Submitted:
21 November 2024
Posted:
22 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Database Description
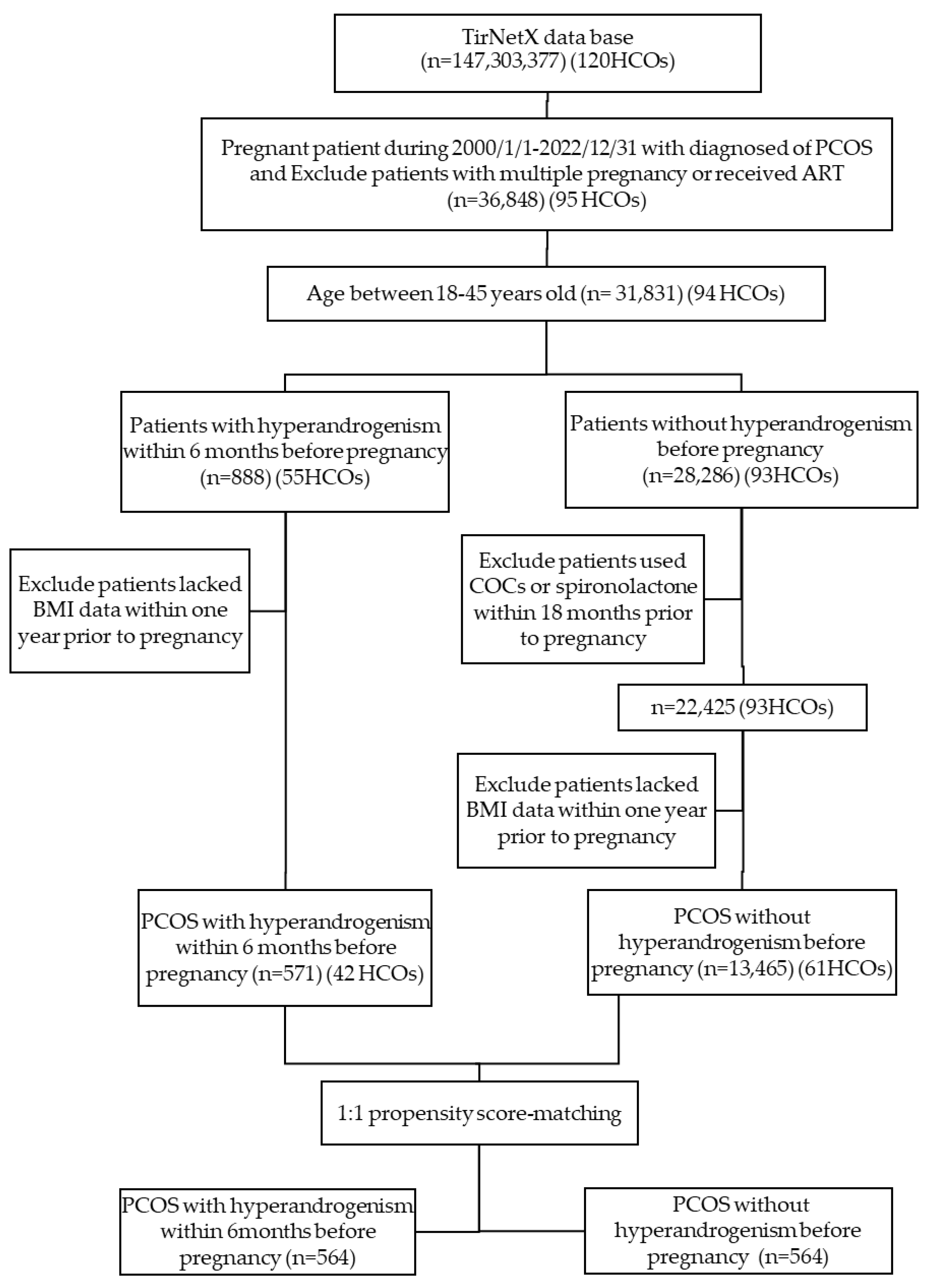
2.2. Study Protocol, and Patient Selection
2.3. Cohort Definitions
2.4. Propensity Score Matching
2.5. Outcome Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
| Variables | Before Matching | P Value | After Matching | P Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCOS with hyperandrogenism (n= 571) | PCOS without hyperandrogenism (n=13,420) | PCOS with hyperandrogenism (n=564) | PCOS without hyperandrogenism (n=564) | |||
| Age, mean (SD), years | 27.4 +/- 4.4 | 29.0 +/- 4.8 | <0.001 | 27.4 +/- 4.4 | 27.4 +/- 4.4 | 0.808 |
| White | 330(58.2) | 8103(60.6) | 0.252 | 329 (58.3) | 351 (62.2) | 0.181 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 13 (2.3) | 799 (6.0) | <0.001 | 13 (2.3) | 10 (1.8) | 0.527 |
| Hypertensive diseases | 42 (7.4) | 1038 (7.8) | 0.756 | 41 (7.3) | 32 (5.7) | 0.276 |
| Ischemic heart diseases | 10 (1.8) | 45 (0.3) | <0.001 | 10 (1.8) | 0 (0) | 0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular diseases | 10 (1.8) | 48 (0.4) | <0.001 | 10 (1.8) | 0 (0) | 0.001 |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 0 (0) | 45 (0.3) | 0.166 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | -- |
| Chronic kidney disease | 0 (0) | 52 (0.4) | 0.137 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | -- |
| Recurrent pregnancy loss | 15 (2.6) | 231 (1.7) | 0.104 | 13 (2.3) | 11 (2.0) | 0.68 |
| Cesarean section | 17 (3.0) | 187 (1.0) | 0.002 | 16 (2.8) | 16 (2.8) | 0 |
| Body mass index, mean (SD), kg/m2 | 31.5 +/- 7.3 | 32.4 +/- 7.8 | 0.016 | 31.5 +/- 7.3 | 31.0 +/- 7.2 | 0.259 |
3.2. Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozdag, G.; Mumusoglu, S.; Zengin, D.; Karabulut, E.; Yildiz, B.O. The prevalence and phenotypic features of polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod 2016, 31, 2841-2855. [CrossRef]
- Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Hum Reprod 2004, 19, 41-47. [CrossRef]
- Bahri Khomami, M.; Joham, A.E.; Boyle, J.A.; Piltonen, T.; Silagy, M.; Arora, C.; Misso, M.L.; Teede, H.J.; Moran, L.J. Increased maternal pregnancy complications in polycystic ovary syndrome appear to be independent of obesity-A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Obes Rev 2019, 20, 659-674. [CrossRef]
- Kjerulff, L.E.; Sanchez-Ramos, L.; Duffy, D. Pregnancy outcomes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a metaanalysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011, 204, 558.e551-556. [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E.W.; Tay, C.T.; Hiam, D.S.; Teede, H.J.; Moran, L.J. Comorbidities and complications of polycystic ovary syndrome: An overview of systematic reviews. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2018, 89, 683-699. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.F.; Chen, H.S.; Rao, D.P.; Gong, J. Association between polycystic ovary syndrome and the risk of pregnancy complications: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e4863. [CrossRef]
- Farland, L.V.; Stern, J.E.; Liu, C.L.; Cabral, H.J.; Coddington, C.C.; Diop, H.; Dukhovny, D.; Hwang, S.; Missmer, S.A. Polycystic ovary syndrome and risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes: a registry linkage study from Massachusetts. Hum Reprod 2022, 37, 2690-2699. [CrossRef]
- Mills, G.; Badeghiesh, A.; Suarthana, E.; Baghlaf, H.; Dahan, M.H. Associations between polycystic ovary syndrome and adverse obstetric and neonatal outcomes: a population study of 9.1 million births. Hum Reprod 2020, 35, 1914-1921. [CrossRef]
- Valgeirsdottir, H.; Sundström Poromaa, I.; Kunovac Kallak, T.; Vanky, E.; Akhter, T.; Roos, N.; Stephansson, O.; Wikström, A.K. Polycystic ovary syndrome and extremely preterm birth: A nationwide register-based study. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0246743. [CrossRef]
- Palomba, S.; de Wilde, M.A.; Falbo, A.; Koster, M.P.; La Sala, G.B.; Fauser, B.C. Pregnancy complications in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod Update 2015, 21, 575-592. [CrossRef]
- de Wilde, M.A.; Lamain-de Ruiter, M.; Veltman-Verhulst, S.M.; Kwee, A.; Laven, J.S.; Lambalk, C.B.; Eijkemans, M.J.C.; Franx, A.; Fauser, B.; Koster, M.P.H. Increased rates of complications in singleton pregnancies of women previously diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome predominantly in the hyperandrogenic phenotype. Fertil Steril 2017, 108, 333-340. [CrossRef]
- Christ, J.P.; Gunning, M.N.; Meun, C.; Eijkemans, M.J.C.; van Rijn, B.B.; Bonsel, G.J.; Laven, J.S.E.; Fauser, B. Pre-Conception Characteristics Predict Obstetrical and Neonatal Outcomes in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019, 104, 809-818. [CrossRef]
- Koster, M.P.; de Wilde, M.A.; Veltman-Verhulst, S.M.; Houben, M.L.; Nikkels, P.G.; van Rijn, B.B.; Fauser, B.C. Placental characteristics in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod 2015, 30, 2829-2837. [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Maliqueo, M.; Benrick, A.; Johansson, J.; Shao, R.; Hou, L.; Jansson, T.; Wu, X.; Stener-Victorin, E. Maternal androgen excess reduces placental and fetal weights, increases placental steroidogenesis, and leads to long-term health effects in their female offspring. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2012, 303, E1373-1385. [CrossRef]
- Naver, K.V.; Grinsted, J.; Larsen, S.O.; Hedley, P.L.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Christiansen, M.; Nilas, L. Increased risk of preterm delivery and pre-eclampsia in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and hyperandrogenaemia. Bjog 2014, 121, 575-581. [CrossRef]
- Mumm, H.; Jensen, D.M.; Sørensen, J.A.; Andersen, L.L.; Ravn, P.; Andersen, M.; Glintborg, D. Hyperandrogenism and phenotypes of polycystic ovary syndrome are not associated with differences in obstetric outcomes. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2015, 94, 204-211. [CrossRef]
- Palchuk, M.B.; London, J.W.; Perez-Rey, D.; Drebert, Z.J.; Winer-Jones, J.P.; Thompson, C.N.; Esposito, J.; Claerhout, B. A global federated real-world data and analytics platform for research. JAMIA Open 2023, 6, ooad035. [CrossRef]
- Topaloglu, U.; Palchuk, M.B. Using a Federated Network of Real-World Data to Optimize Clinical Trials Operations. JCO Clin Cancer Inform 2018, 2, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Sibai, B.M.; Caritis, S.; Hauth, J.; Lindheimer, M.; VanDorsten, J.P.; MacPherson, C.; Klebanoff, M.; Landon, M.; Miodovnik, M.; Paul, R.; et al. Risks of preeclampsia and adverse neonatal outcomes among women with pregestational diabetes mellitus. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Network of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000, 182, 364-369. [CrossRef]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Dunaif, A. Insulin resistance and the polycystic ovary syndrome revisited: an update on mechanisms and implications. Endocr Rev 2012, 33, 981-1030. [CrossRef]
- Daan, N.M.; Louwers, Y.V.; Koster, M.P.; Eijkemans, M.J.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Lentjes, E.W.; Fauser, B.C.; Laven, J.S. Cardiovascular and metabolic profiles amongst different polycystic ovary syndrome phenotypes: who is really at risk? Fertil Steril 2014, 102, 1444-1451.e1443. [CrossRef]
- He, L.R.; Yu, L.; Guo, Y. Birth weight and large for gestational age trends in offspring of pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus in southern China, 2012-2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1166533. [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Cao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhai, J. Association between hyperandrogenism and adverse pregnancy outcomes in patients with different polycystic ovary syndrome phenotypes undergoing in vitro fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gynecol Endocrinol 2021, 37, 694-701. [CrossRef]
- Azziz, R. How prevalent is metabolic syndrome in women with polycystic ovary syndrome? Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2006, 2, 132-133. [CrossRef]
- ACOG Committee opinion no. 549: obesity in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2013, 121, 213-217. [CrossRef]
- Crisosto, N.; Echiburú, B.; Maliqueo, M.; Pérez, V.; Ladrón de Guevara, A.; Preisler, J.; Sánchez, F.; Sir-Petermann, T. Improvement of hyperandrogenism and hyperinsulinemia during pregnancy in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: possible effect in the ovarian follicular mass of their daughters. Fertil Steril 2012, 97, 218-224. [CrossRef]
- Vanky, E.; Stridsklev, S.; Heimstad, R.; Romundstad, P.; Skogøy, K.; Kleggetveit, O.; Hjelle, S.; von Brandis, P.; Eikeland, T.; Flo, K.; et al. Metformin versus placebo from first trimester to delivery in polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized, controlled multicenter study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010, 95, E448-455. [CrossRef]
- Jorquera, G.; Echiburú, B.; Crisosto, N.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R.; Maliqueo, M.; Cruz, G. Metformin during Pregnancy: Effects on Offspring Development and Metabolic Function. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 653. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Shetty, A.; Hamilton, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Maheshwari, A. Obstetric and perinatal outcomes in singleton pregnancies resulting from IVF/ICSI: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update 2012, 18, 485-503. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ruan, X.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Cai, G.; Du, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Mueck, A.O. Comparing the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes of Chinese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome with and without antiandrogenic pretreatment. Fertil Steril 2018, 109, 720-727. [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Carmina, E.; Dewailly, D.; Gambineri, A.; Kelestimur, F.; Moghetti, P.; Pugeat, M.; Qiao, J.; Wijeyaratne, C.N.; Witchel, S.F.; et al. Epidemiology, diagnosis and management of hirsutism: a consensus statement by the Androgen Excess and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Society. Hum Reprod Update 2012, 18, 146-170. [CrossRef]
| Outcomes | PCOS with hyperandrogenism, (n=564) | PCOS without hyperandrogenism, (n=564) | Odds ratio (95% CI) | P value |
| Missed abortion | 42 (7.4) | 38 (6.7) | 1.114 (0.706, 1.756) | 0.643 |
| Placenta previa | 16 (2.8) | 14 (2.5) | 1.147 (0.554, 2.373) | 0.711 |
| IUGR | 40 (7.1) | 39 (6.9) | 1.028 (0.650, 1.624) | 0.907 |
| LGA | 37 (6.6) | 22 (3.9) | 1.730 (1.007, 2.972) | 0.045 |
| Preterm birth | 58 (10.3) | 33 (5.9) | 1.844 (1.183, 2.876) | 0.006 |
| GDM | 78 (13.8) | 57 (10.1) | 1.428 (0.992, 2.053) | 0.054 |
| Gestational hypertension | 83 (14.7) | 67 (11.9) | 1.280 (0.906, 1.808) | 0.161 |
| Preeclampsia/eclampsia | 49 (8.7) | 45 (8.0) | 1.097 (0.719, 1.675) | 0.667 |
| Placenta abruption | 10 (1.8) | 10 (1.8) | 1 (0.413, 2.422) | 1 |
| Cesarean section | 119 (21.1) | 111 (19.7) | 1.091 (0.817, 1.458) | 0.554 |
| Shoulder dystocia | 12 (2.1) | 11 (2.0) | 1.093 (0.478, 2.498) | 0.833 |
| Dysfunctional of labor | 10 (1.8) | 10 (1.8) | 1 (0.413, 2.422) | 1 |
| Instrumental delivery | 16 (2.8) | 15 (2.7) | 1.069 (0.523, 2.183) | 0.855 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





