Submitted:
20 November 2024
Posted:
21 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
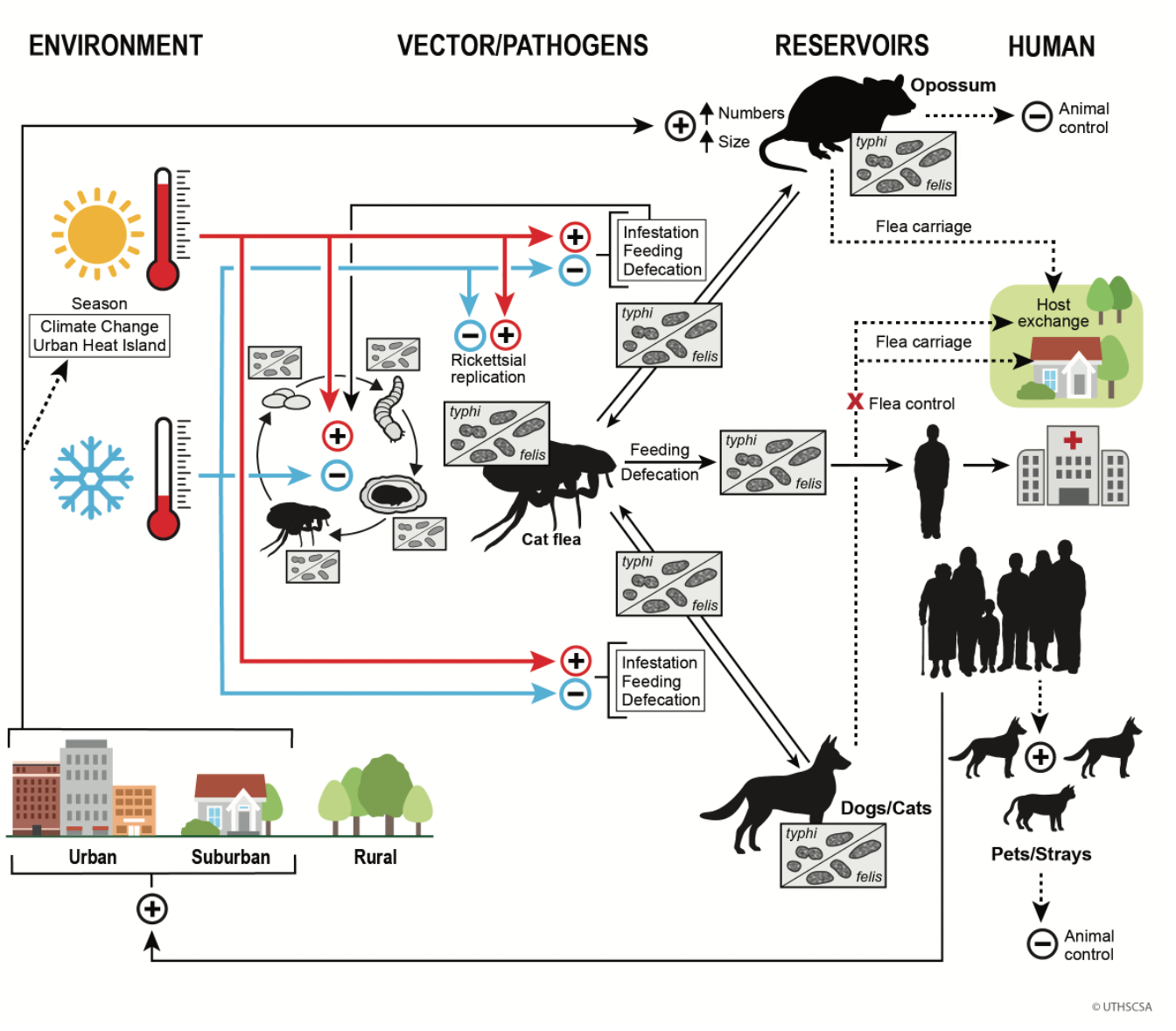
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Historical Epidemiology of Flea-Borne Typhus in Texas, 1923-1999
4. Typhus in Texas in the New Millenium: the 2003-2013 Texas DSHS Study
5. Building a One Health Model. The Epidemiology of Typhus in Texas, 2010-2019
6. The Rickettsiae
6.1. Rickettsia typhi
6.2. Rickettsia felis
7. The Cat Flea and Its Many Hosts
8. Flea-Borne Typhus and Climate Change: General Considerations
9. The Urban Heat Island Effect in Texas
10. The Cat Flea Life History and the Effects of Temperature and Humidity: General Aspects
10.1. Host Seeking and Infestation
10.2. Mating and Oviposition
10.3. Egg Hatching and Larval Development
10.4. The Temperature-Driven Infestation--> Feeding--> Reproduction--> Larval Trophic Cascade
10.5. Pupation and Pupa to Adult Eclosion
10.6. Overall Temperature Effects on the Cat Flea Life Cycle
11. Endosymbionts of the Cat Flea
12. The One Health Model of Flea-borne Typhus Epidemiology in Texas in the Early 21st Century
13. Limitations of the Data
14. Research Questions About FBT in Texas
- #1 What is the magnitude of the stray and feral cat and dogs problem in the high FBT incidence areas of TX and their degree of flea infestation over the course of a year?
- #2 How do the numbers of opossums, dogs, and cats and strays relate to increases in human cases in individual counties?
- #3 What is the net effect of climate change on the flea life cycle (is the decrease in life cycle duration countervailed by the decrease in adult flea life span)?
- #4 Are changes in temperature, rainfall, and relative humidity associated with increased human cases in specific locales?
- #5 What endosymbiotic organisms (Wolbachia pipientis and Steinina ctenocephali) occur within the flea vectors in Texas and how they affect flea survival and infection with R. felis and R. typhi?
- #6 What is the impact of co-infection of R. felis/R. typhi and Bartonella sp. on flea survival and vectorial capacity?
- #7 Are R. felis and R. typhi still co-circulating in TX? Do they vary geographically and by season?
15. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Dedication
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsioutis, C.; Zafeiri, M.; Avramopoulos, A.; Prousali, E.; Miligkos, M.; Karageorgos, S.A. Clinical and laboratory characteristics, epidemiology, and outcomes of murine typhus: a systematic review. Acta Trop. 2017, 166, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chueng, T.; Koch, K.; Anstead, G.M.; Dayton, C. Case report: early doxycycline therapy for potential rickettsiosis in critically ill patients in flea-borne typhus endemic areas. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 101, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, A.F. Epidemiology of murine typhus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1990, 35, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Rickettsia felis, an emerging flea-borne rickettsiosis, Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas Department of Health Services. Flea-borne Typhus Cases in Texas by County Reported, 2008-Available online:. Available online: https://www.dshs.texas.gov/IDCU/disease/typhus/Typhus-2008-2019.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2022).
- Anstead, G.M. History, rats, fleas, and opossums. II. The decline and resurgence of flea-borne typhus in the United States, 1945. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- California Dept of Public Health, Dept of Public Health Vector-Borne Disease Section. “Human Flea-Borne Typhus Cases in California (2001-2019),” Sacramento, California, USA, Available online:. Available online: https://www.CDPH.ca.gov/Programs/CID/DCDC/CDPH%20Document%20Library/Flea-borneTyphusCaseCounts.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2019).
- Texas Department of Health. Murine Typhus. Infectious Diseases Epidemiology and Surveillance Division, Austin, TX, USA, May 2001.
- Sleeman, J.M.; DeLiberto, T.; Nguyen, N. Optimization of human, animal, and environmental health by using the One Health approach. J. Vet. Sci. 2017, 18, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, A.N.; Fogarty, C.; Krueger, L.; Macaluso, K.R.; Odhiambo, A.; Nguyen, K.; Farris, C.M.; Luce-Fedrow, A.; Bennett, S.; Jiang, J.; et al. Rickettsial infections among Ctenocephalides felis and host animals during a flea-borne rickettsioses outbreak in Orange County, California. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0160604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prism Climate Group. Northwest Alliance for Computational Science and Engineering. Available online: https://prism.oregonstate.edu/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Yomogida, K.; Kjemtrup, A.; Martínez-López, B.; Ibrahim, M.; Contreras, Z.; Ngo, V.; Halai, U.A.; Balter, S.; Feaster, M.; Zahn, M.; et al. Surveillance of flea-borne typhus in California, 2011-Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2023, 110, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeno, F.H.; Lasco, T.; Ahmed, A.A.; Al Mohajer, M. Characteristics of Rickettsia typhi infections detected with next-generation sequencing of microbial cell-free deoxyribonucleic acid in a tertiary care hospital. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, J.; Sanosyan, A.; Contreras, Z.A.; Ngo, V.P.; Carpenter, A.; Hacker, J.K.; Probert, W.S.; Terashita, D.; Balter, S.; Halai, U.A. Fleaborne Typhus-Associated Deaths—Los Angeles County, California, MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2023, 72, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas Department of State Health Services. Flea-borne Typhus. Available online: https://www.dshs.texas.gov/notifiable-conditions/zoonosis-control/zoonosis-control-diseases-and-conditions/flea-borne-typhus (accessed on 5 November 2024).
- Tabachnick, W.J. Challenges in predicting climate and environmental effects on vector-borne disease episystems in a changing world. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohls, S.W. Typhus fever in Texas. South. Med. J. 1935, 28, 1162–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langley, B.C. Peanut culture. Texas State Historical Association. Available online: https://www.tshaonline.org/home/ (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Wooster, R. East Texas in World War II. East Texas Hist. J. 2007, 45, Iss–2. Available online: https://scholarworks.sfasu.edu/ethj/vol45/iss2/9 (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- Reece, C.D. Typhus fever in Texas. Texas State J. Med., 1934, 30, 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.E.; Pollard, M. The distribution of murine typhus in rats and humans in San Antonio. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1946, 26, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstead, G.M. History, rats, fleas, and opossums: the ascendency of flea-borne typhus in the United States, 1910. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, R.H.; Ogden, L.J. A survey to determine the prevalence and distribution of typhus in rats in Texas. CDC Bull. 1951, 10, 53. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/55659 (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Irons, J.V.; Cox, G.W. An epidemiological investigation of typhus fever in Texas, 1943. Texas State J. Med. 1946, 42, 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, G.H.; Wiley, J.S. The control of murine typhus in the United States. In Rickettsial Diseases of Man; Moulton, F.R., Ed.; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 1948; pp. 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Boostrom, A.; Beier, M.S.; Macaluso, J.A.; Macaluso, K.R.; Sprenger, D.; Hayes, J.; Radulovic, S.; Azad, A.F. Geographic association of Rickettsia felis-infected opossums with human murine typhus, Texas. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Older, J.J. The epidemiology of murine typhus in Texas. JAMA 1970, 14, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.P.; Betz, T.G.; Rawlings, J.A. Epidemiology of murine typhus in Texas, 1980. JAMA 1986, 255, 2173–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Texas Water Development Board. Water for Texas Jan Austin, TX. Available online: https://www.twdb.texas.gov/publications/state_water_plan/2012/04.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2024).
- Murray, K.O.; Evert, N.; Mayes, B.; Fonken, E.; Erickson, T.; Garcia, M.N.; Sidwa, T. Typhus group rickettsiosis, Texas, USA, 2003-Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rural Health Information Hub. Texas. Available online: https://www.ruralhealthinfo.org/states/texas (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Research Division of the Texas Legislative Council. Definitions of “Rural” in Texas Statutes and the Texas Administrative Code as of April Texas Legislative Council P.O. Box 12128 Austin, Texas 78711. Available online: https://tlc.texas.gov/docs/policy/Def_Rural_Statutes.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2021).
- Eremeeva, M.E.; Warachina, W.R.; Sturgeon, M.M.; Buchholz, A.E.; Olmsted, G.K.; Park, S.Y.; Effler, P.V.; Karpathy, S.E. Rickettsia typhi and R. felis in rat fleas (Xenopsylla cheopis), Oahu, Hawaii. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1613–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdman, R.A.; Ingraham, C. Where cats are more popular than dogs in the U.S.—and all over the world. Washington Post, July 28, 2014.
- Bergman, D.L.; Breck, S.W.; Bender, S.C. Dogs gone wild: feral dog damage in the United States. Proc. 13th Wildlife Damage Management Conf. (J.R. Boulanger, Ed.) 2009, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chasnoff, B. Collaring the problem of stray dogs. San Antonio Express-News Sep 19. Available online: https://www.mysanantonio.com/news/local_news/article/Collaring-the-problem-of-stray-dogs-845675.php (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Slater, M.R. The welfare of feral cats. In: Rochlitz, I. (ed), The Welfare of Cats. Dordrecht: Springer, pp. 141–176, 2005.
- Levy, J.K.; Crawford, P.C. Humane strategies for controlling feral cat populations, J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 225, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.O.; Good, N.E.; Schubert, J.H. Status of murine typhus infection in domestic rats in the United States, 1952, and relation to infestation by Oriental rat fleas. Am. J. Public Health, 1953, 43, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.O. Entomological background of the distribution of murine typhus and murine plague in the United States. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1951, 31, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskey, C.R.; Hemphill, F.M. Relation of reported cases of typhus fever to location, temperature, and precipitation. Public Health Rep. 1948, 63, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.B.; Schmidly, D.J. The mammals of Texas, University of Texas Press, Austin, TX, USA, 1994.
- Buttery, C.M.; Magnuson, L.W.; McLerran, G.; Villarreal, T. Endemic (murine) typhus in Corpus Christi. Tex. Med. 1984, 80, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Statista. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/432924/us-metropolitan-areas-with-the-highest-poverty-rate/ (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Yao, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhan, F.B. Detection of arbitrarily-shaped clusters using a neighbor-expanding approach: a case study on murine typhus in south Texas. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2011, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassell, J.M.; Begon, M.; Ward, M.K.; Fèvre, E.M. Urbanization and disease emergence: dynamics at the wildlife–livestock–human interface. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolhouse, M.E.J. Population biology of emerging and re-emerging pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2002, 10, S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoGiudice, K.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Schmidt, K.A.; Keesing, F. The ecology of infectious disease: effects of host diversity and community composition on Lyme disease risk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2003, 100, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keesing, F.; Holt, R.D.; Ostfeld, R.S. Effects of species diversity on disease risk. Ecol. Lett 2006, 9, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, N.J.; Seddon, J.M.; Šlapeta, J.; Wells, K. Parasite spread at the domestic animal—wildlife interface: anthropogenic habitat use, phylogeny and body mass drive risk of cat and dog flea (Ctenocephalides spp.) infestation in wild mammals. Parasit. Vectors, 2018, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salje, J. Cells within cells: Rickettsiales and the obligate intracellular bacterial lifestyle. Nature Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.R.; Schmidtmann, E.T.; Azad, A.F. Infection of colonized cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché), with a Rickettsia-like microorganism. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1990, 43, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggers, R.J.; Martin, M.C.; Bouyer, D. Rickettsia felis infection rates in an East Texas population. Tex. Med. 2005, 101, 56–58. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, R.; Krueger, L.; Nguyen, K.; Rangel, D.; Penicks, A.; Sims, J. Challenges of responding to flea-borne typhus cases: lessons learned after 15 years of investigations in Orange County. Proc. Mosquito Vector Control Assoc. Calif. 2022, 90, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hurd, H. Manipulation of medically important insect vectors by their parasites. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, K.F.; Rood, M.P.; Krueger, L.; Eremeeva, M.E. Urban focus of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia felis in Los Angeles, California. Vector-Borne Zoonot. Dis. 2011, 11, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedincamp, J., Jr.; Foil, L.D. Vertical transmission of Rickettsia felis in the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis Bouche). J. Vector Ecol. 2002, 27, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirunkanokpun, S.; Thepparit, C.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Horizontal transmission of Rickettsia felis between cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis. Molec. Ecol. 2011, 20, 4577–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morick, D.; Krasnov, B.R.; Khoklova, I.S.; Gutierrez, R.; Fielden, L.J.; Gottlieb, Y.; Harrus, S. Effects of Bartonella spp. on flea feeding and reproductive performance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 3438–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.F.; Sacci, J.B., Jr.; Nelson, W.M.; Dasch, G.A.; Schmidtmann, E.T.; Carl, M. Genetic characterization and transovarial transmission of a typhus-like rickettsia found in cat fleas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1992, 89, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.A.; Sacci, J.B.; Schriefer, M.E.; Endris, R.G.; Azad, A.F. Molecular identification of Rickettsia-like microorganisms associated with colonized cat fleas (Ctenocephalides felis). Insect Mol. Biol. 1994, 3, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-H.; Hsu, M.-S.; Shu, P.-Y.; Tsai, K.-H.; Fang, C.-T. Neglected human Rickettsia felis infection in Taiwan: a retrospective seroepidemiological survey of patients with suspected rickettsiosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, K.E.; Kearney, M.T.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Acquisition of Rickettsia felis by cat fleas during feeding. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, K.P.; Macaluso, K.R. Rickettsia felis: a review of transmission mechanisms of an emerging pathogen. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, S.P.; Brown, L.D.; Hagstrom, M.R.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Transmission effect of Rickettsia felis strain variation on infection, transmission, and fitness in the cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub, R.; Wisseman, C.L.; Fahrang-Azad, A. The ecology of murine typhus, a critical review. Trop. Dis. Bull. 1978, 75, 237–317. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, J.A.; Azad, A.F. Acquisition of murine typhus rickettsiae by fleas. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 590, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, A.F.; Radulovic, S.; Higgins, J.A.; Noden, B.H.; Troyer, J.M. Flea-borne rickettsiosis: ecologic considerations. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, R.J.; Gage, K.L. Transmission of flea-borne zoonotic agents. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2012, 57, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedincamp, J., Jr.; Foil, L.D. Infection and seroconversion of cats exposed to cat fleas (Ctenocephalides felis Bouche) infected with Rickettsia felis. J. Vector Ecol. 2000, 25, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Reif, K.E.; Macaluso, K.B. Ecology of Rickettsia felis: a review. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaluso, K.R.; Pornwiroon, W.; Popov, V.L.; Foil, L.D. Identification of Rickettsia felis in the salivary glands of cat fleas. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2008, 8, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepparit, C.; Hirunkanokpun, S.; Popov, V.L.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Dissemination of bloodmeal acquired Rickettsia felis in cat fleas. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 24, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.D.; Banajee, K.H.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Transmission mechanisms of an emerging insect-borne rickettsial pathogen. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.F.; Traub, R. Experimental transmission of murine typhus by Xenopsylla cheopis flea bites. Med. Vet. Entomol. 1989, 3, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueras, M.M.; Pons, I.; Ortuño, A.; Miret, J.; Pla, J.; Castellá, J.; Segura, F. Molecular detection of Rickettsia typhi in cats and fleas. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eremeeva, M.E.; Karpathy, S.E.; Krueger, L.; Hayes, E.K.; Williams, A.M.; Zaldivar, Y.; Bennett, S.; Cummings, R.; Tilzer, A.; Velten, R.K.; et al. Two pathogens and one disease: detection and identification of flea-borne Rickettsiae in areas endemic for murine typhus in California. J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noden, B.H.; Radulovic, S.; Higgins, J.A.; Azad, A.F. Molecular identification of Rickettsia typhi and R. felis in co-infected Ctenocephalides felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1998, 35, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaluso, K.R.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Cerual, S.M.; Azad, A.F. Rickettsial infection in Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae) inhibits transovarial transmission of a second Rickettsia. J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitam, I.; Dittmar, K.; Parola, P.; Whiting, M.F. Fleas and flea-borne diseases, Internat. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e667–e676. [Google Scholar]
- De Sousa, R.; Edouard-Fournier, P.; Santos-Silva, M.; Amaro, F.; Bacellar, F.; Raoult, D. Molecular detection of Rickettsia felis, Rickettsia typhi and two genotypes closely related to Bartonella elizabethae. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Osorio, C.E.; Zavala-Velázquez, J.E.; Arias León, J.; Zavala-Castro, J.E. Rickettsia felis as emergent global threat for humans. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, A.L.; Jiang, J.; Omulo, S.; Dare, R.; Abdirahman, K.; Ali, A.; Sharif, S.K.; Feikin, D.R.; Breiman, R.F.; Njenda, M.K. Human infection with Rickettsia felis, Kenya. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, C.L.; Krueger, L.; Nguyen, K.; Velten, R.; Bennett, S.; Sun, S.; Cummings, R. Development of an ELISA for determining the presence of rickettsial antibodies in the Virginia opossum, Didelphis virginiana. Proc. Mosquito Vect. Control Assoc. Calif. 2013, 81, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Cleaveland, S.; Laurenson, M.K.; Taylor, L.H. Diseases of humans and their domestic mammals: pathogen characteristics, host range and the risk of emergence. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2001, 356, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, D.; Brinkley, C.; Humphrey, P.T.; Kemps, B.D.; Ostfeld, R.S. It takes a community to raise the prevalence of a zoonotic pathogen. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2011, 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.A.; Kramer, A.M.; Drake, J.M. Global patterns of zoonotic disease in mammals. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolhouse, M.E.J.; Taylor, L.H.; Haydon, D.T. Population biology of multi-host pathogens. Science 2001, 292, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billeter, S.A.; Metzger, M.E. Limited evidence for Rickettsia felis as a cause of zoonotic flea-borne rickettsiosis in Southern California. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, E.; Mediannikov, O.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Rickettsia felis: the complex journey of a emergent human pathogen. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, L.S.; Walker, D.H. Flea-borne rickettsioses and Rickettsiae. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediannikov, O.; Fenollar, F.; Bassene, H.; Tall, A.; Sokhna, C.; Trape, J.F.; Raoult, D. Description of “yaaf”, the vesicular fever caused by acute Rickettsia felis infection in Senegal. J. Infect. 2013, 66, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P. Rickettsia felis: from a rare disease in the USA to a common cause of fever in sub-Saharan Africa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schriefer, M.E.; Sacci, J.B., Jr.; Dumler, J.S.; Bullen, M.G.; Azad, A.F. Identification of a novel rickettsial infection in a patient diagnosed with murine typhus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 949–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peniche Lara, G.; Dzul-Rosado, K.R.; Zavala Velazquez, J.E.; Zavala-Castro, J. Murine typhus: clinical and epidemiological aspects. Colomb. Med. (Cali) 2012, 43, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo-Colín, V.; Sánchez-Montes, S.; Salceda-Sánchez, B.; Huerta-Jiménez, H.; Alcántara-Rodríguez, V.; Becker, I.; Gual-Sill, F.; López-Pérez, A.M. Urban foci of murine typhus involving cat fleas (Ctenocephalides felis felis) collected from opossums in Mexico City. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merhej, V.; Angelakis, E.; Socolovschi, C.; Raoult, D. Genotyping, evolution and epidemiological findings of Rickettsia species. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 25, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, H.; Renesto, P.; Audic, S.; Robert, C.; Blanc, G.; Fournier, P.E.; Parinello, H.; Claverie, J.M.; Raoult, D. The genome sequence of Rickettsia felis identifies the first putative conjugative plasmid in an obligate intracellular parasite. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schriefer, M.E.; Sacci, J.B. Jr; Taylor, J.P.; Higgins, J.A.; Azad, A.F. Murine typhus: updated roles of multiple urban components and a second typhus like rickettsia. J. Med. Entomol. 1994, 31, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, A.F.; Sacci, J.B., Jr.; Nelson, W.M.; Dasch, G.A.; Schmidtmann, E.T.; Carl, M. Genetic characterization and transovarial transmission of a typhus-like rickettsia found in cat fleas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1992, 89, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, K.F.; Wekesa, J.W.; Nwadike, C.N.; Zambrano, M.L.; Karpathy, S.E.; Cecil, D.; Burns, J.; Hu, R.; Eremeeva, E. Rickettsia felis in cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis parasitizing opossums, San Bernardino County, California. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2012, 26, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukaitis, H.J.; Macaluso, K.R. Unpacking the intricacies of Rickettsia-vector interactions. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Kim, L.; Li, Y.; Ferris, K.; Maggi, R.; Lashnits, E. The association of host and vector characteristics with Ctenocephalides felis pathogen and endosymbiont infection. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1137059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irons, J.V.; Bohls, S.W.; Thurman, D.C.; McGregor, T. Probable role of the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis, in transmission of murine typhus. Am. J. Trop. Med. 1944, 24, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.H.; Emmons, R.W.; Brooks, J.E. The changing ecology of murine (endemic) typhus in southern California. Am. J. Trop Med. Hyg. 1970, 19, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traub, R. The coevolution of fleas and mammals. Pp. 295-437 in Kim, K.C. (ed). Coevolution of parasitic arthropods and mammals, Wiley, NY, USA, 1985.
- Krasnov, B.R. Functional and evolutionary ecology of fleas: a model for ecological parasitology, Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA, 2008.
- Yiguan, W.; Jie, T.; Qiyong, L.; Cannan, S.; Wenlong, K.; Henglu, D.; Cheng, X.; Wenzhu, Z.; Fajun, C.; Fengxia, M. Influence of bloodmeal host on blood feeding, egg production, and offspring sex ratio of Ctenocephalides felis felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakely, BN.; Agnew, J.; Gard, C.; Romero, A. Effects of blood meal source on blood consumption and reproductive success of cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, E0011233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rust, M.K.; Dryden, M.W. The biology, ecology, and management of the cat flea. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1997, 42, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penicks, A.; Krueger, L.; Campbell, J.; Fogarty, C.; Rangel, D.; Nguyen, K.; Cummings, R. Flea abundance, species composition, and prevalence of rickettsiosis, from urban wildlife in Orange County, California, 2015-Proc. Vertebr. Pest Conf. 2020, 29, e7. [Google Scholar]
- Penicks, A.; Krueger, L.; Morgan, T.; Nguyen, K.; Campbell, J.; Fogarty, C.; Bennett, S.; Cummings, R. Jumping into the future: an analysis of 50 years of flea data from mammalian wildlife collected during three flea-borne rickettsioses surveys in Orange County, 1967-Proc. Calif. Mosquito Vector Control Assoc. 2019, 87, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Gage, K.; Kosoy, M. Natural history of plague: perspectives from more than a century of research. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2005, 50, 505–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.G. The sex ratio in ectoparasitic insects. Ecol. Entomol. 1981, 6, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryden, M.W.; Gaafar, S.M. Blood consumption by the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1991, 28, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M.K. The biology and ecology of cat fleas and advancements in their pest management: a review. Insects 2017, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, R.; Musella, V.; Descalzo, M.A.; Montoya, A.; Checa, T.R.; Marino, V.; Martín, O.; Cringoli, G.; Rinaldi, L.; Miró, G. Modelling the current distribution and predicted spread of the flea species Ctenocephalides felis infesting outdoor dogs in Spain. Parasit. Vectors, 2017, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Mescht, L.; le Roux, P.C.; Matthee, C.A.; Raath, M.J.; Mattee, S. The influence of life history characteristics on flea (Siphonaptera) species distribution models. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gettinger, D.; Ernest, K.A. Small-mammal community structure and the specificity of ectoparasite associations in central Brazil. Rev. Bras. Biol. 1995, 55, 331–341. [Google Scholar]
- Molyneux, D.H. Climate change and tropical disease: common themes in changing vector-borne disease scenarios. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 97, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.F.; Beard, C.B. Rickettsial pathogens and their arthropod vectors. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1998, 4, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, H.C.; Ahmad, N.W.; Lim, L.H.; Jeffrey, J.; Hadi, A.A.; Othman, H.; Omar, B. Infestation with the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) among students in Kuala Lumper, Malaysia. Southeast Asian, J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2010, 41, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Leelavathi, M.; Norhayati, M.; Lee, Y.Y. Cat flea infestation in a hospital: a case report. Korean J. Parasitol. 2012, 50, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjemian, J.; Parks, S.; McElroy, K.; Campbell, J.; Eremeeva, M.E.; Nicholson, W.L.; McQuiston, J.; Taylor, J. Murine typhus in Austin, Texas, USA, Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chala, B.; Hamde, F. Emerging and re-emerging vector-borne infectious diseases and the challenges for control: a review. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 715759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Centers for Environmental Information. State climate summaries Texas. Available online: https://statesummaries.ncics.org/chapter/tx/ (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- Xie, H.; Chang, N.-B.; Daranpob, A.; Prado, D. Assessing the long-term urban heat island in San Antonio, Texas based on moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer/Aqua data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 043508–10.1117. [Google Scholar]
- Gage, K.L.; Burkot, T.R.; Eisen, R.J.; Hayes, E.B. Climate and vectorborne diseases. Am. J. Prevent. Med. 2008, 35, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostfeld, R.S. Climate change and the distribution and intensity of infectious diseases. Ecology 2009, 90, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R. Effects of climate and climate change on vectors and vector-borne diseases: ticks are different. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, H.E.; Beckmann, B.C.; Comont, R.F.; Hails, R.S.; Harrington, R.; Medlock, J.; Purse, B.; Shortall, C.R. Nuisance insects and climate change. Department Environ, Food Rural Affairs; London, UK. Available online: https://nora.nerc.ac.uk./id/eprint/8332/ (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Bernabeu-Wittel, M.; Pachón, J.; Alarcón, A.; López-Cortés, L.F.; Viciana, P.; Jiménez-Mejías, M.E.; Villanueva, J.L.; Torronteras, R.; Caballero-Granado, F.J. Murine typhus as a common cause of fever of intermediate duration: a 17-year study in the south of Spain. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.G.; Sacci, J.B., Jr.; Schriefer, M.E.; Andersen, E.M.; Fujioka, K.K.; Sorvillo, F.J.; Barr, A.R.; Azad, A.F. Typhus and typhus like rickettsiae associated with opossums and their fleas in Los Angeles County, California. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, Y.L.; Chen, H.F.; Chang, M.C.; Yen, T.Y.; Su, C.L.; Chiu, H.C.; Hu, H.C.; Chung, Y.T.; Shu, P.Y.; Yang, S.L. Epidemiology of murine typhus in Taiwan from 2013 to Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 110, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, S.; McGarry, J.; Noble, P.M.; Pinchbeck, G.J.; Cantwell, S.; Radford, A.D.; Singleton, D.A. Seasonality and other risk factors for fleas infestations in domestic dogs and cats. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2023, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, W.; Boch, K.; Mackensen, H.; Wiegand, B.; Pfister, K. Qualitative and quantitative observations on the flea population dynamics of dogs and cats in several areas of Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.O.; Morlan, H.B. The nature of parasitism of the opossum by fleas in southwestern Georgia. J. Parasitol. 1959, 45, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.; Parker, D.M.; Bulterys, P.L.; Rattanavong, S.; Elliott, I.; Phommasone, K.; Mayxay, M.; Chansamouth, V.; Robinson, M.T.; Blacksell, S.D.; et al. A spatio-temporal analysis of scrub typhus and murine typhus in Laos; implications from changing landscapes and climate. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Chen, Y.H.; Lee, N.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Tsai, J.J.; Lu, P.L.; Chen, T.C.; Hsieh, H.C.; Lin, W.R.; et al. Murine typhus in southern Taiwan during 1992-Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, G.H.; Adelman, Z.N.; Myles, K.M. Temperature-dependent effects on the replication and transmission of arthropod-borne viruses in their insect hosts. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2016, 16, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhold, J.M.; Lazzari, C.R.; Lahondère, C. Effects of the environmental temperature on Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes: a review. Insects 2018, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhang-Azad, A.; Traub, R.; Sofi, M.; Wisseman, C.L., Jr. Experimental murine typhus infection in the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1984, 21, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Global Change Research Program. Available online: https://www.globalchange.gov/our-work/third-national-climate-assessment (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Pham, H.V.; Dang, D.T.; Tran Minh, N.N.; Nguyen, N.D.; Nguyen, T.V. Correlates of environmental factors and human plague: an ecological study in Vietnam. Internat. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 38, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crkvencic, N.; Šlapeta, J. Climate change models predict southerly shift of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis) distribution in Australia. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. The energetic basis of the urban heat-island. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.; Zhang, P.; Wolfe, R.E.; Bounoua, L. Remote sensing of the urban heat island effect across biomes in the continental USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Cai, M. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on climate. Nature 2003, 423, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winguth, A.M.E.; Kelp, B. The urban heat island of the North-Central Texas region and its relation to the 2011 severe Texas drought. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 2418–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.M. A geospatial analysis of the urban heat island effect in Austin, TX. Honors Thesis, Texas State University, San Marcos, TX. Available online: https://digital.library.txst.edu/items/d91efa55-c340-4007-865a-59085cb1c82d (accessed on 27 October 2024).
- Zhang, X. The footprint of urban climates on vegetation phenology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, M.J.; Calvete, C.; Estrada, R.; Castillo, J.A.; Peribanez, M.A.; Lucientes, L. Fleas parasitizing domestic dogs in Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 151, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xhaxhiu, D.; Kusi, I.; Rapti, D.; Visser, M.; Knaus, M.; Lindner, T.; Rehbein, S.; Rehbein, S. Ectoparasites of dogs and cats in Albania. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durden, L.A.; Judy, T.N.; Martin, J.E.; Spedding, L.S. Fleas parasitizing domestic dogs in Georgia, USA: species composition and seasonal abundance. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 130, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, L.; Spera, G.; Musella, V.; Carbone, S.; Veneziano, V.; Iori, A.; Cringoli, G. A survey of fleas on dogs in southern Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, D. Some aspects of the ecology of the Virginia Opossum (Didelphis virginiana virginiana Kerr 1792) in an urban environment. Masters Thesis. Portland State University, Portland, OR, USA. [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Valdivia, E.; Cruz-Vazquez, C.; Ortiz-Martínez, R.; Valdivia-Flores, A.; Quintero-Martínez, M.T. Presence of Ctenocephalides canis (Curtis) and Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché) infesting dogs in the city of Aguascalientes, México. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, O.M. The fleas (Siphonoptera) of Egypt: distribution and seasonal dynamics of fleas infesting dogs in the Nile Valley. J. Med. Entomol. 1966, 3, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Vazquez, C.; Castro Gamez, E.; Parada Fernandez, M.; Ramos Parra, M. Seasonal occurrence of Ctenocephalides felis felis and Ctenocephalides canis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) infesting dogs and cats in an urban area in Cuernavaca, Mexico. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Imani, A.; Ahmadiara, E.; Javadi, S.; Hadian, M. Survey of flea infestation in dogs in different geographical regions of Iran. Korean J. Parasitol. 2010, 48, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osbrink, W.L.A.; Rust, M.K. Fecundity and longevity of the adult cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1984, 21, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akucewich, L.H.; Philman, K.; Clark, A.; Gillespie, J.; Kunkle, G.; Nicklin, C.F.; Greiner, E.C. Prevalence of ectoparasites in a population of feral cats from north central Florida during the summer. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 109, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlapeta, J.; King, J.; McDonell, D.; Malik, R.; Homer, D.; Hannan, P.; Emery, D. The cat flea (Ctenocephalides f. felis) is the dominant flea on domestic dogs and cats in Australian veterinary practices. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 180, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, R.; Gyurkovszky, M.; Solymosi, N.; Beugnet, F. Prevalence of flea infestation in dogs and cats in Hungary combined with a survey of owner awareness. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2009, 23, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franc, M.; Bouhsira, É.; Beugnet, F. Direct transmission of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis) between cats exhibiting social behaviour. Parasite 2013, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.-H.; Wu, W.-J. Off-host observations of mating and postmating behaviors in the cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, S.R.; Meola, R.W. Factors influencing sperm transfer and insemination in cat fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) fed on an artificial membrane system. J. Med. Entomol. 2002, 39, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, B.A.; Koehler, P.G.; Patterson, R.S. Effect of larval diet on cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) developmental times and adult emergence. J. Econ. Entomol. 1991, 84, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhlova, I.S.; Serobyan, V.; Degen, AA.; Krasnov, B.R. Host gender and offspring quality in a flea parasitic on a rodent. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3299–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.J.; Ammerman, N.C.; Beier-Sexton, M.; Sobral, B.S.; Azad, A.F. Louse- and flea-borne rickettsioses: biological and genomic analyses. Vet. Res. 2009, 40, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, W.H., Jr.; Richman, D.L.; Koehler, P.G.; Brenner, R.J. Outdoor survival and development of immature cat fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) in Florida. J. Med. Entomol. 1999, 36, 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, M.H.; Wu, W.J. Effects of multiple mating on female reproductive output in the cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2000, 37, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakson-Aiken, M.; Gregory, L.M.; Shoop, W.L. Reproductive strategies of the cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae): parthenogenesis and autogeny? J. Med. Entomol. 1996, 33, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, M.E.; Rust, M.K. Egg production and emergence of adult cat fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) exposed to different photoperiods. J. Med. Entomol. 1996, 33, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiefer, D.; Warburton, E.M.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Krasnov, B.R. Reproductive consequences of female size in haematophagous ectoparasites. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.H.; Mackinnon, M.J.; Read, A.F. Virulence of mixed-clone and single-clone infections of rodent malaria Plasmodium chabaudi. Evolution 1998, 52, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, N.C. “Fleas.” World Health Organization: Public Health Significance of Urban Pests. (Eds. X. Bonnefoy, H. Kampen, and K. Sweeney). WHO European Centre for Environment and Health, Bonn, Germany, 2008.
- Krasnov, B.R.; Khokhlova, I.S.; Fielden, L.J.; Burdelova, N.V. Development rates of two Xenopsylla flea species in relation to air temperature and humidity. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2001, 15, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, W.; Stickel, M. Interhost migration behavior of Ctenocephalides felis on cats and in their resting sites. Wien Klin. Wochenschr. 2008, 120, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.; Rust, M.K.; Reierson, D.A. Influence of temperature and humidity on survival and development of the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1981, 18, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryden, M.W.; Rust, M.K. The cat flea: biology, ecology and control. Vet. Parasitol. 1994, 52, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.; Rust, M.K. Some abiotic factors affecting the survival of the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). Environ. Entomol. 1983, 12, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, S.; Novak, L. The most and least humid cities in the U.S. (Aug 14, 2023). Available online: https://todayshomeowner.com/moving/guides/most-and-least-humid-cities/ (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Metzger, M.E.; Rust, M.K. Effect of temperature on cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) development and overwintering. J. Med. Entomol. 1997, 34, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, F.; Mencke, N. Flea Biology and Control, Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany, 2001.
- Silverman, J.; Rust, M.K. Extended longevity of the pre-emerged adult cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) and factors stimulating emergence from the pupal cocoon. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, M.E.; Jara-F.A., *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Briones, R.C.; Dubey, A.K.; Slamovits, C.H. Gregarine infection accelerates larval development of the cat flea Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché). Parasitology.
- Alarcón, M.E.; Huang, C.G.; Dubey, A.K.; Benítez, H. A gregarine from the gut of cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché) (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) in Taiwan: dynamic of infection patterns. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 192, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hague, M.T.J.; Caldwell, C.N.; Cooper, B.S. Pervasive effects of Wolbachia on host temperature preference. mBio 2020, 11, 10.1128–mbio.0176820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornwiroon, W.; Kearney, M.T.; Husseneder, C.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Comparative microbiota of Rickettsia felis-uninfected and -infected colonized cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis. ISME J. 2007, 1, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.T. Wolbachia endosymbionts, Rickettsia felis and Bartonella species, in Ctenocephalides felis fleas in a tropical region. J. Vector Ecol. 2013, 38, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hague, M.T.J.; Shropshire, J.D.; Caldwell, C.N.; Statz, J.P.; Stanek, K.A.; Conner, W.R.; Cooper, B.S. Temperature effects on cellular host-microbe interactions explain continent-wide endosymbiont prevalence. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, D.H.; Dumler, J.S. State of the art of diagnosis of rickettsial diseases: the use of blood specimens for diagnosis of scrub typhus, spotted fever group rickettsiosis, and murine typhus. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, T.; Da Silva, J.; Nolan, M.S.; Marquez, L.; Munoz, F.M.; Murray, K.O. Newly recognized pediatric cases of Typhus Group Rickettsiosis, Houston, Texas, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 2068–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

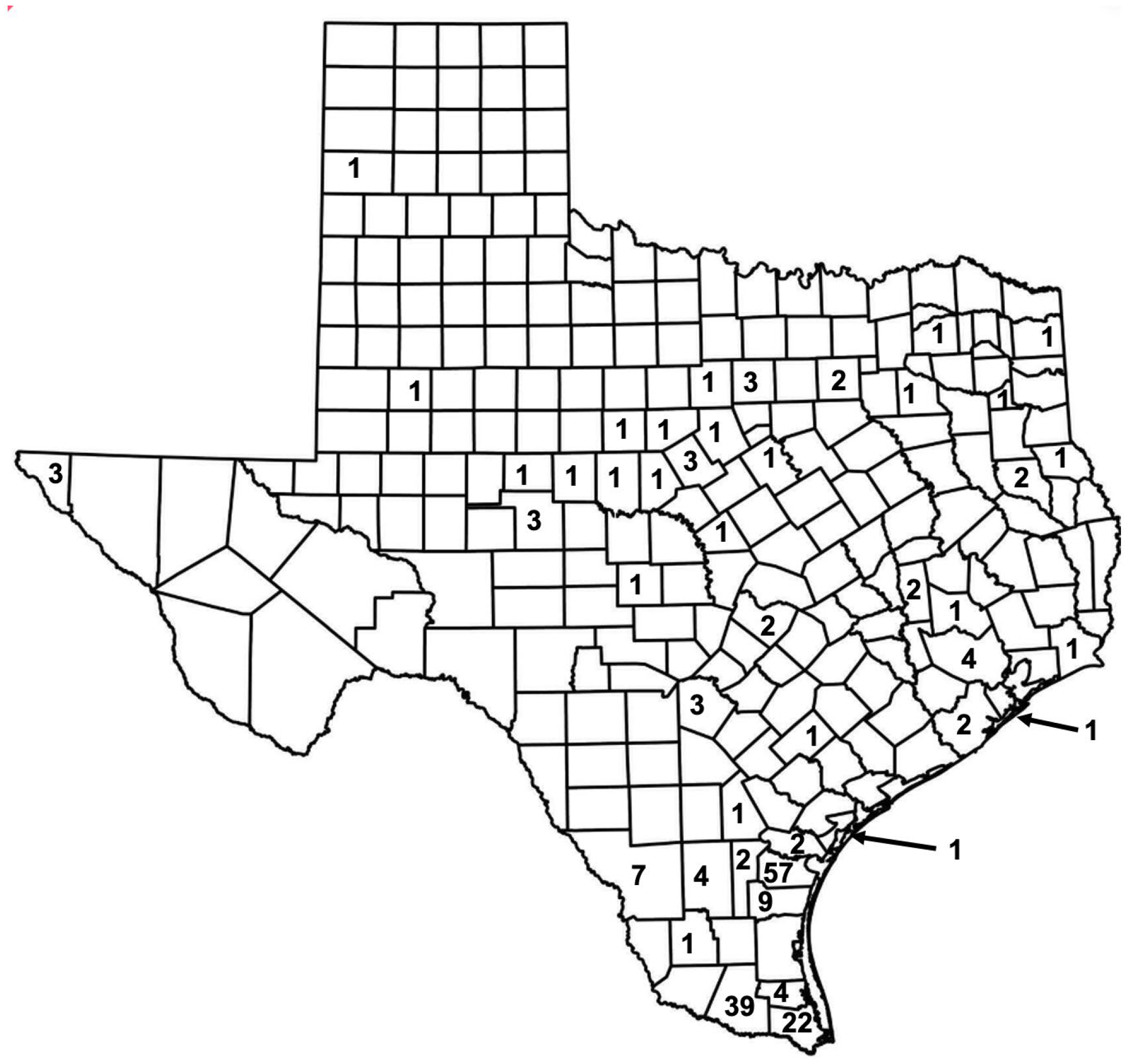
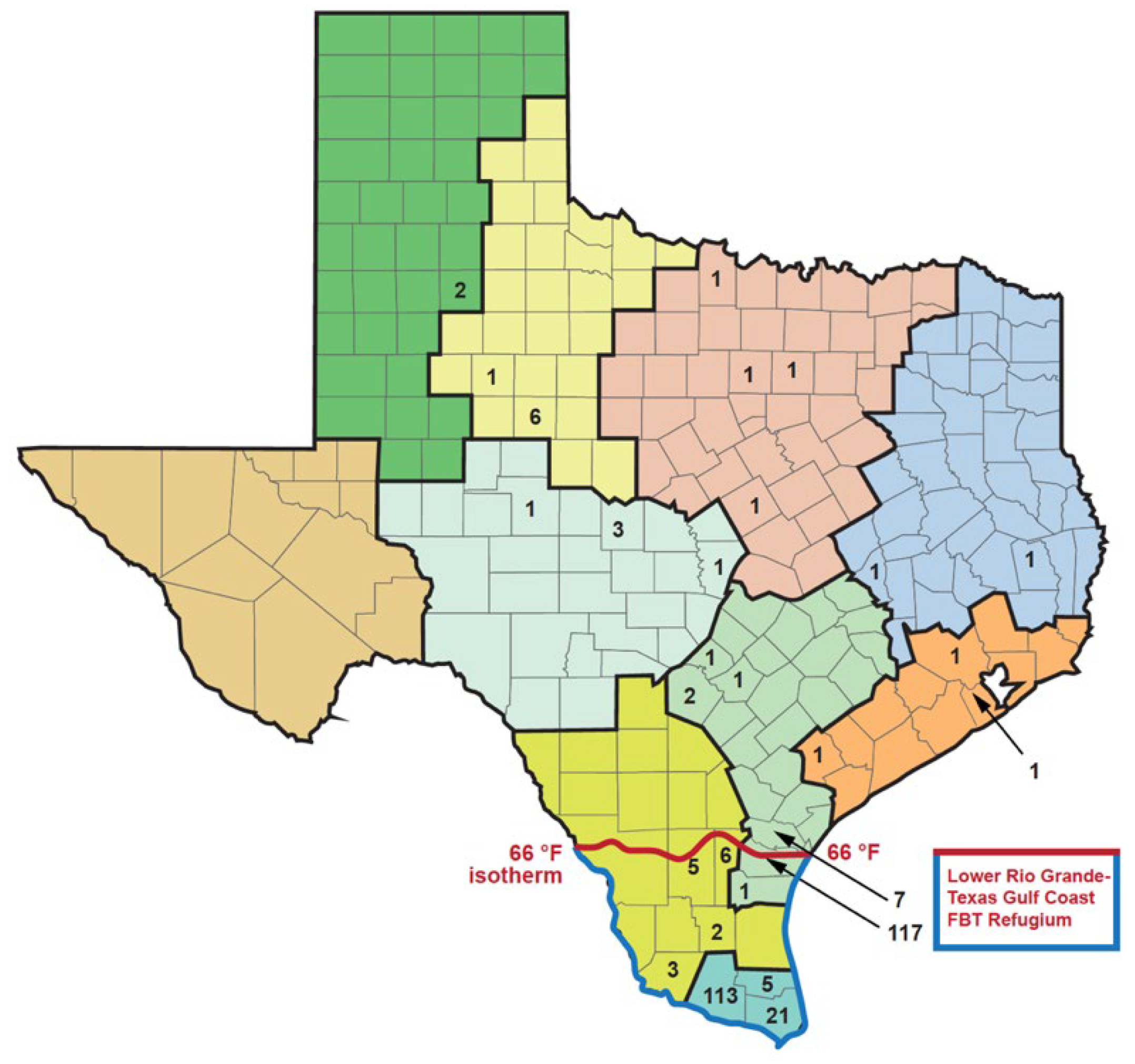
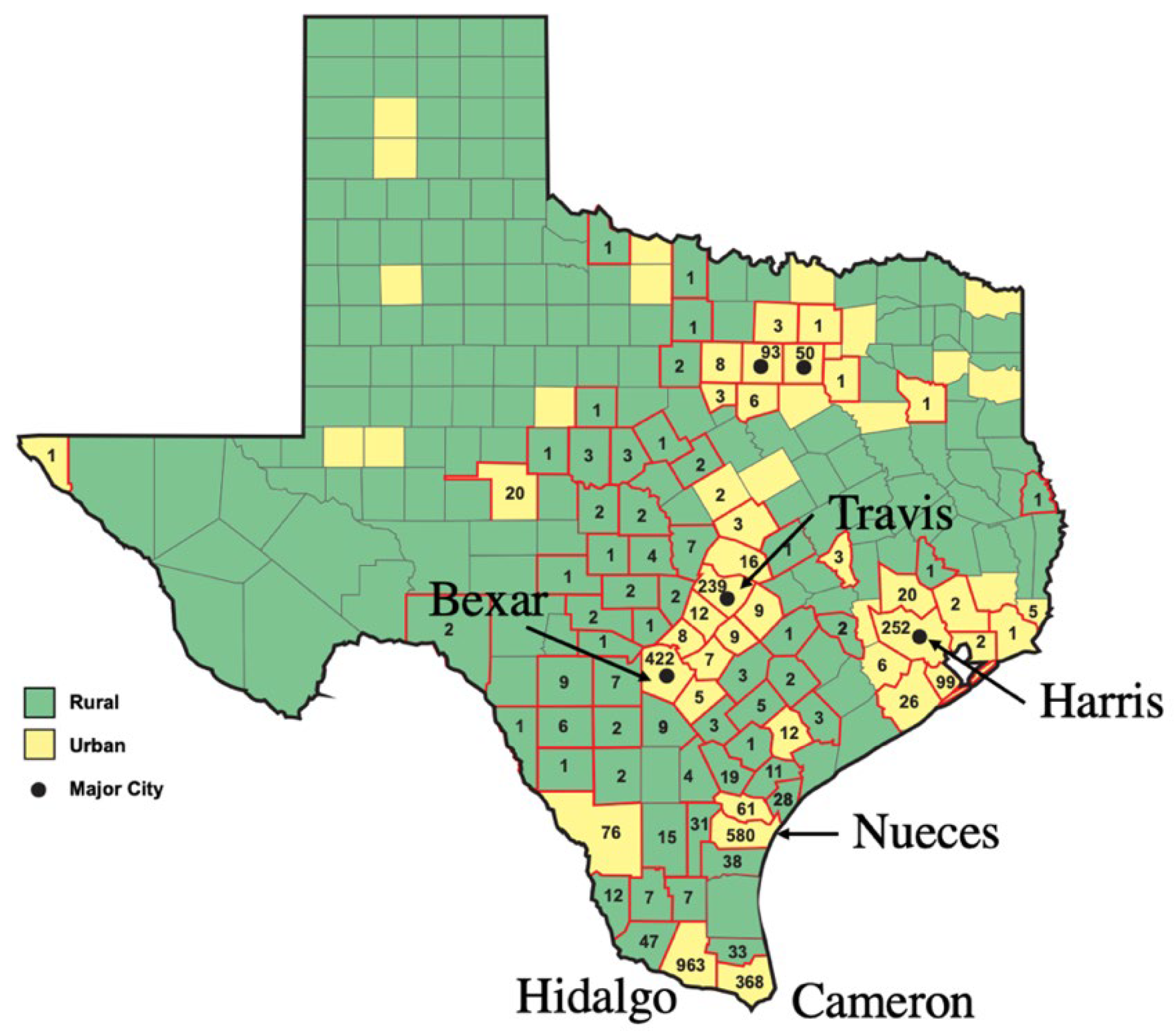
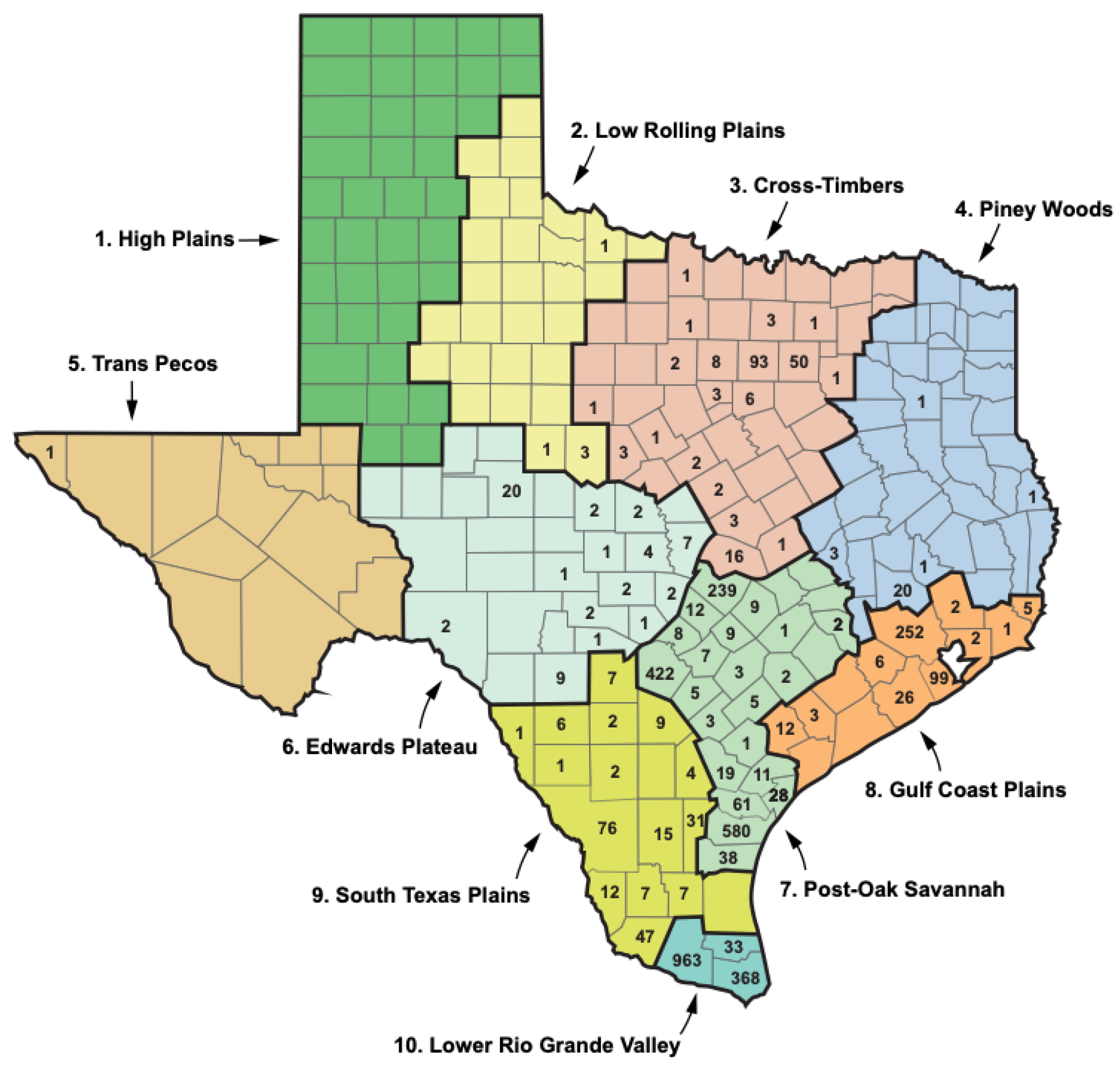
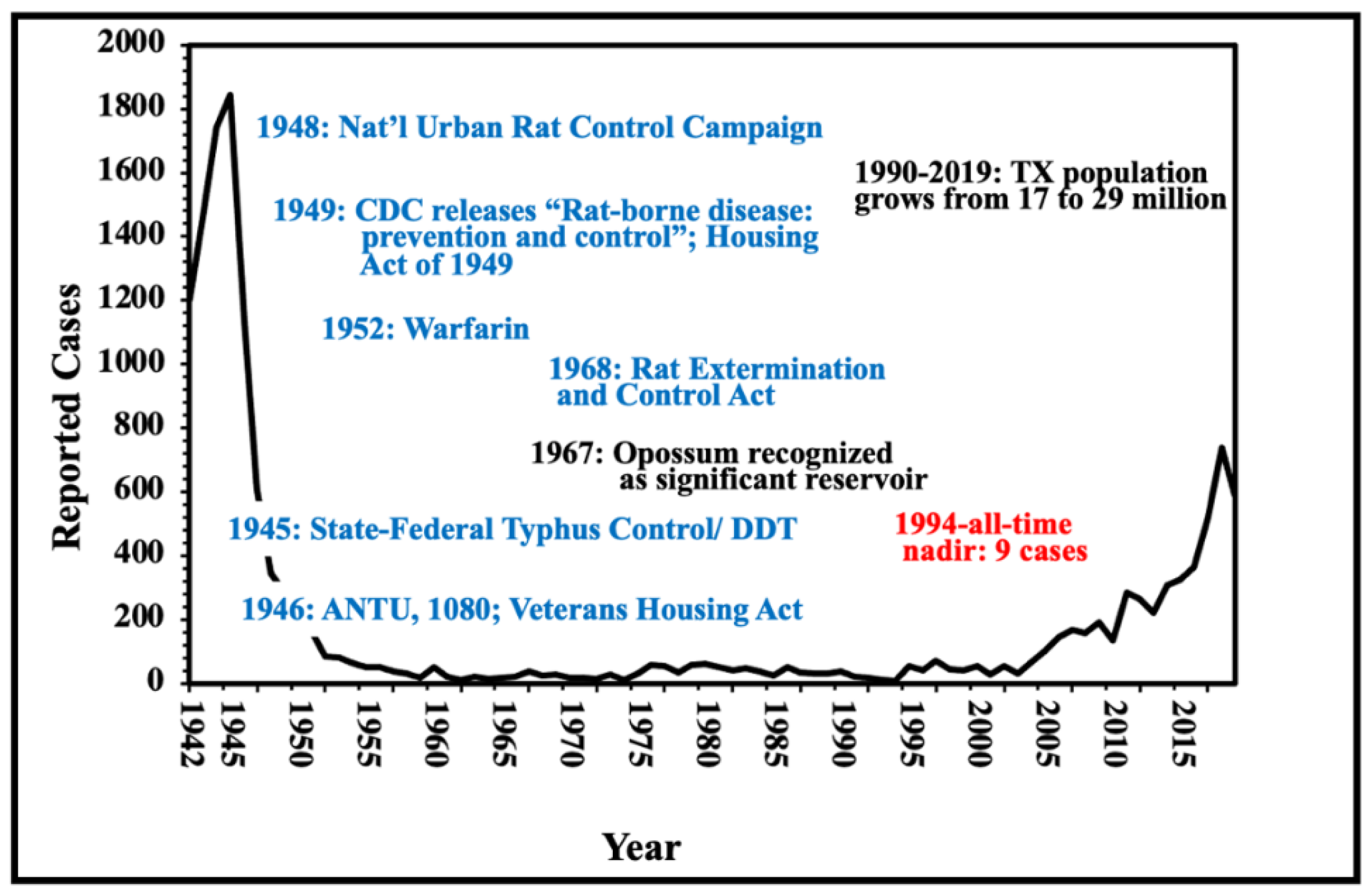
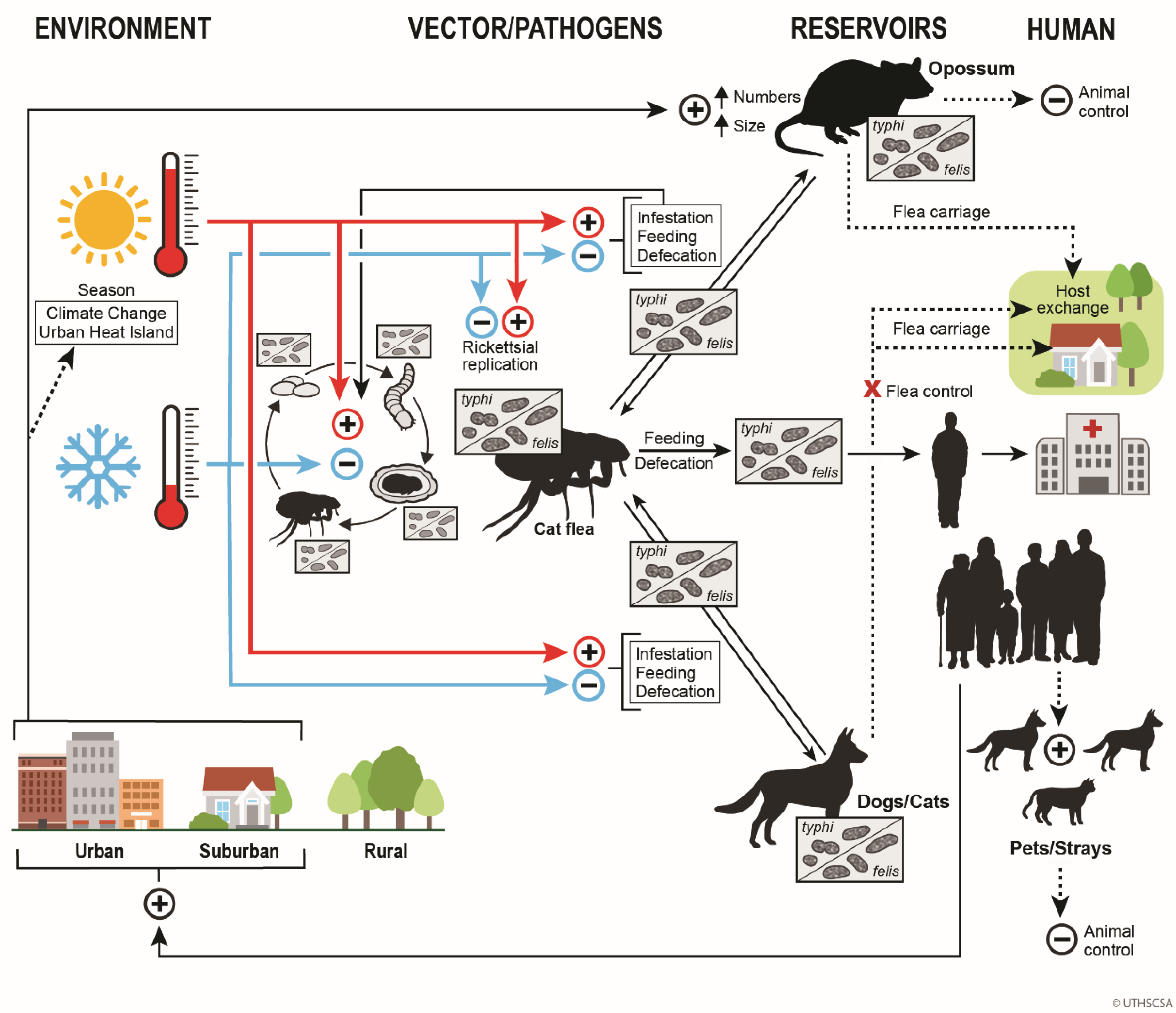
| Abiotic | Biotic | Anthropogenic |
|---|---|---|
| Climate | Abundance of urban exploiter hostsa | Population growth |
| Temperature | Abundance of companion animals | Urbanization/suburbanization |
| Rainfall | Abundance of other wildlife hosts | Agricultural practices |
| Relative humidity | Prevalence of flea endosymbiontsb | Human effects on climate |
| Cat flea clade-Rickettsia compatability | Urban heat island effect | |
| Pet ownership | ||
| Control of urban exploiter hosts | ||
| Flea control: pets/environmental | ||
| Environmental sanitation | ||
| Housing conditions |
| 1990a | 2019 | Percent increase, 1990 to 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Texas | 16,986,510 | 28,995,881 | 70.7 |
|
Metropolitan (% of total) |
14,165,650 (83.4) |
25,920,625 (89.4) |
83.0 |
| non-metro | 2,820,852 | 3,075,261b | 9.0 |
| Bexar | 1,185,394 | 2,004,000 | 67.1 |
| Cameron | 260,120 | 423,163 | 62.7 |
| Harris | 2,833,000 | 4,713,000 | 66.3 |
| Hidalgo | 383,545 | 868,707 | 126 |
| Nueces | 291,145 | 362,294 | 24.4 |
| Travis | 576,407 | 1,274,000 | 121 |
| State or County |
Largest City | total number of cases 2010-2019a |
Avg number of cases/yr, 1990-1999b |
Avg number of cases/yr, 2010-2019a |
Fold increase in avg # of cases, 2010-2019 vs 1990-1999 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Texas | ----- | 3750 | 30.7 | 375.0 | 12.2 |
| Bexar | San Antonio | 422 | 0.2 | 42.2 | 211 |
| Cameron | Brownsville | 368 | 2.1 | 36.8 | 17.5 |
| Harris | Houston | 252 | 0.1 | 25.2 | 252 |
| Hidalgo | McAllen | 963 | 11.3 | 96.3 | 8.5 |
| Nueces | Corpus Christi | 580 | 11.7 | 58.0 | 5.0 |
| Travis | Austin | 239 | 0 | 23.9 | --- |
| County | Avg. Human Pop, 1994/ 1995a |
Est. Pet Dog Pop., 1994/ 1995b |
Est. Stray Dog Pop., 1994/ 1995c |
Est. Total Dog Pop., 1994/ 1995 |
Avg. Human Pop. 2014/ 2015a |
Est. pet dog pop. 2014/ 2015 |
Est. Stray Dog Pop, 2014/ 2015c |
Est. Total Dog Pop, 2014/ 2015 |
Increase in Total Dog Pop. 2014/2015 vs 1994/1995 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bexar | 1,280,000 | 345,600 | 75,294 | 420,894 | 1,876,500 | 506,655 | 110,382 | 617,037 | 196,143 |
| Cameron | 287,204 | 77,545 | 16,894 | 94,439 | 420,705 | 113,590 | 24747 | 138,337 | 43,898 |
| Harris | 3.050,000 | 823,500 | 179,412 | 1,002,912 | 4,506,000 | 1,216,620 | 265059 | 1,481,679 | 478,767 |
| Hidalgo | 468,443 | 126,480 | 27,555 | 154,035 | 868,707 | 234,551 | 51,100 | 285,651 | 131,616 |
| Nueces | 310,079 | 83,721 | 18,240 | 101,961 | 362,294 | 97,819 | 21,311 | 119,130 | 17,169 |
| Travis | 656,303 | 177,202 | 38606 | 215,808 | 1,274,000 | 343,980 | 74,941 | 418,921 | 203,113 |
| County | Avg. Human Pop, 1994/ 1995a |
Est. Pet Cat Pop., 1994/ 1995b |
Est. Stray Cat Pop., 1994/ 1995c |
Est. Total Cat Pop., 1994/ 1995 |
Avg. Human Pop. 2014/ 2015a |
Est. Pet Cat pop. 2014/ 2015 |
Est. Stray Cat Pop, 2014/ 2015c |
Est. Total Cat Pop, 2014/ 2015 |
Increase in Total Cat Pop. 2014/2015 vs 1994/1995 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bexar | 1,280,000 | 268,800 | 107,520 | 376,320 | 1,876,500 | 394,065 | 157,626 | 551,691 | 175,371 |
| Cameron | 287,204 | 60,313 | 24,125 | 84,438 | 420,705 | 88,348 | 35339 | 123,687 | 39,249 |
| Harris | 3.050,000 | 640,500 | 256,000 | 896,500 | 4,506,000 | 946,260 | 378,504 | 1,324,764 | 455,264 |
| Hidalgo | 468,443 | 98,373 | 39,349 | 137,722 | 868,707 | 182,428 | 72,971 | 255,399 | 117,677 |
| Nueces | 310,079 | 65,117 | 26,046 | 91,163 | 362,294 | 76,082 | 30,432 | 106,515 | 15,352 |
| Travis | 656,303 | 137,823 | 55,129 | 192.953 | 1,274,000 | 267,540 | 107,016 | 374556 | 181,603 |
| Region Numbera | Region Name/ Alternate Namea | Descriptionc | Number of FBT Cases, 1990sb | % of Total |
Number of FBT Cases, 2010sc |
% of Total |
Fold-increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | High Plains | Continental steppe or semi-arid savanna | 2 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | Decreased |
| 2 | Low Rolling Plains | Sub-tropical steppe or semi-arid savanna | 7 | 2.3 | 5 | 0.13 | Decreased 0.7 |
| 3 | Cross Timbers/ North Central |
Sub-tropical subhumid mixed savanna, woodlands | 4 | 1.3 | 198 | 5.28 | 49.5 |
| 4 | Piney Woods/ East Texas |
Sub-tropical humid mixed evergreen-deciduous forestland | 2 | 0.7 | 26 | 0.69 | 13 |
| 5 | Trans Pecos | subtropical arid desert | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.027 | ------ |
| 6 | Edwards Plateau | Sub-tropical steppe or semi-arid brushland, savanna | 5 | 1.6 | 56 | 1.49 | 11.2 |
| 7 | Post-Oak Savannah/ South Central |
Sub-tropical subhumid mixed prairie, savanna, woodlands | 129 | 41.3 | 1465 | 39.1 |
11.5 |
| 8 | Gulf Coastal Plains/ Upper Coast |
Sub-tropical humid marine prairies and marshes | 3 | 1.0 | 408 | 10.88 | 136 |
| 9 | South Texas Plains/ Southern | Sub-tropical steppe or semi-arid brushland | 16 | 5.2 | 227 | 6.05 | 14.2 |
| 10 | Lower Rio Grande Valley/ Lower Valley | Subtropical sub-humid marine | 139 | 45.2 | 1364 | 36.37 | 9.8 |
| Totals |
-------- |
------- |
307 |
86.5% in regions 7 and 10 | 3750 | 75.5% in regions 7 and 10 | 12.2 |
| Refugiumd | ------ | ------- | 273 (88.9%) |
2238 (59.7%) | 8.2-X | ||
| Outside Refugium | ------- | -------- | 34 (11.1%) |
1512 (40.3%) |
44.5-X |
| County | Tmin, °F | Tmean, °F | Tmax, °F | ||||||
| 1990s | 2010s | Diff | 1990s | 2010s | Diff | 1990s | 2010s | Diff | |
| Bexar | 58.93 | 59.43 | +0.5 | 69.60 | 70.18 | +0.58 | 80.27 | 80.93 | +0.66 |
| Cameron | 65.25 | 66.2 | +0.95 | 74.23 | 75.18 | +0.95 | 83.19 | 84.13 | +0.94 |
| Harris | 60.59 | 61.9 | +1.31 | 69.80 | 70.86 | +1.06 | 79.04 | 79.8 | +0.76 |
| Hidalgo | 63.98 | 64.61 | +0.63 | 74.73 | 75.51 | +0.78 | 85.46 | 86.37 | +0.91 |
| Nueces | 63.89 | 64.65 | +0.76 | 72.33 | 72.91 | +0.58 | 80.78 | 81.18 | +0.40 |
| Travis | 58.51 | 58.33 | -0.18 | 68.84 | 69.47 | +0.63 | 79.83 | 80.62 | +0.79 |
| Tarrant | 55.67 | 57.72 | + 2.05 | 65.90 | 67.64 | +1.74 | 76.60 | 77.57 | +0.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





