Submitted:
01 April 2025
Posted:
01 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
MSC: 34A34; 34K20
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
3. Bifurcation of the Pest-Present Periodic Solution
4. Existence and Global Attractiveness of the Pest-Present Periodic Solution of System (3)
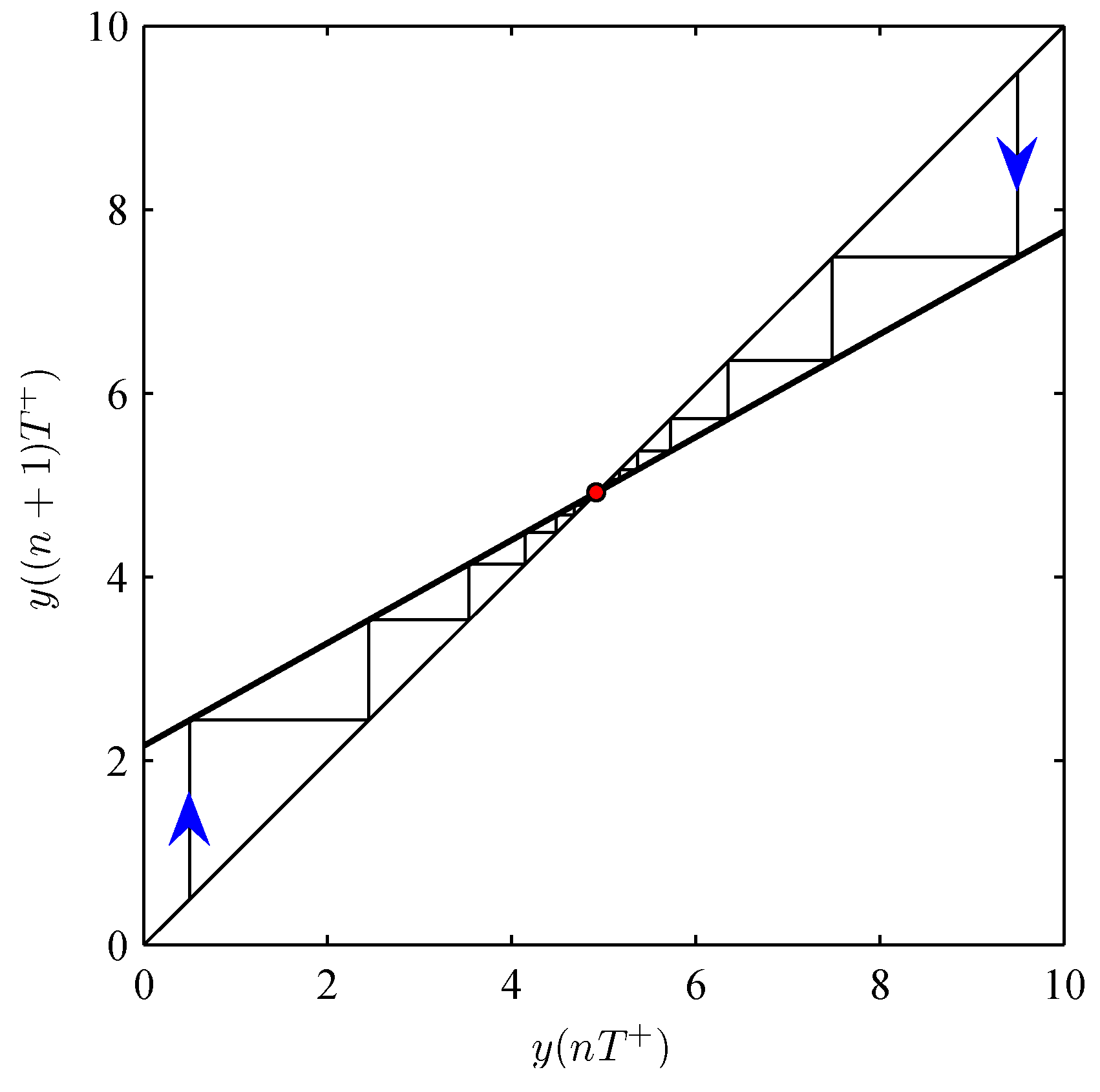
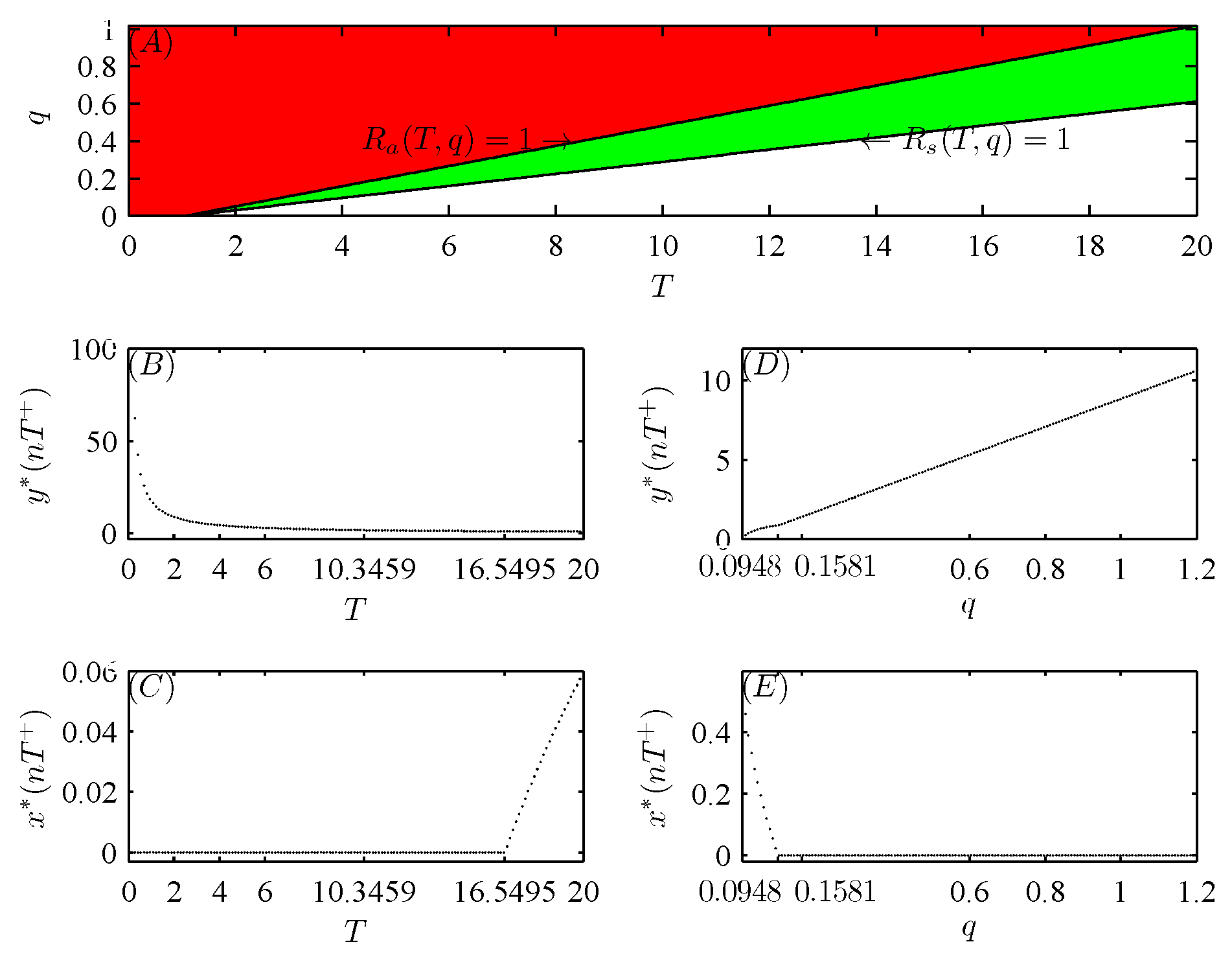
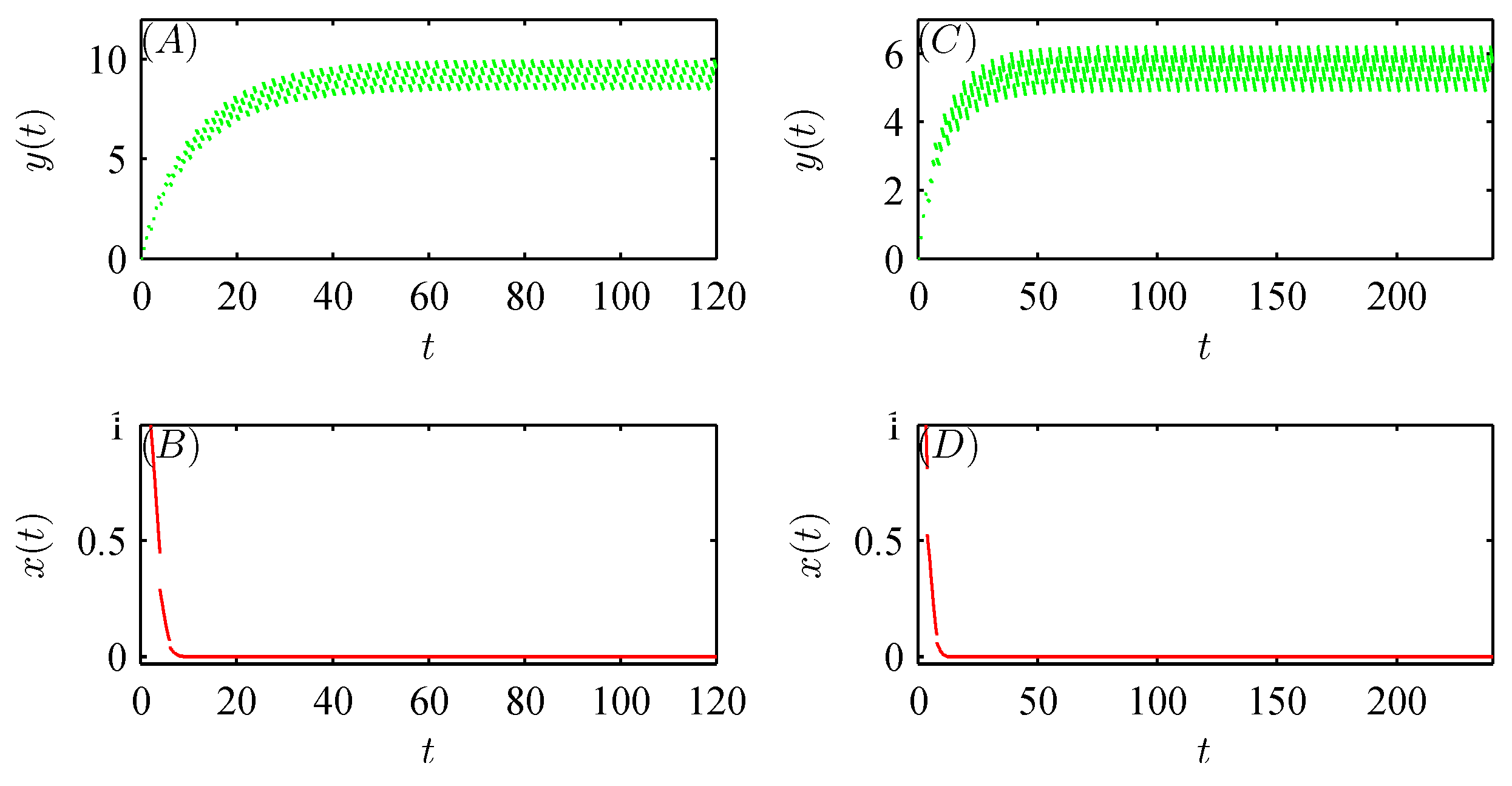
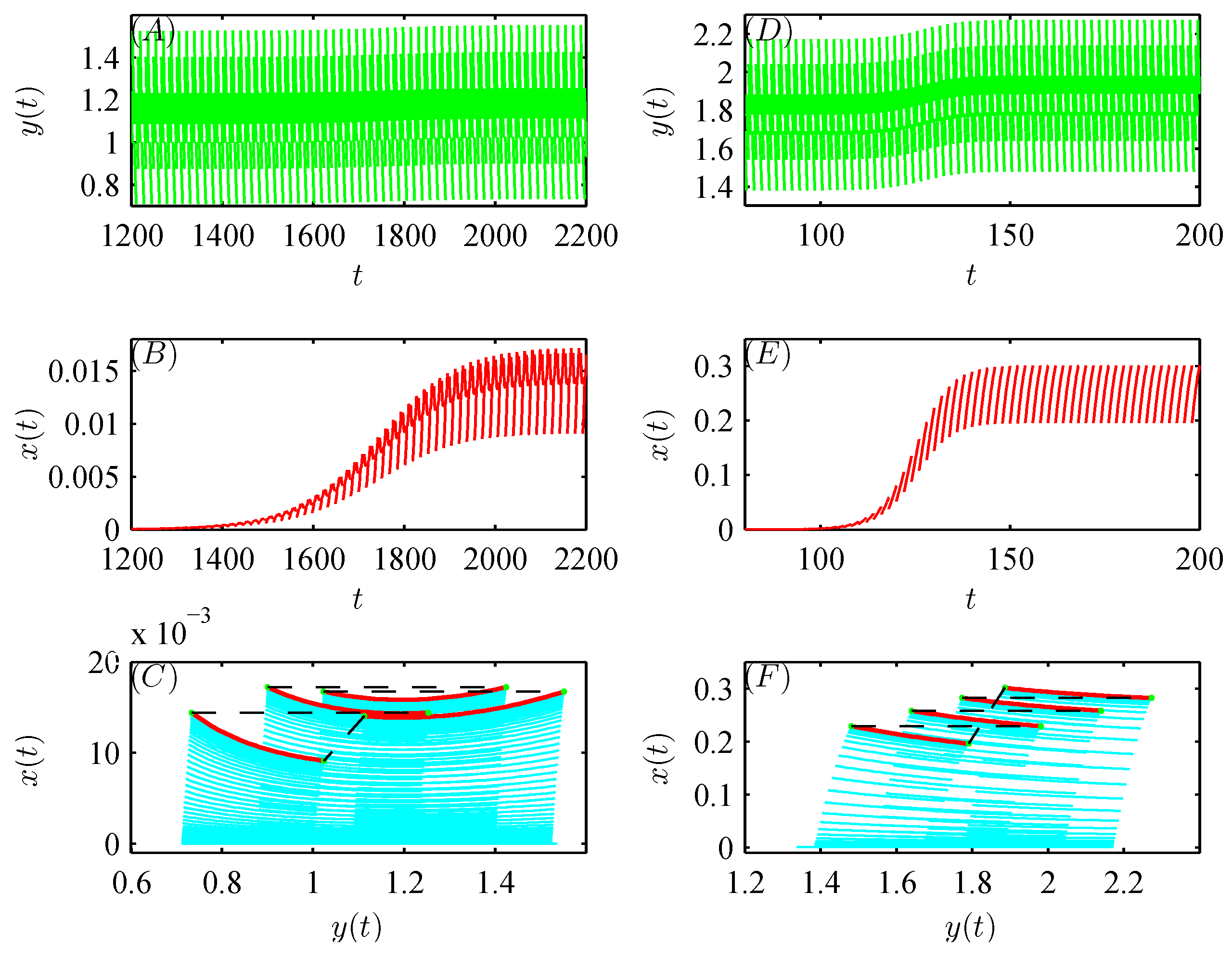
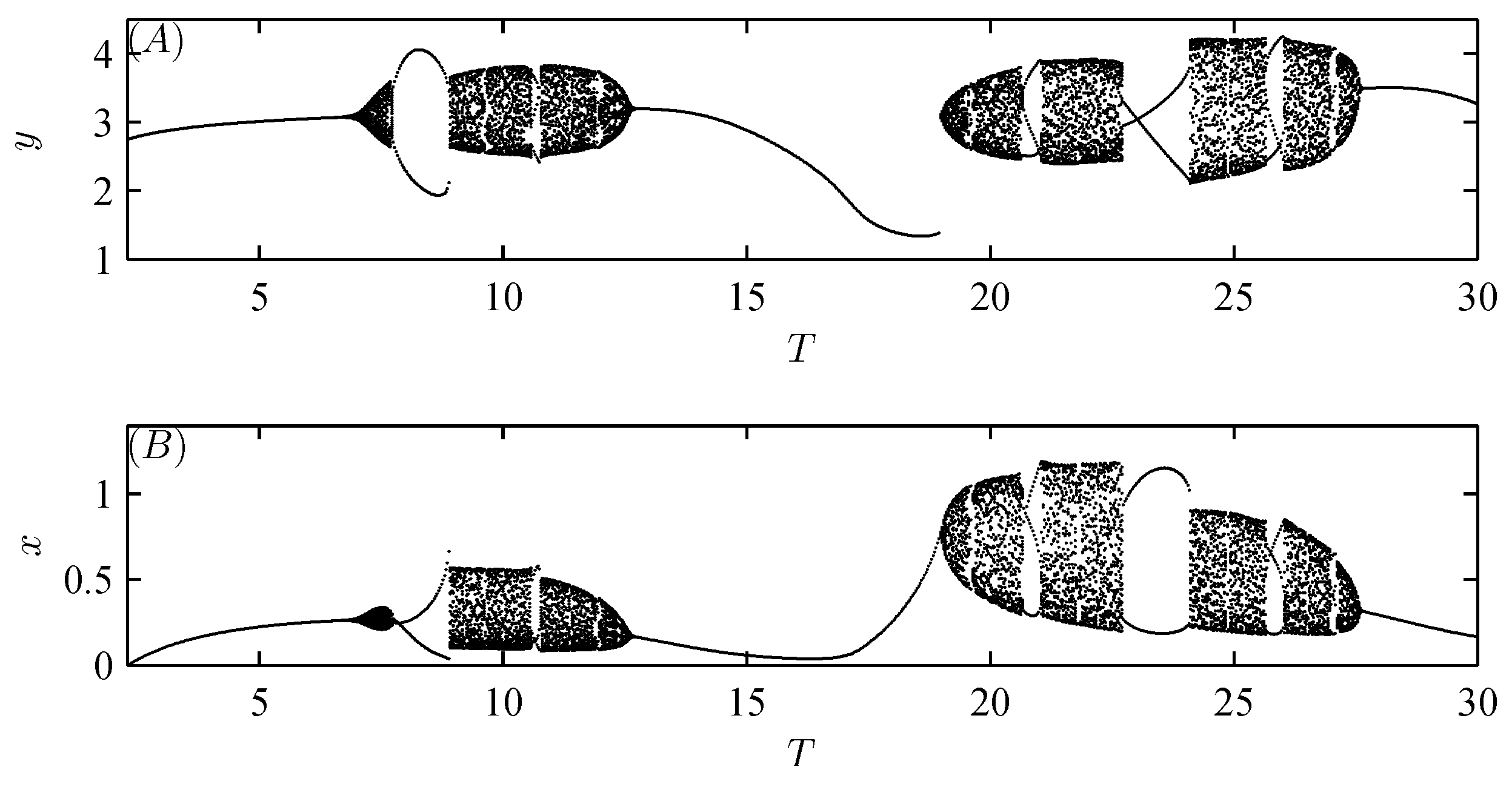
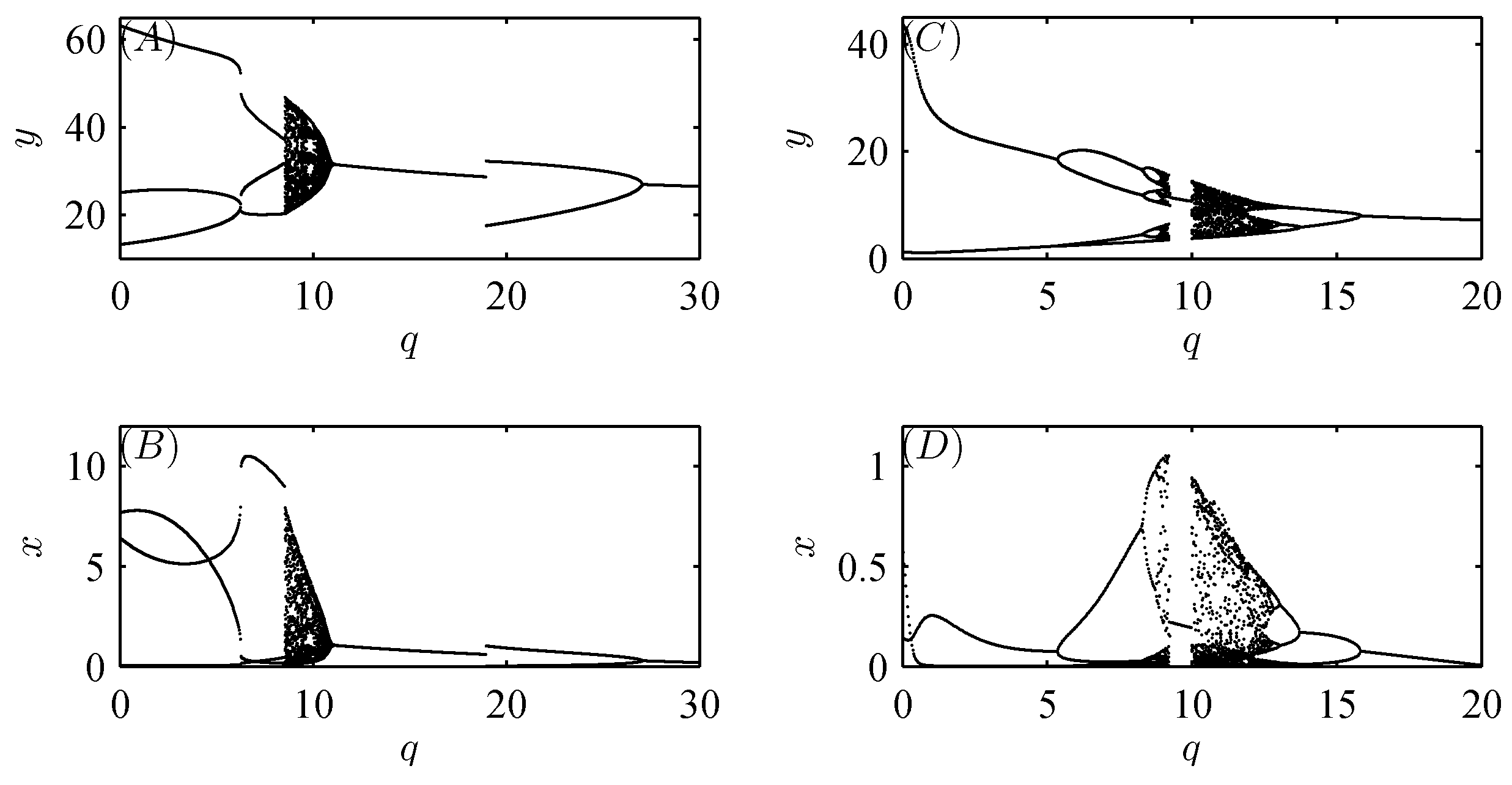
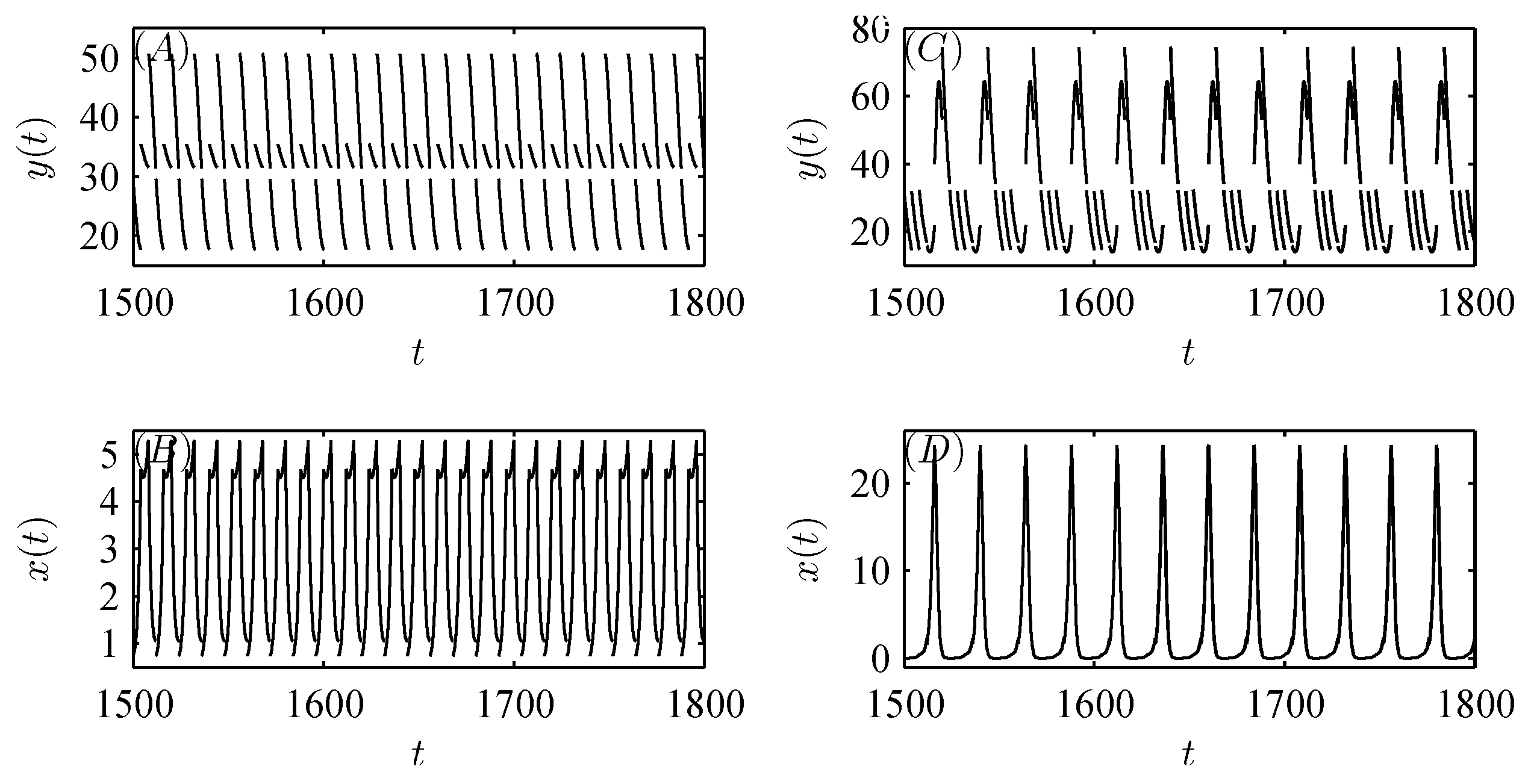
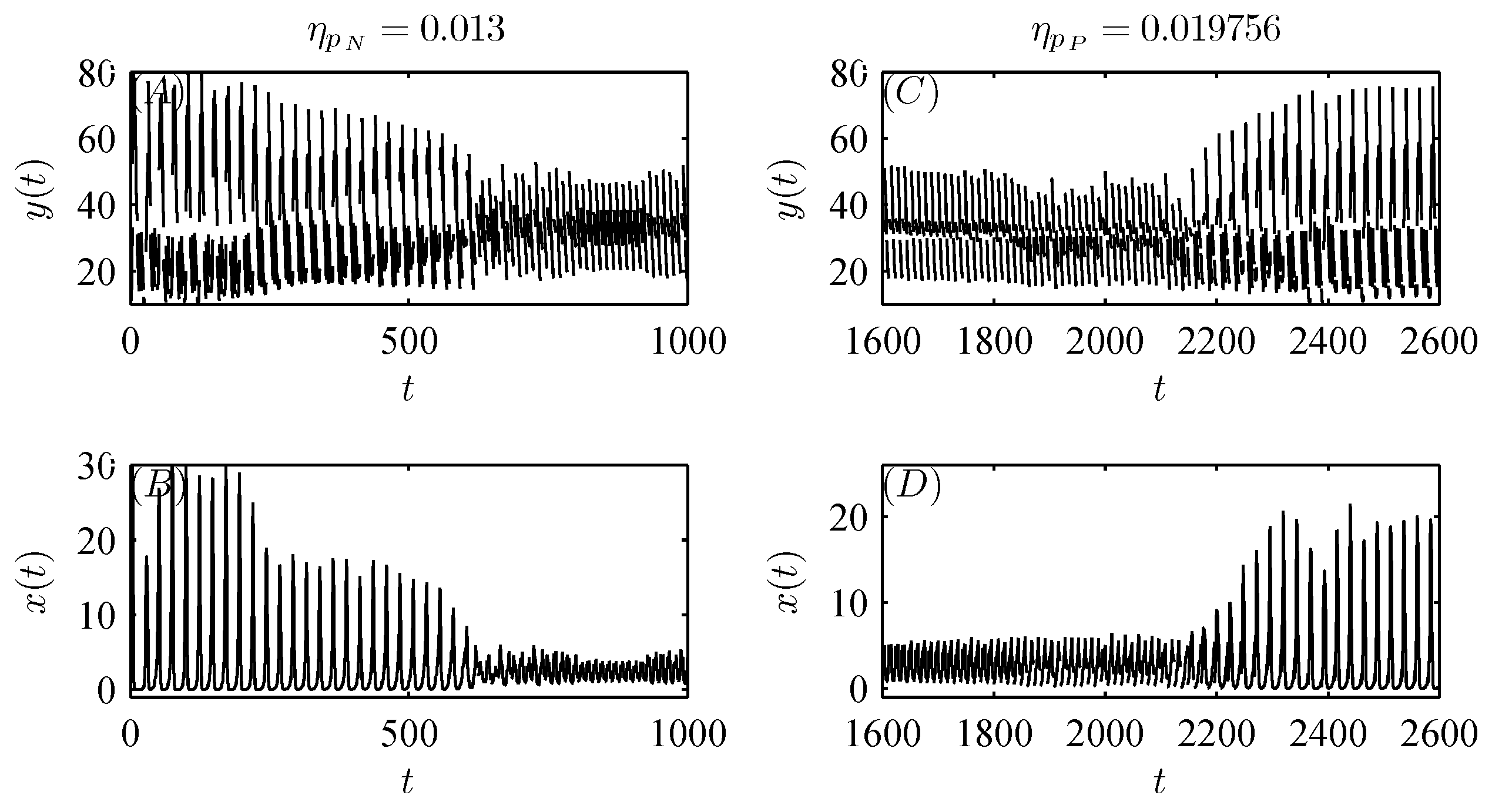
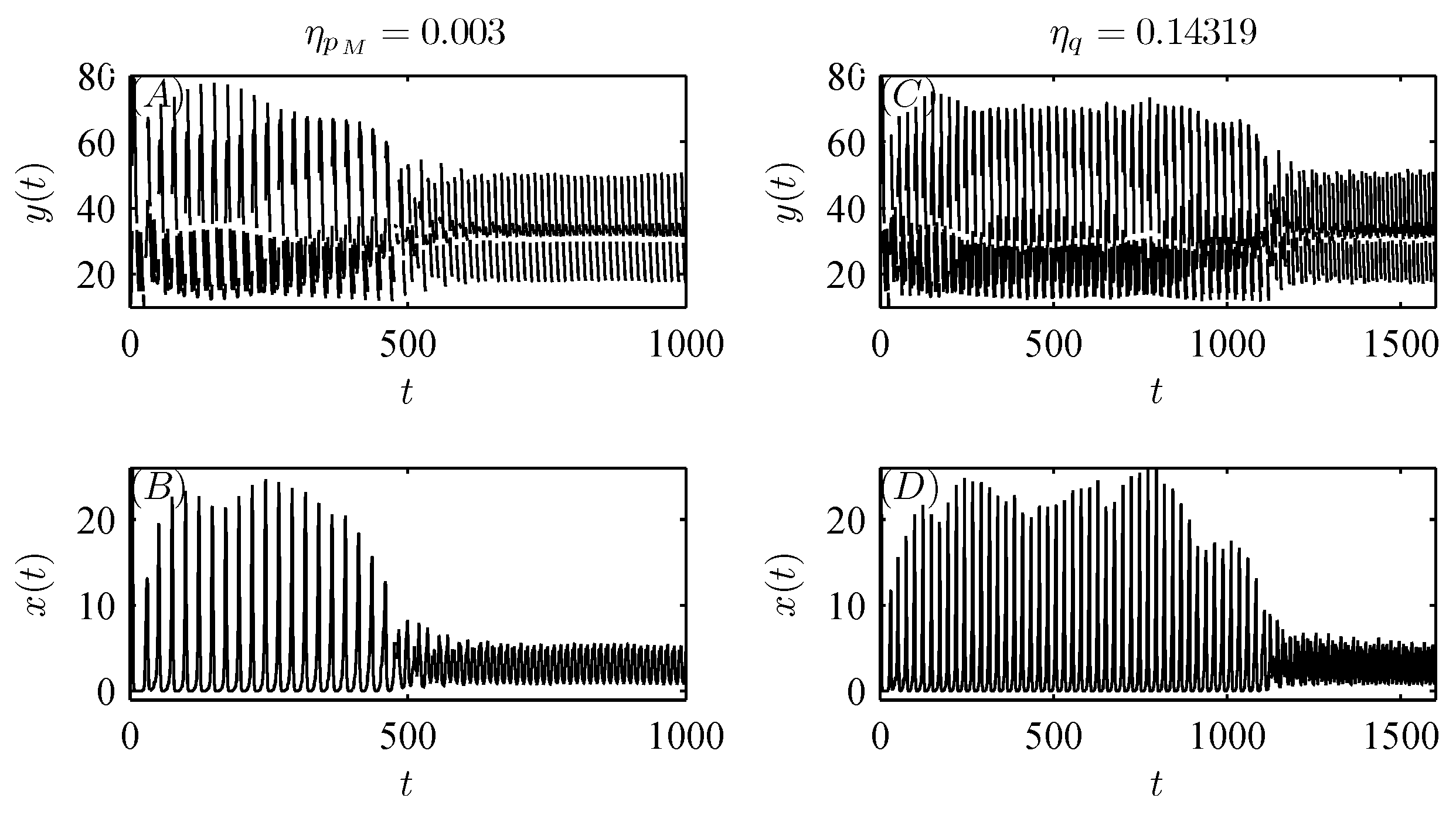
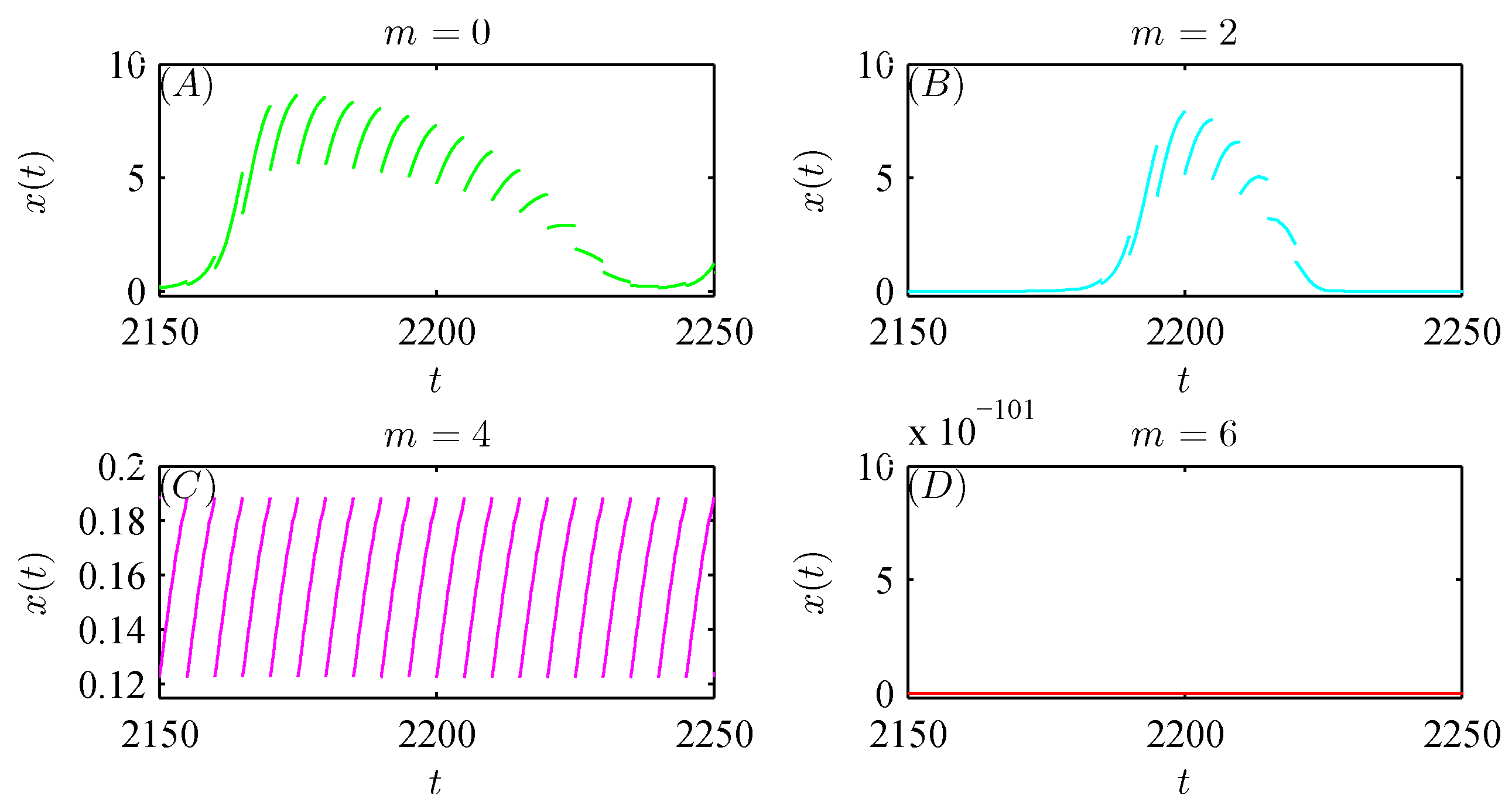
5. Numerical analysis
6. Discussion
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. First-Order Partial Derivatives of y(t) and x(t) with Initial Values
Appendix B. Several Propositions for Determining the Signs of and at Point (Tb, 0)
- (i)
-
If the following condition holds:then the following inqualitieshold for .
- (ii)
-
It is considered thatwhere and .
Appendix C. The Determination of the Sign of at Point
Appendix D. Determination of the Sign of at Point
References
- Li, Z. A disease-specific screening-level modeling approach for assessing the cancer risks of pesticide mixtures. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josea, S.A.; Raja, R.; Zhu, Q.; Alzabut, J.; Niezabitowski, M.; Balas, V.E. An integrated eco-epidemiological plant pest natural enemy differential equation model with various impulsive strategies. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022(1), 4780680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, J.; Al Basir, F.; Cao, X.; Kumar Roy, P. Integrated pest management for Jatropha Carcus plant: an impulsive control approach. Math. Method. Appl. Sci. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Fu, J.; Cheng, H. Sensitivity analysis of pesticide dose on predator-prey system with a prey refuge. J. Appl. Anal. Comput. 2022, 12, 270–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Basir, F.; Chowdhury, J.; Das, S.; Ray, S. Combined impact of predatory insects and bio-pesticide over pest population: impulsive model-based study. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2022, 7(2), 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Yuen, P.W.; Li, F.; Deng, L. Modelling of a seasonally perturbed competitive three species impulsive system. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 3223–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseb, S.A.; Ramachandran, R.; Cao, J.; Alzabut, J.; Niezabitowski, M.; Balas, V.E. Stability analysis and comparative study on different eco-epidemiological models: Stage structure for prey and predator concerning impulsive control. Optim. Contr. Appl. Met. 2022, 43(3), 842–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Yuen, P.; Li, F. A seasonally competitive M-prey and N-predator impulsive system modeled by general functional response for integrated pest management. Mathematics 2022, 10(15), 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C. Dynamic complexity in a prey-predator model with state-dependent impulsive control strategy. Complexity 2020, 2020(1), 1614894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Tang, S. Dynamics of a density-dependent predator-prey biological system with nonlinear impulsive control. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 7318–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, T. Global dynamics of a predator-prey model with fear effect and impulsive state feedback control. Mathematics 2022, 10(8), 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, Z. The state-dependent impulsive control for a general predator-prey model. J. Biol. Dynam. 2022, 16(1), 354–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Zhu, C.Z.; Liu, Y.W. Dynamic analysis of a predator-prey model with state-dependent impulsive effects. Chinese Quarterly Journal of Mathematics 2023, 38(1), 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Huang, M. Dynamics of a Gilpin-Ayala predator-prey system with state feedback weighted harvest strategy. AIMS Math. 2023, 8(11), 26968–26990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xiang, Z. Dynamic analysis of a predator-prey impulse model with action threshold depending on the density of the predator and its rate of change. AIMS Math. 2024, 9(5), 10659–10678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Fu, J. Dynamics analysis of a nonlinear controlled predator-prey model with complex Poincare´ map. Nonlinear Anal-model. 2024, 29, 466–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Basir, F.; Chowdhury, J.; Torres, D.F. Dynamics of a double-impulsive control model of integrated pest management using perturbation methods and Floquet theory. Axioms 2023, 12(4), 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diz-Pita, E.; Otero-Espinar, M.V. Predator-prey models: a review of some recent advances. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, H. Stability and bifurcation analysis of the Bazykins predator-prey ecosystem with Holling type II functional response. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 7877–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feketa, P.; Klinshov, V.; L<i>u</i>¨cken, L. A survey on the modeling of hybrid behaviors: How to account for impulsive jumps properly. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2021, 103, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Yuen, P. Extinction and permanence of the predator-prey system with general functional response and impulsive control. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 88, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Pang, L.; Li, Q. Analysis of a hybrid impulsive tumor-immune model with immunotherapy and chemotherapy. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 2021, 144, 110617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L. Global dynamics of the periodic logistic system with periodic impulsive perturbations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2004, 289(1), 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Quan, Q.; Dai, X. Dynamics of a new impulsive predator-prey model with predator population seasonally large-scale migration. Appl. Math. Lett. 2022, 132, 108096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Jiao, H.; Jiao, J.; Quan, Q. Survival analysis of a predator-prey model with seasonal migration of prey populations between breeding and non-breeding regions. Mathematics 2023, 11(18), 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Dai, X.; Jiao, J. Dynamics of a predator-prey model with impulsive diffusion and transient/nontransient impulsive harvesting. Mathematics 2023, 11(14), 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakmeche, A. Birfurcation of non-trivial periodic solutions of impulsive differential equations arising chemotherapeutic treatment. Dynam. Contin. Discrete Impuls. 2000, 7, 265–287. [Google Scholar]
- Bainov, D.; Simeonov, P. Impulsive Differential Equations: Periodic Solutions and Applications; Longman Scientific & Technical Press: New York, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Yi, M.; Tang, S. Dynamics of an antitumour model with pulsed radioimmunotherapy. Comput. Math. Method. M. 2022, 2022(1), 4692772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; She, A.; Xie, Y. The dynamics analysis of Gompertz virus disease model under impulsive control. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13(1), 10180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zou, X. Qualitative analysis of critical transitions in complex disease propagation from a dynamical systems perspective. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 2016, 26(14), 1650239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Yan, P. Dynamic analysis of impulsive differential chaotic system and its application in image encryption. Mathematics 2023, 11(23), 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Liu, Z.; Cheke, R.A. Periodicity and stability in a single-species model governed by impulsive differential equation. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36(3), 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bohner, M.; Wang, C.K. Impulsive differential equations: periodic solutions and applications. Automatica 2015, 52, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamen, A.T.; Dumont, Y.; Tewa, J.J.; Bowong, S.; Couteron, P. A minimalistic model of tree-grass interactions using impulsive differential equations and non-linear feedback functions of grass biomass onto fire-induced tree mortality. Math. Comput. Simulat. 2017, 133, 265–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Xie, X.; Chen, F.; Lin, Q. Dynamical analysis of a logistic model with impulsive Holling type-II harvesting. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 2018, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhu, H.; Ding, Y. Impulsive control for persistence and periodicity of logistic systems. Math. Comput. Simulat. 2020, 171, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudaoui, A.; Mebarki, K.; Shatanawi, W.; Abodayeh, K. Solution of some impulsive differential equations via coupled fixed point. Symmetry 2021, 13(3), 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, C.; Uzc<i>a</i>´tegui, J.; Ruiz, B.; P<i>e</i>´rez, M. Attractive periodic solutions of a discrete Holling-Tanner predator-prey model with impulsive effect. Bull. Comput. Appl. Mat. 2021, 8(1), 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, K.; Gui, Z. Periodic solution of impulsive predator-prey model with stage structure for the prey undercrowding effect. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2021, 1903, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, C.; Diestra, J.L.H. Positive periodic solutions of a discrete ratio-dependent predator-prey model with impulsive effects. Rev. Union Mat. Argent. 2022, 63(1), 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Vijayakumar, V.; Nisar, K.S.; Singh, A.K.; Udhayakumar, R.; Botmart, T.; Albalawi, W.; Mahmoud, M. An analysis on approximate controllability of semilinear control systems with impulsive effects. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61(12), 12293–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Complex dynamics of Beddington-DeAngelis-Type predator-prey model with nonlinear impulsive control. Complexity 2020, 2020(1), 8829235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisubtawee, S.; Khansai, N.; Charoenloedmongkhon, A. Investigation on dynamics of an impulsive predator-prey system with generalized Holling type IV functional response and anti-predator behavior. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2021, 2021(1), 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Xie, Y.X.; Deng, Q.C. The dynamic behaviors of a new impulsive predator prey model with impulsive control at different fixed moments. Kybernetika 2018, 54(3), 522–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, S. Analyzing a generalized pest-natural enemy model with nonlinear impulsive control. Open Math. 2018, 16(1), 1390–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tang, S.; Cheke, R.A. Complex dynamics and coexistence of period-doubling and period-halving bifurcations in an integrated pest management model with nonlinear impulsive control. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020, 2020, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Fu, S. Dynamical behavior of a predator-prey system incorporating a prey refuge with impulse effect. Complexity 2022, 2022(1), 2422923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathumwan, D.; Trachoo, K.; Maiaugree, W.; Chaiya, I. Preventing extinction in Rastrelliger brachysoma using an impulsive mathematical model. AIMS Math. 2022, 7, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




