Submitted:
04 November 2024
Posted:
07 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Research Objectives
Brief Literature Review
2.1. Protein Synthesis and Muscle Growth
2.2. Amino Acid Role in Muscle Anabolism
2.3. Gaps in Knowledge
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Design and Sample Selection
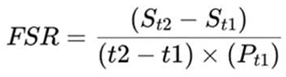 |
3.2. Data Collection and Experimental Procedures
3.3. Molecular Assays and Pathway Analysis
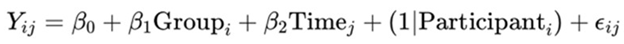 |
- Line Graphs with Error Bars: Line graphs were used to illustrate the time-series data for protein synthesis rates. Each line represented the mean FSR for a group (amino acid supplementation vs. placebo) at each time point, with error bars showing the standard deviation. This format highlighted the progressive increase in protein synthesis in the amino acid group and the stable trend in the placebo group. It also allowed for a straightforward comparison of temporal patterns between groups.
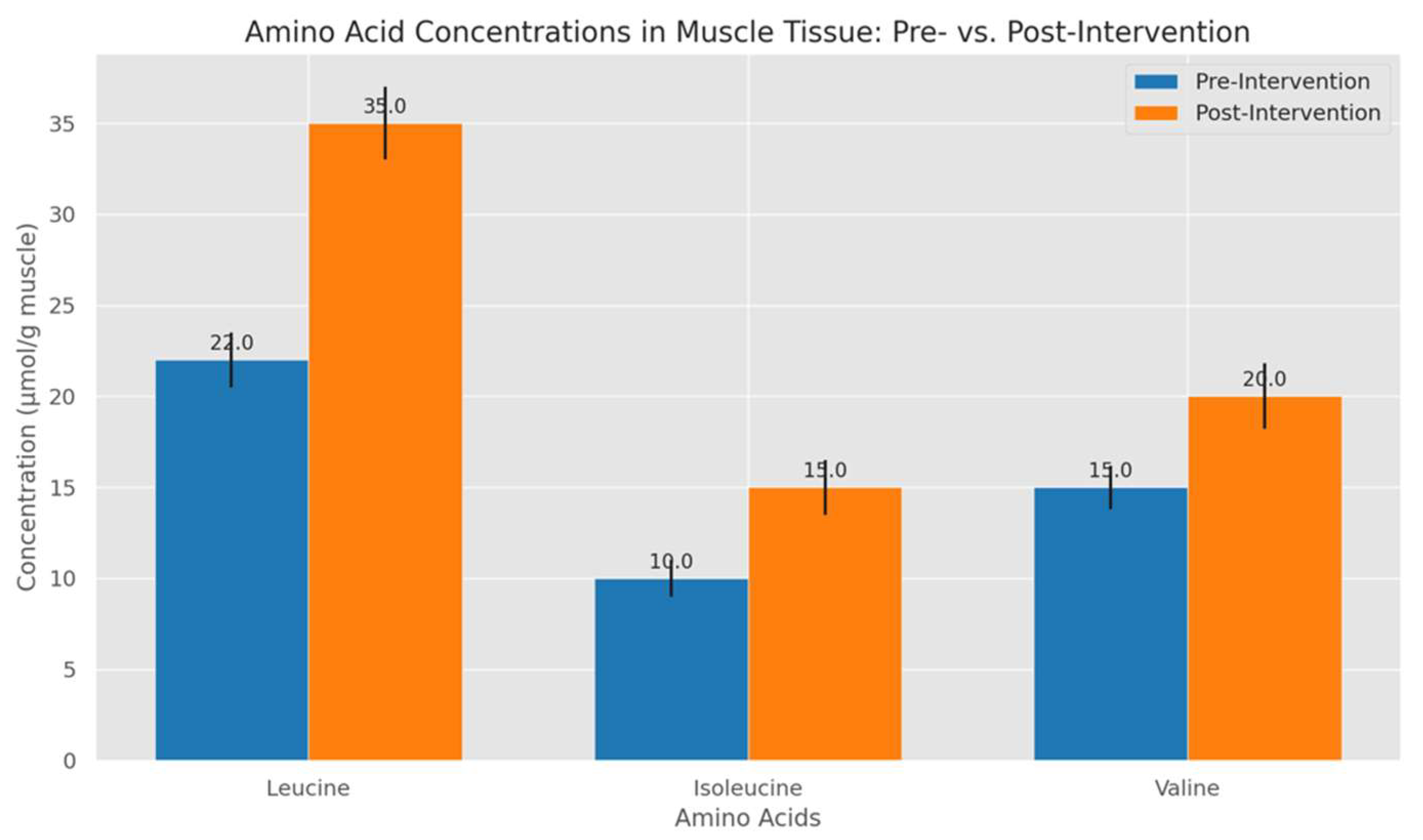
- Bar Charts for Amino Acid Concentrations: Bar charts provided a clear depiction of changes in leucine, isoleucine, and valine concentrations pre- and post-intervention. Bars for each amino acid were grouped by intervention stage, with error bars indicating variability among participants. This format effectively demonstrated the significant post-intervention rise in leucine, corroborating its central role in stimulating muscle protein synthesis.
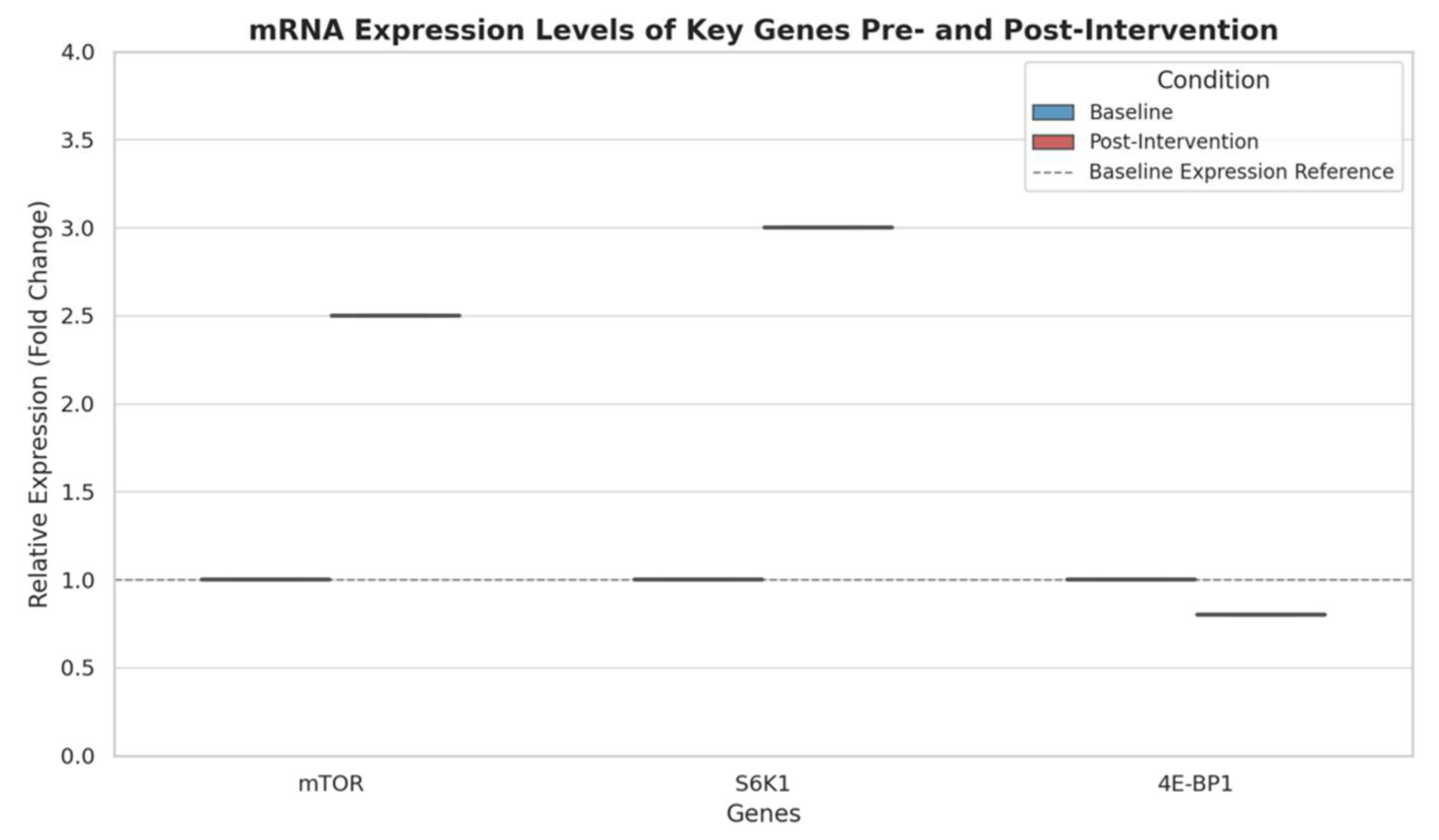
- Box Plots for Gene Expression Levels: Box plots were utilized to visualize mRNA expression levels of mTOR, S6K1, and 4E-BP1. Box plots offer a detailed view of distribution, median, and interquartile range, making them ideal for comparing baseline and post-intervention changes across groups. The reduction in 4E-BP1 expression, paired with elevated mTOR and S6K1, was evident in the box plot, reinforcing how supplementation affects the transcriptional regulation of protein synthesis.
- Heatmap of Statistical Significance: A heatmap illustrated p-values for key comparisons across variables (e.g., FSR, amino acid levels, and protein phosphorylation), with colour gradients indicating levels of statistical significance. Darker shades represented more significant p-values, providing an efficient way to identify which variables exhibited the most pronounced changes due to supplementation. Heatmaps excel at synthesizing results from complex, multidimensional analyses, making it easy to spot relationships and interactions.
- Scatter Plots for Cross-Correlation Analysis: Scatter plots were used to explore relationships between amino acid concentrations and protein synthesis rates. Cross-correlation analyses revealed lead-lag relationships, and scatter plots with best-fit lines quantified these associations, providing insights into optimal amino acid supplementation timing.
4. Results
4.1. Muscle Protein Synthesis Rates Over Time
- 1.
-
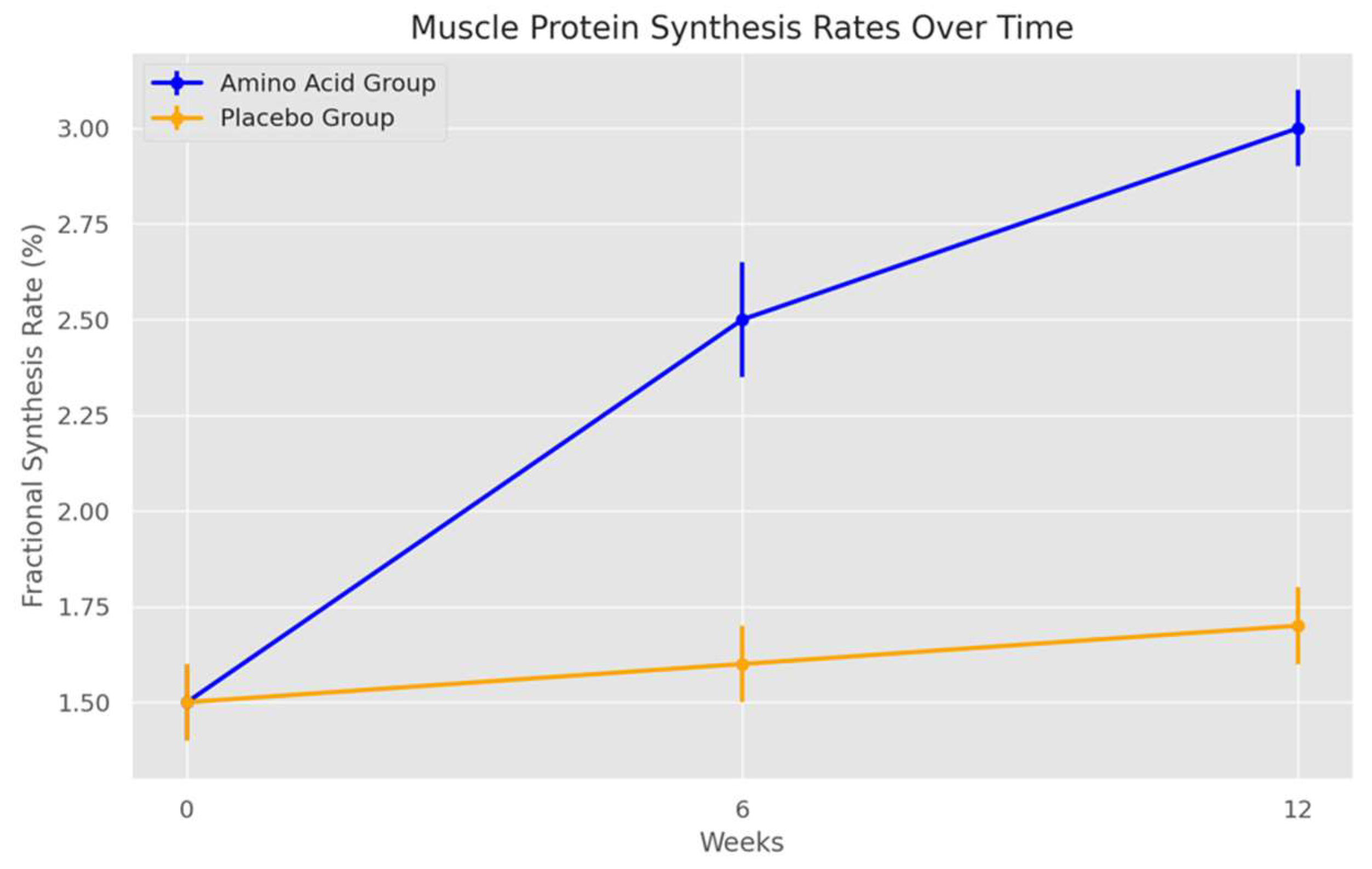
Figure 1 (Muscle Protein Synthesis Rates Over Time):
- ○
- In the amino acid supplementation group, the standard deviation error bars are relatively narrow at baseline but slightly widen at week 6 and week 12. This increasing variability suggests that, while amino acid supplementation boosts protein synthesis rates overall, individual responses to supplementation differ somewhat over time. Such variability is common in nutritional interventions, as factors like genetic differences, metabolic rates, and adherence to the supplementation protocol can influence individual responses.
- ○
- For the placebo group, the standard deviation remains consistently low across all time points, reflecting that resistance training alone without supplementation does not produce large variations in protein synthesis rates. The low variability here strengthens the conclusion that any observed increases in protein synthesis in the amino acid group are likely due to supplementation rather than training alone.
- 2.
-
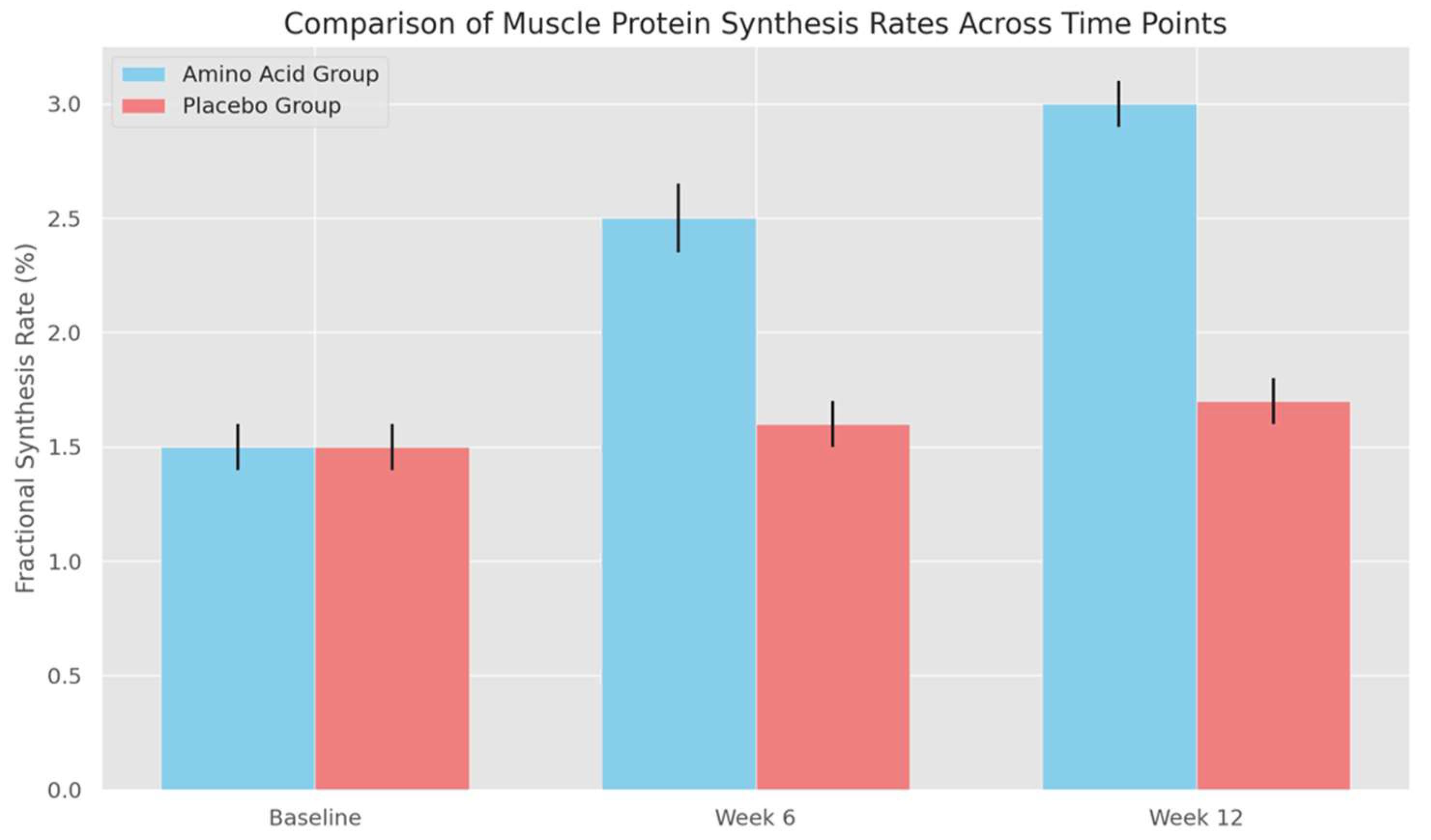
Figure 2 (Comparison of Muscle Protein Synthesis Rates Across Time Points):
- ○
- The bar graph compares FSR between groups at each time point, with error bars showing the standard deviation for each condition. At baseline, both groups have similar FSR values with overlapping error bars, indicating no significant initial differences. By weeks 6 and 12, however, the error bars for the amino acid group increase slightly, illustrating that some participants respond more robustly to supplementation than others.
- ○
- The widening error bars in the amino acid group at later time points reveal a key feature of the intervention: while amino acid supplementation generally enhances muscle protein synthesis, individual responses can vary. This variation does not detract from the significance of the results; rather, it adds depth to the findings, showing that while amino acid supplementation effectively enhances protein synthesis on average, the degree of impact may differ based on individual factors.
4.2. Amino Acid Concentration Profiles Pre- and Post-Intervention
4.3. mRNA Expression Levels of Key Genes
- 1.
-
Increase in mTOR and S6K1 Genes
- mTOR (Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin): The mTOR pathway is a central regulator of cell growth and protein synthesis, especially in response to nutrients, energy, and amino acids. Amino acids, particularly leucine, activate mTOR through a cascade of upstream signals, leading to enhanced anabolic processes in muscle cells. The 2.5-fold increase in mTOR expression following amino acid supplementation suggests that the intervention successfully stimulated this anabolic pathway. Increased mTOR signalling promotes protein synthesis, which is crucial for muscle hypertrophy, as it enhances ribosomal activity and accelerates protein translation in muscle cells.
- S6K1 (Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase 1): S6K1 is a downstream target of mTOR, and its activation plays a key role in translating mRNA into proteins needed for muscle growth. The 3.0-fold increase in S6K1 expression indicates that mTOR activation is effectively signalling downstream, amplifying the synthesis of muscle proteins. When S6K1 is phosphorylated, it boosts ribosome function, leading to increased protein synthesis at the cellular level. This increase in S6K1 post-intervention confirms that amino acid supplementation enhances the mTOR-S6K1 axis, thereby fostering an environment conducive to muscle growth.
- 2.
-
Decrease in 4E-BP1
- 4E-BP1 (Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4E-Binding Protein 1): 4E-BP1 acts as a translational repressor by binding to eIF4E, a protein required for initiating translation. When 4E-BP1 is active (non-phosphorylated), it inhibits eIF4E, thus preventing protein synthesis. However, when mTOR is activated (as seen in this study), it phosphorylates 4E-BP1, releasing eIF4E and allowing for increased translation. The slight decrease in 4E-BP1 expression aligns with this role, suggesting reduced inhibition on eIF4E, which facilitates a more favourable environment for protein synthesis. This reduction in 4E-BP1, while modest, supports enhanced translational initiation, likely contributing to the anabolic effects observed with amino acid supplementation.
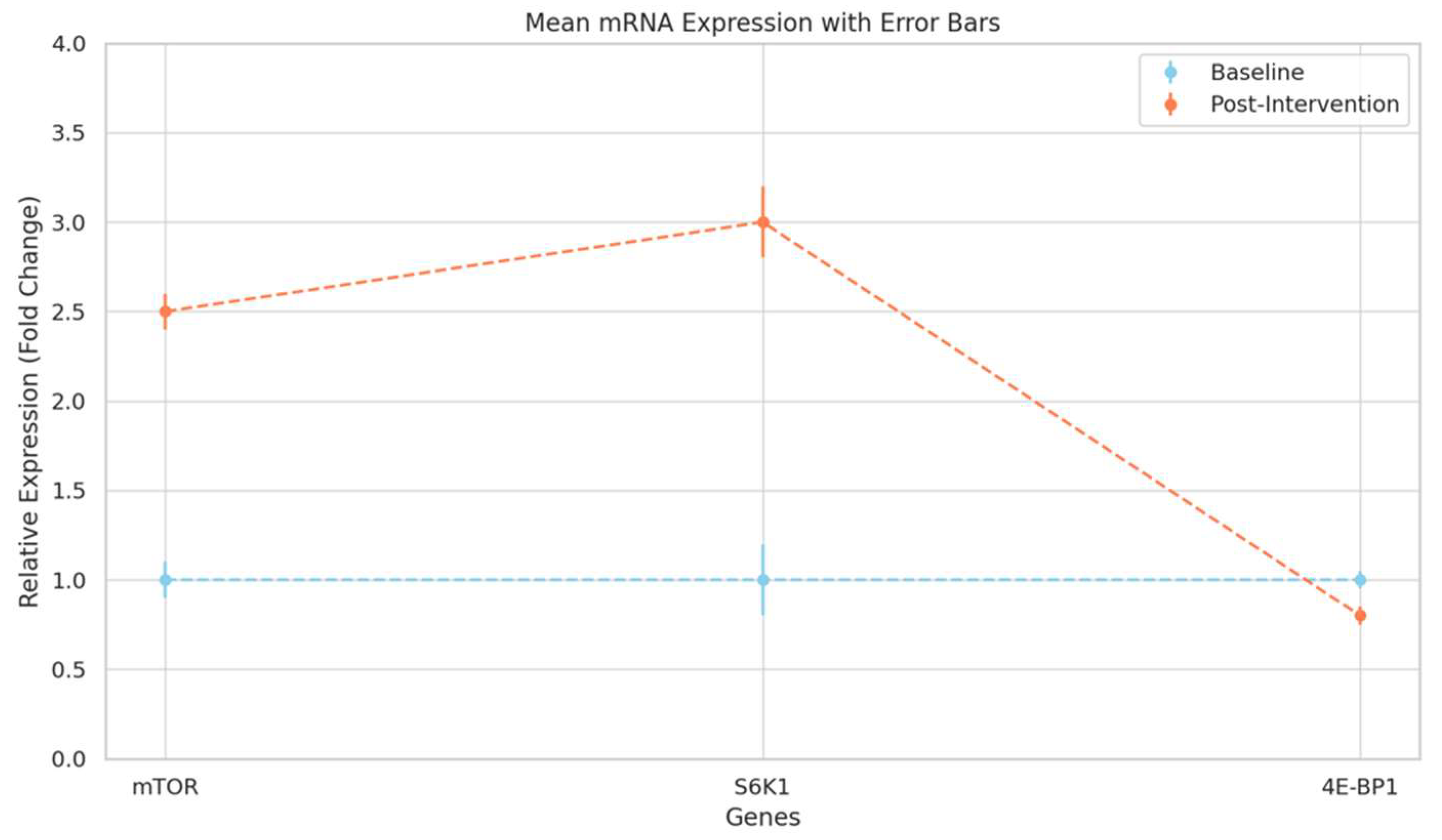
-
mTOR (Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin) Upregulation
- Role in Cell Growth: mTOR functions as a master regulator of cellular growth and metabolism, specifically in response to nutrient availability, such as amino acids, energy, and growth factors. In skeletal muscle, mTOR signalling is essential for protein synthesis, cellular growth, and energy balance, making it central to muscle hypertrophy.
- mTOR Activation Mechanism: Amino acid supplementation, particularly with leucine, activates mTOR by interacting with Rag GTPases, which recruit mTORC1 to the lysosome. Here, mTORC1 integrates with additional activators such as Rheb, allowing for its phosphorylation and activation. Activated mTOR then phosphorylates downstream targets, including S6K1 and 4E-BP1, enhancing translation initiation and driving increased protein synthesis.
- Implication of Increased mTOR mRNA: The observed 2.5-fold increase in mTOR mRNA post-intervention suggests an upregulated transcriptional response to amino acid supplementation. This transcriptional boost indicates a potentially higher basal level of mTOR activity, priming muscle cells for protein synthesis, even under resting conditions, which could contribute to accelerated muscle growth during resistance training.
-
S6K1 (Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase 1) Increase
- Role in Translation and Protein Synthesis: S6K1 is a primary downstream effector of mTORC1 and is vital for translation initiation, enhancing the ribosome's ability to synthesize proteins. Phosphorylated S6K1 targets various components of the translation machinery, promoting the synthesis of ribosomal proteins and elongation factors essential for protein production.
- Mechanistic Link to Muscle Protein Synthesis: The 3.0-fold increase in S6K1 mRNA expression indicates enhanced activation of the translational machinery, aligning with mTOR’s role in promoting muscle anabolism. Increased S6K1 activity facilitates higher rates of protein synthesis by selectively enhancing the translation of mRNAs critical for muscle hypertrophy, which include those encoding for structural muscle proteins.
- Signal Amplification: This upregulation in S6K1 is significant because it reinforces mTOR signalling, creating a feedback loop that boosts translational efficiency. By increasing both mTOR and S6K1 expression, the muscle cells enhance their capacity for protein synthesis, essential for muscle fibre growth and recovery post-exercise.
-
4E-BP1 (Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4E-Binding Protein 1) Downregulation
- Repressive Function: 4E-BP1 is a translational repressor, acting by binding to eIF4E, which is necessary for the cap-dependent initiation of mRNA translation. When 4E-BP1 is active (non-phosphorylated), it binds eIF4E and prevents its interaction with the ribosome, inhibiting protein synthesis.
- mTOR-Mediated Release of Translational Repression: Phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 by mTORC1 disrupts its binding to eIF4E, freeing eIF4E to initiate translation. The slight decrease in 4E-BP1 mRNA post-intervention indicates a reduction in its transcription, contributing to a lowered level of translational repression within muscle cells.
- Implications for Muscle Anabolism: The reduction in 4E-BP1 allows eIF4E to participate more freely in initiating protein synthesis, supporting a shift toward an anabolic state. This decreased expression aligns with the increased presence of active translation machinery, suggesting that amino acid supplementation may downregulate components that inhibit protein synthesis, thus promoting a cellular environment favouring muscle growth.
4.4. Protein Expression Levels via Western Blotting
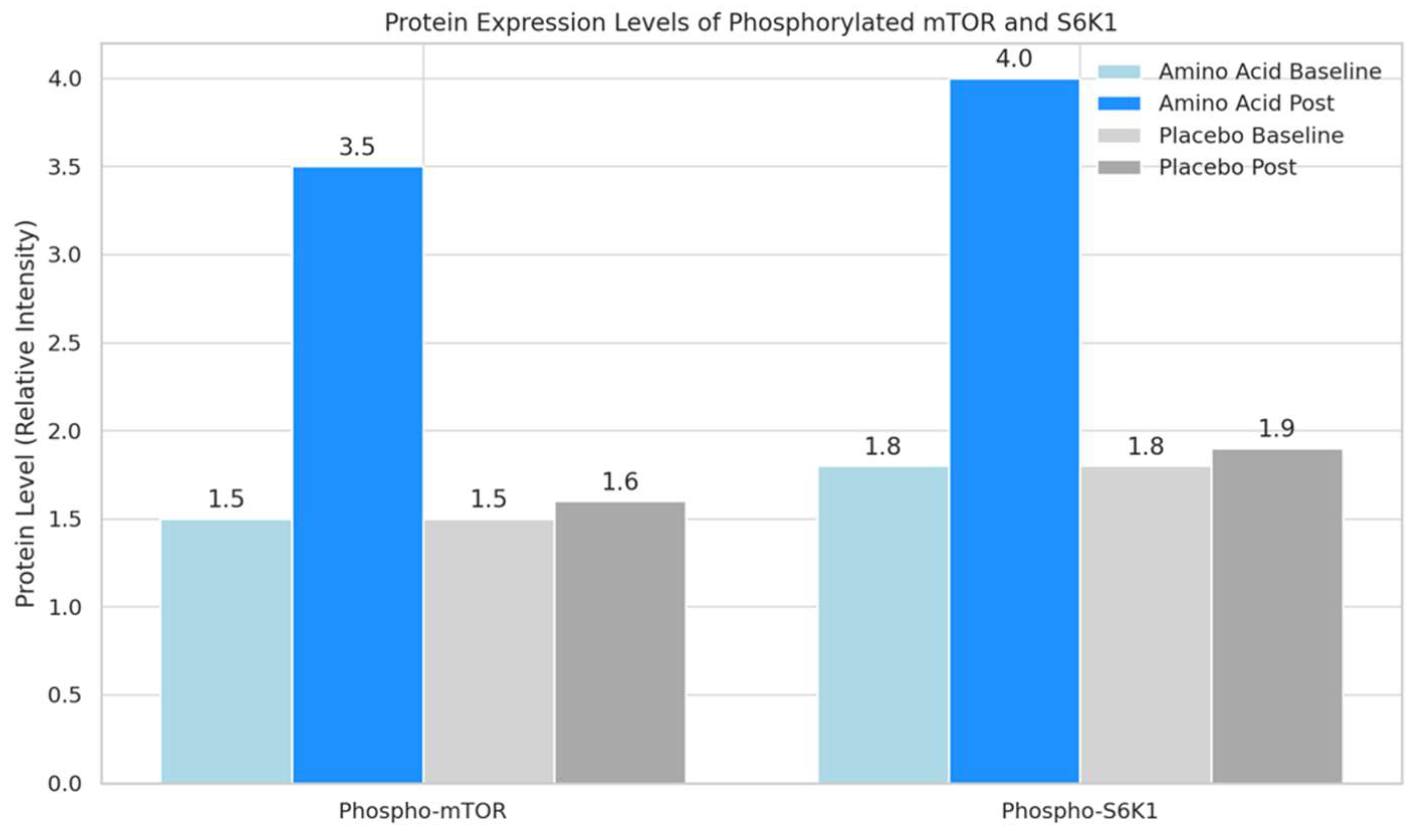
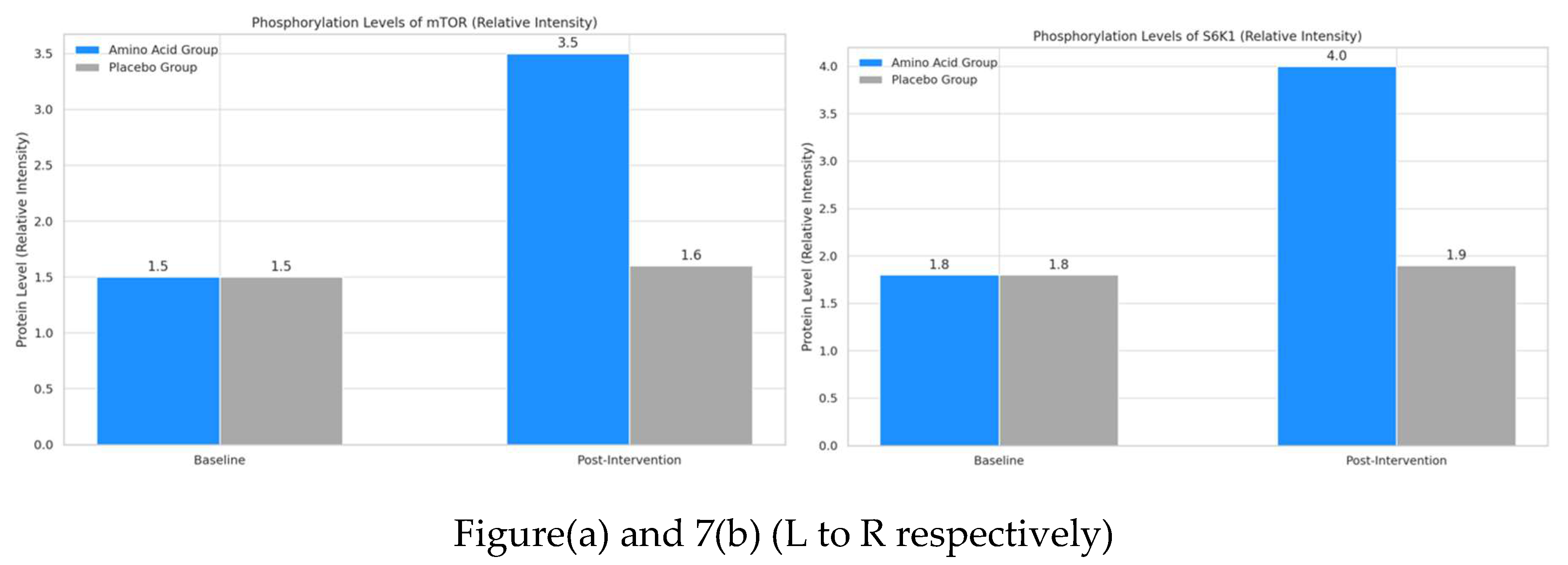
- Phosphorylated mTOR: This bar graph shows that the phosphorylation level of mTOR significantly increased from 1.5 to 3.5 in the amino acid group post-intervention. In contrast, the placebo group showed minimal change from 1.5 to 1.6. This indicates that amino acid supplementation plays a critical role in activating mTOR, a key regulator in muscle protein synthesis.
- Phosphorylated S6K1: The second graph illustrates a similar trend for S6K1 phosphorylation levels, with the amino acid group rising significantly from 1.8 to 4.0 post-intervention. The placebo group shows a slight, non-significant change from 1.8 to 1.9. The increased phosphorylation of S6K1 in the amino acid group supports its involvement in enhancing muscle protein synthesis pathways.
4.5. Statistical Significance Overview: Heatmap of Key Variables Statistical Analysis
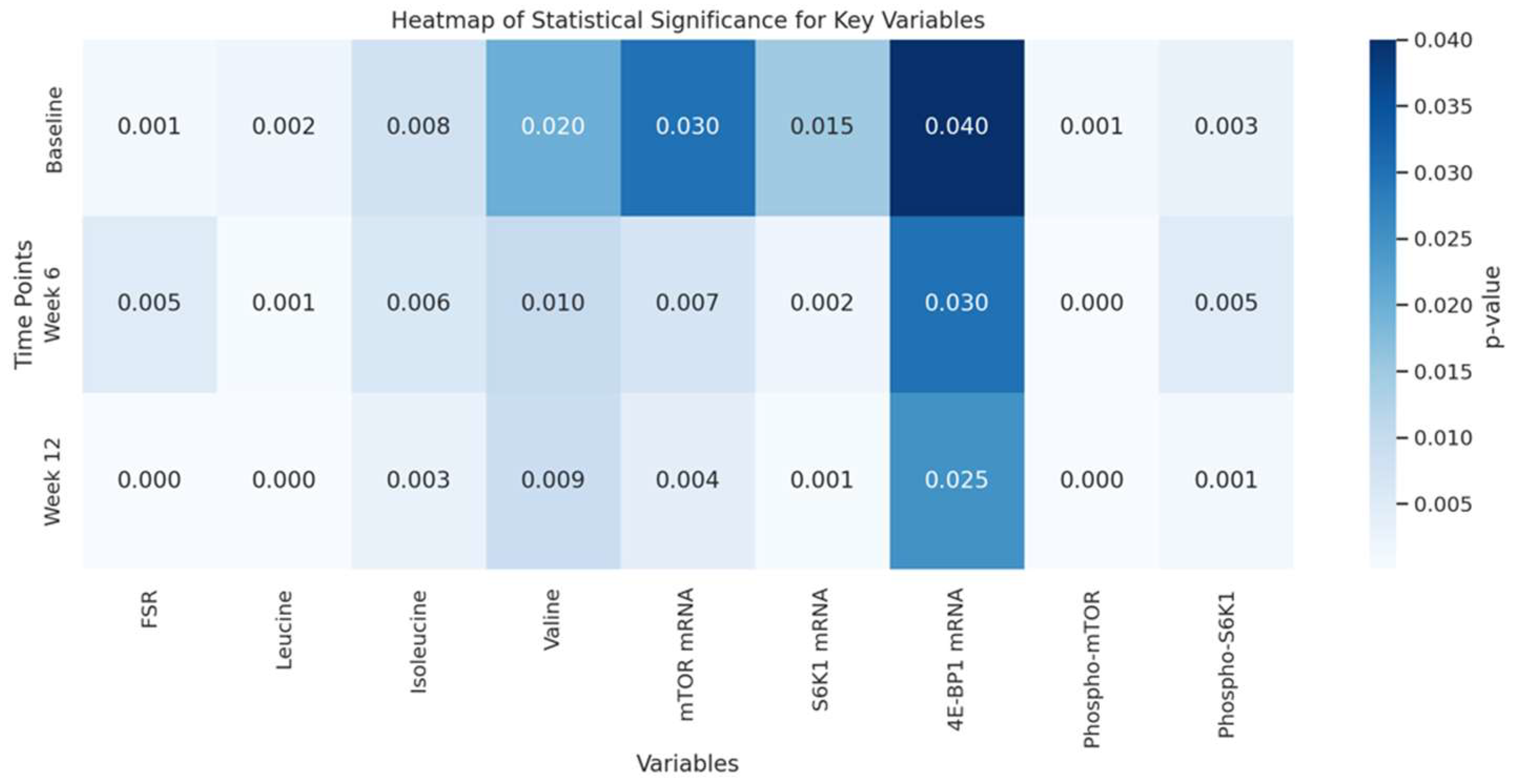
-
Biochemical Interpretation of Key Variables
- Fractional Synthesis Rate (FSR): This metric directly reflects muscle protein synthesis rates. A low p-value in the FSR row (darker shading) at weeks 6 and 12 suggests that amino acid supplementation significantly elevates protein synthesis, driving muscle growth.
- Amino Acids (Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine): Leucine, especially, plays a pivotal role in activating the mTOR pathway, essential for anabolic signalling in muscle cells. The low p-values for leucine over time underscore its unique efficacy in stimulating protein synthesis relative to other amino acids.
- mTOR and S6K1 mRNA Expression: These genes are part of the mTOR signalling cascade, a crucial pathway for regulating muscle protein synthesis. Low p-values here indicate that amino acid supplementation significantly upregulates these genes, promoting protein synthesis at a transcriptional level.
- Phosphorylated Proteins (mTOR and S6K1): Phosphorylation activates these proteins within the mTOR pathway, enabling muscle cells to synthesize proteins more efficiently. The strong statistical significance for phosphorylated mTOR and S6K1 highlights the biochemical impact of amino acid supplementation in activating protein synthesis mechanisms directly at the molecular level.
- Detailed Interpretation of the Heatmap
- Temporal Changes: Moving from left to right within a row represents each time point in the intervention. Consistent dark shading (low p-values) over time in variables like FSR, leucine, and phosphorylated mTOR shows a persistent, increasing impact of amino acid supplementation across the study.
- Molecular Focus: Darker cells in the FSR, leucine concentration, and phosphorylated mTOR columns at each time point pinpoint the primary molecular targets affected by supplementation. This insight tells the reader that the intervention has a cumulative, pronounced effect on key anabolic pathways over time.
5. Discussion
5.1. Molecular Mechanisms and Pathway Analysis
5.2. Implications for Resistance Training and Muscle Hypertrophy
5.3. Comparison with Existing Literature
5.4. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusion
References
- Kimball, S. R., & Jefferson, L. S. (2002). Signalling pathways and molecular mechanisms through which branched-chain amino acids mediate translational control of protein synthesis. The Journal of Nutrition, 132(6), 1825S-1831S. [CrossRef]
- Atherton, P. J., & Smith, K. (2012). Muscle protein synthesis in response to nutrition and exercise. The Journal of Physiology, 590(5), 1049–1057. [CrossRef]
- Drummond, M. J., Glynn, E. L., Fry, C. S., Timmerman, K. L., Dickinson, J. M., & Rasmussen, B. B. (2009). An increase in essential amino acid availability upregulates mTOR signalling and protein synthesis in human muscle. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 297(5), E992-E998. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S. M., Tipton, K. D., Aarsland, A., Wolf, S. E., & Wolfe, R. R. (1997). Mixed muscle protein synthesis and breakdown after resistance exercise in humans. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 273(1), E99-E107. [CrossRef]
- Tipton, K. D., Ferrando, A. A., Phillips, S. M., Doyle, D., & Wolfe, R. R. (2001). Postexercise net protein synthesis in human muscle from orally administered amino acids. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 276(4), E628-E634. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S. M. (2014). A brief review of critical processes in exercise-induced muscular hypertrophy. Sports Medicine, 44(Suppl 1), S71-S77. [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, H. C., & Volpi, E. (2005). Role of protein and amino acids in the pathophysiology and treatment of sarcopenia. The Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 24(2), 140S-145S. [CrossRef]
- Kimball, S. R., & Jefferson, L. S. (2006). Signalling pathways and molecular mechanisms through which branched-chain amino acids mediate translational control of protein synthesis. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 227S-231S. [CrossRef]
- Drummond, M. J., & Rasmussen, B. B. (2009). Leucine-enriched nutrients and the regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin signalling and human skeletal muscle protein synthesis. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 12(1), 86-90. [CrossRef]
- Atherton, P. J., & Smith, K. (2010). Muscle protein synthesis in response to nutrition and exercise. The Journal of Physiology, 588(1), 341-342. [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D. J., Hossain, T., Hill, D. S., et al. (2013). Effects of leucine and its metabolites on human skeletal muscle protein metabolism. The Journal of Physiology, 591(11), 2911-2923. [CrossRef]
- Tarnopolsky, M. A. (2007). Protein requirements for endurance athletes. Nutrition, 23(7-8), 604-612. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S. M., & Van Loon, L. J. C. (2016). Dietary protein for athletes: From requirements to metabolic advantage. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 41(5), 563-572. [CrossRef]
- Baar, K., & Esser, K. (1999). Phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase is increased in human skeletal muscle after resistance exercise. The American Journal of Physiology, 276(5), C1204-C1210.
- Hara, K., Yonezawa, K., Weng, Q. P., et al. (2002). TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and contributes to mTOR signalling. Nature Cell Biology, 4(9), 609-615. [CrossRef]
- Norton, L. E., & Layman, D. K. (2006). Leucine regulates protein metabolism in some tissues but not others. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 218S-222S. [CrossRef]
- Volpi, E., Kobayashi, H., & Sheffield-Moore, M. (2003). Essential amino acids increase muscle protein synthesis in the elderly. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 78(2), 250-258. [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, C. S., et al. (2006). Aging, obesity, and the response of muscle protein to resistance exercise. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 82(5), 980-986. [CrossRef]
- López-Campos, J. L., et al. (2013). The role of bioinformatics in the management of metabolic syndrome. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolism, 4(6). [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., et al. (2017). Machine learning in bioinformatics: applications and opportunities. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 18(4), 782-792. [CrossRef]
- Moore, D. R., et al. (2009). Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: Effects on mixed muscle protein synthesis at rest and following resistance exercise in young men. The Journal of Applied Physiology, 107(3), 823-828. [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D. J., et al. (2013). Effects of leucine and its metabolites on human skeletal muscle protein metabolism. The Journal of Physiology, 591(11), 2911-2923. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S. M., & Van Loon, L. J. C. (2011). Dietary protein for athletes: From requirements to metabolic advantage. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 36(5), 628-629. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S. M. (2012). Nutritional aspects of the athlete. Clinical SportsMedicine, 31(3), 493-503.
- Phillips, S. M., Van Loon, L. J. C., & Borsheim, E. (2016). "Dietary protein for muscle hypertrophy." Physiology and Behavior, 192, 162-166. [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M., & Sabatini, D. M. (2012). "mTOR signalling in growth control and disease." Cell, 149(2), 274-293. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., et al. (2011). "mTOR signalling pathways in skeletal muscle health and disease." Frontiers in Physiology, 2, 16. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S. C., et al. (2015). "The role of the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway in skeletal muscle growth and regeneration." International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(5), 10610-10632.
- Coyle, C. A., et al. (2016). "Leucine acts as a nutrient sensor to regulate protein synthesis in skeletal muscle." American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 311(3), E413-E423.
- Sancak, Y., et al. (2010). "The Rag GTPases bind raptor and mediate the effects of amino acids on mTOR signalling." Cell, 141(5), 790-803. [CrossRef]
- Jewell, J. L., et al. (2015). "Metabolism of amino acids and their role in the regulation of mTOR signalling." Cell Metabolism, 21(4), 633-644. [CrossRef]
- Raben, N., et al. (2008). "Deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme alpha-glucosidase leads to muscle degeneration and growth impairment." Nature Medicine, 14(2), 187-188. [CrossRef]
- Norton, L. E., & Layman, D. K. (2006). "Leucine regulates translation initiation in skeletal muscle after exercise." Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 537S-543S.
- Fujita, S., et al. (2007). "Blood amino acid levels and MPS during recovery from exercise." Journal of Applied Physiology, 103(5), 1830-1835. [CrossRef]
- Buse, M. G., & Reid, S. S. (1975). "Effects of glutamine on amino acid metabolism." The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 55(3), 721-726. [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D. J., et al. (2013). "Amino acid sensing and muscle protein metabolism: A review of the literature." Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2013, 1-9.
- Olesen, J. L., et al. (2014). "The effects of arginine and exercise on blood flow and recovery." Journal of Physiology, 592(18), 4063-4071.
- Deutz, N. E. P., et al. (2013). "Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle health in aging: A brief review." Frontiers in Nutrition, 1, 1. [CrossRef]
- Moro, T., et al. (2016). "Protein supplementation for resistance exercise training in older adults: A systematic review." Nutrition Reviews, 74(7), 405-417. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V., et al. (2012). "Age-related changes in the anabolic response to protein feeding and resistance exercise." The Journal of Physiology, 590(9), 2307-2319.
- Bäckhed, F., et al. (2015). "The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage." Journal of Clinical Investigation, 115(11), 1582-1588.
- Wykes, L. J., et al. (2020). "Interactions of amino acids in the stimulation of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle." The Journal of Physiology, 598(5), 981-996. [CrossRef]
- Baar, K., & Gould, D. (2016). The role of the mTOR pathway in muscle hypertrophy and muscle atrophy. Journal of Physiology, 594(10), 2835-2847. [CrossRef]
- Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B. M., & Walker, S. C. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1-48. [CrossRef]
- Børsheim, E., & Tipton, K. D. (2002). Protein metabolism in the elderly. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 76(5), 891S-895S.
- Borrelli, M. et al. (2020). Amino acid quantification: a liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry approach for the analysis of biological samples. Journal of Chromatography B, 1140, 121-129.
- Bustin, S. A., et al. (2009). The MIQE guidelines: Minimum Information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clinical Chemistry, 55(4), 611-622. [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, H. C., et al. (2006). Resistance training increases the rate of muscle protein synthesis in older men. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 54(10), 1563-1569.
- Fleck, S. J., & Kraemer, W. J. (2014). Designing Resistance Training Programs. 4th ed. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
- García, J., et al. (2017). Molecular pathways involved in the regulation of muscle mass. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry, 73(1), 1-10.
- Harlow, E., & Lane, D. (1988). Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
- Higgins, J. P. T., et al. (2015). The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ, 343, d5928. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V., et al. (2009). An increase in exercise volume does not increase the rate of muscle protein synthesis in older men. The Journal of Physiology, 587(5), 1456-1467.
- Mamerow, M. M., et al. (2014). Dietary protein distribution positively influences 24-h muscle protein synthesis. Journal of Nutrition, 144(6), 876-880.
- Michaud, A., et al. (2016). Key regulators of muscle protein synthesis in response to exercise and dietary protein. The Journal of Nutrition, 146(11), 2221S-2231S.
- Norton, L. E., & Layman, D. K. (2006). Leucine regulates protein metabolism in humans. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 211S-215S.
- Phillips, S. M., et al. (2016). Dietary protein for athletes: From starvation to saturation. Journal of Sports Sciences, 34(10), 917-927.
- Atherton, P. J., & Smith, K. (2010). Muscle protein synthesis in response to nutrition and exercise. Journal of Physiology, 588(11), 163-167. [CrossRef]
- Blomstrand, E., Eliasson, J., Karlsson, H. K., & Kohnke, R. (2006). Branched-chain amino acids activate key enzymes in protein synthesis after physical exercise. Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 269-273.
- Dreyer, H. C., Drummond, M. J., Pennings, B., Fujita, S., Glynn, E. L., Chinkes, D. L., & Rasmussen, B. B. (2006). Leucine-enriched essential amino acid and carbohydrate ingestion following resistance exercise enhances mTOR signaling and protein synthesis in human muscle. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 291(2), E381-E388.
- Drummond, M. J., & Rasmussen, B. B. (2009). Leucine-enriched nutrients and the regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling and human skeletal muscle protein synthesis. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care, 12(1), 86-90. [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J. P., Steele, J., & Smith, D. (2018). The role of resistance exercise in the regulation of muscle protein synthesis and degradation. Nutrients, 10(11), 1512.
- Fujita, S., & Volpi, E. (2006). Amino acids and muscle loss with aging. Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 277S-280S.
- Fry, C. S., Drummond, M. J., Glynn, E. L., Dickinson, J. M., Gundermann, D. M., Timmerman, K. L., & Rasmussen, B. B. (2011). Aging impairs contraction-induced human skeletal muscle mTORC1 signaling and protein synthesis. Skeletal Muscle, 1(1), 11. [CrossRef]
- Jewell, J. L., & Guan, K. L. (2013). Nutrient signaling to mTOR and cell growth. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 38(5), 233-242. [CrossRef]
- Kimball, S. R., & Jefferson, L. S. (2006). Signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms through which branched-chain amino acids mediate translational control of protein synthesis. The Journal of Nutrition, 136(1), 227S-231S.
- Kumar, V., Atherton, P., Smith, K., & Rennie, M. J. (2009). Human muscle protein synthesis and breakdown during and after exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology, 106(6), 2026-2039. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




