Submitted:
29 March 2025
Posted:
31 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Computational Techniques for AAA Simulations
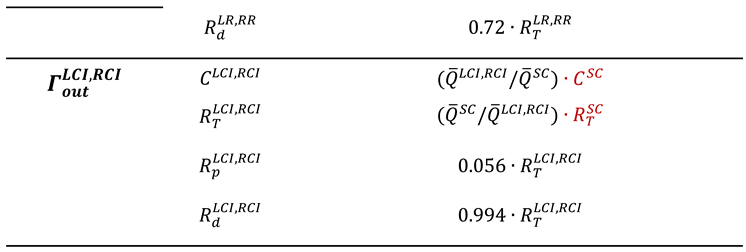
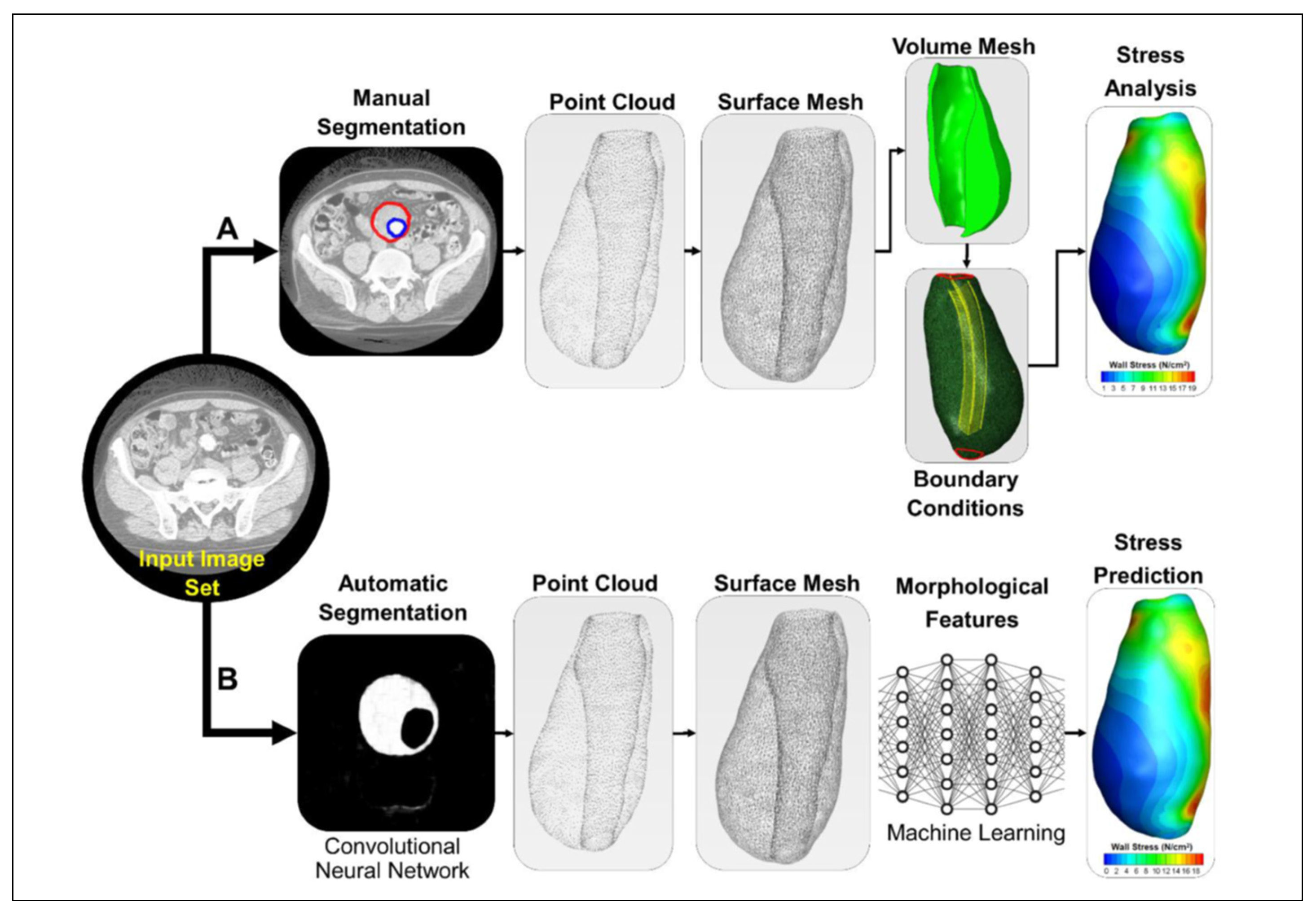
2.1. Patient Specific Modeling Approaches
2.2. Analysis of the Fluid Domain
Constitutive Models for Blood
2.3. Analysis of Solid Domain
2.3.1. Constitutive Models for AAA Wall
- Hyperelastic and Isotropic Models
- Mooney Rivlin Model
- Yeoh Model
- Hyperelastic and Anisotropic Models
- Constitutive Models for ILT
2.4. Coupling of Solid and Fluid Domains: Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI)
3. Modeling Boundary Conditions in Fluid Domain
3.1. Inlet BCs
3.2. Outlet BCs
3.2.1. Prescribed Outlet Pressure
3.2.2. Flow-Split Method
3.2.3. Lumped Parameter Model
3.2.4. Resistance BC
4. Modeling Boundary Conditions in Solid Domain
4.1. Inlet and Outlet of the Wall
4.2. External Wall Boundary
4.3. FSI Boundary: Coupling Solid and Fluid Domains
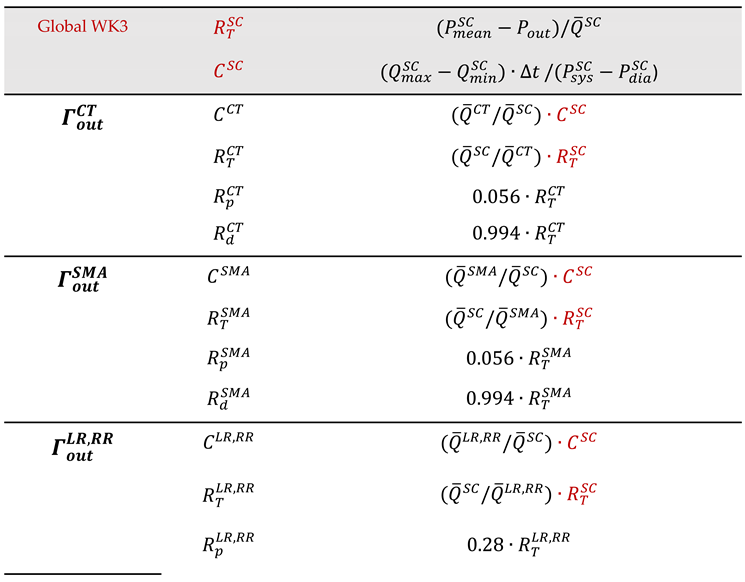
5. Important Post-Processing Indices
6. Recent Findings
7. Potential for Integrating AI and ML in AAA Research
Applications of AI and ML in AAA Flow Simulations
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAA | Abdominal aortic aneurysm |
| ILT | Intraluminal thrombus |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| FEA | Finite element analysis |
| FSI | Fluid structure interaction |
| BC | Boundary condition |
| WK2 | 2-element Windkessel model |
| WK3 | 3-element Windkessel model |
| WK4 | 4-element Windkessel model |
| RC | 2-element Windkessel model |
| RCR | 3-element Windkessel model |
| RLC | 4-element Windkessel model |
| RCR | 3-element Windkessel model |
| WSS | Wall shear stress |
| TAWSS | Time-averaged wall shear stress |
| OSI | Oscillatory shear index |
| ECAP | Endothelial cell activation potential |
| RRT | Relative residence time |
| IR | Infrarenal region |
| SC | Supraceliac region |
| CT | Celiac trunk branch |
| H | Hepatic |
| SM | Superior mesenteric |
| LR | Left renal |
| RR | Right renal |
| ARR | Accessory renal |
| LEI | Left external iliac |
| REI | Right external iliac |
| LII | Left internal iliac |
| RII | Right internal iliac |
| ML | Machine learning |
| DL | Deep learning |
Appendix A
Appendix B
 |
 |
Appendix C
References
- Lech, C.; Swaminathan, A. Abdominal Aortic Emergencies. Emerg Med Clin North Am 2017, 35 (4), 847–867. [CrossRef]
- Sakalihasan, N.; Michel, J. B.; Katsargyris, A.; Kuivaniemi, H.; Defraigne, J. O.; Nchimi, A.; Powell, J. T.; Yoshimura, K.; Hultgren, R. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. Nature Publishing Group December 1, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Dua, M. M.; Dalman, R. L. Hemodynamic Influences on Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Disease: Application of Biomechanics to Aneurysm Pathophysiology. Vascular Pharmacology. July 2010, pp 11–21. [CrossRef]
- Darling, R. C.; Messina, C. R.; Brewster, D. C.; Ottinger, L. W. Autopsy Study of Unoperated Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. The Case for Early Resection. Circulation 1977, 56 (3 Suppl), II161-4.
- Wang, X.; Ghayes, M. H.; Kotousov, A.; Zander, A. C.; Amabili, M.; Dawson, J. A.; Psaltis, P. J. Wang-2023-Biomechanics of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in the Framework Of. Int J Non Linear Mech 2023, 157. [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, N. L. Understanding Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm; 2009. [CrossRef]
- Saphirstein, R. J.; Morgan, K. G. The Contribution of Vascular Smooth Muscle to Aortic Stiffness across Length Scales. Microcirculation 2014, 21 (3), 201–207. [CrossRef]
- Soudah, E.; Ng, E. Y. K.; Loong, T. H.; Bordone, M.; Pua, U.; Narayanan, S. CFD Modelling of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm on Hemodynamic Loads Using a Realistic Geometry with CT. Comput Math Methods Med 2013, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A. J.; Kuhn, D. C. S.; Lozowy, R. J.; Kulbisky, G. P. Low Wall Shear Stress Predominates at Sites of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Rupture. J Vasc Surg 2016, 63 (6), 1613–1619. [CrossRef]
- Scotti, C. M.; Shkolnik, A. D.; Muluk, S. C.; Finol, E. A. Fluid-Structure Interaction in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Effects of Asymmetry and Wall Thickness. Biomed Eng Online 2005, 4. [CrossRef]
- Wolters, B. J. B. M.; Rutten, M. C. M.; Schurink, G. W. H.; Kose, U.; De Hart, J.; Van De Vosse, F. N. A Patient-Specific Computational Model of Fluid-Structure Interaction in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Med Eng Phys 2005, 27 (10), 871–883. [CrossRef]
- Papaharilaou, Y.; Ekaterinaris, J. A.; Manousaki, E.; Katsamouris, A. N. A Decoupled Fluid Structure Approach for Estimating Wall Stress in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. J Biomech 2007, 40 (2), 367–377. [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Raut, S. S.; Jana, A.; Biederman, R. W.; Doyle, M.; Muluk, S. C.; Finol, E. A. Fluid-Structure Interaction Modeling of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: The Impact of Patient-Specific Inflow Conditions and Fluid/Solid Coupling. J Biomech Eng 2013, 135 (8). [CrossRef]
- Rengarajan, B.; Wu, W.; Wiedner, C.; Ko, D.; Muluk, S. C.; Eskandari, M. K.; Menon, P. G.; Finol, E. A. A Comparative Classification Analysis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms by Machine Learning Algorithms. Ann Biomed Eng 2020, 48 (4), 1419–1429. [CrossRef]
- Vorp, D. A. Biomechanics of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. J Biomech 2007, 40 (9), 1887–1902. [CrossRef]
- Blanco, P. J.; Watanabe, S. M.; Dari, E. A.; Passos, M. A. R. F.; Feijoo, R. A. Blood Flow Distribution in an Anatomically Detailed Arterial Network Model: Criteria and Algorithms. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2014, 13, 1303–1330. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Alastruey, J.; Figueroa, C. A. A Systematic Comparison between 1-D and 3-D Hemodynamics in Compliant Arterial Models. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2014, 30 (2), 204–231. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xu, L.; Hao, L.; Xiao, H.; Yao, Y.; Qi, L.; Yao, Y. A Review on Low-Dimensional Physics-Based Models of Systemic Arteries: Application to Estimation of Central Aortic Pressure. BioMedical Engineering Online. BioMed Central Ltd. April 2, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Mirramezani, M.; Shadden, S. C. Distributed Lumped Parameter Modeling of Blood Flow in Compliant Vessels. J Biomech 2022, 140. [CrossRef]
- Zakerzadeh, R.; Cupac, T.; Dorfner, N.; Guy, A. Coupled Hemodynamics and Oxygen Diffusion in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Computational Sensitivity Study. Cardiovasc Eng Technol 2021, 12 (2), 166–182. [CrossRef]
- Ramazanli, B.; Sert, C.; Yavuz, M. M. Effect of Inlet Velocity Profile and Entrance Length on Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Hemodynamics Simulations. Journal of Thermal Science and Technology 2023, 43 (2), 159–174. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Alastruey, J.; Figueroa, C. A. A Systematic Comparison between 1-D and 3-D Hemodynamics in Compliant Arterial Models. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2014, 30 (2), 204–231. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Humphrey, J. D.; Figueroa, C. A. Multi-Scale Computational Model of Three-Dimensional Hemodynamics within a Deformable Full-Body Arterial Network. J Comput Phys 2013, 244, 22–40. [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z. J.; Qin, S.; Chen, R.; Cai, X. C. A Parallel Domain Decomposition Method for Large Eddy Simulation of Blood Flow in Human Artery with Resistive Boundary Condition. Comput Fluids 2022, 232. [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, L.; Karniadakis, G. E. Outflow Boundary Conditions for Arterial Networks with Multiple Outlets. Ann Biomed Eng 2008, 36 (9), 1496–1514. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, F.; Wong, J.; Fujiwara, T.; Ye, W.; Tsubota, K.; Sugawara, M. Multi-Scale Modeling of Hemodynamics in the Cardiovascular System. Acta Mechanica Sinica 2015, 31 (4), 446–464. [CrossRef]
- Sughimoto, K.; Takahara, Y.; Mogi, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Tsubota, K.; Liang, F.; Liu, H. Blood Flow Dynamic Improvement with Aneurysm Repair Detected by a Patient-Specific Model of Multiple Aortic Aneurysms. Heart Vessels 2014, 29 (3), 404–412. [CrossRef]
- Olufsen, M. S. Structured Tree Outflow Condition for Blood Flow in Larger Systemic Arteries. Am J Physiol 1999, 276 (1), 257–268. [CrossRef]
- Alastruey, J.; Khir, A. W.; Matthys, K. S.; Segers, P.; Sherwin, S. J.; Verdonck, P. R.; Parker, K. H.; Peiró, J. Pulse Wave Propagation in a Model Human Arterial Network: Assessment of 1-D Visco-Elastic Simulations against in Vitro Measurements. J Biomech 2011, 44 (12), 2250–2258. [CrossRef]
- Formaggia, L.; Lamponi, D.; Quarteroni, A. One-Dimensional Models for Blood Flow in Arteries. J Eng Math 2003, 47 (3), 251–276. [CrossRef]
- Olufsen, M. S.; Peskin, C. S.; Kim, W. Y.; Pedersen, E. M.; Nadim, A.; Larsen, J. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Validation of Blood Flow in Arteries with Structured-Tree Outflow Conditions. Ann Biomed Eng 2000, 28, 1281–1299.
- Xiao, N.; Humphrey, J. D.; Figueroa, C. A. Multi-Scale Computational Model of Three-Dimensional Hemodynamics within a Deformable Full-Body Arterial Network. J Comput Phys 2013, 244, 22–40. [CrossRef]
- Morris, P. D.; Narracott, A.; Von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Alejandro, D.; Soto, S.; Hsiao, S.; Lungu, A.; Evans, P.; Bressloff, N. W.; Lawford, P. V; Hose, R.; Gunn, J. P. Computational Fluid Dynamics Modelling in Cardiovascular Medicine. Heart 2015, 102, 18–28. [CrossRef]
- Salman, H. E.; Ramazanli, B.; Yavuz, M. M.; Yalcin, H. C. Biomechanical Investigation of Disturbed Hemodynamics-Induced Tissue Degeneration in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Using Computational and Experimental Techniques. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2019, 7. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C. A.; Figueroa, C. A. Patient-Specific Modeling of Cardiovascular Mechanics. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 2009, 11, 109–134. [CrossRef]
- Les, A. S.; Yeung, J. J.; Schultz, G. M.; Herfkens, R. J.; Dalman, R. L.; Taylor, C. A. Supraceliac and Infrarenal Aortic Flow in Patients with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Mean Flows, Waveforms, and Allometric Scaling Relationships. Cardiovasc Eng Technol 2010, 1 (1), 39–51. [CrossRef]
- Les, A. S.; Shadden, S. C.; Figueroa, C. A.; Park, J. M.; Tedesco, M. M.; Herfkens, R. J.; Dalman, R. L.; Taylor, C. A. Quantification of Hemodynamics in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms during Rest and Exercise Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computational Fluid Dynamics. Ann Biomed Eng 2010, 38 (4), 1288–1313. [CrossRef]
- Di Achille, P.; Tellides, G.; Figueroa, C. A.; Humphrey, J. D. A Haemodynamic Predictor of Intraluminal Thrombus Formation in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 2014, 470 (2172). [CrossRef]
- Fonken, J. H. C.; Maas, E. J.; Nievergeld, A. H. M.; van Sambeek, M. R. H. M.; van de Vosse, F. N.; Lopata, R. G. P. Ultrasound-Based Fluid-Structure Interaction Modeling of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Incorporating Pre-Stress. Front Physiol 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Owen, B.; Lowe, C.; Ashton, N.; Mandal, P.; Rogers, S.; Wein, W.; McCollum, C.; Revell, A. Computational Hemodynamics of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Three-Dimensional Ultrasound versus Computed Tomography. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 2016, 230 (3), 201–210. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Wang, Y.; Wen, J.; Zheng, T. Hemodynamic Investigation of a Patient-Specific Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm with Iliac Artery Tortuosity. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2018, 21 (16), 824–833. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, R.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, D.; Zheng, T. Role of Intraluminal Thrombus in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Ruptures: A Hemodynamic Point of View. Med Phys 2019, 46 (9), 4263–4275. [CrossRef]
- Teng, B.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z. Combined Curvature and Wall Shear Stress Analysis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: An Analysis of Rupture Risk Factors. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2022, 45 (6), 752–760. [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, R.; Yuan, H.; Peng, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, Z.; Guo, W.; Gao, T.; Xiong, J.; Chen, D. Retrograde Branched Extension Limb Assembling Stent of Pararenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Longitudinal Hemodynamic Analysis for Stent Graft Migration. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2020, 36 (11). [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Qin, S.; Guo, W.; Chen, R. Hemodynamic Simulation of Aneurysmal Aorta Using a Parallel Algorithm and a Flow-Rate Based Resistance Splitting Method. Computers and Electrical Engineering 2022, 104. [CrossRef]
- Dzieciuchowicz, Ł.; Krzyżański, R.; Nowak, A. Use of Intravascular Ultrasound in Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Postepy w Kardiologii Interwencyjnej. Termedia Publishing House Ltd. 2020, pp 202–205. [CrossRef]
- Van Rooij, W. J.; Sprengers, M. E.; De Gast, A. N.; Peluso, J. P. P.; Sluzewski, M. 3D Rotational Angiography: The New Gold Standard in the Detection of Additional Intracranial Aneurysms. In American Journal of Neuroradiology; 2008; Vol. 29, pp 976–979. [CrossRef]
- Mai, D. V. C.; Drami, I.; Pring, E. T.; Gould, L. E.; Lung, P.; Popuri, K.; Chow, V.; Beg, M. F.; Athanasiou, T.; Jenkins, J. T. A Systematic Review of Automated Segmentation of 3D Computed-Tomography Scans for Volumetric Body Composition Analysis. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle. John Wiley and Sons Inc October 1, 2023, pp 1973–1986. [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2017, 39 (12), 2481–2495. [CrossRef]
- Bhalerao, M.; Thakur, S. Brain Tumor Segmentation Based on 3D Residual U-Net. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer, 2020; Vol. 11993 LNCS, pp 218–225. [CrossRef]
- Mu, N.; Lyu, Z.; Rezaeitaleshmahalleh, M.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J. An Attention Residual U-Net with Differential Preprocessing and Geometric Postprocessing: Learning How to Segment Vasculature Including Intracranial Aneurysms. Med Image Anal 2023, 84, 102697. [CrossRef]
- Mu, N.; Lyu, Z.; Rezaeitaleshmahalleh, M.; Zhang, X.; Rasmussen, T.; McBane, R.; Jiang, J. Automatic Segmentation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms from CT Angiography Using a Context-Aware Cascaded U-Net. Comput Biol Med 2023, 158, 106569. [CrossRef]
- Chung, T. K.; Liang, N. L.; Vorp, D. A. Artificial Intelligence Framework to Predict Wall Stress in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Applications in Engineering Science 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Lan, I. S.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.; Marsden, A. L. Numerical Investigation of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Hemodynamics Using the Reduced Unified Continuum Formulation for Vascular Fluid-Structure Interaction. Forces in Mechanics 2022, 7. [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; He, W.; Huang, X.; Ma, J.; Yuan, T.; Shi, Y.; Wang, S. The Study on the Impact of AAA Wall Motion on the Hemodynamics Based on 4D CT Image Data. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A. C.; Salman, H. E. Effect of Intraluminal Thrombus Burden on the Risk of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Rupture. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis 2023, 10 (6). [CrossRef]
- Brambila-Solórzano, A.; Méndez-Lavielle, F.; Naude, J. L.; Martínez-Sánchez, G. J.; García-Rebolledo, A.; Hernández, B.; Escobar-del Pozo, C. Influence of Blood Rheology and Turbulence Models in the Numerical Simulation of Aneurysms. Bioengineering 2023, 10 (10). [CrossRef]
- Drewe, C. J.; Parker, L. P.; Kelsey, L. J.; Norman, P. E.; Powell, J. T.; Doyle, B. J. Haemodynamics and Stresses in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Fluid-Structure Interaction Study into the Effect of Proximal Neck and Iliac Bifurcation Angle. J Biomech 2017, 60, 150–156. [CrossRef]
- Wang-2023-Biomechanics of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in the Framework Of.
- Jayendiran, R.; Nour, B.; Ruimi, A. Computational Analysis of Nitinol Stent-Graft for Endovascular Aortic Repair (EVAR) of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA): Crimping, Sealing and Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI). Int J Cardiol 2020, 304, 164–171. [CrossRef]
- Kaewchoothong, N.; Algabri, Y. A.; Assawalertsakul, T.; Nuntadusit, C.; Chatpun, S. Computational Study of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms with Severely Angulated Neck Based on Transient Hemodynamics Using an Idealized Model. Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 2022, 12 (4). [CrossRef]
- Moradicheghamahi, J. The Role of Wall Mechanics in the Hemodynamics of a Realistic Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Fluid-Structure Interaction Study. Journal of Engineering 2024, 2024, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Piccinelli, M.; Vergara, C.; Antiga, L.; Forzenigo, L.; Biondetti, P.; Domanin, M. Impact of Hemodynamics on Lumen Boundary Displacements in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms by Means of Dynamic Computed Tomography and Computational Fluid Dynamics. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2013, 12 (6), 1263–1276. [CrossRef]
- Suh, G. Y.; Les, A. S.; Tenforde, A. S.; Shadden, S. C.; Spilker, R. L.; Yeung, J. J.; Cheng, C. P.; Herfkens, R. J.; Dalman, R. L.; Taylor, C. A. Quantification of Particle Residence Time in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computational Fluid Dynamics. Ann Biomed Eng 2011, 39 (2), 864–883. [CrossRef]
- Suh, G. Y.; Les, A. S.; Tenforde, A. S.; Shadden, S. C.; Spilker, R. L.; Yeung, J. J.; Cheng, C. P.; Herfkens, R. J.; Dalman, R. L.; Taylor, C. A. Hemodynamic Changes Quantified in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms with Increasing Exercise Intensity Using MR Exercise Imaging and Image-Based Computational Fluid Dynamics. Ann Biomed Eng 2011, 39 (8), 2186–2202. [CrossRef]
- Bologna, E.; Dinoto, E.; Di Simone, F.; Pecoraro, F.; Ragusa, S.; Siciliano, K.; Zingales, M. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and Finite Element Analysis (FEM) of a Customized Stent-Graft for Endovascular (EVAR) Treatment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurism (AAA). Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 2023, 13 (9). [CrossRef]
- Al-Jumaily, A. M.; Embong, A. H. Bin; AL-Rawi, M.; Mahadevan, G.; Sugita, S. Aneurysm Rupture Prediction Based on Strain Energy-CFD Modelling. Bioengineering 2023, 10 (10). [CrossRef]
- Scotti, C. M.; Finol, E. A. Compliant Biomechanics of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Fluid-Structure Interaction Study. Comput Struct 2007, 85 (11–14), 1097–1113. [CrossRef]
- Scotti, C. M.; Jimenez, J.; Muluk, S. C.; Finol, E. A. Wall Stress and Flow Dynamics in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Finite Element Analysis vs. Fluid-Structure Interaction. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2008, 11 (3), 301–322. [CrossRef]
- Torii, R.; Oshima, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Takagi, K.; Tezduyar, T. E. Numerical Investigation of the Effect of Hypertensive Blood Pressure on Cerebral Aneurysm - Dependence of the Effect on the Aneurysm Shape. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 2007, 54 (6–8), 995–1009. [CrossRef]
- Torii, R.; Oshima, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Takagi, K.; Tezduyar, T. E. Computer Modeling of Cardiovascular Fluid-Structure Interactions with the Deforming-Spatial-Domain/Stabilized Space-Time Formulation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2006, 195 (13–16), 1885–1895. [CrossRef]
- Arzani, A.; Shadden, S. C. Characterizations and Correlations of Wall Shear Stress in Aneurysmal Flow. J Biomech Eng 2016, 138 (1). [CrossRef]
- Bessonov, N.; Sequeira, A.; Simakov, S.; Vassilevskii, Y.; Volpert, V. Methods of Blood Flow Modelling. Math Model Nat Phenom 2016, 11 (1), 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Mirafzal, I.; Rahbary, A.; Shamloo, A.; Naseri, T. Optimization of Nano-Microparticle Size and Shape on Wall-Interaction: A Human Case Study on an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics 2023, 17 (1). [CrossRef]
- Arzani, A. Accounting for Residence-Time in Blood Rheology Models: Do We Really Need Non-Newtonian Blood Flow Modelling in Large Arteries? J R Soc Interface 2018, 15 (146). [CrossRef]
- Biasetti, J.; Hussain, F.; Christian Gasser, T. Blood Flow and Coherent Vortices in the Normal and Aneurysmatic Aortas: A Fluid Dynamical Approach to Intraluminal Thrombus Formation. J R Soc Interface 2011, 8 (63), 1449–1461. [CrossRef]
- Bilgi, C.; Atalik, K. Numerical Investigation of the Effects Ofblood Rheology and Wall Elasticity in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm under Pulsatile Flow Conditions. Biorheology 2019, 56 (1), 51–71. [CrossRef]
- Marrero, V. L.; Tichy, J. A.; Sahni, O.; Jansen, K. E. Numerical Study of Purely Viscous Non-Newtonian Flow in an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. J Biomech Eng 2014, 136 (10). [CrossRef]
- Childress, E. M.; Kleinstreuer, C. Impact of Fluid-Structure Interaction on Direct Tumor-Targeting in a Representative Hepatic Artery System. Ann Biomed Eng 2014, 42 (3), 461–474. [CrossRef]
- Razavi, A.; Shirani, E.; Sadeghi, M. R. Numerical Simulation of Blood Pulsatile Flow in a Stenosed Carotid Artery Using Different Rheological Models. J Biomech 2011, 44 (11), 2021–2030. [CrossRef]
- Morbiducci, U.; Ponzini, R.; Gallo, D.; Bignardi, C.; Rizzo, G. Inflow Boundary Conditions for Image-Based Computational Hemodynamics: Impact of Idealized versus Measured Velocity Profiles in the Human Aorta. J Biomech 2013, 46 (1), 102–109. [CrossRef]
- Mendieta, J. B.; Fontanarosa, D.; Wang, J.; Paritala, P. K.; McGahan, T.; Lloyd, T.; Li, Z. The Importance of Blood Rheology in Patient-Specific Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation of Stenotic Carotid Arteries. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2020, 19 (5), 1477–1490. [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Dabagh, M.; Vasava, P.; Dadvar, M.; Dabir, B.; Jalali, P. Effect of Rheological Models on the Hemodynamics within Human Aorta: CFD Study on CT Image-Based Geometry. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 2014, 207, 42–52. [CrossRef]
- Faraji, A.; Sahebi, M.; SalavatiDezfouli, S. Numerical Investigation of Different Viscosity Models on Pulsatile Blood Flow of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm (TAA) in a Patient-Specific Model. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2023, 26 (8), 986–998. [CrossRef]
- Skiadopoulos, A.; Neofytou, P.; Housiadas, C. Comparison of Blood Rheological Models in Patient Specific Cardiovascular System Simulations. J Hydrodynam B 2017, 29 (2), 293–304. [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y. I.; Kensey, K. R. Effects of the Non-Newtonian Viscosity of Blood on Flows in a Diseased Arterial Vessel. Part 1: Steady Flows. Biorheology 1991, 28 (3–4), 241–262. [CrossRef]
- Leuprecht, A.; Perktold, K. Computer Simulation of Non-Newtonian Effects on Blood Flow in Large Arteries. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2001, 4 (2), 149–163. [CrossRef]
- Quemada, D. Rheology of Concentrated Disperse Systems III. General Features of the Proposed Non-Newtonian Model. Comparison with Experimental Data. Rheol Acta 1978, 17 (6), 643–653. [CrossRef]
- Bilgi, C.; Atalık, K. Effects of Blood Viscoelasticity on Pulsatile Hemodynamics in Arterial Aneurysms. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 2020, 279. [CrossRef]
- Bodnár, T.; Sequeira, A.; Prosi, M. On the Shear-Thinning and Viscoelastic Effects of Blood Flow under Various Flow Rates. Appl Math Comput 2011, 217 (11), 5055–5067. [CrossRef]
- Guranov, I.; Ćoćić, A.; Lečić, M. Numerical Studies of Viscoelastic Flow Using the Software OpenFOAM. PAMM 2013, 13 (1), 591–592. [CrossRef]
- Habla, F.; Tan, M. W.; Haßlberger, J.; Hinrichsen, O. Numerical Simulation of the Viscoelastic Flow in a Three-Dimensional Lid-Driven Cavity Using the Log-Conformation Reformulation in OpenFOAM®. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 2014, 212, 47–62. [CrossRef]
- Elhanafy, A.; Guaily, A.; Elsaid, A. Numerical Simulation of Oldroyd-B Fluid with Application to Hemodynamics. Advances in Mechanical Engineering 2019, 11 (5), 1687814019852844. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Carpenter, H. J.; Ghayesh, M. H.; Kotousov, A.; Zander, A. C.; Amabili, M.; Psaltis, P. J. A Review on the Biomechanical Behaviour of the Aorta. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials. Elsevier Ltd August 1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, G. A.; Ogden, R. W. Constitutive Modelling of Arteries. In Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences; Royal Society, 2010; Vol. 466, pp 1551–1597. [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, J. D.; Holzapfel, G. A. Mechanics, Mechanobiology, and Modeling of Human Abdominal Aorta and Aneurysms. Journal of Biomechanics. March 15, 2012, pp 805–814. [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Holzapfel, G. A. Structure, Mechanics, and Histology of Intraluminal Thrombi in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ann Biomed Eng 2015, 43 (7), 1488–1501. [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, G. A.; Gasser, T. C.; Ogden, R. W. A New Constitutive Framework for Arterial Wall Mechanics and a Comparative Study of Material Models. Journal of elasticity and the physical science of solids 2000, 61 (1), 1–48. https://hal.science/hal-01297725.
- Raghavan, M. L.; Vorp, D. A. Toward a Biomechanical Tool to Evaluate Rupture Potential of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Identi"cation of a "nite Strain Constitutive Model and Evaluation of Its Applicability. J Biomech 2000, 33, 475–482.
- Martino, E. S. Di; Guadagni, G.; Fumero, A.; Ballerini, G.; Spirito, R.; Biglioli, P.; Redaelli, A. Fluid-Structure Interaction within Realistic Three-Dimensional Models of the Aneurysmatic Aorta as a Guidance to Assess the Risk of Rupture of the Aneurysm; 2001; Vol. 23. www.elsevier.com/locate/medengphy.
- Salman, H. E.; Yalcin, H. C. Computational Investigation of the Effect of Wall Thickness on Rupture Risk in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics 2021, 14 (2), 499–513. [CrossRef]
- Javadzadegan, A.; Fakhim, B.; Behnia, M.; Behnia, M. Fluid-Structure Interaction Investigation of Spiral Flow in a Model of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. European Journal of Mechanics, B/Fluids 2014, 46, 109–117. [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Berguer, R. Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis of Turbulent Pulsatile Flow within a Layered Aortic Wall as Related to Aortic Dissection. J Biomech 2009, 42 (16), 2642–2648. [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Ueda, H.; Gang, L.; Okada, H. Fluid Structure Interaction Simulation in Three-Layered Aortic Aneurysm Model under Pulsatile Flow: Comparison of Wrapping and Stenting. J Biomech 2013, 46 (7), 1335–1342. [CrossRef]
- Simsek, F. G.; Kwon, Y. W. Investigation of Material Modeling in Fluid–Structure Interaction Analysis of an Idealized Three-Layered Abdominal Aorta: Aneurysm Initiation and Fully Developed Aneurysms. J Biol Phys 2015, 41 (2), 173–201. [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, A.; Zheng, Q.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Xue, Y.; Chen, W.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. The Biomechanical Effects of Different Membrane Layer Structures and Material Constitutive Modeling on Patient-Specific Cerebral Aneurysms. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Gasser, T. C.; Miller, C.; Polzer, S.; Roy, J. A Quarter of a Century Biomechanical Rupture Risk Assessment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Achievements, Clinical Relevance, and Ongoing Developments. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2023, 39 (4). [CrossRef]
- Bluestein, D.; Dumont, K.; De Beule, M.; Ricotta, J.; Impellizzeri, P.; Verhegghe, B.; Verdonck, P. Intraluminal Thrombus and Risk of Rupture in Patient Specific Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm - FSI Modelling. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2009, 12 (1), 73–81. [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Han, X.; Bi, Y.; Ju, S.; Gu, L. Fluid-Structure Interaction in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Effect of Modeling Techniques. Biomed Res Int 2017, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R. R. F.; Grytsan, A.; Biasetti, J.; Roy, J.; Liljeqvist, M. L.; Christian Gasser, T. Biomechanical Changes during Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Growth. PLoS One 2017, 12 (11). [CrossRef]
- Balzani, D.; Heinlein, A.; Klawonn, A.; Rheinbach, O.; Schröder, J. Comparison of Arterial Wall Models in Fluid–Structure Interaction Simulations. Comput Mech 2023, 72 (5), 949–965. [CrossRef]
- Józsa, T. I.; Paál, G. Boundary Conditions for Flow Simulations of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 2014, 50, 342–351. [CrossRef]
- Keramati, H.; Birgersson, E.; Ho, J. P.; Kim, S.; Chua, K. J.; Leo, H. L. The Effect of the Entry and Re-Entry Size in the Aortic Dissection: A Two-Way Fluid–Structure Interaction Simulation. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2020, 19 (6), 2643–2656. [CrossRef]
- Vande Geest, J. P.; Wang, D. H. J.; Wisniewski, S. R.; Makaroun, M. S.; Vorp, D. A. Towards A Noninvasive Method for Determination of Patient-Specific Wall Strength Distribution in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ann Biomed Eng 2006, 34 (7), 1098–1106. [CrossRef]
- Vande Geest, J. P.; Sacks, M. S.; Vorp, D. A. A Planar Biaxial Constitutive Relation for the Luminal Layer of Intra-Luminal Thrombus in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. J Biomech 2006, 39 (13), 2347–2354. [CrossRef]
- Raut, S. S.; Jana, A.; De Oliveira, V.; Muluk, S. C.; Finol, E. A. The Effect of Uncertainty in Vascular Wall Material Properties on Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Wall Mechanics. In Computational Biomechanics for Medicine: Fundamental Science and Patient-Specific Applications; Springer New York, 2014; Vol. 9781493907458, pp 69–86. [CrossRef]
- Polzer, S.; Gasser, T. C. Biomechanical Rupture Risk Assessment of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Based on a Novel Probabilistic Rupture Risk Index. J R Soc Interface 2015, 12 (113). [CrossRef]
- Federico, S.; Grillo, A.; Giaquinta, G.; Herzog, W. Convex Fung-Type Potentials for Biological Tissues. Meccanica 2008, 43 (3), 279–288. [CrossRef]
- Gasser, T. C.; Ogden, R. W.; Holzapfel, G. A. Hyperelastic Modelling of Arterial Layers with Distributed Collagen Fibre Orientations. J R Soc Interface 2006, 3 (6), 15–35. [CrossRef]
- Chuong, C. J.; Fung, Y. C. Three-Dimensional Stress Distribution in Arteries. J Biomech Eng 1983, 105 (3), 268–274. [CrossRef]
- Holzapfel, G. A.; Gasser, T. C. A Viscoelastic Model for Fiber-Reinforced Composites at Finite Strains: Continuum Basis, Computational Aspects and Applications. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2001, 190 (34), 4379–4403. [CrossRef]
- Choi, H. S.; Vito, R. P. Two-Dimensional Stress-Strain Relationship for Canine Pericardium. J Biomech Eng 1990, 112 (2), 153–159. [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, E. S.; Vorp, D. A. Effect of Variation in Intraluminal Thrombus Constitutive Properties on Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Wall Stress. Ann Biomed Eng 2003, 31 (7), 804–809. [CrossRef]
- Xenos, M.; Labropoulos, N.; Rambhia, S.; Alemu, Y.; Einav, S.; Tassiopoulos, A.; Sakalihasan, N.; Bluestein, D. Progression of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Towards Rupture: Refining Clinical Risk Assessment Using a Fully Coupled Fluid–Structure Interaction Method. Ann Biomed Eng 2015, 43 (1), 139–153. [CrossRef]
- De Borst, R.; Nithiarasu, P.; Tezduyar, T. E.; Yagawa, G.; Zohdi, T. COMPUTATIONAL FLUID-STRUCTURE INTERACTION WILEY SERIES IN COMPUTATIONAL MECHANICS Series Advisors; Wiley Series in Computational echanicsa, 2013.
- Reymond, P.; Crosetto, P.; Deparis, S.; Quarteroni, A.; Stergiopulos, N. Physiological Simulation of Blood Flow in the Aorta: Comparison of Hemodynamic Indices as Predicted by 3-D FSI, 3-D Rigid Wall and 1-D Models. Med Eng Phys 2013, 35 (6), 784–791. [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, P.; Reymond, P.; Deparis, S.; Kontaxakis, D.; Stergiopulos, N.; Quarteroni, A. Fluid-Structure Interaction Simulation of Aortic Blood Flow. Comput Fluids 2011, 43 (1), 46–57. [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, K.; Christopher, J.; Tezduyar, T. E.; Sathe, S. Space-Time Finite Element Computation of Arterial Fluid-Structure Interactions with Patient-Specific Data. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2010, 26 (1), 101–116. [CrossRef]
- Donea, J.; Giuliani, S.; Halleux, J. P. An Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian Finite Element Method for Transient Dynamic Fluid-Structure Interactions. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 1982, 33, 689–723.
- Pirola, S.; Cheng, Z.; Jarral, O. A.; O’Regan, D. P.; Pepper, J. R.; Athanasiou, T.; Xu, X. Y. On the Choice of Outlet Boundary Conditions for Patient-Specific Analysis of Aortic Flow Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. J Biomech 2017, 60, 15–21. [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, A.; Boccadifuoco, A.; Celi, S.; Salvetti, M. V. Hemodynamics and Stresses in Numerical Simulations of the Thoracic Aorta: Stochastic Sensitivity Analysis to Inlet Flow-Rate Waveform. Comput Fluids 2021, 230. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. J.; Vignon-Clementel, I. E.; Figueroa, C. A.; Ladisa, J. F.; Jansen, K. E.; Feinstein, J. A.; Taylor, C. A. On Coupling a Lumped Parameter Heart Model and a Three-Dimensional Finite Element Aorta Model. Ann Biomed Eng 2009, 37 (11), 2153–2169. [CrossRef]
- Bonfanti, M.; Franzetti, G.; Maritati, G.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Balabani, S.; Díaz-Zuccarini, V. Patient-Specific Haemodynamic Simulations of Complex Aortic Dissections Informed by Commonly Available Clinical Datasets. Med Eng Phys 2019, 71, 45–55. [CrossRef]
- Formaggia, L.; Lamponi, D.; Tuveri, M.; Veneziani, A. Numerical Modeling of 1D Arterial Networks Coupled with a Lumped Parameters Description of the Heart. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2006, 9 (5), 273–288. [CrossRef]
- Alastruey, J.; Xiao, N.; Fok, H.; Schaeffter, T.; Figueroa, C. A. On the Impact of Modelling Assumptions in Multi-Scale, Subject-Specific Models of Aortic Haemodynamics. J R Soc Interface 2016, 13 (119). [CrossRef]
- van ’t Veer, M.; Buth, J.; Merkx, M.; Tonino, P.; van den Bosch, H.; Pijls, N.; van de Vosse, F. Biomechanical Properties of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Assessed by Simultaneously Measured Pressure and Volume Changes in Humans. J Vasc Surg 2008, 48 (6), 1401–1407. [CrossRef]
- Youssefi, P.; Gomez, A.; Arthurs, C.; Sharma, R.; Jahangiri, M.; Figueroa, C. A. Impact of Patient-Specific Inflow Velocity Profile on Hemodynamics of the Thoracic Aorta. J Biomech Eng 2018, 140 (1). [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Kidher, E.; Jarral, O. A.; O’Regan, D. P.; Wood, N. B.; Athanasiou, T.; Xu, X. Y. Assessment of Hemodynamic Conditions in the Aorta Following Root Replacement with Composite Valve-Conduit Graft. Ann Biomed Eng 2016, 44 (5), 1392–1404. [CrossRef]
- Pirola, S.; Guo, B.; Menichini, C.; Saitta, S.; Fu, W.; Dong, Z.; Xu, X. Y. 4-D Flow Mri-Based Computational Analysis of Blood Flow in Patient-Specific Aortic Dissection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2019, 66 (12), 3411–3419. [CrossRef]
- Markl, M.; Schnell, S.; Wu, C.; Bollache, E.; Jarvis, K.; Barker, A. J.; Robinson, J. D.; Rigsby, C. K. Advanced Flow MRI: Emerging Techniques and Applications. Clin Radiol 2016, 71 (8), 779–795. [CrossRef]
- Lodi Rizzini, M.; Gallo, D.; De Nisco, G.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Chiastra, C.; Bocchino, P. P.; Piroli, F.; De Ferrari, G. M.; Morbiducci, U. Does the Inflow Velocity Profile Influence Physiologically Relevant Flow Patterns in Computational Hemodynamic Models of Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery? Med Eng Phys 2020, 82, 58–69. [CrossRef]
- Armour, C. H.; Guo, B.; Pirola, S.; Saitta, S.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Xu, X. Y. The Influence of Inlet Velocity Profile on Predicted Flow in Type B Aortic Dissection. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2021, 20 (2), 481–490. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhuang, J.; Wu, Y. The Effect of Womersley Number and Particle Radius on the Accumulation of Lipoproteins in the Human Aorta. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2020, 23 (10), 571–584. [CrossRef]
- Bit, A.; Alblawi, A.; Chattopadhyay, H.; Quais, Q. A.; Benim, A. C.; Rahimi-Gorji, M.; Do, H. T. Three Dimensional Numerical Analysis of Hemodynamic of Stenosed Artery Considering Realistic Outlet Boundary Conditions. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2020, 185, 105163. [CrossRef]
- Colciago, C. M.; Deparis, S.; Domanin, M.; Riccobene, C.; Schenone, E.; Quarteroni, A. Analysis of Morphological and Haemodynamical Indexes in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms as Preliminary Indicators of Intraluminal Thrombus Deposition. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2020, 19, 1035–1053. [CrossRef]
- Arzani, A.; Suh, G. Y.; Dalman, R. L.; Shadden, S. C. A Longitudinal Comparison of Hemodynamics and Intraluminal Thrombus Deposition in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2014, 307 (12), H1786–H1795. [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.; Anupindi, K.; Patnaik, B. S. V. Influence of Wall Shear Stress and Geometry on the Lumen Surface Concentration of Low Density Lipoprotein in a Model Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Physics of Fluids 2019, 31 (1). [CrossRef]
- Hardman, D.; Semple, S. I.; Richards, J. M. J.; Hoskins, P. R. Comparison of Patient-Specific Inlet Boundary Conditions in the Numerical Modelling of Blood Flow in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Disease. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2013, 29 (2), 165–178. [CrossRef]
- Lozowy, R. J.; Kuhn, D. C. S.; Ducas, A. A.; Boyd, A. J. The Relationship Between Pulsatile Flow Impingement and Intraluminal Thrombus Deposition in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Cardiovasc Eng Technol 2017, 8 (1), 57–69. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z. A.; Huddleston, C.; Trusty, P. M.; Singh-Gryzbon, S.; Fogel, M. A.; Veneziani, A.; Yoganathan, A. P. Analysis of Inlet Velocity Profiles in Numerical Assessment of Fontan Hemodynamics. Ann Biomed Eng 2019, 47 (11), 2258–2270. [CrossRef]
- Tzirakis, K.; Kamarianakis, Y.; Kontopodis, N.; Ioannou, C. V. The Effect of Blood Rheology and Inlet Boundary Conditions on Realistic Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms under Pulsatile Flow Conditions. Bioengineering 2023, 10 (2). [CrossRef]
- Womersley, J. R. Method for the Calculation of Velocity, Rate of Flow and Viscous Drag in Arteries When the Pressure Gradient Is Known. J Physiol 1955, 127 (3), 553–563. [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I. C.; Ries, J.; Dhawan, S. S.; Quyyumi, A. A.; Taylor, W. R.; Oshinski, J. N. Effect of Inlet Velocity Profiles on Patient-Specific Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations of the Carotid Bifurcation. J Biomech Eng 2012, 134 (5). [CrossRef]
- Impiombato, A. N.; La Civita, G.; Orlandi, F.; Franceschini Zinani, F. S.; Oliveira Rocha, L. A.; Biserni, C. A Simple Transient Poiseuille-Based Approach to Mimic the Womersley Function and to Model Pulsatile Blood Flow. Dynamics 2021, 1 (1), 9–17. [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, S.; Kemmerling, E. M. C. The Effect of Inlet and Outlet Boundary Conditions in Image-Based CFD Modeling of Aortic Flow. Biomed Eng Online 2018, 17 (1). [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mao, W. Li-2023-A Fast Approach to Estimating Windkessel Model Parameters For. Comput Fluids 2023, 259. [CrossRef]
- Javadzadegan, A.; Simmons, A.; Behnia, M.; Barber, T. Computational Modelling of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Effect of Suprarenal vs Infrarenal Positions. European Journal of Mechanics, B/Fluids 2017, 61, 112–124. [CrossRef]
- Von Spiczak, J.; Crelier, G.; Giese, D.; Kozerke, S.; Maintz, D.; Bunck, A. C. Quantitative Analysis of Vortical Blood Flow in the Thoracic Aorta Using 4D Phase Contrast MRI. PLoS One 2015, 10 (9). [CrossRef]
- Stonebridge, P.; Thompson, A.; Dick, J.; Hunter, G.; Chudek, J. A.; Houston, J.; Belch, J. Non Spiral and Spiral (Helical) Flow Patterns in Stenoses. In Vitro Observations Using Spin and Gradient Echo Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computational Fluid Dynamic Modeling. Int Angiol 2004, 23, 276–283.
- Vignon-Clementel, I. E.; Alberto Figueroa, C.; Jansen, K. E.; Taylor, C. A. Outflow Boundary Conditions for Three-Dimensional Finite Element Modeling of Blood Flow and Pressure in Arteries. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2006, 195 (29–32), 3776–3796. [CrossRef]
- Vignon-Clementel, I. E.; Figueroa, C. A.; Jansen, K. E.; Taylor, C. A. Outflow Boundary Conditions for 3D Simulations of Non-Periodic Blood Flow and Pressure Fields in Deformable Arteries. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2010, 13 (5), 625–640. [CrossRef]
- Gallo, D.; De Santis, G.; Negri, F.; Tresoldi, D.; Ponzini, R.; Massai, D.; Deriu, M. A.; Segers, P.; Verhegghe, B.; Rizzo, G.; Morbiducci, U. On the Use of in Vivo Measured Flow Rates as Boundary Conditions for Image-Based Hemodynamic Models of the Human Aorta: Implications for Indicators of Abnormal Flow. Ann Biomed Eng 2012, 40 (3), 729–741. [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M. J.; McCullough, J. P.; Kelly, S. An Investigation of the Relationship between Hemodynamics and Thrombus Deposition within Patient-Specific Models of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 2012, 226 (7), 548–564. [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, M. J.; McCullough, J. P. An Investigation of the Flow Field within Patient-Specific Models of an Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm under Steady Inflow Conditions. In Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine; 2010; Vol. 224, pp 971–988. [CrossRef]
- Raptis, A.; Xenos, M.; Dimas, S.; Giannoukas, A.; Labropoulos, N.; Bluestein, D.; Matsagkas, M. I. Effect of Macroscale Formation of Intraluminal Thrombus on Blood Flow in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2016, 19 (1), 84–92. [CrossRef]
- Arzani, A.; Gambaruto, A. M.; Chen, G.; Shadden, S. C. Wall Shear Stress Exposure Time: A Lagrangian Measure of near-Wall Stagnation and Concentration in Cardiovascular Flows. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2017, 16 (3), 787–803. [CrossRef]
- Belkacemi, D.; Tahar Abbes, M.; Al-Rawi, M.; Al-Jumaily, A. M.; Bachene, S.; Laribi, B. Intraluminal Thrombus Characteristics in AAA Patients: Non-Invasive Diagnosis Using CFD. Bioengineering 2023, 10 (5). [CrossRef]
- Casciaro, M. E.; Dottori, J.; El-Batti, S.; Alsac, J. M.; Mousseaux, E.; Larrabide, I.; Craiem, D. Effects on Aortoiliac Fluid Dynamics After Endovascular Sealing of Abdominal Aneurysms. Vasc Endovascular Surg 2018, 52 (8), 621–628. [CrossRef]
- Dottori, J.; Casciaro, M.; Craiem, D.; El-Batti, S.; Mousseaux, E.; Alsac, J. M.; Larrabide, I. Regional Assessment of Vascular Morphology and Hemodynamics: Methodology and Evaluation for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms after Endovascular Repair. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2020, 23 (14), 1060–1070. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Urquijo, M.; de Zamacona, R. G.; Mendoza, A. K. M.; Iribarren, M. Z.; Ibarra, E. G.; Bencomo, M. D. M.; Fabiani, M. A. 3D Modeling of Blood Flow in Simulated Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Vasc Endovascular Surg 2021, 55 (7), 677–683. [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K. B.; Shadden, S. C. A Reduced-Dimensional Model for near-Wall Transport in Cardiovascular Flows. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2016, 15 (3), 713–722. [CrossRef]
- McClarty, D. B.; Kuhn, D. C. S.; Boyd, A. J. Hemodynamic Changes in an Actively Rupturing Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. J Vasc Res 2021, 58 (3), 172–179. [CrossRef]
- Rezaeitaleshmahalleh, M.; Lyu, Z.; Mu, N.; Zhang, X.; Rasmussen, T. E.; McBane, R. D.; Jiang, J. Characterization of Small Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms’ Growth Status Using Spatial Pattern Analysis of Aneurismal Hemodynamics. Sci Rep 2023, 13 (1). [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Wen, J.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, T. Numerical Identification of the Rupture Locations in Patient-Specific Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmsusing Hemodynamic Parameters. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2018, 21 (1), 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Poelma, C.; Watton, P. N.; Ventikos, Y. Transitional Flow in Aneurysms and the Computation of Haemodynamic Parameters. J R Soc Interface 2015, 12 (105). [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, T.; Zheng, T.; Yuan, D. Association Between Blood Flow Pattern and Rupture Risk of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Based on Computational Fluid Dynamics. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery 2022, 64 (2–3), 155–164. [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, B. A.; Gharahi, H.; Lim, C. Y.; Jaberi, F. A.; Choi, J.; Lee, W.; Baek, S. Association of Intraluminal Thrombus, Hemodynamic Forces, and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Expansion Using Longitudinal CT Images. Ann Biomed Eng 2016, 44 (5), 1502–1514. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xiong, J.; Chen, Z.; Deng, X.; Xu, Z.; Sun, A.; Fan, Y. Gender Differences of Morphological and Hemodynamic Characteristics of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Biol Sex Differ 2020, 11 (1). [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kleinstreuer, C. Fluid-Structure Interaction Effects on Sac-Blood Pressure and Wall Stress in a Stented Aneurysm. J Biomech Eng 2005, 127 (4), 662–671. [CrossRef]
- Biasetti, J.; Gasser, T. C.; Auer, M.; Hedin, U.; Labruto, F. Hemodynamics of the Normal Aorta Compared to Fusiform and Saccular Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms with Emphasis on a Potential Thrombus Formation Mechanism. Ann Biomed Eng 2010, 38 (2), 380–390. [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; He, W.; Huang, X.; Ma, J.; Yuan, T.; Shi, Y.; Wang, S. The Study on the Impact of AAA Wall Motion on the Hemodynamics Based on 4D CT Image Data. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Ene, F.; Delassus, P.; Morris, L. The Influence of Computational Assumptions on Analysing Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Haemodynamics. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 2014, 228 (8), 768–780. [CrossRef]
- Arzani, A.; Dyverfeldt, P.; Ebbers, T.; Shadden, S. C. In Vivo Validation of Numerical Prediction for Turbulence Intensity in an Aortic Coarctation. Ann Biomed Eng 2012, 40 (4), 860–870. [CrossRef]
- Reymond, P.; Merenda, F.; Perren, F.; Rü, D.; Stergiopulos, N. Validation of a One-Dimensional Model of the Systemic Arterial Tree. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2009, 297, 208–222. [CrossRef]
- Salman, H. E.; Ramazanli, B.; Yavuz, M. M.; Yalcin, H. C. Biomechanical Investigation of Disturbed Hemodynamics-Induced Tissue Degeneration in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Using Computational and Experimental Techniques. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2019, 7. [CrossRef]
- Sherman, T. F. On Connecting Large Vessels to Small The Meaning of Murray’s Law. J Gen Physiol 1981, 78.
- Painter, P. R.; Edén, P.; Bengtsson, H. U. Pulsatile Blood Flow, Shear Force, Energy Dissipation and Murray’s Law. Theor Biol Med Model 2006, 3. [CrossRef]
- Murray, C. D. The Physiological Principle of Minimum Work. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1926, 12 (3), 207–214. [CrossRef]
- Boccadifuoco, A.; Mariotti, A.; Celi, S.; Martini, N.; Salvetti, M. V. Impact of Uncertainties in Outflow Boundary Conditions on the Predictions of Hemodynamic Simulations of Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms. Comput Fluids 2018, 165, 96–115. [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Chen, R.; Wu, B.; Shiu, W. S.; Cai, X. C. Numerical Simulation of Blood Flows in Patient-Specific Abdominal Aorta with Primary Organs. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2021, 20 (3), 909–924. [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Wu, B.; Shiu, W. S.; Yan, Z.; hen, R.; Cai, X. C. Efficient Parallel Simulation of Hemodynamics in Patient-Specific Abdominal Aorta with Aneurysm. Comput Biol Med 2021, 136. [CrossRef]
- Lo, S. C. Y.; McCullough, J. W. S.; Coveney, P. V. Parametric Analysis of an Efficient Boundary Condition to Control Outlet Flow Rates in Large Arterial Networks. Sci Rep 2022, 12 (1). [CrossRef]
- Caballero, A. D.; Laín, S. A Review on Computational Fluid Dynamics Modelling in Human Thoracic Aorta. Cardiovasc Eng Technol 2013, 4 (2), 103–130. [CrossRef]
- Arbia, G.; Vignon-Clementel, I.; Hsia, T. Y.; Gerbeau, J.-F.; Arbia, G.; Vignon-Clementel, I. E.; Hsia, T.-Y.; Gerbeau, J.-F. Modified Navier-Stokes Equations for the Outflow Boundary Conditions in Hemodynamics. European Journal of Me-chanics-B/Fluids 2016, 60, 175–188. [CrossRef]
- Vignon-Clementel, I. E.; Figueroa, C. A.; Jansen, K. E.; Taylor, C. A. Outflow Boundary Conditions for 3D Simulations of Non-Periodic Blood Flow and Pressure Fields in Deformable Arteries. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2010, 13 (5), 625–640. [CrossRef]
- Vignon-Clementel, I. E.; Alberto Figueroa, C.; Jansen, K. E.; Taylor, C. A. Outflow Boundary Conditions for Three-Dimensional Finite Element Modeling of Blood Flow and Pressure in Arteries. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2006, 195 (29–32), 3776–3796. [CrossRef]
- Ladisa, J. F.; Alberto Figueroa, C.; Vignon-Clementel, I. E.; Jin Kim, H.; Xiao, N.; Ellwein, L. M.; Chan, F. P.; Feinstein, J. A.; Taylor, C. A. Computational Simulations for Aortic Coarctation: Representative Results from a Sampling of Patients. J Biomech Eng 2011, 133 (9). [CrossRef]
- Stergiopulos, N.; Westerhof, B. E.; Westerhof, N. Total Arterial Inertance as the Fourth Element of the Windkessel Model; 1999.
- Westerhof, N.; Lankhaar, J. W.; Westerhof, B. E. The Arterial Windkessel. Med Biol Eng Comput 2009, 47 (2), 131–141. [CrossRef]
- Lo, S. C. Y.; McCullough, J. W. S.; Xue, X.; Coveney, P. V. Uncertainty Quantification of the Impact of Peripheral Arterial Disease on Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms in Blood Flow Simulations. J R Soc Interface 2024, 21 (213). [CrossRef]
- Torii, R.; Oshima, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Takagi, K.; Tezduyar, T. E. Computer Modeling of Cardiovascular Fluid-Structure Interactions with the Deforming-Spatial-Domain/Stabilized Space-Time Formulation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 2006, 195 (13–16), 1885–1895. [CrossRef]
- Les, A. S.; Medina, F.; Wicker, R. B.; Mcconneil, M. V; Taylor^, C. A. Ethan 0. Kung In Vitro Validation of Finite-Element Model of AAA Hemodynamics Incorporating Realistic Outlet Boundary Conditions. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Taebi, A.; Pillai, R. M.; Roudsari, B. S.; Vu, C. T.; Roncali, E. Computational Modeling of the Liver Arterial Blood Flow for Microsphere Therapy: Effect of Boundary Conditions. Bioengineering 2020, 7 (3), 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Alastruey, J.; Figueroa, C. A. A Systematic Comparison between 1-D and 3-D Hemodynamics in Compliant Arterial Models. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2014, 30 (2), 204–231. [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Agu, O.; Balabani, S.; Díaz-Zuccarini, V. Development of a Patient-Specific Simulation Tool to Analyse Aortic Dissections: Assessment of Mixed Patient-Specific Flow and Pressure Boundary Conditions. Med Eng Phys 2014, 36 (3), 275–284. [CrossRef]
- Jonášová, A.; Vimmr, J. On the Relevance of Boundary Conditions and Viscosity Models in Blood Flow Simulations in Patient-Specific Aorto-Coronary Bypass Models. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2021, 37 (4). [CrossRef]
- Romarowski, R. M.; Lefieux, A.; Morganti, S.; Veneziani, A.; Auricchio, F. Patient-Specific CFD Modelling in the Thoracic Aorta with PC-MRI–Based Boundary Conditions: A Least-Square Three-Element Windkessel Approach. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2018, 34 (11). [CrossRef]
- Joly, F.; Soulez, G.; Lessard, S.; Kauffmann, C.; Vignon-Clementel, I. A Cohort Longitudinal Study Identifies Morphology and Hemodynamics Predictors of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Growth. Ann Biomed Eng 2020, 48 (2), 606–623. [CrossRef]
- Joly, F.; Soulez, G.; Garcia, D.; Lessard, S.; Kauffmann, C. Flow Stagnation Volume and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Growth: Insights from Patient-Specific Computational Fluid Dynamics of Lagrangian-Coherent Structures. Comput Biol Med 2018, 92, 98–109. [CrossRef]
- Capellini, K.; Gasparotti, E.; Cella, U.; Costa, E.; Fanni, B. M.; Groth, C.; Porziani, S.; Biancolini, M. E.; Celi, S. A Novel Formulation for the Study of the Ascending Aortic Fluid Dynamics with in Vivo Data. Med Eng Phys 2022, 91, 68–78. [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Hoeijmakers, M.; Geronzi, L.; Morgenthaler, V.; Tomasi, J.; Rochette, M.; Biancolini, M. E. Effect of Turbulence and Viscosity Models on Wall Shear Stress Derived Biomarkers for Aorta Simulations. Comput Biol Med 2023, 167. [CrossRef]
- Stokes, C.; Bonfanti, M.; Li, Z.; Xiong, J.; Chen, D.; Balabani, S.; Díaz-Zuccarini, V. A Novel MRI-Based Data Fusion Methodology for Efficient, Personalised, Compliant Simulations of Aortic Haemodynamics. J Biomech 2021, 129. [CrossRef]
- Fonken, J.; Maas, E.; Nievergeld, A.; van Sambeek, M.; van de Vosse, F.; Lopata, R. The Impact of a Limited Field-of-View on Computed Hemodynamics in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Evaluating the Feasibility of Completing Ultrasound Segmentations with Parametric Geometries. Ann Biomed Eng 2023, 51 (6), 1296–1309. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, D.; Wu, P.; Li, X.; Zheng, T. A Two-Fluid Blood Stasis Model for False Lumen Thrombosis after Type B Dissection Repair. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2022, 25 (13), 1499–1508. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xiang, G.; Du, G.; Li, X.; Wu, P.; Du, X. A Hemodynamic Analysis of Fenestrated Physician-Modified Endograft Repair for Complicated Aortic Dissections Involving the Visceral Arteries. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2023, 242. [CrossRef]
- Di Achille, P.; Tellides, G.; Figueroa, C. A.; Humphrey, J. D. A Haemodynamic Predictor of Intraluminal Thrombus Formation in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 2014, 470 (2172). [CrossRef]
- Stokes, C.; Haupt, F.; Becker, D.; Muthurangu, V.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Balabani, S.; Díaz-Zuccarini, V. The Influence of Minor Aortic Branches in Patient-Specific Flow Simulations of Type-B Aortic Dissection. Ann Biomed Eng 2023, 51 (7), 1627–1644. [CrossRef]
- Kandail, H.; Hamady, M.; Xu, X. Y. Effect of a Flared Renal Stent on the Performance of Fenestrated Stent-Grafts at Rest and Exercise Conditions. Journal of Endovascular Therapy 2016, 23 (5), 809–820. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Piccinelli, M.; Leshnower, B. G.; Lefieux, A.; Taylor, W. R.; Veneziani, A. Coupled Morphological–Hemodynamic Computational Analysis of Type B Aortic Dissection: A Longitudinal Study. Ann Biomed Eng 2018, 46 (7), 927–939. [CrossRef]
- Pant, S.; Fabrèges, B.; Gerbeau, J. F.; Vignon-Clementel, I. E. A Methodological Paradigm for Patient-Specific Multi-Scale CFD Simulations: From Clinical Measurements to Parameter Estimates for Individual Analysis. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2014, 30 (12), 1614–1648. [CrossRef]
- Spilker, R. L.; Taylor, C. A. Tuning Multidomain Hemodynamic Simulations to Match Physiological Measurements. Ann Biomed Eng 2010, 38 (8), 2635–2648. [CrossRef]
- Di Achille, P.; Tellides, G.; Humphrey, J. D. Hemodynamics-Driven Deposition of Intraluminal Thrombus in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2017, 33 (5). [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, L. J.; Powell, J. T.; Norman, P. E.; Miller, K.; Doyle, B. J. A Comparison of Hemodynamic Metrics and Intraluminal Thrombus Burden in a Common Iliac Artery Aneurysm. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2017, 33 (5). [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, R.; Yuan, H.; Peng, Y.; Wu, M.; Chen, Z.; Guo, W.; Gao, T.; Xiong, J.; Chen, D. Retrograde Branched Extension Limb Assembling Stent of Pararenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: A Longitudinal Hemodynamic Analysis for Stent Graft Migration. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2020, 36 (11). [CrossRef]
- Feher, J. Multiscale, Multiphysics and Reduced Order Modelling Techniques for Hemodynamics. Ph.D., Politecnico di Milano, 2019.
- Schenkel, T.; Halliday, I. Continuum Scale Non Newtonian Particle Transport Model for Hæmorheology. Mathematics 2021, 9 (17). [CrossRef]
- Saha, S. C.; Francis, I.; Saha, G.; Huang, X.; Molla, M. M. Hemodynamic Insights into Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Bridging the Knowledge Gap for Improved Patient Care. Fluids 2024, 9 (2). [CrossRef]
- Menichini, C.; Xu, X. Y. Mathematical Modeling of Thrombus Formation in Idealized Models of Aortic Dissection: Initial Findings and Potential Applications. J Math Biol 2016, 73 (5), 1205–1226. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shadden, S. C. Coupled Simulation of Hemodynamics and Vascular Growth and Remodeling in a Subject-Specific Geometry. Ann Biomed Eng 2015, 43 (7), 1543–1554. [CrossRef]
- Vignon, I. E.; Taylor, C. A. Outflow Boundary Conditions for One-Dimensional Finite Element Modeling of Blood Flow and Pressure Waves in Arteries. Wave Motion 2004, 39 (4), 361–374. [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Yang, C.; Zheng, J.; Woodard, P. K.; Saffitz, J. E.; Sicard, G. A.; Pilgram, T. K.; Yuan, C. Quantifying Effects of Plaque Structure and Material Properties on Stress Distributions in Human Atherosclerotic Plaques Using 3D FSI Models. J Biomech Eng 2005, 127 (7), 1185–1194.
- Hinnen, J. W.; Koning, O. H. J.; Visser, M. J. T.; Van Bockel, H. J. Effect of Intraluminal Thrombus on Pressure Transmission in the Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. J Vasc Surg 2005, 42 (6), 1176–1182. [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, P.; Reymond, P.; Deparis, S.; Kontaxakis, D.; Stergiopulos, N.; Quarteroni, A. Fluid–Structure Interaction Simulation of Aortic Blood Flow. Comput Fluids 2011, 43 (1), 46–57. [CrossRef]
- Moireau, P.; Bertoglio, C.; Xiao, N.; Figueroa, C. A.; Taylor, C. A.; Chapelle, D.; Gerbeau, J.-F. Sequential Identification of Boundary Support Parameters in a Fluid-Structure Vascular Model Using Patient Image Data. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2013, 12 (3), 475–496. [CrossRef]
- Moireau, P.; Xiao, N.; Astorino, M.; Figueroa, C. A.; Chapelle, D.; Taylor, C. A.; Gerbeau, J.-F. External Tissue Support and Fluid–Structure Simulation in Blood Flows. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2012, 11 (1), 1–18. [CrossRef]
- DA SILVA, M. L. F.; Gonçalves, S. D. F.; Haniel, J.; Lucas, T. C.; Huebner, R. Comparative Study between 1-Way and 2-Way Coupled Fluid-Structure Interaction in Numerical Simulation of Aortic Arch Aneurysms. An Acad Bras Cienc 2023, 95. [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S. I. S.; Campos, J. B. L. M. Numerical Study of Wall Shear Stress-Based Descriptors in the Human Left Coronary Artery. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 2016, 19 (13), 1443–1455. [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, O.; Salman, H. E.; Al-Thani, H.; El-Menyar, A.; Qidwai, U. A.; Yalcin, H. C. How Does Hemodynamics Affect Rupture Tissue Mechanics in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Focus on Wall Shear Stress Derived Parameters, Time-Averaged Wall Shear Stress, Oscillatory Shear Index, Endothelial Cell Activation Potential, and Relative Residence Time. Comput Biol Med 2023, 154. [CrossRef]
- Saqr, K. M.; Rashad, S.; Tupin, S.; Niizuma, K.; Hassan, T.; Tominaga, T.; Ohta, M. What Does Computational Fluid Dynamics Tell Us about Intracranial Aneurysms? A Meta-Analysis and Critical Review. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2020, 40 (5), 1021–1039. [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, B. A.; Gharahi, H.; Lim, C. Y.; Lee, W.; Baek, S. Association of Vortical Structures and Hemodynamic Parameters for Regional Thrombus Accumulation in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2022, 38 (2). [CrossRef]
- Epps, B. Review of Vortex Identification Methods. In 55th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting; AIAA SciTech Forum; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Qi, M.; Wang, X. Comparison of Vortex Identification Criteria for Planar Velocity Fields in Wall Turbulence. Physics of Fluids 2015, 27 (8), 085101. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gao, Y.; Tian, S.; Dong, X. Rortex - A New Vortex Vector Definition and Vorticity Tensor and Vector Decompositions. Physics of Fluids 2018, 30 (3). [CrossRef]
- Fillinger, M. F.; Marra, S. P.; Raghavan, M. L.; Kennedy, F. E. Prediction of Rupture Risk in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm during Observation: Wall Stress versus Diameter. J Vasc Surg 2003, 37 (4), 724–732. [CrossRef]
- Özcan, C.; Kocatürk, Ö.; Işlak, C.; Öztürk, C. Integrated Particle Image Velocimetry and Fluid–Structure Interaction Analysis for Patient-Specific Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Studies. Biomed Eng Online 2023, 22 (1). [CrossRef]
- Rissland, P.; Alemu, Y.; Einav, S.; Ricotta, J.; Bluestein, D. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Risk of Rupture: Patient-Specific FSI Simulations Using Anisotropic Model. J Biomech Eng 2009, 131 (3). [CrossRef]
- Canchi, T.; Saxena, A.; Ng, E.; Pwee, E. C.; Narayanan, S. Application of Fluid Structure Interaction Methods to Estimate the Mechanics of Rupture in Asian Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Bionanoscience 2018, 8. [CrossRef]
- Mesri, Y.; Niazmand, H.; Deyranlou, A. Numerical Study on Fluid-Structure Interaction in a Patient-Specific Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm for Evaluating Wall Heterogeneity and Material Model Effects on Its Rupture. Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics 2017, 10 (6), 1699–1709. [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, M.; Kratzbergö J; Simão Da Silva, E. Heterogeneous, Variable Wall-Thickness Modeling of a Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. In IMECE2004-60018; 2004.
- Raut, S. S.; Jana, A.; De Oliveira, V.; Muluk, S. C.; Finol, E. A. The Importance of Patient-Specific Regionally Varying Wall Thickness in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Biomechanics. J Biomech Eng 2013, 135 (8). [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, L. J.; Powell, J. T.; Norman, P. E.; Miller, K.; Doyle, B. J. A Comparison of Hemodynamic Metrics and Intraluminal Thrombus Burden in a Common Iliac Artery Aneurysm. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 2017, 33 (5). [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.; Berg, N.; Prahl Wittberg, L. Pulsatile Aortic Blood Flow—A Critical Assessment of Boundary Conditions. J Eng Sci Med Diagn Ther 2021, 4 (1). [CrossRef]
- Varble, N.; Kono, K.; Rajabzadeh-Oghaz, H.; Meng, H. Rupture Resemblance Models May Correlate to Growth Rates of Intracranial Aneurysms: Preliminary Results. World Neurosurg 2018, 110, e794–e805. [CrossRef]
- Varshney, M.; Farooqi, M. H.; Usmani, A. Y. Quantifying Hemodynamics within an Aneurysm Exposed to Prolonged Exercise Levels. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2020, 184. [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J. min; Lu, T. dong; Yang, Z. yun; Hu, W. qing; Su, W. Influence of the Flow Field and Vortex Structure of Patient-Specific Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm with Intraluminal Thrombus on the Arterial Wall. Engineering Applications of Computational Fluid Mechanics 2022, 16 (1), 2100–2122. [CrossRef]
- Domingos, P. A Few Useful Things to Know about Machine Learning. Communications of the ACM. October 2012, pp 78–87. [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521 (7553), 436–444. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, M.; Martin, C.; Sun, W. A Deep Learning Approach to Estimate Stress Distribution: A Fast and Accurate Surrogate of Finite-Element Analysis. J R Soc Interface 2018, 15 (138). [CrossRef]
- Taye, M. M. Understanding of Machine Learning with Deep Learning: Architectures, Workflow, Applications and Future Directions. Computers 2023, 12 (5). [CrossRef]
- Larochelle, H.; Bengio, Y.; Louradour, J.; Ca, L. U. Exploring Strategies for Training Deep Neural Networks Pascal Lamblin. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2009, 1, 1–40.
- O’Shea, K.; Nash, R. An Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks. 2015.
- Basha, S. H. S.; Dubey, S. R.; Pulabaigari, V.; Mukherjee, S. Impact of Fully Connected Layers on Performance of Convolutional Neural Networks for Image Classification. Neurocomputing 2020, 378, 112–119. [CrossRef]
- Aloysius, N.; Geetha, M. A Review on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In 2017 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP); 2017; pp 588–592. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Ullah, S.; Khan, M. J.; Khurshid, K. Comparative Analysis of SVM, Ann and Cnn for Classifying Vegetation Species Using Hyperspectral Thermal Infrared Data. In International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences - ISPRS Archives; International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019; Vol. 42, pp 1861–1868. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A Survey of Convolutional Neural Networks: Analysis, Applications, and Prospects. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 2022, 33 (12), 6999–7019. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; King, K.; Rezaeitaleshmahalleh, M.; Pienta, D.; Mu, N.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, J. Deep-Learning-Based Image Segmentation for Image-Based Computational Hemodynamic Analysis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A Comparison Study. Biomed Phys Eng Express 2023, 9 (6). [CrossRef]
- Abdolmanafi, A.; Forneris, A.; Moore, R. D.; Di Martino, E. S. Deep-Learning Method for Fully Automatic Segmentation of the Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm from Computed Tomography Imaging. Front Cardiovasc Med 2023, 9–2022. [CrossRef]
- López-Linares, K.; Aranjuelo, N.; Kabongo, L.; Maclair, G.; Lete, N.; Ceresa, M.; García-Familiar, A.; Macía, I.; González Ballester, M. A. Fully Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Abdominal Aortic Thrombus in Post-Operative CTA Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Med Image Anal 2018, 46, 202–214. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Mao, W.; Sun, W. A Feasibility Study of Deep Learning for Predicting Hemodynamics of Human Thoracic Aorta. J Biomech 2020, 99. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, M.; Martin, C.; Elefteriades, J. A.; Sun, W. A Machine Learning Approach to Investigate the Relationship between Shape Features and Numerically Predicted Risk of Ascending Aortic Aneurysm. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2017, 16 (5), 1519–1533. [CrossRef]
- Rościszewski, P.; Krzywaniak, A.; Iserte, S.; Rojek, K.; Gepner, P. Optimizing Throughput of Seq2Seq Model Training on the IPU Platform for AI-Accelerated CFD Simulations. Future Generation Computer Systems 2023, 147, 149–162. [CrossRef]
- Feiger, B.; Gounley, J.; Adler, D.; Leopold, J. A.; Draeger, E. W.; Chaudhury, R.; Ryan, J.; Pathangey, G.; Winarta, K.; Frakes, D.; Michor, F.; Randles, A. Accelerating Massively Parallel Hemodynamic Models of Coarctation of the Aorta Using Neural Networks. Sci Rep 2020, 10 (1). [CrossRef]
- Hahn, L. D.; Baeumler, K.; Hsiao, A. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Aortic Disease. Curr Opin Cardiol 2021, 36 (6).
- Kim, S.; Jiang, Z.; Zambrano, B. A.; Jang, Y.; Baek, S.; Yoo, S.; Chang, H.-J. Deep Learning on Multiphysical Features and Hemodynamic Modeling for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Growth Prediction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2023, 42 (1), 196–208. [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Bahadori, M. T.; Schuetz, A.; Stewart, W. F.; Sun, J. Doctor AI: Predicting Clinical Events via Recurrent Neural Networks.
- Mushtaq, S.; Singh, O. Convolution Neural Networks for Disease Prediction: Applications and Challenges. Scalable Computing: Practice and Experience 2024, 25 (1), 615–636. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Do, H. N.; Choi, J.; Lee, W.; Baek, S. A Deep Learning Approach to Predict Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Expansion Using Longitudinal Data. Front Phys 2020, 7. [CrossRef]
- Soudah, E.; Rodriguez, J. F.; Lopez, R. Mechanical Stress in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms Using Artificial Neural Networks. J Mech Med Biol 2014, 15 (03), 1550029. [CrossRef]
- Thamsen, B.; Yevtushenko, P.; Gundelwein, L.; Lamecker, H.; Kühne, T.; Goubergrits, L. Unsupervised Learning and Statistical Shape Modeling of the Morphometry and Hemodynamics of Coarctation of the Aorta; 2020. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Choi, J.; Baek, S. Machine Learning Approaches to Surrogate Multifidelity Growth and Remodeling Models for Efficient Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmal Applications. Comput Biol Med 2021, 133. [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Naranjo, A.; Marin-Castrillon, D. M.; Decourselle, T.; Lin, S.; Leclerc, S.; Morgant, M. C.; Bernard, C.; De Oliveira, S.; Boucher, A.; Presles, B.; Bouchot, O.; Christophe, J. J.; Lalande, A. Segmentation of 4D Flow MRI: Comparison between 3D Deep Learning and Velocity-Based Level Sets. J Imaging 2023, 9 (6). [CrossRef]
- Ferdian, E.; Marlevi, D.; Schollenberger, J.; Aristova, M.; Edelman, E. R.; Schnell, S.; Figueroa, C. A.; Nordsletten, D. A.; Young, A. A. Cerebrovascular Super-Resolution 4D Flow MRI – Sequential Combination of Resolution Enhancement by Deep Learning and Physics-Informed Image Processing to Non-Invasively Quantify Intracranial Velocity, Flow, and Relative Pressure. Med Image Anal 2023, 88, 102831. [CrossRef]
- Janiesch, C.; Zschech, P.; Heinrich, K. Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Electronic Markets 2021, 31, 685–695. [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Chen, R.; Wu, B.; Shiu, W. S.; Cai, X. C. Numerical Simulation of Blood Flows in Patient-Specific Abdominal Aorta with Primary Organs. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2021, 20 (3), 909–924. [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, Y. G.; Kanaris, A. G.; Mouza, A. A.; Paras, S. V. Fluid-Structure Interaction in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: Effect of Haematocrit. Fluids 2019, 4 (1). [CrossRef]
- Shibeshi, S. S.; Collins, W. E. The Rheology of Blood Flow in a Branced Arterial System. Applied Rheology 2005, 15 (6), 398–405. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Adrian, R. J.; Balachandar, S.; Kendall, T. M. Mechanisms for Generating Coherent Packets of Hairpin Vortices in Channel Flow. J Fluid Mech 1999, 387, 353–396. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Hussain, F. On the Identification of a Vortex. J Fluid Mech 1995, 285, 69–94. [CrossRef]
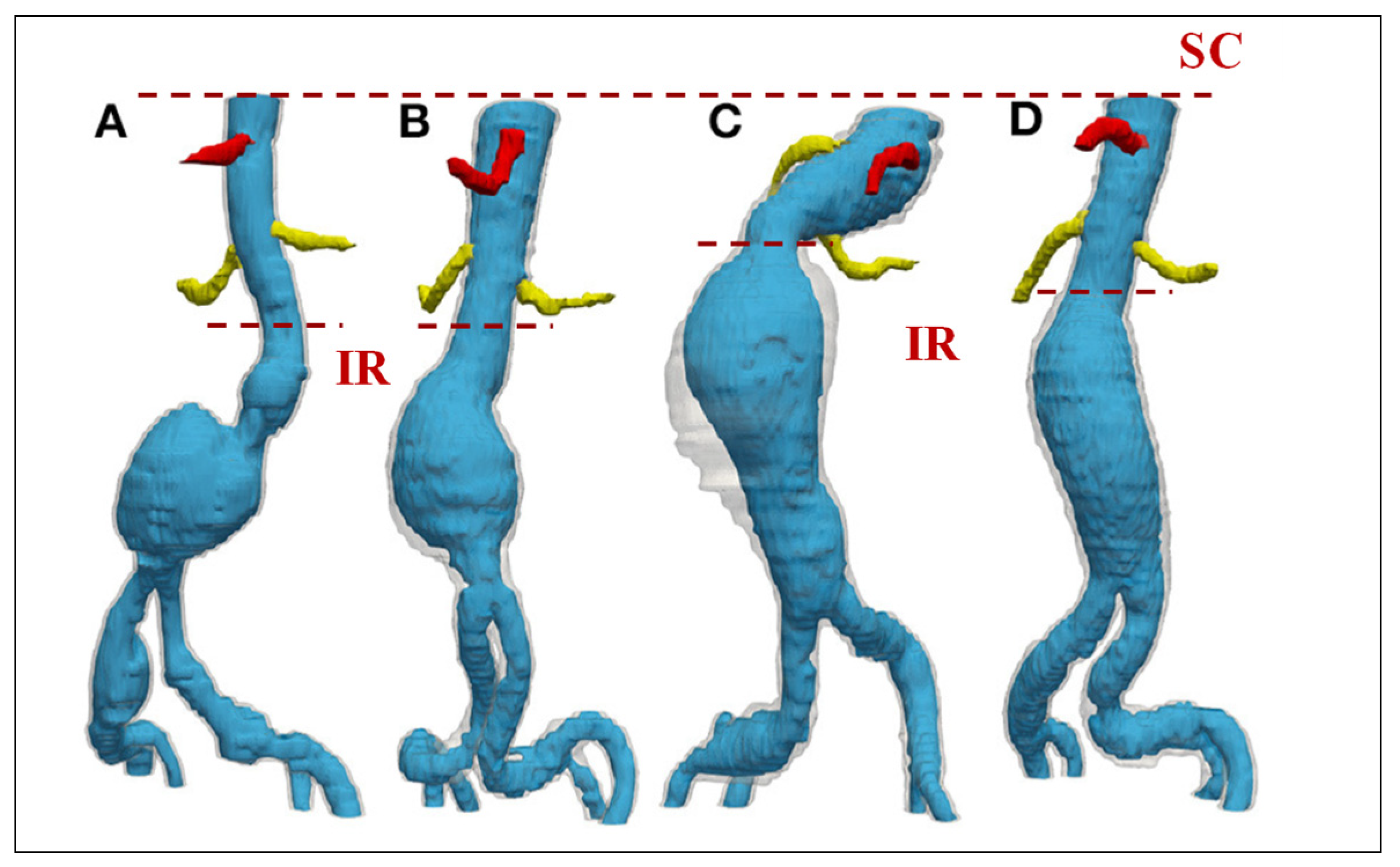
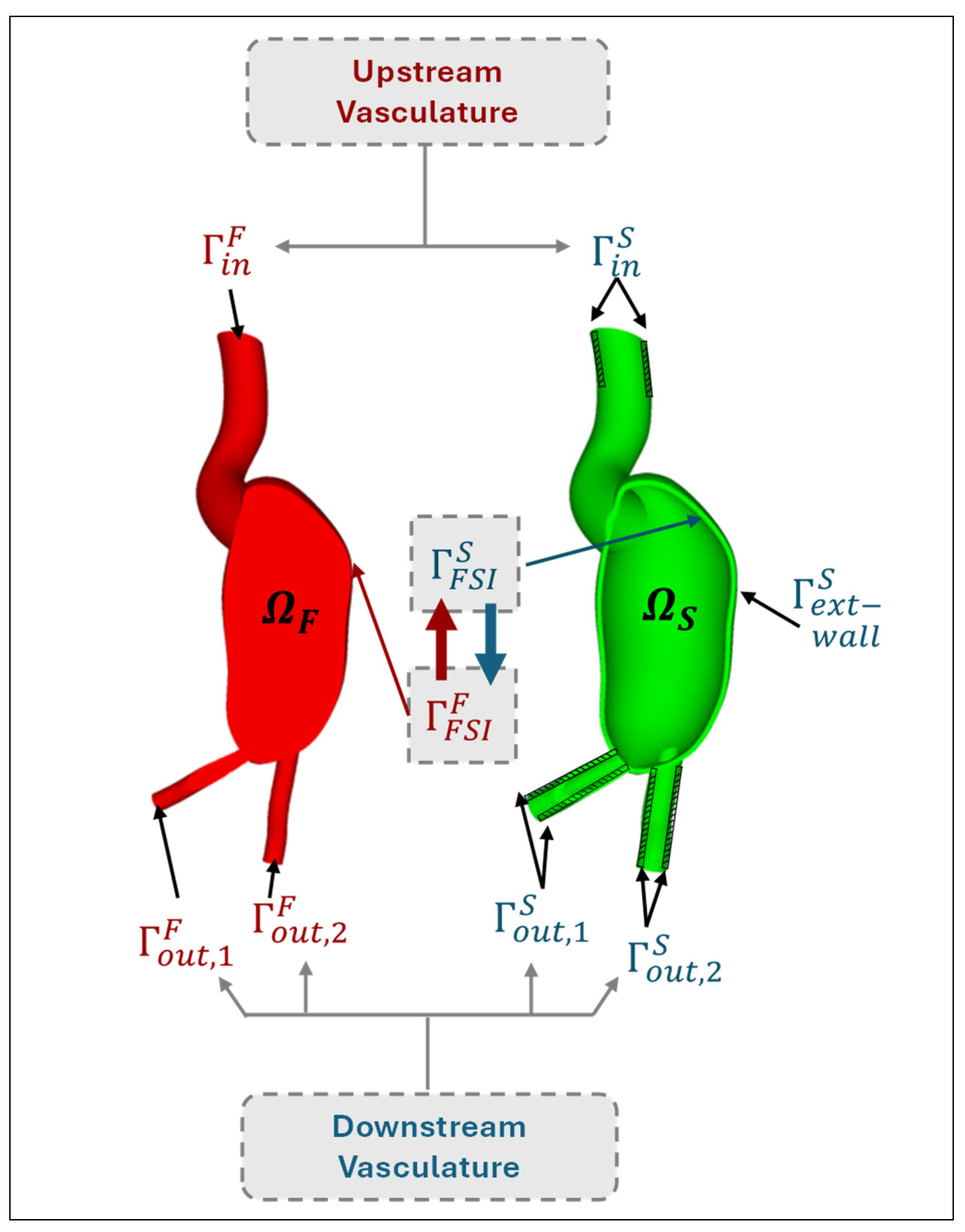
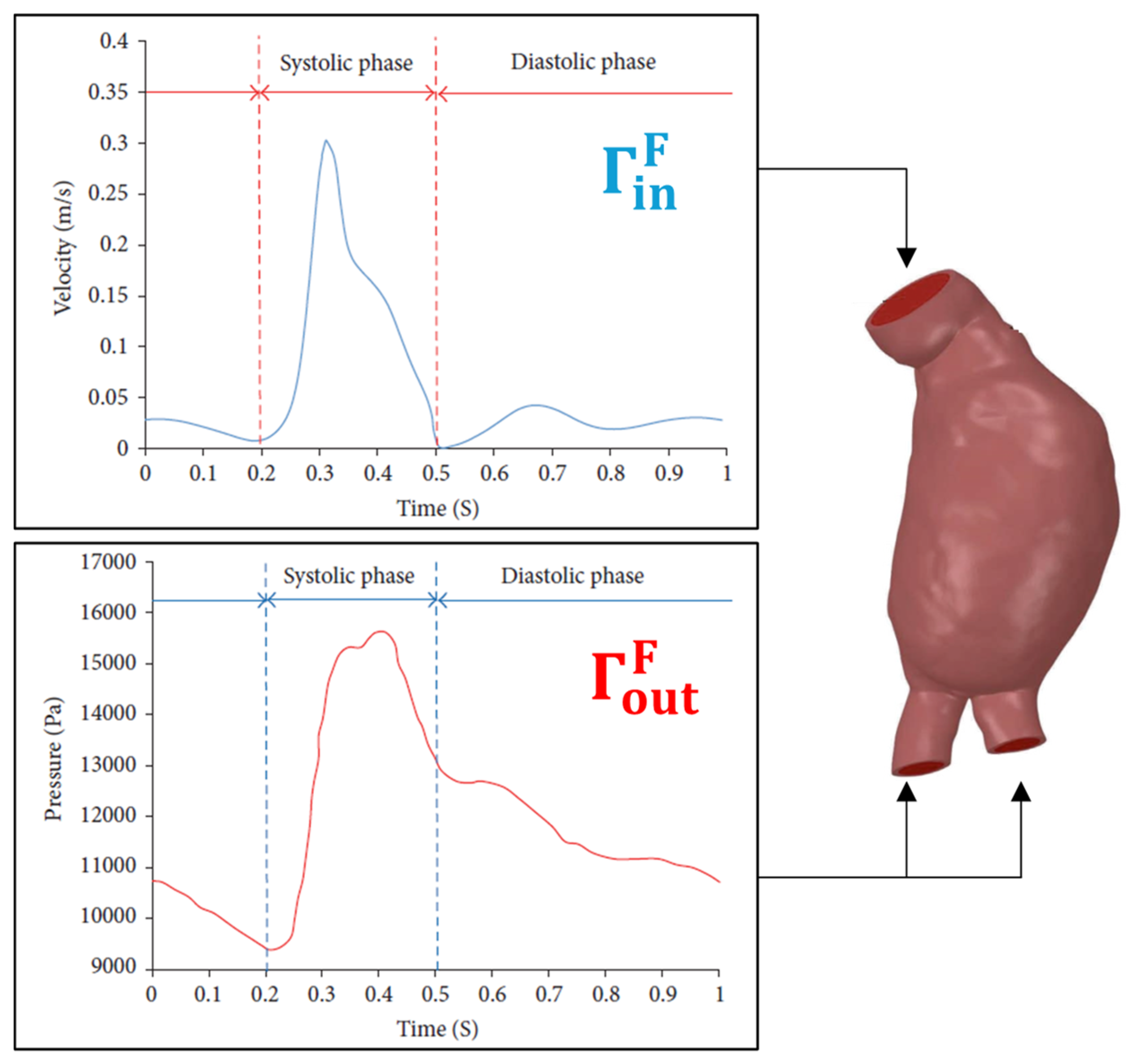
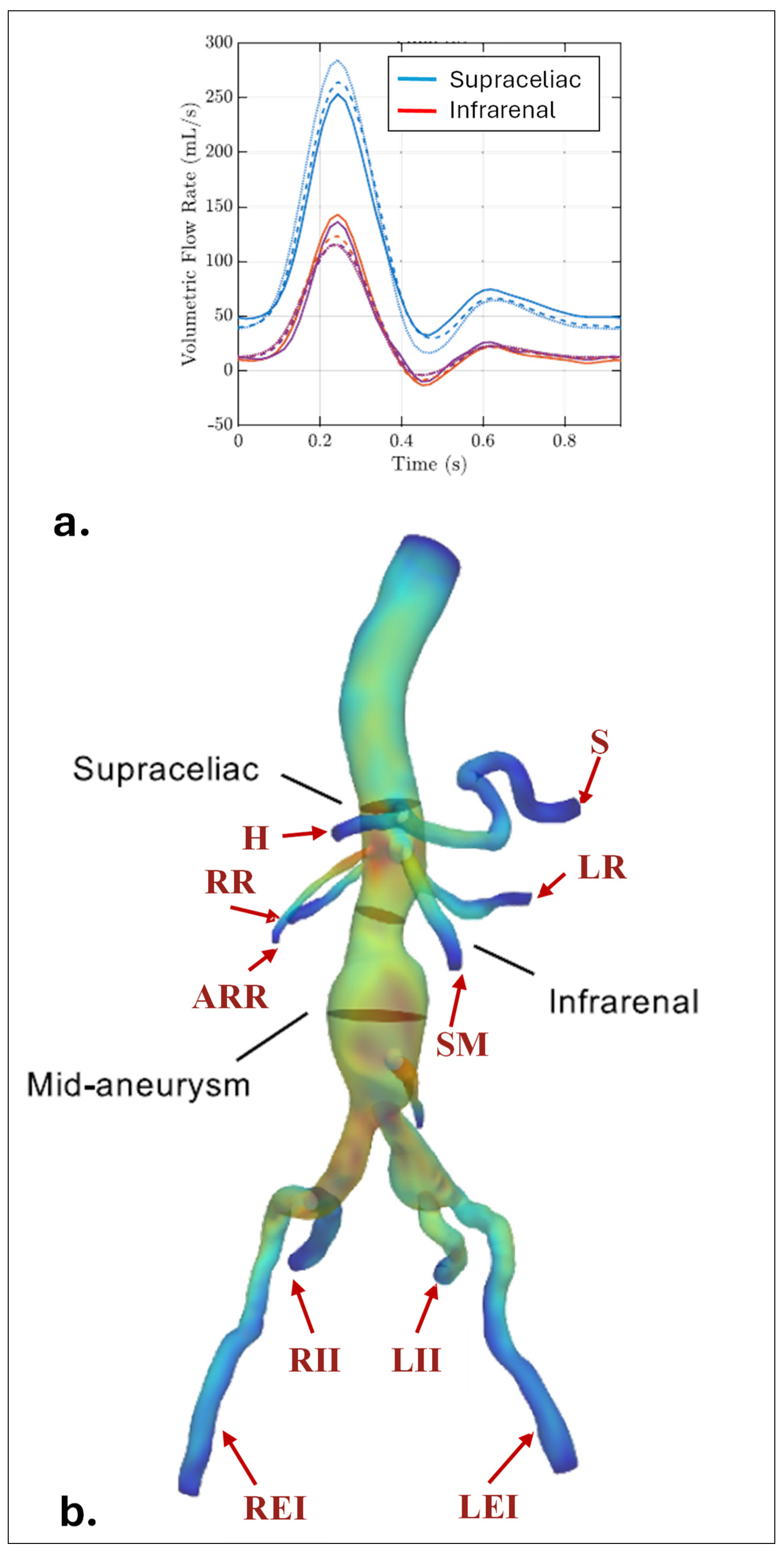
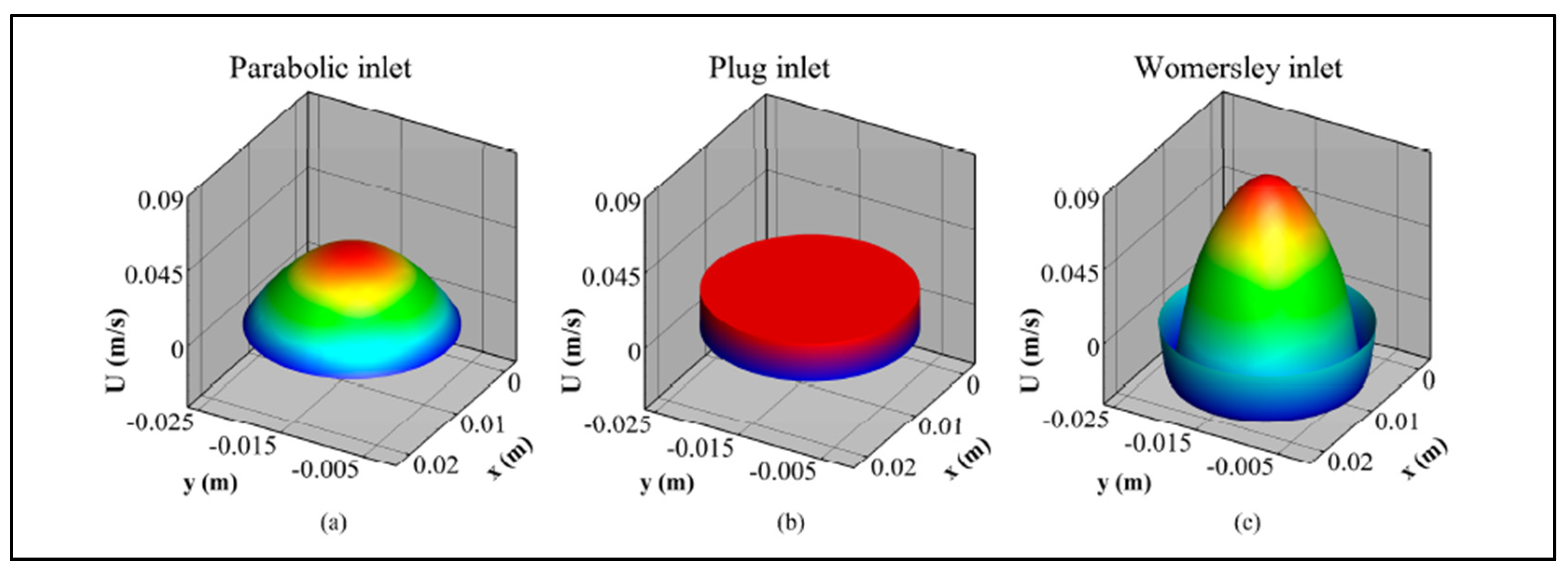
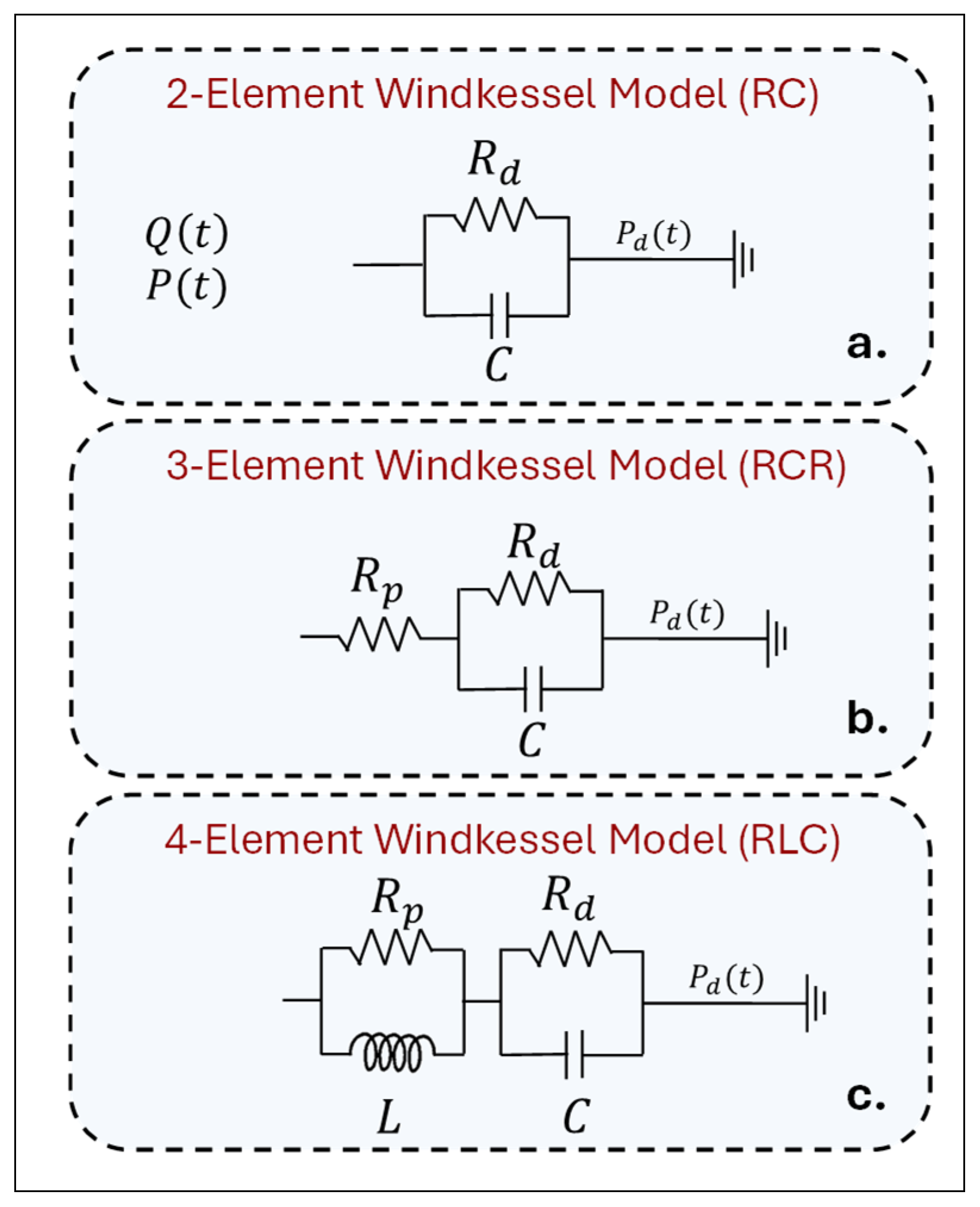
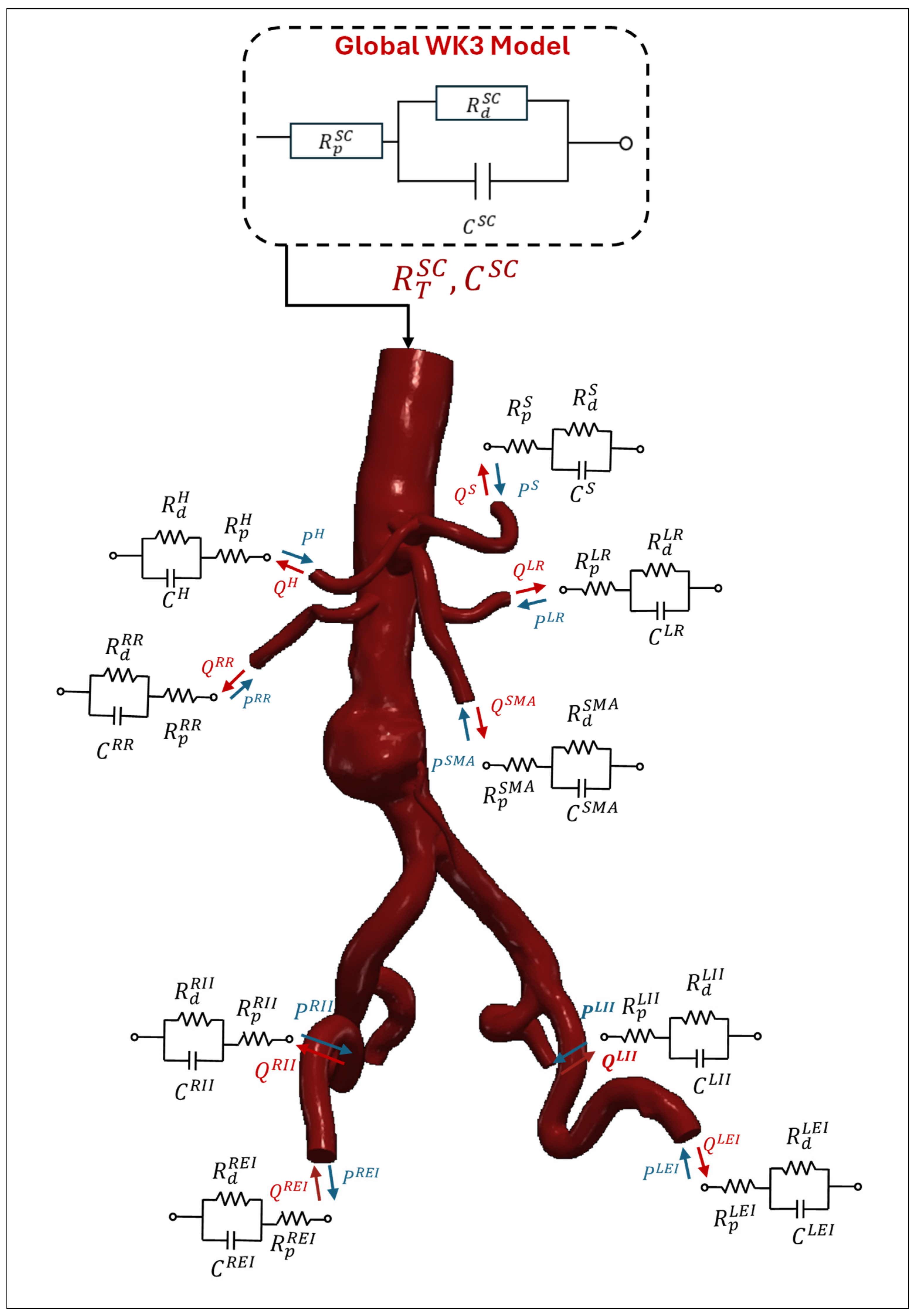
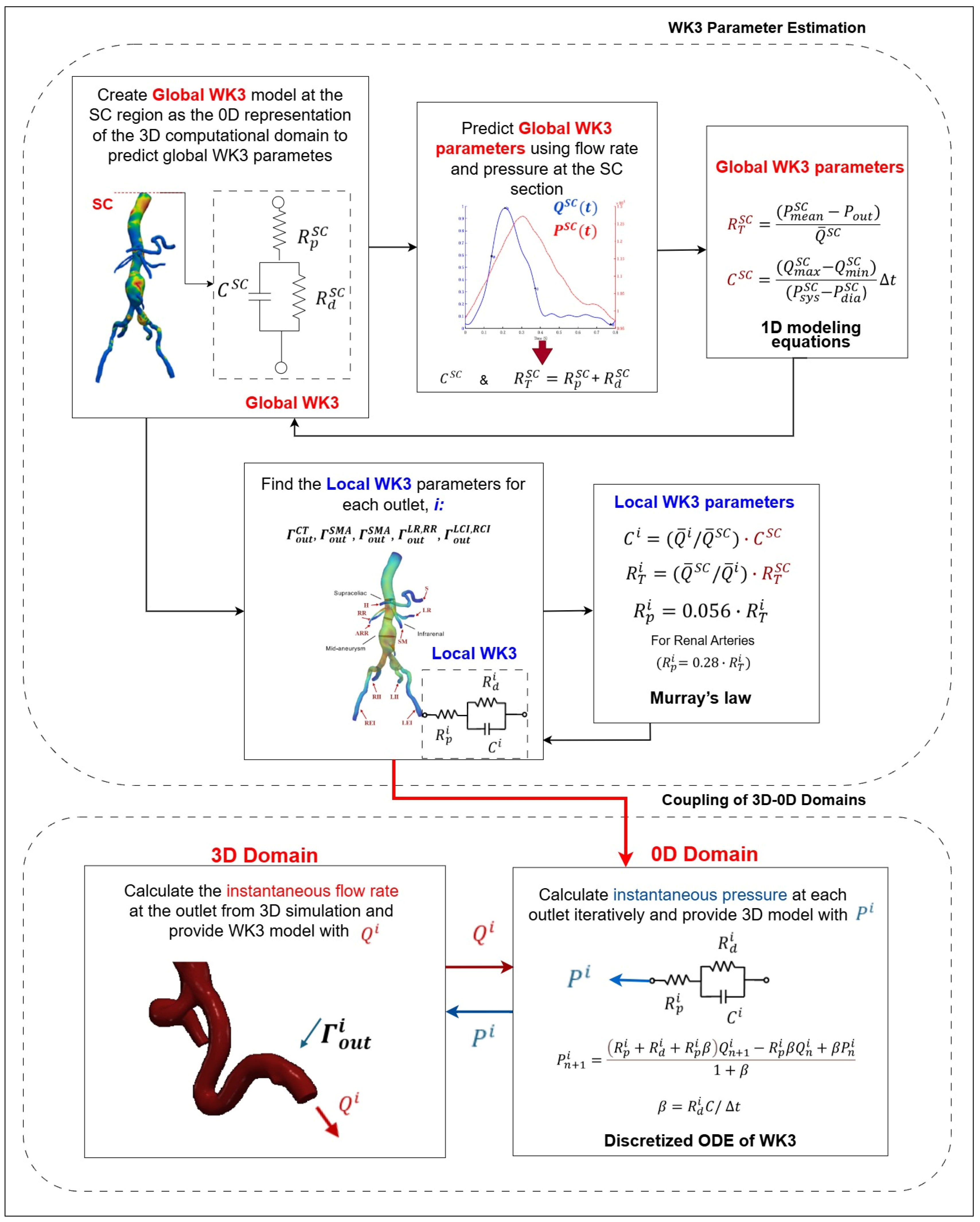
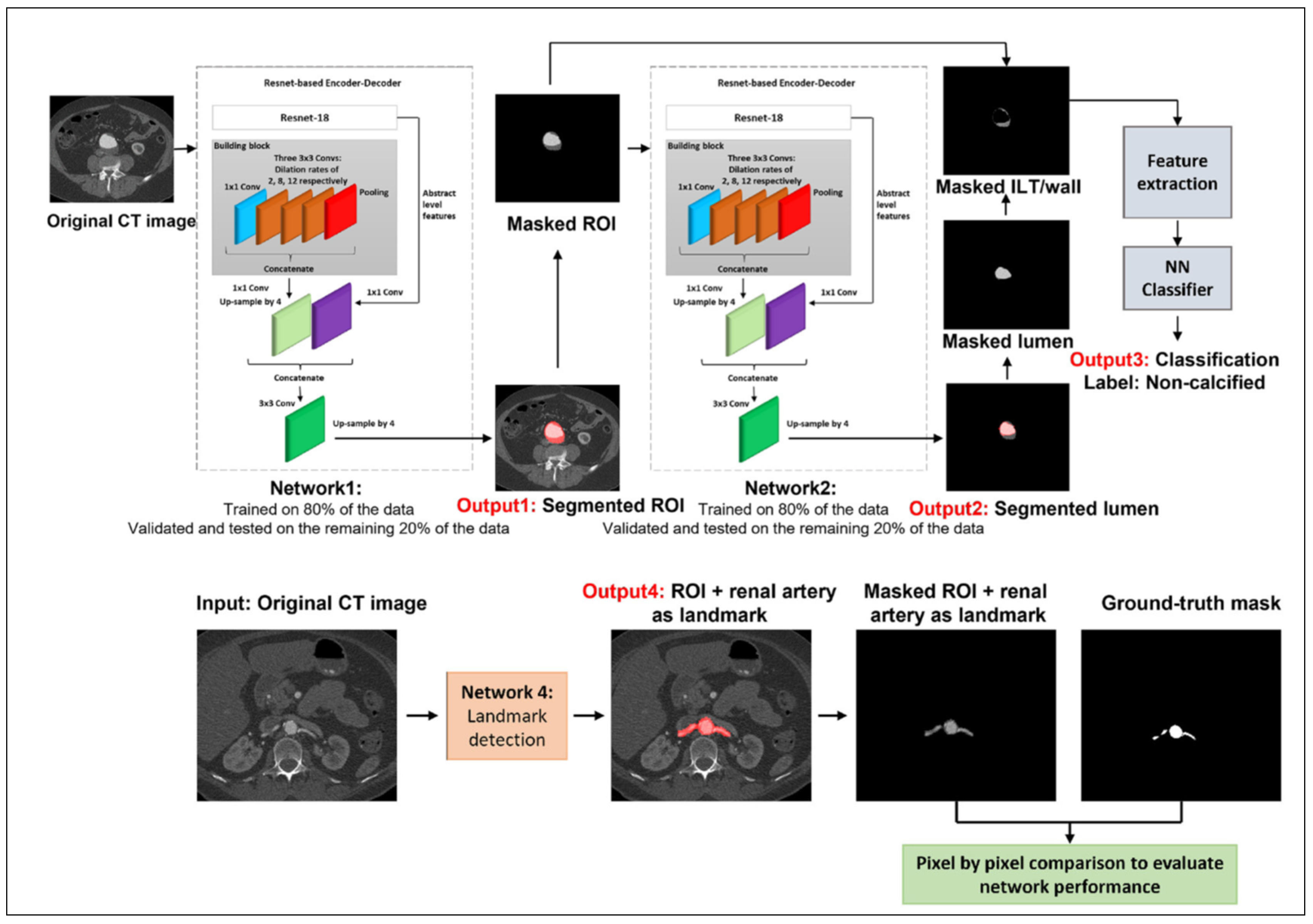
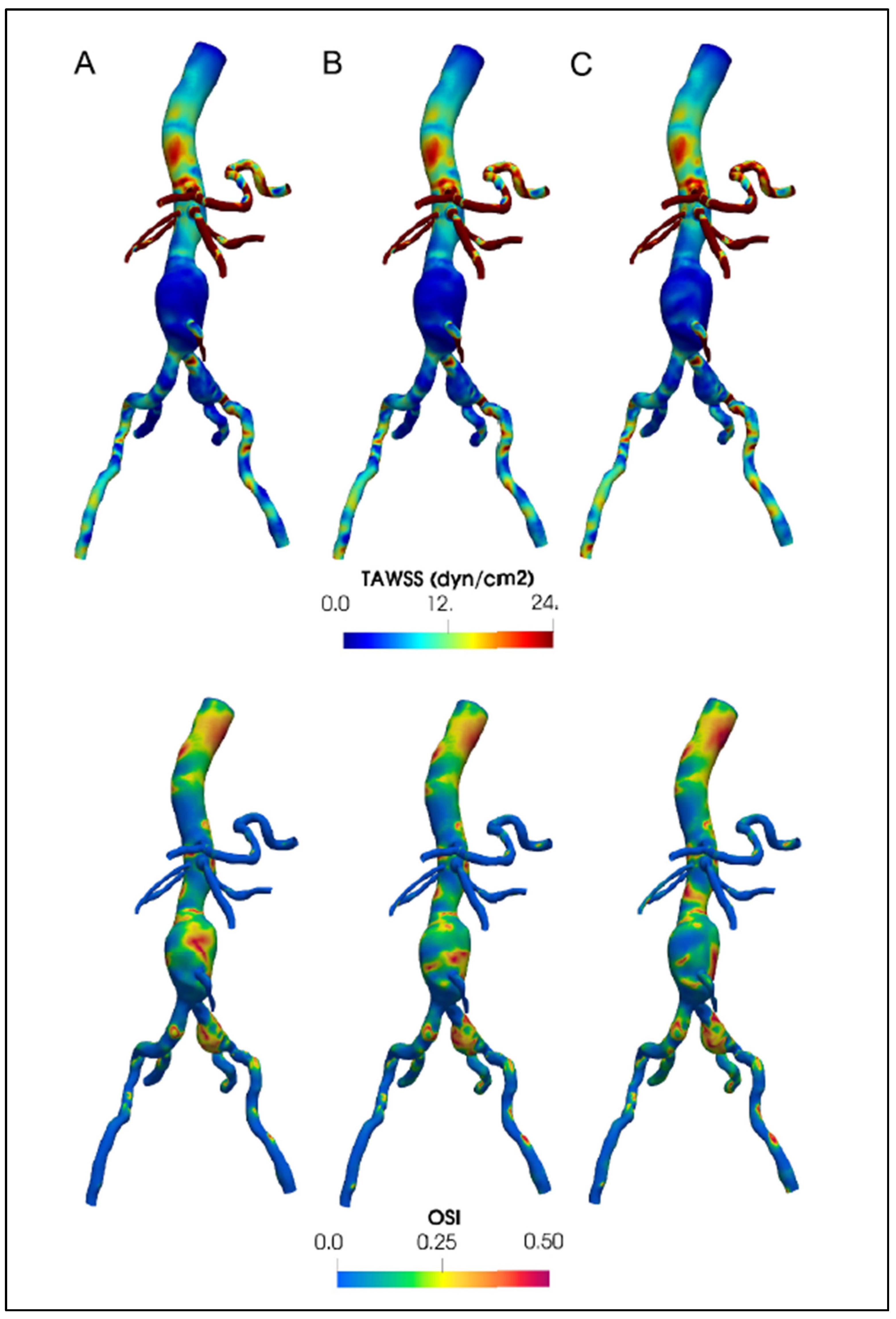
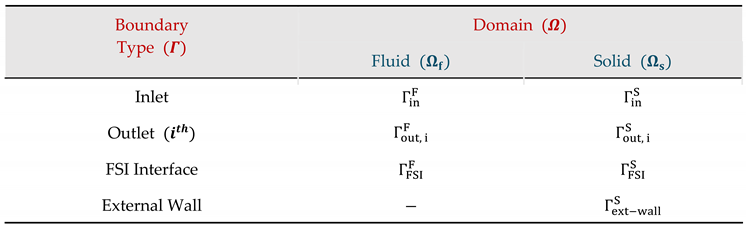 |
| Artery Branch | Flow Split |
| , | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





