Submitted:
22 March 2025
Posted:
27 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Network Retrieval
2.2. Sequencing Assortment
2.3. Functional and Pathway Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Interaction Prediction
3.2. Protein Accession, Amino Acid Sequence Retrieval
3.3. Functional Annotation Analysis and Pathway Analysis after Blast Search
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
References
- Abraham, D. J., Mehanna, A. S., Wireko, F. C., Whitney, J., Thomas, R. P., & Orringer, E. P. (1991). Vanillin, a potential agent for the treatment of sickle cell anemia. Blood, 77(6), 1334–1341. [CrossRef]
- Akagi, K., Hirose, M., Hoshiya, T., Mizoguchi, Y., Ito, N., & Shirai, T. (1995). Modulating effects of ellagic acid, vanillin and quercetin in a rat medium term multi-organ carcinogenesis model. Cancer Letters, 94(1), 113–121. [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, M., Zitta, K., Groenendaal, F., van Bel, F., & Peeters-Scholte, C. (2019). Neuroprotective strategies following perinatal hypoxia-ischemia: Taking aim at NOS. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 142, 123–131. [CrossRef]
- Amor, S., Peferoen, L. A. N., Vogel, D. Y. S., Breur, M., Van Der Valk, P., Baker, D., & Van Noort, J. M. (2014). Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases – an update. Immunology, 142(2), 151–166. [CrossRef]
- Antibacterial mechanism of vanillin against Escherichia coli O157: H7: Heliyon. (n.d.). Retrieved December 13, 2024, from https://www.cell.com/heliyon/fulltext/S2405-8440(23)06488-5.
- Arya, S. S., Rookes, J. E., Cahill, D. M., & Lenka, S. K. (2021). Vanillin: A review on the therapeutic prospects of a popular flavouring molecule. Advances in Traditional Medicine, 21(3), 415–431. [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S., & Saraswathi, N. T. (2016). Vanillin restrains non-enzymatic glycation and aggregation of albumin by chemical chaperone like function. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 87, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Belagali, Y., Ullal, S. D., Shoeb, A., Bhagwath, V., Ramya, K., & Maskeri, R. (2013). Effect of Vanillin on lipid profile in a model of hyperlipidemia, a preliminary study. IJEB Vol.51(04) [April 2013]. http://nopr.niscpr.res.in/handle/123456789/16551.
- Cav, Roda Rita, Amaury Taboada Rodriguez, et al. (2021). Synergistic Antimicrobial Activities of Combinations of.
- Cortés-Rojas, D. F., de Souza, C. R. F., & Oliveira, W. P. (2014). Clove (Syzygium aromaticum): A precious spice. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 4(2), 90–96. [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Rojas, D. F., De Souza, C. R. F., & Oliveira, W. P. (2014). Clove (Syzygium aromaticum): A precious spice. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 4(2), 90–96. [CrossRef]
- Full article: Antifungal activity of vanilla juice and vanillin against Alternaria alternata. (n.d.). Retrieved December 13, 2024, from https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19476337.2019.1586776.
- Gupta, S., & Sharma, B. (2014a). Pharmacological benefits of agomelatine and vanillin in experimental model of Huntington’s disease. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 122, 122–135. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S., & Sharma, B. (2014b). Pharmacological benefits of agomelatine and vanillin in experimental model of Huntington’s disease. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 122, 122–135. [CrossRef]
- Ho, K. L., Yazan, L. S., Ismail, N., & Ismail, M. (2009). Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human colorectal cancer cell line HT-29 induced by vanillin. Cancer Epidemiology, 33(2), 155–160. [CrossRef]
- Ho, K., Yazan, L. S., Ismail, N., & Ismail, M. (2009). Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human colorectal cancer cell line HT-29 induced by vanillin. Cancer Epidemiology, 33(2), 155–160. [CrossRef]
- Ho, K., Yazan, L. S., Ismail, N., & Ismail, M. (2011). Toxicology study of vanillin on rats via oral and intra-peritoneal administration. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 49(1), 25–30. [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, C., Liccardo, M., & Sirangelo, I. (2023). Overview of the Role of Vanillin in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Neuropathophysiological Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 1817. [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, H., Sasaki, Y. F., Matsumoto, K., Watanabe, M., Ohta, T., Shirasu, Y., & Tutikawa, K. (1990). Suppression of 6-TG-resistant mutations in V79 cells and recessive spot formations in mice by vanillin. Mutation Research Letters, 243(2), 151–158. [CrossRef]
- Kafali, M., Finos, M. A., & Tsoupras, A. (2024). Vanillin and Its Derivatives: A Critical Review of Their Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Infective, Wound-Healing, Neuroprotective, and Anti-Cancer Health-Promoting Benefits. Nutraceuticals, 4(4), 522–561. [CrossRef]
- Kamat, J. P., Ghosh, A., & Devasagayam, T. P. A. (2000). [No title found]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 209(1/2), 47–53. [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M., Szklarczyk, D., Pletscher-Frankild, S., Blicher, T. H., Von Mering, C., Jensen, L. J., & Bork, P. (2014). STITCH 4: Integration of protein–chemical interactions with user data. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(D1), D401–D407. [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.-B., Wang, Q., Yang, J.-M., Ma, L., Zhang, W.-J., Zheng, P., Sun, T., Niu, J.-G., Liu, N., & Yu, J.-Q. (2019). Neuroprotective effect of Vanillin on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 118, 109196. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J., Cho, J. Y., Lee, S. Y., Lee, K.-W., Lee, J., & Song, J.-Y. (2014). Vanillin protects human keratinocyte stem cells against Ultraviolet B irradiation. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 63, 30–37. [CrossRef]
- Mourtzinos, I., Konteles, S., Kalogeropoulos, N., & Karathanos, V. T. (2009). Thermal oxidation of vanillin affects its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Food Chemistry, 114(3), 791–797. [CrossRef]
- Neurosupportive Role of Vanillin, a Natural Phenolic Compound, on Rotenone Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells—Dhanalakshmi—2015—Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine—Wiley Online Library. (n.d.). Retrieved December 13, 2024, from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1155/2015/626028.
- Szklarczyk, D., Kirsch, R., Koutrouli, M., Nastou, K., Mehryary, F., Hachilif, R., Gable, A. L., Fang, T., Doncheva, N. T., Pyysalo, S., Bork, P., Jensen, L. J., & Von Mering, C. (2023). The STRING database in 2023: Protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Research, 51(D1), D638–D646. [CrossRef]
- Taboonpong, S., Kiratipaiboon, C., Phiboonchaiyanan, P. P., Junthongjin, P., Trithossadech, P., & Chanvorachote, P. (2017). Vanillin increases stem cell signal and cell adhesion in keratinocytes. Thai Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (TJPS), 41(2), Article 2. http://www.tjps.pharm.chula.ac.th/ojs/index.php/tjps/article/view/368.
- Tai, A., Sawano, T., Yazama, F., & Ito, H. (2011). Evaluation of antioxidant activity of vanillin by using multiple antioxidant assays. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - General Subjects, 1810(2), 170–177. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M. A., & Hamza, A. H. A. (2023). Role of Clove in Human Medical History. SAR Journal of Anatomy and Physiology, 4(02), 10–19. [CrossRef]
- Vanilla modulates the activity of antibiotics and inhibits efflux pumps in drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Biologia. (n.d.). Retrieved December 13, 2024, from https://link.springer.com/article/10.2478/s11756-020-00617-5.
- Vanillin: A review on the therapeutic prospects of a popular flavouring molecule | Advances in Traditional Medicine. (n.d.). Retrieved December 13, 2024, from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/S13596-020-00531-W.
- Xu, C., Zhan, W., Tang, X., Mo, F., Fu, L., & Lin, B. (2018). Self-healing chitosan/vanillin hydrogels based on Schiff-base bond/hydrogen bond hybrid linkages. Polymer Testing, 66, 155–163. [CrossRef]
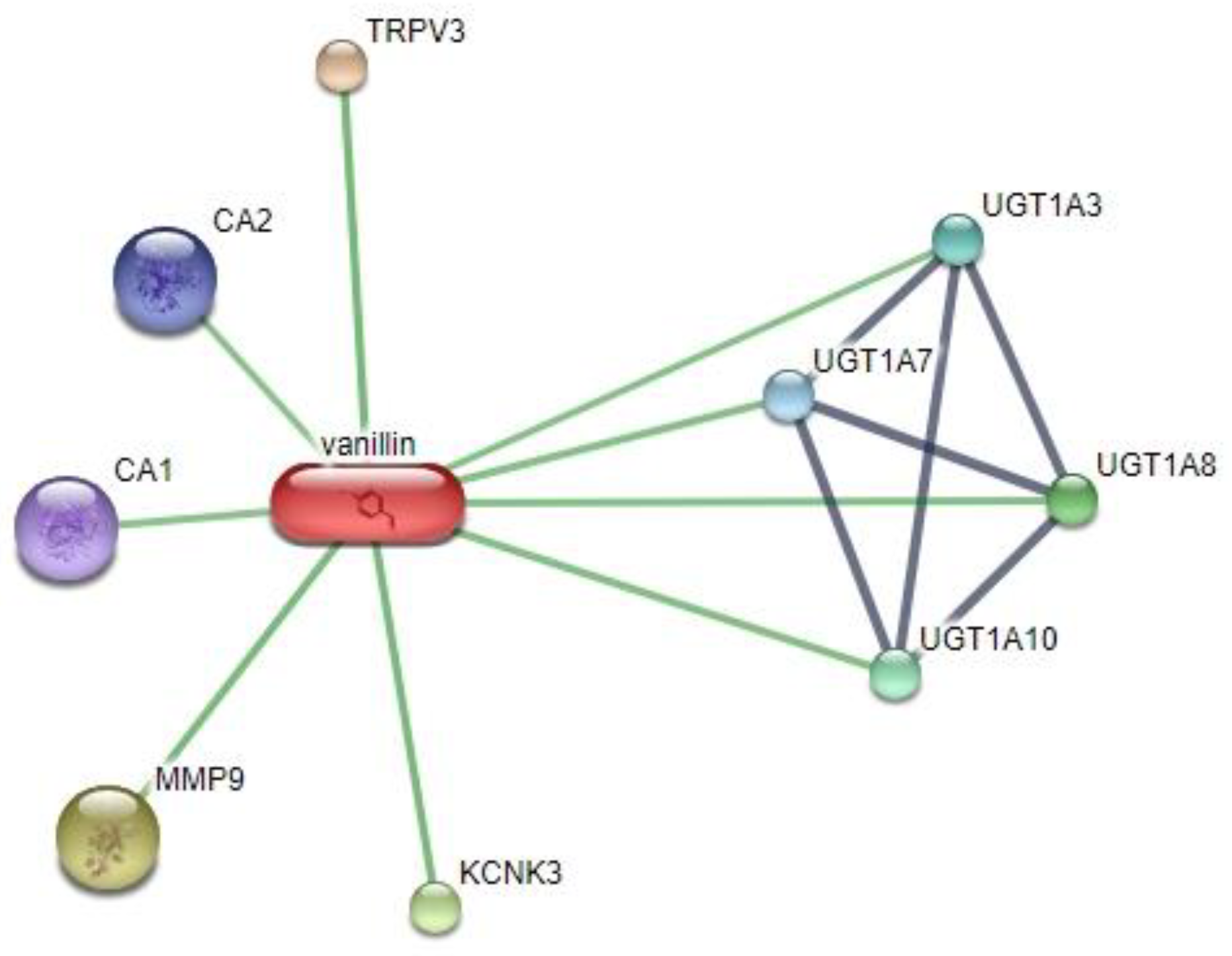
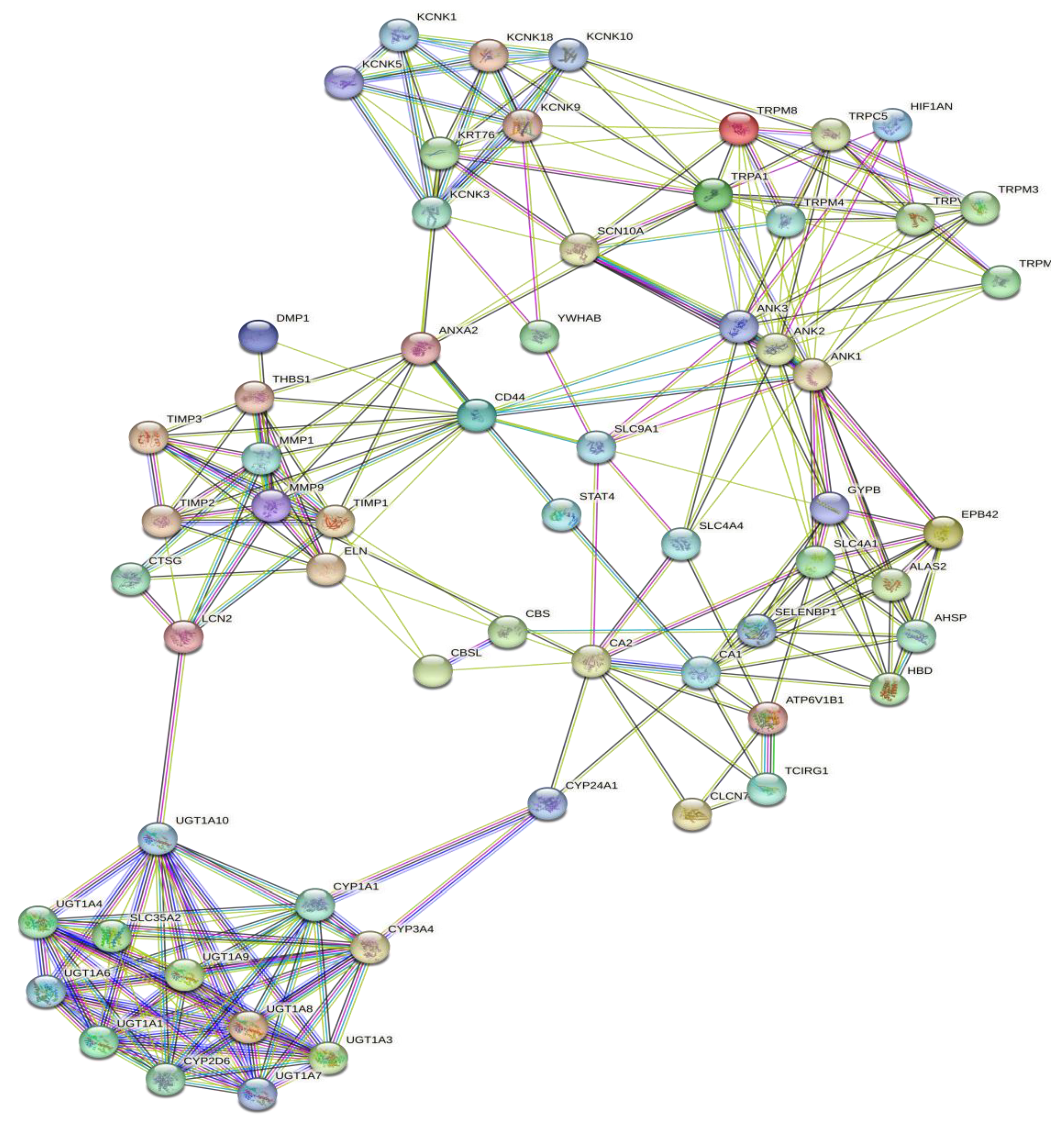
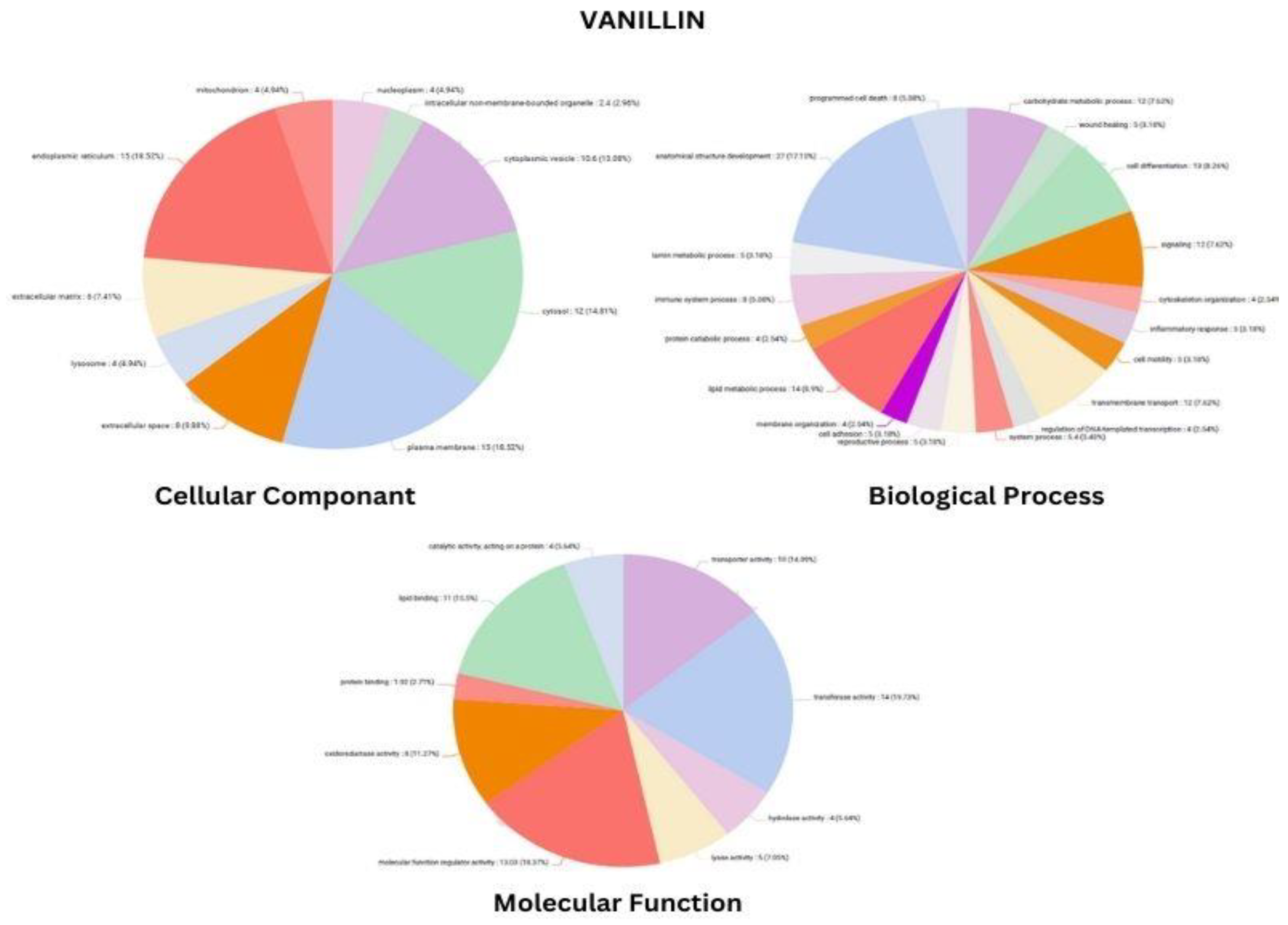
| PROTEIN CODE | ACCESSION NUMBER | INFORMATION | SCORE | AMINO ACID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA1 | ENSP00000430656 | carbonic anhydrase I; | 0.700 | 261 |
| CA2 | ENSP00000285379 | carbonic anhydrase II; | 0.700 | 260 |
| UGT1A7 | ENSP00000362525 | UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A7 | 0.737 | 530 |
| UGT1A3 | ENSP00000418532 | UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A7; | 0.737 | 534 |
| UGT1A10 | ENSP00000343838 | UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A7; | 0.739 | 530 |
| UGT1A8 | ENSP00000362549 | UDP glucuronosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A7; | 0.739 | 530 |
| KCNK3 | ENSP00000306275 | potassium channel, subfamily K, member 3; | 0.800 | 394 |
| MMP9 | ENSP00000361405 | matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase B, 92kDa gelatinase, 92kDa type IV collagenase); | 0.800 | 707 |
| TRPV3 | ENSP00000461518 | transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 3 | 0.818 | 790 |
| Stitch | CA1 | CA2 | UGT1A7 | UGT1A3 | UGTA10 | UGT1A8 | KCNK3 | MMP9 | TRPV3 |
| String | AHSP | CA1 | UGT1A6 | UGT1A9 | UGT1A1 | UGT1A6 | KCNK9 | TIMP1 | TRPM8 |
| ALAS2 | ATP6V1B1 | UGT1A1 | UGT1A6 | UGT1A8 | UGT1A9 | S100A100 | TIMP2 | HIF1AN | |
| HBD | CBS | UGT1A10 | UGT1A1 | UGT1A6 | UGT1A3 | KRT76 | LCN2 | ANK1 | |
| CA2 | CBSL | UGT1A9 | UGT1A8 | UGT1A9 | UGT1A1 | KCNK5 | CD44 | ANK3 | |
| EPB42 | TCIRG1 | UGT1A4 | UGT1A4 | UGT1A4 | UGT1A10 | KCNK18 | THBS1 | ANK2 | |
| SLC4A1 | SLC9A1 | UGT1A8 | UGT1A10 | UGT1A7 | UGT1A4 | KCNK1 | TIMP3 | TRPM3 | |
| GYPB | SLC4A4 | UGT1A3 | UGT1A7 | UGT1A3 | UGT1A7 | KCNK10 | CTSG | TRPM4 | |
| SELENBP1 | SLC4A1 | CYP3A4 | CYP3A4 | CYP3A4 | CYP3A4 | YWHAB | DMP1 | TRPA1 | |
| STAT4 | CYP24A1 | SLC35A2 | CYP2D6 | SLC35A2 | SLC35A2 | SCN10A | ELN | TRPC5 | |
| CYP24A1 | CLCN7 | CYP1A1 | SLC35A2 | CYP1A1 | CYP1A1 | ANXA2 | MMP1 | TRPM7 |
| SL No |
Accession Number | Protein name | Amino acid | SL No |
Accession Number | Protein name | Amino acid | SL No |
Accession Number | Protein name | Amino acid |
| 1 | AAH27890.1 | CA1 | 261 | 18 | NP_659505.1 | 790 | 35 | NP_002091.4 | GYPB | 91 | |
| 2 | CAG38763.1 | CA2 | 260 | 19 | NP_001305151.1 | AHSP | 102 | 36 | CAG33133.1 | SELENBP1 | 472 |
| 3 | AAG30419.1 | UGT1A7 | 530 | 20 | NP_000023.2 | ALAS2 | 587 | 37 | NP_003142.1 | STAT4 | 748 |
| 4 | NP_061966.1 | UDP1A3 | 534 | 21 | NP_000510.1 | HBD | 147 | 38 | NP_000773.2 | CYP24A1 | 514 |
| 5 | AAG30417.1 | UGT1A10 | 530 | 22 | AAH96094.1 | EPB42 | 691 | 39 | NP_066307.1 | UGT1A9 | 530 |
| 6 | NP_061949.3 | UGT1A8 | 530 | 23 | NP_061948.1 | UGT1A10 | 530 | 40 | NP_059488.2 | CYP3A4 | 503 |
| 7 | NP_002237.1 | KCNK3 | 394 | 24 | NP_009051.1 | UGT1A3 | 534 | 41 | NP_001306146.1 | CD44 | 742 |
| 8 | NP_004985.2 | MMP9 | 707 | 25 | NP_005651.1 | SLC35A2 | 396 | 42 | NP_000353.1 | TIMP3 | 211 |
| 9 | NP_001683.2 | ATP6V1B1 | 513 | 26 | NP_003237.2 | THBS1 | 1170 | 43 | NP_056932.2 | KRT76 | 638 |
| 10 | AAH10242.1 | CBS | 551 | 27 | NP_001902.1 | CTSG | 255 | 44 | NP_003731.1 | KCNK5 | 499 |
| 11 | XP_054180901.1 | CBSL | 551 | 28 | NP_004398.1 | DMP1 | 513 | 45 | NP_862823.1 | KCNK18 | 384 |
| 12 | NP_006010.2 | TCIRG1 | 830 | 29 | NP_001265868.1 | ELN | 786 | 46 | NP_002236.1 | KCNK1 | 336 |
| 13 | NP_003038.2 | SLC9A1 | 815 | 30 | NP_002412.1 | MMP1 | 469 | 47 | NP_612190.1 | KCNK10 | 543 |
| 14 | NP_001091954.1 | SLC4A4 | 1079 | 31 | NP_001269463.1 | KCNK9 | 374 | 48 | NP_003395.1 | YWHAB | 246 |
| 15 | NP_001278.1 | CLCN7 | 805 | 32 | NP_002957.1 | S100A10 | 97 | 49 | AAH93056.1 | ANXA2 | 339 |
| 16 | NP_001063.2 | UGT1A6 | 532 | 33 | NP_006505.4 | SCN10A | 1956 | ||||
| 17 | NP_000454.1 | UGT1A1 | 533 | 34 | NP_000333.1 | SLC4A1 | 911 | ||||
| KEGG ID | PATHWAY | KEGG ID | PATHWAY | KEGG ID | PATHWAY |
| Ko04510 | Focal adhesion | Ko05200 | Pathways in cancer | Ko04360 | Axon guidance |
| Ko00941 | Flavonoid biosynthesis | Ko04350 | TGF beta signaling pathway | Ko05171 | Coronavirus disease-COVID19 |
| Ko04115 | P53 signaling pathway | Ko05160 | Hepatitis C | Ko04080 | Neuroactive ligand receptor interaction |
| Ko05204 | Chemical carcinogenesis,DNA adducts | Ko05161 | Hepatitis B | Ko00040 | Pentose and glucuronate interconversions |
| Ko05322 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | Ko04929 | GnRH secretion | Ko05165 | Human papillomavirus infection |
| Ko04750 | Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | Ko04927 | Cortisol synthesis and secretion | Ko00270 | Cysteine and methionine metabolism |
| Ko05169 | Epstein barr virus infection | Ko04928 | Parathyroid hormone synthesis,secretion and action | Ko00791 | Atrazine degradation |
| Ko05323 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Ko04925 | Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | Ko04624 | Toll and Imd signaling pathway |
| Ko04630 | JAK-STAT pathway | Ko00053 | Ascorbate and aldarate metabilism | Ko00830 | Retinol metabolism |
| Ko05202 | Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | Ko04926 | Relaxin signaling pathway | Ko04742 | Taste transduction |
| Ko00944 | Flavone and flavonol biosynthesis | Ko00450 | Selenocompound metabolism | Ko04621 | NOD like receptor signaling pathway |
| Ko04110 | Cell cycle | Ko05219 | Bladder cancer | Ko04066 | HF-1signaling pathway |
| Ko01240 | Biosynthesis of co factor | Ko05215 | Prostrate cancer | Ko05152 | tuberculosis |
| Ko05321 | Inflammatory bowel disease | Ko04640 | Hematopoietic cell lineage | Ko00380 | Tryotophan metabolism |
| Ko04934 | Cushing syndrome | Ko00232 | Caffeine metabolism | Ko04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway |
| Ko04657 | IL-17 signaling pathway | Ko04668 | TNF signaling pathway | Ko00260 | Glycine,serine and threonine metabolism |
| Ko04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | Ko04024 | cAMP signaling pathway | Ko00140 | Steroid hormone biosynthesis |
| Ko04810 | Regulation of actin cytoskeleton | Ko04145 | Phagosome |
Ko04915 | Estrogen signaling pathway |
| Ko04015 | Rap1 signaling pathway | Ko00910 | Nitrogen metabolism | ko04913 | Ovarian steroidogenesis |
| Ko04013 | MAPK signaling pathway-fly | Ko04142 | Lysosome |
Ko05207 | Chemical carcinogenesis-receptor activation |
| Ko03320 | PRAP signaling pathway | Ko05110 | Vibrio cholera infection | Ko04911 | Insulin secretion |
| Ko04371 | Apelin signaling pathway | Ko04260 | Cardiac muscle contraction | Ko05208 | Chemical carcinogenesis –reactive oxygen species |
| Ko00190 | Oxidative phosphorylation | Ko04261 | Adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes | Ko01522 | Endrocrine resistance |
| Ko00071 | Fatty acid degradation | Ko00100 | Steroid biosynthesis | Ko04512 | ECM -receptor interaction |
| Ko00590 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | Ko00980 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | Ko05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer |
| Ko00073 | Cutin,suberine and wax biosynthesis | Ko00860 | Porphyrin metabolism | Ko05206 | microRNAs in cancer |
| Ko00591 | Linoleic acid metabolism | Ko00982 | Drug metabolism-cytochrome P450 | Ko05203 | Viral carcinogenesis |
| Ko00195 | photosynthesis | Ko00983 | Drug metabolism –other enzymes | Ko04114 | Oocyte meiosis |
| Ko05120 | Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection | Ko00363 | Bisphenol degradation | Ko05144 | malaria |
| Ko04670 | Leukocyte transendothelial migration | Ko04613 | Neutrophil extracellular trap formation | Ko05143 | African trypanosomiasis |
| Ko04150 | mTOR signaling pathway | Ko04217 | necroptosis | Ko05131 | Shigellosis |
| Ko04151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | Ko04976 | Bile secreation | Ko05132 | Salmonella infection |
| Ko05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | Ko04614 | Renin angiotensin system | Ko04978 | Mineral absorption |
| Ko04390 | Hippo signaling pathway | Ko04218 | Cellular senescence | Ko04971 | Gastric acid secretion |
| Ko04391 | Hippo signaling pathway-fly | Ko04974 | Protein digestion and absroption | Ko04964 | Proximal tubule bicarbonate reclamation |
| Ko05417 | Lipid and atherosclerosis | Ko04972 | Pancreatic secretion | Ko05415 | Diabetic cardimyopathy |
| Reactome id | Description | Reactome id | Description | Reactome id | Description |
| R-HSA-6805567 | keratinization | R-HSA-5576892 | Phase 0 rapid depolarisation | R-BTA-450513 | Tristetraprolin binds and destabilizes mRNA |
| R-HSA-9020958 | Interleukin-21signaling | R-HSA-8984722 | Interleukin-20 family signaling | R-HSA-727802 | Transport of nucleotide sugars |
| R-HSA-8957275 | Post-translational protein phosphorylation | R-HSA-425986 | Sodium exchange | R-BTA-111447 | Activation of BAD and translocation to mitrochondria |
| R-HSA-5579016 | Defective UGT1A4 causes hyperbilurubinemia | R-HSA-5579002 | Defective UGT1A1 causes hyperbilirubinemia | R-HSA-381426 | Regulation of insulin-like Growth Factor transport and uptake by insulin |
| R-HSA-1592389 | Activation of matrix Metalloproteinases | R-BTA-392517 | Rap 1 signaling | R-HSA-1614603 | Cysteine formation from homocysteine |
| R-HSA-9027307 | Biosynthesis of maresin-like SPMs | R-HSA-3000178 | ECM proteoglycans | R-HSA-77387 | Insulin receptor recycling |
| R-HSA-2022377 | Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins | R-HSA-8854691 | Interleukin-20 family signaling | R-HSA-1222556 | ROS and RNS production in phagocytes |
| R-BTA-5628897 | TP53 regulates metabolic genes | R-HSA-5576886 | Phase 4- resting membrane potential | R-BTA-75035 | Chk1/Chk2 mediatyed inactivation of Cyclin B:cdk1 complex |
| R-HSA-1475029 | Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide | R-BTA-5675221 | Negative regulation of MAPK activation | R-HSA-189493 | Heme degredation |
| R-HSA-447043 | Neurofascin interactions | R-HSA-983712 | Ion channel transport | R-HSA-8950505 | Gene and protein expression by JAK-STAT signaling after interleukin-12 |
| R-HSA-1299308 | Tandem of pore domain in a weak inwardly rectifying K+ channels(TWIK) | R-BTA -5674135 | MAP2K and MAPK activation | R-HSA-211916 | Vitamins |
| R-HSA-447041 | CHL1 interactions | R-HSA-418890 | Role of second messengers in netrin-1 signaling | R-HSA-2672351 | Stimuli-sensing channels |
| R-HSA-9020933 | Interleukin-23 signaling | R-HSA-3295583 | TRP channels | Plant Reactom ID | Description |
| R-HSA-1566948 | Elastic-fibre formation | R-HSA-9660826 | Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection | R-AHA-1119523 | Tetrahydrofolate biosynthesis II |
| R-HSA-1299316 | TWIK-related acid –sensitive K+(TASK) | R-HSA-1237044 | Erythrocyte take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen | R-ACH-1119415 | Leucopelargonidin and leucocyanidin biosynthesis |
| R-HSA-6785807 | Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 signaling | R-HSA-877300 | Interferon gramma signaling | R-ACH-1119322 | Leucodelphinidin biosynthesis |
| R-HSA-425381 | Bicarbonate transporters | R-HSA-9754706 | Atorvastatin ADME | R-ACH-9609573 | Tricin biosynthesis |
| R-BTA-5673000 | RAF activation | R-HSA-448706 | Interleukin-1 processing | R-AHA-1119477 | Starch biosynthesis |
| R-BTA-450385 | BRF1 binds and destabilizes mRNA | R-HSA-2408508 | Metabolism of ingested SeMet,Sec,MeSec into H2Se | R-QLO-5367729 | Strigolactone biosynthesis |
| R-HSA-9623433 | NR1H2 and NR1H3 regulate gene expression to control bile acid homeostate | R-SSC-75205 | Dissolution of fibrin clot | R-AHA-1119265 | Tetra ghydrofolate biosynthesis I |
| R-HSA-983231 | Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production | R-HSA-5423646 | Aflatoxin activation and detoxification | R-AHA-1119465 | Sucrose biosynthesis |
| R-HSA-2160916 | Hyaluronan uptake and degredation | R-HSA-917977 | Transferrin endocytosis and recycling | R-HSA-1234174 | Cellular responses to hypoxia |
| R-HSA-9757110 | Prednisone ADME | R-HSA-9027307 | Biosynthesis of maresin-like SPMs | R-HSA-189451 | Heme biosynthesis |
| R-HSA-6798695 | Neutrophil degranulation | R-HSA-2672351 | Stimuli-sensing channels | R-HSA-9717207 | Sensory perception of sweet,bitter and umami taste |
| R-BTA-166208 | mTORC1- mediated signaling | R-HSA-211916 | Vitamins |
R-HSA-114608 | Platelate degranulation |
| R-BTA-5625740 |
RHO GTPases activate PKNs | R-HSA-1299344 | TRESK | R-HSA-5619072 | Defective SLC35A2 causes congential disorder of glycosylation 2M |
| R-HSA-1299344 | TWIK-related spinal cord K+ channel | R-HSA-9639288 | Amino acids regulate mTORC1 | R-HSA-196791 | Vitamin D metabolism |
| R-HSA-9639288 | Amino acids regulate mTORC1 | R-HSA-9635465 | Suppression of apoptosis | R-HSA-1234174 | Cellular responses to hypoxia |
| R-HSA-9635465 | Suppression of apoptosis | R-HSA-1989781 | PPARA activates gene expressions | R-HSA-189451 | Heme biosynthesis |
| R-HSA-1989781 | PPARA activates gene expression | R-HSA-447038 | NrCAM interactions | R-HSA-9717207 | Sensory perception of sweet,bitter and umami taste |
| R-HSA-447038 | NrCAM interactions | R-BTA-170968 | Frs2-mediated activation | R-BTA-114608 | Platelate degranulation |
| R-HSA-170968 | Frs2-mediated activation | R-HSA-202733 | Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall | R-HSA-5619072 | Defective SLC35A2 causes congential disorder of glycosylation 2M |
| R-HSA-202733 | Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall | R-HSA-156588 | glucuronidation | R-HSA-6803157 | Antimicrobial peptides |
| R-HSA-156588 | glucuronidation | R-BTA-2028269 | Signaling by Hippo | R-HSA-6807878 | COPI-mediated anterograde transport |
| R-HSA-2028269 | Signaling by Hippo | R-HSA-6783783 | Interleukin-10 signaling | R-HSA-6809371 | Formation of the cornifide envelope |
| R-HSA-6783783 | Interleukin-10 signaling | R-HSA-445095 | Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins | R-HSA-9753281 | Paracetamol ADME |
| R-HSA-1592389 | Activation of Matrix MEtalloproteinases | R-HSA-9749641 | Asprine ADME | R-HSA-8936459 | RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation |
| R-HSA-211981 | xenobiotics | R-HSA-5619050 | Defective SLC4A1 causes hereditary spherocytosis type 4 | R-HSA-1299503 | TWIK related potassium channel |
| R-HSA-1247673 | Erythrocytes take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide | R-HSA-5619054 | Defective SLC4A4 causes renal tubular acidosis,poximal | R-HSA-6803157 | Antimicrobial peptides |
| R-HSA-5579010 | Defective CYP24A1 causes HCAI | R-BTA-96144399 | Regulation of localization of FOXO transcription factors |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





