1. Introduction
The rapid evolution of cyber threats over the past decade has underscored the need for robust, adaptive, and scalable cybersecurity solutions. Traditional intrusion detection systems (IDS), rule-based filters, and signature-based antivirus software have proven insufficient against increasingly sophisticated and polymorphi attacks [
1]. Modern cyber adversaries leverage advanced evasion techniques, zero-day exploits, and complex social engineering tactics, necessitating a more holistic and dynamic approach to security [
2]. Simultaneously, the proliferation of connected devices and emerging technologies—particularly the Internet of Things (IoT)—has created an expansive and often vulnerable attack surface [
3]. Protecting these distributed, resource-constrained networks requires security frameworks that balance computational efficiency with strong threat detection mechanisms.
Hybrid cybersecurity methodologies, which integrate machine learning (ML), fuzzy logic, and cryptographic techniques, have attracted significant research interest as a means to meet these challenges. ML-based methods excel in pattern recognition and adaptive learning, enabling security systems to detect anomalies and previously unknown threats [
4]. Fuzzy logic adds interpretability and resilience to uncertain or incomplete data scenarios, providing robust decision-making under ambiguity [
5]. Cryptographic techniques, on the other hand, ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, fortifying communication channels and data storage [
6]. The fusion of these technologies, augmented by distributed computing frameworks and optimization heuristics, promises more effective and flexible cybersecurity defense mechanisms.
This survey presents a comprehensive review of hybrid cybersecurity approaches that combine ML, fuzzy systems, and cryptographic techniques. We begin by examining the fundamental principles of each component and their synergistic potential. We then discuss recent research endeavors spanning multiple application domains, including phishing detection, IoT anomaly detection, and quantum-resilient cryptography. We explore the role of feature selection, ensemble learning, and privacy-preserving models in achieving high detection accuracy and robustness.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section II provides an overview of the motivations for hybrid cybersecurity systems and the challenges they address. Section III delves into machine learning-based solutions, highlighting their strengths and limitations. Section IV explores the role of fuzzy systems and their integration with ML in cybersecurity. Section V reviews cryptographic techniques crucial for IoT and large-scale data analytics. Section VI examines advanced approaches, including quantum-resistant cryptography and privacy-preserving ML. Section VII identifies open challenges, research gaps, and future directions. Finally, Section VIII concludes the survey.
2. Motivation and Challenges in Modern Cybersecurity
Cyberattacks have grown in complexity, targeting not only individuals but also large organizations, critical infrastructures, and emerging technological ecosystems. Attack vectors such as phishing exploit human vulnerabilities, while IoT botnets leverage resource-constrained devices to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks [
7]. Advanced persistent threats (APT) infiltrate networks stealthily and maintain long-term unauthorized access, making static defenses obsolete [
8].
Signature-based methods struggle to detect novel or obfuscated threats, while rule-based systems often fail to scale or adapt to rapidly evolving attacks [
9]. The reliance on human expertise for updating rules and signatures imposes substantial delays and creates potential blind spots. The inability of conventional approaches to handle large-scale, multi-modal, and noisy data further diminishes their efficacy.
Combining ML, fuzzy systems, and cryptographic methods can produce complementary strengths: ML provides data-driven pattern recognition and anomaly detection capabilities; fuzzy logic introduces interpretability and resilience under uncertainty; and cryptography ensures data protection and trustworthiness [
10]. By blending these techniques, it becomes possible to build dynamic, scalable, and more secure defense frameworks that can evolve over time [
11].
Resource efficiency is critical, especially in IoT environments where computing power, memory, and energy are limited [
12]. Hybrid approaches must be lightweight while maintaining robust security properties. This may involve using optimized ML models, lightweight cryptographic protocols, and adaptive fuzzy rule bases that reduce computational overhead without compromising effectiveness [
13].
3. Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
ML is widely employed to classify network traffic, detect malicious behavior, and identify anomalies in large and complex datasets. Techniques range from supervised learning (e.g., decision trees, random forests, support vector machines) to unsupervised methods (e.g., clustering, autoencoders) and deep learning architectures (e.g., convolutional neural networks, recurrent neural networks) [
14,
15,
16].
Table 1 compares various ML techniques applied in cybersecurity tasks.
Feature selection is paramount to improving model accuracy, reducing training time, and mitigating overfitting. Almseidin et al. proposed a Spark-based Multi-Verse Optimizer (MVO) for feature selection in phishing detection tasks [
1]. By harnessing distributed computing frameworks, the MVO approach scales efficiently with large datasets, achieving higher detection accuracy and shorter training times than traditional optimization methods such as genetic algorithms or particle swarm optimization.
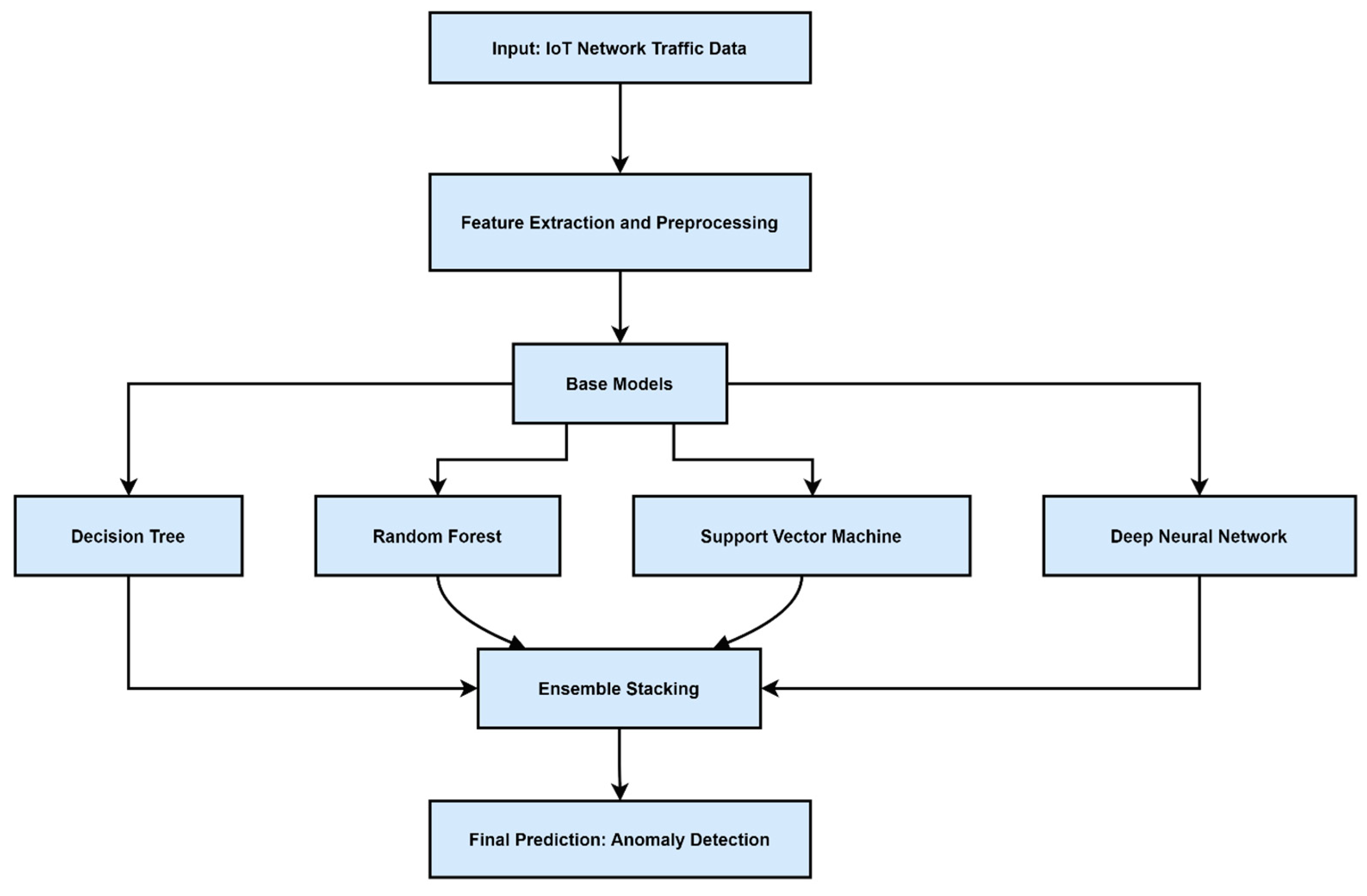
Ensemble methods combine multiple base learners to improve detection performance, stability, and generalization. Rawashdeh et al. introduced a stacked ensemble model for IoT network attack detection, enhancing both precision and recall [
2]. Such ensembles capitalize on the diversity of base models, reducing sensitivity to noisy features and adversarial manipulation.
Figure 1 provides an overview of the ensemble learning pipeline in IoT security contexts.
Machine learning models excel at identifying deviations from normal behavior, making them particularly suitable for zero-day attack detection. Al Attar et al. deployed a machine learning-based solution to detect IoT device anomalies, focusing on behavioral analysis [
6]. Their work confirms that ML-based anomaly detection is well-suited to resource-constrained settings, though the challenge of maintaining high performance under limited computational budgets remains unresolved.
Explainability is an emerging requirement in cybersecurity as operators must understand why a model flags certain behaviors as malicious. This transparency increases trust, facilitates regulatory compliance, and aids in model debugging. Methods like local interpretable model-agnostic explanations (LIME) and Shapley values provide insights into ML decision-making [
17], although their integration into large-scale, online cybersecurity systems remains an area ripe for exploration.
Adversaries have begun leveraging adversarial machine learning to deceive ML-based detectors by manipulating input data [
18]. Research must focus on developing robust training schemes, anomaly detection strategies, and defense mechanisms—such as adversarial training, input denoising, and gradient masking—to ensure that ML models remain resilient against these sophisticated threats.
4. Fuzzy Systems and Decision-Making Frameworks
A. Introduction to Fuzzy Logic in Security
Fuzzy logic provides a mathematical framework to handle imprecision, vagueness, and uncertainty inherent in cybersecurity data. Rather than relying on crisp boundaries, fuzzy systems enable partial membership, leading to more nuanced decision-making [
5].
B. Fuzzy Interpolative Reasoning
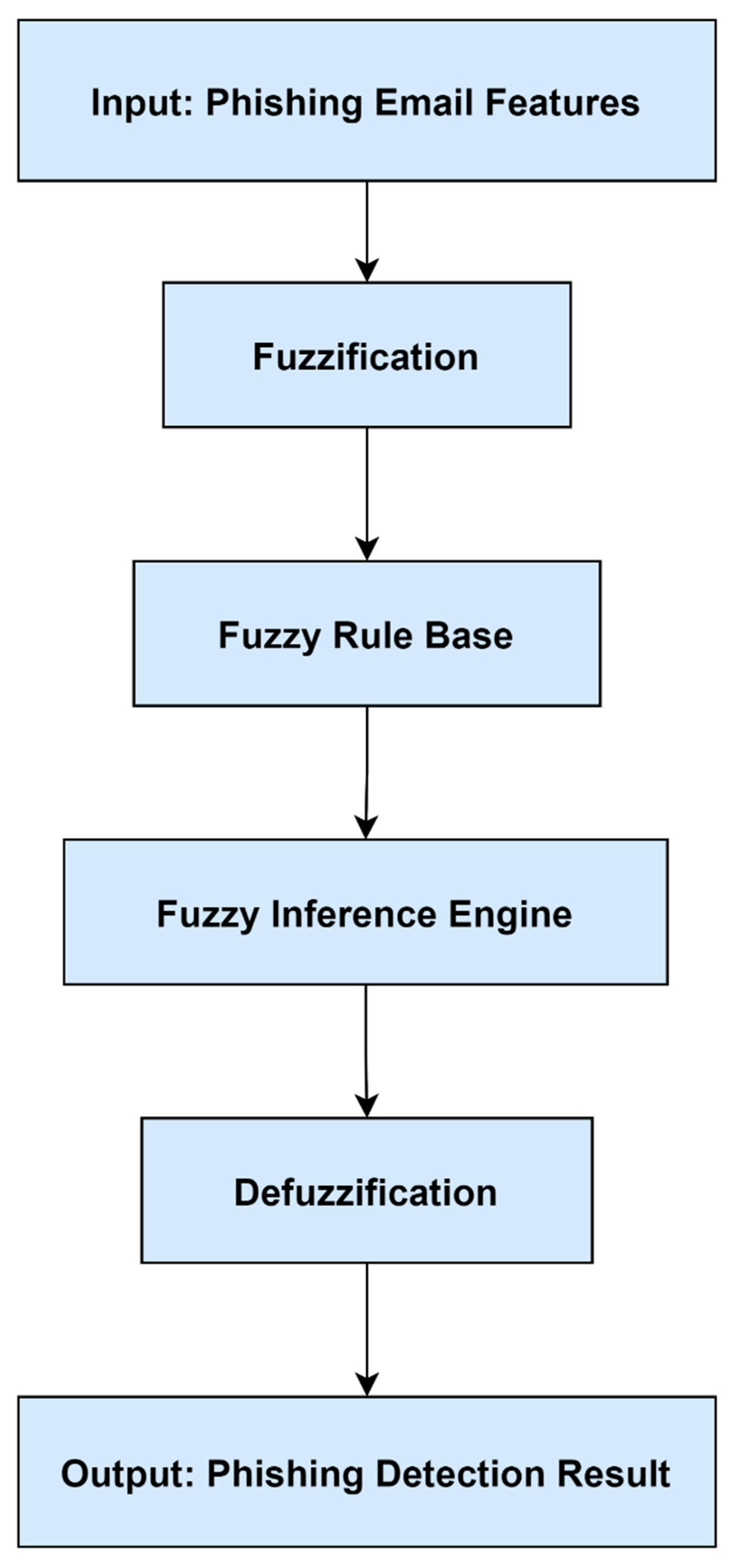
Fuzzy rule interpolation (FRI) methods are particularly useful when dealing with sparse or incomplete rule bases. Almseidin et al. introduced a fuzzy interpolative reasoning system designed for phishing detection, achieving enhanced accuracy and reduced computational overhead [
3]. Alzubi et al. proposed the EI-FRI method, extending fuzzy interpolation to handle multidimensional antecedents and extrapolation [
14].
Figure 2 illustrates the fuzzy inference process, highlighting how fuzzy sets and rules map uncertain inputs to crisp outputs.
C. Comparative Analyses of Fuzzy Techniques
Selecting the right FRI technique is crucial for system performance. Alzubi et al. conducted comparative analyses of various fuzzy interpolation methods, identifying their respective advantages and drawbacks [
13].
Table 2 summarizes key fuzzy methods, their complexity, and application areas.
D. Integration with ML
When combined with ML, fuzzy systems can enhance interpretability and robustness. Hybrid fuzzy-ML models can smooth decision boundaries, reduce false alarms, and improve resilience against noisy inputs. For example, fuzzy clustering can pre-process data for ML classifiers, or fuzzy rules can guide feature selection and model tuning. These integrations also facilitate intuitive explanations for system administrators, increasing trust and usability.
E. Applications in Access Control and Intrusion Detection
Fuzzy logic has proven valuable in intrusion detection systems (IDS) and access control mechanisms, where authentication decisions depend on uncertain or incomplete evidence. Fuzzy systems can weigh context, historical data, and risk levels dynamically, ensuring more informed and flexible security policies [
19].
5. Cryptographic Techniques for Cybersecurity
A. Lightweight Cryptography for IoT
IoT devices often have limited computing capabilities and must rely on lightweight cryptographic protocols. Alauthman et al. introduced cryptographic schemes optimized for resource-constrained environments, ensuring energy efficiency and practical deployment without compromising security [
10].
Table 3 compares selected lightweight cryptographic primitives, highlighting their key attributes and performance metrics.
B. Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning
As data sharing and collaboration become common, privacy-preserving ML techniques protect sensitive information from potential leaks. Homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation allow model training and inference without exposing raw data [
12]. These techniques support federated learning setups, where multiple parties collaboratively train a global model while maintaining data privacy [
20].
C. Post-Quantum Cryptography
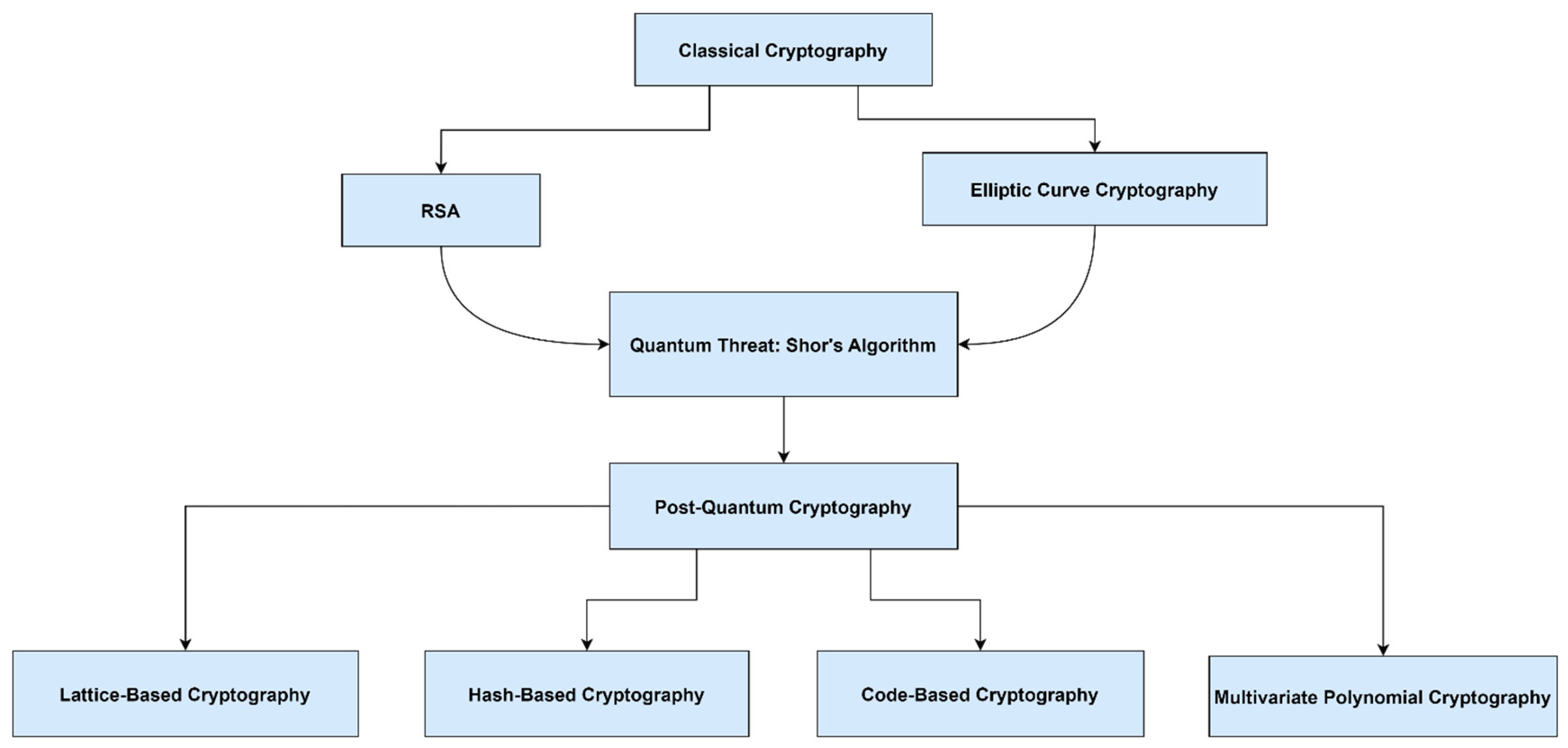
Quantum computing threatens to break widely used public-key cryptosystems such as RSA and ECC. Alauthman et al. conducted a comparative analysis of classical and quantum techniques, emphasizing the urgent need for quantum-resistant cryptography [
9]. Lattice-based, code-based, and hash-based cryptosystems, among others, are proposed as candidates for post-quantum security.
Figure 3 depicts the transition from classical to quantum-resistant cryptography, illustrating how emerging quantum algorithms challenge current standards.
D. Cryptography for Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Large-scale data analytics platforms and business intelligence solutions rely on cryptographic controls to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Khaldy et al. explored cryptographic frameworks that balance computational efficiency with robust security for analytics workflows [
11]. Implementations include attribute-based encryption, tokenization, and privacy-preserving queries.
E. Integration with ML and Fuzzy Systems
By merging cryptographic controls with ML and fuzzy logic, it is possible to create end-to-end secure pipelines where data is encrypted during transfer and storage, ML models learn from encrypted features, and fuzzy systems interpret encrypted outputs under uncertainty. Such integrated frameworks are ideal for distributed IoT ecosystems and cloud-based platforms.
6. Hybrid Cybersecurity Applications and Datasets
IoT devices monitor and manage a wide range of critical functions, from smart home appliances to industrial control systems [
2,
4]. Unfortunately, many IoT devices lack robust security features due to cost constraints or design limitations, making them attractive targets for attackers [
7,
10]. Hybrid approaches that combine ML-based anomaly detection, fuzzy logic decision-making, and lightweight cryptographic protocols can thwart intrusions without overwhelming device resources [
1,
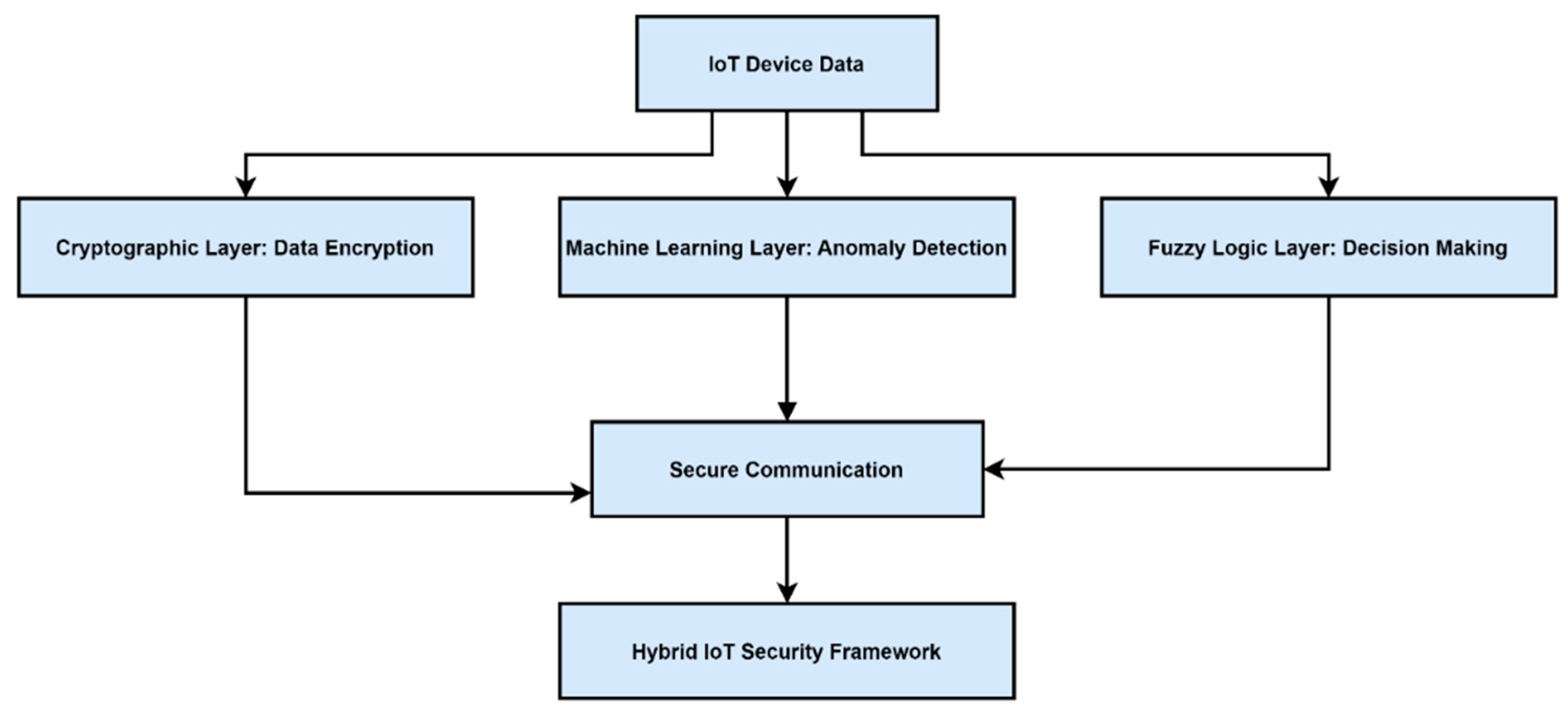
2]. For instance, an ML classifier might detect a suspicious spike in traffic, triggering a fuzzy inference engine to determine the severity of the anomaly [
3]. Concurrently, cryptographic measures ensure that sensitive system commands and data remain inaccessible to unauthorized actors [
10].
Figure 4 shows a conceptual model of how hybrid approaches integrate ML, fuzzy logic, and cryptographic layers for end-to-end IoT security.
Phishing campaigns remain one of the most ubiquitous and effective cyberattack vectors, using deceptive emails, websites, or messages to trick users into disclosing credentials or downloading malware [
1,
3]. Hybrid systems can combat phishing by automating the detection of suspicious URLs, domain names, or email patterns [
1]. Machine learning models classify these features, fuzzy rules interpret borderline cases (e.g., newly registered domains that resemble a legitimate site), and cryptographic measures secure the user’s session or data during verification [
10]. Additionally, optimization heuristics improve feature selection, ensuring that classifiers are both accurate and computationally efficient [
1,
15].
Critical infrastructures, including power grids, water treatment facilities, and transportation networks, are increasingly reliant on digital communications and automation [
4,
19]. When these systems fall victim to cyberattacks, the repercussions can be enormous, affecting both safety and national security [
4,
8]. Hybrid security approaches are particularly crucial in these sectors, where real-time monitoring and response are paramount [
4]. Anomaly detection models can identify sudden fluctuations in sensor data, cryptographic protocols can secure command messages, and fuzzy logic can weigh the various levels of suspicion [
3,
10]. By fusing these layers, critical infrastructure operators gain a dynamic defense mechanism capable of neutralizing threats before they escalate into catastrophic failures [
4].
Table 4 lists notable datasets, their characteristics, and intended use cases, supporting more realistic and comprehensive evaluation of IDS and anomaly detection models.
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based platforms have attracted significant attention from cybercriminals, who target wallets, exchanges, and mining protocols [
7]. Hybrid cybersecurity solutions can analyze blockchain traffic for anomalies, detect suspicious transactions using ML classification, and employ cryptographic techniques such as threshold signatures to preserve privacy [
22]. Fuzzy systems may also be used to rate the riskiness of transactions based on several vague parameters, such as frequency, anonymity levels, or transaction size [
3]. This multidimensional approach enhances transparency, trust, and security within decentralized ecosystems [
7,
21].
Detecting malicious activity within network traffic is a cornerstone of cybersecurity, informing network segmentation, threat intelligence, and incident response [
2,
21]. Hybrid methods can excel here by leveraging the speed and accuracy of ML-based classification, the nuanced decision-making of fuzzy logic, and the data integrity guaranteed by cryptography [
1,
10]. The ultimate goal is to provide accurate, real-time threat detection that does not sacrifice data privacy. Efficient sampling techniques and model optimization ensure that traffic classification remains feasible across diverse network environments, from small corporate LANs to global data centers [
2].
7. Discussion: Current Challenges and Future Directions
As data volumes continue to surge, achieving real-time analysis and scalable protection becomes both complex and critical [
1,
2]. ML models are often data-hungry, and high-dimensional datasets can cause rapid model degradation if not managed correctly [
15]. Moreover, integrating fuzzy logic and cryptographic routines can introduce extra latency. Strategies to address these concerns include:
Distributed Computing and Edge Intelligence: Deploying lightweight models at the network edge reduces the bandwidth and latency associated with sending raw data to central servers [
1]. This approach also allows local decisions without constant cloud connectivity [
6].
Stream Processing: By processing data in small batches or micro-batches, the system can respond to unfolding events in near real-time [
1].
Incremental or Online Learning: ML models can be updated incrementally with newly observed data, enabling timely adaptations without lengthy retraining sessions [
2,
6].
Cybercriminals increasingly exploit vulnerabilities in ML workflows—through data poisoning, evasion, or direct manipulation of the model [
18]. Fuzzy logic, while resilient to slight data uncertainties, can still be undermined if rules are systematically distorted [
3]. Cryptographic measures secure data channels but do not inherently prevent adversarial ML attacks [
9,
12]. Some potential defenses include:
Robust Training Protocols: Adversarial training, where models are exposed to crafted adversarial examples, helps them learn more resilient decision boundaries [
18].
Model Verification and Validation: Automated tests, auditing procedures, or formal proofs of ML model resilience could become standard in high-assurance environments [
9].
Secure Model Updates: When models are trained collaboratively, cryptography ensures that updates cannot be easily manipulated or intercepted [
9,
12,
20].
Modern regulations emphasize the importance of transparent and auditable AI-driven decisions [
17,
18]. In cybersecurity contexts, operators need to trust the system’s alerts and diagnose false positives or negatives. Enhancing explainability can be pursued through:
Human-Readable Fuzzy Rules: Fuzzy logic can transform numeric data into linguistic terms that operators can quickly understand [
3,
5].
Local and Global Interpretability Techniques: Approaches that highlight which features influenced a particular decision or detection outcome [
17].
Governance and Compliance Mechanisms: Organizational frameworks that set guidelines for deploying, monitoring, and updating AI-based defenses in compliance with privacy laws and security standards [
11,
12].
While quantum computers with large-scale capabilities are not yet mainstream, their potential to break widely used cryptosystems cannot be overlooked [
9]. Research into integrating quantum-safe algorithms with ML and fuzzy frameworks is ongoing. Important considerations include:
Performance Trade-offs: Post-quantum algorithms typically require larger key sizes and more computational overhead, which could hamper deployments in resource-limited environments [
9].
Hybrid Cryptographic Schemes: Transitional approaches that combine classical and post-quantum elements may ease the migration to purely quantum-safe systems [
9].
Future-Proofing: For data needing long-term protection—medical records, national defense secrets—a proactive shift to post-quantum cryptography is crucial [
9].
Developing a cybersecurity architecture that orchestrates ML, fuzzy logic, and cryptography seamlessly involves many moving parts [
3,
10]. Potential improvements include:
Modular and Interoperable Frameworks: Designing plug-and-play modules for ML classification, fuzzy inference, and cryptographic operations can simplify system updates and expansions [
12].
Configuration Management: Automated tools that tune fuzzy thresholds, re-key cryptographic functions, and retrain ML models based on usage patterns or new threats can streamline system maintenance [
10].
Benchmarking and Standardization: Common datasets, performance metrics, and testbeds allow consistent evaluations of hybrid solutions, enabling fair comparisons and accelerating research progress [
4,
25].
In IoT ecosystems, industrial controls, and embedded devices, computational constraints pose a significant hurdle [
6]. Ensuring security without overwhelming small processors or draining battery power entails:
Lightweight Algorithms: Both ML and cryptographic routines must be tailored or pruned to fit within strict resource budgets [
10].
Pruned or Quantized Models: Techniques that reduce model size while preserving most of its predictive power [
1,
2].
Adaptive Sampling: Sampling network data or sensor logs judiciously to feed ML algorithms, thus lowering overhead and focusing on critical events [
15].
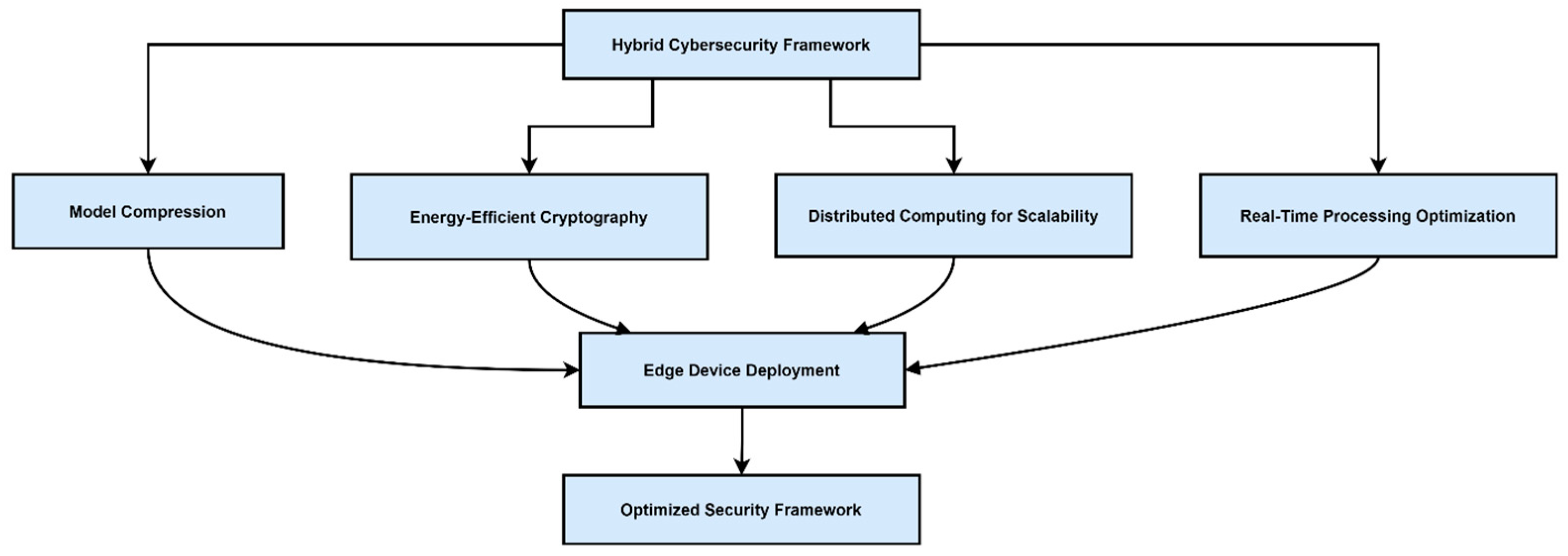
Future research should optimize ML and fuzzy models for deployment on edge devices, employing techniques like model compression, quantization, and energy-efficient cryptographic protocols.
Figure 5 depicts potential optimization strategies for hybrid cybersecurity architectures in constrained environments.
In addition to addressing immediate challenges, research in hybrid cybersecurity is beginning to converge with broader trends in computing and data science:
Federated Learning: Federated or decentralized approaches allow multiple entities to collaborate on shared models without revealing private datasets [
20]. This method reduces single points of failure and fosters collective security intelligence [
1].
Blockchain-Assisted Trust: Some solutions store ML model updates or fuzzy rule sets on blockchains, ensuring integrity and transparency of updates [
21]. This intersection could evolve into an auditable ecosystem for threat intelligence sharing [
22].
Automation and Orchestration: Tools such as Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms may soon integrate fuzzy inference and ML modules out of the box [
9]. This synergy could reduce human error and manual overhead while accelerating responses to attacks.
Neuro-Symbolic AI: Blending symbolic reasoning with deep learning to achieve more robust and interpretable AI solutions may also intersect with fuzzy logic for advanced threat detection [
14,
16].
Table 5.
Challenges and Future Directions.
Table 5.
Challenges and Future Directions.
| Challenge/Topic |
Description |
Proposed Solutions/Strategies |
Key References |
| A. Scalability and Real-Time Processing |
- Data volumes are growing rapidly, making near real-time analysis complex.
- High-dimensional data can degrade ML model performance.
- Fuzzy logic and cryptographic routines add extra latency to the pipeline. |
- Distributed Computing and Edge Intelligence: Deploy lightweight models at the edge to reduce network overhead and latency.
- Stream Processing: Process data in small or micro-batches for timely reactions.
- Incremental/Online Learning: Update ML models on new data without full retraining. |
[1,2,6,15] |
| B. Adversarial Robustness |
- Attackers exploit ML workflows (data poisoning, evasion, backdoor) to compromise models.
- Fuzzy logic is resilient to slight noise but can still be manipulated by systematic distortion.
- Cryptography secures data channels but does not inherently prevent adversarial ML attacks. |
- Robust Training Protocols: Incorporate adversarial examples in training to harden decision boundaries.
- Model Verification and Validation: Implement auditing and formal proofs of model resilience.
- Secure Model Updates: Use cryptographic methods for trusted collaborative training. |
[3,9,12,18,20] |
| C. Explainability and Governance |
- Regulations demand transparent, auditable AI decisions (e.g., GDPR).
- Operators need to understand alerts (false positives/negatives).
- Lack of clarity or interpretability can erode trust and compliance. |
- Human-Readable Fuzzy Rules: Translate numeric data into linguistic terms for easier operator interpretation.
- Local/Global Interpretability: Provide insight into the most influential features in decisions.
- Governance Mechanisms: Establish policies for continuous monitoring and updates. |
[3,5,11,12,17,18] |
| D. Quantum-Resilient Solutions |
- Quantum computing threatens classical cryptosystems (RSA, ECC).
- Emerging post-quantum algorithms (lattice-based, code-based, etc.) require larger keys and more resources.
- Preparing early is crucial for long-term data protection. |
- Performance Trade-offs: Evaluate quantum-safe cryptography’s overhead for resource-limited devices.
- Hybrid Cryptographic Schemes: Combine classical and post-quantum methods for transitional deployment.
- Future-Proofing: Shift critical systems to post-quantum security gradually. |
[9] |
| E. Harmonizing Hybrid Components |
- Integrating ML, fuzzy logic, and cryptography seamlessly involves many moving parts.
- Interoperability and modular designs are needed for easier updates and expansions.
- Consistent benchmarking is needed to compare solutions fairly. |
- Modular/Interoperable Frameworks: Develop plug-and-play modules for classifiers, fuzzy inference, and cryptographic functions.
- Configuration Management: Automate parameter tuning, key management, and retraining.
- Benchmarking & Standardization: Use common datasets and metrics. |
[3,4,10,12,25] |
| F. Resource-Constrained Environments |
- IoT, industrial controls, and embedded systems have limited CPU, memory, and energy.
- Security measures must be optimized to avoid excessive overhead.
- ML and cryptographic algorithms must be tailored to minimal-resource platforms. |
- Lightweight Algorithms: Adapt or prune ML and cryptographic functions to fit embedded constraints.
- Pruned/Quantized Models: Reduce model size with minimal loss in accuracy.
- Adaptive Sampling: Selectively feed data to ML models to lower overhead while maintaining performance. |
[1,2,6,10,15] |
| G. A Look Ahead: Emerging Trends and Possibilities |
- Hybrid cybersecurity intersects with broader computing trends.
- Innovations like federated learning, blockchain-assisted trust, and SOAR automation are on the horizon.
- Neuro-symbolic AI may further enhance interpretability and resilience. |
- Federated Learning: Share model insights without divulging private data, reducing single points of failure.
- Blockchain-Assisted Trust: Store model or fuzzy rule updates on a blockchain for integrity and auditability.
- Automation & Orchestration: Incorporate fuzzy/ML in SOAR platforms. |
[1,9,14,16,20,21] |
8. CONCLUSION
Hybrid cybersecurity architectures present a promising avenue for addressing the limitations of traditional security measures and adapting to the rapidly evolving threat landscape. By integrating machine learning, fuzzy logic, and cryptographic techniques, these frameworks offer a multi-pronged defense that can identify anomalies, interpret ambiguous signals, and protect sensitive data—crucial capabilities in today’s interconnected world.
Machine learning delivers adaptive threat detection and predictive analytics, essential for guarding against zero-day exploits and emerging threats. Fuzzy logic captures the nuance of uncertain data, fostering interpretability and reducing reliance on absolute thresholds. Meanwhile, cryptographic methods underpin the secure exchange of information, assuring stakeholders that sensitive data remains confidential and unaltered.
Despite their strengths, hybrid approaches must overcome practical and theoretical challenges. Scaling these systems to handle massive data streams with minimal latency, ensuring resilience against adversarial manipulation, and implementing cryptographic routines that remain viable in a post-quantum era are all pressing concerns. In parallel, regulatory demands for transparent, explainable security solutions highlight the need for user-friendly interfaces and governance frameworks that integrate smoothly with existing processes.
Looking forward, researchers, practitioners, and policymakers will likely invest in refining hybrid techniques for broader applicability. Future work includes developing lightweight ML and cryptographic implementations for edge devices, refining fuzzy rule engines for improved clarity and dynamism, and pioneering quantum-safe architectures. Ultimately, hybrid cybersecurity aims to balance the technical sophistication required for robust protection with the practical realities of deployment and maintenance—offering a glimpse into a more secure digital future where advanced threats are met with equally advanced, adaptive defenses.
References
- Al-Sawwa, J.; Almseidin, M.; Alkasassbeh, M.; Alemerien, K.; Younisse, R. Spark-based multi-verse optimizer as wrapper features selection algorithm for phishing attack challenge. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Rawashdeh, A.; Alkasassbeh, M.; Alauthman, M.; Almseidin, M. A stacked ensemble approach to identify internet of things network attacks through traffic analysis. Bull. Electr. Eng. Informatics 2024, 13, 4316–4326. [CrossRef]
- Almseidin, M.; Alzubi, M.; Al-Sawwa, J.; Alkasassbeh, M.; Alfraheed, M. A Threefold Approach for Enhancing Fuzzy Interpolative Reasoning: Case Study on Phishing Attack Detection Using Sparse Rule Bases. Computers 2024, 13, 291. [CrossRef]
- R. Younisse and M. AlKasassbeh, "SGID: A semi-synthetic dataset for injection attacks in smart grid systems," in Proc. 15th Int. Conf. Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), 2024, pp. 1-8. [CrossRef]
- T. Takagi and M. Sugeno, "Derivation of fuzzy control rules from human operator's control actions," IFAC Proceedings Volumes, vol. 16, no. 13, pp. 55-60, 1983. [CrossRef]
- R. Al Attar, M. Alkasassbeh, M. Al-Dala'ien, and M. Alohaly, "Detecting anomalies in IoT devices: A machine learning-based solution," Preprints, 2024. [CrossRef]
- M. Alauthman, A. Al-Qerem, M. Alkasassbeh, N. Aslam, and A. Aldweesh, "Malware threats targeting cryptocurrency: A comparative study," in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. Cyber Resilience (ICCR), 2024, pp. 1-8. [CrossRef]
- S. Chen, R. Xiang, and H. Wang, "Defending against advanced persistent threats: A survey," IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 115-145, 2021.
- M. Alauthman et al., "Quantum computing for cybersecurity: A comparative study of classical and quantum techniques," in Innovations in Modern Cryptography. IGI Global, 2024, pp. 75-99. [CrossRef]
- M. Alauthman et al., "Cryptographic protocols for internet of things (IoT) security lightweight schemes and practical deployment," in Innovations in Modern Cryptography. IGI Global, 2024, pp. 431-448. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Al Khaldy et al., "Cryptography in business intelligence and data analytics," in Innovations in Modern Cryptography. IGI Global, 2024, pp. 352-375. [CrossRef]
- M. Alauthman et al., "Privacy-preserving machine learning cryptographic techniques for secure data analysis," in Innovations in Modern Cryptography. IGI Global, 2024, pp. 405-430. [CrossRef]
- Alzubi, M.; Almseidin, M.; Alkasassbeh, M.; Al-Sawwa, J.; Aldweesh, A. Comparative Analysis of Fuzzy Rule Interpolation Techniques Across Various Scenarios Using a Set of Benchmarks. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 33140–33153. [CrossRef]
- M. Alzubi, M. Almseidin, S. Kovacs, J. Al-Sawwa, and M. Alkasassbeh, "EI-FRI: Extended incircle fuzzy rule interpolation for multidimensional antecedents, multiple fuzzy rules, and extrapolation using total weight measurement and shift ratio," Journal of Robotics and Control, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 217-227, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Almseidin, M.; Al-Sawwa, J.; Alkasassbeh, M.; Alzubi, M.; Alrfou, K. DT-ARO: Decision Tree-Based Artificial Rabbits Optimization to Mitigate IoT Botnet Exploitation. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 2023, 32, 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.; Bharti, T.S.; Prakash, S. A hybrid Data-Driven framework for Spam detection in Online Social Network. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 218, 124–132. [CrossRef]
- M. T. Ribeiro, S. Singh, and C. Guestrin, "Why should I trust you? Explaining the predictions of any classifier," in Proc. 22nd ACM SIGKDD Int. Conf. Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 2016, pp. 1135-1144. [CrossRef]
- N. Papernot, P. McDaniel, A. Sinha, and M. Wellman, "SoK: Security and privacy in machine learning," in Proc. IEEE European Symp. Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), 2018, pp. 399-414. [CrossRef]
- AlMasri, M. Alkasassbeh, and A. Aldweesh, "Towards generating a practical SUNBURST attack dataset for network attack detection," Computer Systems Science & Engineering, vol. 47, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. Kairouz et al., "Advances and open problems in federated learning," Foundations and Trends in Machine Learning, vol. 14, no. 1-2, pp. 1-210, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Almomani, M. Alauthman, M. Alkasassbeh, G. Samara, and R. W. Liu, "A proposed darknet traffic classification system based on max voting algorithms," in Int. Conf. Cyber Security, Privacy and Networking, 2021, pp. 349-355. [CrossRef]
- K. Liu, V. K. Wei, and D. S. Wong, "Linkable spontaneous anonymous group signature for ad hoc groups," in Information Security and Privacy, ACISP 2004, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 3108, pp. 325-335, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Winderix, J. T. Mühlberg, and F. Piessens, "Compiler-assisted hardening of embedded software against interrupt latency side-channel attacks," in Proc. IEEE European Symp. Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), 2021, pp. 667-682. [CrossRef]
- R. Kendall, "A database of computer attacks for the evaluation of intrusion detection systems," Ph.D. dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, 1999.
- Sharafaldin, I.; Lashkari, A.H.; Ghorbani, A.A. Toward generating a new intrusion detection dataset and intrusion traffic characterization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy, Funchal, Portugal, 22–24 January 2018; pp. 108–116.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).