1. Introduction
In the 20
th century Japanese engineer Genichi Taguchi said that “quality is the virtue of design” [
1]. The principal challenge for engineers is to design and produce devices that meet the expectations and needs of its end user. Nevertheless, a task of equal importance is the production of a high-quality product. Any high standard system not only functions properly as expected but also over a long period of time without any faults. It can be said that robust product is reliable, useful, functional, easy to maintain and efficient. With this in mind, it’s possible to fully understand what is meant by the first sentence of this paragraph. What’s more the reliable technology of high-quality is important for further development of science and new innovations. Ambitious space programs and long-term scientific programs must be supported by tools they use. Once again referring to Taguchi’s philosophy, the product should not only be free of any defects when leaving the production line but it is necessary to ensure high-quality during its use. The reliability of the device must be maintained regardless of operating conditions throughout the whole nominal period of use. In unfavorable circumstances, which can be called noise, the product should still meet the requirements. It is worth adding that designers are responsible for the robustness of the product. Regardless of how technologically advance the factory is mediocre designs will always result in mediocre products. [
1]
Unfortunately flawed, low-quality products some even designed to fail over time are becoming bigger issue every day. This problem has two faces, ecological and economical. The trouble of poor-quality products does concern all industries however here let’s focus on electronical sector. According to the Sustainable Development Goals 2020 report issued by the United Nations, the average resident of our planet every year for the last decade produces from 5.3 to 7.3 kilograms of e-waste [
2]. The amount of waste is constantly growing. Equally alarming is the fact that globally less than 20% of e-waste is recycled. Raw materials such as copper, silver, gold and rare earth metals used in electronics are irretrievably lost. Moreover every year devices worth billions of dollars are thrown into the trash. This particularly affects pockets of the individual customers who are forced to buy a new product because the previous one broke down very quickly.
To address the above issue, an experiment was conducted that constitutes the basis of this paper. The aim of the research was to answer the question, how do particular stages occurring in the production process affect the aging of electrical connections on flexible Printed Circuit Boards (PCB)? The connections were fabricated by metalizing holes. Interconnect Stress Test (IST) was selected and used as aging tests during the experiment. This method made it possible to determine the resistance of the printed circuit board to rigorous assembly techniques or operating conditions of an electronic device. The experiment was planned according to the Taguchi method, which allowed to reduce the number of tests and determine most favorable factors during production process. The research results have enabled the selection of optimized conditions and factors occurring in the process of manufacturing end products of the Internet of Things and critical applications of Industry 4.0, including sensors.
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) technology has been present in the electronics industry for several decades. It is a response to the miniaturization and growing quality requirements of electronic equipment. Printed circuit boards made of flexible materials, such as polyimide and polyesters, offer design freedom in electronic devices and, in particular, save space, thereby reducing the size and weight of electronic equipment. Flexible laminates have another great advantage that distinguishes them from traditional, rigid glass-epoxy laminates. They solve the sever problem of mismatch of Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) of laminate and copper in Plated Through Holes (PTH). Differences in the degrees of expansion of materials leads to excess stress generated in the components and electronic connections. In the worst case, this causes their breakage and circuit failure. However, a usage of flexible substrate, even if it is not fully plastic due to the assembly of components or use of a connection with a rigid laminate, has ability to reduce the effect of mismatch of coefficients of thermal expansion, while maintaining high reliability and low costs [
3,
4]. Flexible printed circuit boards have found application in relatively small devices such as notebooks, smartphones and especially thanks to its elasticity in wearable devices [
5,
6].
As it was previously noted, reliability of products should be a key requirement for their manufactures. At the prototyping and testing stage, it is checked in many ways. In the case of printed circuit boards, these are not just functionality tests. PCBs are often used in critical applications (in medical, space, military or automotive applications and high-power devices) or work in demanding conditions (such as high humidity environments or where mechanical shocks or rapid temperature changes occur). To check how PCBs behave in such conditions, they are subjected to many environmental tests. In order to ensure devices safety, reliability and compliance with the requirements and standards products should pass successfully analyses mentioned above. All tests should be performed in accordance with the IEC 60068 standard, which specifies a number of environmental testing methods. It specifies various atmospheric conditions for measurement to assess the ability of samples to perform under diverse scenarios [
7]. These tests include accelerated HALT/HASS tests, water absorption tests (in a highly humid environment), vibration tests and thermal shock tests. Each of them allows to verify the device from a different side for a particular assignments.
In this research, the Interconnect Stress Tests were selected to check the reliability of flexible printed circuits. IST testing, also known as Thermal Cycling Induced by Direct Current Testing, is an accelerated aging test method developed in the 1990s to measure changes in resistance of plated through hole and reliability of interconnect in printed circuit boards. They arose from the need for fast, repeatable and reproducible research, the results of which would additionally correspond to those obtained from existing methods. Moreover, the new technology was supposed to be cheap and easy to analyze the results. The idea of IST is based on the flow of direct current through the Plated Through Holes on the board. This current heats the metallization and the surrounding laminate. Eventually as a result of cyclic heating and cooling of the PCB, failure occurs. The primary cause of failure in IST testing is considered to be a mismatch in the coefficient of thermal expansion between the epoxy resin and fiberglass in the substrate materials and the copper in the through holes. The effect of failure is crack in metallization of plated hole. IST relies on specially designed sample coupons placed on PCB fabrication panels [8-11].
Environmental tests, IST especially, allow to observe the behavior of individual technological solutions in high-power applications, such as GaN semiconductor technology. [
12] The aim of these activities is, among others, the production of circuits with high electrical and thermal reliability for modern solutions that include GaN technology. This fits into the global trends in the development of the so-called Green Power Electronics. Efficient power supply and charging of electronic devices and electric vehicle batteries is now becoming a necessity. Combining the efficiency of GaN with the resistance of flexible materials allows for significant increases in productivity and reliability.
This particular study investigated the reliability of flexible printed circuits by the environmental thermal tests. The tests included samples differing in the number of conductive layers, the type and thickness of the laminate used, the diameter of the metalized holes, and those made using different values of current density in the electroplating copper plating bath. The use of various production factors was aimed at determining which of them had the greatest impact on the reliability of the tested samples. The qualitatively best variant of the board construction was indicated using the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and analysis of variance (ANOVA) method for each factor. For better understanding the processes present in tested PCBs, samples were analysed by metallographic cross-section, along with observation under a scanning microscope and an infrared camera.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Experimental Factors
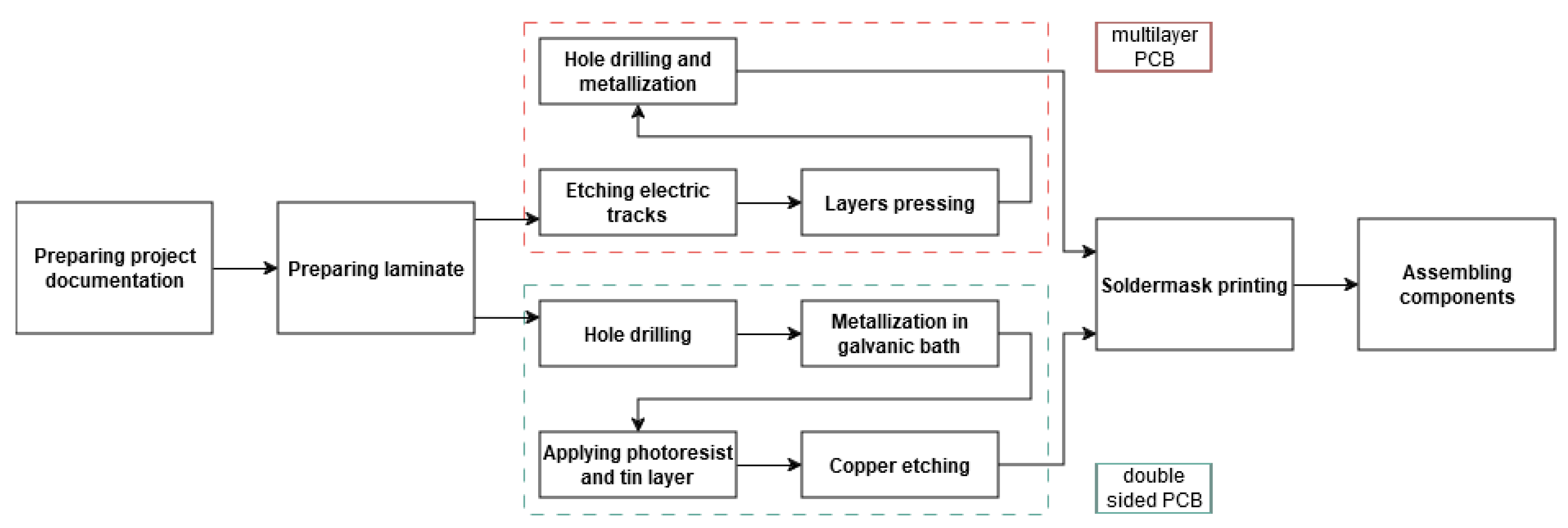
The production process of printed circuit boards is extremely complex. It consists of many stages and is influenced by many different factors. The path through which the PCB passes in the factory from the raw laminate to the finished product is shown in
Figure 1. The first step in designing the experiment is to select several factors among all others. It is necessary due to the multitude of elements in the PCB production process and limited time and material resources. In this paper the focus was on factors that can provide the condition of flexibility of the board and on elements of the PCB structure playing critical role during Interconnect Stress Test. During selection the elements that will be a part of the experiment, those that are directly influenced by the designer of PCB (or after a consultation with the producer) were taken into account.
Five factors were chosen, which may have the biggest impact on the life of Flexible Printed Circuits. These were:
Type of the laminate; polyimide and glass-epoxy (FR4) laminate
Number of conductive layers; 2 and 4 layers
Thickness of the laminate; 50 and 100 µm
Diameter of the plated holes; 0.3 and 0.4 mm
Current density in the galvanic bath; 1 and 2 A/dm2 – constant thickness of the metallization equal to 20 µm
2.1.1. Type of the Laminate
The first choice for the base material for FPC is polyimide, a polymer plastic material. As it is one of the basic laminates used in the production of flexible printed circuits. This is due to the flexibility of the material and its durability when working at higher temperatures. However, its big disadvantage is the high price. [
13] In order to compare its performance in thermal stress tests, it was decided to analyze samples produced on glass-epoxy laminate, in its the most popular variant, FR4. [
13] The problem with glass-epoxy laminate is its rigidity. It comes from subsequent layers of glass fibers stack one on another. However if enough thin base material will be used than the laminate should be flexible and meet the requirement of the application. Keeping this in mind the purpose of comparing these two base materials was to investigate whether a traditionally used laminate will endure comparable environmental conditions to polyimide material.
2.1.2. Number of Conductive Layers
Number of two conductive layers, where copper plays the role of the conductor, is dictated by the nature of the IST analysis. It is possible to design and fabricate Plated Through Holes only when PCB has no less than two layers where conductor is located on both sides of the laminate. Currently, in advanced systems where Integrated Circuits with very numerous pinouts or Ball Grid Arrey (BGA) package are used, it is necessary to design multi-layer boards. Despite the increased complexity of the structure and production process, this solution has many advantages [
14]. The second simplest PCB design after the double-layer board is four-layer board. Therefore the reliability of the device was checked depending on the complexity of the construction of a PCB.
2.1.3. Thickness of the Laminate
Most flexible films come in a narrow range from 12 μm to 125 μm of material thickness. [
3] Hence it was decided to arbitrarily chose two values from the middle of the range, 50 μm and 100 μm. It is worth noticing that the practice shows that thinner laminates cause more problems during PCB production. It's necessary to find a golden mean between the application requirements and the manufacturer's capabilities. The choice of material thickness as next factor allowed to check whether thin laminate is more resistant to thermal exposure. The thickness of a single laminate layer and the number of conductive layers sum and together affect the total thickness of the PCB.
2.1.4. Diameter of the Plated Hole
Diameter of the plated holes varies a lot from 100 µm to several millimeters. This is due to the many roles that PTHs play. They can be used as electronic interconnection between different parts of the circuit, heat sink, mechanical support for component assembly and many more. As the size of plated through holes decreases their durability also decreases. [
15] On the other hand the reliability of vias is highly influenced by the ratio of its diameter to depth (the smaller the ratio, the more durable connection). It was also important to select commonly used hole sizes. [
16] Bearing all this in mind, to maximize the potential of thermal stress testing it was decided to make holes of 0.3 mm and 0.4 mm.
2.1.5. Current Density in the Galvanic Bath
Shortening production time of a single product is in top of mind of every manufacturer. In case of PCB one way to obtain this goal is by controlling the current density value during electroplating process. The higher the current density, the faster the process copper deposition. [
17] Increasing the current density to the maximum possible value is a common practice in production plants. Thanks to this, the bath time is shorter and a larger number of printed circuits can be produced. However, alternating current density changes the crystal structure of the deposited metal. Because of that the last element of the production process that have been taken into account when planning the experiment was the process of metallization of holes in the galvanic bath. It is the electrochemical deposition of a metal coating into a hole drilled in the laminate using direct electric current. The coated surface serves as the cathode of the electrolytic cell. Anode is a block of conductive material. [
13] Copper is deposited by cation reduction. After consultation with the factory that produced the test samples, it was decided to choose two metallization variants using a current density of 1 A/dm
2 and 2 A/dm
2. The aim was to find an answer to the question whether the shape of copper crystals in the holes has an impact on reliability.
Selected factors and their levels are shown in the
Table 1 placed below.
2.2. Design of the Experiment
The experiment was designed and planned according to the method proposed by Genichi Taguchi. Designing experiments is part of his entire approach to the problem of product quality loss. The basic concept of Taguchi's philosophy is the reduction of system instability at its output and therefore improvement of device’s quality. The situations when the observed characteristics at the output of the received product differ from the ideal or the desired one are called quality loss. In consideration of quality, Taguchi introduces the classic signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). [18, 19] The signal power here is the desired response, and the noise power is the deviation from the ideal product characteristics:
The best design is not the one that maximizes signal strength, but rather the one that effectively reduces the impact of noise. The SNR value should be as high as possible regardless of external factors that uncontrollably affect the system. Therefore, the goal of quality improvement efforts can be expressed as striving for a maximum signal-to-noise ratio. Taguchi’s method aim is to reduce the variability of the final product under different conditions in the work environment. It ensures that the choices made in the lab remain also valid during production and use. [18, 19]
Going through the theory of quality loss, Taguchi comes to a point where he proposes a way to plan the experiment. His idea is based on partial-factorial design of experiment (DOE) and the planning of subsequent studies based on orthogonal array. [18, 19] Thanks to that Taguchi’s method reduces the number of test runs required to perform. The orthogonal arrays are an extension of Latin squares. Written in the following form, L
N(s
m), they are matrices of n rows by m columns. A specific property of orthogonal arrays is that in each pair of columns, each of the possible ordered pairs of elements appears the same number of times. The columns correspond to individual factors, the contents of cells in the columns correspond to factor levels and the rows correspond to test runs. Taguchi suggested a catalog of 20 arrays (including 18 orthogonal ones), but over time the concept was developed and further suggestions were created. It is also possible to create submatrices by removing some columns from the array. In this way, many different multivariate experimental designs can be generated. [
20]
The experiment was conducted based on the selected criteria. In this case for a full-factorial design of the experiment, 2
5 = 32 tests would be necessary to perform. It was decided to design the experiment by using fractional-factorial design and Taguchi method was chosen for this purpose. Thanks to that the number of tests required to perform the research was reduced. The first step in designing the experiment according to Taguchi is to construct an orthogonal array. Because, as it was explained in the previous paragraph, 5 factors, 2 levels each were selected, it was decided to use L
8(2
7) orthogonal array. (Array L
8 has 8 rows and 7 columns, so in case of the research described in this paper, 2 columns remained unused). Therefore the entire experiment will be carried out on the basis of 8 tests. The constructed orthogonal array for the purpose of the experiment is shown in
Table 2. A four time saving in number was achieved as a benefit of using the fractional-factorial design of the experiment according to the Taguchi’s method, in comparison to full-factorial design of the experiment. This is a huge reduction of costs of time and materials intake. In order to eliminate accidental errors that could distort the statistics obtained at the end of the study, from each produced PCB construction variant, three copies will be drawn and tested within the experiment.
2.3. Design of Printed Circuit Board
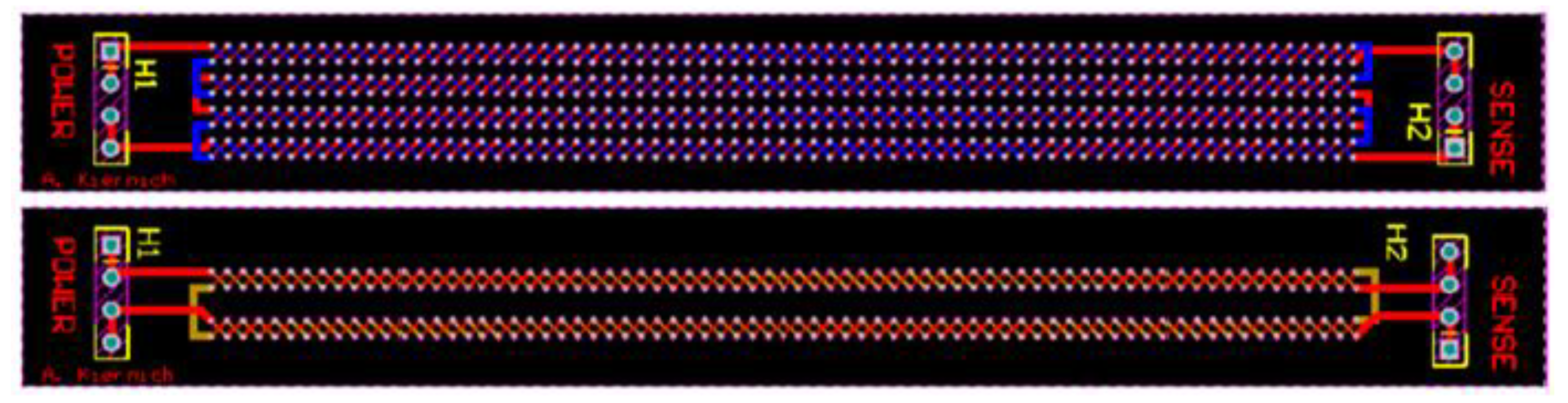
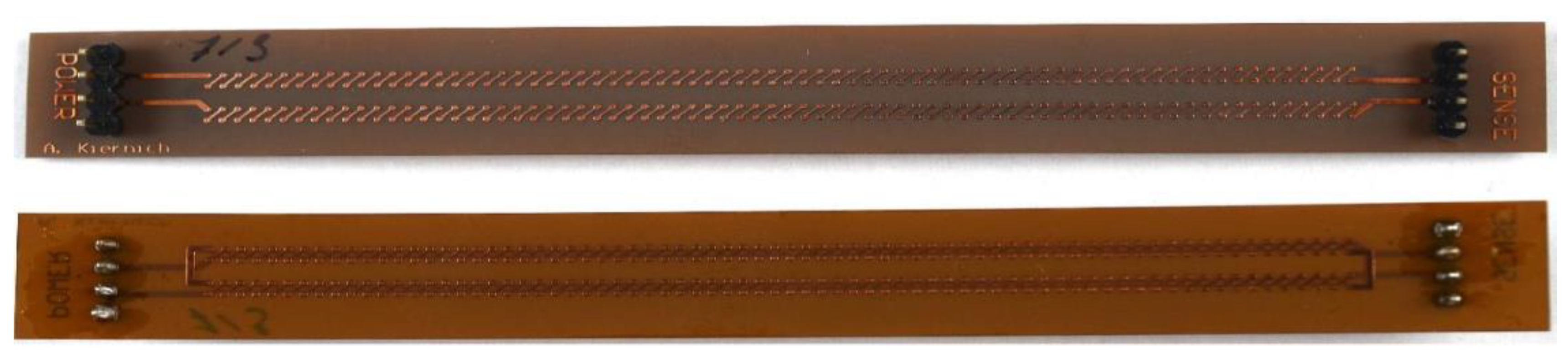
Tests performed for the purpose of the experiment required specifically designed and manufactured PCBs. Samples were not only fabricated in accordance with the selected factors but also they must be adequate for IST. IPC (formerly Institute for Printed Circuits) standard number 650-TM 2.6.26 gives guidelines on how the samples should be designed. Design of samples is shown in
Figure 2 and an example of a PCB used as the sample is shown in
Figure 3.
The standard distinguishes between two possibilities of routing tracks. In the first method, named "Method A", there are two or more independent tracks on the test board. Power supply and heating circuit is marked as POWER, and the measuring circuit resistance as SENSE. In both methods, direct current flowing through the tracks heats the entire board to the set temperature, which then is cooled to room temperature. However “Method A” was chosen because it allows the measurement of resistance both on the sensing and power supply circuits [
21]
The basic design requirement for samples was the dense arrangement of a large number of connections between the board layers. The aim of such a solution was to maximize the chance of a failure. The distance between successive metalized holes was 1.25 mm. The holes have been planned along the entire length of the board. The power supply and measurement circuits were arranged in a way resembling a braid.
During designing the board, a decision was made to use a laminate with a 17.5 µm thick copper foil layer. In the technological process of producing the printed circuit mosaic, approximately another 17.5 µm was applied to the tracks. This makes the total thickness of a single track was approximately 35 μm. The thickness of the metallization in the holes was about 20 µm as a result of electroplating. As it was previously mentioned, one of the characteristic parameters of the electroplating process of copper is its duration. In the production of the test boards, previously selected current densities were used in two variants. At a current density of 1 A/dm2 and with an efficiency of 100%, 0.2 μm of copper is deposited in one minute. For the established galvanic bath parameters, the deposition of the desired copper thickness takes 110 minutes for 1 A/dm2 and 55 minutes for 2 A/dm2. As it can be observed increasing the current density significantly affects the production time.
Each PCB measured 14 mm x 120 mm. The standard recommends that the test sample should have the shape of a rectangle, usually with dimensions of 0.6 and 5 inches, i.e. respectively 1.524 and 12.7 centimeters. They should have pinouts for power supply and measurement circuits on both short edges, male connectors with a spacing of 2.54 mm. [
21] Thickness of the PCBs in different variants along with the rest of information about test samples are presented in
Table 3. In case of the laminate made of polyimide a material from the DuPont manufacturer Pyralux AP series was used. Depending on the desired laminate thickness, AP8525R or AP8545R laminate was used (50 μm or 100 μm rightly).
2.3.1. Microvia
During designing the test boards, the concept of used type of connections was clarified. In the case of a two-layer board, plated through holes were used, while in four-layer boards blind micro holes. This design was chosen because it enabled testing these two solutions and check them for durability and robustness.
A micro-hole, or micro-via, is a blind one according to the definition of the IPC-T-50 standard a structure with a maximum aspect ratio of 1:1, which at most it can have depth not more than 0.25 mm. [
22] Blind micro holes are characterized by a thinner layer of metallization near the neck of the microvia. This is the place where cracks occur most often. This happens because the expanding substrate presses down onto the neck of the microvia. For this reason producing PCBs with this solution gave an idea of the difference in work of microvias and PTHs.
2.4. Permorfed Aging Tests
The entire IST procedure with details of individual stages and explanations are provided below.
The first step in the sample testing procedure was to measure the resistance of the POWER and SENSE circuits. Then the exposure current was determined. The resistance values of the circuits on the boards differed slightly, it forced the individual determination of the exposure current for each sample. According to the IPC-TM-650 standard, 30-second, 60-second and pre-tests could be performed in order to adjust the exposure current. The 30-second and 60-second tests were used to pre-adjust the exposure currents to prevent the sample from heating up too quickly. Any number of 30-second and 60-second tests could be performed. After the initial estimation of the exposure currents, it was obligatory to proceed to pre-tests. The sample was under full exposure for 3 minutes. If the sample reached the required temperature, the process of determining the exposure current was considered completed and the sample was accepted for subsequent cycles. The temperature reached in 180 seconds should be ±1 °C of the nominal value specified in the IPC standard. [
21]
Full exposure of samples could be progressed after positive result of pretest. The maximum number of cycles was set to 10 000 and the possible relative change in resistance at the maximum and ambient temperature was set to 10%. The heating time in single cycle is 180 seconds. After 3 minutes, the sample was cooled to room temperature by a forced air. Cooling time was a function of the overall thickness and design of the board. Following the suggestion from the standard IPC-650-TM from 1999, the maximum cooling time was set at 2 minutes [
11]. The resistance is measured every 2 seconds during heating in both circuits, POWER and SENSE, however, during cooling only in the SENSE circuit.
When change of resistance crossed the threshold of 10% or the 10 000th cycle was reached process of sample exposure stopped. The measurement system recognized six different possible reasons for the test termination. The first was the successful completion of all planned exposure cycles. The remaining five determine the reason for interrupting the test, these were: a break in the POWER circuit, a break in the SENSE circuit, exceeding the maximum temperature, exceeding dR (acceptable resistance change) at the ambient temperature and exceeding dR at the maximum temperature. Throughout the cycle, the system compared the current resistance with the value measured during the first cycle at the maximum and ambient temperatures. If the change in resistance during heating was more than ten times the initial value, the system considered it as a break in the POWER or SENSE circuit. If the change was one and a half times greater than acceptable at the maximum temperature, it was treated as a temperature exceedance. However, if at the end of the heating or cooling process the change in resistance exceeded the acceptable value, the test was terminated due to exceeding dR at the maximum or room temperature.
The sample temperature was calculated based on the measured resistance using the following formula:
where:
T – temperature of POWER or SENSE circuit;
α – temperature coefficient (for copper it is equal to );
RT – resistance at temperature T;
Renv – resistance at room temperature;
Tenv – ambient temperature.
The summary of IST procedure is presented in
Table 4 placed below.
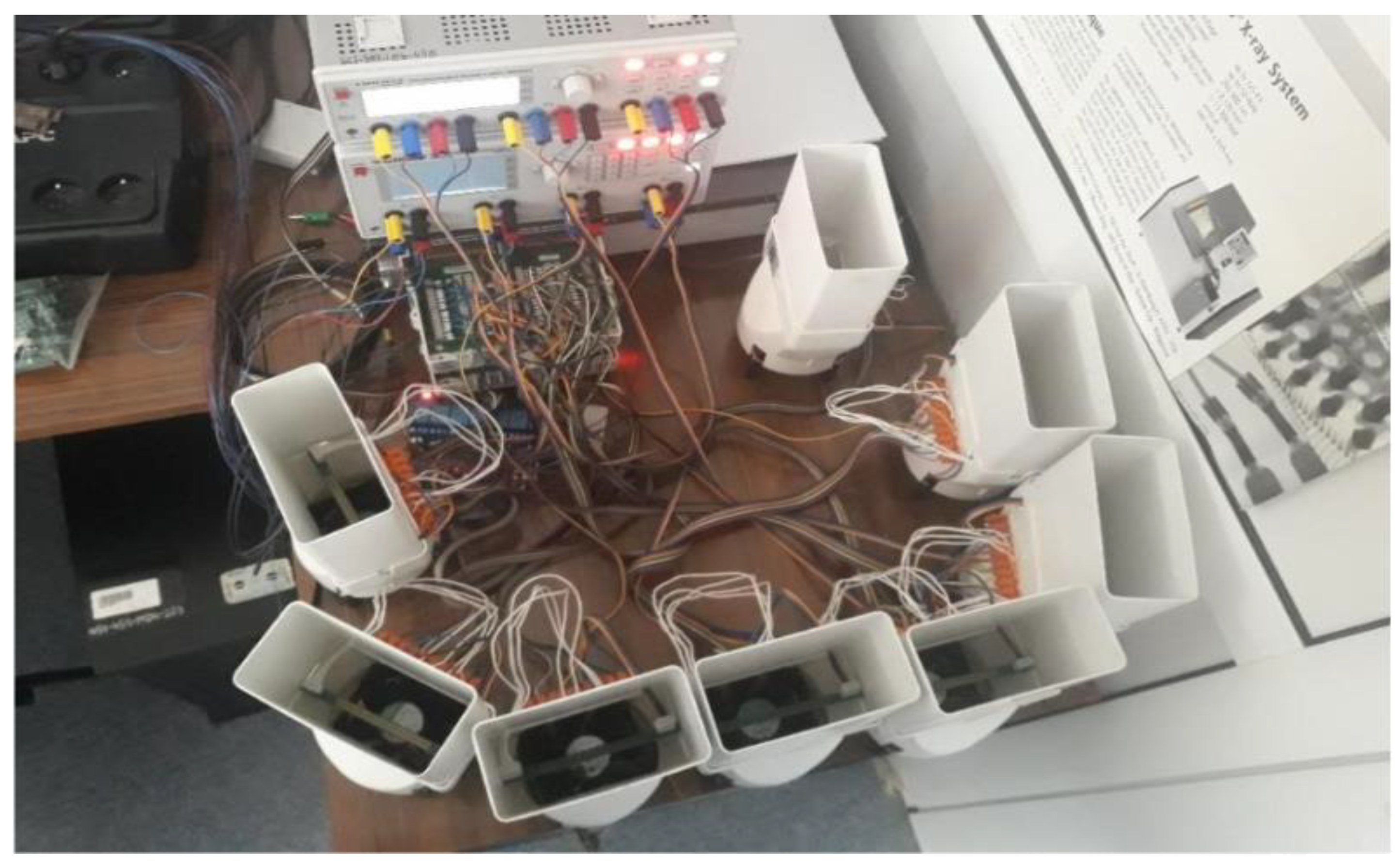
2.4.1. Workstation
The workstation was composed of the following elements:
Control computer – laptop from DELL;
Six-channel digital multimeter – 3706A-NFP from Keithley;
Power supply I – HMP2030 from Rohde & Schwarz;
Power supply II – HMP2040 from Rohde & Schwarz;
Temperature sensor - USB-Tset electronic thermometer from Aqua Lab;
12V computer fan from Arctic.
The workstation is presented in
Figure 4. The control unit was connected to other devices via a USB interface. The resistance in the SENSE circuit was measured with an ohmmeter in the range of 5 Ω with a resolution 1 mΩ. During heating, the resistance of the POWER circuit was measured using the indirect method by reading the current and voltage (with a resolution of 1 mA and 1 mV, respectively), and then resistance calculation. Eight samples were tested simultaneously. Each test plate was cooled individually by its own fan, and each POWER circuit was individually powered from a programmable power supply. In order to minimize the impact of the external environment on the test result the station was placed in an air-conditioned room, and the sample and the fan were covered with a screen.
3. Results
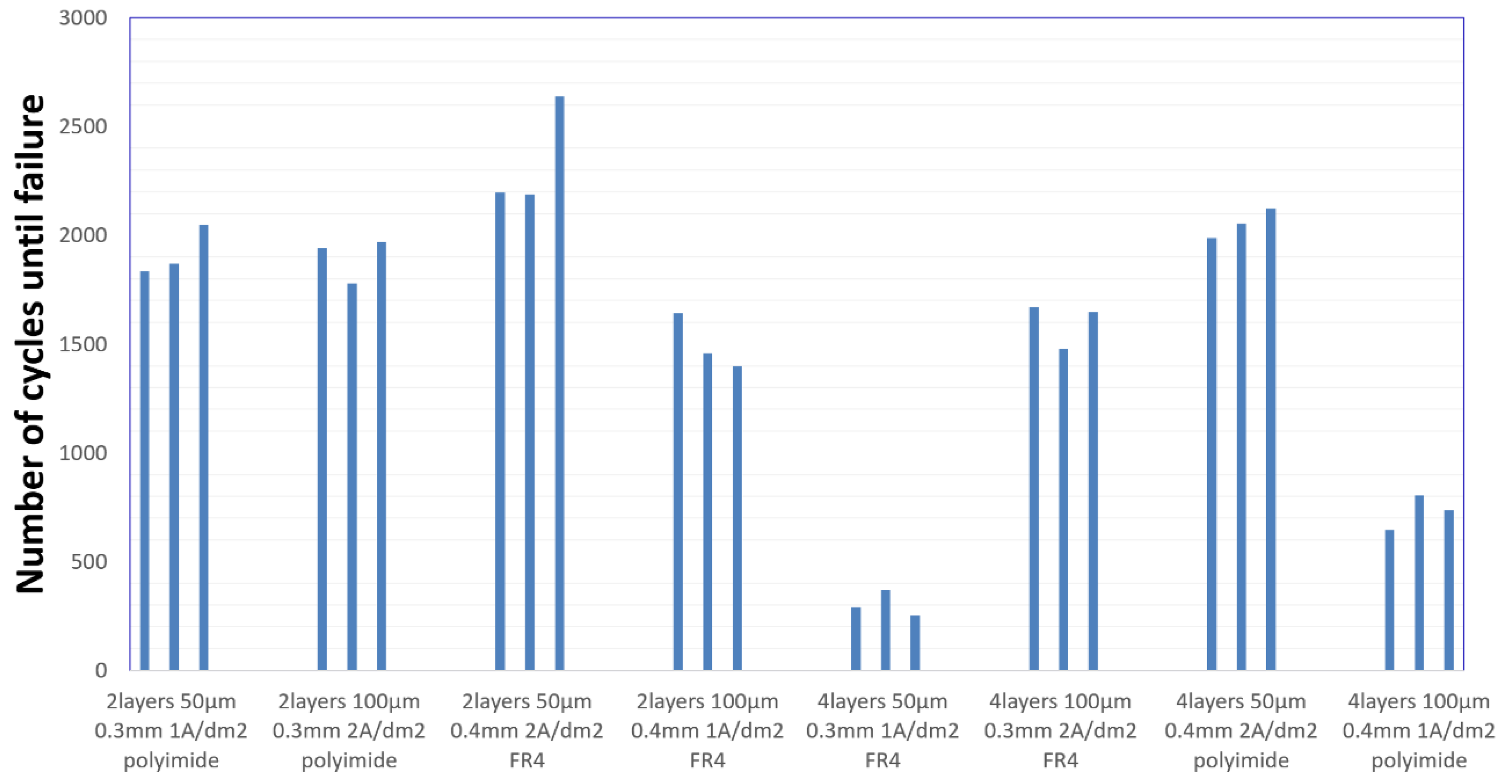
The Interconnect Stress Test results are presented in the
Figure 5. The test results are grouped into eight clusters that correspond to each of the board construction variant.
The
Figure 5 shows the results of the experiment in an illustrative way. However, just by observing the graph itself, it can be seen that in the case of the variant of two-layer boards with plated through holes, the number of cycles achieved is significantly higher than in the case of the construction with microvias. It can also be seen that the smallest deviation in results is for the fifth experiment, while the largest for the third.
Table 5 presents the basic statistical data. The arithmetic mean for each variant independently and for the entire population was calculated. The standard deviation for each variant was also provided and the signal-to-noise ratio was calculated according to Taguchi's concept. In the conducted experiment the more cycles the test board survived, the better, therefore, the formula for SNR is as follows:
where:
An integral part of the analysis of the results is the calculation of main effects, independent factors influencing the dependent variable. In the case of the conducted tests, this is the effect of individual parameters of the production process on the durability of the test boards.
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9 and
Figure 10 (a) contain tables of the main effect, their arithmetic mean values and the SNR coefficient for individual cases. The optimal parameter value is highlighted by bolded font.
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9 and
Figure 10 (b) show illustration of the above analysis results. They show the track of the SNR parameter depending on the level of partial factors.
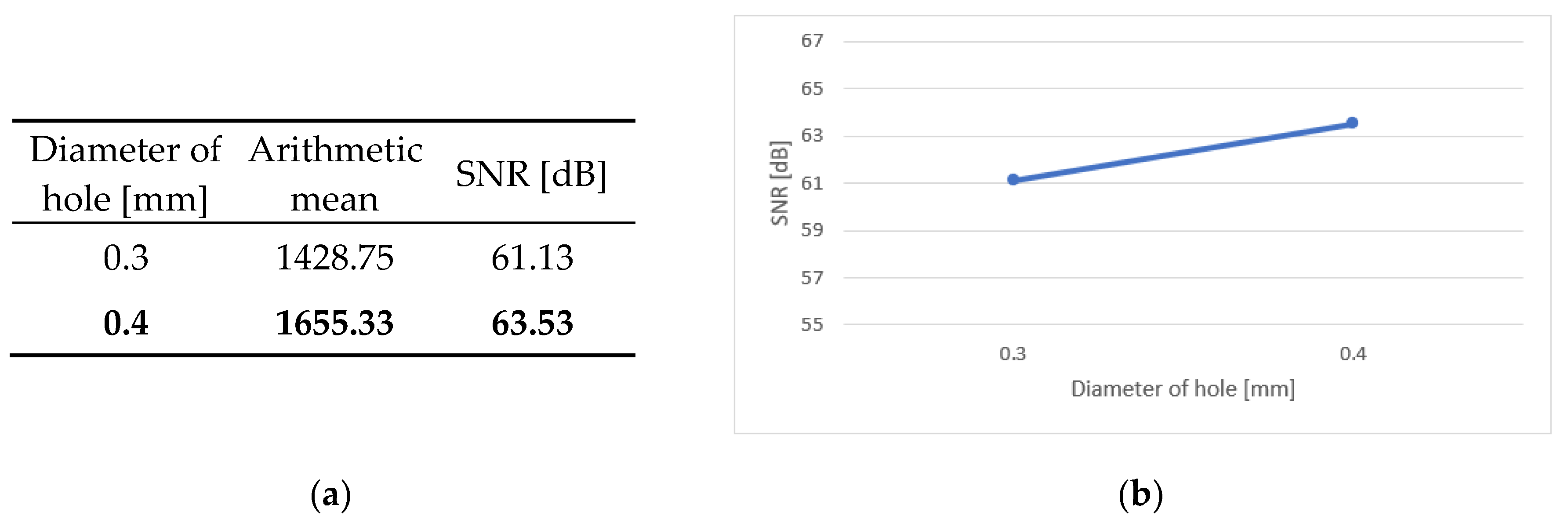
Based on the obtained results and above data, it can be concluded that the optimal variant is a two-layer printed circuit board, manufactured on a polyimide laminate, with a laminate layer 100 μm thick, a hole diameter of 0.4 mm and a current density of 2 A/dm2 in the galvanic bath. The factors that have an upward trend are the laminate thickness, the diameter of holes and the current density in the galvanic bath. This means that the higher the value of a given parameter, the better the signal-to-noise ratio. In addition, the above graphs show that metalized through holes and a polyimide laminate perform better than microvias and a glass-epoxy laminate.
In addition to the study proposed by Taguchi, a complicated mathematical instrument, the analysis of variance was performed. This tool allows to assess the significance of differences between the means of individual groups. Conducting this type of analysis allows to determine the correlation between selected parameters of the production process and the reliability of flexible printed circuits. Moreover ANOVA allows for considering cases with many independent factors. [
23] In case of this research an analysis was carried out for five factors. The calculation results are presented in the
Table 6.
For a significance level of 99%, the F statistic in all considered cases takes the value of 8.285. [
24] Based on the observation of the data from the table above, it can be concluded that the durability of the connections is equally influenced by two factors: the number of layers (type of connection) and the current density. For a lower significance level, only 90%, the F statistic has a value read from the table equal to 3.00698. [
24] The final result is significantly influenced by two more factors: the laminate thickness and the hole diameter. The type of laminate does not have a significant effect on the final result.
In the case of the most important factors, the number of conductive layers and the metallization warrant, ANOVA confirms the results obtained after the analysis using the Taguchi method. Additionally, the percentage share of each factor in the overall scatter of observation values is given in column P. These values once again confirm the previous results.
3.1. Additional Research
The aim of an additional tests carried out on test boards was to indicate the cause or effect of connection failures on the tested printed circuit boards. As part of the tests, photos were taken with a thermal camera, metallographic cross-sections were made and the surface of the metallized holes was observed using a scanning electron microscope.
3.1.1. Analysis by Thermal Camera
The temperature to which the sample heats up was checked using a thermal camera. This device images the recorded infrared radiation emitted by the tested object. This test served as a control. It also allowed to observe how the dissipated heat was distributed on the test board. Below are thermographic,
Figure 11 and
Figure 12 show of the sample during heating and failure. The thermal imaging camera A320 from Teledyne FLIR was used for the tests.
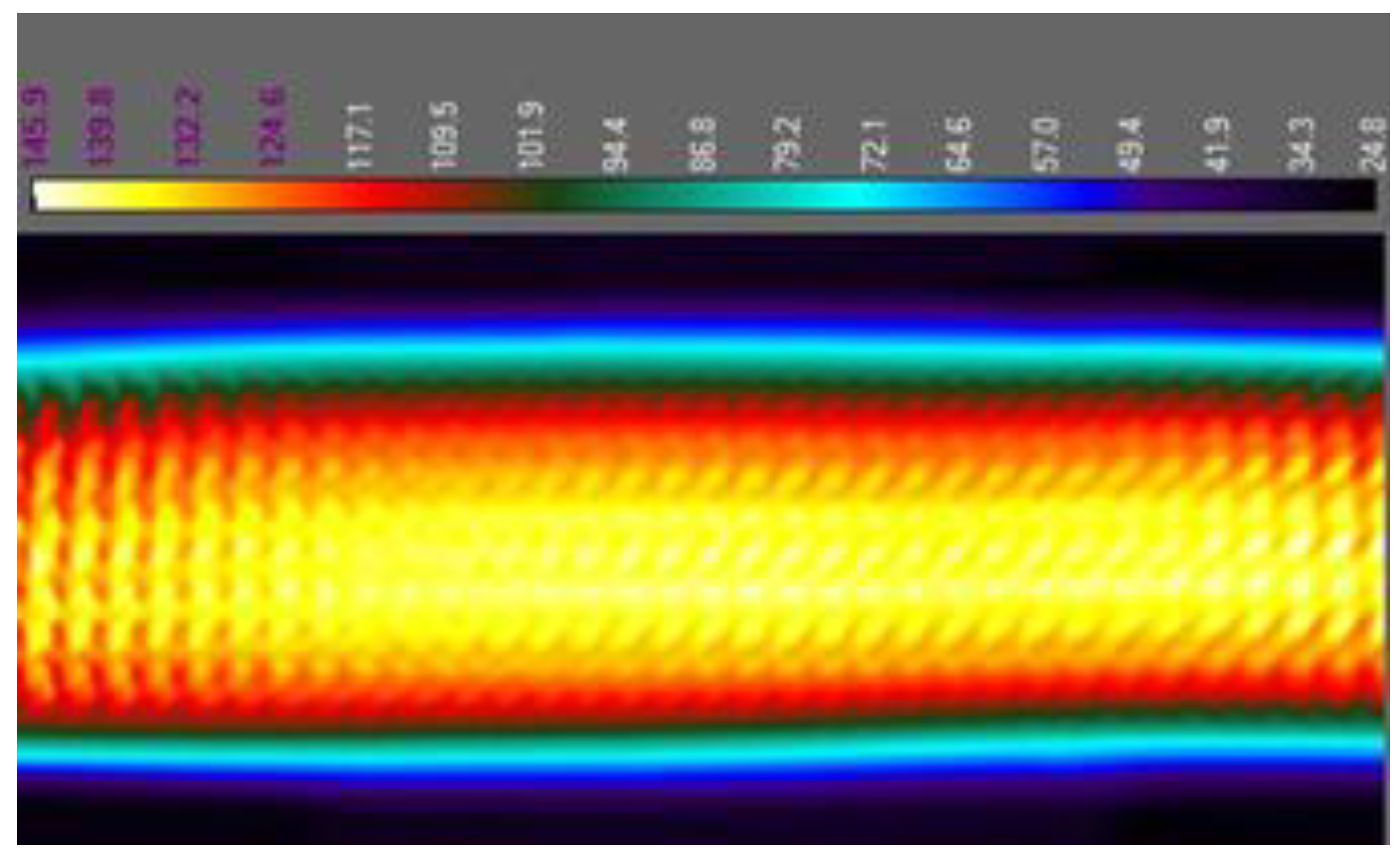
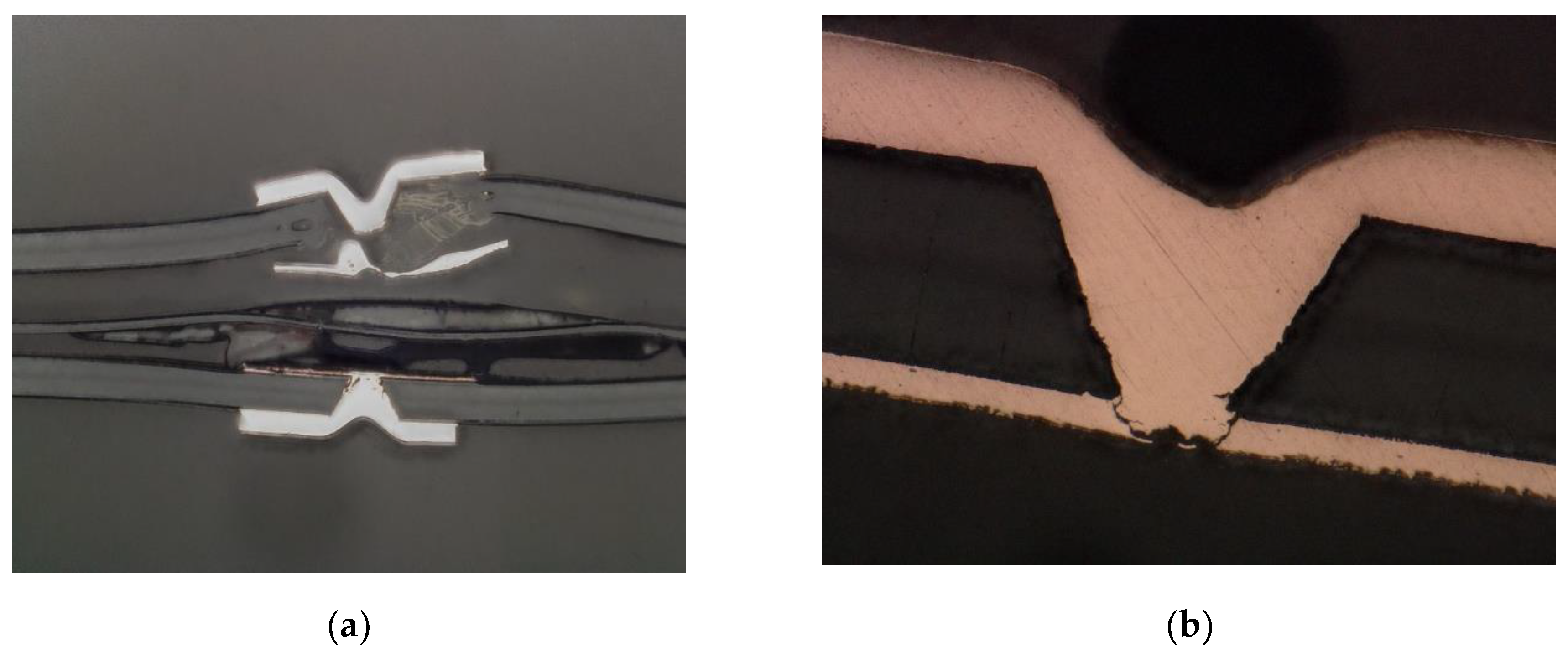
The first conclusion that comes to mind is that the highest temperature is reached in the middle of the board, as can be seen in the
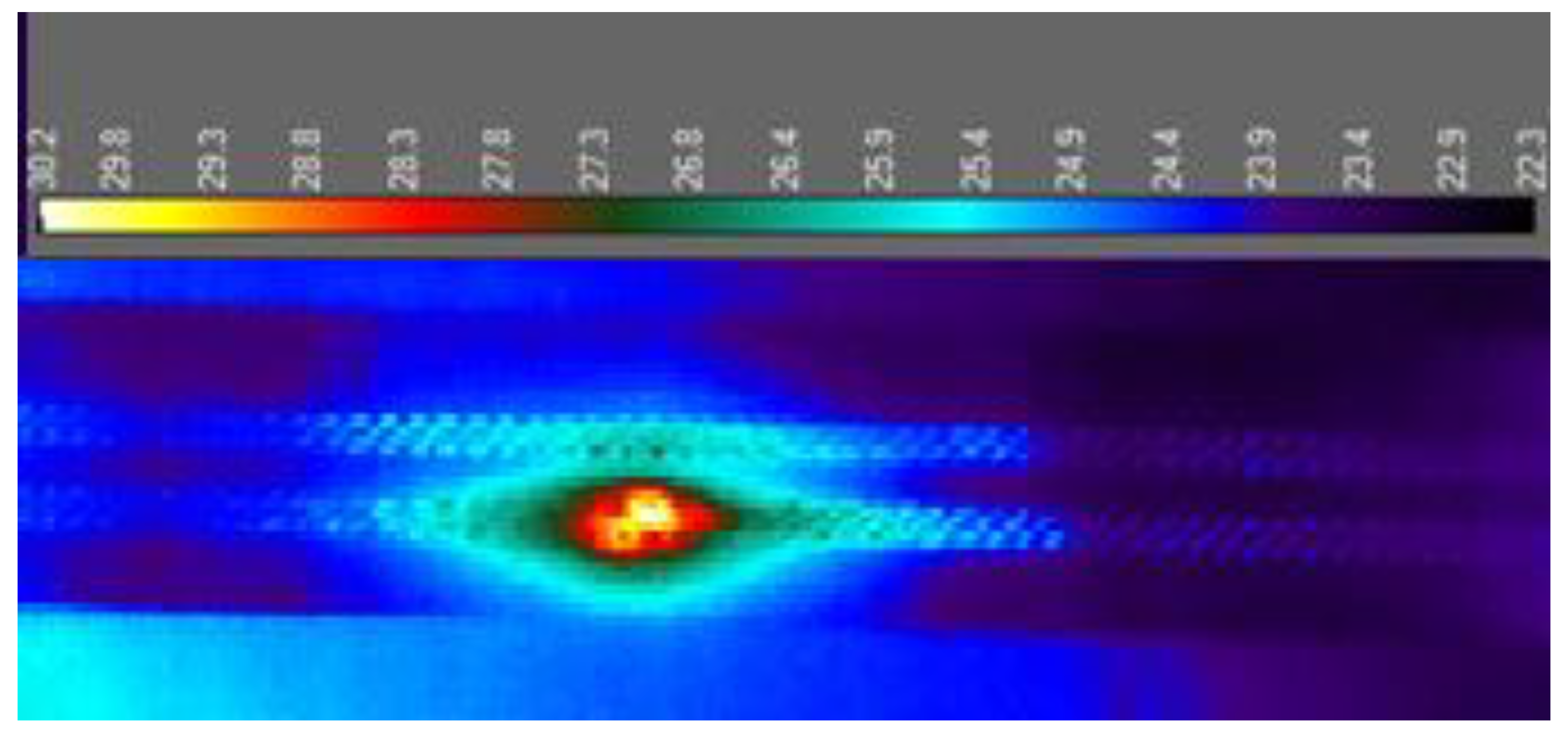
Figure 11. The dissipated heat is distributed evenly along its entire length of the sample. The measurement performed with the thermal camera also made it possible to make sure that the measurement system is working properly and that the samples were heating up to the planned temperature. This examination also made it possible to locate the failure point. The resistance increased in the place where the metallization was damaged. The thermographic image shown in
Figure 12 clearly shows a hotter spot on the surface of the test board. Even at low exposure currents, order of magnitude smaller than current used during tests, the difference was sufficient to select a place for a later metallographic microsection to assess the degree of damage.
3.1.2. Analysis by Metallographic Cross-Section
In order to analyze the places of metallization cracks as a result of stresses caused by IST aging tests, metallographic cross-sections of selected test boards were performed. Based on the results of observations with a thermal camera, places were selected where failure of the metallized connection occurred with high probability. Cross-sections were made for the indicated places. The samples for analysis were prepared on the MECAPOL P262 metallographic cross-section unit, Presi, and the MetaSery 250, BUEHLER. Observations were carried out on the Eclipse L-150 metallographic microscope from Nikon, and the VHX6000 digital microscope from Keyence. The analysis results are presented in
Figure 13 and
Figure 14. The evaluation of metallographic sections was based on the criteria suggested by the IPC-A-600 standard. [
25]
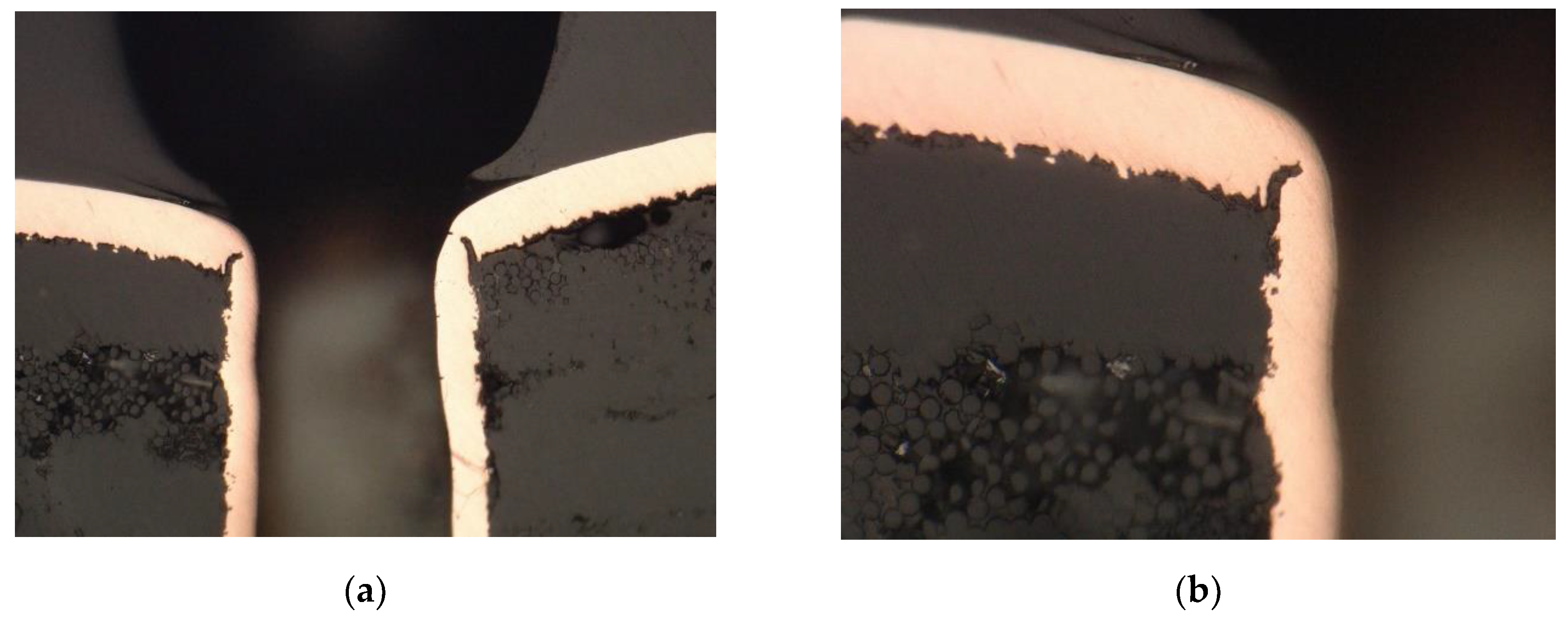
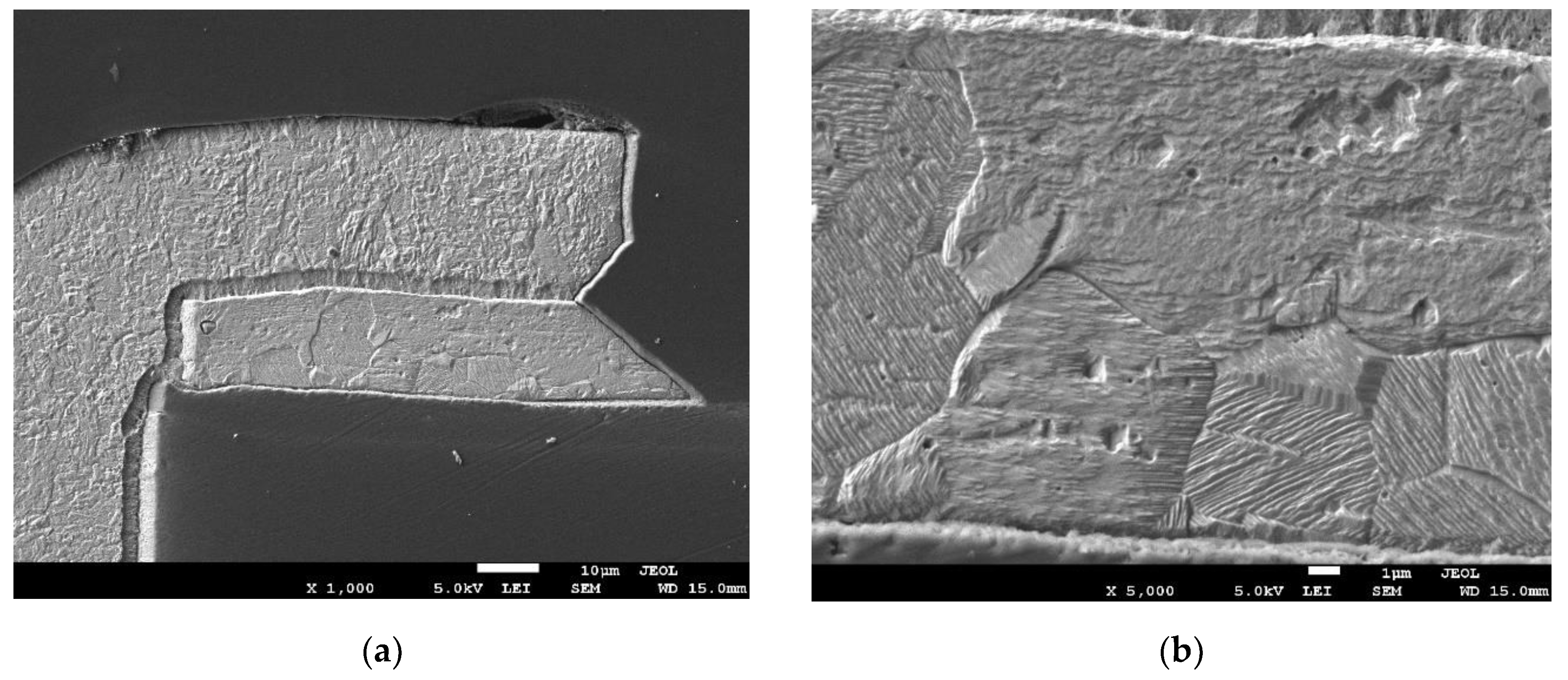
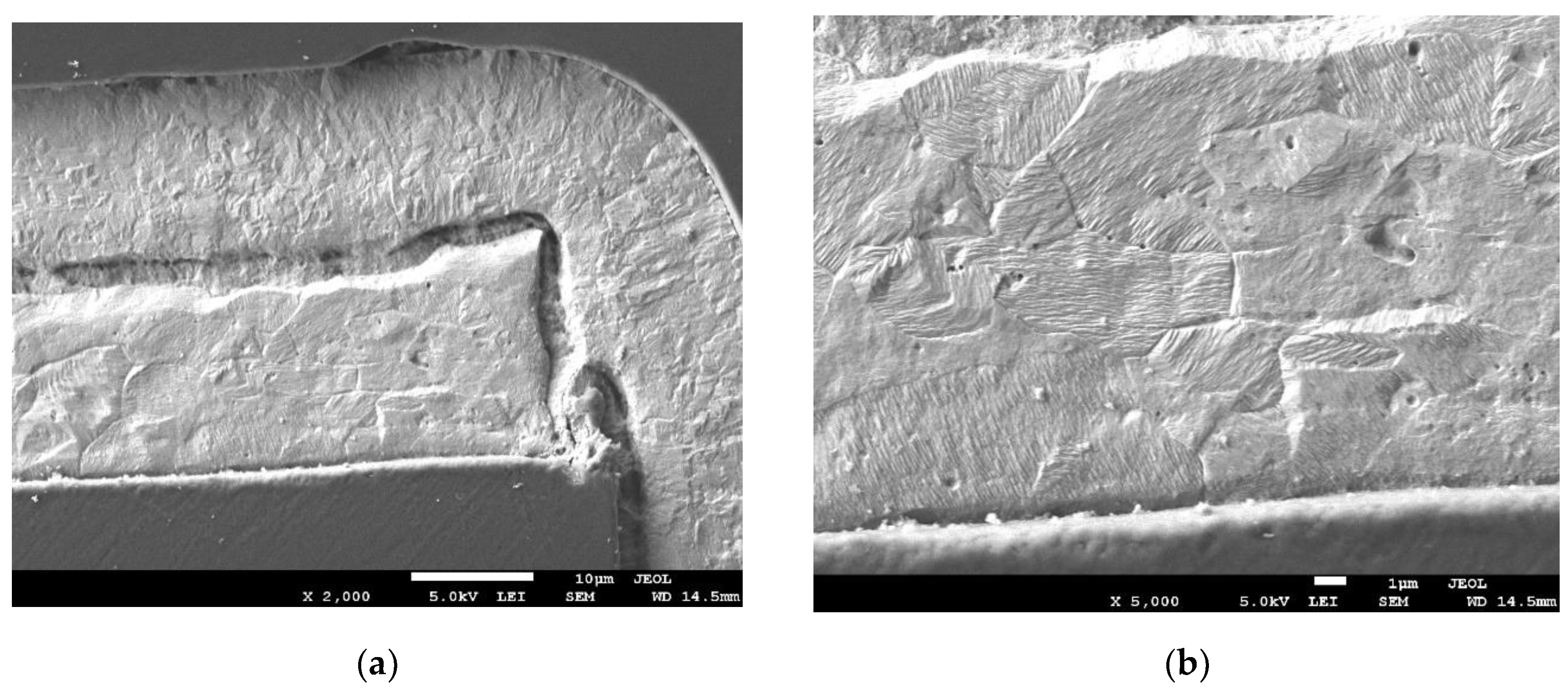
All of the cross-sections clearly show the place of crack and damage to the metallization in the plated holes. Characteristic failure locations can also be observed on the cross-sections. For PTH, this is the point of contact between the plated hole and the copper ring on the board surface. For microvias, this is the so-called neck. The sections also show that in the case of PTHs, the crack starts from the "center" of the board. A similar observation could not be made for microvia due to the complete damage to the connection.
In addition to the damage to the metallization resulting from the cracks, another effect of thermal stress and the effect of the failure can also be observed on the sections. On the damaged boards, the laminate delamination occurred, the separation of individual components of the laminate from each other (fibers from resin or Kapton from glue). Voids and cracks in the laminate and the complete separation of individual components of the base material from each other can be observed in the
Figure 13(a). In the case of PTHs, another defect occurred. Lifted land above the board surface. A void has appeared between the annular ring and the laminate. All the defects described above disqualify the printed circuits from further use.
3.1.3. SEM/EDX
Further tests were carried out using a scanning electron microscope SEM JSM-7600F with EDX spectrometry from Jeol. Cross-sections were made from two samples of PTHs with metallization obtained after bathing with current density of 1 A/dm2 and 2 A/dm2, and then copper was etched using a solution of ammonium hydroxide with hydrogen peroxide. Cross-sections were made using a metallographic sample preparation system type MECAPOL P262, PRESI, and MetaServ 250, BUEHLER. Thanks to this, it was possible to observe the structure of individual copper layers on the laminate.
Figure 15 shows layers of copper foil and electroplated with 1 A/dm2.
Figure 16 shows copper layers with the second current density variant. The tests were performed on samples that were not subjected to thermal stresses.
In the case of both samples, it is easy to distinguish between the copper that covered the plate in the galvanic bath and the copper foil that the manufacturer applied to the laminate. The latter has large crystals, with the same shape and structure on both samples. In the case of copper applied galvanically, the metal crystals are much smaller, creating a fine structure. The crystals of copper applied galvanically are several times smaller than those from copper foil. In the case of copper applied as a result of the galvanic bath, the difference in the size of the crystals for different variants is also clearly visible. The structure for the variant with a current density of 1 A/dm2 is finer.
4. Discussion
After conducting the experiments and analyzing the results, the following summary was compiled for the factors considered in the experiment.
The factor that turned out to be statistically the most significant is the current density in galvanic bath. Meaning that this is the factor that had the greatest impact on the robustness of printed circuits. The samples with variant of 2 A/dm2 have the SNR 6.88 dB higher than for the second one. The use of higher current density in the galvanic bath turned out to be more advantageous for the quality of metalized connections. Although fine-grained crystals are more resistant to mechanical stress, they are characterized by higher resistance. This second parameter turned out to be crucial in terms of the IST.
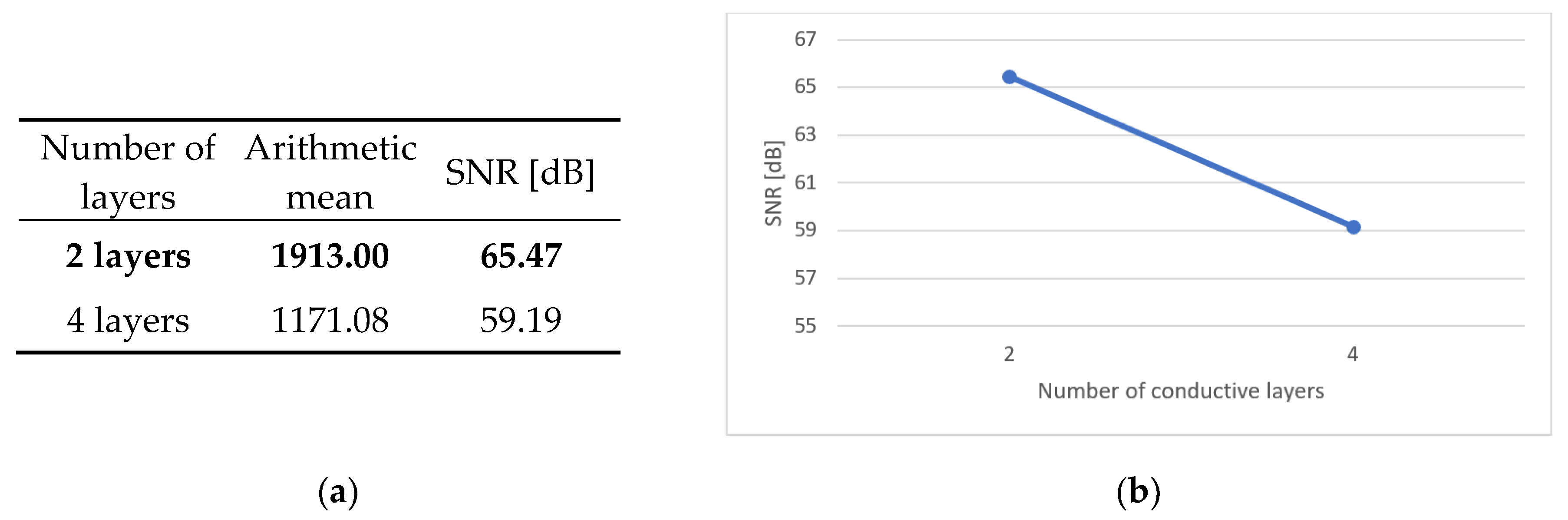
The number of conductive layers also plays a significant role. After final decisions related to the construction of the test boards, a different type of connection was assigned to each variant of the parameter. The specificity of the PTH and microvia constructions determined the role that the number of layers plays in the reliability of printed circuits. Plated through holes proved to be much more reliable than microvias. The SNR coefficient for samples with PTHs is 6.29 dB higher than for the second variant of connections. In future studies, an additional advantage would be to conduct tests also for buried holes.
The thickness of the laminate layer has a small effect on the quality of the product. Unexpectedly, it turned out that the thicker the laminate, the better. However, the difference is so small that it is almost imperceptible, difference of SNR for two variants is equal to 0.41 dB. This may be due to the flexibility of the boards. For both thicknesses, 50 μm and 100 μm, the printed circuits are flexible, even though in the worst case the entire board is 405 μm thick. Samples made of both polyimide and glass-epoxy laminates were not rigid. In the case of IST tests, where the work of the material and its resistance to thermal expansion are important, flexibility turned out to be a huge advantage. Despite the fact that in the case of a thin laminate the effect of volume increase with increasing temperature is smaller than in the case of a thick material, the thicker laminate turned out to be slightly better. On the other hand, we can refer once again to the previously discussed parameter. It should be noted that two-layer boards performed much better than four-layer ones. Their performance could have been influenced not only by the construction of the connection itself, but also by the thickness of the entire board.
The diameter of the holes also has a small effect on the final reliability. In accordance with the predictions, the larger the hole coped better. However, it should be noted here that the obtained experimental results in many cases exceed 1000 cycles. These are very high performances. In order to increase the failure rate of the test boards the ratio of the hole diameter to its depth, i.e. aspect ratio, should be reduced. Currently, this factor is from 0.125 : 1 to 0.(3) : 1. In future studies, the aspect ratio should be reduced, for example by using smaller diameter of the holes. In case of the samples analyzed during the research, the smallest metalized hole had a diameter of 0.3 mm. However, this value is close to the technology limit. Not many manufacturers are able to fabricate metalize holes with the diameter smaller than 0.1 mm. Not only the drilling process may be problematic but their metallization as well. For this reason, making such small holes is difficult to implement. The advantage here is the small thickness of the laminate, which can facilitate the production process itself. Another way to reduce the shape factor is to increase the thickness of the base material. However, it should be noted that this can lead to the loss of the basic requirement for the board, which is their flexibility. Additionally, in the case of microvia, the limitation is the maximum value of the aspect ratio, i.e. 1: 1.
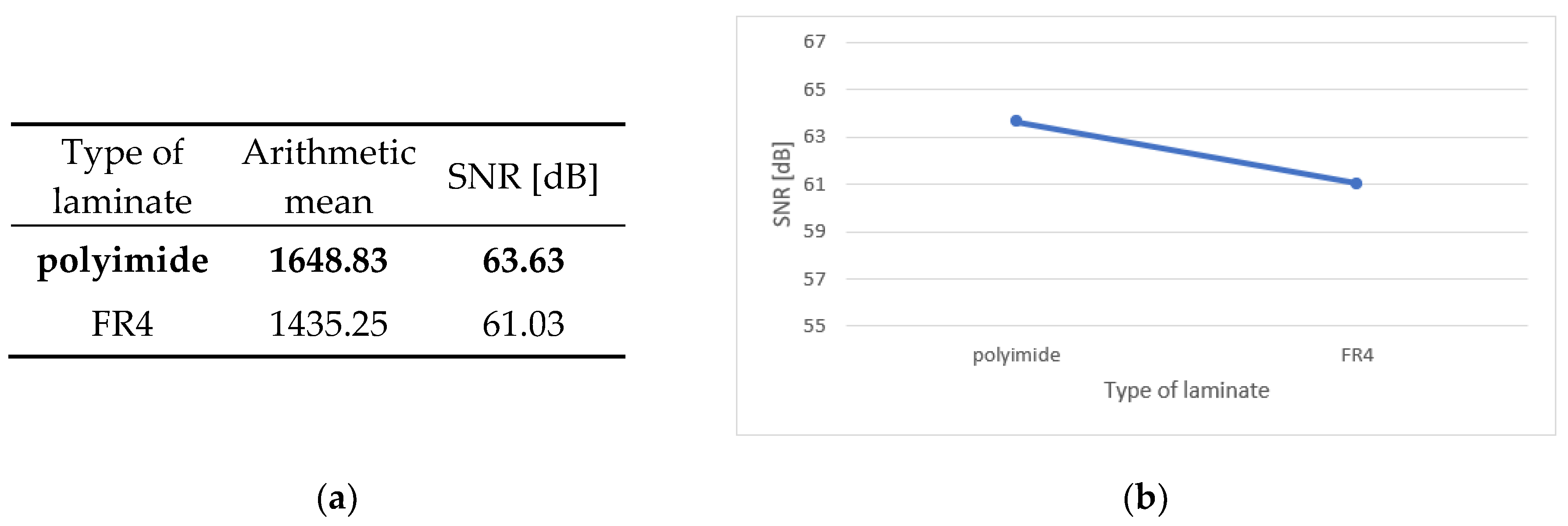
The type of laminate used achieved a similar difference in SNR coefficients as the diameter of the holes, about 3 dB, but according to the analysis of variance, this factor is insignificant. The polyimide as a base material performed better than the classic glass-epoxy. The small difference may result from the previously discussed properties of the tested circuits, namely their flexibility.
The above discussed three factors, the laminate thickness, the diameter of the metalized holes and the type of the laminate did not play a major role in the conducted experiment. The tested printed circuits in all variants of the structure were relatively thin and retained their flexibility. These two properties of the test boards turned out to be of great importance for their reliability during IST analysis.
In order to confirm the obtained results, an additional verification experiment was conducted. The test samples were manufactured based on the optimized factors. The printed circuit board for verification of the results were manufactured with two conductive layers placed on a polyimide laminate, where the laminate layer is 100 μm thick, the diameter of the holes is equal to 0.4 mm and the current density of 2 A/dm2 was applied in the galvanic bath. IST tests were performed for three samples. The obtained results are presented in the
Table 7 below.
Based on the observation of the results obtained from the verification experiment and the previous ones, it can be concluded that the specified optimal production factors of flexible printed circuits have a positive and noticeable effect on the durability of the electronic connections. Ultimately, the goal of improving the quality of the product is to find the best values of the factors under control that occur in the production process in order to maximize the SRN coefficient. The signal-to-noise ratio value for the verification experiment is the best of all those obtained in the conducted experiments. The research showed that the theory behind the designing of experiments using the Taguchi method brings the desired effect in the form of indicating the optimal solution.
Two parameters turned out to have a major impact on the final result. More research is needed to check whether the observed trends in the impact of factors on reliability will be maintained. For this reason three levels of the factor with the greatest impact on the result, the current density in the galvanic bath, should be prepared and analyzed. In continuation of the research it is also worth checking how holes with smaller aspect ratios will behave, in several variants. An experiment with factors of three levels or more will provide a more complete picture of how they affect the robustness of flexible printed circuits.
5. Conclusions
Based on the evaluation of the results obtained from the experiment planned using the Taguchi method to examine the reliability of flexible printed circuits using the Interconnect Stress Test, the best variant of the board construction was qualitatively determined, which ensures a high-quality final product with a low failure rate. The analysis was performed using the signal-to-noise ratio and analysis of variance for each factors taken into account during the experiment. The factors that turned out to be the most important in terms of reliability are the number of conductive layers and the current density in the galvanic bath. In contrast to the type and thickness of laminate, and the diameter of the metalized holes, which have a relatively small impact on the result. A higher value of current density in the plating bath will result in greater robustness. Research shows that a two-layer structure is more reliable than a four-layer structure and at the same time plated through holes are more reliable than microvias. The thickness of the laminate, the diameter of the vias and the type of base material do not have a significant impact on the test results, because the printed circuit boards in all considered cases were relatively thin and retained their flexibility. In the end the optimal variant of the board construction is two conductive layers, on a polyimide laminate, where laminate layer is 100 μm thick, hole diameter equal to 0.4 mm and current density of 2 A/dm2 in the galvanic bath.
Based on the optimal factors, samples for the verification test were produced. Based on the observations of the results obtained from the verification experiment and previous experiments, it can be concluded that the specified parameters of the production process of flexible printed circuits have a positive and noticeable impact on the durability of the connections. They therefore have an innovative impact on the quality of products, and high reliability opens up applications in Internet of Things, space, medical and Industry 4.0 applications. Moreover the research methodology shown high durability of particular variants of the PCB construction to thermal stress. PTH works well as heat sink which has significant importance in application of GaN technology in high-power semiconductor devices. [
12] This experiment achieved the set goal and presented a number of factors that determine the quality of the PCB. The answer to the question of how to achieve high-quality and reliable electronic products while limiting the consumption of raw materials and reducing the amount of waste was found.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K., J.K., W.S., M.K. and A.C.; methodology, A.K., J.K., W.S., M.K. and A.C.; software, A.K.; validation, A.K., J.K.; formal analysis, A.K.; investigation, A.K.; resources, A.K., W.S.; data curation, A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.; writing—review and editing, A.K., J.K., W.S., M.K. and A.C.; visualization, A.K.; supervision, J.K.; project administration, A.K., J.K.; funding acquisition, W.S., M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was co-financed by the President of the Łukasiewicz Center as a part of the project GANSUP – Opracowanie zasilaczy liniowych w technologii GaN do zastosowań w oświetleniu i sieciach typu smart grid (grant no. 1/Ł-IEL/CŁ/2022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data of the experiments can be requested from the authors.
Acknowledgments
The presented research was part of the master’s diploma thesis titled “Wpływ czynników występujących w procesie produkcyjnym na niezawodność elastycznych obwodów drukowanych” defended in 2023 by MSc Andrzej Kiernich supervised by PhD Jerzy Kalenik on the Warsaw University of Technology
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Taguchi, Genichi, Clausing, Don, Robust Quality, Harvard Business Review, January – February 1990, Available online:. Available online: https://hbr.org/1990/01/robust-quality (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- United Nation. Sustainable Development Goals Report 2020; United Nation: New York, 2020; ISBN 978-92-1-101425-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fjelstad; Joseph. Flexible Circuit Technology; BR Publishing: Seaside, 2006; ISBN 0-9667075-0-8. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, I.C.; Wagner, S. Overview of Flexible Electronics Technology, In Flexible Electronics: Materials and Applications; Wong, W.S., Salleo, A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarrait, R. , Ullah-Khan, M., Dietzel, A. et al., A Flexible Double-Sided Curvature Sensor Array for Use in Soft Robotics. Sensors 2024, 24, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwonil, P.; Minoo, P.K. Advancements in Flexible and Stretchable Electronics for Resistive Hydrogen Sensing: A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard IEC 60068-1:2013. Environmental testing - Part 1: General and guidance.
- Winco, K.C.; Yung, Hai Ming Liem, Henry H. S. Choy, and Yuen Wah Man, Correlating Interconnect Stress Test and Accelerated Thermal Cycling for Accessing the Reliabilities of High Performance Printed Circuit Boards. Packaging and Manufacturing Technology 2011, 1, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougal, Stewart, Interconnect stress testing (IST) - an overview of its development and capabilities. Circuit World 2003, 29. [CrossRef]
- Cauwe, M. , Vandevelde, B., Nawghane, C. et al., Challenges in introducing high-density interconnect technology in printed circuit boards for space applications. CEAS Space Journal 2023, 15, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard IPC-TM-650:1999. Number 2.6.26; Test Methods Manual - DC Current Induced Thermal Cycling Test.
- Bi, W.; Kuo, H.; Ku, P.; Shen, B. Handbook of GaN Semiconductor Materials and Devices; CRC Press, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R. Handbook of Printed Circuit Manufacturing; Van Nostrand Reinhold Company: New York, 1985; ISBN 978-94-011-7014-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoto, T.; Matsui, K.; Kikuchi, K.; et al. New high-density multilayer technology on PCB. IEEE Transactions on Advanced Packaging 1999, 22, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, W.; Liem, H.; Choy, H.; Man, Y. Correlating Interconnect Stress Test and Accelerated Thermal Cycling for Accessing the Reliabilities of High Performance Printed Circuit Boards. IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging and Manufacturing Technology 2011, 1, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matisoff, B.S. Handbook of electronics packaging design and engineering; Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, 1990; ISBN 978-94-011-7049-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, M.E.; King, M.J.; Sole, K.C. Davenport, William G., Extractive Metallurgy of Copper; Elsevier, 2011; ISBN 978-0-08-096789-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddi, A.; Salmon, M. Design Principles and Methodologies From Conceptualization to First Prototyping with Examples and Case Studies; Springer: Bolonia, 2019; ISBN 978-3-319-95341-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnad, K. Quality Control, Robust Design and the Taguchi Method; Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole Advanced Books & Software: Pacific Grove, 1989; ISBN 978-1-4684-1474-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzaҫebi, C.; et al. Taguchi method as a robust design tool. Quality Control-Intelligent Manufacturing, Robust Design and Charts; IntechOpen, 2020; ISBN 978-1-83962-498-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard IPC-TM-650:2014. Revision A - Number 2.6.26, Test Methods Manual – DC Current Induced Thermal Cycling Test.
- Standard IPC-T-50. Revision N, Terms and Definitions for Interconnecting and Packaging Electronic Circuits.
- Rutherford, A. ANOVA and ANCOVA: a GLM Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, 2011; ISBN 978-0-470-38555-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Online Computational Resource, F-Distribution Tables. Available online: http://www.socr.ucla.edu/Applets.dir/F_Table.html (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Standard IPC-A-600:2010. Revision H, Acceptability of Printed Boards.
Figure 1.
Scheme of production path of PCB.
Figure 1.
Scheme of production path of PCB.
Figure 2.
Design of samples, two-layer PCB above, four-layer PCB below.
Figure 2.
Design of samples, two-layer PCB above, four-layer PCB below.
Figure 3.
Example of a PCB used as the sample.
Figure 3.
Example of a PCB used as the sample.
Figure 4.
Work station used during the experiment.
Figure 4.
Work station used during the experiment.
Figure 6.
Main effect – number of conductive layers (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 6.
Main effect – number of conductive layers (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 7.
Main effect – thickness of laminate (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 7.
Main effect – thickness of laminate (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 8.
Main effect – type of laminate (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 8.
Main effect – type of laminate (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 9.
Main effect –diameter of hole (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 9.
Main effect –diameter of hole (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 10.
Main effect – current density in galvanic bath (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 10.
Main effect – current density in galvanic bath (a) Table showing statistics of arithmetical mean and SNR; (b) Graph showing the track of SNR coefficient.
Figure 11.
The test board during heating cycle.
Figure 11.
The test board during heating cycle.
Figure 12.
Location of failure on the test board.
Figure 12.
Location of failure on the test board.
Figure 13.
Crack of metallization in PTH (a) metallographic cross-section – magnification x700; (b) metallographic cross-section – magnification x1500.
Figure 13.
Crack of metallization in PTH (a) metallographic cross-section – magnification x700; (b) metallographic cross-section – magnification x1500.
Figure 14.
Crack of metallization in microvia (a) metallographic cross-section – magnification x500; (b) metallographic cross-section – magnification x1000.
Figure 14.
Crack of metallization in microvia (a) metallographic cross-section – magnification x500; (b) metallographic cross-section – magnification x1000.
Figure 15.
Copper layers with metallization 1 A/dm2 (a) magnification x1000; (b) magnification x5000.
Figure 15.
Copper layers with metallization 1 A/dm2 (a) magnification x1000; (b) magnification x5000.
Figure 16.
Copper layers with metallization 2 A/dm2 (a) magnification x2000; (b) magnification x5000.
Figure 16.
Copper layers with metallization 2 A/dm2 (a) magnification x2000; (b) magnification x5000.
Table 1.
Factors taken into account during the experiment.
Table 1.
Factors taken into account during the experiment.
| Factor |
Levels |
| Level I |
Level II |
| Type of the laminate |
polyimide |
glass-epoxy |
| Number of conductive layers |
2 |
4 |
| Thickness of the laminate |
50 µm |
100 µm |
| Diameter of plated hole |
0.3 mm |
0.4 mm |
| Current density in galvanic bath |
1 A/dm2
|
2 A/dm2
|
Table 2.
Orthogonal array of designed experiment where: A - number of conductive layers, B - diameter of the metalized hole, C - type of laminate, D - laminate thickness, E - variant of the galvanic metallization process of holes.
Table 2.
Orthogonal array of designed experiment where: A - number of conductive layers, B - diameter of the metalized hole, C - type of laminate, D - laminate thickness, E - variant of the galvanic metallization process of holes.
| Number of experiment |
|
| A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
| 1 |
2 layers |
0.3 mm |
polyimide |
50 µm |
1 A/dm2
|
| 2 |
2 layers |
0.3 mm |
polyimide |
100 µm |
2 A/dm2
|
| 3 |
2 layers |
0.4 mm |
FR4 |
50 µm |
2 A/dm2
|
| 4 |
2 layers |
0.4 mm |
FR4 |
100 µm |
1 A/dm2
|
| 5 |
4 layers |
0.3 mm |
FR4 |
50 µm |
1 A/dm2
|
| 6 |
4 layers |
0.3 mm |
FR4 |
100 µm |
2 A/dm2
|
| 7 |
4 layers |
0.4 mm |
polyimide |
50 µm |
2 A/dm2
|
| 8 |
4 layers |
0.4 mm |
polyimide |
100 µm |
1 A/dm2
|
Table 3.
Parameters of test samples.
Table 3.
Parameters of test samples.
| PCB parameter |
Two-layer PCB |
Four-layer PCB |
| Dimension |
14 mm x 120 mm |
14 mm x 120 mm |
| Thickness |
120 µm or 170 µm
(depending on variant) |
305 µm or 405 µm
(depending on variant) |
| Number of conductive layers |
2 |
4 |
| Number of plated holes |
636 |
636 |
| Interconnections |
Top - Bottom |
Top – 1st signal layer
2nd signal layer – Bottom |
| Diameter of plated holes |
0.3 mm or 0.4 mm
(depending on variant) |
0.3 mm or 0.4 mm
(depending on variant) |
| Thickness of metallization in holes |
20 µm |
20 µm |
| Width of tracks |
0.254 mm |
0.254 mm |
| Thickness of tracks |
35 µm |
35 µm |
Table 4.
IPC-TM-650 IST “Method A” review [
21].
Table 4.
IPC-TM-650 IST “Method A” review [
21].
| Test parameter |
Value |
| Temperature |
150 |
| Time of heating |
3 minutes |
| Time at the maximum temperature |
At least 1 second |
| Failure threshold |
Change of resistance by 10% |
| Cooling method |
By forced air |
| Resistance observation |
Continuous |
| Temperature of sample |
Calculated on based of measured resistance |
Table 5.
Experiment statistics.
Table 5.
Experiment statistics.
| Number of experiment |
Arithmetic mean |
Standard deviation |
SNR [dB] |
| 1 |
1917.33 |
93.43 |
65.62 |
| 2 |
1895.67 |
83.83 |
65.53 |
| 3 |
2340.67 |
210.27 |
67.29 |
| 4 |
1498.33 |
104.01 |
63.45 |
| 5 |
304.00 |
48.93 |
49.34 |
| 6 |
1598.00 |
86.73 |
64.03 |
| 7 |
2054.33 |
55.11 |
66.24 |
| 8 |
728.00 |
65.46 |
57.13 |
| Mean |
1542.04 |
Sum |
498.65 |
Table 6.
ANOVA table.
Source of
variation |
Sum of squares |
Degrees of freedom |
Mean square |
F value |
P [%] |
| Number of layers |
3302642.04 |
1 |
3302642.04 |
34.20 |
31.87 |
| Thickness of laminate |
301280.04 |
1 |
301280.04 |
3.12 |
2.91 |
| Diameter of plated hole |
308040.04 |
1 |
308040.04 |
3.19 |
2.97 |
Current
density |
4440180.38 |
1 |
4440180.38 |
45.99 |
42.84 |
Type of
laminate |
273707.04 |
1 |
273707.04 |
2.83 |
2.64 |
| Error |
1738007.42 |
18 |
96555.97 |
|
16.77 |
| Total |
10363856.96 |
23 |
|
|
100 |
Table 7.
Results of the verification test.
Table 7.
Results of the verification test.
| |
Sample 1 |
Sample 2 |
Sample 3 |
SNR |
| Verification test |
2816 |
2586 |
2675 |
68.59 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).