1. Introduction
The digital economy is an economic form based on digital technology, with information networks as carriers and data as core resources. In the context of the global digital economy, the tea industry is undergoing significant changes, and traditional marketing models of tea companies are no longer able to meet the diverse needs of modern consumers (Chen et al., 2022) .
From the perspective of industrial development, China, as the world's largest producer and consumer of tea, produces a wide variety of tea products, including green tea, black tea, oolong tea, white tea, yellow tea, black tea, and other categories, which can meet the needs of different consumers at home and abroad and play an important role globally. In China, tea is a special economic crop, and the tea industry is an important component of China's traditional agricultural industry, holding a significant position in the country's agricultural economy. In recent years, with the expansion of tea plantation area year by year, the tea production in China has also been continuously increasing. In 2023, the tea plantation area in China was 51.4976 million mu, an increase of 1.5436 million mu year-on-year, with a growth rate of 3.09%. The tea production was 3.55 million tons, an increase of 6.1%, ranking first in both planting area and output in the world. Among the 31 provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities directly under the central government) in China, 22 provinces are involved in large-scale production of tea. The Chinese government attaches great importance to the development of the tea industry and has introduced multiple policies to promote high-quality development of the tea industry. Secondly, China has the world's largest tea drinking population, and as a green and pollution-free beverage, tea leaves are becoming increasingly popular among consumers(Jiang , 2022).
From an industry perspective, the global tea sales market is fiercely competitive, with severe product homogenization, and the market presents a trend towards diversified consumer demand. In China, tea products have not yet formed standardization, and the tea market layout is relatively scattered. The sales entities in the Chinese tea market are mostly individual tea shops, and the marketing model still mainly relies on traditional relationship marketing methods. However, there are currently not many representative tea companies in the industry. Apart from the successful listing of "Tianfu Tea" and "Lancang Ancient Tea" on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, there have been no other tea listed companies in China. These industry representative enterprises also have a large number of directly operated or franchised tea shops, and their marketing methods are mostly in the early stage of digital marketing, with less adaptation to the era of digital economy to carry out omnichannel marketing. In the context of digital economy, tea enterprises are trending towards omnichannel marketing(Chen et al., 2018; Jiang , 2022;Li et al., 2022;Zhou et al., 2022).
From the perspective of enterprises, the digital transformation of the tea industry is crucial for the development of tea companies. In the context of the digital economy, tea companies should pay more attention to interaction and relationship building with consumers when pursuing maximum profits. Through omni channel marketing, tea companies can establish closer connections with consumers. By analyzing big data and artificial intelligence, combining online and offline channels for multi-channel marketing, they can provide customized products and services for consumers, improve consumer satisfaction, effectively enhance consumer loyalty, and promote tea company revenue growth(Chen et al., 2018; Jiang et al., 2022;Li et al., 2022;Zhou et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2022).
At present, channel management for enterprise development is receiving increasing attention from scholars. Many scholars have conducted research from different perspectives on how to carry out channel management reasonably. In the research literature related to enterprise channel management, most scholars focus on how to build enterprise channel management in various industries and how to optimize enterprise omnichannel in the digital economy era from a content perspective. Although it seems comprehensive, overall research is not deep enough. Few scholars in China use specialized quantitative or qualitative research methods to conduct in-depth research, only elaborating and analyzing problems and current situations, and then formulating countermeasures; At present, there are many literature in the field of marketing optimization for tea enterprises, but there is relatively little research on the omnichannel optimization of tea enterprises under the background of digital economy, which highlights the theoretical value of this research topic(Li et al., 2021;Shen et al., 2021; Hu et al., 2023;Liu et al., 2023).
In summary, optimizing the omni channel marketing strategy of tea enterprises under the background of digital economy has gradually become an important direction for optimizing the tea industry. Developing omni channel marketing models through digital transformation can help tea enterprises adjust their supply side and improve their competitiveness in the market. It can better meet the diverse needs of consumers on the demand side and further promote the innovative and sustainable development of the tea supply chain, forming a closed loop for the benign upgrading and development of the tea industry.
Therefore, based on the research literature of existing scholars, this study conducts research on the omni channel of tea enterprises, and defines the digital economy as an economic form that uses digital technology and Internet platform, takes data as the core, and drives economic growth and innovative development through information flow, sharing and interaction; Omnichannel marketing is defined as the comprehensive integration of brand, product, marketing channels, sales, and other aspects by enterprises to achieve model innovation, information sharing, and business collaboration, thereby achieving all-round and full process marketing of products; The omnichannel of tea enterprises is defined as a marketing model in which enterprises adopt diversified sales channels and marketing strategies, integrate online and offline channel resources, provide diverse consumer experiences and services, and meet personalized consumer needs. Then, taking tea enterprises that are undergoing omnichannel marketing transformation as the research object, this study explores the factors that affect omnichannel marketing of tea enterprises, analyzes the influencing factors of omnichannel marketing of tea enterprises, formulates relevant strategies that are in line with omnichannel marketing of tea enterprises, enriches the scope of application of marketing theory, provides theoretical reference for research on omnichannel marketing of tea enterprises, and also provides reference for omnichannel marketing practices of traditional tea enterprises in other countries around the world(Verhoef P C et al., 2015; Sese F J et al., 2016; Ren et al., 2022;Peng et al., 2022; Sfakianaki E et al., 2022).
2. Theoretical Foundations
2.1. PEST Theory
PEST theory is a framework used to analyze the macro environment. It includes four elements, namely political, economic, social, and technological aspects. This theory is used to study the impact of the macro environment on business operations and competition. Political refers to the impact of political environment, policies, laws, government agencies, and other factors on business operations and competition. Economics refers to the impact of economic factors on a company, including interest rates, inflation, economic cycles, etc. Social refers to the various social factors that a company experiences during its business operations. Technological refers to the impact of technological elements on enterprises, which includes various factors such as technological progress, information technology, and innovation (Dong et al., 2023; Kannan M.et al., 2023).
2.2. Precision Marketing Theory
Precision marketing theory is a marketing strategy developed based on the Internet and big data technology(Zhou , 2021). Its core idea is to shift the focus of marketing from products and services to the audience and needs, and achieve precision marketing for the audience by deeply mining the needs and behavior data of the audience. The implementation of precision marketing mainly relies on the following three aspects:
Firstly, big data analysis. Through data mining and analysis of consumers' search, browsing, click, purchase and other behaviors on the Internet, we can deeply understand consumers' needs and behavior characteristics, and achieve accurate push and personalized services.
Secondly, precise positioning. By effectively categorizing and labeling consumers, we can better understand their interests, needs, and behavioral habits, providing basic data support for precision marketing.
Thirdly, personalized push notifications. Push personalized advertisements, discounts, services, etc. to target consumers through various channels such as email, mobile SMS, social media, etc., to improve the effectiveness of precision marketing.
2.3. Five Forces Model Theory
The Five Forces Model is a competitive analysis model proposed by Michael E. Porter in 1979, used to evaluate the competitive situation among competitors in an industry (Zhao , 2022).
Firstly, the competitiveness of existing competitors in the industry refers to factors such as market share, market share, and brand influence of existing competitors in the industry. Secondly, the threat of potential competitors: refers to whether there are other companies in the industry that have not yet entered the market but may enter and bring competition. Thirdly, the threat of substitutes or alternative services: refers to the existence of other products, services, or technologies in the market that are similar or replaceable to those in the industry. Fourthly, the bargaining power of suppliers: refers to the price bargaining power that suppliers can exercise for the raw materials, components, and other items purchased by the enterprise. Fifthly, the bargaining power of buyers: refers to the price bargaining power between buyers who purchase products or services and enterprises.
By analyzing the above five abilities, the level of competition in the industry and the potential for industry profits can be determined. The more intense the industry competition, the smaller the profit margin. On the contrary, if the five abilities are weak or non-existent, the industry will be more attractive.
2.4. Consumer Behavior Theory
The theory of consumer behavior mainly studies the psychology, attitude, and behavior of consumers in the process of purchasing and using products or services (Sheoran M et al., 2022). Consumer behavior theory is an emerging research discipline that focuses on studying consumers' choices of specific products and their impact on their behavior. The basic content of consumer behavior theory is (Lin et al., 2022; Florence E S et al., 2022; Vidal-Ayuso F et al., 2023; Li et al., 2023; Yan et al., 2023):
Firstly, the theory of demand fulfillment: The core of consumer purchasing decisions is to satisfy their needs and desires. This theory divides human needs into physiological needs, safety needs, social needs, esteem needs, and self actualization needs.
Secondly, cognitive theory: Cognitive theory focuses on the information processing process of consumers in purchasing decisions. Consumers make reasonable decisions by collecting, receiving, storing, organizing, and extracting information.
Thirdly, psychological theory: Psychological theory mainly explores the impact of consumer perception, emotions, attitudes, motivations, and other psychological factors on purchasing decisions.
Fourth, social factor theory: This theory holds that the environment such as family, friends, social networks, social groups, etc. will have a certain impact on their shopping behavior.
Fifth, cultural and personal values theory: This theory suggests that consumers' purchasing decisions are influenced by culture, values, and personality traits. Different cultural backgrounds and values lead to differences in consumer behavior, such as individualism and collectivism, long-term orientation and short-term orientation.
By studying and applying these consumer behavior theories, marketers can better understand the reasons and motivations behind consumer behavior, thereby developing more effective marketing strategies, enhancing brand image, meeting consumer needs, and achieving business goals. The omni channel marketing studied in this paper is based on this theory and the development of Internet technology, aiming to ensure better sales of products by meeting more consumer needs.
3. Market Analysis
3.1. Analysis of PEST Environment for Tea Enterprises' Omnichannel Marketing Under the Background of Digital Economy
3.1.1. Political Environment Analysis
In the context of the digital economy, the omnichannel marketing of Chinese tea enterprises faces the influence of the political environment, which is manifested in three aspects(Wu et al., 2018; Liao et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022).:
(1)Government policies: The government's policies and attitudes will affect the omnichannel marketing of Chinese tea companies. Whether the government encourages and supports tea companies to carry out omnichannel marketing, as well as policies related to taxation, market access, and regulation, will have an impact on the omnichannel marketing of tea companies.
(2)Support and cooperation from local governments:The support and willingness of local governments to cooperate with tea enterprises are influenced by the political environment. Tea companies need to closely monitor changes in the local political environment, establish good cooperative relationships with the government, and obtain government support. Tea companies can actively participate in various tea culture festivals, exhibitions, and other events organized by local governments, and communicate with social organizations related to the tea industry to obtain more policy information and support from partners.
(3) Cross border business and political environment in various countries. In the context of the digital economy, tea companies expand their overseas markets by engaging in cross-border e-commerce business. The changes in the international political environment will have an impact on the omnichannel marketing of tea companies. For example, trade wars, international sanctions, etc. will have a certain impact on the export and cross-border trade of tea companies. Tea companies should closely monitor changes in the international political environment and develop corresponding response strategies.
3.1.2. Economic and Social Environment Analysis
From the perspective of economic and social environment, tea enterprises' omnichannel marketing under the background of digital economy mainly faces the following three aspects (Lu et al., 2019; Du , 2020; Deka B et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2023 ):
(1) Changes in consumer consumption concepts. Firstly, pursue personalized and healthy consumption. In the digital economy era, consumers are increasingly focusing on personalized and healthy consumption. Tea, as a natural and healthy beverage, not only satisfies consumers' taste needs but also fulfills their pursuit of health and wellness. Secondly, pay attention to the importance of the brand image and cultural heritage of the enterprise. With the development of the digital economy, people pay more attention to the brand image and cultural connotation of enterprises. Tea companies must create tea brands with brand cultural connotation, create distinctive tea drink culture, and gain consumer recognition and trust. Thirdly, pay attention to the personalized needs of consumption. With the development of the digital economy, people's demand for personalized shopping is also increasing. Consumers expect convenience and speed in the purchasing process, a wide range of choices, and comprehensive after-sales service. When conducting omnichannel sales, tea companies should pay attention to providing consumers with diversified shopping channels, including physical stores, online stores, and social media. Fourthly, attach importance to the brand reputation and social responsibility of enterprises. With the improvement of product quality and food safety traceability in tea enterprises, their environmental protection awareness and social responsibility are also constantly increasing. Tea enterprises should adhere to the principle of "honesty and trustworthiness", ensure the quality and safety of tea, and increase supervision over tea processing.
(2)The impact of e-commerce development trends. The impact of the e-commerce development trend brought about by the digital economy has profoundly changed the marketing methods of tea companies. Tea companies need to embrace this change and constantly adapt and innovate. The impact of e-commerce development trends on the omni channel marketing of Chinese tea enterprises in the context of the digital economy is mainly manifested in the following two aspects: firstly, the development of e-commerce has become an important component of omni channel marketing for tea enterprises. Most consumers prefer to purchase goods on e-commerce platforms, and this trend has also been validated in the tea consumption market. Tea companies can enhance brand awareness, influence, and brand value through various marketing methods. Second, with the rapid development of mobile Internet, e-commerce technologies such as mobile APP, WeChat, Alipay, and small programs are constantly rising, and their applications are becoming more and more extensive. Tea companies should study consumers' purchasing habits and new technologies and models in the mobile field, develop more intelligent e-commerce platforms, and achieve diversified marketing models to meet consumers' needs and purchasing experiences.
(3)The rise of social media marketing. Social media marketing has become an important means of omnichannel marketing for tea companies, with its prominent advantages being user centered precision marketing, extensive exposure, and low cost. Tea companies can respond to consumers' questions and feedback through social media platforms, share tea production methods, tasting techniques, health plans, and other content with consumers, and enhance the interactive relationship between tea companies and consumers. Social media marketing can help tea companies better understand the concerns and needs of target consumers. With the information interaction and analysis functions of social media platforms, tea companies can collect feedback and opinions from consumers, better understand the needs and interests of target consumers, and improve marketing effectiveness and attractiveness.
3.1.3. Technical Environment Analysis
The rapid development of the digital economy has provided broader development space for tea enterprises' omnichannel marketing. In the context of the digital economy, the technological environment is crucial for the omnichannel marketing of Chinese tea companies (Roy S et al., 2020;Li et al., 2022; Dai et al., 2022;Zhang et al., 2022).
(1) The development of Internet technology has an impact on the omni channel marketing of tea enterprises. With the help of Internet technology, tea enterprises can quickly disseminate tea related information to consumers through e-commerce platforms, social media and search engines, so that consumers can more conveniently and quickly obtain relevant information about tea enterprises, thus improving consumers' willingness to buy. Secondly, Internet technology can realize the omni channel sales of tea enterprises. With the rapid development of e-commerce, tea companies can not only rely on their own official website platforms, but also on third-party e-commerce platforms such as Taobao and JD.com, fully utilizing social media platforms to expand consumers, achieve all-round marketing, broaden their sales channels, and more conveniently meet consumer purchasing needs. Finally, the intellectualization of Internet technology can enable tea enterprises to better understand consumers. Big data analysis, intelligent interaction, artificial intelligence, etc. have laid a solid foundation for the development of tea enterprises, which can discover consumers' preferences and needs, and explore potential market opportunities
(2) Big data technology has an impact on omnichannel marketing for tea companies. In the era of digital economy, big data technology has gradually become an important tool for tea companies to conduct omnichannel marketing. Through the analysis of big data technology, tea companies can quickly obtain consumer information and formulate more accurate marketing strategies, grasp the current market situation and consumption trends, and make timely adjustments to their marketing strategies.
(3) Artificial intelligence technology has an impact on omnichannel marketing for tea companies. Through artificial intelligence technology, automated sales and customer service can be achieved in the omnichannel marketing of tea enterprises. Tea companies can use artificial intelligence to interact with customers and automatically identify and answer their questions, quickly push the best sales information, better promote sales, and improve sales efficiency. In addition, tea companies can use artificial intelligence technology, combined with their own sales information, to promote the optimization of data models, achieve precise product customization and sales management, and also develop personalized marketing strategies to better maintain relationships with customers.
3.2. Competitive Environment Analysis of Tea Enterprises' Omnichannel Marketing Under the Background of Digital Economy
According to the Five Forces Model, the analysis of the competitive environment can be composed of five aspects: supplier bargaining power, buyer bargaining power, potential competitor entry ability, substitute substitution ability, and the current competitive ability of competitors in the industry. Therefore, this study also analyzes the competitive environment of omnichannel marketing for tea enterprises in the context of the digital economy from these five aspects (Cai et al., 2023).
3.2.1. Supplier Bargaining Power
The positioning and scale of tea suppliers will affect their bargaining power. Larger suppliers usually have more bargaining chips and can have an advantage in bargaining. Secondly, if the supplier's product quality is better than its peers and their market reputation is more excellent, it will give them stronger control over negotiations. Furthermore, suppliers can optimize their bargaining power based on market expectations. If the market expects less supply, suppliers can confidently demand higher prices in negotiations. Finally, tea suppliers can enhance their bargaining power through long-term stable cooperative relationships.
3.2.2. Buyer Bargaining Power
In the tea market, there are many types and quantities of tea, and consumers have more choices. Compared to buyers, tea company brands have stronger pricing power and bargaining conditions. However, consumers have the right to choose tea company brands, and there are enough choices in the market. Therefore, in order to reduce customer loss, tea company brands will also adjust the product structure and selling prices of their stores. At the same time, they will layout or invest in other price bands of tea products, enrich various consumption scenarios, and create a multi brand matrix. In the digital economy, consumers' ability to obtain information and compare shopping has been greatly improved. It is easy to compare the products, prices and services of different tea enterprises through the Internet, so buyers have relatively strong bargaining power.
3.2.3. Potential Competitors' Ability to Enter
In 2023, the main distribution of tea industry enterprises in China will be in Yunnan (11795), Fujian (10530), Guangdong (3784), Sichuan (3636), and Anhui (3231), with less than 3000 enterprises in other provinces. The increase in industry concentration has raised the threshold for potential competitors to enter the industry. There are also tea beverage brands such as Heytea, Nayuki Tea, and Meixue Ice City, which have both scale effect and brand effect. In the current market environment, both online and offline channel expansion are facing higher rental and labor costs than before. The development of the digital economy has lowered the threshold for market entry, making it possible for more potential investors to enter the tea enterprise market. These potential investors may bring new technologies, innovative business models, and lower prices, posing a threat to existing tea companies.
3.2.4. Substitution Capability of Substitutes
From a product perspective, tea drinks can help with weight loss and fat burning, quench thirst and cool down, and have a rich and stimulating taste. Their substitutes mainly include fruit juice, bottled water, coffee, sparkling water, etc. From the perspective of consumer scenarios, the increase in the repurchase rate of Yuan Ye tea is driven by consumers' self satisfaction and social needs. So, their substitutes are various spaces with more emotional and social attributes. In the context of the digital economy, alternatives for tea companies may include other beverages such as coffee and milk tea, as well as digital beverage consumption methods such as online tea ordering services. These substitutes may pose a threat to the market share and profitability of tea companies.
3.2.5. Current Competitive Ability of Competitors in the Industry
The Chinese freshly brewed tea beverage market grew from 42.2 billion yuan to 113.6 billion yuan between 2015 and 2020. It is expected that by 2025, the overall market size of China's freshly brewed tea beverage market is expected to reach 340 billion yuan. This means that freshly made tea beverage brands can gain market share through their own growth, without the need to use intense price wars to seize market share from competitors. In the context of the digital economy, competition between new tea drinks and tea companies may become more intense. This is because digital marketing methods such as social media marketing, search engine optimization, etc. make it easier for companies in the industry to reach potential consumers, while also increasing the number of competitors and the intensity of competition.
Through the study of the Five Forces model, it can be found that in the digital economic environment, tea enterprises will face more challenges and opportunities. To adapt to these changes, tea companies must actively adapt to digitalization, innovate their business models and market strategies, in order to better meet consumer needs and achieve sustainable development.
4. Research Methods
This study adopts qualitative analysis method for analysis, collects relevant data through literature review and interview methods, analyzes the relevant data using grounded theory, and finally obtains relevant results.
4.1. Research Case - Shan Guo Yin Yi Company
Shan Guo Yin Yi Company was founded in 2002 and is headquartered in Xiamen. It is a comprehensive industrial group that integrates production and research and development, omnichannel operation, and cultural tourism. Its business scope covers many fields such as tea, tea sets, tea daily necessities, tea estate tourism, etc. It has large organic ecological tea estates, Shan Guo Yin Yi tea processing factories, Shan Guo Yin Yi tea set centers, Shan Guo Yin Yi logistics centers, Shan Guo Yin Yi tea culture centers, Xiamen Shangke Tea Industry Co., Ltd. (e-commerce) and other industries. After 21 years of deep cultivation and development, Shanguo Yinyi Tea Industry has opened 1137 chain stores in China (as of February 18, 2024), and its products are exported to more than 60 countries and regions around the world. It has been awarded the title of "Top 100 Franchise Chain Enterprises in China" and recognized as a key leading enterprise in agricultural industrialization at the provincial level in Fujian.
4.2. Method Overview
Grounded theory is a social science research method mainly used to generate theories and explain phenomena. Through the collection and analysis of data, problems are discovered, concepts are extracted, and theories are generated from actual phenomena. Researchers continuously conduct data analysis and feedback while collecting data, in order to generate new concepts and theories and further advance research. The concept of grounded theory must come from raw materials, placing complex concepts and their relationships within a dense theoretical environment, enhancing the correlation between theoretical concepts and other concepts, and having theoretical sensitivity to the problems of the parties involved, providing a theoretical basis for analyzing and solving problems (He et al., 2022; Ma et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023).
The specific operational process of analyzing grounded theory mainly includes five steps:
The first step is to determine the research question. Firstly, it is necessary to clarify the research question or phenomenon and gain a preliminary understanding of it. The goal of this step is to determine the direction and scope of the research, providing guidance for subsequent data collection and organization.
The second step is data collection. Collect relevant data based on the research question. The data for this study can be obtained from literature review, interview data, observation data, and questionnaire surveys. In this process, it is necessary to ensure the breadth and richness of the sample in order to provide a solid foundation for subsequent theoretical construction.
The third step is data organization and analysis. Organize and analyze the collected data, including classification, coding, induction, and other related tasks. During the analysis process, researchers need to constantly compare and contrast data, search for correlations and patterns, and provide a basis for theoretical construction.
The fourth step is theoretical construction. On the basis of analyzing data, gradually form a theoretical framework. This process requires continuous revision and improvement of existing theories, while also proposing new theoretical perspectives and concepts. In this step, researchers need to maintain an open and flexible attitude, constantly exploring and discovering new possibilities.
The fifth step is theoretical testing and validation. The constructed theory needs to be tested and validated to ensure its reliability and effectiveness. This can be achieved in various ways, such as comparing existing theories, predicting new phenomena, etc. If a theory has been fully validated and tested, it can be considered a relatively stable and reliable theoretical framework.
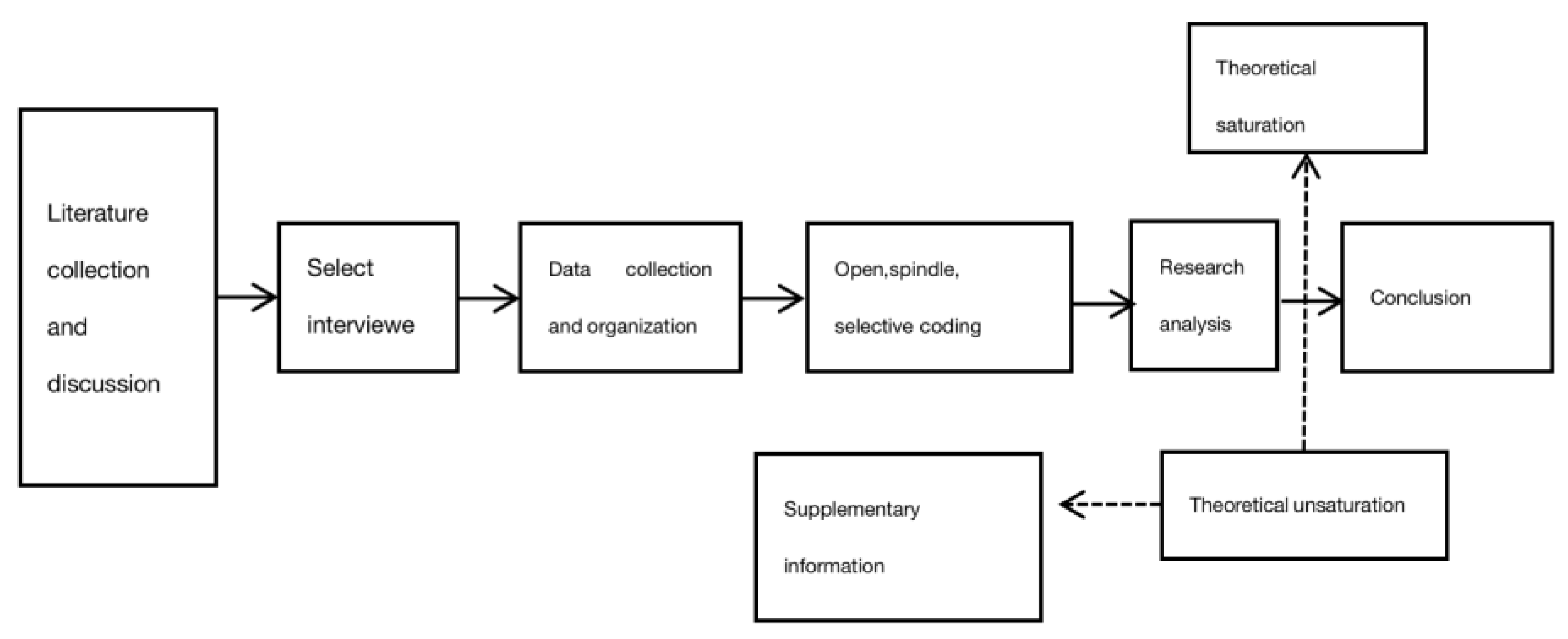
The specific research process is shown in
Figure 1.
4.3. Research Samples and Design
Based on the research questions and theoretical concepts, combined with the current strategies of omnichannel marketing in tea enterprises, this study conducted semi-structured interviews with 81 marketing department employees, including the marketing director of Shanguo Yinyi Company, including the managers responsible for channels in the marketing department; The responsible persons of the main marketing channels, product managers, the main responsible persons of the customers with the largest terminal usage, and the top 41 sales consultants in terms of sales ranking are shown in
Table 1.
The specific outline of this interview is shown in
Table 2, and the topic design is based on previous scholars' research summaries and the specific situation of Shan Guo Yin Yi's omnichannel marketing. The in-depth interviews with interviewers are mainly recorded in text form during the interview process, which facilitates the organization, summarization, and comparison with the original data. Finally, the initial interview data is used as the final effective material for the coding of basic information resources.
4.4. Data Collection
After completing the preliminary interviews, the collected data is first classified, followed by the practical construction of core theories, the planning of basic links, and finally a large amount of coding is carried out on the collected data, and open coding is applied to these materials for further selective coding according to different situations. In this process, the commonly used grounded research method is applied to construct conceptual data and demonstrate their characteristics by comparing relevant vocabulary such as events, connections between events, and event concepts. When conducting open coding, it is a tedious research process to break down and crush various different concepts, and then re code them according to their respective characteristics.
During the specific analysis process, based on the research theory, open coding was applied to the data collected from 81 in-depth interviews. During this process, a definite label is formed for encoding, and after a series of continuous comparative analyses, an abstract independent concept is formed. In the open coding stage, some scattered nodes will also be summarized into the data and then find their logical positions. Due to the fact that the initial identification phenomenon and the subsequent research on categories and convergence issues were all carried out in an open coding, both abstract and specific sporadic concepts need to be continuously deepened and developed in grounded theory, and in this process, the correlation between fragmented concepts in the whole needs to be improved. This is also a key significance of grounded theory for studying the analysis of the Shan Guo beverage art market. In the open coding, more than 30 nodes related to the liberalization of various aspects of Shanguo Yinyi's omnichannel marketing were obtained. If we want to achieve holistic category optimization of concepts, we need to analyze and organize these scattered original concepts.
At the same time, attention should be paid to the significance of memory patterns as an influencing factor in implementing records, so the time correspondence of encoding all concepts is particularly important. Based on this, more than 30 pairs of nodes previously encoded were analyzed and organized, resulting in 15 concepts. Then summarize these 15 concepts into 7 categories.
4.5. Data Analysis
The data analysis process in this article mainly follows the programmatic grounded theory approach and can be roughly divided into three processes: open decoding, main axis decoding, and selective decoding.
4.5.1. Open Encoding
Programming is another process of analyzing data in grounded theory research, which is open numbering. This is also the basic process of programmatic grounded theory research and analysis, and the implementation process of spindle numbering and selective numbering is also based on open numbering. According to the coding characteristics studied by grounded theory, the process of open numbering first involves numbering the accessed data line by line and sentence by sentence, that is, "defining phenomena" . In order to minimize the negative impact of researchers' subjective thinking on research results, this article will select the original words of the respondents as much as possible in an open-ended numbering process for numbering. After completing the line by line coding work using 81 interview materials, the coding results obtained from the line by line coding workflow were conceptualized and categorized separately. About 198 initial languages were obtained from 81 interviews, with a large number of initial languages and a certain degree of language overlap. Categorization is the process of redefining categories, removing initial categories with minimal overlap (frequency less than or equal to 2 times) and selecting categories with overlap frequency of three or more times. Finally, a total of 29 initial categories were obtained, and detailed information on some cases can be found in
Table 3.
4.5.2. Spindle Coding
The main task of main axis coding is to find the direct potential logical relationship between categories, summarize and organize the previous concept, and thus find its main category and sub category. The researchers summarized the 29 categories mentioned above based on their interrelationships and logical ordering at each category level, and identified 7 main categories. The corresponding open codes for each main category will be presented in
Table 4.
4.5.3. Selective Encoding
Selective coding has excavated the core categories from the main scope, and by studying the connections between the core scope, the main paradigm, and other scopes, the core scope is connected in the form of story clues, and the connected stories are actually the final new theoretical framework formed. As the final step in the decoding process of programmatic grounded theory, it mainly involves analyzing open coding techniques and the main axis coding process to extract the core content. After a re examination of the original sample data, as well as continuous classification, comparison, and summary of 29 scope and 7 main scope data, combined with the specific implementation of Shan Guo Yin Yi's existing omni channel marketing strategy, a Shan Guo Yin Yi omni channel marketing strategy optimization model was finally developed. The core categories and inclusion relationships are shown in
Table 5. By comparison, it can be seen that the core paradigm is a simplification and concentration of the main paradigm, which is a comprehensive summary based on the content of the main paradigm.
4.5.4. Theoretical Saturation Test
After obtaining the core paradigm, it is necessary to conduct preliminary verification of its theoretical saturation properties. When the information and data obtained by researchers are verified using the same three-level encoding method, once no new important concepts appear again, no new important constituent factors are generated in the main concept, and no new concepts appear in the interaction between new concepts, it can be considered that the theory has reached saturation. This research project mainly adopts theoretical sampling and deep access methods for scientific research path, and also conducts data encoding analysis. The specific selective encoding results are shown in
Table 6.
As shown in the table above, the data obtained through continuous comparison can further improve and modify the theory, and constant saturation tests have been conducted on the theory under construction. Finally, the original data generated by randomly sampled participants were analyzed using three-level encoding again, and it was concluded that no new categories had been generated yet. Therefore, it can be pointed out that this research paradigm has achieved theoretical saturation.
4.6. Analysis of Grounded Theory Results
Based on the data of the grounded theory mentioned above, it can be seen that the main problems in the current omnichannel marketing strategy of Shan Guo Yin Yi include the following:
(1) The existing product promotion channels are single: from the results of grounded theory, it can be seen that the product promotion channels of Shan Guo Yin Yi are very important. In the digital economy era, the diversity and interactivity of marketing channels have become the core of enterprise competition. However, in enterprises like Shanguo Yinyi, there is a problem of single product promotion, and their main promotion channels are still physical stores, lacking a fully integrated and unified online sales and e-commerce model, which cannot adapt to the rapid changes and development of the digital economy era.
(2) The inventory problem is prominent: Unlike other products, tea has obvious seasonality, so the inventory problem is currently a problem that Shan Guo Yin Yi has to face in its omnichannel marketing process. This problem is mainly manifested in the following aspects: firstly, there is a prominent issue of seasonal inventory in Shan Guo Yin Yi; Secondly, the marketing activities of Shan Guo Yin Yi lack personalization and customization. In the digital economy era, consumers have an increasing demand for personalized services and customized products. Finally, the marketing activities of Shan Guo Yin Yi lack effective channels for dissemination and promotion. In the era of digital economy, social media and online platforms have become the mainstream channels for information dissemination and consumer interaction.
(3) The degree of integration between online and offline is poor: From the results of the grounded theory, it can be seen that in enterprises like Shanguo Yinyi, the integration of online and offline is very important for omnichannel marketing. But the current problem is that firstly, Shan Guo Yin Yi often sees online and offline as two relatively independent channels, lacking integration. Secondly, the online and offline marketing of Shan Guo Yin Yi lacks a unified strategic goal and unified approach. Finally, Shanguo Yinyi also needs to further enhance its digital capabilities and the integration of online and offline technologies.
(4) The current marketing campaign lacks appeal: Based on the results of grounded theory, it can be seen that Shan Guo Yin Yi is crucial in omnichannel marketing. At present, there is a problem of unattractive marketing activities in Shanguo Yinyi. Firstly, the marketing activities of Shan Guo Yin Yi lack innovation and interactivity that are compatible with the digital economy. Secondly, the marketing activities of Shan Guo Yin Yi lack personalization and customization. Finally, the marketing activities of Shan Guo Yin Yi lack effective channels for dissemination and promotion.
(5) Poor user service experience: The arrival of the digital economy has brought new changes and challenges to the operation and marketing of enterprises. Based on the results of grounded theory, it can be seen that the service experience is crucial in the omnichannel marketing of Xia Guoyin Art in this context. Currently, the company has a problem of poor service experience. The online experience of Shan Guo Yin Yi has problems and the omni channel service is not smooth. In addition, the implementation cost of Shan Guo Yin Yi's omni channel service is relatively high.
(6) Insufficient data analysis and precision marketing: With the continuous development of the digital economy, more and more companies are turning their attention to omnichannel marketing, and Shan Guo Yin Yi is no exception. The results of grounded theory indicate that data analysis and precision marketing are key to omnichannel marketing for enterprises. At present, the company still has problems with inadequate data analysis and precision marketing. On the one hand, Shanguo Yinyi lacks a comprehensive data analysis system; On the other hand, Shan Guo Yin Yi has shortcomings in precision marketing.
(7) Poor brand image: Through in-depth research on Shan Guo Yin Yi's products, it has been found that the construction of its brand image in the omnichannel market is a topic worthy of attention and an urgent problem that enterprises are facing. Firstly, the brand positioning of "Shan Guo Yin Yi" products is chaotic; In addition, the popularity of "Shan Guo Yin Yi" in the market is not enough. In today's digital economy, enterprises need to use various marketing methods and social media platforms to gain a competitive edge. Shanguo Yinyi has a significant gap in brand marketing and promotion compared to its competitors, resulting in low product awareness and affecting the formation of specific brand images.
5. Conclusion and Suggestions
Summarizing the results of the grounded theory mentioned above and the specific situation of Shan Guo Yin Yi's omni channel marketing, combined with the analysis of its grounded theory, it can be concluded that in the context of the digital economy, Shan Guo Yin Yi needs to improve many problems in order to achieve omni channel marketing. To achieve sustainable development of omnichannel marketing for the enterprise in the context of the digital economy, optimization should be carried out for the above five issues, which can be specifically addressed from the following aspects (Peng et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2022):
(1) Broaden the existing marketing channels: Shanguo Drink Art can actively push tea related information and various promotional activities through WeChat official account, Weibo, APP, Tiktok and other media platforms, communicate with consumers, enhance the brand awareness of the enterprise, and also can cooperate with various offline businesses and events to create a new promotion model, provide consumers with omni channel tea retail and experience, and expand the marketing and service fields. In addition, at the level of consumer experience, we will continue to improve the design of store space, tea service, and product display to enhance consumers' psychological experience and create a high-quality brand experience.
(2) Promote digital inventory management: Adopt IoT technology for inventory management, achieve real-time monitoring and recording of tea storage temperature, humidity, time and other indicators, and ensure product quality. At the same time, through big data analysis, predict sales demand, adjust procurement and production plans, and reduce the risk of inventory backlog. Utilize digital means to carry out online marketing activities, such as e-commerce platforms, social media, etc., to expand the marketing channels of tea enterprises and increase sales. Meanwhile, through data analysis and personalized recommendations, optimize marketing effectiveness and service experience. Utilizing information systems such as ERP to achieve unified management of tea enterprise inventory, implement inventory management and warning mechanisms, timely detect inventory anomalies, and take measures to avoid risks such as inventory backlog.
(3) Online and offline combination based on "Internet plus+data": through the online platform, consumers can order favorite tea products anytime and anywhere, improving the convenience of consumers' purchase. In addition, brands can also leverage third-party e-commerce platforms such as Taobao, Tmall, JD.com, etc. to expand their sales coverage and attract more consumers. Integrate and promote online and offline resources in an orderly manner, allowing consumers to enjoy better products and services. For example, online shopping allows consumers to book goods, while offline stores can provide a physical shopping experience; Offline stores provide consumers with online ordering and offline pickup services.
(4) Enhance the attractiveness of scenario based marketing activities: Utilize AR technology to innovate its unique cultural connotations and beverage features, creating more interactive and effective offline activities. Using UCC short videos to easily lead fashion trends and young consumers. Shan Guo Yin Yi can invite some social networking experts or film and television stars to showcase its unique products and tea knowledge, or highlight new product launches in their videos, attracting fans' attention and sharing.
(5) Enhance omnichannel user service experience: By optimizing our own online platform, we aim to improve service quality. For example, online customer service can be added to answer consumers' questions through online platforms and enhance the fun of online shopping. Simultaneously set up a 24-hour customer service hotline to provide consumers with quick problem handling and after-sales service, enhancing their trust and sense of security in the product. We can provide personalized services to consumers based on their different needs, such as analyzing their shopping history, interests, and hobbies on online platforms, conducting detailed analysis, and providing personalized product recommendations based on their preferences.
(6) Strengthen data processing capabilities: Establish a tea enterprise all-weather data processing center, formulate relevant security management regulations and systems, strengthen information security and maintenance, and protect the data security of Shanguo Yinyi itself and consumers. With the help of big data analysis platforms, CRM, ERP and other data can be visualized and processed to more finely grasp consumer usage and accurately formulate corresponding marketing plans. Targeting consumers, utilizing big data and other methods to analyze the most valuable consumer groups, and deeply mining their characteristics, preferences, and needs, in order to develop marketing strategies that meet consumer needs.
(7) Creating a unique KOL image for tea companies: By integrating the brand with the story through channels such as the brand's official website, social media, and offline stores, using text, images, videos, and other methods to enhance consumers' awareness and emotional recognition of the brand, and improve the brand impression. Organizing tea art competitions, tea tasting events, offline activities, and other means enables consumers to better integrate into product development and establish deeper relationships with the brand.
6. Discussion
6.1. Innovative Ideas and Methods for Tea Companies to Conduct Omnichannel Marketing
In the context of the digital economy, omnichannel marketing has become an important means for enterprises to improve their market competitiveness and effectiveness. Tea companies can innovate their ideas and methods in omnichannel marketing by combining it with the digital economy background. First, tea enterprises can create a unique brand culture, form a unique cultural connotation and values of the brand, combine the historical accumulation of Chinese culture, and promote the consumption concept of modern tea culture with the rise of China-Chic culture. Secondly, tea companies can adopt creative marketing methods to enhance their influence and appeal, attracting consumer attention. The "VIP Day" event not only provides consumers with a series of promotional activities, but also offers diverse tea tasting experiences to meet the needs of multi-level consumers. Such creative activities can inspire other enterprises to continuously innovate marketing methods, attract consumer attention, and enhance brand value. The third is to strengthen the market promotion of big data. In the context of digital economy, the business model of enterprises needs to pay more attention to data analysis and accurate market sales. On the one hand, a complete database can be built to integrate various data resources, unify the sorting, management and utilization of data, make data more sourced, refined and efficient, better grasp consumer needs, and formulate more accurate and efficient marketing plans. On the other hand, due to the popularity of the internet and mobile phones, people's purchasing behavior has also changed. Tea enterprises can use the internet and mobile phones to carry out more accurate market promotion, such as through the establishment of enterprise official websites, social media promotion, APP promotion, etc., improve the omnichannel marketing network system, and establish valuable market promotion platforms (Jiang et al., 2022; Su et al., 2023).
6.2. Omnichannel Marketing Helps Enterprises Enhance Their Market Competitiveness
In the context of the digital economy, omnichannel marketing is of great significance for enterprises to enhance their market competitiveness.
Firstly, tea companies should utilize omnichannel marketing to expand their market coverage. In the era of digital economy, consumers' purchase behavior is moving online, and the Internet and mobile terminals have become important shopping channels. Tea enterprises can achieve omni channel coverage and attract more consumers by establishing offline stores nationwide and promoting them on the Internet and mobile terminals. Secondly, omnichannel marketing helps to enhance the influence and awareness of tea companies. In the context of digital economy, the recognition and trust of tea companies towards their brands are key factors affecting consumer purchasing behavior. Companies attach great importance to brand building, using their unique brand concepts and communication methods to enhance their visibility and reputation, establish their own brand concepts and unique brand culture, and use innovative marketing methods to attract consumers' attention, thereby improving their brand influence and awareness. Thirdly, omnichannel marketing enhances communication and interaction between tea companies and consumers. In the context of digital society, people's demand for personalization and diversification is becoming increasingly strong. Tea companies can promote their products through creative marketing, which can better provide customers with diversified tea drinking experiences, enhance interaction with consumers, and use various promotional activities to provide personalized services. This can bring consumers closer and increase their loyalty. Fourth, optimize the consumer shopping experience through omnichannel marketing. With the convenience of the Internet and mobile terminals, consumers can shop anytime and anywhere, but offline stores are still the main places for consumers to experience products and services. Through innovative store design and optimizing service quality, consumers can provide comfortable and pleasant brand experience, improve consumers' shopping experience, enhance satisfaction, establish a good corporate image and enhance the viscosity with customers.
6.3. Omnichannel Marketing Promotes the Leapfrog Development of Tea Enterprises
In the current context of digital economy, omnichannel marketing can bring more market opportunities, expand its development space, and promote its leapfrog development for Shanguo Yinyi. Firstly, through omnichannel marketing, a variety of channels can be established, including physical stores, e-commerce platforms, brand websites, social media, and other forms, which can attract different types of consumers to shop at different times and places, improve product exposure, overall image, and awareness, and promote a significant increase in product sales. Secondly, omnichannel marketing can utilize various methods to conduct sales and services, collect more useful information to understand consumers' needs and preferences, and provide consumers with more personalized and accurate services and products. Thirdly, through omnichannel marketing, the overall image of the enterprise can be enhanced, attracting more consumers' attention and recognition, strengthening the loyalty between the enterprise and consumers, increasing consumers' trust in the brand, and promoting consumption conversion. Fourthly, omnichannel sales can provide consumers with a more comprehensive, convenient, reliable, and enjoyable consumption experience. By purchasing and inquiring through multiple channels, and through two-way communication through multiple channels, consumers can improve their purchasing convenience and satisfaction, and increase the success rate of transactions.
7. Limitations of the Study
Shan Guo Yin Yi needs to rely on "omnichannel" to achieve comprehensive development in the digital age, but overall, this study still has certain limitations.
Firstly, in terms of expanding the research content, this study focuses on optimizing the omnichannel marketing strategy of tea enterprises, without delving into the management and operation of other links such as supply chain management and financial management. Therefore, in order to have a comprehensive understanding of the overall business situation and competitiveness of tea enterprises, it is necessary to consider them comprehensively.
Secondly, in terms of research methodology, this article adopts a combination of literature review and case studies. Although these two methods can obtain a lot of useful information, they are constrained by sampling, collection methods, and other factors, which inevitably lead to some errors or biases. Therefore, this study intends to further enhance the accuracy and credibility of the research results through extensive literature research, on-site investigation, and other means in the future.
Finally, the omnichannel marketing strategy of tea enterprises is a complex process influenced by various factors such as market environment, consumer demand, and competitive situation. This study cannot fully reflect the above issues from a comprehensive perspective, which makes it limited in practice.
In short, the omnichannel marketing of Shan Guo Yin Yi is the key to the development of digital economy, but it still faces shortcomings in theme expansion, methods, and practical application in practice, which urgently need to be effectively avoided and solved.
8. Research Prospects
Based on the above limitations, the future development direction of this topic can be:
Firstly, further expand the scope of research. To gain an overall understanding of the business status and competitiveness of tea enterprises, the research content can also be expanded to other fields such as supply chain management and financial management. Through case studies, field research, and other methods, a profound understanding and analysis of the role of omnichannel marketing in tea enterprises can be achieved, in order to achieve a relatively complete research result.
Secondly, adopt more quantitative research methods. In terms of data collection and case studies, a large amount of data collection and statistical analysis are used, such as empirical research and field investigations. By quantitatively analyzing the data and testing the actual situation, the research results are made more accurate and reliable. At the same time, it is possible to evaluate and predict the marketing decisions of tea enterprises by constructing an omni channel marketing decision model or using simulation methods.
Thirdly, introduce more practical application data analysis. On this basis, combined with various factors such as the market environment, consumer demand, and market environment of tea enterprises, the marketing model of tea enterprises is proposed. By conducting practical case studies with tea companies, collecting relevant information, and conducting empirical tests on theoretical achievements. On this basis, by studying the omni channel marketing strategies of tea enterprises, analyzing the consumer response and demand of tea enterprises across all channels, and making corresponding optimizations and adjustments.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the author.
Acknowledgments
Bingsheng Fu and Dongkai Lin constructed the theoretical framework and research model of this study, designed a questionnaire, completed data organization and analysis, and wrote the original draft. Jinke Lin provided guidance and suggestions for the logic and writing of the entire article. Bingsheng Fu is responsible for helping with questionnaire collection. Dongkai Lin is responsible for screening and proposing invalid questionnaires and are responsible for modifying the format.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- Chen Xiaohong, Li Yangyang, Song Lijie. Theoretical System and Research Prospects of Digital Economy. Managing the World 2022, 38, 208–224.
- Jiang, Li. Analysis of the Omnichannel Marketing Model for Tea. Fujian Tea 2022, 44, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Li Xiaozhong, Li Junyu. Research on the Impact of Digital Economy Development on the Income Gap between Urban and Rural Areas. Agricultural Technology and Economics 2022, 2, 77.
- Zhou Xiongwei, Wei Die, Cai Dan. Pricing and Service Capability Allocation Strategies of Omnichannel Service Providers from a Fair Perspective. Control and Decision 2022, 37, 1649–1655.
- Chen Wanmei, Ouyang Youquan. Research on the construction of Internet ecological marketing channels for agricultural products - taking Anxi Tieguanyin Tea, Fujian Province as an example. Sustainable Development 2018, 8, 276.
- Li Zonghuo, Yang Wensheng, Sun Hao. Manufacturer brand and retailer's own brand discount coupon promotion in an omni channel environment. Chinese Management Science 2021, 29, 157–167.
- Shen Pengyi, Wan Demin, Lu Chunhong. Research on the Mechanism of the Impact of Omnichannel Retail Experience Value Co creation Behavior on Brand Assets. Journal of Central University of Finance and Economics 2021, 104–117.
- Zhao Xiaofei. Theoretical Framework and Guarantee Mechanism of Agricultural Product Supply Chain Integration under Omnichannel Mode. Business Economics and Management 2022, 42, 5–17.
- Hu Jiao, Li Li, Zhu Xingzhen. Two stage omnichannel advertising placement and dynamic pricing decision-making considering consumer strategic behavior. Operations Research and Management 2023, 32, 114.
- Liu Jian, Yin Rongrong, Chen Jie. Research on Inventory of Omnichannel Retailers Based on Customer Channel Preferences. Chinese Management Science 2023, 31, 184–194.
- Ren Na and Tian Ziye Exploration of Omnichannel Marketing Model in China's Retail Industry. Chinese market 2022, 126–129.
- Peng Yang, Lu Jinhang, Yan Xiaoming. Research on the Density Strategy of Omnichannel Store Layout for Online Retailers. Operations Research and Management 2022, 31, 21.
- Verhoef, P.C.; Kannan, P.; Inman, J.J. From Multi-Channel Retailing to Omni-Channel Retailing. J. Retail. 2015, 91, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, I.; Sese, F.J.; Verhoef, P.C. Recasting the Customer Experience in Today's Omni-channel Environment. Universia Business Review 2016, 2016, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfakianaki, E.; Vrechopoulos, A.; Lazaris, C. Conceptualizing Green Strategies' Effects on Customer Experience in the Context of Omnichannel Retailing. International Journal of Innovation and Technology Management 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong Hongli, Yu Xingshang. Research on Digital Humanities Service Strategies of University Libraries from the Perspective of SWOT-PEST. 2023; 8.
- Kannan M, Bojan N, Swaminathan J, et al. Nanopesticides in agricultural pest management and their environmental risks: A review[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2023, 1-26.
- Zou Xuelian. Research on Precision Marketing of Enterprises under the Background of Big Data. Market Weekly Theoretical Edition 2021, 2.
- Zhao Zhonggang. Research on the Competitiveness of Postal Delivery Industry in the Digital Economy Era: A Perspective Based on Porter's Five Forces Model Theory. Journal of Hubei University of Science and Technology 2022, 42, 7.
- Sheoran M, Kumar D. Conceptualisation of sustainable consumer behaviour: converging the theory of planned behaviour and consumption cycle[J]. Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 2022, 17, 103–135.
- Lin Meiyan, Mali Jun, Wang Lan. Research on supply chain ordering pricing decisions considering consumer thinking behavior in uncertain supply environments. Journal of Management Engineering 2022, 36, 247–256.
- Florence E S, Fleischman D, Mulcahy R, et al. Message framing effects on sustainable consumer behaviour: a systematic review and future research directions for social marketing[J]. Journal of Social Marketing 2022, 12, 623–652.
- Vidal-Ayuso F, Akhmedova A, Jaca C. The circular economy and consumer behaviour: Literature review and research directions[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 137824.
- Li Ting, Kong Xiangbo, Wang Fenghua. The impact of loneliness on consumer behavior and its theoretical explanation. Progress in Psychological Science 2023, 31, 1078.
- Yan Yan, Liu Wumei, Wang Xuefeng. The influence of others' and one's own dressing style on consumer behavior: an interpretation based on the theory of regulatory orientation. Progress in Psychological Science 2023, 31, 2419.
- Wu Meiling, Zhao Liping. Research on the Development Strategy of Shandong Tea Industry Based on SWOT-PEST Analysis. Fujian Tea 2018, 58.
- Liao Xiangqian, Wu Shengbin. SWOT-PEST Analysis of Tea Industry Development in Anshun City. Agricultural Technology Services 2022, 39, 111–114.
- Li Junling, Jiang Shuangfeng, Zhang Yang, etc. Anhui Agricultural Science 2022, 50, 205–207.
- Lu Jiutian, Chen Canping, Yu Yuhua. Research on the Development Strategy of Anhua Black Tea Industry Based on PEST Analysis. Tea Newsletter 2019, 4.
- Du Haonan. Research on the integrated development of tea tourism in China from the perspective of the "the Belt and Road" - based on SWOT-PEST analysis. Fujian Tea 2020, 42, 165–166.
- Deka B, Babu A, Baruah C, et al. Nanopesticides: A systematic review of their prospects with special reference to tea pest management[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition 2021, 8, 686131.
- Sister Zhu Shan, daughter of Wu Shui Research on the Competitive Situation of Knife Tea Industry in Zhejiang Province Using the Kiding SWOT-PEST Model. Fujian Tea 2023, 45, 10–12.
- Roy S, Barooah A K, Ahmed K Z, et al. Impact of climate change on tea pest status in northeast India and effective plans for mitigation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2020, 40, 432–442.
- Li Guo, Li Xiaohong, Yang Lu, etc. SWOT-PEST analysis of Guizhou tea industry under the background of rural revitalization. 2022; 62–67.
- Dai Xinyi, Xiong Yueling, Wang Yu. Discussion on the Development of Tea Industry in Ya'an City Based on SWOT-PEST Model. Southern Agriculture 2022, 16, 189–192.
- Zhang Yu, Zhang Liping. Research on the New Business Model of Tea Tourism Integration in Anhua County. Fujian Tea 2022, 44, 4.
- Observation and Research Report Network In depth analysis of the current situation and development prospects of China's tea industry (2023-2030) https://www.sohu.com/a/741167946_121222943.
- Cai Xiaocong, Liu Rui. Research on Marketing Strategies of Tea Enterprises from the Perspective of Market Competitiveness [D] Fujian Tea. 2023.
- Shanguo Yinyi official website. http://www.sumgotea.com/.
- He Muye, Liu Dianzhi. The Application of Grounded Theory: Misconceptions and Strategies. Psychological Science 2022, 45, 1273.
- Ma Guimei, Ma Hong, Zhang Xu, etc. Research on the Quality of Employee Feedback Based on Grounded Theory: Content Structure, Measurement, and Mechanism of Action. Management Review 2022, 34, 227.
- Wang Haijun, Yu Jiawen, Tian Xiaoran, etc. The Mechanism of Intelligent Manufacturing on Disruptive Innovation in Enterprises: A Case Study of Haier from Grounded Theory. Technological Progress and Countermeasures 2023, 40, 102–113.
- Peng Yang, Lu Jinhang, Yan Xiaoming. Research on the Density Strategy of Omnichannel Store Layout for Online Retailers. Operations Research and Management 2022, 31, 21–27.
- Huang Baili, Wu Zhiming, Lv Ying. Research on Marketing Strategies of Children's Clothing Enterprises from the Perspective of Experience Economy. Woolen Textile Technology 2022, 50, 7.
- Jiang Runtian, Jin Peng, Wu Yan, etc. Clothing brand IP marketing strategy based on SIPS model. Journal of Textiles 2022, 043.
- Su Yan, Shi Yuting. Exploration of Vlogs Empowering Brand Marketing Strategies in the 5G Era. Packaging Engineering 2023, 44, 5.
Table 1.
Composition of Interviewees.
Table 1.
Composition of Interviewees.
| Job Distribution |
Number of people |
Proportion(%) |
| Marketing Director |
2 |
2.47 |
| Marketing Director |
5 |
6.17 |
| Sales Consultant |
41 |
50.62 |
| product manager |
5 |
6.17 |
| Plan |
5 |
6.17 |
| Design |
12 |
14.81 |
| Customer service |
11 |
13.58 |
Table 2.
Interview Outline Design.
Table 2.
Interview Outline Design.
| Question items |
Concrete problems |
| 1 |
What is the significance of omnichannel marketing in the context of digital economy for Shan Guo Yin Yi, and how can we respond to the challenges and opportunities in the digital economy? |
| 2 |
What is the biggest problem for enterprises in the omnichannel marketing practice of Shan Guo Yin Yi? |
| 3 |
What are the most important points that people pay attention to when formulating the omnichannel marketing strategy for Shan Guo Yin Yi? |
| 4 |
In the practice of omnichannel marketing, how should Shanguo Yinyi provide personalized products and services through data analysis and mining? |
| 5 |
What does innovative marketing activities on social media mean for Shan Guo Yin Yi's omnichannel marketing? Can you share some successful social media marketing cases? |
| 6 |
How can traditional offline channels achieve information sharing and collaborative marketing with online channels in the context of the digital economy? |
| 7 |
Does the current omnichannel marketing strategy of enterprises have limitations? How to overcome these limitations and further improve the practice of omnichannel marketing? |
| 8 |
As for the omnichannel marketing of Shan Guo Yin Yi, how to utilize technology and tools under the background of digital economy to achieve user growth and brand value enhancement? |
| 9 |
What are the future development trends, innovative directions, and key areas of omnichannel marketing for Shan Guo Yin Yi in the context of the digital economy? |
| 10 |
What is your future outlook for the omnichannel marketing of Shan Guo Yin Yi? How do you think it will play an important role in the industry? |
Table 3.
Categories and concepts formed by open coding.
Table 3.
Categories and concepts formed by open coding.
| Number |
Initial category |
Initial concept and connotation |
Representative statement |
| A001 |
E-commerce platform |
E-commerce platforms, also known as e-commerce platforms, refer to online trading platforms and payment systems that allow users to buy, sell, and transact goods or services through the internet. |
I think omnichannel marketing must consider e-commerce platforms, otherwise the channels may be perceived as inadequate. (Sales Director) |
| A002 |
Social media |
It refers to digital tools and platforms that promote communication, share content and establish social relations between users through the Internet and mobile platforms. |
I think the advantage of social media is that it allows for direct interaction with consumers and timely feedback from users. (Sales Director) |
| A003 |
Search Engines |
It is a web service tool that searches the web page information on the Internet through automatic programs (also called spiders and crawlers) and provides relevant search results according to the keywords entered by users. |
We have conducted a comprehensive evaluation and monitoring of the investment and effectiveness of search engine optimization to continuously improve ROI. (Sales Supervisor) |
| A004 |
Industry vertical websites |
Industry vertical websites refer to websites specifically designed for a particular industry or field, providing relevant information, services, and resources to users in that field. |
We attach great importance to the role of industry vertical websites, as they can provide us with more accurate and timely industry information and business opportunities. (Sales Supervisor) |
| A005 |
Offline stores |
Refers to actual physical stores or sales points, as opposed to online e-commerce. |
The purpose of our offline stores is to provide consumers with a more direct understanding and exposure to our products, as well as to offer more thoughtful and personalized services. (Sales Supervisor) |
Table 4.
The main paradigm of spindle encoding form.
Table 4.
The main paradigm of spindle encoding form.
| Number |
Core categories |
Main category |
Concept and connotation |
| B001 |
Product promotion channels |
A001 E-commerce platform, A002 Social media, A003 Search engine, A004 Industry vertical website, A005 Offline stores, A006 Exhibition |
The general term for various promotional methods adopted by enterprises to sell products or services, including online and offline channels such as telecommunications marketing, advertising, e-commerce, direct sales, prop promotion, event marketing, etc. |
| B002 |
Inventory management |
A007 Seasonal inventory management, A008 Inventory cycle, A009 Product structure, A010 Product attributes |
Improving inventory management effectiveness through digital inventory management. |
| B003 |
Combining online and offline |
A011 O2O platform, A012 Client, A013 Physical store, A014 Express logistics |
Marketing and service are achieved through the combination and interaction of online and offline channels to achieve marketing objectives. |
| B004 |
Attraction of marketing activities |
A015 Gift giveaway, A016 Promotional offer, A017 Brand promotion ambassador, A018 Limited time flash sale, A019 Lucky draw activity |
The degree and effectiveness of attracting target audience participation in the design and execution of marketing activities. The attractiveness of marketing activities can be enhanced through attractive activity creativity and marketing innovation. |
| B005 |
Service Experience |
A020 7x24 hour online customer service, A021 Professional consulting consultants, A022 Product experience session |
It refers to the various aspects and overall experience that consumers have during the use of a product or service, including product design, purchase, delivery, after-sales, and user experience. |
| B006 |
Data analysis and precision marketing |
A023 Data mining, A024 User profile analysis, A025 Big data quantification, A026 Precise recommendation |
Data analysis and precision marketing: refers to a way of achieving personalized, precise, and efficient marketing through data collection, analysis, and strategy optimization, thereby improving marketing effectiveness. |
| B007 |
Brand image |
A027 Dissemination channels, A028 Word-of-mouth evaluation, A029 Cultural shaping |
It refers to the comprehensive manifestation of a company's brand image and reputation through extensive promotion, craftsmanship in manufacturing, as well as comprehensive quality assurance, service assurance, and other aspects. The process of gaining consumer recognition and trust for a company's products, services, and image in its business activities is called brand building or brand image building. |
Table 5.
Core Paradigm for Optimizing the Omnichannel Marketing Strategy of Shan Guo Yin Yi.
Table 5.
Core Paradigm for Optimizing the Omnichannel Marketing Strategy of Shan Guo Yin Yi.
| Number |
Core paradigm |
Main paradigm |
| C001 |
Product promotion channels |
A002 Social media, A003 Search engine, A006 Exhibition |
| C002 |
Inventory management |
A007 Seasonal inventory, A010 Product attributes |
| C003 |
Combining online and offline |
A011 O2O platform, A012 Client, A013 Physical store |
| C004 |
Attraction of marketing activities |
A016 Promotion discounts, A018 Limited Time flash sale, A019 Lottery activities |
| C005 |
Service Experience |
A021 Professional consulting advisor, A022 Product experience segment |
| C006 |
Data analysis and precision marketing |
A024 User profile analysis, A025 Big data quantification, A026 Precise recommendation |
| C007 |
Brand image |
A027 Dissemination channels, A028 Word-of-mouth evaluation, A029 Cultural shaping |
Table 6.
Theoretical saturation test.
Table 6.
Theoretical saturation test.
| Original statement |
Initial concept |
Sub category |
Main category |
| I think we need to constantly arrange and combine products in different ways to promote them better, and omnichannel promotion is an inevitable step. |
Omnichannel promotion |
Promotion needs |
Product promotion channels |
| Actually, I think omnichannel marketing is not just about the company's own marketing, but also about managing inventory well, which is determined by the uniqueness of tea enterprises. |
Inventory management |
Inventory management |
Inventory management optimization |
| Sometimes I would first look at the product online and then go to a physical store to make a purchase, which I think is the only way to feel at ease. |
Both online and offline are important |
Combining online and offline |
Combining online and offline promotion |
| I often shop impulsively, attracted by marketing activities of certain products, and the same goes for buying Shan Guo Yin Yi tea. The probability of impulse consumption is high. |
Impulsive consumption |
Marketing activities |
Attraction of marketing activities |
| I am more concerned about the service experience of a store. If the service is not good, no matter how good the marketing is, it is useless. |
Service Experience |
Marketing Service Experience |
Service Experience |
| As a marketing manager, I think we still need to speak with data, and marketing adjustments based on data analysis are the most scientific. |
Data analysis |
Precision marketing |
Data analysis and precision marketing |
| The brand image of a company is one of the criteria for my shopping because brand image is a result of sedimentation, and a good image indicates that the company's products are good. |
Brand image sedimentation |
Brand |
Brand image |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).