1. Introduction
Despite postoperative chemo and radiotherapy, almost 100% of glioma patients suffer a post-treatment recurrence of their tumors with 80-90% around the margins of the surgical resection cavity [
1,
2,
3]. The efficacy of chemo and radiotherapy (RT) is greatly limited by the blood brain barrier on the one, whereas normal brain tissue toxicity limits the RT dose allowable. Achieving local tumor control therefore, inevitably fails. Strategies for augmenting the effectiveness of combined chemotherapy and RT would therefore be of substantial value.
One method of increasing the efficacy of RT is the use of a radiation-sensitizing agent (RS) that selectively enhances cell killing from irradiation in tumor cells. [
4,
5,
6]. Unfortunately, RS clinical trials for GBM, thus far, have been disappointing [
7,
8,
9]. In the reported clinical trials, RS was given intravenously, and therefore, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) limited the concentration of these agents at the tumor site. Due to their intrinsic toxicity, the drug dose that could have been administered was systemically proved inadequate.
The local delivery of therapeutic agents by implanted slow-release hydrogels at the tumor site or in the tumor resection cavity has the potential to bypass the BBB [
10,
11]. Direct drug delivery permits an increasing drug dose that is able to reach the remaining infiltrative tumor cells in the brain parenchyma while avoiding systemic side effects. Additionally, the drug is protected from degradation and clearance until released.
One form of hydrogel, fibrin glue (FG), has several characteristics that make it well-suited for this form of drug delivery. Its lack of toxicity is proven in its clinical use in surgery as a sealant and in obtaining hemostasis for decades. FG loaded with chemotherapeutic drugs or radiation sensitizers, therefore has been researched as a localized controlled release vehicle [
12,
13].
Hydrophilic drugs have a significantly greater loading ability into hydrogels compared to hydrophobic drugs. On the other hand, many highly effective chemotherapeutic agents are large and water-soluble, and therefore do not easily penetrate plasma membranes but are actively transported into cells by endocytosis. Their poor ability to escape from the resulting intracellular endosomes leads to their inactivation.
Photochemical internalization (PCI) is a novel technology that utilizes the principles of photodynamic therapy (PDT) to enhance the intracellular delivery of macromolecules in a site and temporal-specific manner. [
14]. Macromolecules and select chemo-therapeutic agents that are internalized into cells via endocytosis become trapped in intracellular endosomes and lysosomes. PCI is based on the use of photosensitizers, which localize in the cell membrane and are carried into the cell, covering the inner leaflet of the endosomal membranes. The photosensitizer remains in the endosome membrane while the macromolecule remains localized within the lumen. Specific amphiphilic photosensitizers like Al phthalocyanine desulphonated (AlPcS2a) and meso-tetraphenyl chlorin desulphonated (TPCS2a) preferentially accumulate in the membranes of endosomes and lysosomes. Upon light exposure, the photosensitizer interacts with ambient oxygen to produce singlet oxygen, which ruptures the vesicular membrane. Therefore, the released agent can exert its full biological activity, contrary to being degraded by lysosomal hydrolases following endo-lysosomal fusion.
PCI has been demonstrated to significantly enhance the efficacy of the anti-cancer agent bleomycin (BLM-PCI) [
15,
16,
17,
18]. In particular, BLM-PCI before external-beam radiotherapy has been shown to improve local control in a mouse sarcoma model compared to BLM or radiation acting alone [
19].
The aim of the present in vitro research is designed to evaluate the ability of PCI of both free and FG-released drug to enhance the effectiveness of BLM as a radiation sensitizer. Multicell 3-dimensional tumor spheroids, formed from glioma tumor cells, are used as an in vitro model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
The rat glioma line (F98) was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). The BT4C cell line, originally derived from transformed fetal rat brain cells after exposure to ethyl–nitrosourea, was a gift from Dr. Dag Sorensen (University in Oslo, Oslo, Norway). Both cell types were maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) with high glucose (Life Technologies Corp., Carlsbad, CA, USA) supplemented with 2% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 25 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.4), penicillin (100 U ml-1) and streptomycin (100 μg/ml-1) at 37°C and 5% CO2.
2.2. Chemicals
The photosensitizer, aluminum phthalocyanine disulfonate (AlPcS2a,) was obtained from Frontier Scientific, Inc. (Logan, UT, USA). The chemotherapeutic drug Bleomycin (BLM) was obtained from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.3. Fibrin Glue and Drug Harvest
The fibrin glue was obtained from EMD Millipore Calbiochem (Temecula, CA, USA) and was composed of a 1:1 ratio of fibrinogen and thrombin, with BLM added to the thrombin. 0.2 ml of the drug-loaded thrombin was combined with 0.2 ml of fibrinogen in the wells of a 24-well microplate. The glue was allowed to gel for 20 min at 37°C. The wells were washed twice to remove any free drug and 1.6 ml of drug-free culture medium was added to the well. The supernatant covering the FG layer, containing the released BLM was harvested after 48 hours for use in the majority of the experiments.
2.4. Spheroid Formation
F98 or BT
4C cells were used to form spheroids through a modified centrifugation method as previously described [
16]. Briefly, 2.5×10
3 F98 or BT
4C cells in 100μl of culture medium per well were allotted into the wells of ultra-low attachment surface 96-well round-bottomed plates (Corning In., NY). The plates were centrifuged at 500g for 10 min. Immediately following centrifugation, the tumor cells formed into a disk shape. The plates were maintained at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator for 24 hours for formation of the usual 3-dimensional spheroid form. The spheroids formed were uniform in size and approximately 0.2 mm in diameter. Determination of spheroid growth was carried out by digitally measuring the diameters of each spheroid using an inverted microscope (BZ-X810 Fluorescence Microscope. KEYENCE, Itasca, IL U.S.A) and their volume calculated assuming a perfect sphere.
2.5. Radiation and PCI Treatment
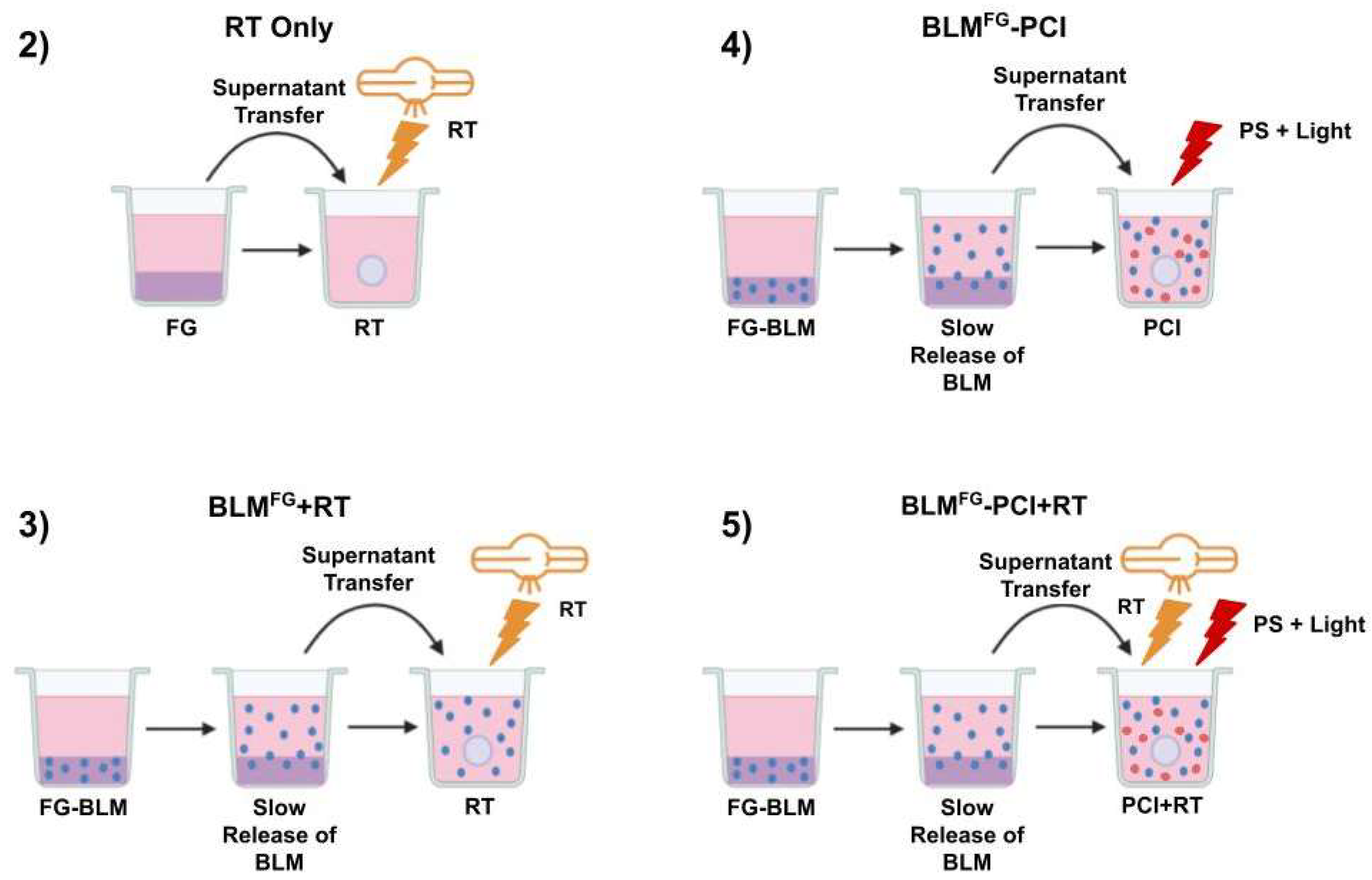
The basic experimental protocol for the FG-released drug is shown in
Figure 1. and consisted of five arms: 1) Non-treatment controls (NTC) not shown, 2) RT only, 3) BLM
FG -PCI only, 4) BLM
FG +RT only and 5) BLM
FG -PCI+RT.
BLM was added to the cultures either as free drug or BLM released from FG, designated BLMFG. The formed spheroids were incubated together with 0.1ml of 0.03 or 0.06 μg/ml of free AlPcS2a and 0.1 ml of either BLMFG, (collected at 48 hours) or with BLM as pure drug at increasing concentrations ranging from 0–4.8 μg/ml. One hour after the addition of AlPcS2a, BLM or BLMFG was added. Light treatment, λ=670 nm, from a diode laser (Intense; New Jersey USA) at an irradiance of 2.0 mW/cm2 was administered for 6, 8, or 10 min., corresponding to 0.72, 0.96 or 1.2 J/cm2 respectively. Spheroids received RT either immediately after or delayed BLM-PCI application. Radiation was administered at a constant dose rate of 1.02 Gy/min at a 50cm beam distance for varying time intervals to obtain different radiation doses. All RT was done in an X-Rad 320 cabinet irradiator (Precision X-Ray Irradiation, Madison, CT, USA). Treatment was given at Irradiation voltage, and amperage was set to 320 kV and 12.5 mA, respectively. An F2 filter composed of 0.75 mm Tin, 0.25 mm Copper, and 1.5 mm Aluminum was used. Following treatment, the plates were returned to the incubator. Typically, 8-16 spheroids were followed for each category in 3 independent experiments for up to 14 days of incubation. Culture medium in the wells was exchanged after 7 days.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Data analysis and graphing was done using Microsoft Excel. Mean and standard deviation were used throughout. Significance was calculated via Student’s and Welch’s t-test. Two values are considered distinct when p-values were below 0.05. The following equation determined if the FG-RS+RT effect was synergistic, antagonistic, or additive:
SFa, growth following RT only. SFb, growth following BLM-PCI only. SFab, growth following BLM-PCI+RT. α > 1, synergistic. α <1, antagonistic. α = 1, additive.
3. Results
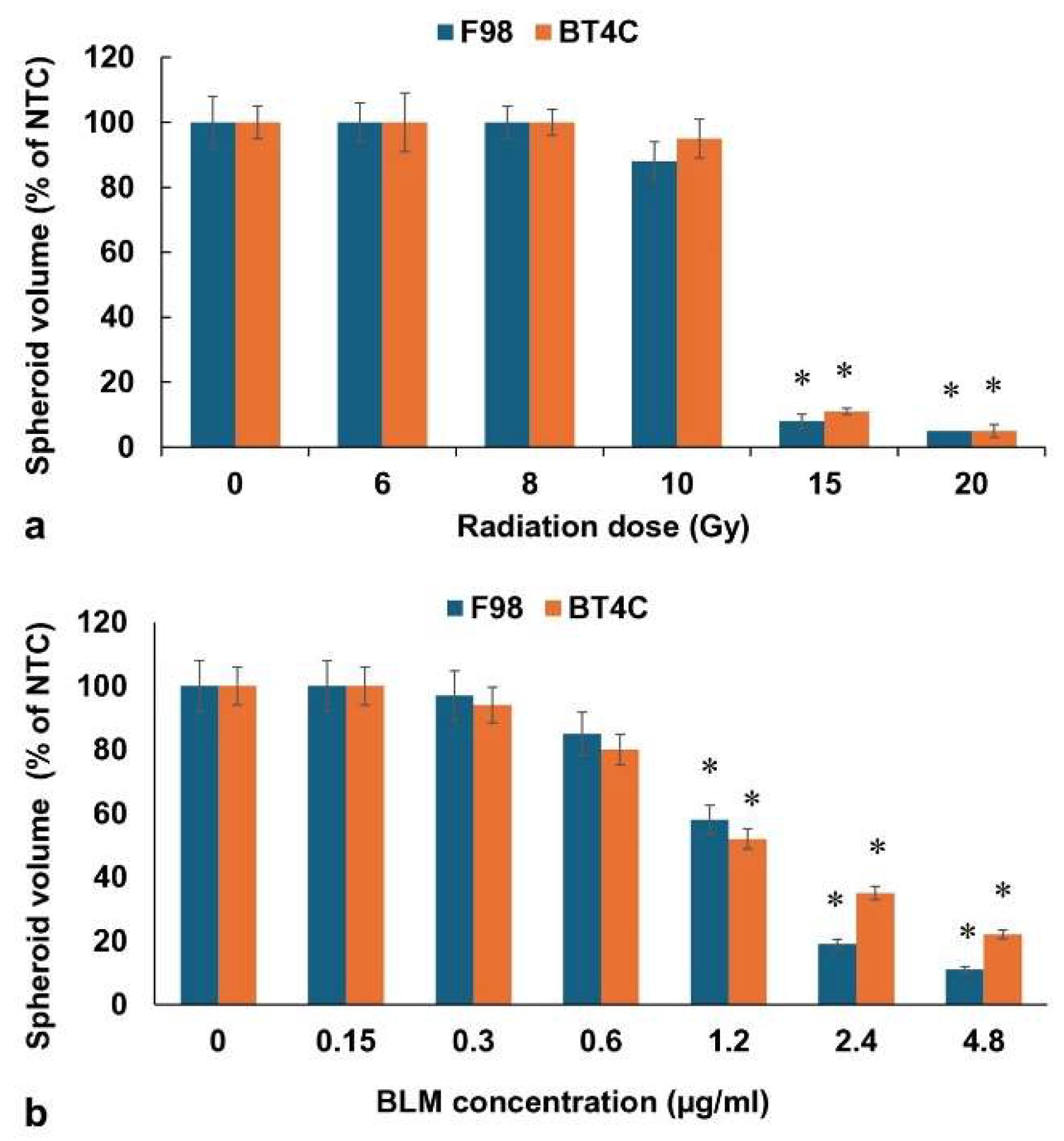
3.1. Effects on Spheroid Growth of RT and BLM-PCI as Single Treatment
The effects on F98 or BT
4C spheroids, exposed to increasing doses of RT (0-20 Gy), is shown in
Figure 2a.
RT as a single treatment was suboptimal, up to 10 Gy, with spheroids usually reaching 90-100% of NTC volume after 14 days in culture. RT alone, however, did produce a growth delay compared to NTC at 8 and 10 Gy with RT-treated spheroids reaching only 56% of NTC final volume on day 9 compared to 92% for control spheroids. In contrast, radiation doses of 15 and 20 Gy completely inhibited spheroid growth.
In order to establish relevant BLM concentrations to be used in subsequent BLM-PCI procedures, experiments were performed using free drug over a range of increasing BLM concentrations from 0-4.8μg/ml with 0.06 μg/ml. of free AlPcS
2 and light treatment, 0.96J/cm
2. The results for both cell lines are shown in
Figure 2b. BLM concentrations of 1.2μg/ml and above as a single PCI treatment gave significant spheroid growth inhibition, which if used in combination with RT could potentially mask the additional effects of RT. For this reason, BLM concentrations of either 0.3 or 0.6 μg/ml were used in all of the following experiments.
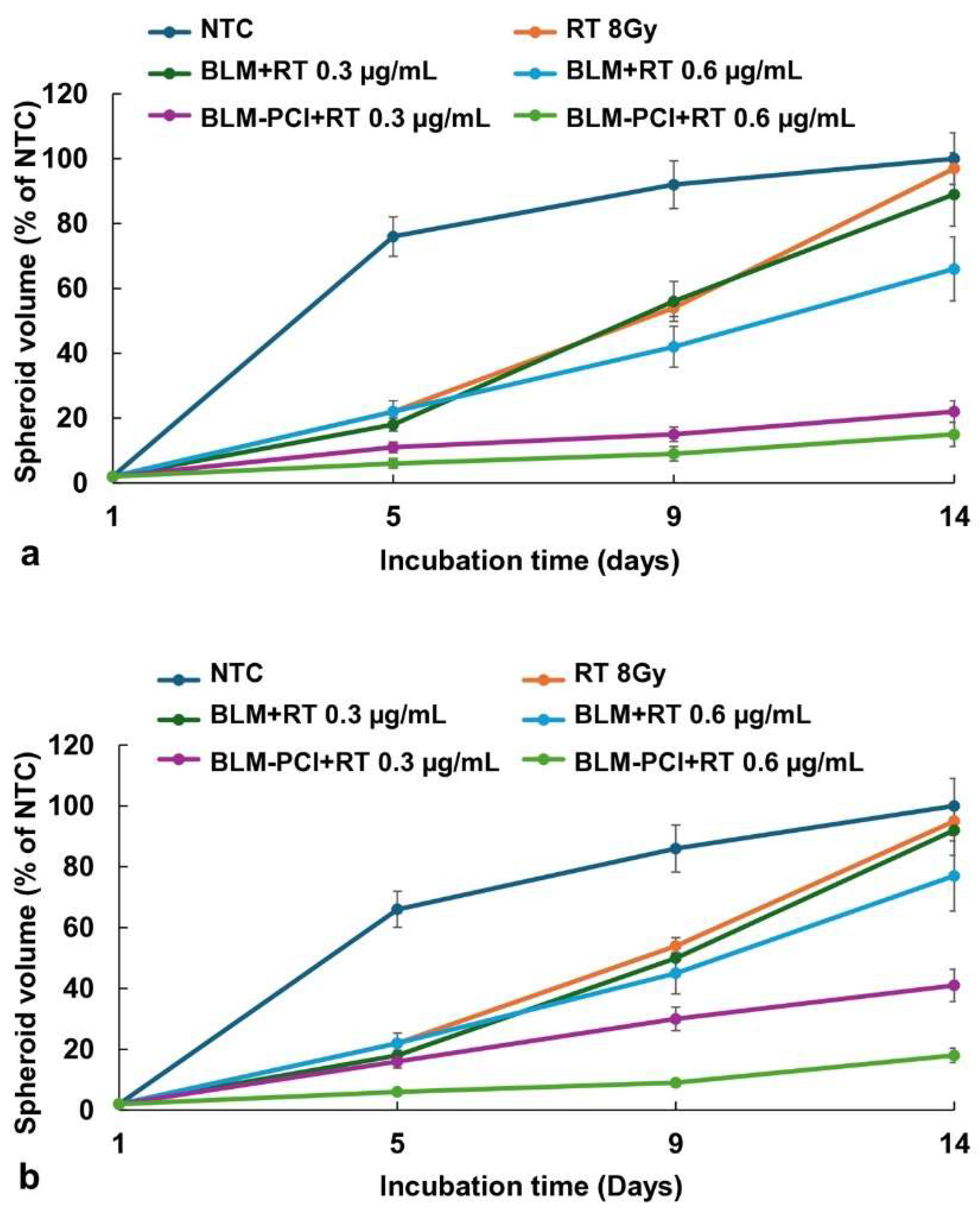
3.2. RT Effects on Spheroid Growth by BLM and BLM-PCI as Free Drug
BLM, as a free drug, included four groups: 1) NTC, 2) RT, 3) BLM+RT, 4) BLM-PCI+RT.
Figure 3a displays the effects of RT (8 Gy) on the growth of F98 and BT4C spheroid volume combined with BLM or BLM-PCI as a free drug. AlPcS2a concentration was 0.06 μg/ml and light radiance of 0.96J/cm2 was used for all PCI experiments.
The kinetics of F98 and BT4C spheroid growth pattern, following NTC, RT, BLM+RT, and BLM-PCI+RT are illustrated in
Figure 3a,b. RT only (8 Gy) resulted in a significant delay in spheroid growth, but growth continued, and spheroid volume was equal to NTC volume after 14 days in culture. The ability of BLM to act as a radiation sensitizer (BLM+RT) was significant only at the highest BLM concentration of 0.6μg/ml, with the spheroids reaching 66% of control values. In contrast, a significant inhibiting effect was seen with RT in combination with increasing BLM-PCI (BLM-PCI+RT) at both BLM concentrations tested. At a BLM-PCI concentration of 0.6μg/ml, the treated spheroid volume was 15% of control values after 14 days of growth. Similar but less pronounced results were obtained on the cell line BT
4C, (
Figure 3b) with the spheroid volume of 18% of NTC volume at the highest BLM concentration.
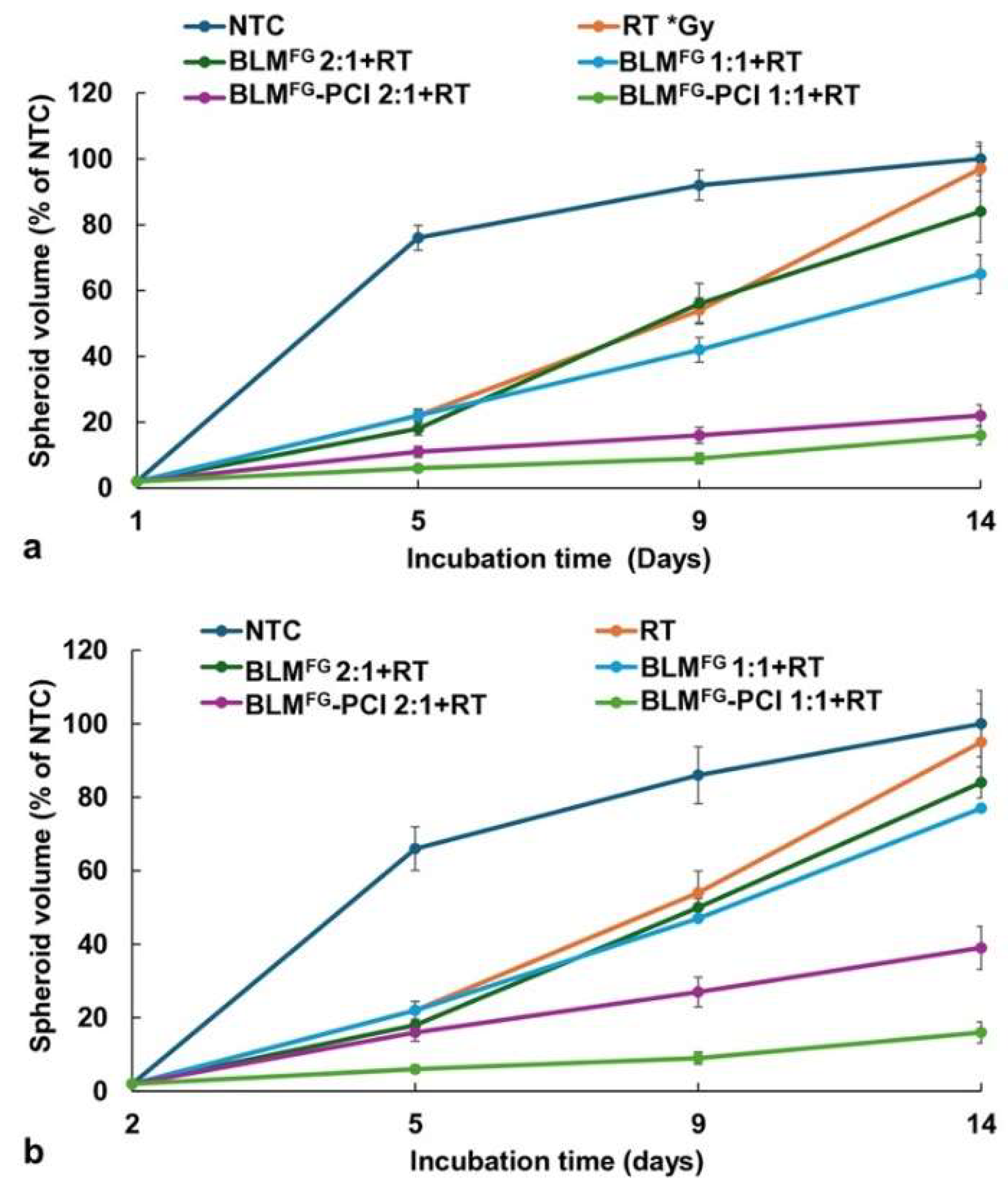
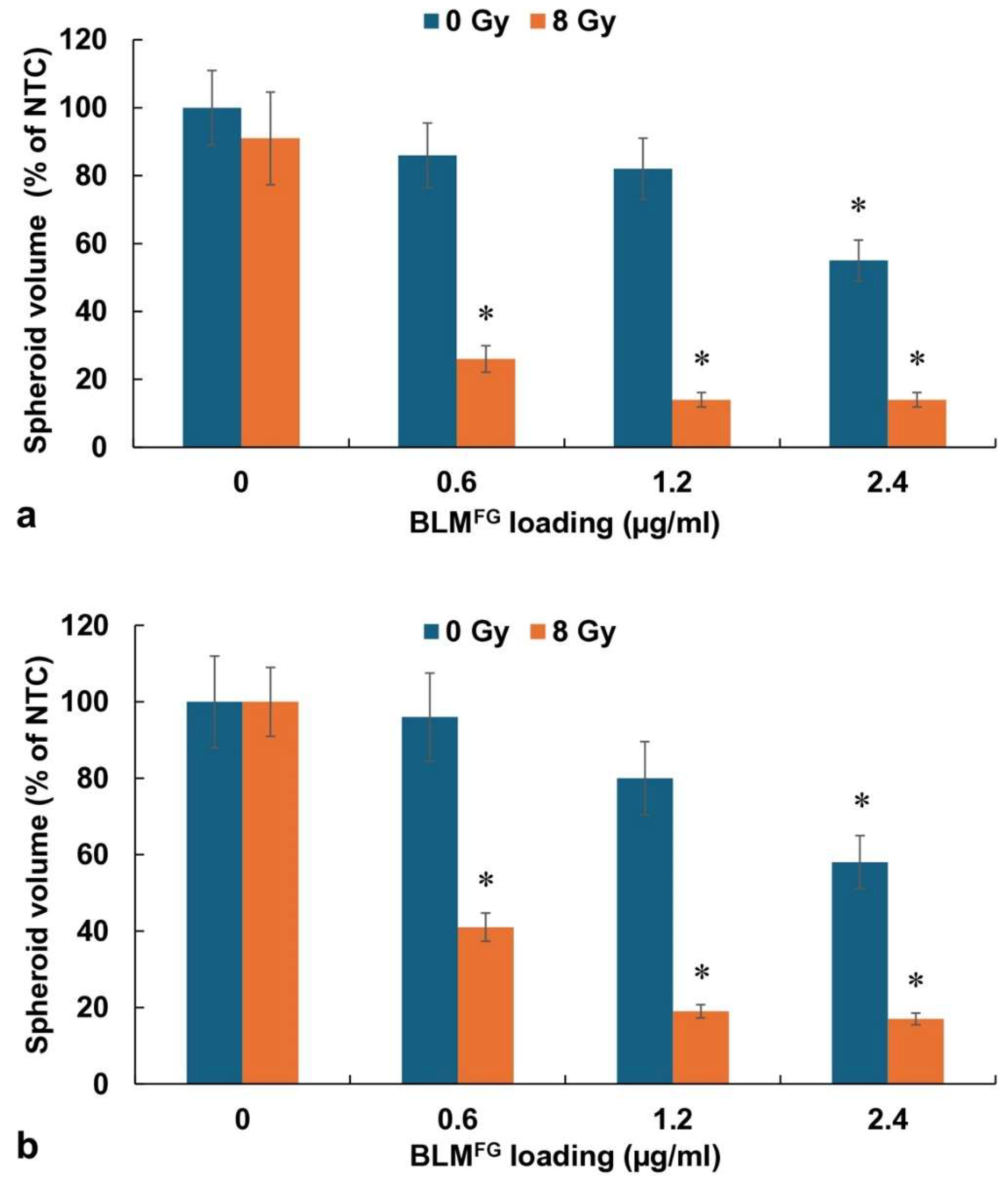
3.3. RT Effects on Spheroid Growth by BLMFG and BLMFG -PCI as FG Released Drugs
The basic experimental setup is pictured in
Figure 1. The optimal time for drug harvest was determined by fluorescence emission spectroscopy and reported in a previous study [
13]. The FG was loaded with 1.2μg of BLM in 0.4ml of FG and overlaid with 1.6ml of medium. Previous results demonstrated that although BLM was slowly released over the entire 72-hour time interval tested, the difference between the BLM concentration after 48 and 72 hours was not significant. In all subsequent experiments supernatants harvested after 48 hours were used. BLM
FG as a released drug included the same four groups as used for free drug: 1) NTC 2) RT 3) BLM
FG +RT, 4) BLM
FG-PCI+RT. Loading FG with 1.5μg of BLM was done as described in the materials and methods section. The AlPcS2a concentration was 0.06 μg/ml, and a light radiance of 0.96J/cm
2 was used for all PCI experiments. As seen in
Figure 4a, for F98 and
Figure 4b for BT
4C spheroids, BLM-PCI
FG combined with 8 Gy RT showed significant growth-inhibiting effects compared to BLM
FG+RT as a single treatment. At the BLM-PCI
FG dilutions of 2:1, and 1:1 combined with 8 Gy, RT resulted in spheroid volumes of 41% and 17% for F98 spheroids and 39% and 16% of control volumes for BT
4C spheroids, respectively.
3.4. Simultaneous Release Both BLM and AlPcS2a
In the above-described experiments, BLM
FG was combined with free photosensitizer (AlPcS2a) to allow the results to be directly compared to the results obtained using both free drug and photosensitizer. This protocol, however, does not completely represent expected in vivo conditions, where both photosensitizer and drug will be simultaneously and continually released. Experiments were therefore performed where both BLM (0.6, 1.2, 2.4 μg) and AlPcS2a (0.12μg) were loaded into the FG. The results shown in
Figure 5a (F98) and b (BT4C) clearly indicate that simultaneous FG release of both drug and photosensitizer-mediated PCI (BLM
FG-PCI +RT) can induce significant spheroid growth inhibition at all the drug loading dosages used.
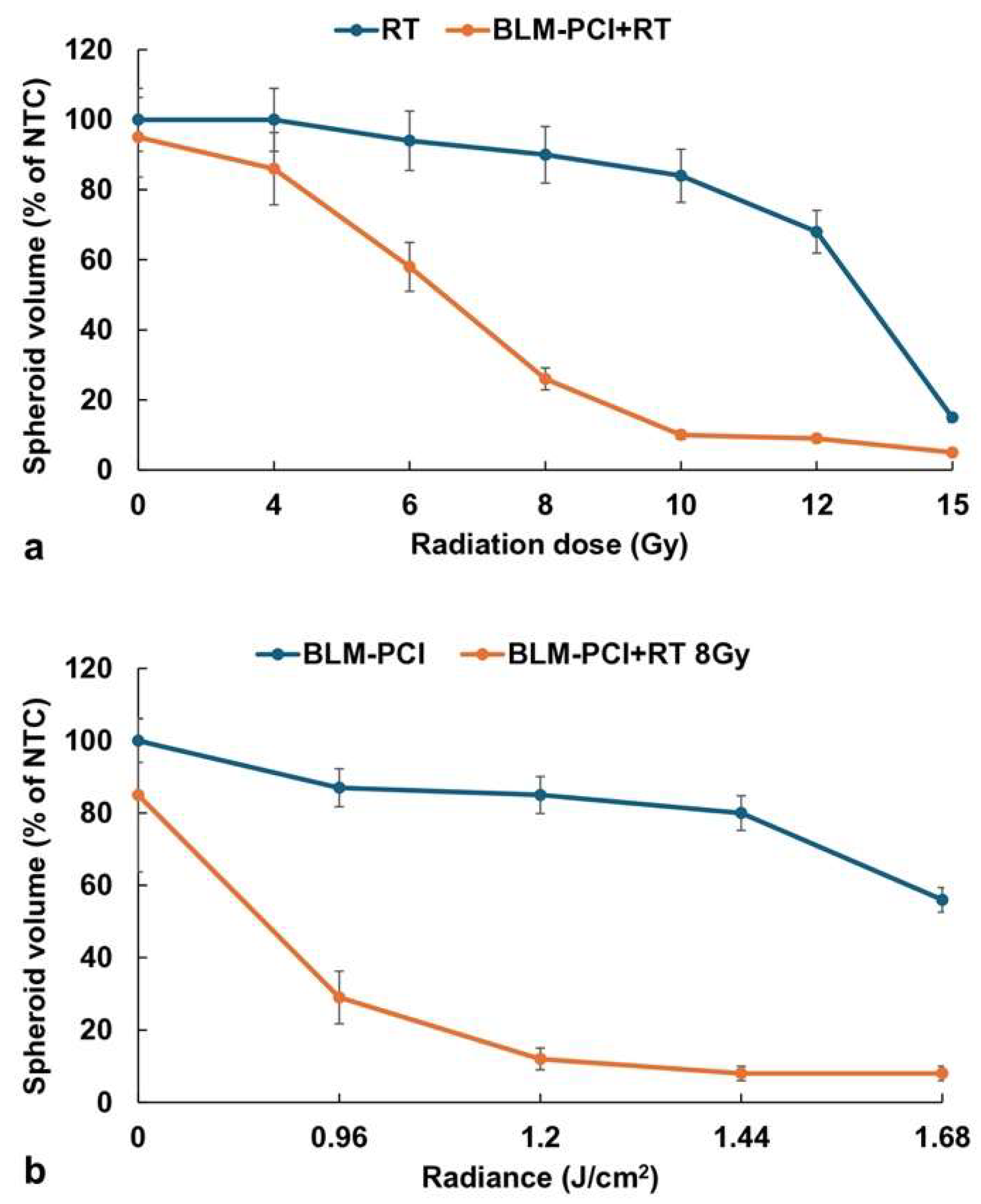
3.5. Comparison of RT and Light Radiation Dose on the Effects of BLM-PCI+RT
The basic hypothesis being tested in this study is that a significantly lower RT dose is required when combined with BLM-PCI than that needed for RT alone to obtain an equivalent efficacy. Experiments were performed over an RT dose range from 0-15 Gy with and without BLM-PCI. AlPcS2a concentration was 0.06 μg/ml, BLM concentration of 0.6μg/ml, and light radiance of 0.96J/cm
2. The results are shown in
Figure 6a. An RT dose of 15 Gy was necessary to significantly inhibit spheroid growth down to 15% of the NTC spheroid volume. For an equivalent effect, only approximately 9 Gy was required when combined with BLM-PCI at the experimental values tested.
The effects of light radiance levels of BLM-PCI with and without RT are shown in
Figure 6b. AlPcS2a concentration was 0.06 μg/ml, BLM concentration of 0.6μg/ml, and light radiance in a range of 0-1.68 J/cm
2 was used. The degree of growth inhibition increased, as expected, with increasing radiance both for the BLM-PCI and the BLM-PCI+RT groups. The addition of RT greatly increased the toxic effects of BLM-PCI at all the radiance levels tested compared to BLM-PCI alone (p < 0.05).
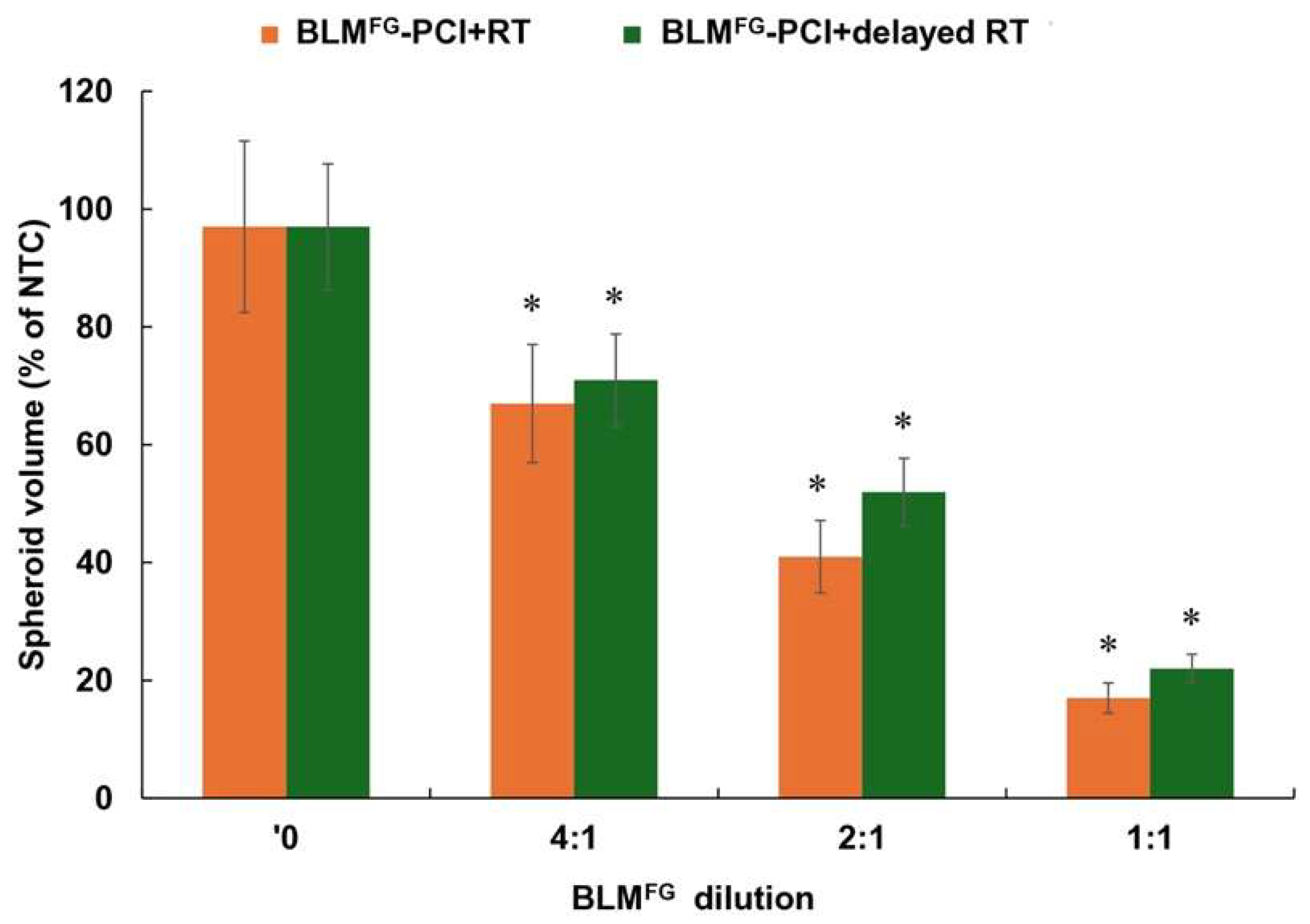
3.6. Effects of Treatment Delay Between BLMFG-PCI and RT
Experiments were performed comparing RT delivered either immediately after or delayed 24 hours after BLM
FG-PCI. F98 cells were used in both groups. FG was loaded with 2μg of BLM, then supernatants were harvested after 48 hours. The AlPcS2a concentration was 0.06 μg/ml, and a light radiance of 0.96J/cm
2 and RT of 8 Gy was used. The results for serial dilutions of SN are shown in
Figure 7. Compared to BLM+RT, significant inhibition (p < 0.05) of spheroid growth was demonstrated for both the immediate and delayed BLM
FG -PCI and RT groups. As shown in the figure, the effects of immediate BLM
FG -PCI before RT were slightly greater than those obtained with a 24-hour delay, but the difference at all the dilutions tested was not significant (p > 0.05).
Since the addition of either BLM or BLM-PCI to RT is a technique that relies on the combination of drug and RT exposure, the resultant toxicity should show more than an additive effect of the single modalities. The degree of synergism was calculated both for free BLM+RT and BLM-PCI +RT and for BLMFG and BLMFG-PCI+RT for F98 spheroids using the formula described in materials and methods. The data used for the calculation of the α values shown in
Table 1 were derived from the experiment using F98 cells, 0.6μg/ml BLM, 0.96J.cm2, and a supernatant dilution of 1:1. As evident from the calculated α values shown in
Table 1, BLM+RT and BLMFG+RT demonstrated marginal synergy at all the radiation doses evaluated. In contrast, a significant and equivalent synergistic effect (α > 1), was obtained for both free and FG released drug combined with PCI, particularly at radiation levels of 8 and 10Gy. Similar results were also obtained using the BT4C cell line (data not shown).
4. Discussion
Since radiation therapy forms one of the main modalities for the treatment of GBM, improving its efficacy while reducing its neuro-toxicity is an important goal. One direction, mainly through advances in high-precision technologies, has achieved significant advances in local dose escalation without undue toxicities. Techniques, such as linear accelerators with motion-tracking and beam modulation, inverse planning-based intensity modulation, as well as Gamma Knife, Cyberknife, and Tomo-therapy, have greatly contributed to this end.
Another approach, to widen the therapeutic index of RT, is the use of radio-sensitizing agents that selectively enhance the cell killing from irradiation in tumor cells while exhibiting limited single-agent toxicity on tumor or normal tissues. Injectable hydrogel direct delivery systems have been reported for radiation enhancers [
20,
21]. It is this approach that forms the basis for the experimental results presented here. The combination of hydrogels as direct delivery systems for radiation sensitizers with light-activated PCI produces a highly targeted site and temporal-specific treatment modality for increasing the therapeutic index of RT. The surgically targeted placement of the radiation sensitizer in a slow-release vehicle allows for high drug concentration at the local site (the resection cavity) while reducing systemic side effects by bypassing the BBB.
Additionally, the rapid attenuation of light in the brain confines the PCI drug activation effect to a limited area, since the effect is localized to the illuminated area.
In a previous study, we demonstrated that the drug 5FU, both as a free drug and released from FG, could act as a radiation sensitizer, significantly enhancing the effects of RT [
21]. That this was not the case for BLM is clearly shown in
Figure 3 for free drug and
Figure 4 for FG-released drug. Even at relatively high BLM doses, the ability of BLM to enhance the effects of RT was limited. This is, in all probability, due to the hydrophilic and large-size character of BLM. The drug does not diffuse through cell plasma membranes but is actively taken up into cells by endocytosis. Its poor ability to escape from endosomes leads to inactivation by hydrolytic enzymes and complexing molecules in secondary endosomes.
In contrast, BLM-PCI greatly increased RT’s ability to inhibit spheroid growth, also shown in
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 6. PCI is known to promote endosomal escape, and once BLM is released in the cell cytosol, it quickly diffuses into the nucleus, where it has a significant effect, causing multiple double DNA strand breaks per molecule [
22,
23]. Double-stranded breaks are also the most common form of DNA damage associated with ionizing radiation. After these breaks are generated, a cascade of enzymatic processes is triggered to attempt DNA repair. Our interpretation of the clear synergistic effects, as shown in
Table 1, between BLM-PCI and RT is that the DNA damage caused by both modalities overwhelms the ability of the cell to repair this damage, pushing the cell into apoptosis.
By employing the supernatant harvest system used in these experiments, it is assumed that, after an incubation interval of 48 hours, an equilibrium drug concentration will be reached between the FG layer and the surrounding culture medium. In the experimental protocol used here, the drug-containing FG layer was 0.4 ml in volume while the overlaying supernatant was 1.6 ml, which totals 2 ml. For example, 1.2μg of BLM loaded into the FG will, after equilibrium is reached, acquire a BLM concentration of 0.6μg/ml in the supernatant. Adding the supernatant undiluted into the spheroid wells will, therefore, approximate the 0.6μg/ml concentration used in the free drug experiments. This allows comparisons of the efficacy of free versus FG-released drug. The results indicate that BLM released from FG is as active as free drug and does not appear to be degraded. Additionally, comparing the α values, shown in
Table 1, for free versus FG-released BLM corroborates the finding that the drug is released in an active form.
The only previous report on the ability of PCI to enhance the effects of RT has shown that introducing a delay interval between BLM-PCI and RT did not alter the treatment efficacy but did significantly reduce normal tissue damage [
19] The results shown in
Figure 7 could also demonstrate no significant differences between immediate and delayed BLM
FG -PCI.
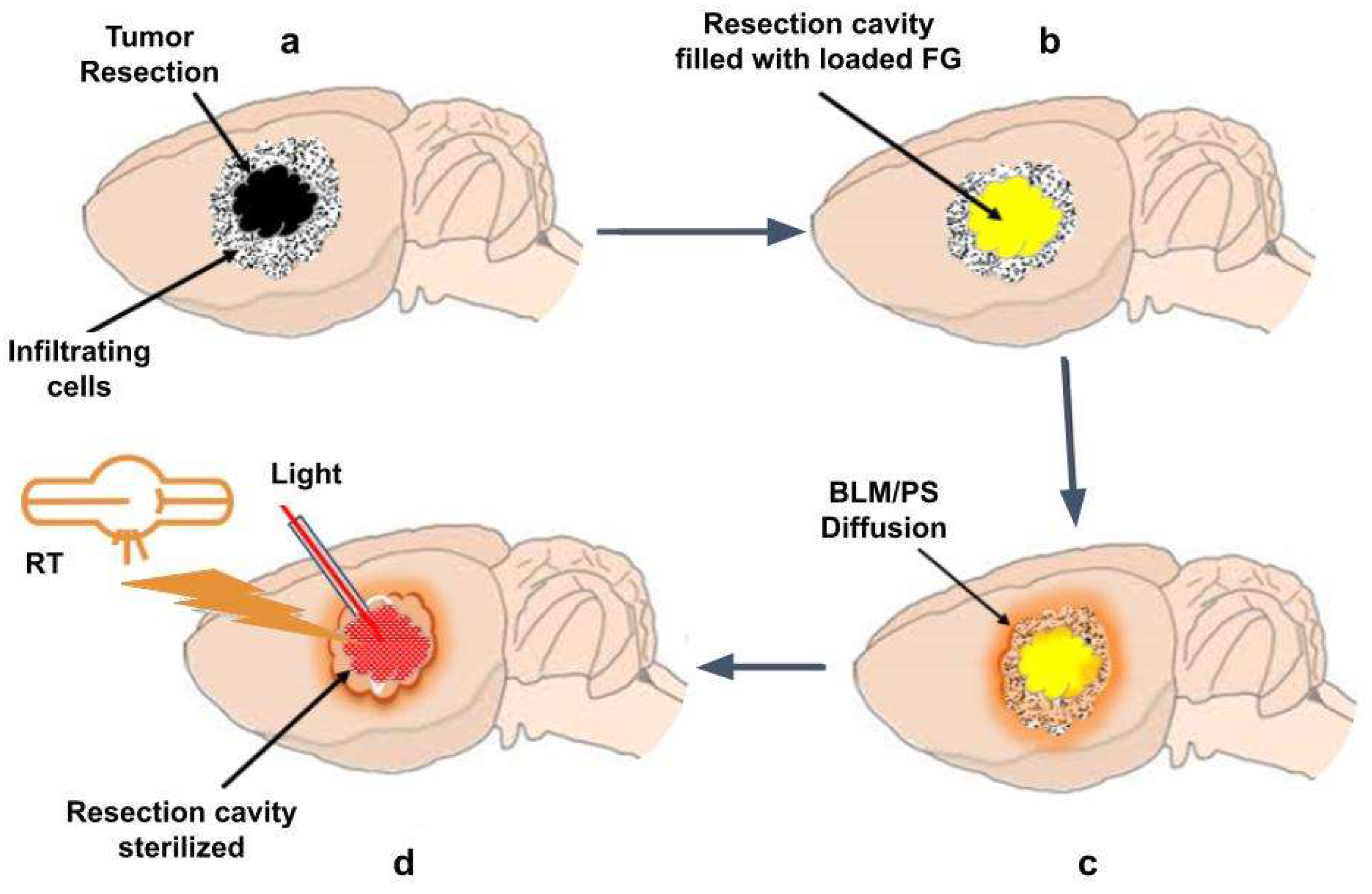
4.1. In Vivo Translation
In order to allow for wound healing, postoperative external beam radiation and chemotherapy are delayed several weeks, allowing for disease progression to occur untreated. To obtain equivalent efficacy, a significantly lower RT dose is required when combined with BLM-PCI compared to what is required for RT alone. This, in turn, allows treatment to be initiated shortly after surgical resection and during the time interval of drug release. Several methods for both light and RT administration are available. A proposed translation to a rat animal GBM model is shown in
Figure 8.
One method for implementing light administration is the temporary implantation in the FG of fiber optic catheters. The FG is semitransparent and would therefore act as a light diffuser assuring even light delivery.
The external beam RT approaches such as linear accelerators with motion-tracking and beam modulation radiotherapy would be well suited to deliver targeted therapy in this interval. Another promising method is Flash radiotherapy, characterized by the delivery of ultra-high radiation doses (>40 Gy/sec) in a very short interval. Flash RT has shown considerable potential for improving cancer treatment by minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues while effectively targeting tumors [
24,
25].
5. Conclusions
The tendency of tumor cells to exhibit invasive and migratory behavior leads to recurrent tumors in almost all cases. Individual cells, as well as micro-colonies of tumor cells, infiltrate in or beyond a region of the brain where the blood-brain barrier is still relatively intact. In 80% of all cases, recurrent tumor growth is within a 2-3 cm margin of the surgical resection cavity.
Radiation sensitizer-loaded gels, localized to the resection cavity, would lead to increased drug concentration in the remaining infiltrative tumor cells in the brain parenchyma while greatly reducing systemic drug side effects.
The results of the present study show that active non-degraded BLM was released from FG layers in a prolonged manner, measured in days. Although FGBLM did not prove to be an efficient radiation sensitizer, BLMFG -PCI greatly increased the efficacy of RT. A time delay of 24 hours between BLMFG -PCI and RT did not significantly alter the results compared to those obtained from experiments with a minimal interval between BLMFG-PCI and RT. To obtain equivalent RT efficacy, a significantly lower RT dose was required when combined with BLMFG-PCI than what required for RT as a single treatment. The in vitro results reported here form the basis for translation to in vivo animal experiments and eventually patient treatment protocols as FG is widely clinically approved.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.H.; methodology, H.H.; Validation, H.H.; formal analysis, S.L., K.G. and H.H.; investigation, S.L., K.G., J.N., A.C., J.L. and H.H.; resources, H.H.; data curation, H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L., K.G. and H.H.; writing—review and editing, S.L., K.G., K.B. and H.H.; visualization, H.H.; supervision, H.H.; project administration, H.H.; funding acquisition, H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Norwegian Radium Hospital Research Foundation, Grants SE 1305 and SE 1503.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals, performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chamberlain, M.C. Radiographic patterns of relapse in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 2011, 101, 319–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobelbower M.C., Burnett III O.L., Nordal R.A., Nabors L.B., Markert J.M., Hyatt M.D., Fiveash J.B. Patterns of failure for glioblastoma multiforme following concurrent radiation and temozolomide. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 2011, 55, 77–81. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrecca K., Guiot M.C., Panet-Raymond V., Souhami L. Failure pattern following complete resection plus radiotherapy and temozolomide is at the resection margin in patients with Glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 2013, 111, 19–23. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citrin D.E., Mitchell J.B. Altering the response to radiation: sensitizers and protectors. Semin Oncol 2014, 41(6), 848–59. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, R.R. Radiobiological modifiers in clinical radiation oncology: current reality and future potential. Future Oncol 2014, 10(15), 2359–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong L., Zhang Y., Liu C., Zhang M., Han S. Application of Radiosensitizers in Cancer Radiotherapy. Int J Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 1083–1102. [CrossRef]
- Chang J.E., Khuntia D., Robins H.I., Mehta M.P. Radiotherapy and radiosensitizers in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2007, 5, 894–915.
- Alexander B.M., Ligon K.L., Wen P.Y. Enhancing radiation therapy for patients with glioblastoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2013, 13(5), 569–81. [CrossRef]
- Brachman D.G., Pugh S.L., Ashby L.S., et al. Phase 1/2 trials of Temozolomide, Motexafin Gadolinium, and 60-Gy fractionated radiation for newly diagnosed supratentorial glioblastoma multiforme: final results of RTOG 0513. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2015, 91(5), 961–967. [CrossRef]
- Bastiancich C., Malfanti A., Préat V., Ruman R. Rationally designed drug delivery systems for the local treatment of resected glioblastoma. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2021, 177, 113951. [CrossRef]
- Bastiancich C., Bozzato E., Henley I., Newland B. Does local drug delivery still hold therapeutic promise for brain cancer? A systematic review. J Control Release 2021, 337, 296–305. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anai S., Hide T., Takezaki T., Kuroda J., et al. Antitumor effect of fibrin glue containing temozolomide against malignant glioma. Cancer Sci 2014, 105, 583–91. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen S.J., Devarajan A.G., Chandekar A., Nguyen L., Hirschberg H. Fibrin glue as a local drug and photosensitizer delivery system for photochemical internalization: Potential for bypassing the blood-brain barrier. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2023, 41, 103206. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerjes W., Theodossiou T.A., Hirschberg H., et al. Photochemical Internalization for Intracellular Drug Delivery. From Basic Mechanisms to Clinical Research. J Clin Med 2020, 9(2), 528. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg K., Dietze A., Kaalhus O., Høgset A. Site-specific drug delivery by photochemical internalization enhances the antitumor effect of bleomycin. Clin. Cancer Res 2005, 11(1), 8476–8485. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews M.S., Blickenstaff J.W., Shih E.C., et al. Photochemical internalization of bleomycin for glioma treatment. Biomed Opt 2021, 17(5), 058001.
- Gederaas O.A., Hauge A., Ellingsen P.G., et al. Photochemical internalization of bleomycin and temozolomide – in vitro studies on the glioma cell line F98. Photochem Photobio. Sci 2015, 14(7), 1357–66. [CrossRef]
- Sultan A.A., Jerjes W., Berg K., et al. Disulfonated tetraphenyl chlorin (TPCS2a)-induced photochemical internalization of bleomycin in patients with solid malignancies: a phase 1, dose-escalation, first-in-man trial. Lancet Oncol 2016, 17(9), 1217–29. [CrossRef]
- Norum O.J., Bruland Ø.S., Gorunova L., Berg K. Photochemical internalization of bleomycin before external-beam radiotherapy improves locoregional control in a human sarcoma model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phy 2009, 75(3), 878–85. [CrossRef]
- Xie Y., Liu M., Cai C., Ye C., Guo T., Yang K., Xiao H., Tang X., Liu H. Recent progress of hydrogel-based local drug delivery systems for postoperative radiotherapy. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1027254. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen J., Chandekar A., Laurel S., Dosanjh J., Gupta K., Le J., Hirschberg H. Fibrin glue mediated direct delivery of radiation sensitizers results in enhanced efficacy of radiation treatment. Discov Oncol 2024, 15(1), 101. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddevin B., Orlowski S., Belehradek J., Mir L.M. Very high cytotoxicity of bleomycin introduced into the cytosol of cells in culture. Biochem Pharmacol 1991, 42, S67–S75. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pron G., Mahrour N., Orlowski S. Internalization of the bleomycin molecules responsible for bleomycin toxicity: a receptor-mediated endocytosis mechanism. Biochem Pharmacol 1999, 57(1), 45–56. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhis J., Montay-Gruel P., Gonçalves Jorge P., et.al. Clinical translation of FLASH radiotherapy: Why and how? Radiother Oncol 2019, 139, 11–17. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montay-Gruel P., Acharya M.M., Gonçalves Jorge P., et.al. Hypofractionated FLASH-RT as an Effective Treatment against Glioblastoma that Reduces Neurocognitive Side Effects in Mice. Clin Cancer Res 2021, 27(3), 775–784.
Figure 1.
Experimental protocol. Supernatants harvested from BLM-loaded FG or non-loaded fibrin glue coated in media at varying time intervals were transferred to spheroid cultures in multi-well plates. Five experimental arms. (1) Non-treatment controls (not shown) (2) RT only (3) BLMFG +RT (4) BLMFG (supernatant harvested from BLM-loaded FG) (5) BLMFG +PCI+RT.
Figure 1.
Experimental protocol. Supernatants harvested from BLM-loaded FG or non-loaded fibrin glue coated in media at varying time intervals were transferred to spheroid cultures in multi-well plates. Five experimental arms. (1) Non-treatment controls (not shown) (2) RT only (3) BLMFG +RT (4) BLMFG (supernatant harvested from BLM-loaded FG) (5) BLMFG +PCI+RT.
Figure 2.
(a) RT effect on growth of F98 and BT4C spheroids over a range of radiation doses, 0-20 Gy. (b) Effect of BLM-PCI at varying BLM concentrations on F98 and BT4C spheroid growth. Data points are the average volumes of spheroids after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation and * represents significant differences (p < 0.05) when compared to controls.
Figure 2.
(a) RT effect on growth of F98 and BT4C spheroids over a range of radiation doses, 0-20 Gy. (b) Effect of BLM-PCI at varying BLM concentrations on F98 and BT4C spheroid growth. Data points are the average volumes of spheroids after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation and * represents significant differences (p < 0.05) when compared to controls.
Figure 3.
(a) Kinetics of F98 spheroid growth pattern after exposure to RT of 8 Gy. (b) Kinetics of BT4C spheroid growth pattern after exposure to RT of 8 Gy. Spheroids were treated with BLM at 0.3 or 0.6 μg/ml, combined with AlPcS2a at 0.06 μg/ml, and light, 0.96J/cm2. Data points are the average spheroid volumes after 14 days in culture, from 2 independent experiments, represented as a % of the non-treatment controls. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Figure 3.
(a) Kinetics of F98 spheroid growth pattern after exposure to RT of 8 Gy. (b) Kinetics of BT4C spheroid growth pattern after exposure to RT of 8 Gy. Spheroids were treated with BLM at 0.3 or 0.6 μg/ml, combined with AlPcS2a at 0.06 μg/ml, and light, 0.96J/cm2. Data points are the average spheroid volumes after 14 days in culture, from 2 independent experiments, represented as a % of the non-treatment controls. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Figure 4.
(a) The effect of varying dilutions of BLM-PCI on growth kinetics of F98 spheroid growth pattern combined with RT of 8 Gy. (b) Kinetics of BT4C spheroid growth pattern after varying dilutions of BLM-PCI combined with RT of 8 Gy. Spheroids were treated with BLMFG, combined with AlPcS2a at 0.06 μg/ml and light. Data points are the average volumes of spheroids from 3 independent experiments after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Figure 4.
(a) The effect of varying dilutions of BLM-PCI on growth kinetics of F98 spheroid growth pattern combined with RT of 8 Gy. (b) Kinetics of BT4C spheroid growth pattern after varying dilutions of BLM-PCI combined with RT of 8 Gy. Spheroids were treated with BLMFG, combined with AlPcS2a at 0.06 μg/ml and light. Data points are the average volumes of spheroids from 3 independent experiments after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Figure 5.
(a) Effect of increased concentration of BLM loading in FG, 0-2.4 ug/mL on F98 spheroids that received no RT or received 8 Gy of RT. (b) BT4C spheroids with increasing concentration of FG-released BLM and given no RT or 8 Gy of RT. The average volumes of spheroids after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation and * represents significant differences (p < 0.05) when compared to controls.
Figure 5.
(a) Effect of increased concentration of BLM loading in FG, 0-2.4 ug/mL on F98 spheroids that received no RT or received 8 Gy of RT. (b) BT4C spheroids with increasing concentration of FG-released BLM and given no RT or 8 Gy of RT. The average volumes of spheroids after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation and * represents significant differences (p < 0.05) when compared to controls.
Figure 6.
(a) Effects of varying RT doses with and without BLM-PCI on spheroids, 0-15 Gy. (b) Effects of light radiance levels from BLM-PCI with and without RT, 0-1.68 J/cm2. The average volumes of spheroids after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Figure 6.
(a) Effects of varying RT doses with and without BLM-PCI on spheroids, 0-15 Gy. (b) Effects of light radiance levels from BLM-PCI with and without RT, 0-1.68 J/cm2. The average volumes of spheroids after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation.
Figure 7.
Effects of delay between BLMFG-PCI and RT. Spheroids received RT immediately after BLMFG-PCI or 24 hours post BLMFG-PCI. Data points represent the average volumes of spheroids after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation and * represents significant differences (p < 0.05) when compared to the controls.
Figure 7.
Effects of delay between BLMFG-PCI and RT. Spheroids received RT immediately after BLMFG-PCI or 24 hours post BLMFG-PCI. Data points represent the average volumes of spheroids after 14 days in culture, represented as a % of the non-treatment control spheroid volumes. Error bars indicate standard deviation and * represents significant differences (p < 0.05) when compared to the controls.
Figure 8.
Light and RT administration to residual tumor cells in tumor resection cavity. (a) Residual tumor cells in tumor resection cavity; (b) Resection cavity implanted with FG loaded with BLM/photosensitizer; (c) BLM/ photosensitizer released from FG diffuses into tumor sites; (d) Administration of RT by external beam and light by an implanted fiber optic catheter in the tumor resection cavity.
Figure 8.
Light and RT administration to residual tumor cells in tumor resection cavity. (a) Residual tumor cells in tumor resection cavity; (b) Resection cavity implanted with FG loaded with BLM/photosensitizer; (c) BLM/ photosensitizer released from FG diffuses into tumor sites; (d) Administration of RT by external beam and light by an implanted fiber optic catheter in the tumor resection cavity.
Table 1.
Synergistic effect of BLM-PCI and RT.
Table 1.
Synergistic effect of BLM-PCI and RT.
| BLM |
Radiation |
| 6 Gy |
8 Gy |
10 Gy |
| Free BLM |
1.05±0.11 |
1.07±0.12 |
1.04±0.14 |
| Free BLM-PCI |
1.2±0.14 |
4.9±0.30 |
5.6±0.36 |
| FGBLM
|
1.15±0.12 |
1.46±0.11 |
1.3±0.25 |
| FGBLM -PCI |
1.85±0.14 |
5.0±0.39 |
4.9±0.29 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).