Chapter One Introduction
1.1. Background of the Study
The capital asset pricing model (CAPM) of William Sharpe (1964 (Bruce Hearn)) and John Linter (1965) marks the conception of holding evaluating theory. Four decades later, the CAPM is still broadly utilized as a part of requisitions, for example evaluating the expense of capital for firms and assessing the execution of administered portfolios.
The fascination of the CAPM is that it offers influential and instinctively satisfying forecasts about how to measure hazard and the connection between wanted return and danger. Lamentably, the exact record of the model is poor—poor enough to discredit the way it is utilized within provisions (H. Jamal Zubairi, 2013) The CAPM's experimental issues might reflect theoretical failings, the consequence of numerous disentangling presumptions. However they might likewise be initiated by troubles in executing good tests of the model. For instance, the CAPM says that the danger of a stock must to be measured with respect to a far reaching "market portfolio" that in guideline can incorporate exchanged budgetary holdings, as well as customer durables, land and human capital
1.2. Statement of Problem
The motive of this study is to evaluate and measure the empirical formation of CAPM model so as to know the practical implementation of the risk factor that is estimated in Karachi Stock Exchange taking the oil and gas industry as the field of interest.
The research is to determine the model of CAPM and to know its performance in the oil and Gas sector.
1.3. Justification
It is a worldwide marvel "Higher the risk higher will be the return". Assuming that we take the same articulation for money related markets then this could be restated as higher the risk of the monetary possessions higher the return. Yet the issue is the method by which to quantify the risk in order to measure the return for it. Provided that this might be solved it will be of extraordinary help in issues like capital planning, cost profit examination, portfolio determination and for other choice identifying with the learning of risk and return
1.4. Purpose of the Study
1.4.1. General Purpose
The overall objective of this study of is to assess the determinants of the CAPM model such as
Rf, Ri, MV and beta factor. Whereas oil and Gas sector in the KSE-100 index has been chosen as the main financial institution for the research.
1.4.2. Specific Purpose
Capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is utilized to figure out a suitable obliged rate of return of an asset, if that holding is to be added to an as of recently overall enhanced portfolio, given that asset's non-diversifiable risk. The model considers the stake's affectability to non-diversifiable risk (otherwise called systematic hazard or market hazard), regularly spoke to by the amount beta (β) in the fiscal business, and the normal return of the business sector and the normal return of a theoretical risk free asset by centering KSE-100 index of Oil and Gas division in Pakistan.
1.4. Basic Assumptions
CAPM accepts that capital markets are productive, all securities and stakes are rightly evaluated and there are no arbitrage chances. Investors are risk opposed and mean-difference analyzers. For a particular level of risk they will lean toward higher returns and for a particular needed return they will lean toward easier hazard. The decision of holdings is built just with respect to the risk tendency and tendency to businesses or stakes are avoided.
The business portfolio is accepted to comprise of all holdings in all business sectors, yet numerous possessions, for example land, human capital and others are not incorporated. Accordingly the business portfolio is a constrained form of the true showcase portfolio.
An alternate supposition of CAPM is that there are numerous investors and all speculators are value takers i.e. their transactions have no impact available.
Investors want to contribute over the same time skyline(horizon) and are intrigued by stand out period ahead. They settle on their venture choices at the start of the period and there are not any progressions throughout the speculation skyline.
There is a risk free holding that pays investment rate Rf in zero net supply. Investors can obtain and give at an altered risk free rate over the venture skyline.
There are no assessments on returns or transactions expenses, for example requisitions, administration charges. In actuality, the pay from investment, profits or capital additions is assessable and requisitions and charges might be gathered. This can influence the decision of the investor as to stocks and portfolios.
-
Data is openly accessible to everybody; henceforth all investors have the same data and homogeneous desires about the appropriation of returns. Assumes that returns are circulated regularly and specified by mean and standard deviation, the last being a measure of risk.
Definition of key term
KSE stands for Karachi stock exchange
KIBOR stands for Karachi interbank offering rate CAPM stands for Capital asset pricing model
1.5. Scope
The spirit of CAPM is correct. The beneficiaries of this study are the investors. It provides a usable measure of risk that helps investors to determine what return they deserve for putting their money at risk. For Achieving Better Returns in their Portfolio
1.6. Limitations
The limitations or basically hurdles faced during this research are:
And so on many hurdles were faced!
Chapter Two Literature
CAPM has been studied at very large scale in literature in which discusses the risky assets. The existence of a significant positive linear relationship between beta and stock returns has been extensively reviewed.
Dayaratne, Dharmaratne and Haris measure the risk and performance in plantation sector using CAPM based Jensen’s, their paper published in Alpha department of accountancy and finance Sabaragamuwa University, Belihuloya 2000-2006 sabagramauwa university journal volume 6 no.1 The data has been taken from Colombo stock exchange and the GDP was considered where as plantation sector was taken as the area of interest. Calculations are obtained through the regression method and the variance whereas standard deviation was taken as the risk factor the results. By beta estimation, estimating the risk premium, Evaluating company performance, assumption of the model (CAPM), he conclude that the unsystematic risk component is higher than the systematic risk in the plantation sector which means that the fluctuation of the market price of stocks is mostly influenced by company specific factors such as weather condition, production capacity and CWC union actions (D.A.I. Dayaratne, 2006)
Van Kessel conduct his research on “Asset pricing in a bearish market The beta-expected return relationship of the European stock market”, his paper was published in faculteit der economische wetenschappen universiteit van Amsterdam, Bedrijfseconomie in 31-07-2007 The data used in the research are Return Indices (RI) from data stream. The advantage of using the RI instead of the prices is that it accounts for the dividends and therefore closely matches the fair prices of the stocks. The market return index of Euro next 150 is used as a proxy for the market method used was capital asset pricing model, testing the Best-Beta, capital asset pricing model testing the Dichotomous asset pricing model Fama-MacBeth test .The results show that, with exception of CAPM on full market, all models hold, when they are tested with daily data. This means that according to those models and with a statistical significance level of 0.05 there exists a linear relation between the risk and the expected return of an investment. Theoretically one would expect the relationship between the expected return and the beta coefficient to drop in a bearish period. The intuition behind this is that for the same risk investors expect lower returns. When the models are tested on the Euro next 150 and the results under a total market are compared with the results under a bearish market. (Kessel, 2007)
Nikhil Gupta did research on “The Size Effect and the Capital Asset Pricing Model “. His paper was published in ECON 381: Econometrics 1996-2009. He considers returns on twenty stocks from 1996 to the present: the ten largest firms by market capitalization listed on the S&P 500 index in 2008 and ten firms selected from the Russell 2000 small market capitalization index. First result shows the negative coefficient on market betas that exists both when market betas are the sole explanatory variable and when size is included in the FM regressions. This suggests that for our basket of securities and market proxy, increased risk does not lead to increased returns even when risk is taken to be the sole explanation of variations in security returns. If market proxy is taken to be a good approximation of the true market portfolio, this is an indictment of the CAPM. no evidence found a positive relationship between market beta and security return in the returns of twenty stocks over the period 1998 – 2009. No evidence found for the size effect in data. Some evidence against the CAPM, cannot unambiguously reject the CAPM because of uncertainty arising from the joint-hypothesis problem and the low statistical power of tests. (Gupta, 2010)
Fama and French conducted their research on The Capital Asset Pricing Model: Theory and Evidence. The paper was published in Journal of Economic Perspectives Volume 18, Number 3Summer1963- 2004 They tests on Risk Premiums , Testing Whether Market Betas Explain Expected Returns , Recent Tests , Stock return data are from CRSP, and book equity data are from Compustat and the Moody’s Industrials, Transportation, Utilities and Financials manuals. Stocks are allocated to ten portfolios at the end of June of each year t (1963 to 2003) using the ratio of book equity for the fiscal year ending in calendar , divided by market equity at the end of December of t _ 1. The estimated beta for the portfolio with the highest book-to-market ratio and the highest average return is only 0.98. With an average annualized value of the risk free interest rate Rf of 5.8 percent and an average annualized market premium, Rm , Rf, of 11.3 percent. CAPM estimates of the cost of equity for high beta stocks are too high estimates for low beta stocks are too low , the high average returns on value stocks imply high expected returns, CAPM cost of equity estimates for such stocks are too low. Stock portfolios produce abnormal returns if their investment strategies involve tilts toward CAPM problems. (French, 2003)
Nel conducted research on “The application of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM): A South African perspective “.His paper was published in Department of Accounting, Stellenbosch University, South Africa. Accepted 26 January, 2011 As it was a qualitative research, draft survey was prepared and a link to an electronic database was emailed, questionnaire and the database was cleared of these pilot responses emphasis of this paper falls on seven questions in the survey, this survey was conducted from lecturers of academia practitioners agree that the CAPM is the best approach to calculate the cost of equity. In terms of first will result in a rate of return which is lower than the Rf, second will result in a rate of return which is equal to the Rf, which is also not plausible. This paper has highlighted the need for academia and investment practitioners in South Africa investment practitioners should perhaps take note of the APT as an alternative to the CAPM. Investment practitioners should also consider adjusting The Rf for tax purposes, as suggested by academia. The research results provide an insight and guideline to finance lecturers and investment practitioners, in terms of the perception in academia regarding the calculation of the cost of equity and the application of the CAPM. (Nel, 2011)
H. Naylor and Francis Taponi research on “Capital asset pricing model: An evaluation of its potential as a strategic planning tool “published in management sciences Vol. 28, No. 10, October 1982 Printed in U.S.A The capital asset pricing model (CAPM) point out how it might possibly be used as a tool for strategic planning by corporations that own a portfolio of businesses. Also point out some of the assumptions underlying the CAPM which must be satisfied if it is to be used for strategic planning .A critical appraisal of the CAPM as a strategic planning tool. Finally, the case for linking competitive strategy models, CAPM models, and business simulation models. Capital asset pricing models do offer some promise as a conceptual framework for strategic planning in companies which manage a portfolio of businesses. In no sense should management rely exclusively on the narrow criteria of risk, return, and value of the business to make strategic decision the capital asset pricing model framework combined with the competitive strategy models of The Boston Consulting Group, and a linkage to corporate simulation models may offer management an extremely powerful analytical tool for strategic planning. (TAPONI, 1982)
Sim Matricola researched on “Detecting premium portfolios in higher-order moments CAPM “published in Corso di Laurea Specialistica in Economia, curriculum models and methods of quantitative economics per la gestione dell’Impresa , Foscari University of Venice 2009 / 2010 data was taken from daily Stock Price of market portfolio (S&P500 Indices) , daily rate of return of market portfolio (S&P500 Indices), daily stock price of riskless asset (US FED funds). Daily rate of return of riskless Asset (US FED FUNDS), calculating the linear market model, quadratic market model and cubic market model, systematic risk measures can be calculated directly from their definitions (C moments), or deduced from the cubic market model or four-moment CAPM fundamental relation. For the systematic risk beta and systematic kurtosis, the result appears to have small variant amongst these methods. However, when considering the systematic skewers big differences emerge between cubic market model and four-moment CAPM fundamental relation. When introducing L moments instead of C-moments (i.e., replacing C-(co)moment by L- (co)moments) the result seems to diverge from the others (as before, except for systematic risk, beta). However, our study of L-(co)moments is not yet complete. This may be interesting if the robust features of L-(co)moments can be further examined and employed in higher-order moments CAPM. a problem of redundant elements when computing C moment matrices using the definition they propose in the theoretical part. It will be advantageous in term of computing accuracy if we can eliminate these redundancies. Lastly, the method that proposes to obtain the two premium portfolios may not be globally optimal. It can thus be our interest in the future to search for the most likely one. (Matricola, 2010).
Agrawal, Mohapatra, and Pollak conduct their research on Empirical Evidence Against CAPM: Relating Alphas and Returns to Betas and their research published in IEEE Journal Using data from 1971 to 2010 taken from U S stock market ,empirically analyze the capital asset pricing model (CAPM)in the context of the U.S. stock market, by constructing and tracking over time several portfolios consisting of shares of large publicly traded U.S. companies regarding the validity of some of the model’s assumptions, as well as inconsistencies between CAPM’s predictions and empirical observations. In particular, there exists a significant body of empirical research contradicting. There is economically and statistically significant evidence contradicting CAPM in the U.S. stock market over the past 40 years. Empirical data from the U.S stock market contradicts CAPM.A new statistic was proposed for testing this conclusion and have analyzed an implementable investment strategy which is based on this statistic. If CAPM applied to the U.S. stock market, then the strategy’s expected profit would be zero (Mayur Agrawal, 2011)
Anisha, Alex P. Taylor did their research on” What is the Consumption-CAPM missing? An Information-Theoretic Framework for the analysis of asset pricing models this paper was published in financial market group using six different sets of assets: the market portfolio, the 25 Fama-French portfolios, the 10 size-sorted portfolios, the 10 book-to-market-equity-sorted portfolios, the 10 momentum- sorted portfolios, and the 10 industry-sorted portfolios. Proxy for the market return is the Center for Research in Security Prices (CRSP) value-weighted index of all stocks on the NYSE, AMEX, and NASDAQ. The proxy for the risk-free rate is the one-month treasury bill rate obtained from the CRSP. Methodology developed in this paper is considerably general and may be applied to any model that delivers heterogeneous agents, limited stock market participation, and fragile beliefs, as long as the SDF can be factorized into an observable component and a potentially unobservable one. Results are robust to the choice of test assets used in the construction of the bounds as well as the frequency of the data. Moreover, comparing the non-parametrically extracted SDF with those implied by the above asset pricing models , substantial empirical support for the long run risks framework. a large class of dynamic asset pricing models, The external habit models and the housing model of require very high levels of risk aversion to satisfy the bounds while the long run risks model bounds for reasonable levels of risk aversion (Taylorx, 2011)
Johan Linden, Sylvestor Jarlee conducted research ‘A test of the Capital Asset Pricing Model: studying stocks on the Stockholm Stock exchange ‘his paper was published in Maladalen’s university institute of mathematics and physics Vasteras, Sweden. The data chosen for the study from monthly stock return for twenty eight firms listed on the Stockholm stock exchange are used. The data ranges from January 2001 to December 2006, a period of six years. To test the CAPM in this paper, time – series test as well as cross sectional test. It turns out that each of the investigation conducted is a confirmation of the other that the empirical investigations carried out during this study do not fully hold up with CAPM. The data did not provide evidence that higher beta yields higher while the slope of the security market line is negative and downward sloping. The data also provide a difference between average risk free rate, risk premium and their estimated value. However, a linear relationship between beta and return is established. This investigation has only evaluated CAPM in combination with historical data of stocks obtain from Stockholm stock exchange. This study doe’s not present evidence for any other model even thought it may present inconsistency with CAPM. (Jarlee, 2007)
Chapter Three Research Methodology
3.1. Population
This research is an empirical study of CAPM in which oil and gas producing companies has been taken for the purpose of population. There are twelve listed companies listed in this sector in KSE- 100 index Karachi stock exchange (KSE) which is the biggest and most liquid exchange in Pakistan
3.2. Sample
A sample is used as a parameter which have measureable aspects of population, for example mean and so on which are fact measures. Example ought to be chosen by any examining system which hinges on upon the extent of the population or chose tests though inspecting strategy is a method for selecting sample components from a population. An arbitrary number table is a rundown of numbers made out of digits as 0,1,2,3,4,5,6, . numbers in the agenda are organized with the goal that every digit has no foreseeable association with undertaking or preceding numbers as they are arranged randomly. Along these lines, there choice ought to be completely by possibility.
| No. |
Symbol |
Company |
| 1 |
APL |
Attock Petroleum |
| 2 |
ATRL |
Attock Refinery XD |
| 3 |
BPL |
Burshane LPG |
| 4 |
BYCO |
Byco Petroleum |
| 5 |
MARI |
Mari Petroleum |
| 6 |
NRL |
National refinery |
| 7 |
OGDC |
Oil and Gas developing company |
| 8 |
POL |
Pakistan Oil fields |
| 9 |
PPL |
Pakistan Petroleum Limited |
| 10 |
PSO |
Pakistan State Oil |
| 11 |
SHEL |
Shel Pakistan Limited |
Simple random sampling refers to an inspecting technique that is the population comprise of N objects whereas example comprise of n objects so all conceivable examples of n items are just as like to happen. Basic simple random sampling procedure is taken for choosing organizations for this study.
Benefit of simple random sampling is that it permits analysts to utilize factual systems to find out test effects. Case in point, given a simple random sampling, specialists can utilize measurable systems to characterize a confidence interval around a sample mean. . Statistical analysis is not appropriate when non-random sampling methods are used.
For this study five oil and gas generating organizations are chosen through simple random sampling as the aggregate number of population here is eleven.
3.3. Time Series Data
During this study the data of selected companies has been taken is of five years ranging from 2008 to 2017 on quarterly basis.
3.4. Research and Techniques
To test the CAPM of Sharpe (1964) and Linter (1965) for the selected oil and gas producing companies listed in KSE-100 index in Pakistan, the related data of stocks has been taken through internet. The historical market rates were also available on a website. The KIBOR rates are also considered as a proxy for risk free rate because it has the certainty.
For this study time series data has been taken of five companies which has been drawn through simple random sampling from the population of eleven listed companies in KSE. After calculating the returns we used them to measure the CAPM using linear regression. The use of regression to make quantitative predictions of one variable from the values of another .
We take market rate of returns on x-axis whereas
Chapter Four Data Analysis
4.1. Methodology
A model unfolding the connection between risks and predictable return is used in the pricing of risky securities. CAPM says that the expected return of a security or a collection equals the rate on a risk-free security plus a risk payment. If this expected return does not meet or beat the obligatory return, then the investment should not be undertaken
To conduct this research of CAPM on oil and gas producing companies the following equation has been used:
Ri = Rf + β (Rm − Rf) stated as Equation 1. Risk-Free Rate of Return (Rf)
Rf symbolize the payment accepted by the backer for setting cash in a holding with practically totally certain normal (nominal) return. As it were, the standard deviation of the little profit needed for such a holding equivalents zero. The profit for government securities is for the most part utilized as a substitute for this return. With the end goal of this study, Karachi Interbank (KIBOR) was utilized as the risk free rate given the actuality it is an earnestly utilized benchmark with a high level of conviction. KIBOR was likewise utilized as a substitute for measuring needed profit for a stake with zero systematic risk
Return on Market (Rm)
Rm is the expected rate of return on the stock market. In this study, KSE 100 index was selected as an appropriate proxy for the Pakistani stock market. Quarterly change in this standard was taken as a measure for expected rate of return on the market for the purpose of this study.
Beta (β)
Beta is a measure of systematic or non-diversifiable risk of the asset. Beta was calculated by dividing covariance between quarterly stock and market returns during the period 2008-12 with the variance of the market over the same period. Beta was assumed to be constant while calculating CAPM based returns during each quarter.
Return on Risky Asset (Ri)
The required rate of return (Ri) was calculated for each quarter and then compared with corresponding actual return on the stock to assess the validity of CAPM. Genuine quarterly returns on stock were dead set utilizing change within stocks costs i.e. contrast between the opening and shutting cost isolated by the opening cost. The impact of profits was not considered while calculating genuine stock returns because of challenge in gathering information
4.1. Results
This segment exhibits the outcomes of the regression investigation. The elucidation and itemized talk of the exact discoveries are additionally reported in this segment. At long last, a conceivable description, on the premise of the financial theories inspected above, is exhibited to explicate the experimental discoveries.
Table 1.
Regression Results.
Table 1.
Regression Results.
| Companies |
ARL |
NRL |
PSO |
OGDC |
MARI |
| Multiple R |
0.939774253 |
0.80829552 |
0.19259865 |
0.939774253 |
0.855646684 |
| R Square |
0.883175646 |
0.65334165 |
0.03709424 |
0.883175646 |
0.732131247 |
| Adjusted R Square |
0.877026995 |
0.63509647 |
-0.01358501 |
0.877026995 |
0.718032892 |
| Standard Error |
0.095115441 |
0.20682113 |
0.2730714 |
0.095115441 |
0.144027478 |
| CAPM |
3.66 |
-3.10766 |
8.577844 |
0.65015 |
1.994454 |
| NRL |
Coefficients |
Standard Error |
t Stat |
P-value |
| Intercept |
-0.012344 |
0.045359023 |
-0.27214 |
0.78845 |
| X |
1.02030478 |
0.170503689 |
5.9840628 |
9.29E-06 |
| OGDC |
|
|
|
|
| Intercept |
-0.023384739 |
0.020757602 |
-1.126562642 |
0.27395549 |
| X |
0.841026375 |
0.070173957 |
11.98487884 |
2.6467E-10 |
| PSO |
|
|
|
|
| Intercept |
-0.03439558 |
0.06028545 |
-0.57055 |
0.574994 |
| X |
0.07727892 |
0.090328112 |
0.855536 |
0.402915 |
| MARI |
|
|
|
|
| Intercept |
0.019144071 |
0.032063421 |
0.597069 |
0.5575102 |
| X |
0.71151686 |
0.098735869 |
7.206265 |
7.63E-07 |
| ARL |
|
|
|
|
| Intercept |
0.03224512 |
0.055432648 |
-0.28048 |
0.782142 |
| X |
0.66581442 |
0.241025218 |
2.762426 |
0.012396 |
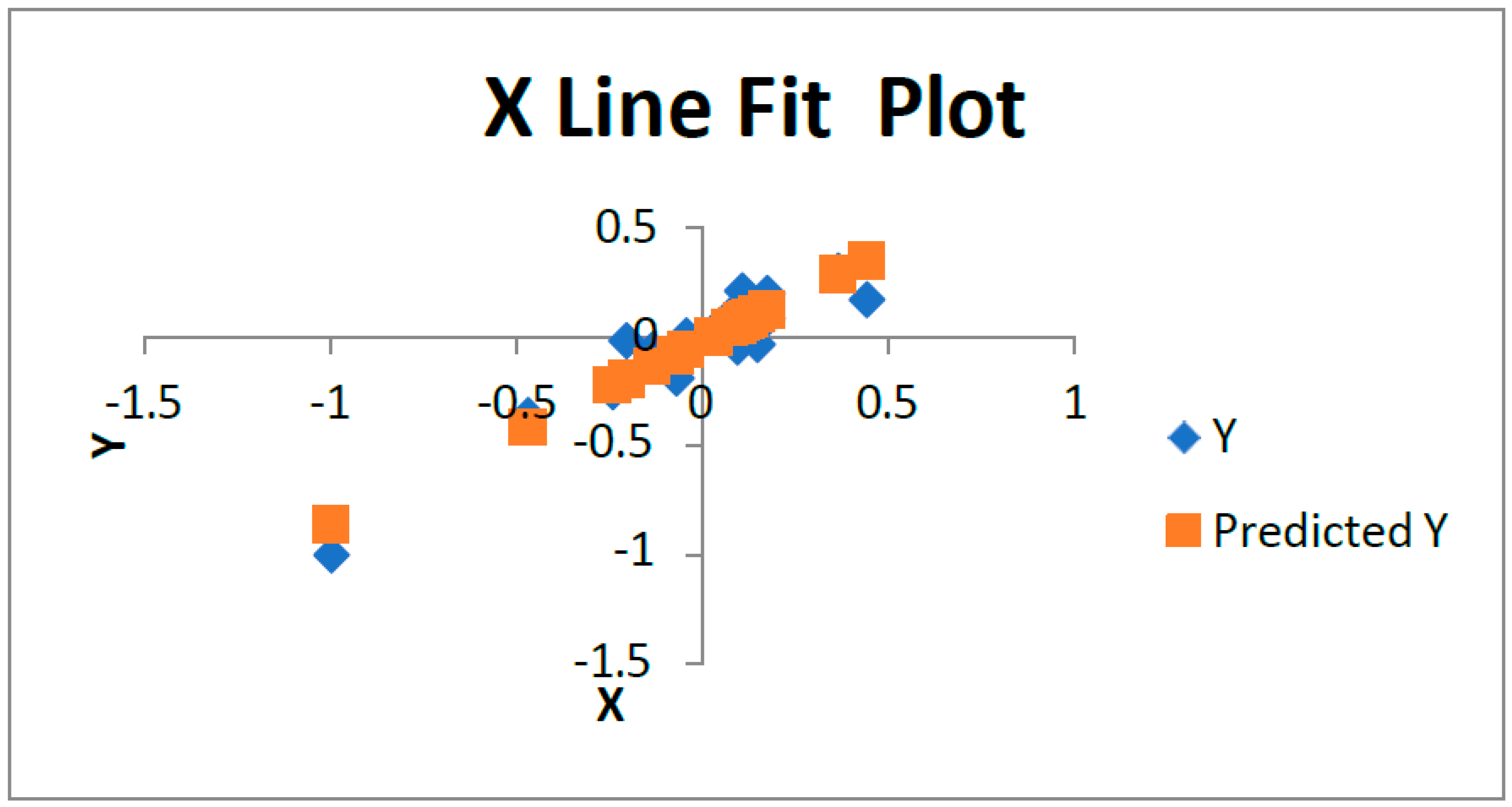
As this graphical representation shows the position of this company in last five years. Company’s stocks are not much high but this industry has grown in last five years.
This graph is representing that company have poor value of stocks in last five years but according to the industry growth they are going to be in better position.
This graph shows relation between market index returns and stock returns. Here market index as well as stocks both are slow in last five years
This graph represent the movement of stocks as well as industry both were good in last five years. So for investor’s point of view it is good to invest in such type of condition
The upward movement in this graph also shows the positive side. It means that this company is growing and having good position in stocks.
The computed t-statistic reveals a significance level at which the intercept value is high. Additionally, low R-squared value implies that variation in realized excess return is explained by CAPM. High standard deviation of realized excess return shows that there is low consistency in stock price performance of oil and gas producing companies listed on the KSE. The above results show that the CAPM model does not explain variations in realized excess return. Inefficiency and volatility in emerging markets such as Pakistan may be the underlying reasons for this behavior.
Conclusion
In this study, data of a sample of five oil and gas producing companies listed on KSE was analyzed through a regression model to determine whether CAPM is valid determinant of the realized excess return on these companies. The study was based on quarterly data for the period 2008-2017.This resulted in 21 observations for the regression analysis. The data analysis reveals almost no correlation between realized excess returns and the expected return based on CAPM. With respect to APT model, the study reflects that changes in GDP, inflation, exchange rate and market return do not serve as valid determinants of returns on oil, gas and fertilizer stocks. These results are generally in line with other studies conducted on listed companies in Pakistan, while minor differences are observed when the same results are compared with those of similar studies conducted on stock exchanges of other developed and developing countries
Market inefficiency and uncertain political/economic situation in the country appear to be major factors responsible for the inapplicability of these models on local scrips. Volatile market conditions result in unexpected changes in systematic risk due to which predictability of returns based on constant beta values tends to result in deviations of actual returns from values determined through these models. Also it may be the case that stock prices are subject to manipulation by a small number of key players.
It is pertinent to mention here that the study has some limitations such as a small size of 17 companies belonging to only oil, gas and fertilizer sectors. Further, the study was restricted to unconditional version of CAPM not taking into account other factors like size and book to market value factors.
Summary
This research paper is an empirical study of capital asset pricing model focusing on oil and gas sector companies listed in KSE-100index. To calculate the CAPM, finance textbooks often recommend using the Sharpe-Lintner CAPM risk-return relation to estimate the cost of equity capital. The prescription is to estimate a stock’s market beta and combine it with the risk-free interest rate and the average market risk premium to produce an estimate of the cost of equity. The typical market portfolio in these exercises includes just common stocks. But empirical work, old and new, tells us that the relation between beta and average return is flatter than predicted by the Sharpe-Lintner version of the CAPM. CAPM estimates of the cost of equity for high beta stocks are too high (relative to historical average returns) and estimates for low beta stocks are too low.
The CAPM is also often used to measure the performance of mutual funds and other managed portfolios . The approach to estimate the CAPM time-series regression for a portfolio and use the intercept (alpha) to measure abnormal performance . The problem is that, because of the empirical failings of the CAPM, even passively managed stock portfolios produce abnormal returns if their investment strategies involve tilts toward CAPM problems. For example, funds that concentrate on low beta stocks, small stocks or value stocks will tend to produce positive abnormal returns relative to the predictions of the Sharpe Lintner CAPM, even when the fund managers have no special talent for picking winners.
The five years quarterly data is used including 21 observations of oil and gas producing companies to calculate the capital asset pricing model. It has been observed that most of the variables assumed to be constant which are not stable as to be assumed to calculate this model. The data was gathered by a reputable source of KSE of the KSE-100 index. It is observed that beta factor effect the expected return of stocks but to predict the future of stocks this model is not enough for any future prediction of those stocks.
The CAPM as an introduction to the fundamental concepts of portfolio theory and asset pricing, to be built on by more complicated models . But we also warn students that despite its seductive simplicity, the CAPM’s empirical problems probably invalidate its use in applications.
This research paper is an experimental investigation of capital stock evaluating model keeping tabs on oil and gas segment organizations recorded in KSE-100index. To calculate the CAPM, fund course readings frequently suggest utilizing the Sharpe-Lintner CAPM risk- return relation to gauge the cost of value capital. The remedy is to gauge a securities exchange's beta and join together it with the risk free premium rate and the normal business sector risk premium to prepare a gauge of the expense of value. The ordinary advertise portfolio in these activities incorporates just regular stocks. Anyway experimental work, old and new, lets us know that the connection between beta and normal return is compliment than anticipated by the Sharpe-Lintner form of the CAPM. CAPM gauges of the expense of value for high beta stocks are too high (with respect to verifiable normal returns) and gauges for low beta stocks are too low.
The CAPM is likewise regularly used to measure the execution of shared stores and other oversaw portfolios . The methodology to gauge the CAPM time-arrangement regression for a portfolio and utilize the capture (alpha) to measure irregular . The issue is that, on account of the exact failings of the CAPM, even latently oversaw stock portfolios produce unusual if their speculation techniques include tilts to CAPM issues . For instance, subsidizes that focus on low beta stocks, little stocks or worth stocks will have a tendency to generate positive irregular in respect to the expectations of the Sharpe Lintner CAPM, actually when the trust directors have no unique ability for picking winners.
The five years quarterly time series data is used incorporating 21 observations of oil and gas producing companies to compute the capital asset pricing model. It has been observed that a large portion of the variables thought to be steady which are not stable as to be accepted to ascertain this model. The information was accumulated by a legitimate wellspring of KSE of the KSE-100 list. It is watched that beta element impact the normal return of stocks yet to anticipate what's to come for stocks this model is insufficient for any anticipated expectation of the aforementioned stocks.
The CAPM as an introduction to the major concepts of portfolio analysis and asset pricing, to be built on by more complicated models . Anyhow we additionally caution understudies that in spite of its seductive simplicity, the CAPM's exact issues likely discredit its use in provisions.
Recommendations
Despite the constraints illustrated above, capital stake evaluating models seem to offer an organization that claims a portfolio of risky organizations a suitable reasonable schema for survey the issue of long haul key arranging. Nonetheless, this reasonable structure is only one of some choices accessible to vital organizers. The capital possession estimating models focus on risk, return, and the worth of a business . Aggressive procedure is a vital component in an organization's general key plan. Then again, corporate simulation displays empower administration to look at a mixed bag of key choices, and to assess their results on a variety of budgetary, showcasing, and processing pointers. To be suitable to administration, capital holding valuing models must be connected to some kind of corporate simulation display. That is, one can anticipate an arrangement of business simulation shows, one for every business in the organization's portfolio, each of which creates a quality for Ri for that business and in addition other yield variables of investment to administration. A corporate union demonstrate that registers the quality of the organization additionally be required. A combined model should what's more treat the interdependencies around the organizations in the organization's portfolio, and the organization's association with the business portfolio through Rm. Particularly , the united model must have an ability to figure correct needed return without having steady variables thought to be in business sector. In short, we are proposing the utilization of the capital possession evaluating model theoretical structure as a critical yield of a corporate simulation demonstrate. Moreover, the development impart grid and experience bends upheld by The Boston Consulting Group and others could be treated as yields of business simulation demonstrates. The significant focal point of joining business simulation models to focused procedure models and CAPM models is that business simulation models can generously enhance the illustrative force of both intense method models and CAPM displays by connecting each of these logical instruments again to a model of the firm dependent upon sound monetary hypothesis. Therefore intense procedure models and CAPM models get compelling descriptive instruments for assessing the financial and budgetary results of elective systems which may be sought after by a given business or portfolio of organizations. The capital holding valuing models do offer some guarantee as a reasonable schema for key arranging in organizations which deal with a portfolio of organizations. In no sense may as well administration depend only on the restricted criteria of risk, return, and esteem of the business to settle on key choice. Nonetheless, the capital possession evaluating model structure consolidated with the intense procedure models, and a linkage to corporate simulation models might offer administration an amazingly compelling expository instrument for vital arranging.
References
- (2013, feb 27). Retrieved from http://cgr.umt.edu.pk/icobm2013/papers/Papers/IC3-Jan-2013-073.pdf.
- Bruce Hearn, J. P. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://www.kcl.ac.uk/sspp/departments/management/research/papers/theme/ibcmm/finance/capitala sset.pdf.
- D.A.I. Dayaratne, D. D. (2006). Retrieved from http://view.officeapps.live.com/op/view.aspx?src=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.sab.ac.lk%2FAcade- Activity%2Fvol_6%2F6.DOC.
- French, E. F. (2003, august). Retrieved january 2004, from http://faculty.chicagobooth.edu/finance/papers/capm2004a.pdf.
- Gupta, N. (2010, january 1). Retrieved from http://digitalcommons.macalester.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1008&context=econaward.
- Jarlee, S. (2007, may 30). Retrieved from http://econ.net23.net/econ/edu/cup/reports/2007/capm.pdf Kessel, P. v. (2007, 7 31).
- Matricola, T. S. (2010, june). Retrieved from http://erasmus-mundus.univ- paris1.fr/fichiers_etudiants/2952_dissertation.pdf.
- Mayur Agrawal, D. M. (2011, may 24). Retrieved from http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~magrawal/ICASSP_2011.pdf.
- Nel, W. S. (2011, january 26). Retrieved from http://academic.sun.ac.za/accounting/soon/Nel2.pdf.
- TAPONI, T. H. (1982, october). Retrieved from http://dukespace.lib.duke.edu/dspace/bitstream/handle/10161/2608/Naylor_The_Capital_Asset.pdf?se quence=1.
- Taylorx, A. G. (2011, october). Retrieved from http://www.lse.ac.uk/fmg/workingPapers/discussionPapers/fmgdps/dp691.pdf.
-
wikipedia. (n.d.). Retrieved from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karachi_Stock_Exchange.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).