Submitted:
19 February 2025
Posted:
19 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Semantic communication is an effective technological approach for the integration of intelligence and communication, enabling more efficient and context-aware data transmission. In this paper, we propose a bit-conversion-based semantic communication transmission framework to ensure the compatibility with existing wireless system. Specifically, a series of physical-layer processing modules in the end-to-end transmission are designed. Additionally, we develop a semantic communication simulator to implement and evaluate this framework. To optimize the performance of this framework, we introduce a novel physical-layer metric, termed Integer Error Rate (IER), which provides a more suitable evaluation criterion for semantic communication compared to the conventional Bit Error Rate (BER). On the basis of IER, a minimum Manhattan distance constellation mapping scheme is proposed, which can improve the transmission quality of semantic communication under the same BER condition. Furthermore, we propose a hybrid Joint Source-Channel Coding (JSCC) and Separate Source-Channel Coding (SSCC) transmission scheme. This scheme decouples the semantic quantization output from the modulation order by segmenting the bits to be transmitted. Simulation results demonstrate that the hybrid JSCC/SSCC transmission scheme can improve the semantic performance such as Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) at the low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) environment while reducing bandwidth usage by up to 50% compared to the benchmark scheme.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- The specific physical layer procedure of bit-conversion JSCC transmission framework for semantic communication is designed. Furthermore, a semantic communication simulator is developed to implement and verify this transmission framework.
- A novel physical layer metric, IER (Integer Error Rate), is proposed as a physical layer metric for semantic information transmission. And we prove that IER is more suitable than BER for semantic communication by simulation.
- We present a minimum Manhattan distance constellation mapping scheme for m-QAM modulation to optimize the transmission quality in the bit-conversion JSCC transmission framework.
- Lastly, based upon this minimum Manhattan distance constellation mapping scheme, we propose a hybrid transmission scheme to adapt different quantization levels, which can separate the semantic quantization output from the modulation order. Meanwhile, this hybrid transmission scheme can improve the transmission quality of semantic communication at the low SNR range while leveraging the bandwidth-saving advantage of semantic communication [14,17,23,24].
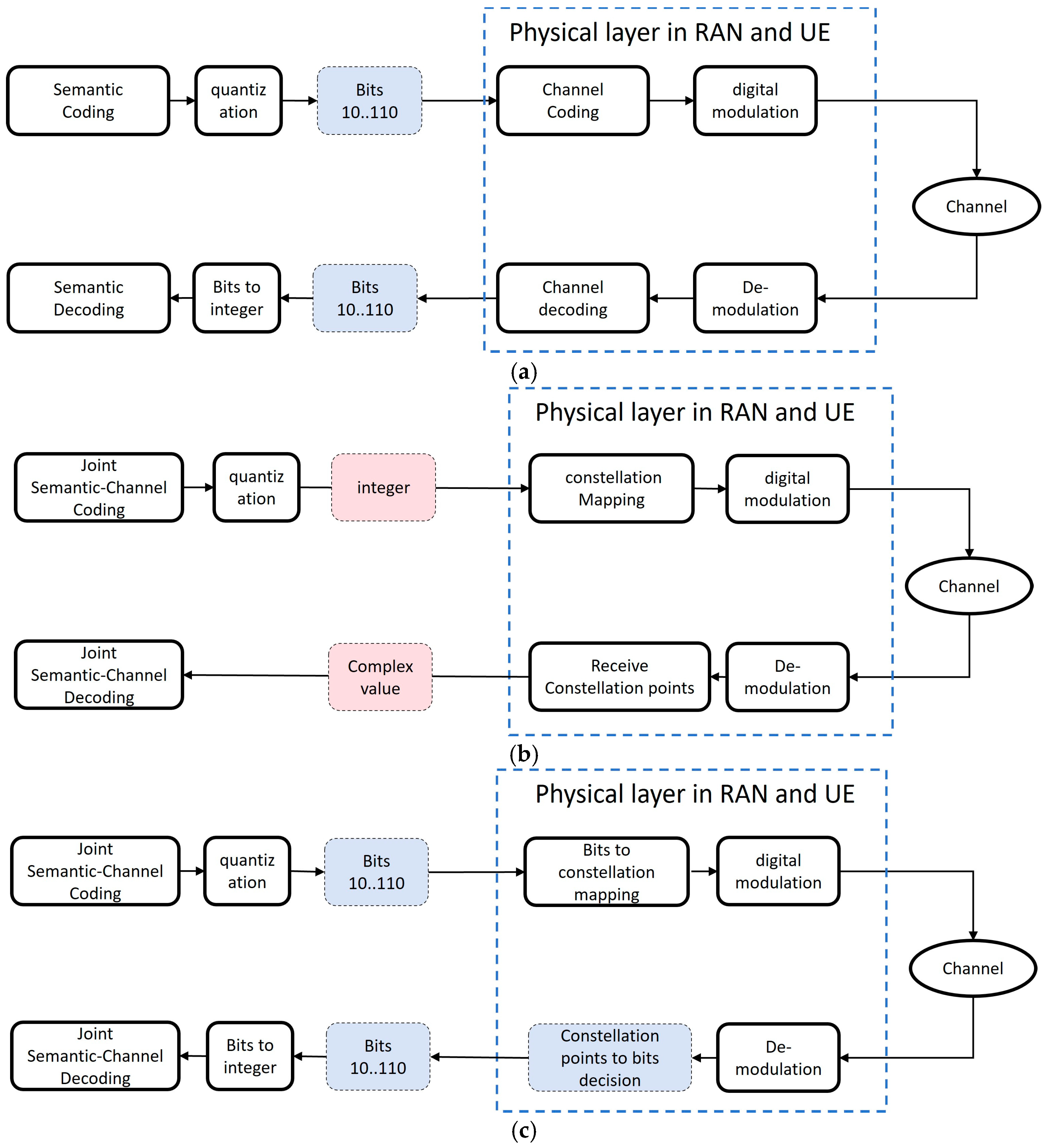
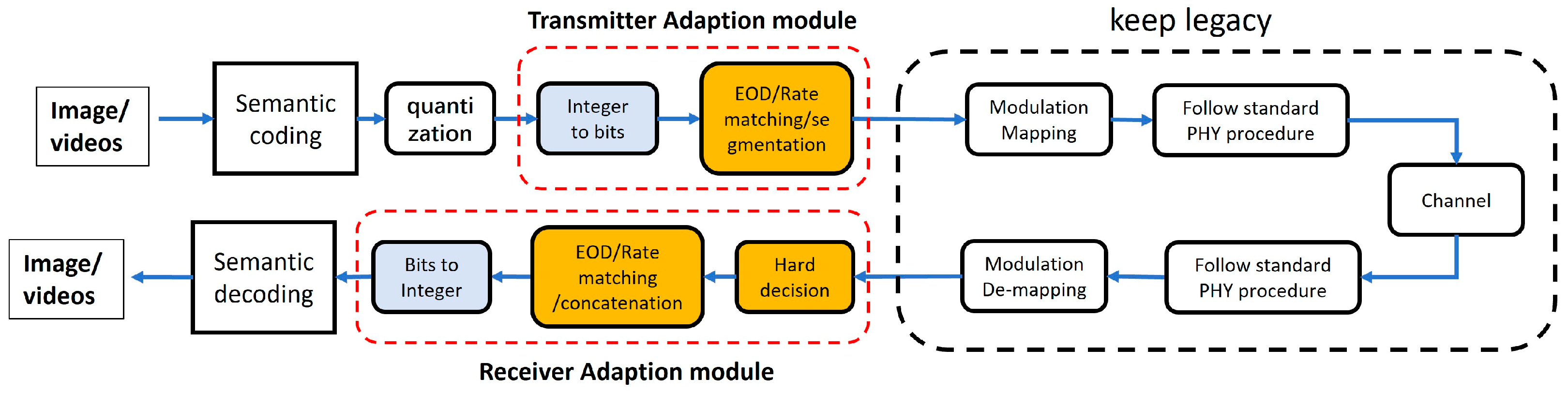
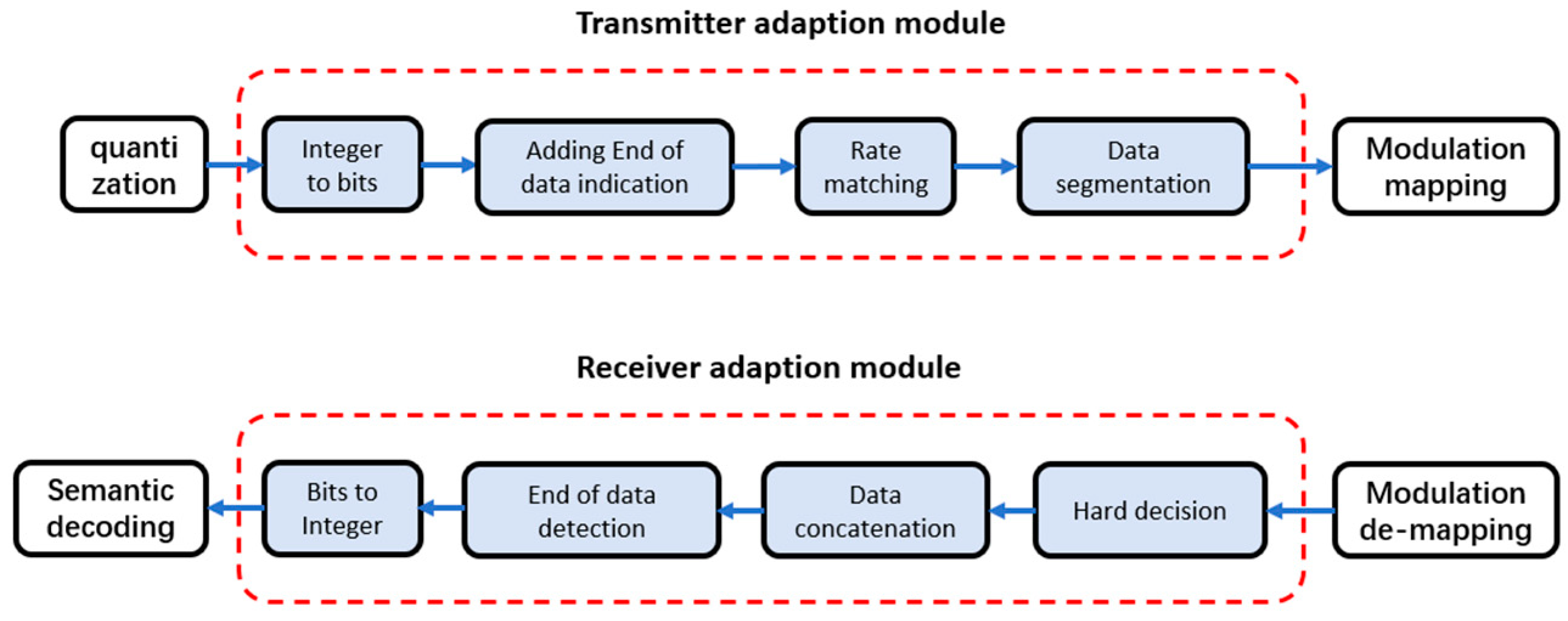
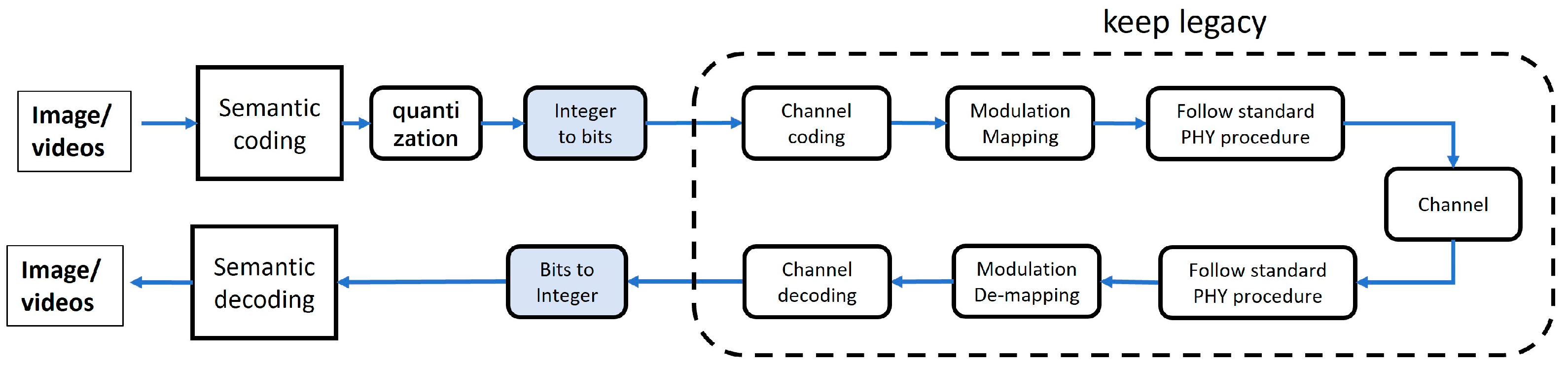
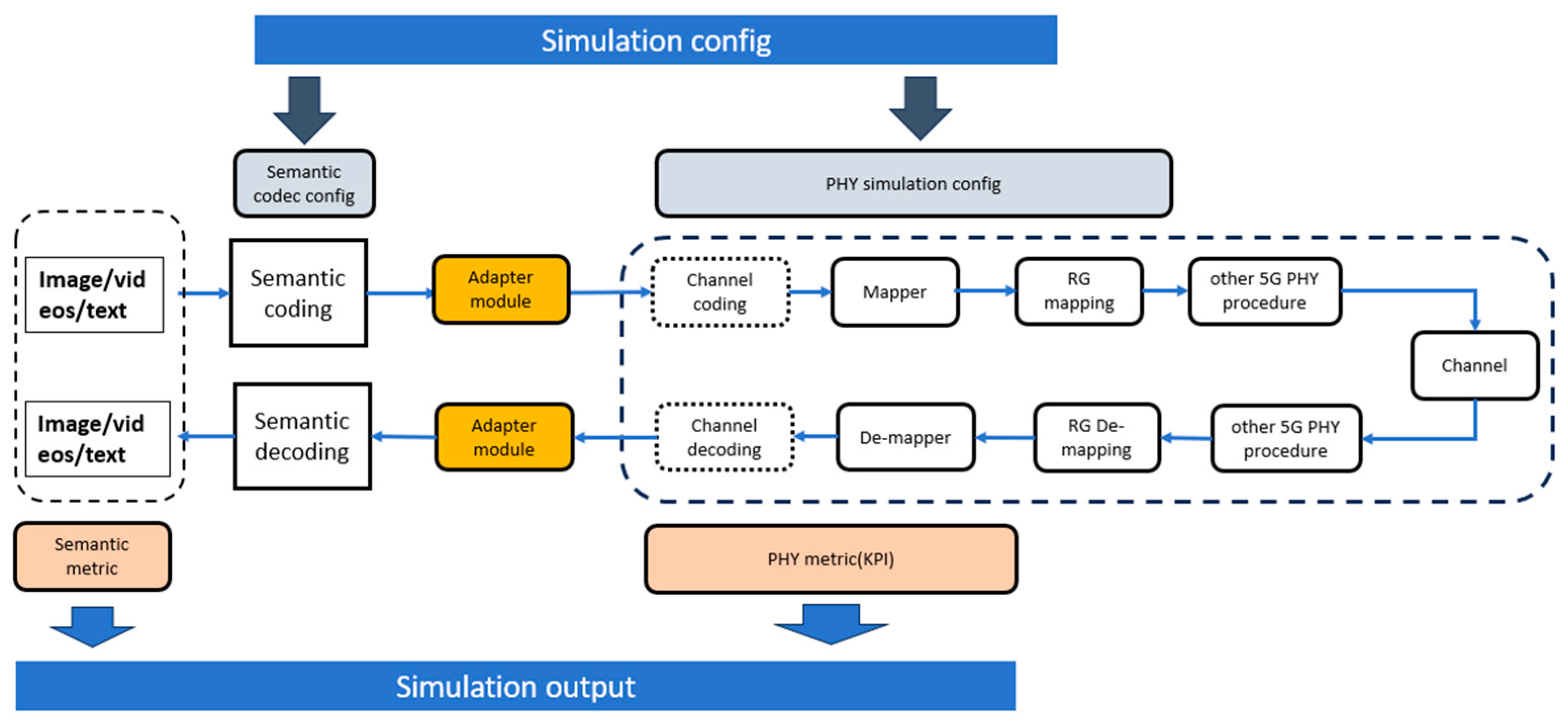
2. Bit-Conversion-Based JSCC Transmission Framework and Simulator
2.1. Bit-Conversion-Based JSCC Transmission Framework
2.2. Simulation Planform for E2E Semantic Communication
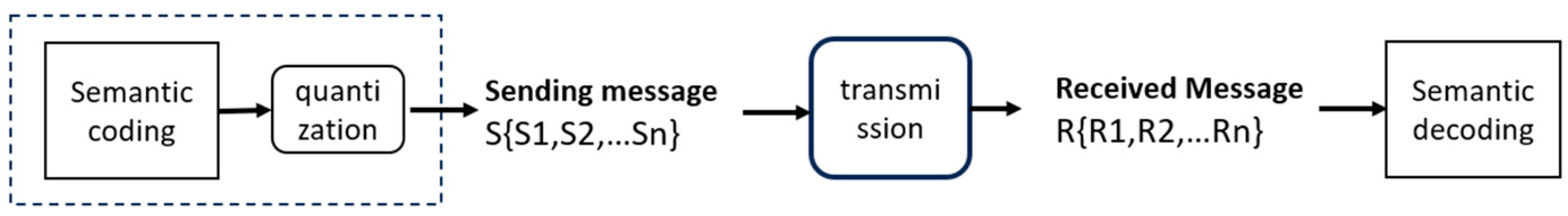
3. IER—A Novel Physical-Layer Semantic Metric
3.1. Definition of IER (Integer Error Rate)
- Hamming distance and BER (bit error rate)
- Manhattan distance and IER (Integer Error Rate)
3.2. Relation Between BER and IER
| Message Vector |
integer- valued |
Manhattan distance to vector S | Nature binary coding | Hamming distance to vector S | BER | IER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | [1, 2, 5, 7] | 0 | [001, 010, 101, 111] | 0 | 0% | 0% |
| R1 | [0, 3, 5, 6] | 3 | [000, 011, 101, 110] | 3 | 25% | 9% |
| R2 | [5, 2, 1, 3] | 12 | [101, 010, 001, 011] | 3 | 25% | 37% |
| R3 | [5, 6, 5, 7] | 8 | [101, 110, 101, 111] | 2 | 16% | 13% |
3.3. Relation Between IER BER and Semantic Metric
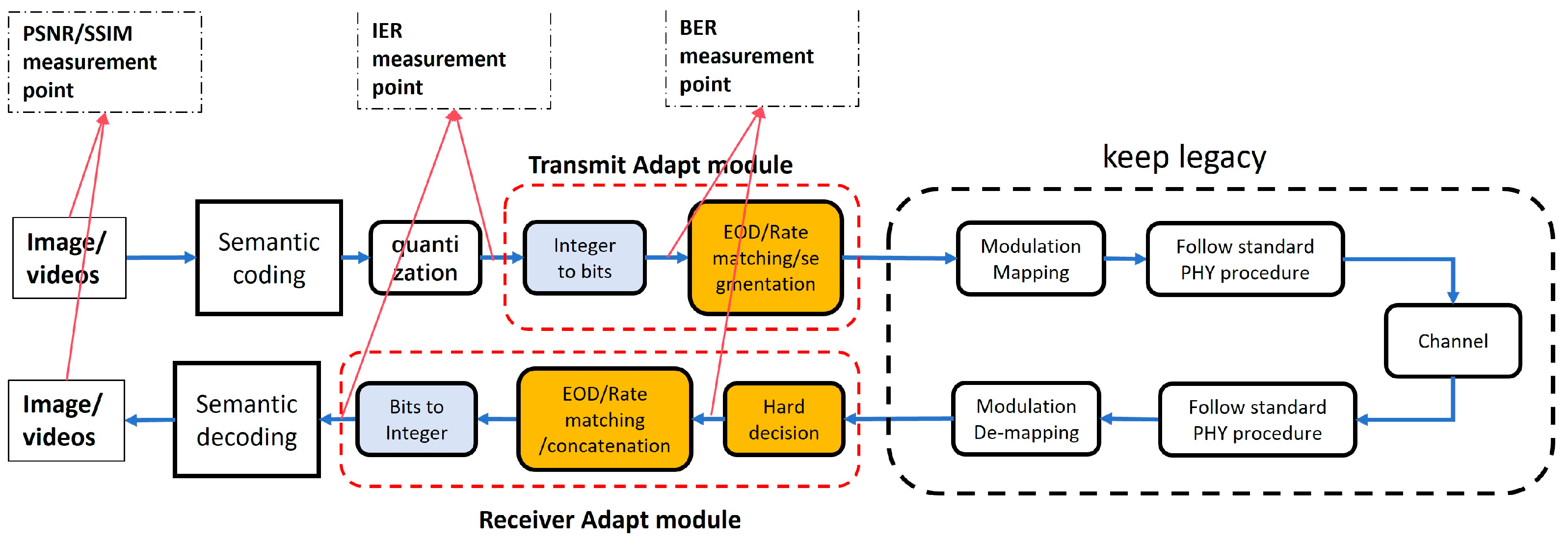
4. Optimization for the Bit Conversion JSCC Scheme
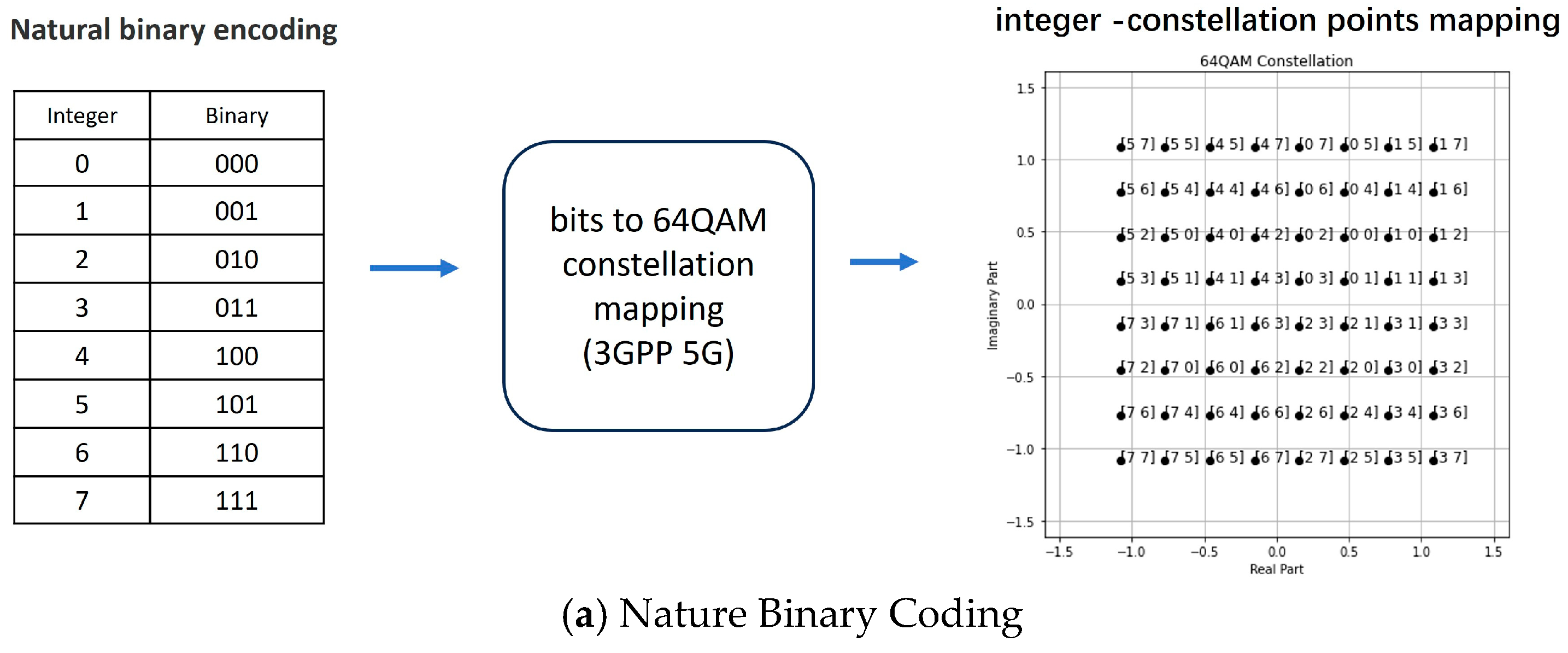
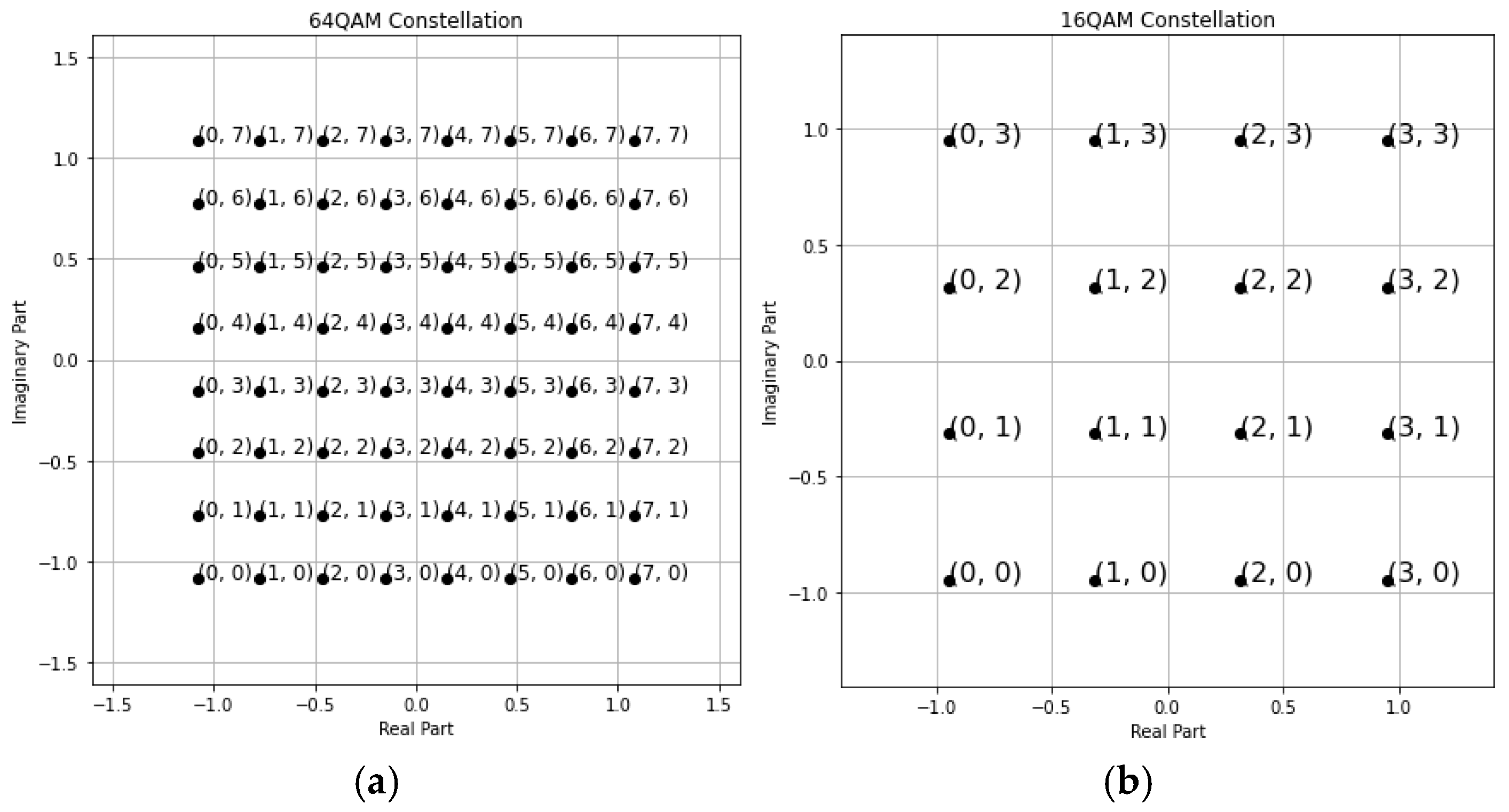
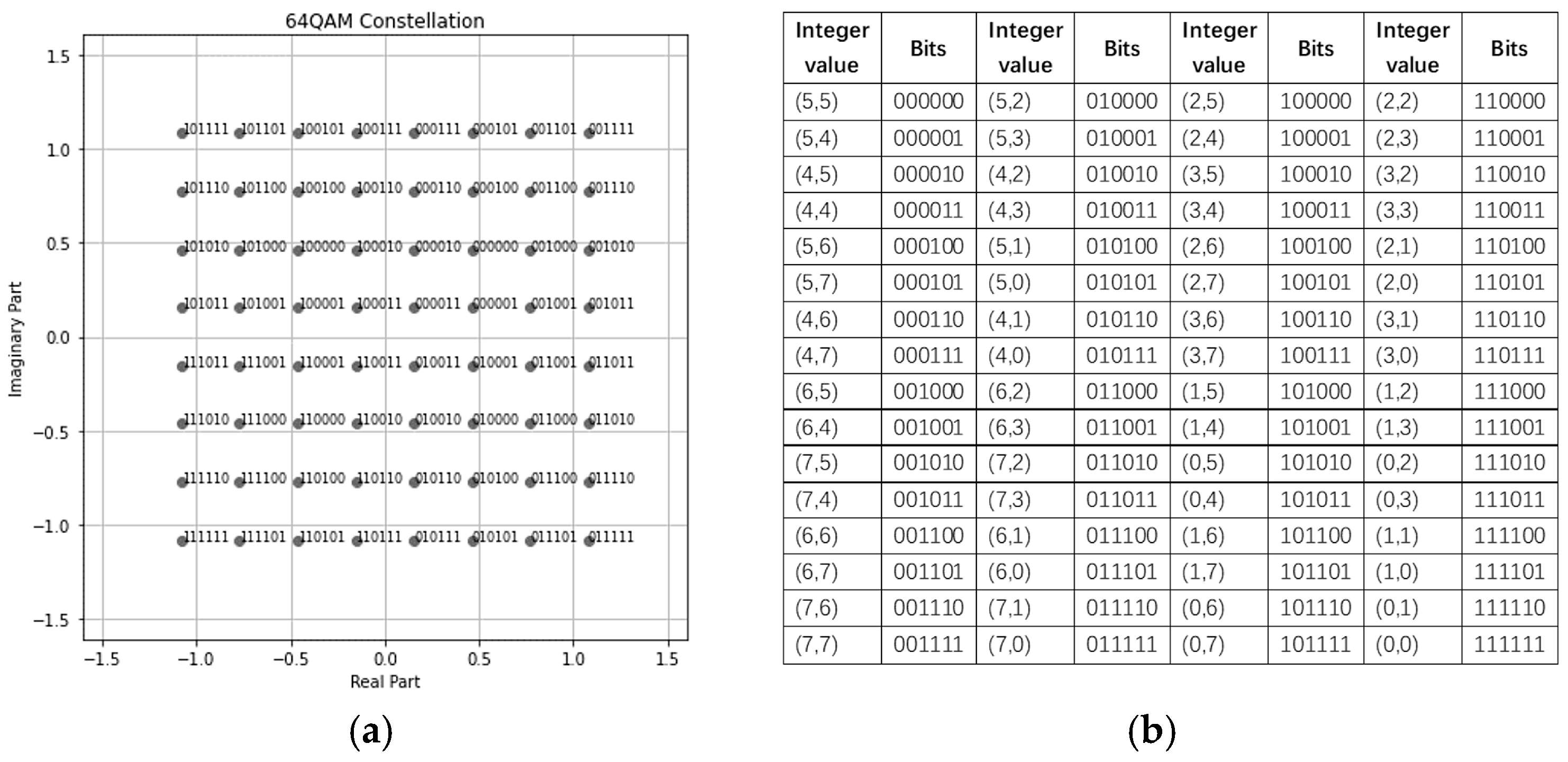
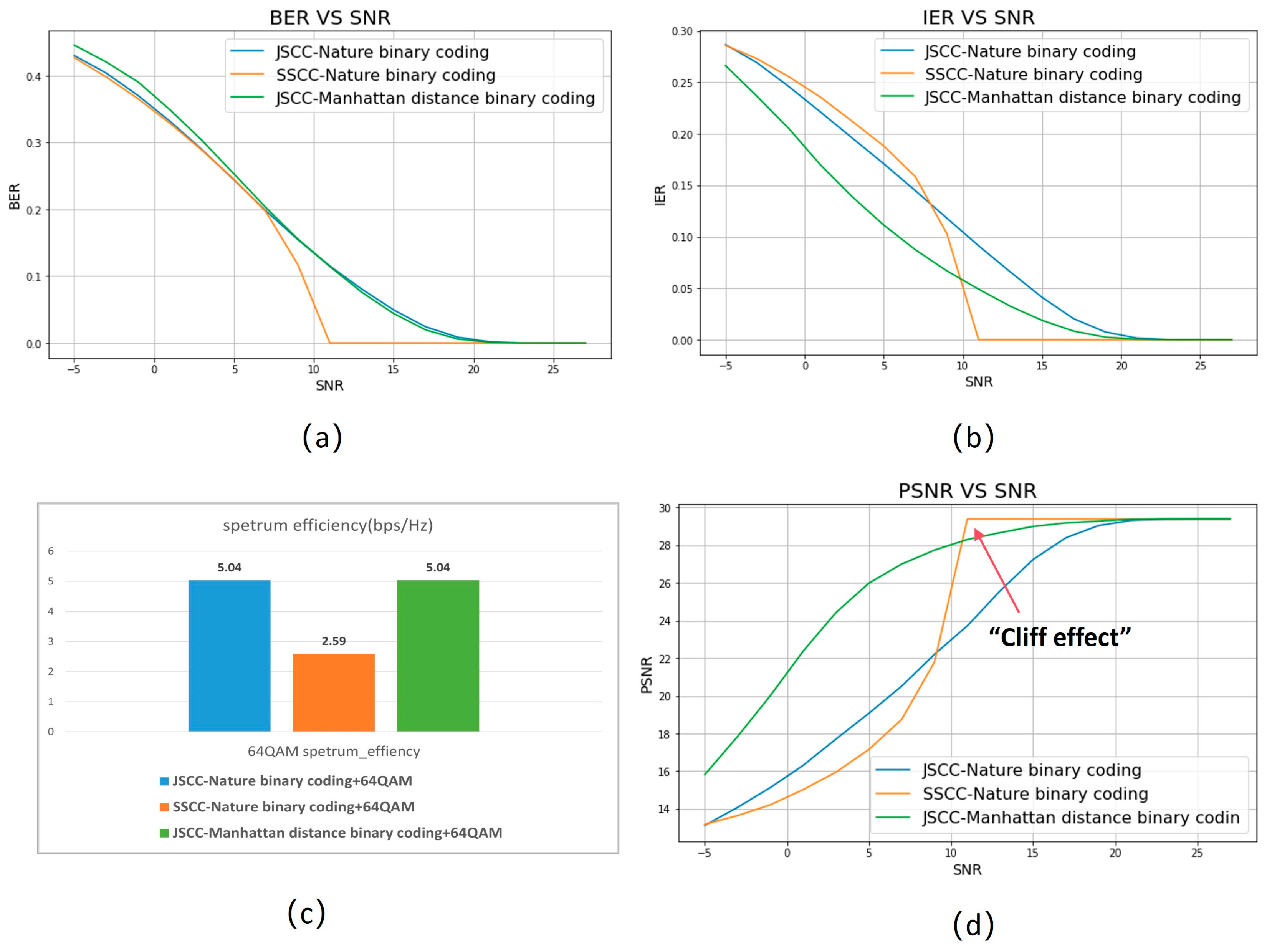
4.1. Minimum Manhattan Distance Constellation Mapping Scheme
| Test case | JSCC-Nature binary coding | JSCC-Manhattan distance binary coding |
SSCC-Nature binary coding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semantic transmission Framework: | Bit-conversion JSCC | Bit-conversion JSCC |
Bit-conversion SSCC |
| Source file | image | image | image |
| Semantic codec: | LSCI | LSCI | LSCI |
| Quantization range: | [0-7] | [0-7] | [0-7] |
| Data to binary Codec: |
Nature binary coding | Manhattan distance binary coding |
Nature binary coding |
| Channel coding | NO | NO | LDPC CR=0.5 |
| Bits constellation Mapping: |
3GPP 5G | 3GPP 5G | 3GPP 5G |
| Modulation: | 64QAM | 64QAM | 64QAM |
| Simulation SNR range | [-5 ~30] | [-5 ~30] | [-5 ~30] |
| Channel model | AWGN | AWGN | AWGN |
| channel equalization | LMMSE | LMMSE | LMMSE |
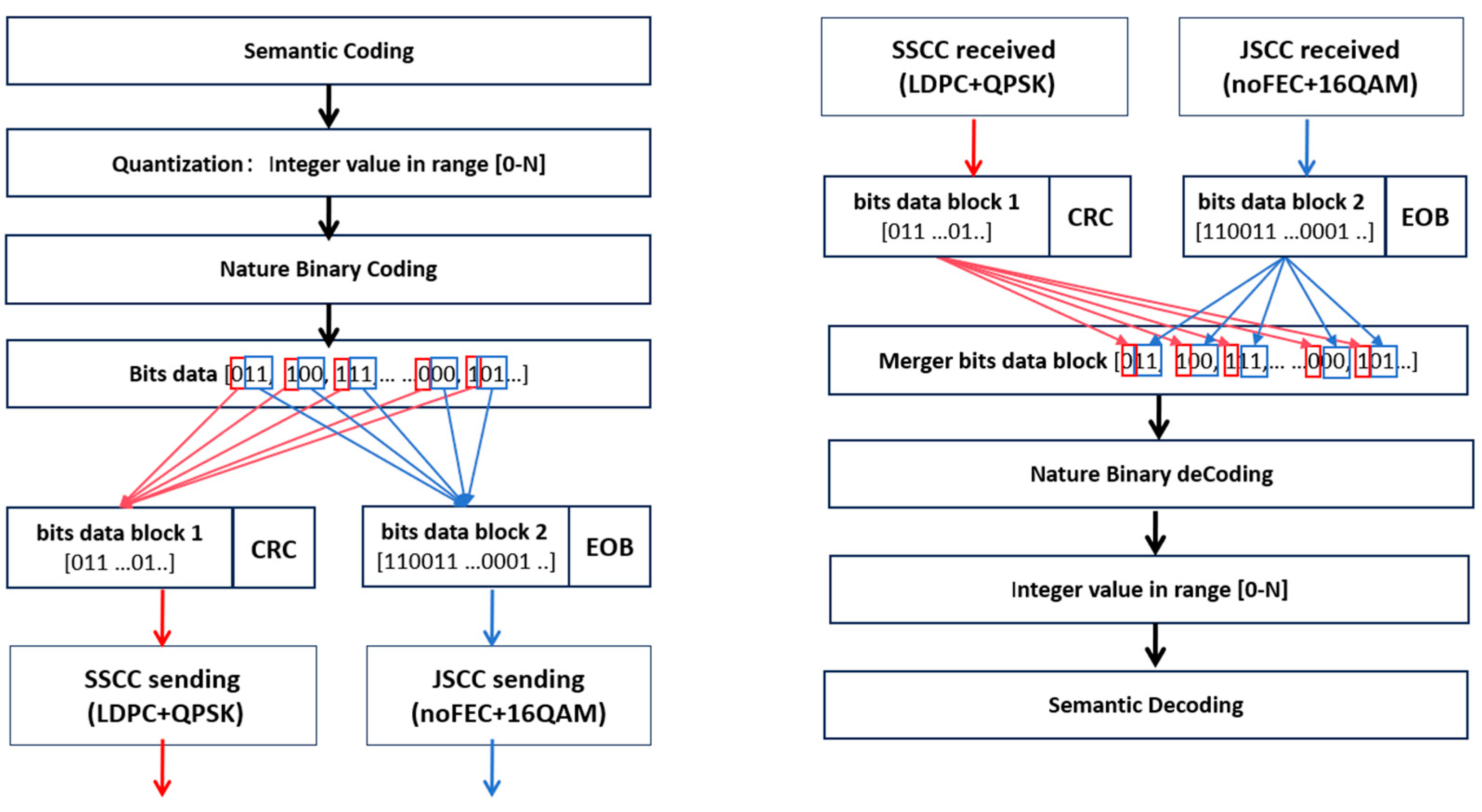
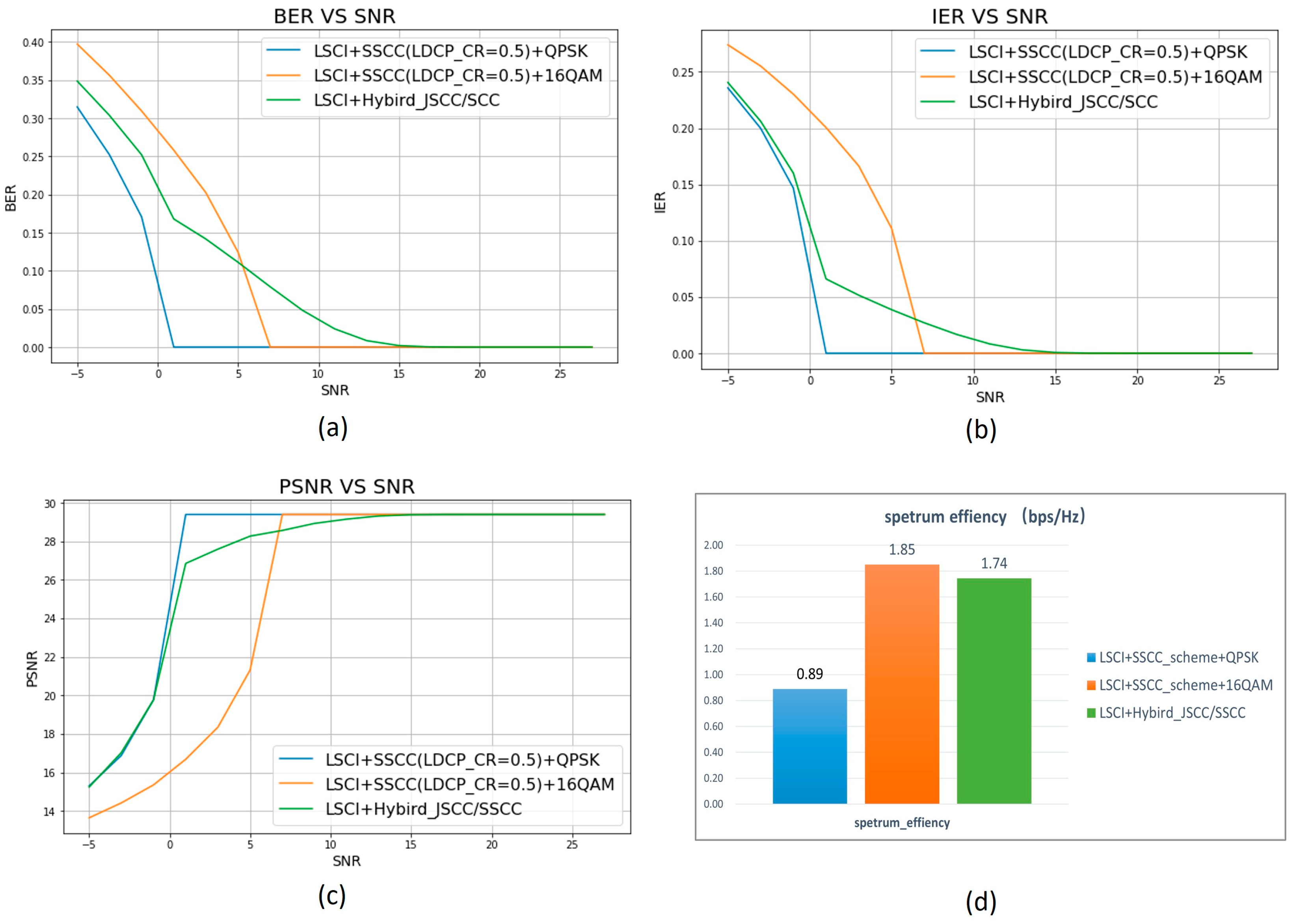
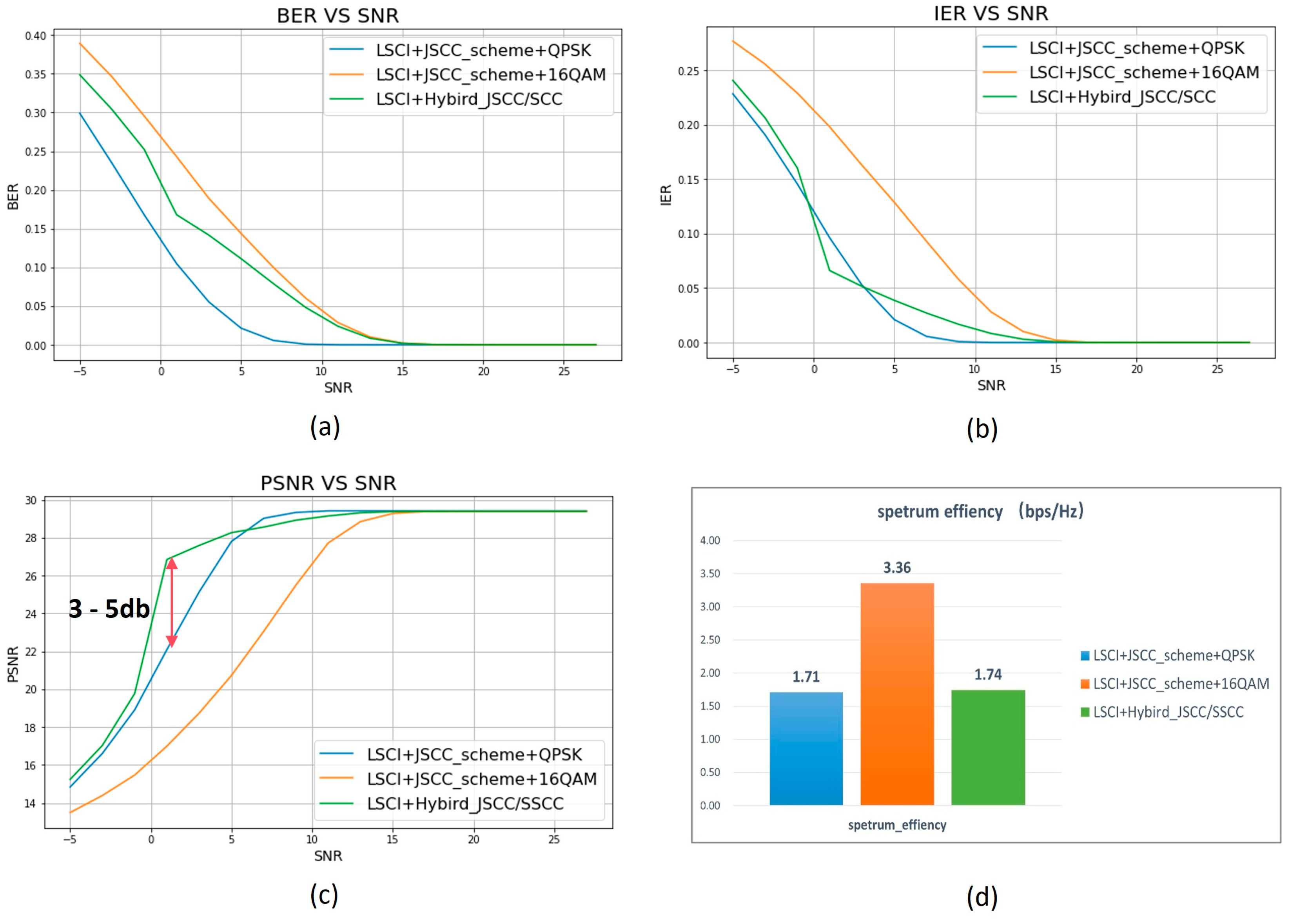
4.2. Hybrid JSCC/SSCC Transmission Scheme
- At transmitter:
- At receiver:
- Simulation verification-1:
- Simulation verification-2:
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ping Zhang, Wenjun Xu, Hui Gao, Kai Niu, Xiaodong Xu, Xiaoqi Qin, Caixia Yuan, Zhijin Qin, Haitao Zhao, Jibo Wei, Fangwei Zhang; Toward Wisdom-Evolutionary and Primitive-Concise 6G: A New Paradigm of Semantic Communication Networks, Engineering 2021, 8, 60–73.
- Y. Wang, Z. Gao, D. Zheng, S. Chen, D. Gunduz, and H. V. Poor, ‘‘Transformer-empowered 6G intelligent networks: From massive MIMO processing to semantic communication,’’ IEEE Wireless Commun., early access, Nov. 23, 2022.
- E. Calvanese Strinati and S. Barbarossa, ‘‘6G networks: Beyond Shannon towards semantic and goal-oriented communications,’’ Comput. Netw., vol. 190, May 2021, Art. no. 107930. [CrossRef]
- Xuefei Zhang, Jing Gu, Xiaoxian Li, Qimei Cui, and Xiaofeng Tao, "Current Status and Prospects of Semantic Communication Research," China Basic Science: Policy and Review, April 2023.
- Yufei Bo, Yiheng Duan, Shuo Shao, Meixia Tao, “Joint Coding-Modulation for Digital Semantic Communications via Variational Autoencoder” IEEE Transactions on Communications.
- Qifan Fu, Huiqiang Xie, Zhijin Qin, Gregory Slabaugh, Xiaoming Tao, “Vector Quantized Semantic Communication System” IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol 12,2023.
- Xuewen Luo,Hsiao-Hwa Chen,Qing Guo,“Semantic Communications: Overview, Open Issues, and Future Research Directions” IEEE Wireless Communications,vol 29,2022.
- Z. Weng and Z. Qin, “Semantic communication systems for speech transmission,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 39, no. 8, pp. 2434–2444, 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. Han, Q. Yang, Z. Shi, S. He, and Z. Zhang, “Semantic-preserved communication system for highly efficient speech transmission,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 245– 259, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Xie, Z. Qin, G. Y. Li, and B.-H. Juang, “Deep learning enabled semantic communication systems,” IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, vol. 69, pp. 2663–2675, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Q. Zhou, R. Li, Z. Zhao, C. Peng, and H. Zhang, “Semantic communication with adaptive universal transformer,” IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 453–457, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Shao, Y. Mao, and J. Zhang, “Learning task-oriented communication for edge inference: An information bottleneck approach,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 197–211, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Xie, Z. Qin, and G. Y. Li, “Task-oriented multi-user semantic communications for VQA,” IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 553–557, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Bourtsoulatze, D. B. Kurka, and D. Gündüz, “Deep joint source channel coding for wireless image transmission” IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw., vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 567–579, Sep. 2019.
- D. B. Kurka and D. Gündüz, "DeepJSCC-f: Deep joint source-channel coding of images with feedback", IEEE J. Sel. Areas Inf. Theory, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 178-193, Dec. 2020.
- T.-Y. Tung, D. B. Kurka, M. Jankowski, and D. Gunduz, “DeepJSCC-Q: Constellation constrained deep joint source-channel coding” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Information Theory, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 720–731, 2022.
- Ke Yang,Sixian Wang,Jincheng Dai,Kailin Tan,Kai Niu,Ping Zhang, “WITT: A Wireless Image Transmission Transformer for Semantic Communications”, ICASSP 2023 - 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP).
- Keigo Matsumoto; Yoshiaki Inoue; Yuko Hara-Azumi; Kazuki Maruta; Yu Nakayama; Daisuke Hisano; “Impact of Quantization Noise on CNN-based Joint Source–Channel Coding and Modulation” 2023 IEEE 20th Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC).
- Amir Gholami; Sehoon Kim; Zhen Dong; Zhewei Yao; Michael W. Mahoney; Kurt Keutzer; “A Survey of Quantization Methods for Efficient Neural Network Inference”.
- Zhicheng Bao; Chen Dong; Xiaodong Xu; “sDAC—Semantic Digital Analog Converter for Semantic Communications”, arXiv:2405.02335v1 [cs.IT] 26 Apr 2024.
- Xiaoyi Liu; Haotai Liang; Zhicheng Bao; Chen Dong; Xiaodong Xu; “A Semantic Communication System for Point Cloud”, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 74, NO. 1, JANUARY 2025.
- Gangtao Xin; Pingyi Fan; Khaled B. Letaief; Chenghui Peng; “Deep Conditional Generative Semantic Communication for Image Transmission”, WS06 IEEE ICC 2024 Workshop on Task-Oriented and Generative Communications for 6G.
- Sixian Wang, Jincheng Dai, Zijian Liang, Kai Niu, Zhongwei Si, Chao Dong, Xiaoqi Qin, Ping Zhang “Wireless Deep Video Semantic Transmission” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol 41,2023.
- P. Jiang, C.-K. Wen, S. Jin, and G. Y. Li, “Wireless semantic communications for video conferencing” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 230–244, 2023.
- Z. Weng and Z. Qin, “Semantic communication systems for speech transmission” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 39, no. 8, pp. 2434–2444, 2021.
- Keigo Matsumoto; Yoshiaki Inoue; Yuko Hara-Azumi; Kazuki Maruta; Yu Nakayama; Daisuke Hisano, “Impact of Quantization Noise on CNN-based Joint Source–Channel Coding and Modulation”, 2023 IEEE 20th Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), 2023.
- Chen Dong, Haotai Liang, Xiaodong Xu, Shujun Han, Bizhu Wang, Ping Zhang, “Semantic Communication System Based on Semantic Slice Models Propagation”, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 41, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Michel Deza, Michel Petitjean, Krassimir Markov (eds.) "Mathematics of Distances and Applications" held at Varna, Bulgaria, July 2-5, 2012.
- 3GPP TS 38.211 V16.10.0 Physical channels and modulation, chapter5.1 Modulation mapper.



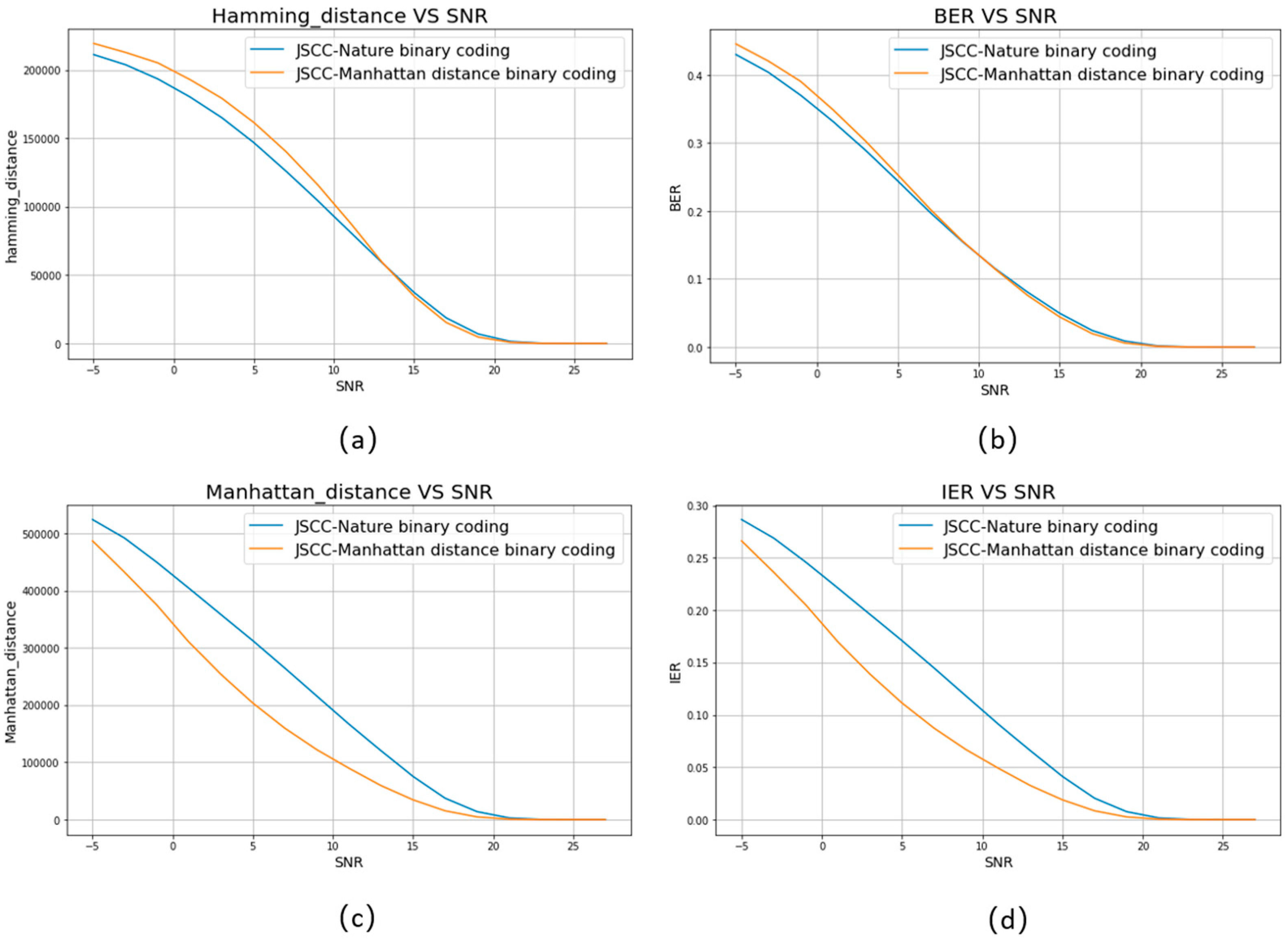
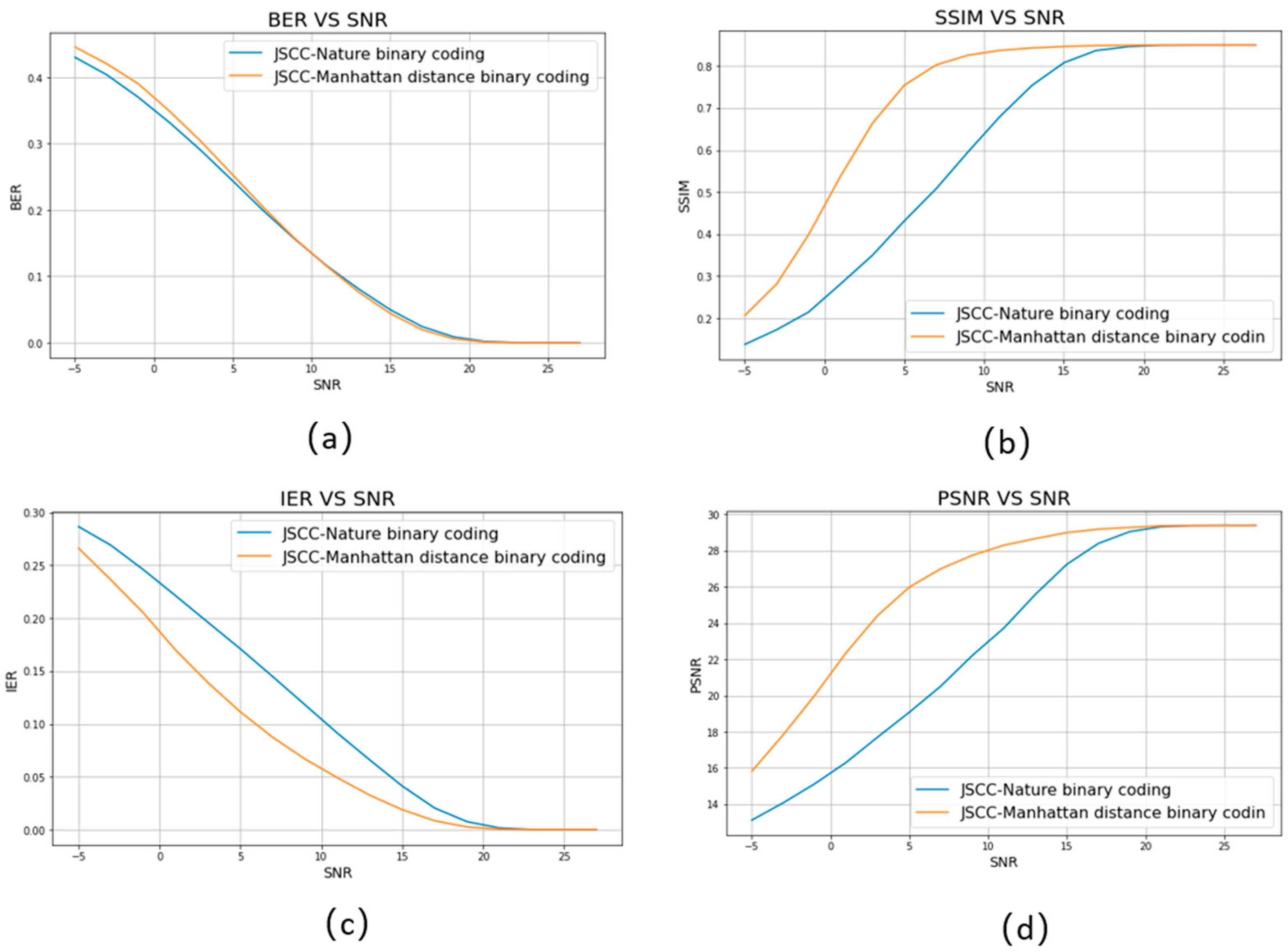
| Test case | binary coding | Manhattan distance binary coding |
|---|---|---|
| transmission Framework: | Bit-conversion JSCC | Bit-conversion JSCC |
| Source file | image | image |
| Semantic codec: | LSCI | LSCI |
| Quantization output range: | [0-7] | [0-7] |
| integers-to-bits coding: | Nature binary coding | Manhattan distance binary coding |
| Channel coding | NO | NO |
| Bits constellation Mapping: | 3GPP 5G | 3GPP 5G |
| Modulation: | 64QAM | 64QAM |
| Simulation SNR range | [-5 ~30] | [-5 ~30] |
| Channel model | AWGN | AWGN |
| channel equalization | LMMSE | LMMSE |
| Algorithm Manhattan distance binary coding generation | |
| 1, | Input: |
| 2, | m-QAM modulation order |
| 3, | m-QAM standard bit constellation mapper |
| 4, | Integer constellation mapper |
| 5, | data process: |
| 6, | -> |
| 7, | for i from 0 to : |
| 8, | for integer in range [0, -1]: |
| 9, | find that == |
| 10, | then mapping (): |
| 11, | End for |
| 12, | End for |
| 13, | output: |
| 14, | Manhattan distance binary coding mapping table |
| test case | modulation | binary codec | channel coding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid JSCC/SSCC transmission (QPSK+16QAM) | QPSK (1/3 data) |
nature binary coding | LDPC(CR=0.5) |
| 16QAM (2/3 data) |
Manhattan distance binary coding | NO | |
| SSCC-QPSK | QPSK | nature binary coding | LDPC(CR=0.5) |
| SSCC-16QAM | 16QAM | nature binary coding | LDPC(CR=0.5) |
| test case | modulation | binary codec | channel coding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid JSCC/SSCC transmission (QPSK+16QAM) | QPSK (1/3 data) |
nature binary coding | LDPC(CR=0.5) |
| 16QAM (2/3 data) |
Manhattan distance binary coding | NO | |
| JSCC-QPSK | QPSK | nature binary coding | NO |
| JSCC-16QAM | 16QAM | nature binary coding | NO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





