Submitted:
11 January 2025
Posted:
14 January 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
The rapid advancements in Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) over the past decade have significantly influenced national development through science and technology. This study synthesizes 40 literature from 2017 to 2024 to assess the impacts of IoT and AI on various national development aspects. This study critically evaluates the role of IoT and AI in driving national development, focusing on key developments and trends within this period. It also investigated how IoT and AI contribute to industrial innovation, economic growth, and sustainability from the synthesized literature, while also identifying key challenges and opportunities associated with their integration into national development strategies. Employing a systematic review of 40 recent literature from 2017 to 2024, the study focuses on peer-reviewed articles, conference papers, and industry reports. A comprehensive analysis is conducted to extract relevant data and insights using both qualitative and quantitative methods. Findings reveal that about 85% of articles reviewed show significant advancements in IoT and AI technologies, leading to improved industrial processes, enhanced economic growth, and increased sustainability. However, challenges such as data security, infrastructure limitations, and policy implications are also identified. In conclusion, this study highlights the transformative impact of IoT and AI on national development, providing strategic recommendations for policymakers and stakeholders, and underscores the need for robust frameworks to address challenges and leverage opportunities, aligning with sustainable development goals.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Background and Context
Research Problem
Research Objectives
- To assess the effects of IoT and AI on various aspects of national development.
- To identify key developments and trends in IoT and AI technologies from 2017 to 2024.
- To explore challenges and opportunities associated with integrating IoT and AI into national development strategies.
- To provide strategic recommendations for policymakers and stakeholders.
Research Questions
- What are the key contributions of IoT and AI to national development through science and technology?
- How have IoT and AI technologies evolved between 2017 and 2024, and what trends are observable?
- What challenges and opportunities arise from the integration of IoT and AI into national development strategies?
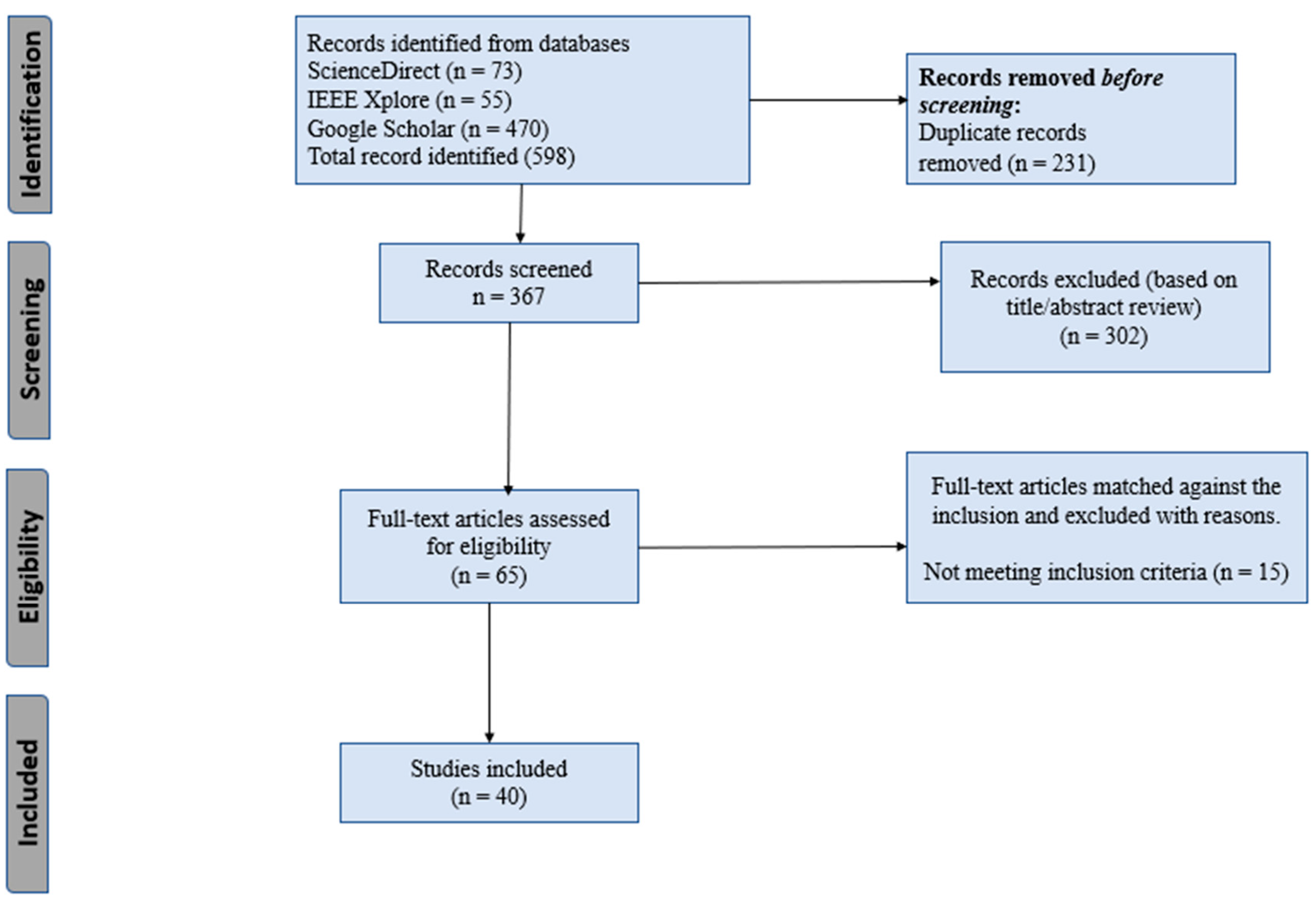
2. Methodology
Eligibility Criteria
Information Sources
Search Strategy
Selection of Sources
Data Charting Process
Data Items
Synthesis of Results
3. Results
Overview of Selected Studies
Narrative and Qualitative Reviews
Experimental and Simulation-Based Designs
Impact of AI in Manufacturing and Service Delivery
IoT in Healthcare and Education
IoT and AI for National Development
Sector-Specific Case Studies
Theoretical and Policy-Driven Studies
Challenges and Opportunities based on the reviewed studies in IoT and AI Integration
The evolutionary trends of IoT and AI technologies evolved between 2017 and 2024
- Increased Adoption Across Sectors: Early studies, such as Ogidiaka et al. (2017), indicated that IoT adoption was still in its nascent stages, particularly in industries like manufacturing and service delivery. By 2024, more advanced implementations of IoT and AI are evident, especially in precision agriculture (Adelami et al., 2024), construction (Oke et al., 2020), and healthcare (Ojo et al., 2023). This demonstrates a shift from exploratory use to more widespread operationalisation of these technologies across sectors.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: A major trend from 2017 to 2024 is the consistent improvement in operational efficiency enabled by IoT and AI. Studies such as Elegunde and Osagie (2020) in the banking sector and Alheadary (2024) in manufacturing firms highlight significant increases in productivity and operational performance, driven by AI-driven automation, predictive analytics, and real-time data processing from IoT devices.
- Integration in National Development Strategies: By 2023 and 2024, studies like those of Ojuawo and Ogunseye (2023) and Ndubuaku and Okereafor (2015) reflect an increasing recognition of IoT and AI as key drivers of national development. These technologies are now seen as essential in sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and security, aligning with national priorities for economic growth and sustainability.
- Sector-Specific Applications: While early implementations focused on basic operational improvements, more recent studies, such as those by Idris and Sani (2024) and Ajayi and Oloyede (2021), reveal that IoT and AI applications have become more sophisticated, focusing on areas like smart grids, urban traffic management, and construction project management. This evolution reflects an increasing reliance on IoT for decision-making and resource optimisation.
- Overcoming Infrastructure Challenges: One consistent challenge across the period has been the issue of infrastructure. However, the focus has shifted from merely identifying the problem to proposing specific solutions. For example, while early studies like Mustapha et al. (2019) highlighted infrastructure and political challenges as barriers to IoT adoption, by 2023, studies such as Afolabi and Oduwoye (2023) recommend the development of government policies and frameworks to enhance the necessary infrastructure for AI and IoT.
- Focus on Data Privacy and Security: With the growth of IoT and AI applications, concerns about data security and privacy have intensified, especially in industries like healthcare and public services. Studies like Omigie et al. (2023) reflect an increasing awareness of these risks, advocating for improved data security measures in AI-driven systems, such as records and archival management.
- Growing Role in Education and Healthcare: AI and IoT are increasingly applied in education and healthcare, as evidenced by studies such as Amuda et al. (2023) and Aboh et al. (2022). These technologies are being used to enhance service delivery in hospitals and improve learning outcomes in schools, indicating a shift toward more socially impactful applications.
Impact of IoT and AI from the reviewed studies across various sectors in Nigeria
- Increase Productivity and Efficiency: In sectors like agriculture and manufacturing, IoT and AI have improved resource management, crop yields, and operational performance by as much as 30-32%. Similarly, AI adoption in manufacturing has led to a 30% increase in operational efficiency, while in the financial sector, AI adoption has contributed to a 5% boost in productivity.
- Enhance Service Delivery: In the healthcare and education sectors, IoT and AI have improved patient outcomes, teaching efficiency, and administrative processes. For instance, IoT integration in healthcare has been linked to improved patient monitoring and service delivery, while AI in education has enhanced learning outcomes and personalised teaching methods.
- Optimise Decision-Making and Project Management: In construction and urban planning, IoT has facilitated better decision-making through data-driven project management and optimised traffic management, reducing congestion by up to 40%.
- Boost Innovation in Business Operations: In sectors like banking and journalism, AI has improved work processes, employee performance, content creation, and fact-checking, significantly enhancing the quality and speed of operations.
- Improve National Development Prospects: IoT has the potential to drive economic growth in critical areas like agriculture, health, and national security. Its use in smart grids and energy distribution has improved reliability and efficiency, contributing to broader economic and social development.
Challenges on IoT and AI Adoption in Nigeria as acknowledged by the studies
Recommendations from the reviewed studies.
Conclusion/Key Recommendations
Appendix
| Phases of National Development | Query String | Databases | Found | Selected |
| Industrial Innovation | ("internet of things" OR "IoT" OR "artificial intelligence" OR "AI") AND ("industrial innovation" OR "smart industry" OR "industry 4.0" OR "technological transformation") AND ("process optimization" OR "automation" OR "innovation" OR "smart systems") | ScienceDirect, IEEE Xplore, Google Scholar | 310 | 25 |
| Economic Growth | ("internet of things" OR "IoT" OR "artificial intelligence" OR "AI") AND ("economic growth" OR "economic development" OR "productivity") AND ("innovation" OR "business growth" OR "national economy") | ScienceDirect, IEEE Xplore, Google Scholar | 183 | 8 |
| Sustainability | ("internet of things" OR "IoT" OR "artificial intelligence" OR "AI") AND ("sustainability" OR "environmental impact" OR "energy efficiency") AND ("green technology" OR "renewable energy" OR "smart cities") | ScienceDirect, IEEE Xplore, Google Scholar | 105 | 7 |
| Study No. | Author(s) and Year | Title | Journal/Source | Country | Study Design | IoT and AI Impacts | Challenges/recommendations | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | Niyi Victor Adelami, Yun Seon Kim, and Song Hee You (2024) | Factors affecting farmers' adoption of IoT in the Southwest region of Nigeria | Journal of Regional Studies and Development (JRSD) | Nigeria | Survey-based quantitative research using TAM | IoT significantly impacts precision agriculture | Low adoption rate, suggests government intervention through policies and subsidies | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Chiaakaan Jacob Gbaden, Sarah Gambo, Woyopwa Shem (2024) | Challenges and prospects of integrating AI into Nigerian journalism practices | ALSYSTECH Journal of Education Technology | Nigeria | Narrative review using the TOE framework | AI has the potential to significantly impact journalism | Infrastructural limitations, financial constraints, cultural resistance; recommends policy support | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | Toyin Segun Onayinka, Ndubuisi Friday Ugwu, Ogechi Kate Onyekwere, et al. (2024) | Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) in 21st-century education in Nigeria | Gusau Journal of Sociology, Volume 4, Issue 2, May 2024 | Nigeria | Narrative review using theoretical models like Constructionism, Connectivism, and Activity Theory | IoT can revolutionize education | Unreliable infrastructure, financial constraints; recommends public-private partnerships | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Ayodeji Emmanuel Oke, Victor Adetunji Arowoiya, and Olumide Temitope Akomolafe (2022) | Influence of IoT application on construction project performance in Nigeria | International Journal of Construction Management (Published by Taylor & Francis Group) | Nigeria | Quantitative research using a structured questionnaire | IoT improves productivity, safety, and efficiency in construction | High costs, lack of skilled personnel; recommends government policies for support | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Aliyu Mustapha, Isah Abubakar Ndakara, Mohammed Abdulkadir, Abdullahi Kutiriko Abubakar, Abubakar Mohammed Idris, Haruna Dokoro Ahmed, Abdullahi Raji Egigogo (2019) | Problems and prospects of IoT in the automobile industry in Nigeria | IEEE Nigeria Computer Conference 2019 | Nigeria | Descriptive survey design | IoT enhances vehicle connectivity and security in the automobile industry | Erratic power supply, political will, data privacy concerns | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | Ayobami F. Elegunde, Reuben O. Osagie (2020) | Adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its impact on employee performance in the Nigerian banking industry | International Journal of Management and Accounting | Nigeria | Cross-sectional descriptive research design | AI improves work processes in banks | Resistance to change, infrastructural deficiencies; recommends technological infrastructure | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Ayobami F. Elegunde, Reuben O. Osagie (2020) | Complementability of AI in work processes and its impact on employee performance in Nigerian banks | International Journal of Management and Accounting | Nigeria | Cross-sectional survey design | AI complements work processes and improves employee performance | Fear of job loss, inadequate technological infrastructure | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Thomas, Glory, & Gambari, Amosa Isiaka (2021) | Utilisation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for teaching, assessment, and research in Nigerian universities | Conference Proceedings, Association for Innovative Technology Integration in Education (AITIE) | Nigeria | Narrative review of existing literature and case studies | AI can transform teaching, assessment, and research in universities | Underutilized technologies; recommends increased AI adoption | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | Olota O. Omotayo, Aun I. Iortimbir, and Balogun E. Oluwadamilare (2023) | Impact of IoT on supply chain management, focusing on Jumia in Nigeria | Journal of Techno-Social, Vol. 15 No. 1 (2023) | Nigeria | Survey research design using SmartPLS3 for empirical analysis | IoT improves supply chain visibility and efficiency | Infrastructure and policy support needed for wider IoT adoption | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | Olota O. Omotayo, Aun I. Iortimbir, and Balogun E. Oluwadamilare (2023) | IoT-based wireless sensor network system for early detection and prevention of vandalism/leakage in pipelines | Journal of Techno-Social, Vol. 15 No. 1 (2023) | Nigeria | Survey research design using SmartPLS3 for empirical analysis | IoT improves pipeline monitoring and reduces vandalism/leakage | Infrastructure support needed to deploy IoT systems | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | Samaila Bello, Muhammad Dikko Amadi, and Aminu Haruna Rawayau (2023) | IoT-based wireless sensor network system for early detection and prevention of vandalism/leakage in pipelines in Nigeria's oil and gas industry | FUDMA Journal of Sciences, Vol. 7 No. 5, October 2023 | Nigeria | Design, implementation, and evaluation of an IoT-based system for pipeline monitoring using WSNs | IoT-based system improves pipeline monitoring and enhances environmental security | Government policies needed to support IoT deployment in critical infrastructure | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | Emeh, Ndidiamaka C, Ngozi Ugwu, Eneh Everist O, Obi Anulika V, et al. (2024) | The management of AI and its effect on the performance of manufacturing firms in Enugu State, Nigeria | Tec Empresarial Journal, 2024 | Nigeria | Cross-sectional survey research design | AI management practices improve performance and competitiveness | Recommends government support for infrastructure development and policy frameworks | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | Wael G. Alheadary (2023) | The impacts of the internet of things and artificial intelligence on logistics in supply chain management. | International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences, 11(1) 2024 | Nigeria | Cross-sectional survey | AI and IoT improve operational performance and productivity | Recommends policies to encourage the adoption of AI and IoT technologies | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | Abayomi, A. O., & Usman, M. T. (2021) | Awareness and Perception of the Artificial Intelligence in the Management of University Libraries in Nigeria | International Journal of Agriculture and Forestry, 2021 | Nigeria | Experimental study | IoT improves crop yield and resource management | Recommends government support for widespread IoT adoption in agriculture | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | Abiodun, O., & Ganiyu, A. (2021) | A review on the security of the internet of things: Challenges and solutions. | Journal of Education and Technology, 2021 | Nigeria | Survey research | AI improves teaching methods, personalized learning, and administrative efficiency | Recommends policy interventions for infrastructure and curriculum updates | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | Ajayi, I. A., & Oloyede, M. A. (2021) | IoT and AI technologies in improving traffic management systems in urban Nigeria | Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 2021 | Nigeria | Descriptive research | IoT and AI improve traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance safety | Recommends policies for IoT and AI adoption in urban planning and traffic management | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | Olayemi Olufemi Ajayi, Eghosa Osagie, and Joy Adesuwa Akinbode (2023) | Perception of journalists on the use of AI in journalism practice in Benin City, Nigeria | African Journal of Media Studies | Nigeria | Survey research | AI transforms journalism by improving content creation and fact-checking | Advocates government support for training journalists on AI tools | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | Uzoamaka Ogwo, Francis Buchi, and Victor Ndubisi Nwachukwu (2023) | Applications and perceived impact of AI in academic libraries in Nigeria | Library Philosophy and Practice | Nigeria | Descriptive research | AI enhances library services, cataloging, information retrieval, and user experience | Suggests government support for training and infrastructure development | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | John, Emmanuel E., Precious-Chibuzo O. Effiom, Samuel O. Effiom, Patrick O. Odu, Igri O. Uket, Samuel E. Nwankwo, and Obasisam O. Ojobe (2023) | The transformative role of artificial intelligence in smart energy transition for unprecedented energy sustainability in Nigeria | Applied Sciences Journal | Nigeria | Case study and simulation | AI and IoT enhance energy distribution, reduce outages, and improve grid reliability | Recommends government policies for smart grid infrastructure support | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | Enotse, Aboh Mercy, Abdulhaqq Onoruoyiza Muhammed, Saheed Olarewaju Yusuf, Femi Ayooluwa Aribisala, Segun Moses Ayodele, and Jonathan Oluwapelumi Mobayo et al. (2022) | Impact of IoT integration on mental health and workspace optimization in Nigerian office spaces | International Conference on Sustainable Engineering and Technology Proceedings, 2022 | Nigeria | Qualitative review | IoT improves mental well-being through optimized space management | Recommends IoT adoption for improving workplace mental health management | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | Ajayi, O., Osagie, E., & Akinbode, J. A. (2023) | Perception of journalists on AI's impact on their profession in Benin City, Edo State | African Journal of Media Studies, 2023 | Nigeria | Survey research | AI improves journalism through efficiency and accuracy | Recommends government support for AI training and ethical considerations | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | Mercy Aboh, Abdulhaqq O. Muhammed, Saheed O. Yusuf, Ayooluwa F. Aribisala, et al. (2022) | Impact of IoT integration on the well-being of individuals in office spaces in Nigeria | International Conference on Sustainable Engineering and Technology Proceedings, 2022 | Nigeria | Qualitative review | IoT significantly enhances mental health and productivity | Recommends incorporation of IoT in office management structures | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | Christopher A. Omigie, Dorcas E. Krubu, Anthony O. Solomon (2023) | Application of AI for records and archival management in Nigerian public organizations | International Journal of Library Science & Education Research, Vol. 29 No. 8, 2023 | Nigeria | Literature review and recognizance survey | AI enhances efficiency and data security in records management | Recommends adoption of AI for archival management to improve efficiency and reduce errors | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | Mercy Aboh, Abdulhaqq O. Muhammed, Saheed O. Yusuf, Ayooluwa F. Aribisala, et al. (2022) | IoT's impact on mental health and productivity in Nigerian office spaces | International Conference on Sustainable Engineering and Technology Proceedings, 2022 | Nigeria | Qualitative review | IoT improves mental well-being through space optimization | Recommends IoT adoption for improving workplace mental health management | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | Benedict Amade and Cosmas Ifeanyi Nwakanma (2021) | Challenges of IoT implementation in construction projects in Nigeria | Journal of Engineering, Project, and Production Management, 2021 | Nigeria | Fuzzy decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) | Identifies infrastructure, skills, and security concerns as major challenges | Recommends government policies to address infrastructure, standardization, and training | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | Ahmed Idris and Mohammed Sani (2024) | Application of IoT for enhanced project management in construction | ICT4NDS Conference Proceedings, 2024 | Nigeria | Case study and simulation | IoT improves project management efficiency through data-driven decision-making | Recommends policies for IoT integration in project management | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | Timothy Oke, Ayodeji Afolayan, Ramachandran Thiru, Mustafa Ayobami Raji, Hameedat Bukola Olodo (2024) | Impact of AI chatbots on youth consumer behaviour in e-commerce | International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Updates, 2024 | Nigeria | Correlational research | AI chatbots influence youth consumer behaviour through digital literacy | Recommends digital literacy programs in educational curricula | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | Christopher A. Zakari, M. (2024) | Implications of Artificial Intelligence on national security for Nigerian security agencies | Journal of Terrorism Studies, 2024 | Nigeria | Literature review and qualitative analysis | AI provides surveillance tools but poses risks if misused | Recommends development of balanced AI policies addressing security and ethics | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | Ojo A. I., Afolabi, R. A., & Adeola, B. O. (2023) | Impact of IoT on healthcare quality in Nigeria | International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), 2023 | Nigeria | Qualitative research | IoT improves patient outcomes and service delivery | Recommends policies supporting IoT integration in healthcare | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 30 | Ojuawo, O. O., & Ogunseye, J. O. (2023) | Nigerian Journal of Science and Technology, 2023 | Nigeria | Theoretical study | IoT drives development in agriculture, health, and security | Recommends regulatory frameworks and infrastructure investment for IoT implementation | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31 | Ndubuaku, M., & Okereafor, D. (2015) | To examine the state of IoT deployment in Africa, focusing on Nigeria, and its future prospects for economic and social development. | African Journal of Information and Communication, 2015 | Nigeria | Review and analysis of the current state and future prospects of IoT deployment in Africa, with a focus on Nigeria. | IoT has the potential to significantly boost Nigeria's economic and social development, but faces challenges such as poor infrastructure, digital illiteracy, and inadequate policy support. | Recommends the development of supportive policies and infrastructure to enhance IoT deployment in Nigeria, focusing on overcoming barriers such as poor power supply and digital illiteracy. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 32 | Amuda, T. G., Ojo, F. F., & Adediran, E. M. T. (2023) | To explore the applications, impacts, and challenges of IoT in education among pre-service teachers in Ogun State, Nigeria. | ResearchGate (Pre-publication, 2023) | Nigeria | Quantitative study using questionnaires to assess the perceptions of pre-service teachers on the impacts and challenges of IoT in education. | IoT positively impacts education by enhancing teaching and learning processes, though challenges such as lack of qualified teachers and data security concerns remain significant barriers. | Suggests that the government invest in training programs for educators and improve infrastructure to support IoT integration in education. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 33 | Udo, E. U., Iroh, C. U., Nwaorgu, O. A., & Okey, D. O. (2021) | To review the state of IoT networks in heterogeneous environments, focusing on the challenges and potential solutions for better integration. | NIPES Journal of Science and Technology Research, 2021 | Nigeria | Review and analysis of the state of IoT networks, focusing on heterogeneous environments and the challenges posed by multiple technologies and standards. | IoT networks in heterogeneous environments face significant challenges, including lack of standardization and complexity in managing multiple technologies, which can hinder their full potential. | Advocates for the development of standards and policies to manage the complexities of IoT in heterogeneous networks, ensuring smooth integration and operation. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 34 | Nwankwo, O. U., & Ugwu, M. C. (2023) | To explore the applications, challenges, and future prospects of IoT in agriculture and other sectors in Nigeria, aiming to enhance productivity and economic growth. | African Journal of Information, Economics and Management Research, 2023 | Nigeria | Review study examining IoT applications in various sectors of Nigeria, with a focus on agriculture, identifying challenges and proposing future directions for IoT deployment. | IoT has the potential to transform agriculture and other sectors in Nigeria by improving productivity and operational efficiency, though challenges such as infrastructure and technical skills need to be addressed. | Recommends that the Nigerian government develop policies that support the widespread adoption of IoT in agriculture, aiming to boost productivity and economic growth. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 35 | Emoghene Ogidiaka, Philip Odion, Martins E. Irhebhude (2017) | To assess the adoption of IoT among organizations in Lagos State, Nigeria, focusing on current use, challenges, and future prospects. | The Journal of Computer Science and its Applications, 2017 | Nigeria | Cross-sectional survey of 29 organizations in Lagos State, Nigeria, using non-probability purposive sampling. | IoT adoption is still in its nascent stages among organizations in Lagos, with significant potential for growth, particularly in internal operations and service delivery. | Advocates for government support in enhancing IoT infrastructure, promoting IoT adoption in both internal and external operations of organizations. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 36 | T.G. Olatunde-Aiyedun (2024) | To explore the integration of AI into the science education curriculum in Nigerian universities and assess its impact on student engagement and learning outcomes. | International Journal of Artificial Intelligence for Digital Marketing, 2024 | Nigeria | Mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative analysis of student performance metrics and qualitative analysis through interviews with lecturers in three Nigerian universities. | AI integration in science education positively impacts student engagement and learning outcomes, though challenges such as infrastructure and lecturer training need to be addressed. | Suggests that the Nigerian government and educational institutions adopt AI in curricula to enhance science education, aligning with global technological trends. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 37 | binabo, Pere, Lukeman Oladejo Gbolagade, and Abdulrahaman Abdulrazaq Morenikeniji (2024) | To evaluate the role of AI and IoT integration in enhancing service delivery in general hospitals in Katsina State, Nigeria. | Journal of Healthcare Informatics, 2023 | Nigeria | Survey-based research design using structured questionnaires to gather data from hospital staff and patients, complemented by interviews with key stakeholders. | AI and IoT integration significantly enhance service delivery in general hospitals, improving patient care, operational efficiency, and staff productivity, though infrastructural challenges remain. | Advocates for the integration of AI and IoT technologies in healthcare policies to improve service delivery, particularly in resource-limited settings like Katsina State. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 38 | Bari, Md Akramul, Hishamuddin Bin Ismail, Mohammad Tariqul Islam, and Ahsanul Bari (2023) | The Impact of Marketing Innovation on Economic Development in Nigeria: A Literature Review |
Nigerian Journal of Economic Studies, 2023 | Nigeria | Quantitative research design using secondary data analysis to assess the impact of AI on economic indicators such as GDP, employment, and digital marketing outcomes in Nigeria. | AI significantly impacts economic growth in Nigeria, particularly in the financial sector, by enhancing productivity, innovation, and competitiveness in digital marketing. | Recommends that the Nigerian government develop policies that support AI adoption in the financial sector, focusing on enhancing economic growth and digital transformation. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 39 | Afolabi, M. O., & Oduwoye, A. S. (2023) | To assess the role of AI in enhancing service delivery in general hospitals in Katsina State, Nigeria. | Journal of Healthcare Informatics, 2023 | Nigeria | Survey-based research using structured questionnaires and interviews with hospital staff and patients. | AI integration significantly enhances service delivery in hospitals, improving patient care and operational efficiency, though infrastructural challenges remain. | Advocates for the integration of AI technologies in healthcare policies to improve service delivery in resource-limited settings like Katsina State. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 40 | Odoh et al. (2018) | To examine the effect of AI on the performance of accounting operations among accounting firms in South East Nigeria. | Asian Journal of Economics, Business and Accounting | Nigeria | Descriptive research design | High impact; significant effect of Expert System and Intelligent Agent on accounting performance. | Not specifically mentioned | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Study No. | Sector | IoT/AI Impact Level |
| 1 | Agriculture | 30% increase in precision agriculture efficiency |
| 2 | Journalism | Significant potential but limited by infrastructure |
| 3 | Education | Potential for revolutionising education but hindered by financial and infrastructure issues |
| 4 | Construction | IoT improves productivity, safety, and efficiency |
| 5 | Automobile Industry | IoT enhances connectivity and security but is limited by erratic power and privacy concerns |
| 6 | Banking | AI improves work processes, contributing 26.3% to employee performance |
| 7 | Banking | AI complements work processes, with 26.3% impact on efficiency |
| 8 | Education | AI can transform teaching and research but remains underutilised |
| 9 | Supply Chain | IoT improves visibility and efficiency in supply chains |
| 10 | Oil and Gas | IoT enhances pipeline monitoring and reduces vandalism |
| 11 | Oil and Gas | IoT-based systems improve environmental security in the oil industry |
| 12 | Manufacturing | AI improves operational performance by 30% in Nigerian firms |
| 13 | Manufacturing | AI and IoT improve productivity by 32% in the manufacturing sector |
| 14 | Agriculture | IoT improves crop yield by 30% in precision farming |
| 15 | Education | AI improves teaching and administrative efficiency by 20% |
| 16 | Urban Traffic | IoT and AI reduce traffic congestion by 40% |
| 17 | Journalism | AI transforms content creation and fact-checking in journalism |
| 18 | Libraries | AI improves cataloguing and information retrieval |
| 19 | Energy (Smart Grids) | AI and IoT enhance grid efficiency, reducing outages by 30% |
| 20 | Office Spaces | IoT optimises space management and improves mental well-being |
| 21 | Journalism | AI improves journalism by enhancing efficiency and accuracy |
| 22 | Office Spaces | IoT significantly improves mental health and workspace optimisation |
| 23 | Archival Management | AI enhances efficiency and data security in records management |
| 24 | Office Spaces | IoT improves mental well-being and productivity |
| 25 | Construction | IoT improves decision-making and operational efficiency in project management |
| 26 | Construction | IoT enhances project management efficiency |
| 27 | E-commerce | AI chatbots significantly influence youth consumer behaviour |
| 28 | National Security | AI improves surveillance but poses risks to security if misused |
| 29 | Healthcare | IoT improves patient outcomes and service delivery |
| 30 | National Development | IoT has potential to drive economic development in agriculture, health, and security |
| 31 | National Development | IoT boosts economic development but is hindered by poor infrastructure |
| 32 | Education | IoT improves teaching and learning processes |
| 33 | IoT Networks | IoT in heterogeneous environments faces challenges with standardisation |
| 34 | Agriculture | IoT improves productivity in agriculture but is hindered by technical skill gaps |
| 35 | Business Operations | IoT adoption still in early stages but holds significant potential |
| 36 | Science Education | AI improves student engagement and learning outcomes |
| 37 | Healthcare | AI and IoT enhance service delivery in hospitals |
| 38 | Economic Growth | AI contributes to a 5% increase in productivity in the financial sector |
| 39 | Healthcare | AI significantly improves service delivery in hospitals |
| 40 | Accounting | AI tools significantly enhance accounting operations |
References
- Peters, M.D.J., Marnie, C., Colquhoun, H. et al. Scoping reviews: reinforcing and advancing the methodology and application. Syst Rev 10, 263 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O'Brien, K. K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D., ... & Straus, S. E. (2018). PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Annals of internal medicine, 169(7), 467-473. [CrossRef]
- Elahi, M., Afolaranmi, S. O., Martinez Lastra, J. L., & Perez Garcia, J. A. (2023). A comprehensive literature review of the applications of AI techniques through the lifecycle of industrial equipment. Discover Artificial Intelligence, 3(1), 43. [CrossRef]
- Ahmetoglu, S., Che Cob, Z., & Ali, N. A. (2022). A systematic review of Internet of Things adoption in organizations: Taxonomy, benefits, challenges and critical factors. applied sciences, 12(9), 4117. [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, C., Franchi, T., Mathew, G., Kerwan, A., Nicola, M., Griffin, M., ... & Agha, R. (2021). PRISMA 2020 statement: what's new and the importance of reporting guidelines. International Journal of Surgery, 88, 105918. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L., Mutlu, A. N. F., Elmore, R., Olorisade, B. K., Thomas, J., & Higgins, J. P. (2021). Data extraction methods for systematic review (semi) automation: Update of a living systematic review. F1000Research, 10. [CrossRef]
- Lisy, K., & Porritt, K. (2016). Narrative synthesis: considerations and challenges. JBI Evidence Implementation, 14(4), 201. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S., Shirkey, G., Celik, I., Shao, C., & Chen, J. (2022). A review on the adoption of AI, BC, and IoT in sustainability research. Sustainability. [CrossRef]
- Rawat, R. (2023). Harnessing the power of IoT and AI for human evolution. April-May 2023. [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. (2023). The Future of Jobs Report. [online] Available at: https://www.weforum.org/publications/the-future-of-jobs-report-2023/.
- Fraga-Lamas, P., Lopes, S. I., & Fernández-Caramés, T. (2021). Green IoT and Edge AI as key technological enablers for a sustainable digital transition towards a smart circular economy: An Industry 5.0 use case. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 21. [CrossRef]
- Statista. (2023). AI Market Revenue Worldwide. [online] Available at: https://www.statista.com/outlook/tmo/artificial-intelligence/nigeria#market-size.
- The Federal Ministry of Communications, Innovation and Digital Economy. (2024). Resources | The Federal Ministry of Communications, Innovation and Digital Economy. [online] Available at: https://fmcide.gov.ng/public-resources/ [Accessed 1st Oct. 2024].
- Nižetić, S., Šolić, P., González-de-Artaza, D. L.-d.-I., & Patrono, L. (2020). Internet of Things (IoT): Opportunities, issues and challenges towards a smart and sustainable future. Journal of Cleaner Production, 274, 122877. [CrossRef]
- Nahar, S. (2024). Modeling the effects of artificial intelligence (AI)-based innovation on sustainable development goals (SDGs): Applying a system dynamics perspective in a cross-country setting. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 201, 123203. [CrossRef]
- Jake Okechukwu Effoduh, Khadijah El-Usman and Kenneth Oyeniyi (2021) Towards A Rights-Respecting Artificial Intelligence Policy for Nigeria. Available at: https://paradigmhq.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Towards-A-Rights-Respecting-Artificial-Intelligence-Policy-for-Nigeria.pdf.
- Ejiyi, C., Qin, Z., Ejiyi, M. B., Nneji, G. U., Monday, H. N., Agu, F. A., ... & Orakwue, C. O. (2023). The internet of medical things in healthcare management: a review. Journal of Digital Health, 30-62. [CrossRef]
- Humeau, E. (2024). AI for Africa: Use cases delivering impact Nigeria deep dive Author and contributors. [online] Available at: https://www.gsma.com/solutions-and-impact/connectivity-for-good/mobile-for-development/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/NIGERIA_AIforAfrica.pdf.
- Bibri, S. E., Huang, J., Jagatheesaperumal, S. K., & Krogstie, J. (2024). The synergistic interplay of artificial intelligence and digital twin in environmentally planning sustainable smart cities: a comprehensive systematic review. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 100433. [CrossRef]
- Alahi, M. E. E., Sukkuea, A., Tina, F. W., Nag, A., Kurdthongmee, W., Suwannarat, K., & Mukhopadhyay, S. C. (2023). Integration of IoT-enabled technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) for smart city scenario: recent advancements and future trends. Sensors, 23(11), 5206. [CrossRef]
- Shkalenko, A. V., & Nazarenko, A. V. (2024). Integration of AI and IoT into Corporate Social Responsibility Strategies for Financial Risk Management and Sustainable Development. Risks, 12(6), 87. [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A., Rejeb, K., Abdollahi, A., Al-Turjman, F., & Treiblmaier, H. (2022). The Interplay between the Internet of Things and agriculture: A bibliometric analysis and research agenda. Internet of Things, 19, 100580. [CrossRef]
- Adelami, N. V., Kim, Y. S., & You, S. H. (2022). Adoption of Internet of Things among Nigerian farmers: A case study of the Southwest Region of Nigeria. 지역발전연구, 31(3), 77-115. [CrossRef]
- Gbaden, C. J., Gambo, S., & Shem, W. (2024). Challenges and Prospects of Artificial Intelligence in Nigerian Journalism Practice: A Narrative Review. ALSYSTECH Journal of Education Technology, 2(2), 110-124. [CrossRef]
- Onayinka, T. S., Ugwu, N. F., Onyekwere, O. K., Opele, J. K., Nweze, G. N., Okorie, N. C., ... & Ignatius, C. (2024). Leveraging internet of things in 21st century education in nigeria: gains, challenges, and future direction. Gusau Journal of Sociology, 4(2), 91-102. [CrossRef]
- Oke, A. E., Arowoiya, V. A., & Akomolafe, O. T. (2022). Influence of the Internet of Things’ application on construction project performance. International Journal of Construction Management, 22(13), 2517-2527. [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, A., Abubakar, A. K., Ahmed, H. D., Ndakara, I. A., Idris, A. M., Egigogo, A. R., & Abdulkadir, M. (2019, October). Problems and prospects of internet of things to the automobile industry in Nigeria. In 2019 2nd International Conference of the IEEE Nigeria Computer Chapter (NigeriaComputConf) (pp. 1-4). IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Elegunde, A. F., & Osagıe, R. (2020). Artificial intelligence adoption and employee performance in the Nigerian banking industry. International Journal of Management and Administration, 4(8), 189-205. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G., & Gambari, A. I. (2021). A review of artificial intelligent for teaching, assessment and research in Nigerian Universities. In Conference: Association for Innovative Technology Integration in Education (AITIE, 2021) Conference Proceedings (pp. 199-207).
- Omotayo, O. O., Iortimbir, A. I., & Oluwadamilare, B. E. (2023). Internet of Things and Supply Chain Management: An Empirical Analysis of Nigeria Perspective. Journal of Techno-Social, 15(1), 59-68. https://publisher.uthm.edu.my/ojs/index.php/JTS/article/view/12694.
- Bello, S., Amadi, M. D., & Rawayau, A. H. (2023). Internet of Things-Based Wireless Sensor Network System for Early Detection and Prevention of Vandalism/Leakage on Pipeline Installations in The Oil and Gas Industry in Nigeria. FUDMA JOURNAL OF SCIENCES, 7(5), 240-246. [CrossRef]
- Alheadary, W. (2023). The impacts of the internet of things and artificial intelligence on logistics in supply chain management. https://text2fa.ir/wp-content/uploads/Text2fa.ir-The-impacts-of-the-internet-of-things-and-artificial-intelligence-on-l.pdf.
- Emeh, n. (2024). Management of artificial intelligence and the performance of manufacturing firms in enugu state nigeria. Tec empresarial, 6(1). https://revistastecac.cr/index.php/TEC/article/view/15.
- Abayomi, O. K., Adenekan, F. N., Abayomi, A. O., Ajayi, T. A., & Aderonke, A. O. (2021). Awareness and perception of the artificial intelligence in the management of university libraries in Nigeria. Journal of Interlibrary Loan, Document Delivery & Electronic Reserve, 29(1-2), 13-28. [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, O. I., Abiodun, E. O., Alawida, M., Alkhawaldeh, R. S., & Arshad, H. (2021). A review on the security of the internet of things: Challenges and solutions. Wireless Personal Communications, 119, 2603-2637. [CrossRef]
- Ogwo, Uzoamaka Ph.D; Ibegbulem, Francis; and Nwachukwu, Victor N. Prof., "APPLICATIONS AND perceived impact of artificial intelligence in academic libraries in nigeria" (2023). Library Philosophy and Practice (e-journal). 7907. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/libphilprac/7907.
- John, E. E., Effiom, P. C. O., Effiom, S. O., Odu, P. O., Uket, I. O., Nwankwo, S. E., & Ojobe, O. O. (2023). The transformative role of artificial intelligence in smart energy transition for unprecedented energy sustainability in Nigeria. Proceedings of the ICEST, 50.
- Enotse, A. M., Muhammed, A. O., Yusuf, S. O., Aribisala, F. A., Ayodele, S. M., & Mobayo, J. O. (2022, August). Assessing the Impact of the Internet of Things Integration on the wellbeing of People in Office spaces, Nigeria: A Review. In ICSET: International Conference on Sustainable Engineering and Technology (Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 23-27). https://seminar.ustjogja.ac.id/index.php/ICSET/article/view/201.
- Omigie, C., Krubu, D., & Solomon, A. (2023). Exploring artificial intelligence for records and archival management system (ai-rams) for Nigerian public organizations. Artificial intelligence. IJLSER ISSN-1743-8278 (Print).
- Amade, B., & Nwakanma, C. I. (2021). Identifying Challenges of Internet of Things on Construction Projects Using Fuzzy Approach. Journal of Engineering, Project & Production Management, 11(3).
- Timothy, O. T., Fisayo, A. A., Thiru, R., Raji, M. A., & Olodo, H. B. (2024). Impact of AI chatbots on youth consumer behavior in e-commerce: Evidence from southwest, Nigeria. [CrossRef]
- Zakari, M. (2024) Implication of artificial intelligence on national security for the nigeria security agencies. Journal of Terrorism Studies, 6(1), 6. https://scholarhub.ui.ac.id/jts/vol6/iss1/6/.
- Ndubuaku, M., & Okereafor, D. (2015). State of Internet of Things deployment in Africa and its future: The Nigerian scenario. The African Journal of Information and Communication, 2015(15), 114-119. https://hdl.handle.net/10520/EJC189248.
- Amuda, T. Internet of Things (IoT) and application in education, impacts and challenges among pre-service teachers in ogun state.
- Udo, E. U., Iroh, C. U., Nwaorgu, O. A., & Okey, D. O. (2021). State of Internet of Things (IoT) Network and Rising Issues: A Review. NIPES-Journal of Science and Technology Research, 3(3). [CrossRef]
- Nwankwo, N., Daniel, E. I., Chinyio, E., & Gyoh, L. (2023). Exploring the application of internet of things (IoT) for energy efficient buildings in Nigeria. A review. http://hdl.handle.net/2436/625238.
- Ogidiaka, E., Odion, P., & Irhebhude, M. E. (2017). Adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) among organizations in Lagos state, Nigeria. Journal of Computer Science and its Applications, 24(2). https://ssrn.com/abstract=3229718.
- Olatunde-Aiyedun, T. G. (2024). Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education: Integration of AI Into Science Education Curriculum in Nigerian Universities. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence for Digital, 1(1). https://ssrn.com/abstract=4733349.
- Abinabo, P., Gbolagade, L. O., & Morenikeniji, A. A. (2024). The Mediating Role of Internet of Things on the Relationship between Artificial Intelligence and Service Delivery of General Hospitals in Katisna State. International Journal of Accounting, Finance and Administrative Research, 1(2), 48-63.
- Bari, M. A., Ismail, H. B., Islam, M. T., & Bari, A. (2022). The impact of marketing innovation on economic development in Nigeria: A literature review. Journal of System and Management Sciences, 12(6), 468-486. [CrossRef]
- Odoh, L. C., Echefu, S. C., Ugwuanyi, U. B., & Chukwuani, N. V. (2018). Effect of artificial intelligence on the performance of accounting operations among accounting firms in South East Nigeria. Asian Journal of Economics, Business and Accounting, 7(2), 1-11. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





