Submitted:
15 November 2024
Posted:
19 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
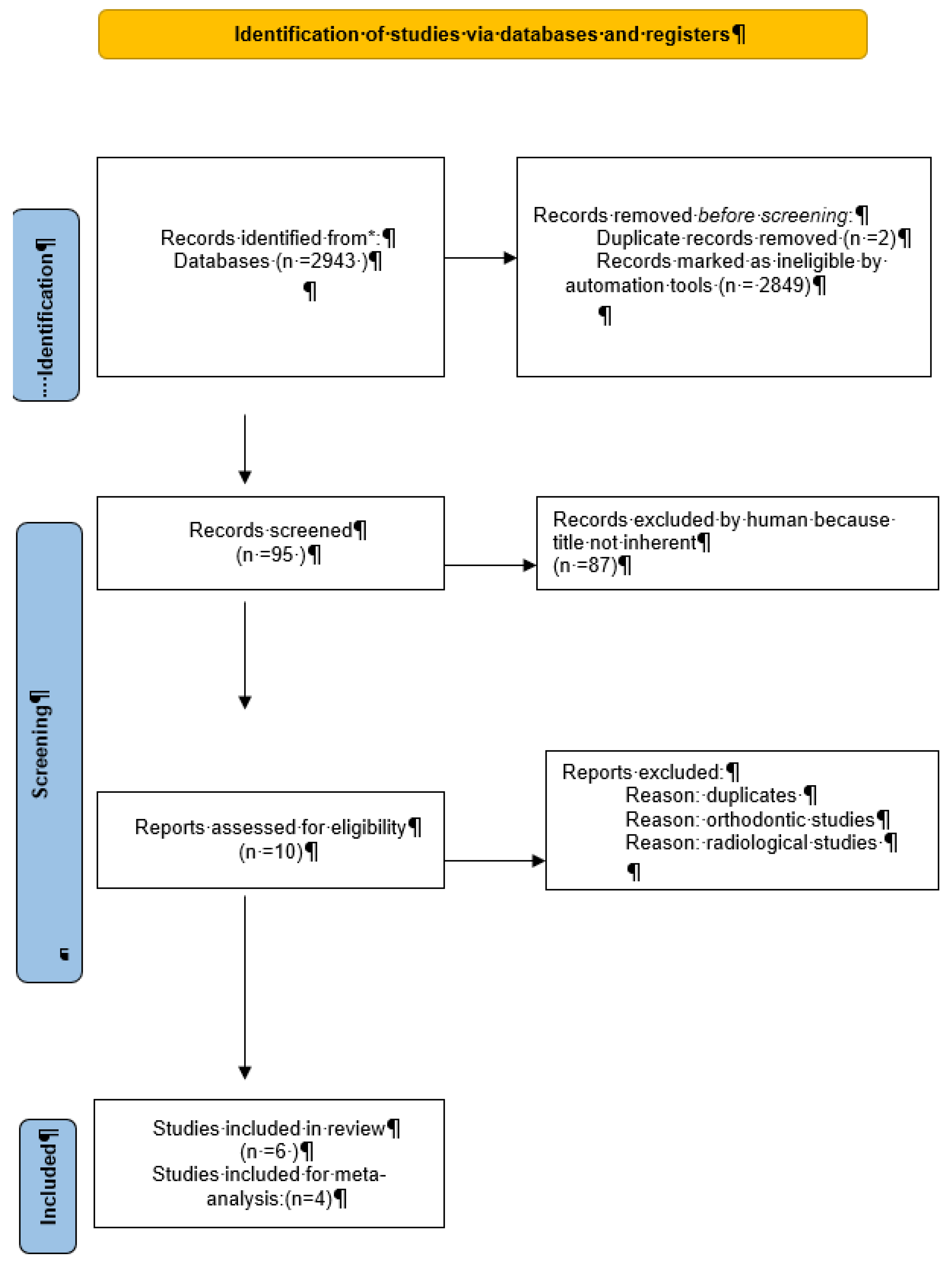
2.1. Study Selection:
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Ethical Approval
Informed Consent
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renton, T., & Al-Haboubi, M. (2012). What has been the United Kingdom's experience with retention of third molars? Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 70(9), S48-S57. [CrossRef]
- Liversedge, R. L. (2000). The removal of wisdom teeth: NICE guidelines. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 38(4), 350-353. [CrossRef]
- Berge, T. I. (1996). Complications associated with removal of impacted third molars: a prospective study of 4338 cases. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica, 54(5), 281-286. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes MJ, Ogden GR, Pitts NB, Ogston SA, Ruta DA.”Actuarial life-table analysis of lower impacted wisdom teeth in general dental practice.” Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2010 Feb;38(1):58-67. [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. (2000). Guidance on the Extraction of Wisdom Teeth. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta1.
- Shepherd, J. P., & Brickley, M. (1994). Surgical removal of third molars. BMJ, 309(6955), 620-621. [CrossRef]
- Song, F., O'Meara, S., Wilson, P., Golder, S., Kleijnen, J. (2000). The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of prophylactic removal of wisdom teeth. Health Technology Assessment, 4(15). Available from: https://www.journalslibrary.nihr.ac.uk/hta/hta4150.
- Celikoglu M, Miloglu O, Kazanci F.” Frequency of agenesis, impaction, angulation, and related pathologic changes of third molar teeth in orthodontic patients.” J Oral MaxillofacSurg. 2010 May;68(5):990-5. [CrossRef]
- McArdle, L. W., & Renton, T. F. (2012). The effects of NICE guidelines on the management of third molar teeth. British Dental Journal, 213(5), 231-236. [CrossRef]
- American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons (AAOMS). (2016). Management of Third Molar Teeth. White Paper on Third Molar Data. Available from: https://www.aaoms.org.
- Chiapasco Matteo, Manuale Illustrato di Chirurgia Orale, Edra Masson terza edizione 2013.
- Pitros P, Jackson I, O'Connor N. ”Coronectomy: a retrospective outcome study.” Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Dec;23(4):453-458. [CrossRef]
- Vignudelli E, Monaco G, Antonella Gatto MR, Costi T, Marchetti C, Corinaldesi G. ”Stability of Periodontal Healing Distal to the Mandibular Second Molar After Third Molar Coronectomy: A 3-Year Follow-Up Study.” J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Feb;77(2):254-261. [CrossRef]
- Baykul, T., Saglam, A. A., Aydin, U., & Basak, K. (2005). Incidence of cystic changes in radiologically normal impacted lower third molar follicles. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology, 99(5), 542-545. [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, D., Gider, Y., Ozer, I., & Ozan, B. (2007). Pathologic changes in soft tissues associated with asymptomatic impacted third molars. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontology, 103(1), 36-42. [CrossRef]
- Celikoglu, M., Miloglu, O., & Kazanci, F. (2010). Frequency of agenesis, impaction, angular positions, and related pathologic changes of third molar teeth in orthodontic patients. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 68(5), 990-995. [CrossRef]
- Göksel, S., Salcıoğlu, Z., & Saruhan, N. (2011). The prevalence of pathologies related to impacted third molars among Turkish patients. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 40(10), 1245-1250. [CrossRef]
- Ryalat, S., Alawneh, T. N., & Hassona, Y. (2018). Impaction of lower third molars and their association with age: radiological perspectives. BMC Oral Health, 18(1), 58. [CrossRef]
- Naraya, A. S., Sharma, S., & Kumar, P. (2023). Evaluation of the incidence of complications related to impacted third molars: A cross-sectional study. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 17(3), ZC12-ZC16. [CrossRef]
- Alberto Enrico Maraolo,” Una bussola per le revisioni sistematiche: la versione italiana della nuova edizione del PRISMA statement “, Unità Operativa Complessa di Malattie Infettive a Indirizzo Neurologico – AORN dei Colli, Ospedale Cotugno – Napoli, Medici Oggi, Anno XXV, anno 2021.
- Yamaoka, DDS, PhD* Akihiro Tambo, DDS† Kiyofumi Furusawa, DDS, “Incidence of inflammation in completely impacted lower third molars.” Minoru PhDAustralian Dental Journal 1997;42:(3):153-5.
- Simşek-Kaya G, Özbek E, Kalkan Y, Yapici G, Dayi E, Demirci T.”Soft tissue pathosis associated with asymptomatic impacted lower third molars.” Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011 Nov 1;16(7):e929-36. [CrossRef]
- Gülsün Yildirim 1, Hanife Ataoğlu, Ahmet Mihmanli, Dilek Kiziloğlu, Mustafa Cihat Avunduk,”Pathologic changes in soft tissues associated with asymptomatic impacted third molars”Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008 Jul;106(1):14-8. [CrossRef]
- Kugelberg Carl F., Ulf Ahlstr JM, Sune E. and Anders H.,“Periodontal healing after impacted lower third molar surgery. A retrospective study” Departments of Oral Surgery, Dental Radiology and Periodontology, the Institute for Postgraduate Dental Education, Jdnkoping, Sweden, Int. J. Oral Surg. 1985: 14: 29-40.
- Saravana a,∗, Krishnaraj Subhashraj b a, ”Cystic changes in dental follicle associated with radiographically normal impacted mandibular third molar G.H.L. “Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, KGF College of Dental Science, Karnataka, India b Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Pondicherry, India Accepted 11 February 2008.
- John Adelsperger, DDS,a John H. Campbell, DDS, MS,b David B. Coates, DDS,c Don-John Summerlin, DMD, MS,d and Charles E. Tomich, DDS, MSD,”Early soft tissue pathosis associated with impacted third molars without pericoronal radiolucency “, Indianapolis, Ind INDIANA UNIVERSITY, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2000;89:402-6.
- Kan KW, Liu JKS, Lo ECM, Corbet EF, Leung WK, Residual periodontal defects distal to the mandibular second molar 6–36months after impacted third molar extraction. A retrospective cross-sectional study of young adults. J Clin Periodontol 2002; 29: 1004–1011. CBlackwell Munksgaard, 2002.
| Study | Pts | Third molars | Age, mean | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baykul et al. 2005 | 94 | 94 | 21,1 | 30 | 64 |
| Yilidirim et al. 2007 | 115 | 120 | 24,74 | 38 | 77 |
| Celikoglu et al.2010 | 351 | 444 | 22,8 | 153 | 198 |
| Goksel et al. 2011 | 50 | 50 | 21,0 | 22 | 28 |
| Ryalat et al. 2018 | 1198 | 1810 | 566 | 632 | |
| Naraya et al. 2023 | 355 | 414 | 22,4 | 167 | 247 |
| Study | Third molars | Mesioangular | Horizontal | Vertical | Distoangular |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baykul et al. 2005 | 94 | 57 (60.6) | 22 (23.4) | 12 (12.8) | 3 (3.2) |
| Yilidirim et al. 2007 | 120 | 44 (36.7) | 14 (11.7) | 58 (48.3) | 4 (3.3) |
| Celikoglu et al.2010 | 444 | 222 (50.0) | 36 (8.1) | 135 (30.4) | 51 (11.5) |
| Goksel et al. 2011 | 50 | 17 (34.0) | 8 (16.0) | 18 (36.0) | 7 (14.0) |
| Ryalat et al. 2018 | 1810 | 1196 (66.1) | 273 (15.1) | 340 (18.8) | |
| Naraya et al. 2023 | 414 | 344 (83.1) | 126 30.4) | 249 (60.1) 39 (9.4) | |
| Pathologic changes | |||||
| Baykul et al. 2005 | 94 | 22 (38.6) | 14 (63.6) | 9 (75.0) | |
| Yilidirim et al. 2007 | 120 | 13 (29.5) | 3 (21.4) | 12 (20.7) | |
| Celikoglu et al.2010 | 444 | 18 (8.1) | 20 (55.6) | 4 (3.0) | 4 (7.8) |
| Goksel et al. 2011 | 50 | 2 (11.8) | 1 (12.5) | 1 (5.6) | 1 (14.3) |
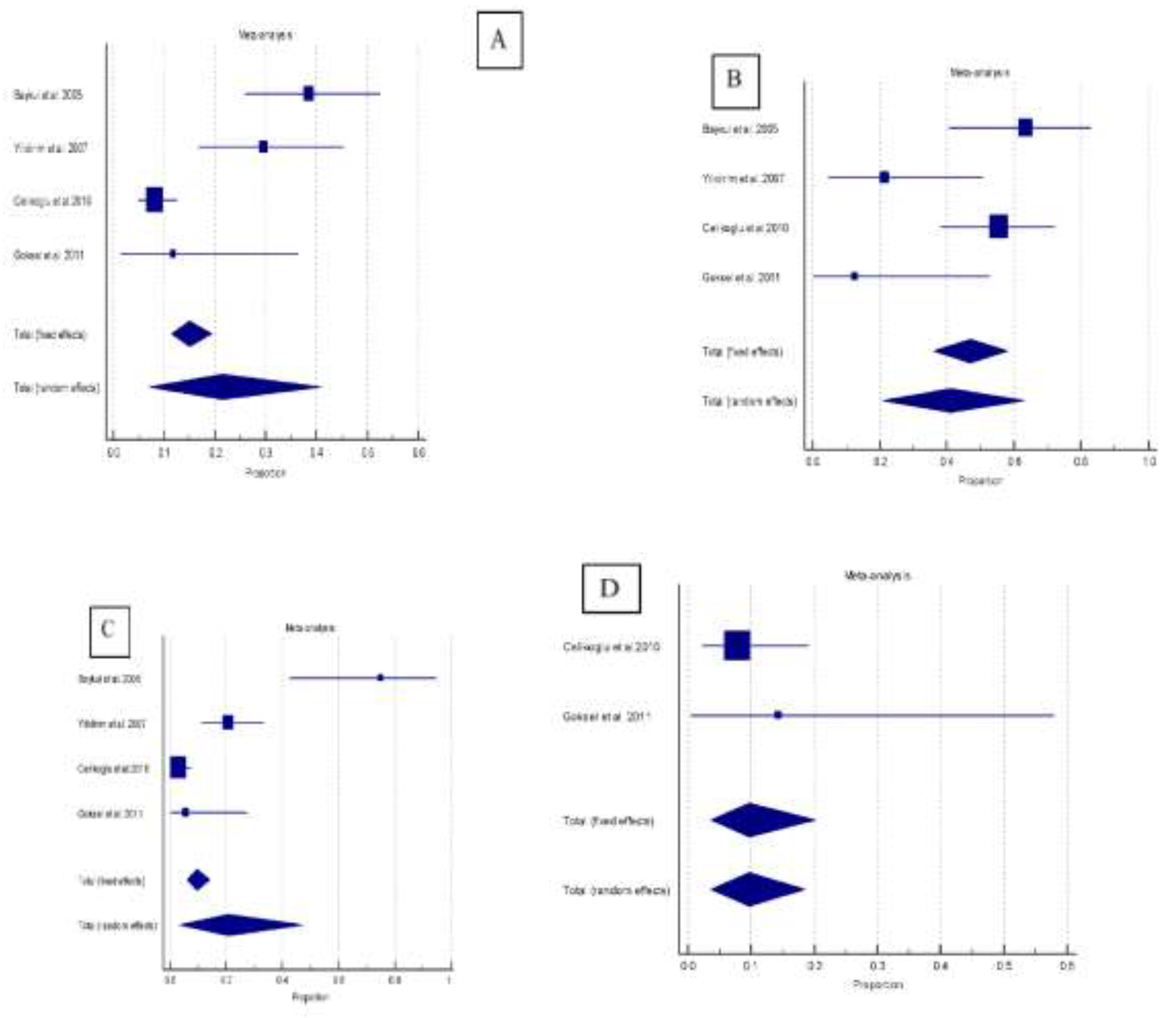
| Sample size | n. event | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathologic changes | ||||
| Mesioangular | 340 | 55 | 21.4 | 7.0 to 40.9 |
| Horizontal | 80 | 38 | 41.1 | 20.9 to 63.0 |
| Vertical | 223 | 26 | 20.7 | 3.4 to 47.4 |
| Distoangular | 58 | 5 | 9.7 | 3.6 to 18.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





