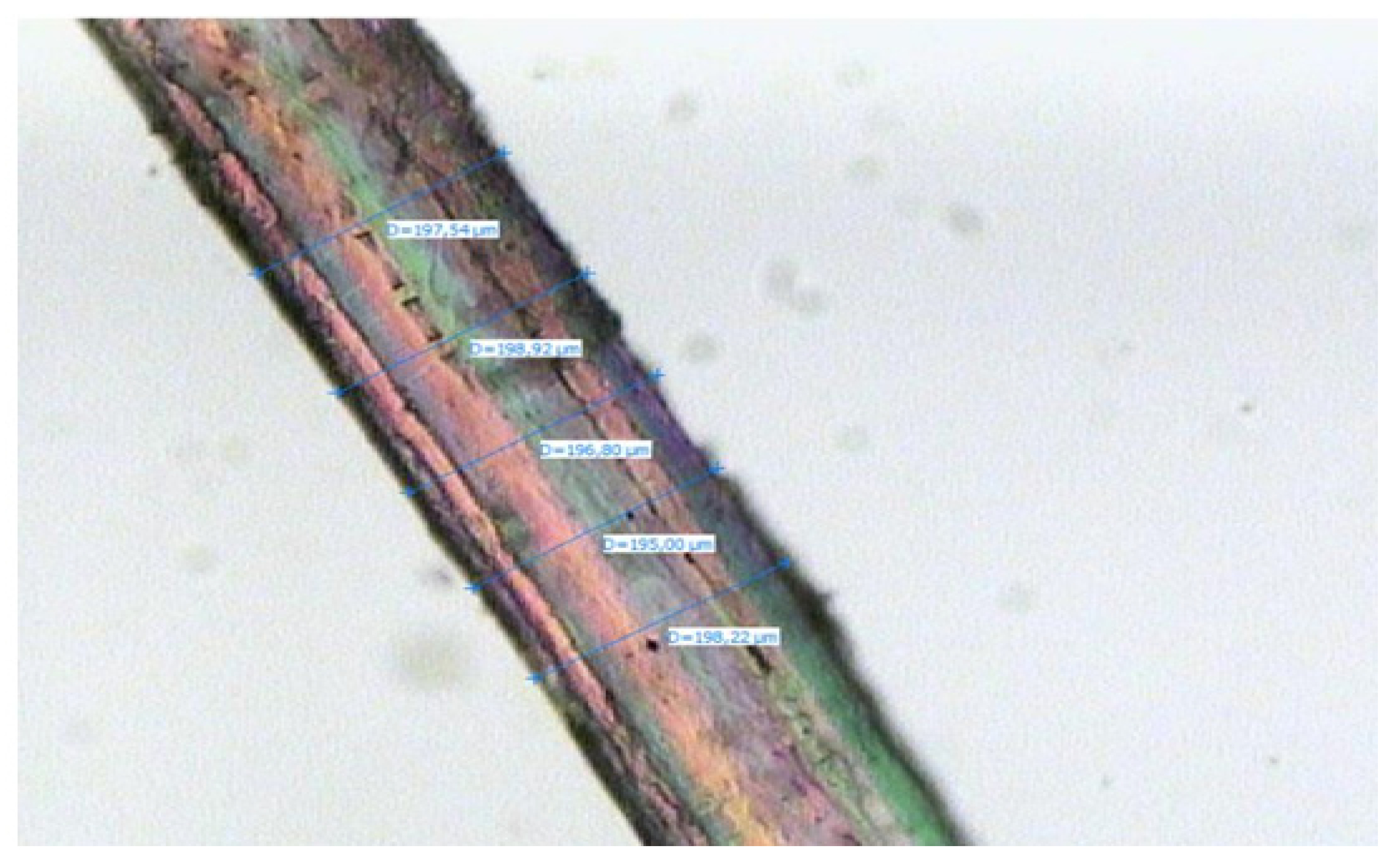
The Leica biological microscope shown in
Figure 1 is used to compute the diameter of the flax fiber with a maximum magnification of up to 100
×. Bundles of fibers are cut into very small pieces and mounted on the microscopic slide. The magnified surface features and the diameter of the fiber are observed through the microscope. Five measurements have taken along the length of the each fiber.
3.2. Density of Fiber
The hydrophilic and porous nature of the fiber necessitates the use of a pycnometer for accurate density determination, following ASTM D792 standards. The fiber density (
) can then be calculated using Equation (2) [
19].
where; W1 = the weight of empty clean dry pycnometer, W2 = the weight of the pycnometer containing the sample, W3 = the weight pycnometer containing the sample and kerosene, W4 = the weight of the pycnometer containing kerosene, and
= the density of kerosene
3.3. Tensile Testing of Flax Fiber
The tensile strength of the fiber is found by using the universal tensile testing machine 5DZ as shown in
Figure 2a. The universal tensile testing machine has a maximum load cell of 5 KN, a 100mm/min speed at the time of testing, and a 50mm/min speed at which to return to the original position. The tested samples are seven single fibers with 250mm long as per the ASTM D3379-75 standard as shown in
Figure 2b [
20]. The tensile strength and modulus of single fibers were obtained by a relation called Tex. Flax fibers do not have a regular shape as observed in the microscope. Therefore, the tensile strength and Young’s modulus of the fiber were determined in terms of linear density or tex by the following relation of Equation (3) [
21] and the elastic modulus of fiber can be determined by Equation (4).
3.4. Composite Preparation
To prepare flax fiber-reinforced EPS composites, flax fibers were manually mixed with the EPS matrix in various weight proportions. A mold was constructed using glass sheets measuring 200 mm x 200 mm x 5 mm as shown in
Figure 1a. The glass plates were coated with wax to facilitate easy sample removal. The fiber-matrix mixture was poured into the mold and compressed to remove air and ensure a smooth surface for the composite as shown in
Figure 3b. The molded composites were then cured at room temperature for 15 days. Samples of prepared composites are shown in
Figure 3c. Finally, the composites were cut into specimens according to ASTM D638 standards for tensile testing.
3.5. Composite Tensile Properties Testing
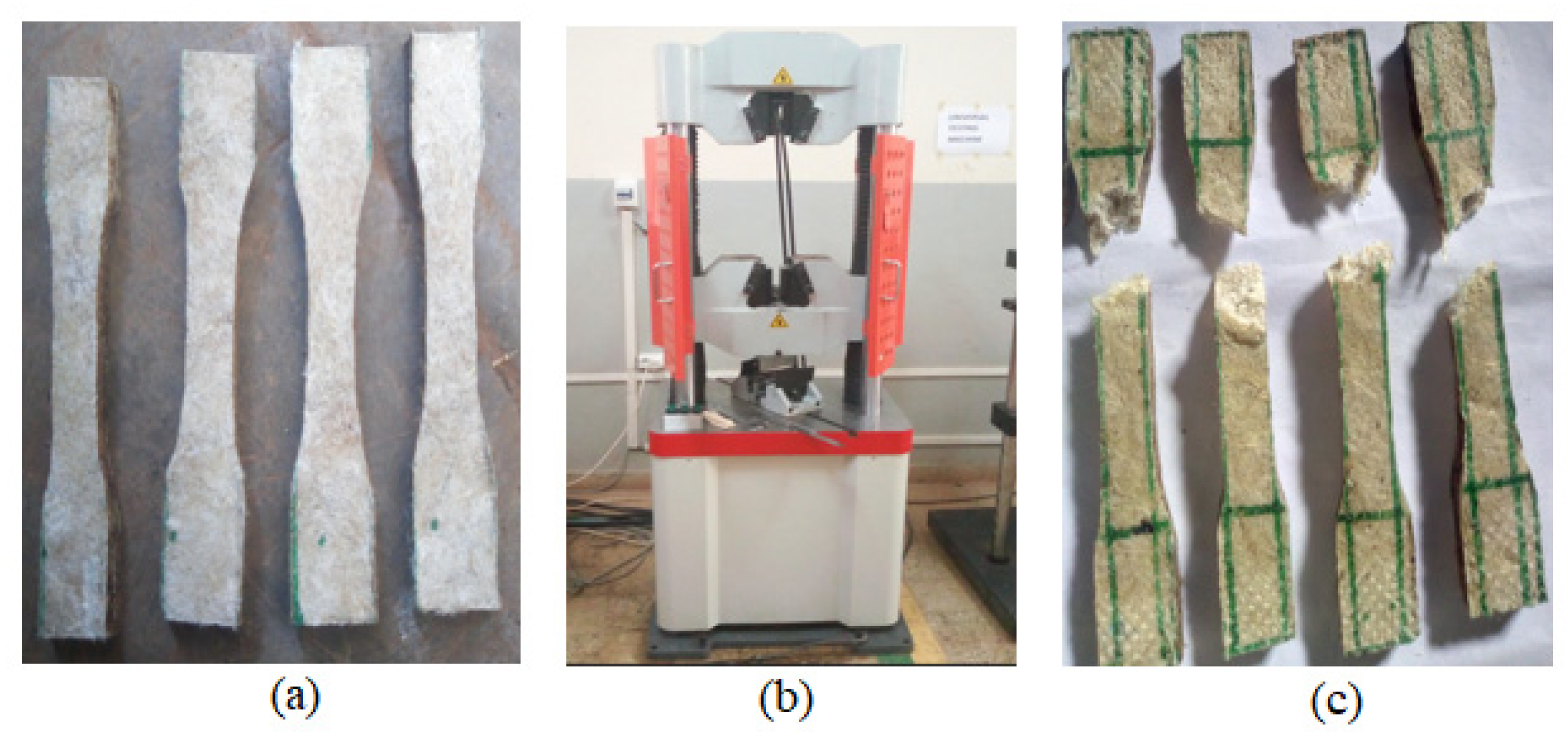
The samples are prepared as per ASTM D638 with dimensions of 115×19×5 mm and a gauge length of 60mm [
22] as shown
Figure 4a. The tensile testing is done on a Universal Testing Machine (UTM) shown in
Figure 4b at across head speed of 5mm/min. The tensile strength of five samples was tested for each fiber-matrix combination and average values were reported. The specimens were mounted in the lower and upper grips of the machine carefully to avoid slippage and applying it to tension until it fractured as shown in
Figure 4c. As the load is increased on the specimen, the elongation is automatically recorded and displayed on the computer. Equation (5) is used to determine the tensile modulus of the composite.
where ∆σ and ∆ε are the straight-line portions of the change in stress and strain respectively.
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Diameter and Density of Flax Fiber
The diameter and density of treated flax fiber are essential for calculating the analytical analysis of mechanical properties of composite material. The measured flax fiber diameter is presented in
Table 1 and average measured result is shown in
Figure 4 along the length of fiber. From
Figure 4, it is noted that the diameter of flax fiber obtained in this study is consistent with the data presented in the literature as varying in the range of 12-600 µm [
23,
24]. The density of treated flax fiber is also tabulated in
Table 1 is also consistent with the literature and its values are reported in the range of 1.4-1.5 g/cc [
25]. This indicates that the flax fiber grown in Ethiopia has similar properties to that of other countries and is applicable for composite production.
4.2. Tensile Testing of Flax Fiber
A tensile test was performed on treated flax fiber to find the tensile properties of the fiber and to predict the tensile strength of the formulated composite. The maximum load and elongation data of different samples of fiber is presented in
Table 1. The tensile strength and modulus of elasticity of flax fiber are calculated using Equations (4) and (5) respectively and its corresponding values are presented in
Table 1.
4.3. Theoretical and Experimental Results of the Tensile Properties of Composites
Several theoretical models as reported in the literature [
13,
14,
15,
17] predict the tensile modulus and tensile strength of natural fiber polymer-based composite. However, there were no exact theoretical models that predict the experimental tensile properties of short fiber thermoplastic composite material due to the complexity of fiber-matrix stress distribution. In this study, the ROM series, Einstein and Guth model, Cox-Krenchel model, Hirsch model and modified Bader and Bowyer model are also used to predict both the tensile modulus and tensile strength in addition to the experimental results.
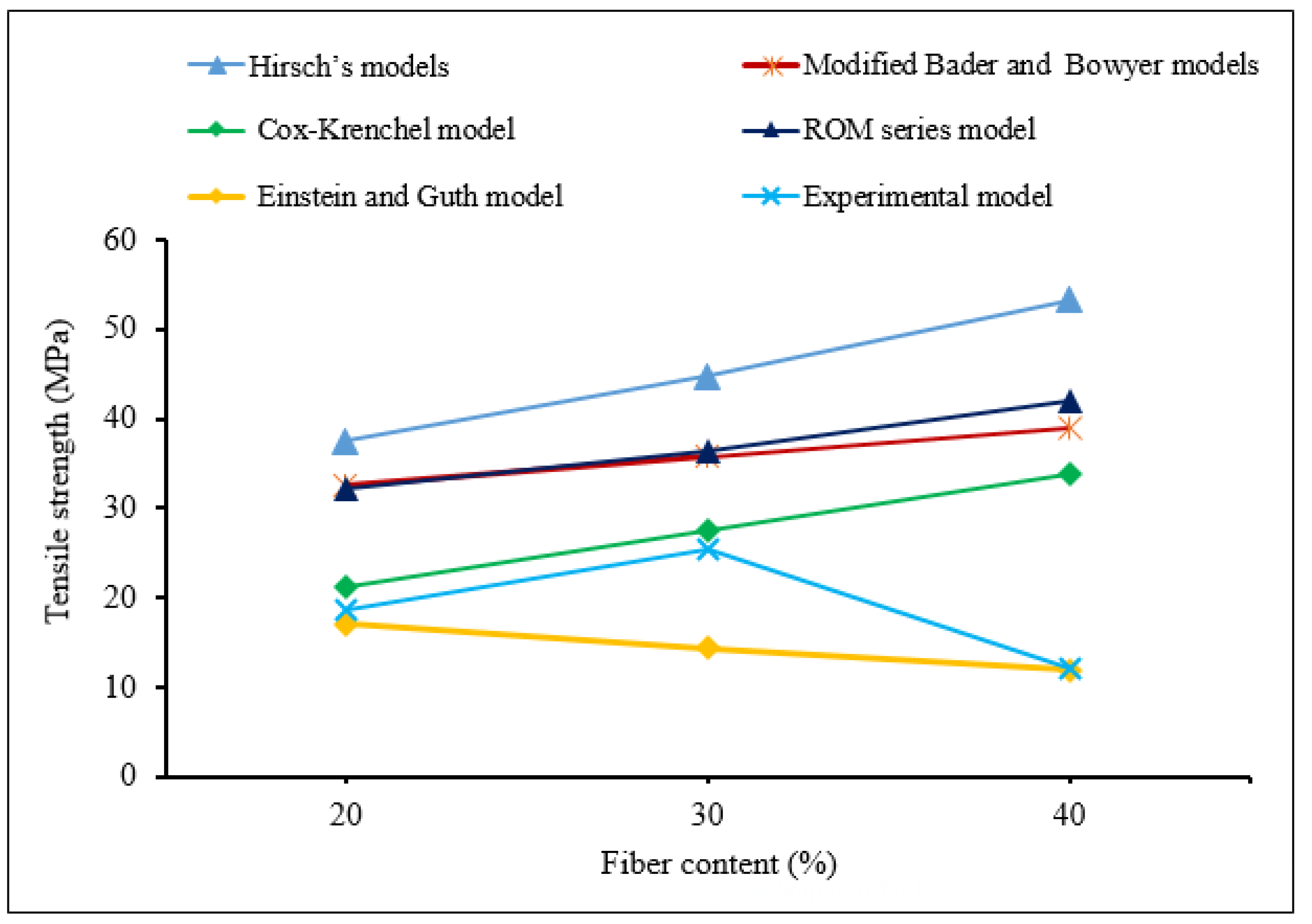
Figure 5 shows the comparison of the results by different theoretical models and experimental results of the tensile strength of randomly oriented short flax fiber EPS (FFEPS) composites with different fiber loadings of 6mm long fibers. In this study, the experimental and theoretical models are in better fit in the case of Cox-Krenchel and modified Bader and Bowyer models at 30% of fiber content with an error of 2.8% and 29% respectively. The other models, ROM series and Hirsch’s models are in less agreement with the experimental values, and in the case of Einstein and Guth model, the theoretical values are in close agreement at both low and high fiber loadings with a percentage error of 8.5% and 1.6% at 20% and 40% fiber loadings respectively compared to other models. At low fiber loadings, modified Bader and Boyer, Cox-Krenchel and Einstein models are in close relation with the experimental results. This is because, at low fiber content, the uniform distribution of stress in the matrix and fiber results in a close agreement between the experimental and theoretical strength properties of the composite. However, the theoretical values are far away and in less agreement with experimental results happened with an increase in fiber content. The reason behind this is that at high fiber loading, the fibers are concentrated in only one place over the matrix, which produces a non-uniform distribution of stress and strain in the composite. On the other hand, at high fiber content, the interfacial bond between the matrix and fiber is weak due to the poor wettability of the matrix. This phenomenon is not considered in the theoretical estimation, which causes deviation of the results from the experimental values. The Hirsch model overestimates the experimental value with a maximum percentage error of 77.33% compared to other models at 40% fiber content. The maximum percentage error of 136.8% was observed in the studies reported in the literature also for the ROM series model [
14]. The theoretical model has close agreement with the experimental result in the order of the Cox-Krenchel model > modified Bader and Bowyer model > Einstein and Guth model > Hirsch’s model > ROM series.
The variation in results of some of the models with that of the experimental results is due to variation in fiber-matrix interaction, non-uniform distribution of stress or strain in the composites and the assumptions considered in the theoretical models. The most difficult thing to predict the theoretical tensile strength of short fiber polymer composite is due to the complexity of stress transfer in the fiber and matrix. In the case of random short fiber composite, the stress transfer is largely contingent on stress concentration at the fiber ends, the fiber content, fiber length and fiber orientations, etc. [
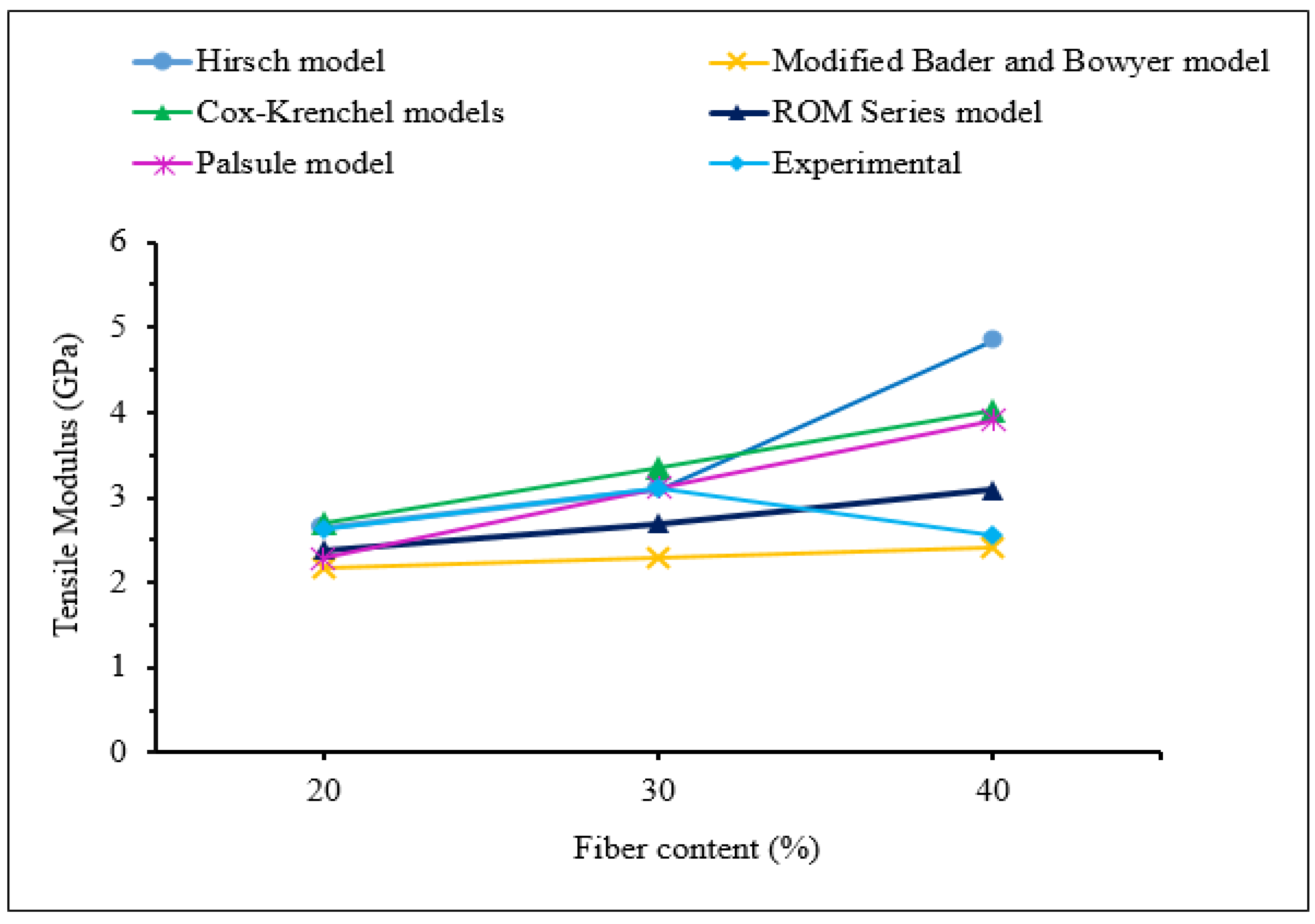
26,
27].The comparison of experimental tensile modulus with the corresponding values obtained from theoretical models of randomly oriented short FFEPS composites is shown in Figure 4.4. The Figure confirms that the tensile modulus predicted by the theoretical model is in close agreement with the experimental result at low fiber content for cases of Hirsch and Cox-Krenchel models with a maximum percentage error of 1.8%. Whereas, the ROM Series, Palsule, and Modified Bader and Bowyer models were underestimated the experimental result. The reason behind this is a uniform distribution of stress in the matrix and fiber as a result, a near agreement between experimental and theoretical models at low fiber weight fraction. Similar to the tensile stress, the value of theoretical tensile modulus also is in less agreement with the experimental result at high fiber loading. This is due to the occurrence of fiber agglomeration and fiber dispersion in the matrix.
Figure 6.
Comparison of experimental and theoretical tensile modulus values vs percentage of fiber content.
Figure 6.
Comparison of experimental and theoretical tensile modulus values vs percentage of fiber content.
In this study, all the theoretical models have positive deviation with experimental values except for ROM series and Bader and Bowyer models. These two models reveal negative deviation with a maximum error of 15.4% and 35.6% at 30% of fiber content respectively. In the Hirsch model, the parameter x expressed in Equation (2.6) is 0.06, which is in good correlation with the experimental values for the FFEPS composite. The theoretical tensile modulus value best fits for the case of Hirsch, Palsule and Cox model with an error of 0.48%, 0.48% and 0.69% at 30% of fiber loadings. Generally, there is no exact theoretical formula to predict the experimental values for the case of randomly oriented short fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Therefore, the maximum percentage error observed in this study also occurred in many researchers reported in the literature [
13,
14,
28,
29].
5. Conclusion
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of composites made from randomly oriented flax fibers reinforced with recycled expanded polystyrene (EPS) waste. By investigating the effects of varying flax fiber volume fractions (20%, 30%, and 40%) on tensile strength and tensile modulus, we established a clear relationship between fiber content and mechanical performance. Several theoretical models, including the rule of mixtures (ROM), modified Bader and Bowyer, Hirsch, Cox-Krenchel, Einstein-Guth, and Palsule models were used to compare with the experimental result. It can be revealed that the Cox-Krenchel predicted closely aligned with experimental tensile strength results. While, the Cox-Krenchel, Palsule and Hirsch models were found to be effectively predict the tensile modulus at a 30% fiber loading. All models predict a close agreement with experimental tensile modulus value at low fiber loadings. There is no exact theoretical model that predicts the tensile properties of randomly oriented natural fiber polymer composites. Due to some assumptions in the theoretical model, the experimental result gives a different result especially at higher fiber loadings. In the future, researchers account with the combination of one or more factors such as fiber anisotropy, void content, stress transfer area of fiber, and fiber matrix bindings into the current theoretical models to better predict physical and mechanical properties of natural fiber polymer composite. Overall, this research highlights the viability of combining natural fibers with recycled materials to create eco-friendly composites that not only enhance mechanical performance but also support sustainable practices in material development.
References
- Towards sustainable and ecofriendly polymer composite materials from bast fibers: a systematic review Towards sustainable and ecofriendly polymer composite materials from bast fi bers: a systematic review. Eng. Res. Express 2024, 6, 1–27.
- Lotfi, A.; Li, H.; Dao, D.V.; Prusty, G. Natural fiber – reinforced composites: A review on material, manufacturing, and machinability. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater., vol. xx, no. x, pp. 1–47, 2019.
- Seid, A.M.; Adimass, S.A. Heliyon Review on the impact behavior of natural fiber epoxy based composites. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.; Kar, F. Properties of concrete containing waste expanded polystyrene and natural resin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xu, J.; Li, Y. Mechanical properties of expanded polystyrene lightweight aggregate concrete and brick. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) fibre reinforced polymer composite materials: A review on preparation, properties and prospects. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 102, 109–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, N.; Heslop-Harrison, J.S.; Adugna, W. Diversity in 198 Ethiopian linseed (Linum usitatissimum) accessions based on morphological characterization and seed oil characteristics. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2015, 62, 1037–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tabil, L.; Panigrahi, S. Effects of chemical treatments on mechanical and physical properties of flax fiber-reinforced composites. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2008, 15, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, K.N.; Basavarajappa, S. Applications of biocomposite materials based on natural fibers from renewable resources: A review. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2016, 23, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshwaran, N.; Elayaperumal, A. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2011, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.A.; Palsule, S. Jute fiber reinforced chemically functionalized polypropylene self-compatibilizing composites by Palsule process. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Raharjo, W.P.; Soenoko, R.; Purnowidodo, A.; Choiron, M.A. Experimental and micromechanical modelling of randomly oriented zalacca fibre/low-density polyethylene composites fabricated by hot-pressing method. Cogent Eng. 2018, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Joseph, P.; G.Mathew.; Joseph, K. Mechanical Properties of Short Sisal Fiber-Reinforced Polypropylene Composites: Comparison of Experimental Data with Theoretical Predictions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, N.G.; Ishak, Z.A.M. Predicting the Tensile Modulus of Randomly Oriented Nonwoven Kenaf/Epoxy Composites. in Procedia Chemistry 2016, 19, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, M.W.; et al. , Tensile properties prediction of natural fibre composites using rule of mixtures: A review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2019, 38, 211–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munde, Y.S.; Ingle, R.B. Theoretical Modeling and Experimental Verification of Mechanical Properties of Natural Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastics. Procedia Technol. 2015, 19, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaprasad, G.; Joseph, K.; Thomas, S.; Pavithran, C. Theoretical modelling of tensile properties of short sisal fibre-reinforced low-density polyethylene composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 4261–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koay, S.C.; Subramanian, V.; Chan, M.Y.; Pang, M.M.; Tsai, Y.; Cheah, K.H. Preparation and Characterization of Wood Plastic Composite Made Up of Durian Husk Fiber and Recycled Polystyrene Foam. in MATEC Web of Conferences 2018, 02019, 0–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, N.; Navaneethakrishnan, P.; Rajsekar, R.; Shankar, S. Effect of Pretreatment Methods on Properties of Natural Fiber Composites: A Review. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2016, 24, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilankeeran, P.K.; Mohite, P.M.; Kamle, S. Axial Tensile Testing of Single Fibres. Mod. Mech. Eng. 2012, 2012, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Panigrahi, S.; Tabil, L.; Crerar, W. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Pre-treatment of Flax Fibers for use in. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2007, 26, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Finkenstadt, V.L.; Nimmagadda, Y. Mechanical properties and water absorption behavior of injection-molded wood fiber/carbon fiber high-density polyethylene hybrid composites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2019, 2, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Chouw, N.; Jayaraman, K. Flax fibre and its composites - A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 56, 296–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittenber, D.B.; Gangarao, H.V.S. Critical review of recent publications on use of natural composites in infrastructure. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, M.; Davies, P.; Martin, N.; Baley, C. Recommended flax fibre density values for composite property predictions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 114, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, H.L.; Müssig, J.; van den Oever, M.J.A. Mechanical properties of short-flax-fibre reinforced compounds. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaiah, P.; Thevy, C.; Manickam, S. ScienceDirect Improved Mechanical Properties and Theoretical Prediction of Young Modulus of Polylactide Composites Reinforced with Sisal Fibers. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 22494–22505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumer, A.N.; Bachtiar, D. Modeling and Experimental Validation of Tensile Properties of Sugar Palm Fiber Reinforced High Impact Polystyrene Composites. fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, P.A.; Joseph, K.; Unnikrishnan, G.; Thomas, S. Comparative study on mechanical properties of sisal-leaf fibre-reinforced polyester composites prepared by resin transfer and compression moulding techniques. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).