1. Introduction
The effects of gravitational changes on skeletal, muscular, cardiovascular, immune, and vestibular systems have been well-documented [
1]. The vestibular system plays a crucial role in sensing and adapting to gravity [
2,
3], leading to extensive research on how it responds to gravitational changes [
2,
4,
5,
6]. However, the effects of altered gravity on the auditory system, which shares functional and structural similarities with the vestibular system, remain insufficiently studied. Recent advancements in space exploration and aviation technology have increased, human exposure to gravitational changes [
7], raising concerns about their potential impact on auditory function [
8].
The effects of hypergravitational stimulation on hearing may occur through several mechanisms. First, it can induce physical stress on inner ear structures, particularly the cochlea [
9]. Second, it may alter blood flow to the inner ear, affecting the supply of oxygen and nutrients to hearing cells [
8,
10]. Third, gravitational changes can affect cellular structures, connectivity, and functional signal transmission in the vestibular system, potentially influencing inner ear sensory functions and hearing [
2,
10]. earing loss, characterized by impaired sound perception [
11], has been linked to poor balance [
12,
13], underscoring the intricate relationship between hearing and balance. This study explores the effects of hypergravitational stimulation on hearing loss.
We investigated patterns of hearing changes, the underlying neurological mechanisms, and the effects on inner ear structure and function in animal models exposed to 4G hypergravity stimulation for 24 hours, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks. We evaluated the effects of hypergravity stimulation on the auditory system using auditory brainstem responses (ABRs) and histological analyses.
To confirm the close association between the presynaptic ribbon and the postsynaptic receptor complex, we quantified and analyzed structural synaptic plasticity using immunostaining methods. Our aim was to provide a broad perspective on synaptic plasticity alterations and maintenance following long-term hypergravity stimuli exposure. The results of this study will deepen our understanding of the effects of hypergravity on the auditory system and provide important baseline medical preparations for future space exploration.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats, aged 6weeks and weighing 250-300g, were used in this study. The rats were purchased from Orient Bio Inc. (Seongnam, Korea). All experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Inha University (INHA 240610-937). All methods were conducted in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
2.2. Hypergravity Stimulation
Hypergravity conditions were created using a centrifuge equipped with two rotatory arms that accommodated cages. The animals were exposed to 4G hypergravity and allowed a 1-hour rest period at the same time daily, during which they received adequate food and water. Hypergravity exposure durations were 24 hours, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks, with experiments performed at the end of each stimulation period to assess the effects.
2.3. Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Test
ABR recordings were conducted simultaneously at the endpoints of hypergravity exposure (Control, 24-hour, 2-week, and 4-week groups; 10 rats per group). Rats were anesthetized with ketamine (100 mg/kg; Yuhan Corporation, Seoul, Korea) and xylazine (1 mg/kg; Rumpun, Korea Elanco, Seoul, Korea) before being placed in a sound-attenuated chamber. Body temperature was maintained at 37℃ using a heating pad. Ground and recording electrodes were placed subcutaneously on the scalp, and a calibrated transducer (Tucker Davis) was placed in the right pinna.
The clicks and pure-tone pips at 4, 8, 16, 24, and 32 kHz were presented at 10 dB to 90 dB sound pressure levels (SPL;rms for click stimuli) in 10 dB increments. After click and pure-tone recordings, the amplitude (nV) and latency (ms) were analyzed in wave 1 and wave 2.
2.4. Immunostaining Assay
After ABR recordings, all animals were euthanized, and their cochleae were dissected from the temporal bone and fixed in 10% paraformaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) overnight on a rocker at 4℃. The samples were decalcified in 0.25 M ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) solution for up to 21 days (duration was age-dependent), with daily solution changes. Decalcified cochleae were micro-dissected at the apex, middle, and basal turns, and the tectorial and Reisner’s membranes were removed. Each sample was permeabilized in 0.05% Triton X-100 in PBS for 30 minutes and then in a blocking solution containing 10% bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 60 minutes. The samples were incubated with the primary antibody overnight at 4℃. The washed tissues were then incubated with a fluorescent dye-conjugated secondary antibody for 4 hours at room temperature. The following primary and secondary antibodies were used: MyoVIIa (santa cruz biotechnology, INC), anti-CtBP2 (BD Biosciences), anti-Glutamate Receptor 2&3 (Merck Millipore), NF200 (proteintech), Alexa FluorTM 488 Goat anti-Mouse IgG1 (Thermo Fisher, a-21121), Alexa FluorTM 546 Goat anti-Mouse IgG2a (Thermo, a-21133), Alexa FluorTM 647 Goat anti-Rabbit (Thermo, a-21245). Images were captured with Leica Stellaris 5 confocal microscopes.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism (Version 8.0.1, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). A paired t-test was used to compare thresholds between the control and hypergravity groups (4G-24hour, 4G-2week, and 4G-4week). Statistical significance was defined as *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001.
3. Results
3.1. ABR Recordings
Using a hypergravity device, a gravity stimulation animal model was established by exposing animals to 4G stimulation for 24 hours, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks. ABRs were analyzed at the end of hypergravity stimulation. Analyses of hearing thresholds in response to clicking and pure-tone chirps (4, 8, 16, 24, and 32 kHz) showed a significant increase in sound levels (
Figure 1). In the case of click threshold, compared to control group, hearing loss of approximately 10 dB (Control group: Mean 22.222
6.667 dB, 4G-4weeks group: Mean 33.000
12.517 dB) was observed in the group exposed to hypergravity for 4 weeks, which was statistically significant (**
P=0.0023). At the tone burst, the threshold was increased by about 15 dB (Control group: Mean 33.333
5.000 dB, 4G-4weeks group: Mean 48.000
10.328 dB) at 4 kHz, about 16 dB (Control group: Mean 31.111
5.000 dB) at 8 kHz. Additionally, the threshold was increased by about 30 dB at high frequencies (Control group: Mean 24.444
5.270 dB, 4G-4weeks group: Mean 59.000
13.703 dB at 16 kHz, Control group: Mean 31.111
9.280 dB, 4G-4weeks group: Mean 62.000
13.984 dB at 24 kHz, and Control group: Mean 32.222
6.667 dB, 4G-4weeks group: Mean 59.000
17.288 dB at 32 kHz).
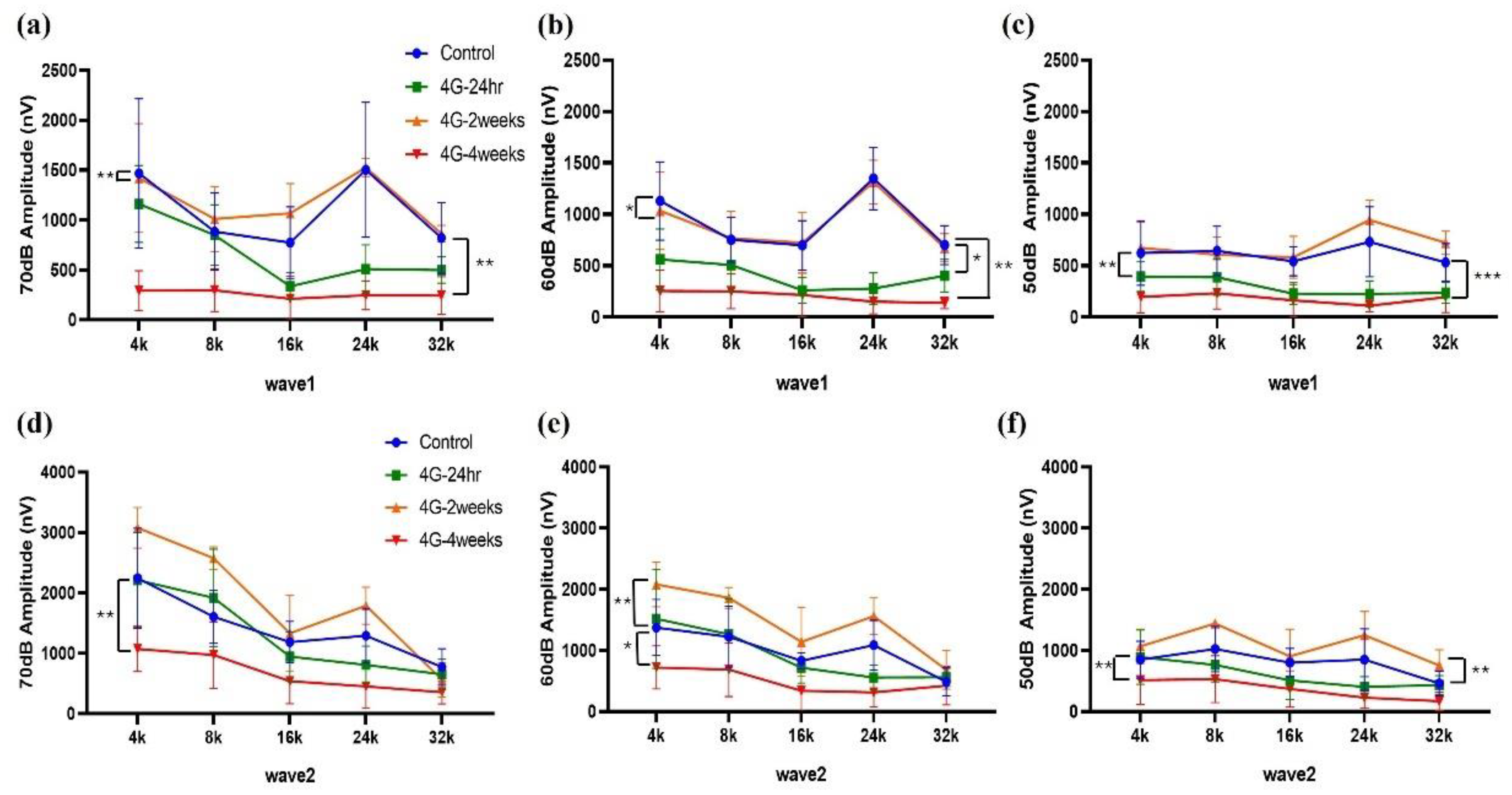
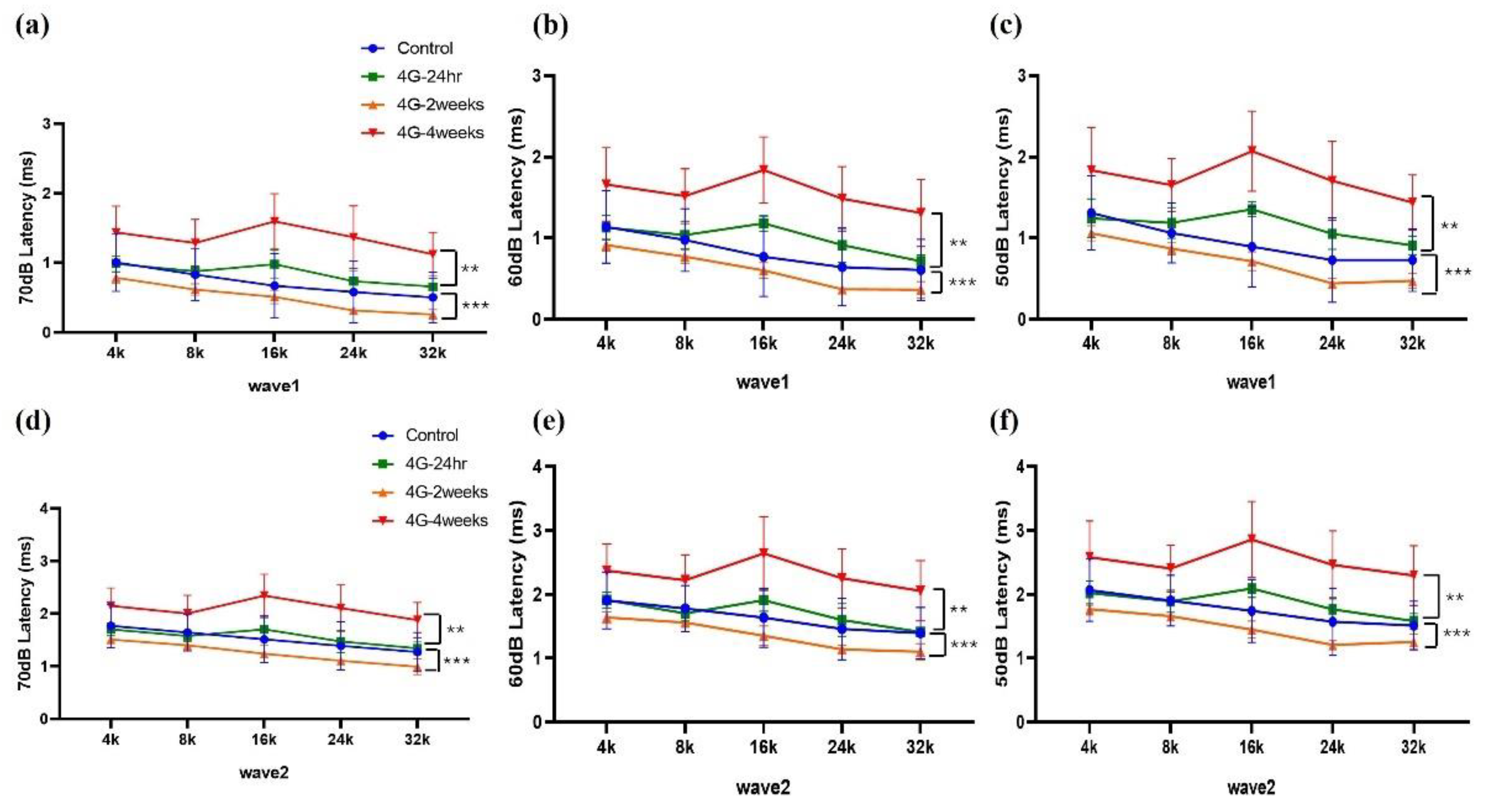
Changes in amplitude and latency according to frequency were analyzed for wave 1 and wave 2. At wave 1 of 70 dB, 60 dB, and 50 dB, the amplitude was significantly reduced in the 4G-4weeks group compared to the control group (
Figure 2a-c), and latency was delayed (
Figure 3a-c). The amplitude decreased from 70 to 50 dB in wave 2, with the latency delayed (
Figure 3d-e). In pure-tone pips, hearing damage was observed in the 4G-4weeks group compared to the control group at all frequencies. In particular, distinct hearing changes were observed in wave 1 and wave 2 at high frequencies. This suggests that prolonged exposure to hypergravity stimulation affects hearing loss and that high-frequency subjects are more sensitive to gravitational stimulation than low-frequency subjects.
3.2. Immunostaining of Cochlear Hair Cells
We performed immunostaining of whole-mount cochlear tissue using a Myo 7a antibody to visualize and assess cochlear hair cells. Samples were examined from three regions: apex, middle, and basal turns of the cochlea.
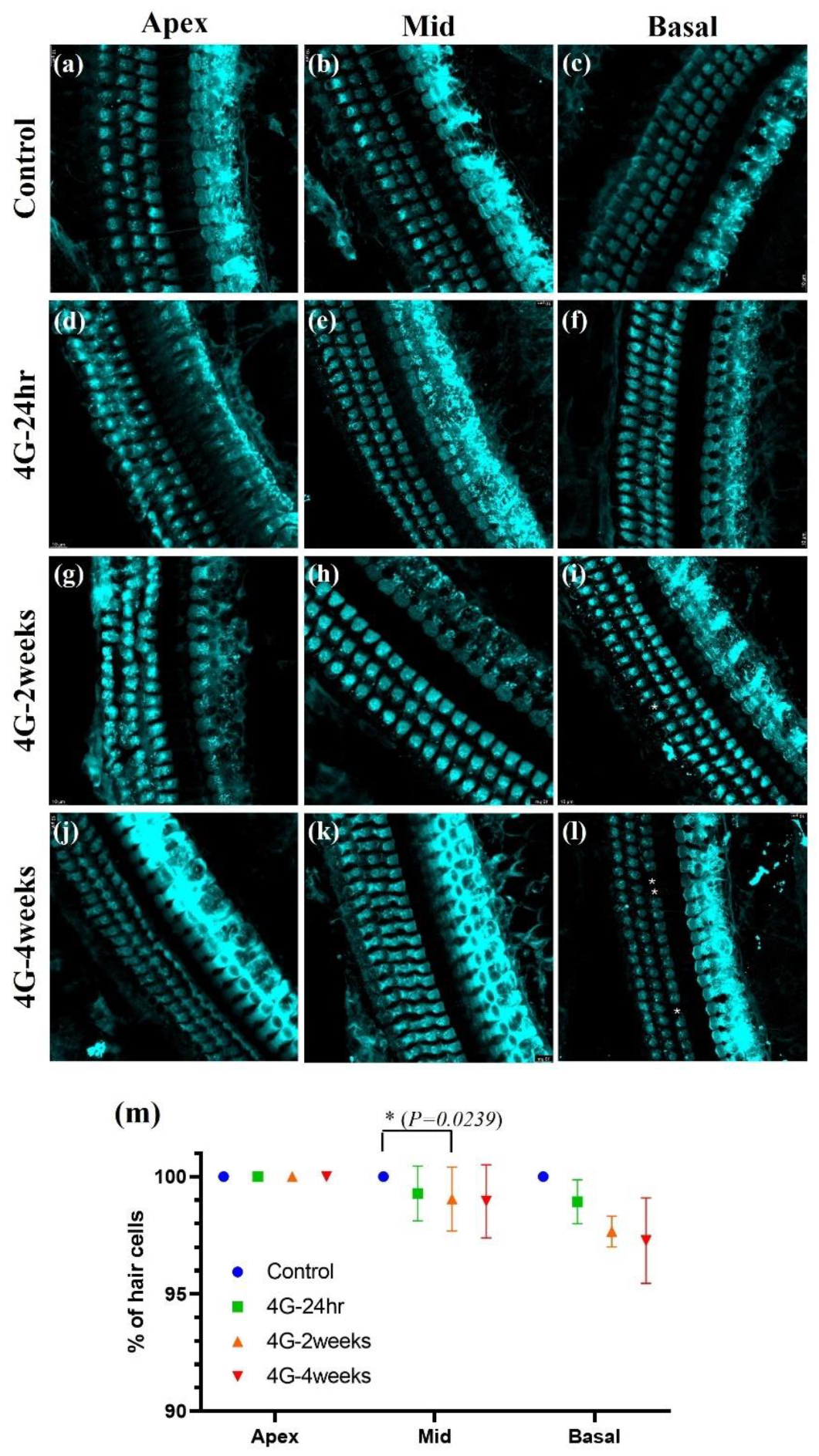
Figure 4.
Image of hair cells exposed to hypergravity (4G). Whole-mount preparation showing Myo 7a-positive hair cells in the cochlea. Three rows of outer hair cells and a single row of inner hair cells were present in all groups. (a-c) Control group: Normal morphology of hair cells. (d-f) 4G-24hr group. (g-i) 4G-2weeks group: Loss of OHC was observed during the basal turn. (j-l) 4G-4weeks group: OHC loss occurred in the middle and basal turns. (m) Graph showing the percentage of hair cell survival: In the middle and basal turns hair cell loss was observed in the OHC in the 4G-4weeks group.
Figure 4.
Image of hair cells exposed to hypergravity (4G). Whole-mount preparation showing Myo 7a-positive hair cells in the cochlea. Three rows of outer hair cells and a single row of inner hair cells were present in all groups. (a-c) Control group: Normal morphology of hair cells. (d-f) 4G-24hr group. (g-i) 4G-2weeks group: Loss of OHC was observed during the basal turn. (j-l) 4G-4weeks group: OHC loss occurred in the middle and basal turns. (m) Graph showing the percentage of hair cell survival: In the middle and basal turns hair cell loss was observed in the OHC in the 4G-4weeks group.
In the control group, we observed a typical cochlear structure: three rows of outer hair cells (OHCs) and a single row of inner hair cells (IHCs), all intact and without any apparent loss. This normal morphology was consistent across all cochlear turns. However, in the groups exposed to 4G hypergravity for 2 and 4 weeks, we observed notable changes in hair cell morphology, particularly in OHCs. The most striking difference was the loss of OHCs, which was evident in both the 2-week and 4-week exposure groups. Interestingly, hair cell loss showed a gradient effect along the cochlear turns. The most pronounced loss was observed in the basal turn, which was responsible for the detection of high-frequency sounds. This suggests that high-frequency hearing is more susceptible to damage from prolonged exposure to hypergravity. These findings indicate that extended exposure to hypergravity can lead to significant structural changes in the cochlea, particularly affecting the outer hair cells. The preferential loss of hair cells during the basal turn suggests that high-frequency hearing is more vulnerable to hypergravity-induced damage.
3.3. Neurofilament Analysis
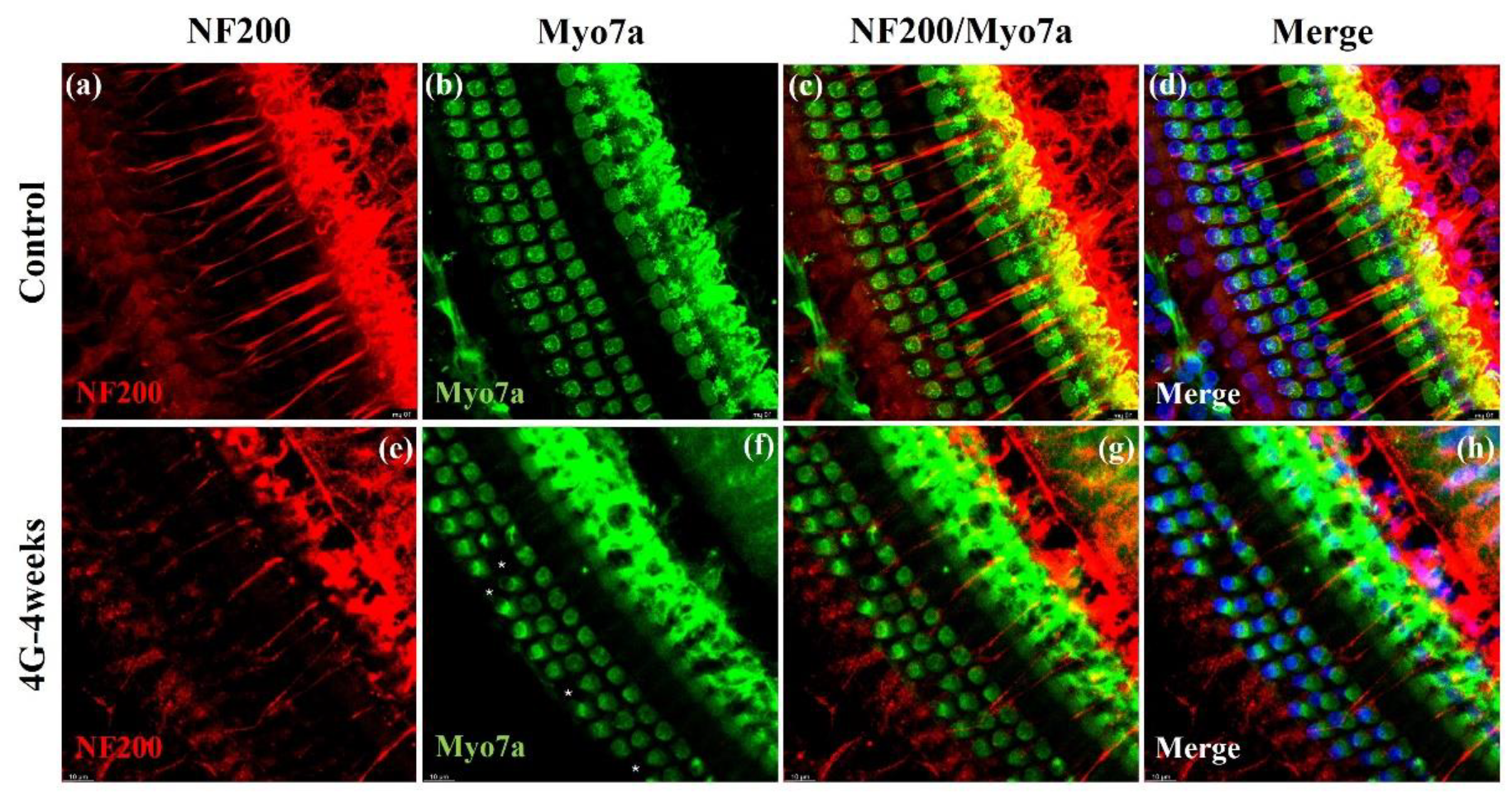
We used NF 200, a characterized neural marker for both type I and type II Spiral Ganglion Neurons (SGNs), to assess the impact of hypergravity on cochlear neural structures [
14]. Confocal imaging of cochlear surface preparations co-stained with NF 200 and Myo 7a allowed us to visualize both auditory nerve fibers (afferent and efferent) and hair cell morphology.
Our analysis showed significant changes in the 4G-4weeks group compared to the control group. The NF200-positive fiber density was markedly decreased in the 4G-4weeks group compared to the control group (
Figure 5a and 5e). This reduction suggests the loss or degeneration of auditory nerve fibers following prolonged hypergravity exposure. Hair cells exhibited normal morphology (
Figure 5b) with intact structures and organization in the control group. However, in 4G-4weeks group, consistent with our previous results, a significant loss of OHCs was noted (
Figure 5f). These findings provide strong evidence that prolonged exposure to hypergravity conditions (4G-4weeks) induces substantial changes in cochlear neural architecture. The observed reduction in NF200-positive fiber density coupled with the loss of OHCs strongly suggests that hypergravity exposure leads to both neural and sensory cell damage in the inner ear. Collectively, these results indicate that exposure to hypergravity can induce significant structural changes in the cochlea, potentially leading to impaired hearing. The concurrent loss of neural fibers and hair cells underscores the comprehensive impact of hypergravity on the auditory system, affecting both its neural and sensory components.
3.4. Analysis of Synapse
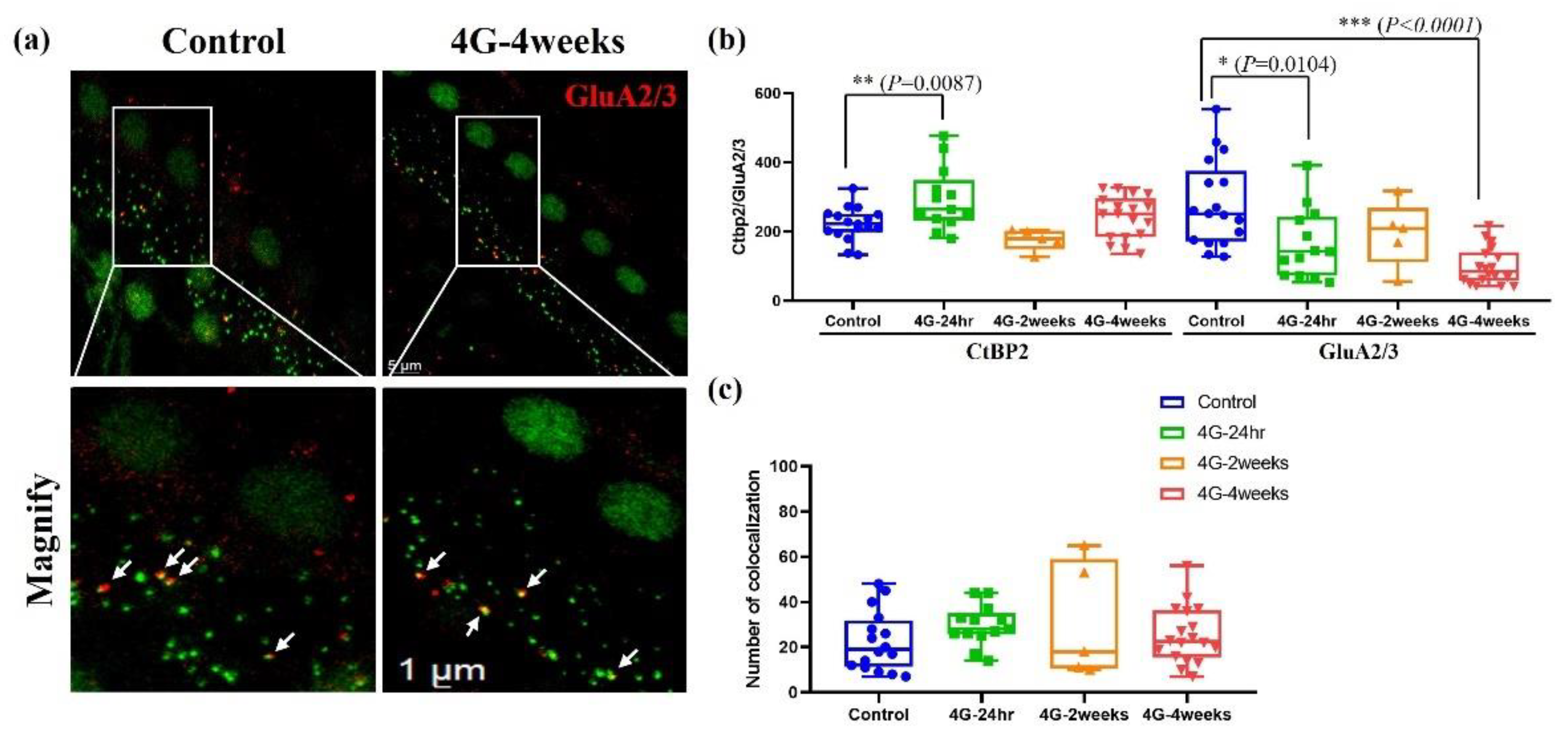
The strategy for imaging whole-mounted cochlea is illustrated in
Figure 6, which compares a control group with the 4G-4week group stained using a presynaptic marker (anti-CtBP2, green) and a postsynaptic marker (anti-GluA2/3, red). The distribution of synapses in the inner hair cells of the cochlea was quantified using immunohistochemical image analysis (
Figure 6). Compared to the control group, the presynaptic ribbon showed a temporary increase in the hair cells of the group exposed to hypergravity stimulation for 24 hours. However, this increase returned to baseline levels with continued exposure for 2 weeks and 4 weeks. Conversely, a gradient decrease in postsynaptic density was observed with prolonged 4G exposure (
Figure 6b). Additionally, no significant differences were detected in the co-localization of presynaptic ribbons and postsynaptic receptors (
Figure 6c). These findings highlight the capacity of hair cells to exhibit synaptic plasticity when adapting to persistent gravitational environments. These results align closely with reports of decreased hearing function observed in astronauts after returning from spaceflight, emphasizing the potential impacts of prolonged gravitational changes on auditory synapses.
4. Discussion
Previous studies have extensively investigated structural changes in the vestibular organ and alterations in utricular hair cell synapse density [
6,
15,
16]. Space sickness typically occurs at the onset of spaceflight and transitions into an adaptation phase with continued exposure to stimulation [
17,
18]. This condition arises from mismatched signals between different sensory organs [
4,
7]. When space sickness occurs, astronauts may be unable to perform tasks effectively, making it a significant challenge in space medicine [
19,
20]. Due to problems such as reduced quality of life and the inability to carry out daily life activities resulting from space motion sickness, many researchers are conducting studies to better understand the mechanisms of space motion sickness and the role of the vestibular system [
4,
18,
21]. However, the cochlea, despite its structural and functional similarities to vestibular organs and close anatomical proximity, remains largely unexplored. It is reasonable to infer that if space stimulation significantly affects the vestibular system to cause motion sickness, a similar impact may occur in the auditory system.
Interestingly, 100% of astronauts experience temporary hearing threshold shifts during spaceflight, and 81% report permanent hearing loss [
22]. Hearing loss can severely affect quality of life, leading to depression and social isolation, placing a burden on the patient and those around them [
23,
24].
This study comprehensively investigated the effects of hypergravitational stimulation on the auditory system. Using an animal model exposed to a 4G hypergravity environment for 24 hours, 2 weeks, and 4 weeks, hearing thresholds, hair cell loss, changes in neural structure, and changes in synapse density were evaluated to demonstrate various aspects of hearing impairment. First, the auditory brainstem response (ABR) analysis showed that hearing thresholds increased with prolonged hypergravity exposure. In particular, hearing loss was observed in the high-frequency region, suggesting heightened vulnerability of high-frequency hearing to hypergravity. This phenomenon is similar to hearing loss caused by aging and oxidative stress [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30]. OHCs were more sensitive than IHCs, particularly in high-frequency regions [
31]. These results align with reports of hearing loss among astronauts upon their return to Earth and provide important insights into the long-term effects of hypergravity on the auditory system. Second, the loss of OHCs was observed using immunofluorescence analysis. In particular, the significant loss in the basal turn demonstrates that hypergravity stimulation can have direct effects on inner ear structures. This result is consistent with high-frequency hearing loss, suggesting that high-frequency areas should be considered when establishing hearing protection strategies in hypergravity. In conclusion, we found that long-term exposure to hypergravity stimulation deteriorates hearing function, a significant result that demonstrates the functional and structural changes in the inner ear caused by a single gravity stimulation environment. Third, neurofilament (NF 200) analysis showed that hypergravity stimulation affects auditory nerve structures. A decrease in NF200-positive fiber density suggests loss or degeneration of auditory nerve fibers, which is an important finding for understanding the neurological mechanisms of hearing loss. Lastly, synaptic density analysis demonstrated the inner ear adaptation mechanism to hypergravity. The initially observed transient increase in presynaptic ribbons, followed by recovery, can be viewed as an immediate compensatory mechanism of the nervous system to adapt to new environments. We propose that in response to 4G hypergravity stimulation for 24 hours, the cochlear presynapse initially hyper-reacted and increased the number of synapses. In contrast, the postsynaptic density gradually decreased. This can be attributed to several factors. First, the damage was caused by constant stress. As the hypergravity environment persists, accumulated stress may occur in the postsynaptic structures, resulting in the progressive loss of synapses [
15]. Second, there is an imbalance in neurotransmitters. Excessive early activation of the presynapse can lead to neurotransmitter imbalances, which can cause long-term damage to postsynaptic structures [
32]. Finally, there are changes in the energy metabolism. Sustained hypergravity may impair cochlear energy metabolism, leading to problems with the energy supply required to maintain postsynaptic structures [
33]. This phenomenon demonstrates the complex impact of hypergravity on the auditory system and suggests different adaptation mechanisms at the pre- and postsynapses. Taken together, these findings provide important clues for understanding how long-term stay in an altered gravity environment affects the auditory system.
Interestingly, despite differences in presynaptic and postsynaptic responses to hypergravity stimulation, their colocalization remained unchanged. This phenomenon can be explained by neurotransmitter maintenance mechanisms [
34,
35,
36,
37]. First, synaptic plasticity must remain balanced. Despite individual changes in presynaptic and postsynaptic structures, homeostatic mechanisms in the nervous system likely maintain overall synaptic ability [
37]. This may be an adaptive response that maintains the functional stability of neural circuits. Second, functional compensation may occur. Quantitative changes that occur in presynaptic and postsynaptic structures could offset each other, thereby maintaining functionally significant colocalization [
38]. Finally, balance between synapse formation and elimination [
39,
40] might sustain colocalization. During the initial increase in presynapses and the continued decrease in postsynapses, the formation of new synapses and the elimination of existing synapses may have been balanced to maintain overall colocalization. These phenomena reflect the complexity of neuroplastic mechanisms [
41]. Hypergravity stimulation increases activity in tissues related to the vestibular system, which can be interpreted as adaptive changes in the nervous system.
These findings imply that hearing protection in hypergravity environments must extend beyond mere sound isolation to encompass comprehensive strategies for safeguarding the inner ear’s structure and function. Future research is needed to explore the reversibility and long-term effects of these changes, as well as possible prevention and treatment strategies. While our study provides valuable insights, its generalizability could be improved by increasing the sample size and including a more diverse population (e.g., different ages and genders). Additionally, future studies could examine the chronic effects over periods of 4 weeks or longer and compare the effects of hypergravity and microgravity [
42]. Additionally, research is needed to elucidate the exact molecular and cellular pathways involved in hypergravity-induced hearing impairment. Finally, changes in auditory function caused by other space-related stressors (e.g., radiation, sleep deprivation, and isolation) need to be studied [
43]. Addressing these limitations and expanding future research will contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the effects of gravity on the auditory system.
5.Conclusions
This study aimed to investigate the functional and morphological changes in the inner ear following hypergravity stimulation. The results indicated a significant hearing threshold shift and latency delay, as well as observable hair cell loss and alterations in nerve fiber density after hypergravity exposure. These findings suggest that hypergravity can induce substantial changes in the inner ear. Although this study was limited to hypergravity stimulation, it contributes valuable insights into the mechanisms of hearing impairment. To enhance the generalizability of these findings, future studies should consider increasing the sample size and incorporating a more diverse population, including various ages and genders. This approach will be in developing a more comprehensive understanding of the effects of hypergravity on the auditory system.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, J.S.C. and H.J.K.; methodology, J.S.C.; software, K.S.K.; validation, J.S.C. and H.J.K.; formal analysis, J.S.C.; investigation, J.S.C.; resources, K.S.K.; data curation, J.S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S.C.; writing—review and editing, J.S.C. and H.J.K.; visualization, J.S.C.; supervision, H.J.K.; project administration, K.S.K.; funding acquisition, K.S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2018R1A6A1A03025523).
Conflicts of Interest
authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ABR |
Auditory Brainstem Response |
| BSA |
Bovine Serum Albumin |
| EDTA |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| IHC |
Inner Hair Cell |
| NF |
Neurofilament |
| OHC |
Outer Hair Cell |
| PBS |
Phosphate-buffered Saline |
| SD |
Sprague-Dawley |
| SGN |
Spiral Ganglion Neuron |
References
- Adamopoulos K, Koutsouris D, Zaravinos A, Lambrou GI. Gravitational Influence on Human Living Systems and the Evolution of Species on Earth. Molecules. 2021;26(9). [CrossRef]
- Jamon M. The development of vestibular system and related functions in mammals: impact of gravity. Front Integr Neurosci. 2014;8:11. [CrossRef]
- Morita H, Kaji H, Ueta Y, Abe C. Understanding vestibular-related physiological functions could provide clues on adapting to a new gravitational environment. J Physiol Sci. 2020;70(1):17. [CrossRef]
- Carriot J, Mackrous I, Cullen KE. Challenges to the Vestibular System in Space: How the Brain Responds and Adapts to Microgravity. Front Neural Circuits. 2021;15:760313. [CrossRef]
- Dememes D, Dechesne CJ, Venteo S, Gaven F, Raymond J. Development of the rat efferent vestibular system on the ground and in microgravity. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2001;128(1):35-44. [CrossRef]
- Sultemeier DR, Choy KR, Schweizer FE, Hoffman LF. Spaceflight-induced synaptic modifications within hair cells of the mammalian utricle. Journal of Neurophysiology. 2017;117(6):2163-78. [CrossRef]
- Newberg AB. Changes in the central nervous system and their clinical correlates during long-term spaceflight. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1994;65(6):562-72.
- Masè M, Viziano A, Strapazzon G, Alessandrini M, Micarelli A. Auditory function in humans at high altitude. A scoping review. Plos one. 2023;18(9):e0291919. [CrossRef]
- Lin X. Perception of sound and gravity by TMC1 and TMC2. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(12):4633-6. [CrossRef]
- Neng L, Shi X. Vascular pathology and hearing disorders. Current Opinion in Physiology. 2020;18:79-84. [CrossRef]
- Blazer DG. Hearing Loss: The Silent Risk for Psychiatric Disorders in Late Life. Clin Geriatr Med. 2020;36(2):201-9. [CrossRef]
- Carpenter MG, Campos JL. The effects of hearing loss on balance: a critical review. Ear and hearing. 2020;41:107S-19S. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Zhong M, Li Y, Liu Y, Tong B, Qiu J, et al. Association Between Hearing Loss, Asymmetric Hearing, and Postural Instability. Ear and Hearing. 2024;45(4):827-36.
- Lang H, Li M, Kilpatrick LA, Zhu J, Samuvel DJ, Krug EL, et al. Sox2 up-regulation and glial cell proliferation following degeneration of spiral ganglion neurons in the adult mouse inner ear. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2011;12(2):151-71. [CrossRef]
- Liberman LD, Wang H, Liberman MC. Opposing gradients of ribbon size and AMPA receptor expression underlie sensitivity differences among cochlear-nerve/hair-cell synapses. J Neurosci. 2011;31(3):801-8. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman LF, Ross MD, Varelas J, Jones SM, Jones TA. Afferent synapses are present in utricular hair cells from otoconia-deficient mice. Hearing research. 2006;222(1-2):35-42. [CrossRef]
- Golding JF. Motion sickness susceptibility. Auton Neurosci. 2006;129(1-2):67-76.
- Lackner JR, DiZio P. Space motion sickness. Experimental brain research. 2006;175:377-99.
- Hodkinson P, Anderton R, Posselt B, Fong K. An overview of space medicine. BJA: British Journal of Anaesthesia. 2017;119(suppl_1):i143-i53.
- Braddock M. Ergonomic challenges for astronauts during space travel and the need for space medicine. J Ergonomics. 2017;7(221):2.
- Kornilova L, Naumov I, Glukhikh D, Ekimovskiy G, Pavlova A, Khabarova V, et al. Vestibular function and space motion sickness. Human Physiology. 2017;43:557-68. [CrossRef]
- Kadem M. The etiology of spaceflight-associated hearing loss. University of Western Ontario Medical Journal. 2018;87(1):31-3. [CrossRef]
- Ellis S, Sheik Ali S, Ahmed W. A review of the impact of hearing interventions on social isolation and loneliness in older people with hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;278(12):4653-61. [CrossRef]
- Podury A, Jiam NT, Kim M, Donnenfield JI, Dhand A. Hearing and sociality: the implications of hearing loss on social life. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1245434. [CrossRef]
- Batsaikhan T, Choi JS, Ha SM, Ahn Y, Seo YJ. D-Galactose and Hypoxia Induce the Early Onset of Age-Related Hearing Loss Deterioration in a Mouse Model. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(5):779-87. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Puel JL. Presbycusis: An Update on Cochlear Mechanisms and Therapies. J Clin Med. 2020;9(1). [CrossRef]
- Yang W, Zhao X, Chai R, Fan J. Progress on mechanisms of age-related hearing loss. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1253574. [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto C, Yamasoba T. Oxidative stresses and mitochondrial dysfunction in age-related hearing loss. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:582849. [CrossRef]
- Teraoka M, Hato N, Inufusa H, You F. Role of Oxidative Stress in Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(8). [CrossRef]
- Li P, Li S, Wang L, Li H, Wang Y, Liu H, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in hearing loss: Oxidative stress, autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1119773. [CrossRef]
- Ospeck M, Dong XX, Iwasa KH. Limiting frequency of the cochlear amplifier based on electromotility of outer hair cells. Biophys J. 2003;84(2 Pt 1):739-49.
- Yu Y, Chen R, Mao K, Deng M, Li Z. The Role of Glial Cells in Synaptic Dysfunction: Insights into Alzheimer's Disease Mechanisms. Aging Dis. 2024;15(2):459-79.
- Clemente-Suarez VJ, Beltran-Velasco AI, Redondo-Florez L, Martin-Rodriguez A, Yanez-Sepulveda R, Tornero-Aguilera JF. Neuro-Vulnerability in Energy Metabolism Regulation: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2023;15(14). [CrossRef]
- Teleanu RI, Niculescu AG, Roza E, Vladacenco O, Grumezescu AM, Teleanu DM. Neurotransmitters-Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11). [CrossRef]
- Pendyam S, Mohan A, Kalivas PW, Nair SS. Role of perisynaptic parameters in neurotransmitter homeostasis--computational study of a general synapse. Synapse. 2012;66(7):608-21. [CrossRef]
- Mohan A, Pendyam S, Kalivas PW, Nair SS. Molecular diffusion model of neurotransmitter homeostasis around synapses supporting gradients. Neural Comput. 2011;23(4):984-1014. [CrossRef]
- Davis GW, Muller M. Homeostatic control of presynaptic neurotransmitter release. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:251-70.
- Abuhassan K, Coyle D, Belatreche A, Maguire L. Compensating for synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease. J Comput Neurosci. 2014;36(1):19-37. [CrossRef]
- Kiyoshi C, Tedeschi A. Axon growth and synaptic function: A balancing act for axonal regeneration and neuronal circuit formation in CNS trauma and disease. Dev Neurobiol. 2020;80(7-8):277-301. [CrossRef]
- Chung WS, Baldwin KT, Allen NJ. Astrocyte Regulation of Synapse Formation, Maturation, and Elimination. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2024;16(8). [CrossRef]
- Toricelli M, Pereira AAR, Souza Abrao G, Malerba HN, Maia J, Buck HS, et al. Mechanisms of neuroplasticity and brain degeneration: strategies for protection during the aging process. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(1):58-67. [CrossRef]
- Gnyubkin V, Guignandon A, Laroche N, Vanden-Bossche A, Normand M, Lafage-Proust MH, et al. Effects of chronic hypergravity: from adaptive to deleterious responses in growing mouse skeleton. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015;119(8):908-17. [CrossRef]
- Desai RI, Limoli CL, Stark CEL, Stark SM. Impact of spaceflight stressors on behavior and cognition: A molecular, neurochemical, and neurobiological perspective. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022;138:104676. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).