Submitted:
21 November 2024
Posted:
25 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Animals and Drug
2.3. Effects of Hal on Commercial Enzyme AChE
2.4. AChE Activity Distribution in Different Tissues of the Brain and Inhibitory Effects of Hal
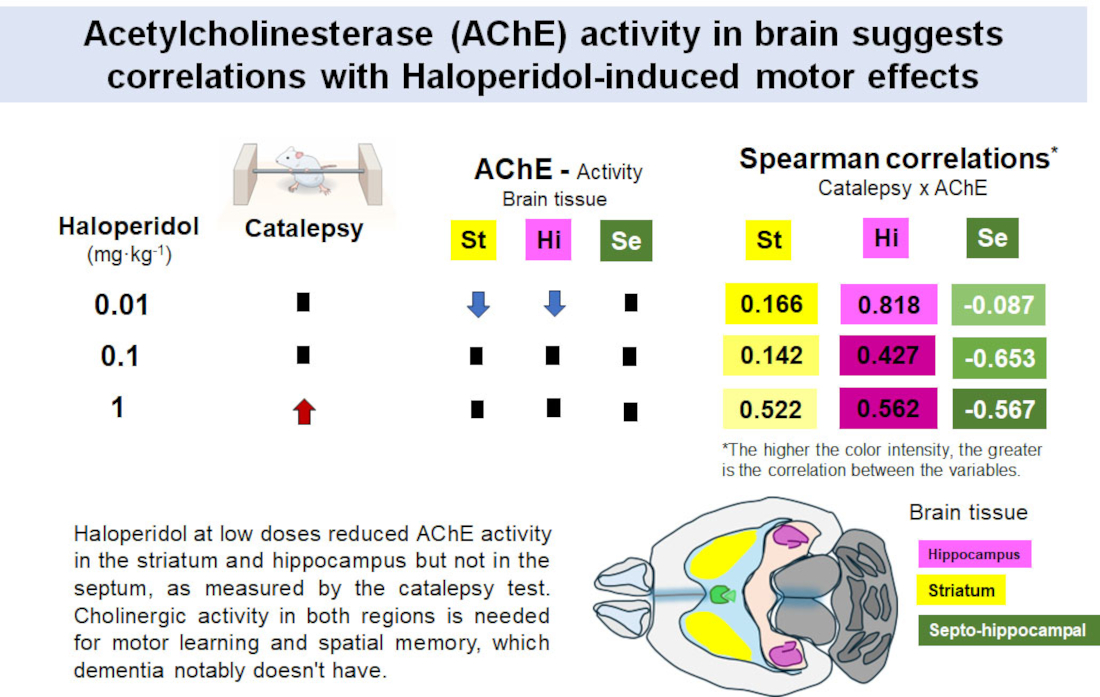
2.5. Catalepsy Test and AChE Activity in Striatum, Hippocampus, Septo-Hippocampal System
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
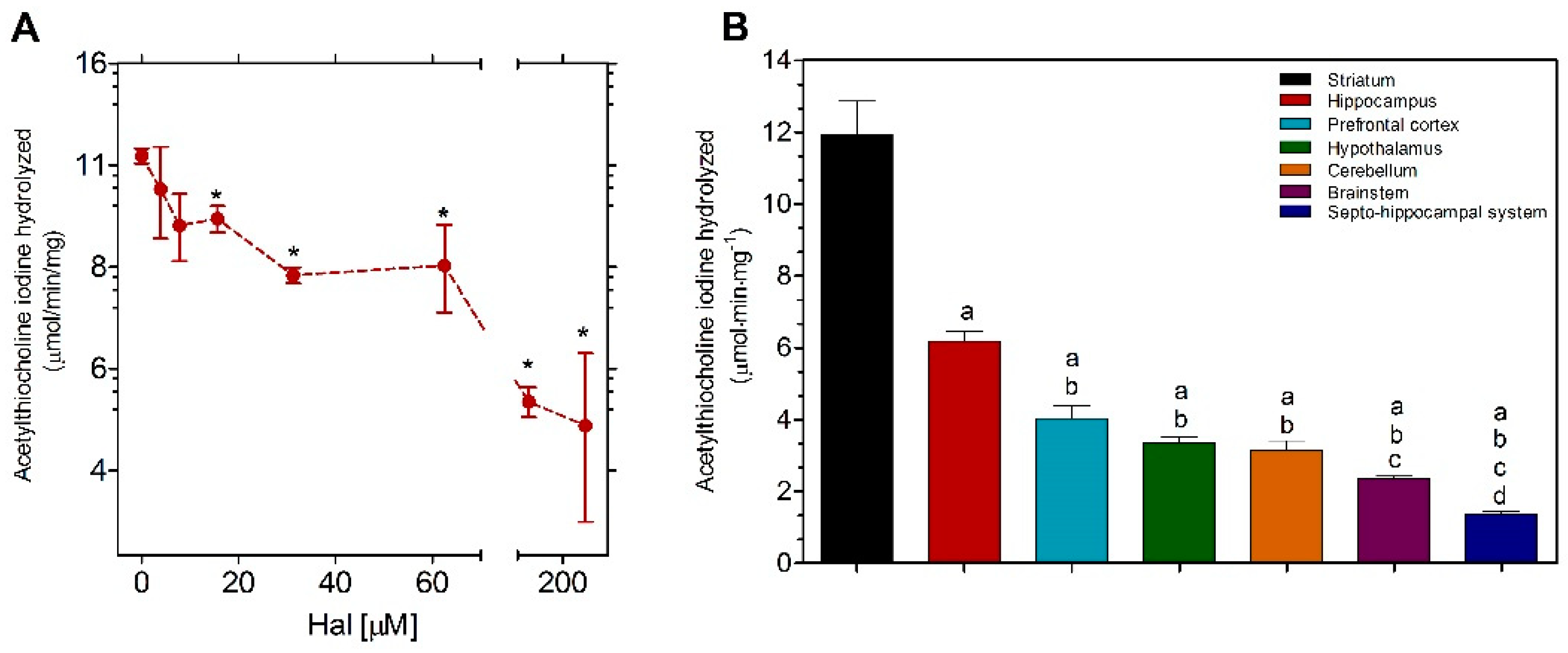
3.1. Inhibitory Effects of Hal on the Commercial Enzyme AChE from Electrophorus Electricus
3.2. Distribution of AChE Activity in Several Mouse Brain Regions
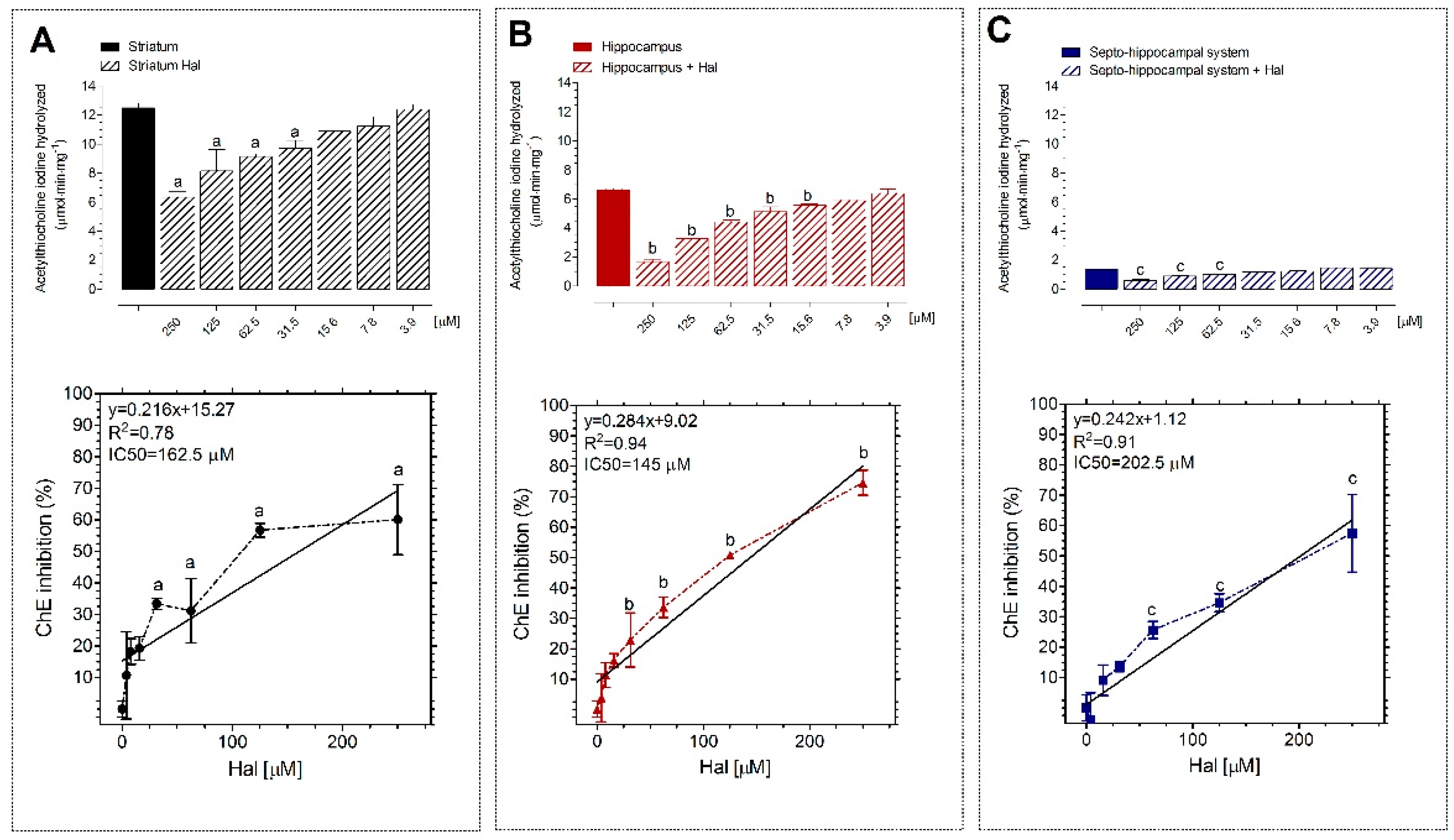
3.3. Inhibitory Effects of Hal on AChE Activity In Vitro in Homogenate Obtained from Striatum, Hippocampus, and Septo-Hippocampal System
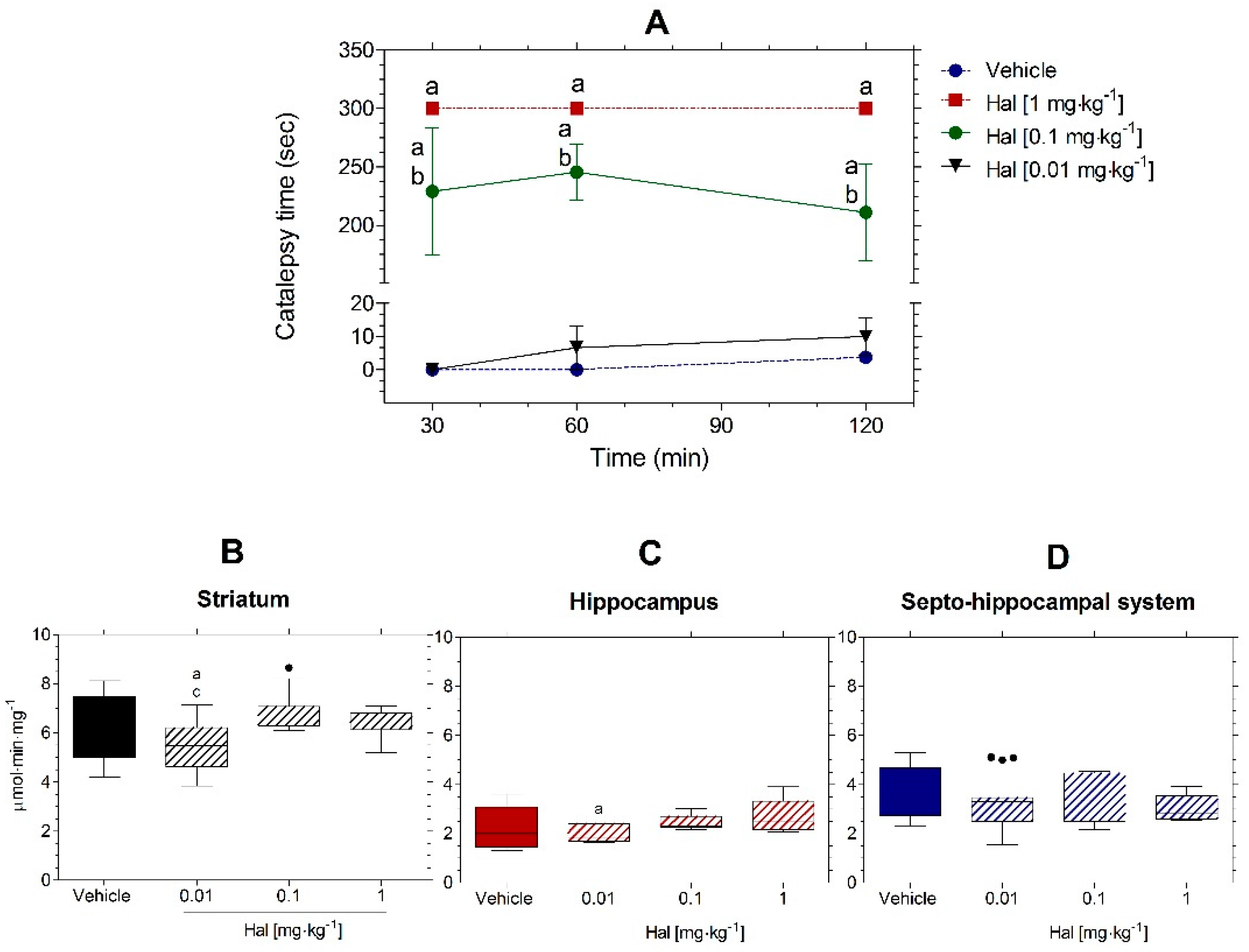
3.4. Effects of Hal on Catalepsy
3.5. Effects of Hal on AChE Activity In Vivo in Striatum, Hippocampus, and Septo-Hippocampal System
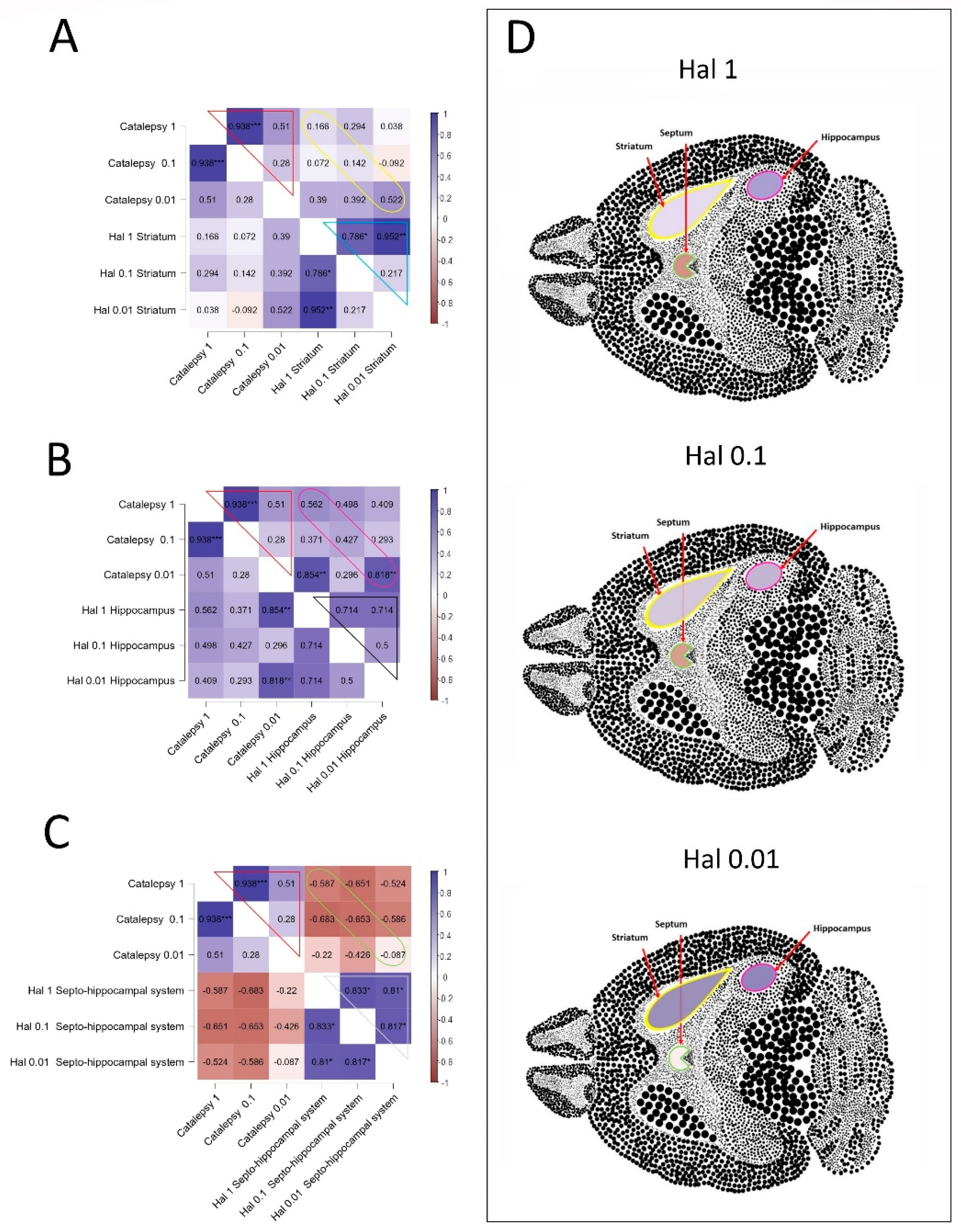
3.6. Correlations Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding Information
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Consent for Publication
Availability of Data and Materials
Acknowledgments
Competing Interests
Abbreviations
References
- Ballard C, Kales HC, Lyketsos C, et al. Psychosis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2020; 20. [CrossRef]
- Podsiedlik M, Markowicz-piasecka M, Sikora J. The Influence of Selected Antipsychotic Drugs on Biochemical Aspects of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2022; 23. [CrossRef]
- Remington G, Hahn MK, Agarwal SM, et al. Schizophrenia: Antipsychotics and drug development. Behavioural brain research 2021; 414. [CrossRef]
- Grinchii D, Dremencov E. Mechanism of Action of Atypical Antipsychotic Drugs in Mood Disorders. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Prieto SG, Silva JCS, De Lima MO, et al. Cross-tolerance between nitric oxide synthase inhibition and atypical antipsychotics modify nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide phosphate-diaphorase activity in mouse lateral striatum. Behavioural pharmacology 2019; 30: 67–78. [CrossRef]
- Shen WW. A history of antipsychotic drug development. Compr Psychiatry 1999; 40: 407–414. [CrossRef]
- Lacasse H, Perreault MM, Williamson DR. Systematic review of antipsychotics for the treatment of hospital-associated delirium in medically or surgically ill patients. Ann Pharmacother 2006; 40: 1966–1973. [CrossRef]
- Ozbolt LB, Paniagua MA, Kaiser RM. Atypical antipsychotics for the treatment of delirious elders. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2008; 9: 18–28. [CrossRef]
- Porcelli S, Crisafulli C, Calabrò M, et al. Possible biomarkers modulating haloperidol efficacy and/or tolerability. Pharmacogenomics 2016; 17: 507–529. [CrossRef]
- De la Casa LG, Cintado MA, González-Tirado G, et al. Conditioned catalepsy vs. Increase in locomotor activity induced by haloperidol. Neurosci Lett 2023; 802. [CrossRef]
- Waku I, Magalhães MS, Alves CO, et al. Haloperidol-induced catalepsy as an animal model for parkinsonism: A systematic review of experimental studies. Eur J Neurosci 2021; 53: 3743–3767. [CrossRef]
- Kharkwal G, Brami-Cherrier K, Lizardi-Ortiz JE, et al. Parkinsonism Driven by Antipsychotics Originates from Dopaminergic Control of Striatal Cholinergic Interneurons. Neuron 2016; 91: 67–78. [CrossRef]
- Prasasty V, Radifar M, Istyastono E. Natural Peptides in Drug Discovery Targeting Acetylcholinesterase. Molecules 2018; 23. [CrossRef]
- H S, S S. Acetylcholinesterase--new roles for an old actor. Nat Rev Neurosci 2001; 2: 294–302. [CrossRef]
- Wevers A. Localisation of pre- and postsynaptic cholinergic markers in the human brain. Behavioural brain research 2011; 221: 341–355. [CrossRef]
- Lane CA, Hardy J, Schott JM. Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol 2018; 25: 59–70. [CrossRef]
- Obara K, Fujii A, Arie C, et al. Inhibition of Recombinant Human Acetylcholinesterase Activity by Antipsychotics. Pharmacology 2019; 104: 43–50. [CrossRef]
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E. Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 1992; 260.
- Tenjin T, Miyamoto S, Ninomiya Y, et al. Profile of blonanserin for the treatment of schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2013; 9: 587–594. [CrossRef]
- Bymaster FP, Calligaro DO, Falcone JF, et al. Radioreceptor binding profile of the atypical antipsychotic olanzapine. Neuropsychopharmacology 1996; 14: 87–96. [CrossRef]
- Richelson E, Souder T. Binding of antipsychotic drugs to human brain receptors focus on newer generation compounds. Life Sci 2000; 68: 29–39. [CrossRef]
- Pimentel VC, Gomes JL, Zanini D, et al. Evaluation of acetylcholinesterase and adenosine deaminase activities in brain and erythrocytes and proinflammatory cytokine levels in rats submitted to neonatal hypoxia-ischemia model. Mol Cell Biochem 2013; 378: 247–255. [CrossRef]
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 1976; 72: 248–254. [CrossRef]
- Harry J, Tilson HA, Padilla S, et al. Biochemical Measurement of Cholinesterase Activity. In: Neurodegeneration Methods and Protocols. 2003: 237–246.
- Sebens JB, Koch T, Ter Horst GJ, et al. Olanzapine-induced Fos expression in the rat forebrain; cross-tolerance with haloperidol and clozapine. Eur J Pharmacol 1998; 353: 13–21. [CrossRef]
- Bardin L, Kleven MS, Barret-Grévoz C, et al. Antipsychotic-like vs. cataleptogenic actions in mice of novel antipsychotics having D2 antagonist and 5-HT1A agonist properties. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006; 31: 1869–1879. [CrossRef]
- Echeverry MB, Salgado ML, Ferreira FR, et al. Intracerebroventricular administration of nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase inhibitors induces catalepsy in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2007; 194: 271–278. [CrossRef]
- Del Bel EA, Guimarães FS. Sub-chronic inhibition of nitric-oxide synthesis modifies haloperidol-induced catalepsy and the number of NADPH-diaphorase neurons in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000; 147: 356–361. [CrossRef]
- Prieto SG, Almeida MC, Silva JCS, et al. Extrapyramidal Side Effects with Chronic Atypical Antipsychotic Can Be Predicted by Labeling Pattern of FosB and phosphoThr34-DARPP-32 in Nucleus Accumbens. Biomedicines 2023; 11. [CrossRef]
- Lacasse H, Perreault MM, Williamson DR. Systematic review of antipsychotics for the treatment of hospital-associated delirium in medically or surgically ill patients. Ann Pharmacother 2006; 40: 1966–1973. [CrossRef]
- Arai M. Parkinsonism onset in a patient concurrently using tiapride and donepezil. Intern Med 2000; 39: 863. [CrossRef]
- Magnuson TM, Keller BK, Burke WJ. Extrapyramidal side effects in a patient treated with risperidone plus donepezil. Am J Psychiatry 1998; 155: 1458–1459. [CrossRef]
- Bourke D, Druckenbrod RW. Possible association between donepezil and worsening Parkinson’s disease. Ann Pharmacother 1998; 32: 610–611. [CrossRef]
- Klemm WR. Cholinergic-dopaminergic interactions in experimental catalepsy. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983; 81: 24–27. [CrossRef]
- Mahadik SP, Laev H, Korenovsky A, et al. Haloperidol alters rat CNS cholinergic system: enzymatic and morphological analyses. Biol Psychiatry 1988; 24: 199–217. [CrossRef]
- Wu D, Yu N, Gao Y, et al. Targeting a vulnerable septum-hippocampus cholinergic circuit in a critical time window ameliorates tau-impaired memory consolidation. Mol Neurodegener 2023; 18. [CrossRef]
- Grisaru D, Sternfeld M, Eldor A, et al. Structural roles of acetylcholinesterase variants in biology and pathology. Eur J Biochem 1999; 264: 672–686. [CrossRef]
- McNaughton N, Ruan M, Woodnorth MA. Restoring theta-like rhythmicity in rats restores initial learning in the Morris water maze. Hippocampus 2006; 16: 1102–1110. [CrossRef]
- Cai Y, Ford CP. Dopamine Cells Differentially Regulate Striatal Cholinergic Transmission across Regions through Corelease of Dopamine and Glutamate. Cell Rep 2018; 25: 3148-3157.e3. [CrossRef]
- Sethy VH. Effects of chronic treatment with neuroleptics on striatal acetylcholine concentration. J Neurochem 1976; 27: 325–326. [CrossRef]
- Seibt KJ, da Luz Oliveira R, Rico EP, et al. Typical and atypical antipsychotics alter acetylcholinesterase activity and ACHE expression in zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 2009; 150: 10–15. [CrossRef]
- Klemm WR. Evidence for a cholinergic role in haloperidol-induced catalepsy. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1985; 85: 139–142. [CrossRef]
- Sklan EH, Berson A, Birikh KR, et al. Acetylcholinesterase modulates stress-induced motor responses through catalytic and noncatalytic properties. Biol Psychiatry 2006; 60: 741–751. [CrossRef]
- Kaygisiz B, Aydin S, Yildirim E, et al. The effects of galangin in prepulse inhibition test and experimental schizophrenia models. Acta Neuropsychiatr 2022; 34: 37–46. [CrossRef]
- Nair A, Jacob S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J Basic Clin Pharm 2016; 7: 27. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




