Introduction
BDO Unibank, Inc. is the largest banking company in the Philippines, most popular for providing a wide range of financial services including retail banking, corporate lending, investment banking, wealth management, and digital banking solutions. It was established in 1968 as Acme Savings Bank and grew through strategic mergers and expansion, especially under the SM Group's management, into a Philippine banking giant.

BDO's rapid expansion and use of technology have made it the market leader with millions of clients across the country. Alongside the expansion, BDO has been dealing with some massive challenges relating to risk management. Specifically, the bank has over the last few years faced significant challenges regarding breaches of cybersecurity, system outages in mobile banking, and gaps in regulatory compliance. These incidents pointed to serious vulnerabilities in its compliance, operational, and financial systems, prompting a concerted effort by the bank to enhance its internal controls, infrastructure, and customer protection programs.
The experiences of the company point to the importance of sound risk management practices, especially in the era of rapid digital transformation and heightened regulatory scrutiny in the banking industry.
Objectives
The key aims of the case study on Risk Management at BDO Unibank are:
1. To examine how BDO Unibank addressed major financial, operating, and compliance risks over the last few years, in particular cases such as the cyber fraud attack of December 2021 and the disruptions in operations during 2022.
2. To review the risk management models and strategies BDO adopted in response to such challenges, and identify measures for improving cybersecurity, operational resilience, and regulatory compliance.
3. To review the effectiveness of BDO's risk management approaches and their impact on the bank's stability, resilience, and reputation.
4. To obtain valuable implications and recommendations for banks during the handling of financial, operating, and regulatory risks, in the context of a more digitized banking process.
Problem Statement
The main issue focused on in this case study is BDO Unibank's exposure to material financial, operational, and compliance risks, as specifically evidenced by the large-scale cyber fraud in December 2021. This attack had compromised customer accounts, eroded customer trust, caused liquidity pressures, and exposed vulnerabilities in cybersecurity controls. Operational issues were also seen in the form of recurring system downtime and transaction delays in the bank's mobile services in 2022, fuelling customer discontent and regulatory attention.
The convergence of these problems revealed vulnerabilities in BDO's risk management system, namely:
1. Cyber fraud losses and liquidity strains.
2. System downtimes impacting digital service reliability.
3. Penalties by the regulators for non-compliance with security measures.
The major issue discussed in this case study is BDO Unibank's vulnerability to major financial, operational, and compliance risks, which significantly affected the stability and reputation of the bank. BDO suffered a massive cyber fraud in December 2021, which led to hacked customer accounts, heavy financial losses, liquidity stress, and eroded customer and investor confidence. Also, operational vulnerabilities cropped up in 2022 with relentless system shutdowns and payment delays that led to service interruptions in mobile banking, severely affecting customer satisfaction and experience. The outages also exposed compliance shortfalls, placing the company at risk of regulatory penalties in the form of BSP-imposed fines for failure to meet mandated cybersecurity standards. All these concerns help bring out the importance of effective risk management techniques in an effort to shield financial institutions against substantial monetary loss, regulation penalties, as well as irreversible reputational damage.
Analysis
Data Collection
The BDO Unibank Risk Management case study was based on qualitative research with the study heavily relying on secondary data. Data were collected from the bank's official reports, predominantly the 2021 Annual Report, and official statements regarding the bank's financial performance, risk management practice, cybersecurity, and compliance procedures. Further sources included internal governance documents that provide details on the responsibilities and roles of BDO's Board of Directors, Risk Management Committee, and Risk Management Group. The analysis also borrowed from regulatory documents and public statements made by the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) regarding security procedures and regulatory compliance requirements.
Analysis
The case analysis identifies BDO Unibank's high exposure to three key risk areas: financial, operational, and compliance risks, assessed based on Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) principles. Financially, the December 2021 cyber fraud significantly impacted BDO's liquidity and market risks since unauthorized access breached several customer accounts, leading to significant financial losses, immediate liquidity stress due to required reimbursements, and serious loss of customer and investor confidence. Putting ERM principles into practice, the Board and Risk Management Committee of BDO forthwith reassessed the risk appetite levels, tolerance limits, and internal control systems of the bank to align strategy and restore customer confidence. At the operational level, the routine system failures throughout 2022 exposed glaring loopholes in the IT infrastructure of BDO, especially in mobile banking services. Weak infrastructure resilience under the ERM model was identified as a core issue, which resulted in customer complaints, reputation loss, and increased regulatory scrutiny.
To balance these shortcomings, BDO invested heavily in overhauling digital infrastructure, completing its Next Gen IT Transformation Program, deploying end-to-end branch automation, and introducing state-of-the-art security features such as biometric and QR code-enabled ATMs. BSP fine compliance risks since the cyber attack highlighted serious regulatory lapses in cybersecurity operations, internal controls, and anti-fraud protection systems. As a measure of strengthening compliance procedures, BDO underwent strict internal audits, implemented global security standards such as ISO 27001, and increased internal control processes to meet stringent regulatory requirements of the BSP.
This combined analysis utilized frameworks such as Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) that emphasize a strategic and enterprise-level response with active leadership from the Board of Directors and risk expert committees. It also utilized the COSO Framework with an emphasis placed on good internal controls, best governance practices, and continuous monitoring of risks, and ISO 27001 standards to systemically manage and counter cybersecurity threats.
The case applied relevant models and frameworks such as:
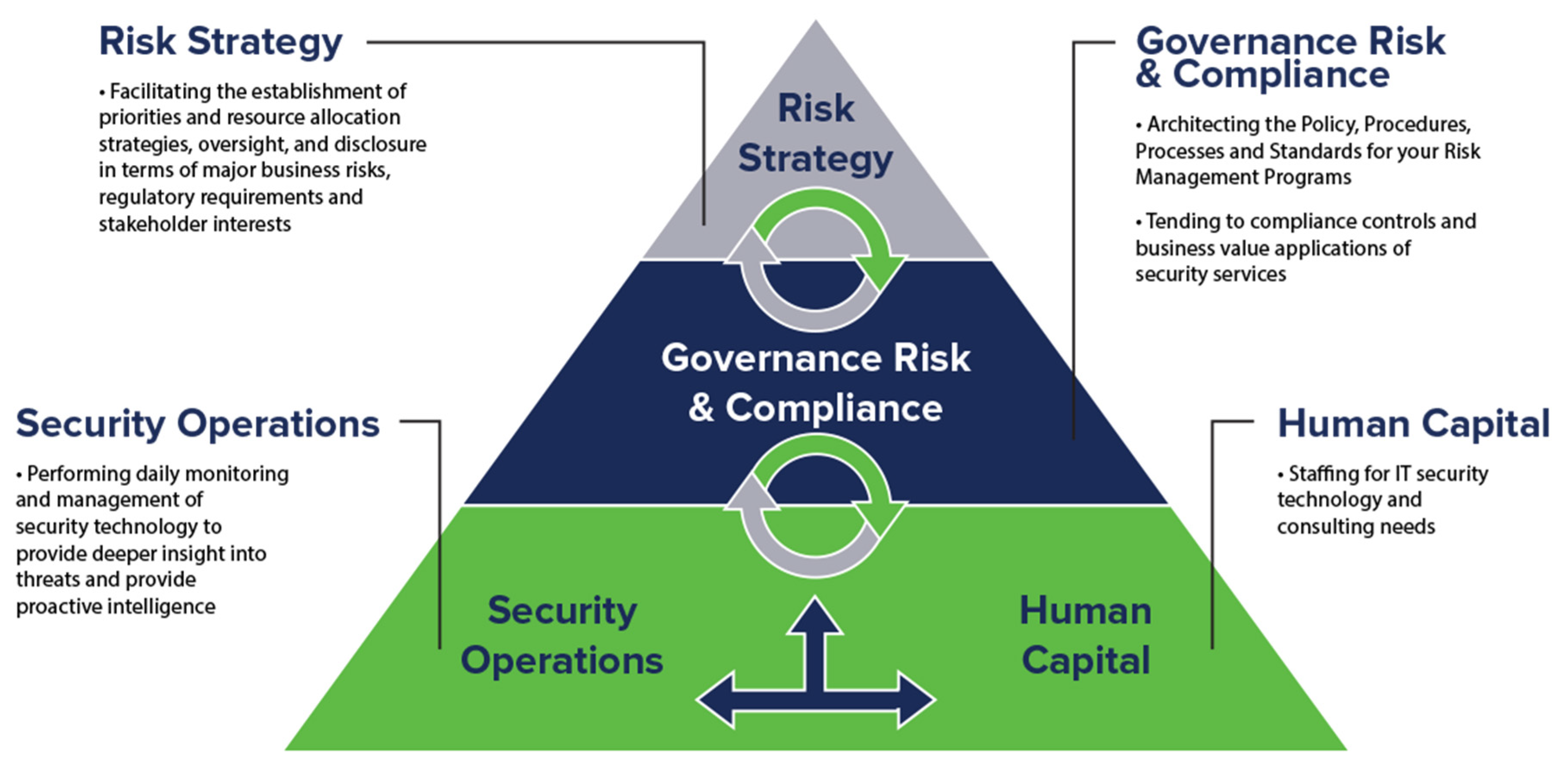
Enterprise Risk Management
Figure 1.
Enterprise Risk Management.
Figure 1.
Enterprise Risk Management.
According to Brown et al. (2019), It includes the collection of activities employed to respond to risk in advance and on a strategic level institution-wide with specific focus on nonfinancial risks including operational, compliance, and cyber risk. ERM is having a combined, institution-wide plan for identification, measurement, and controlling such risks utilizing all its business functions. Underlying this strategy is the governance presented by the Board of Directors and found at the highest level of governance. It is aided by expert panels and committees which help ensure the risk management practice of the firm remains aligned at all times with its strategic objectives and overall tolerance for risk, facilitating an institutionalized culture of risk-awareness and informed decision-making across the organization.
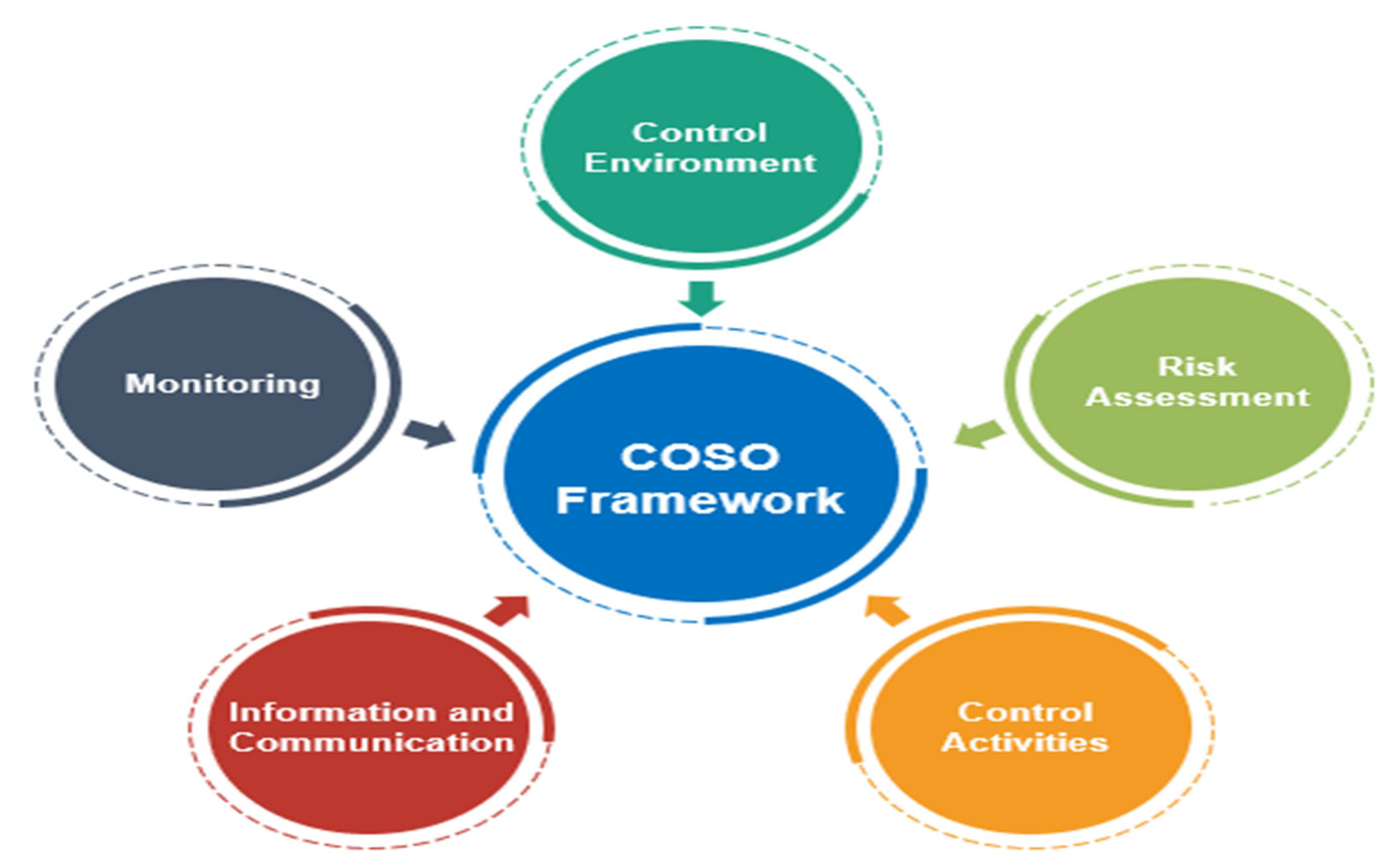
COSO Framework
The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) framework is a process ensuring a risk-managing mechanism for effective internal controls, good governance, and risk monitoring on a continuous basis. The COSO framework specifically has been referred to as a helpful tool to mitigate risks with the aim to foster the efficiency of operations for science parks and technology incubators (Wonglimpiyarat, 2017). By applying this model, organizations are able to regulate risks systematically, improve internal controls, and form effective governance principles, eventually supporting strategic innovation and sustainable growth in technology-oriented environments.
Solution
To respond to the imperative security risks and business disruption highlighted by recent developments, BDO Unibank devised a multi-pronged solution anchored on strong Enterprise Risk Management (ERM). The solution was to bolster cybersecurity infrastructure with the implementation of cutting-edge technologies like multi-factor authentication (MFA), real-time fraud detection systems, and biometric security, and strengthening operational resilience through extensive infrastructure upgrade.
Also initiated were customer education and awareness initiatives to reduce susceptibilities and increase resilience against repeated cyber attacks in the future. Further, following Rodriguez (2024) advise on embracing frontier digital technologies, the bank was focused on integrating its risk management policies with globally recognized standards like ISO 27001 to have assurance of information security, quality, and conformance. Emphasizing Pinheiro and Júnior's (2015) and Wonglimpiyarat's (2017) recommendations, BDO embraced structured risk management frameworks like the COSO model, with emphasis on sound internal controls, governance, and continuous monitoring.
The bank's Next Gen IT Transformation Program was successfully completed as part of implementation, enhancing operational responsiveness through biometric and QR-enabled ATMs and end-to-end branch automation. In addition, customer-centric workforce training and education campaigns were launched systematically with a view to broadly minimizing vulnerability to cyber attacks and operational breakdown. In line with suggestions by current research (Pinheiro and Júnior, 2015; Wonglimpiyarat, 2017), improving internal controls and governance practices were given high importance on an ongoing basis.
Implementation
The solutions were strategically implemented through BDO’s comprehensive Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework. At the highest organizational level, the Board of Directors and specialized committees, particularly the Risk Management Committee, provided leadership and oversight, establishing clear risk appetite and risk tolerance limits. BDO completed its Next Gen IT Transformation Program in April 2021, transitioning to a plug-and-play IT infrastructure designed for greater agility, scalability, security, and resilience. Simultaneously, the bank rolled out advanced digital services such as BDO Pay (a mobile wallet), fully digital account opening, and biometric authentication in branches and ATMs. Internal compliance was reinforced through rigorous internal audits, implementation of the ISO 27001 information security management system, and continuous employee training programs to embed a stronger risk-aware culture throughout the organization.
Expected Outcomes
The proposed and implemented solutions were expected to significantly enhance BDO’s operational resilience, financial stability, and regulatory compliance. Specifically, the strengthened cybersecurity framework was anticipated to substantially reduce future financial losses from cyber incidents, protect customer accounts, and restore consumer trust. Operationally, investments in IT infrastructure and automation were expected to improve service efficiency, minimize system downtimes, and enhance customer satisfaction. On the compliance front, adherence to international security standards (ISO 27001) and improved internal control systems were projected to minimize regulatory risks, reduce exposure to compliance fines, and sustain BDO’s strong reputation in the market. Collectively, these solutions aimed to reinforce BDO’s market position, resilience, and long-term sustainability in the highly competitive Philippine banking landscape.
Results
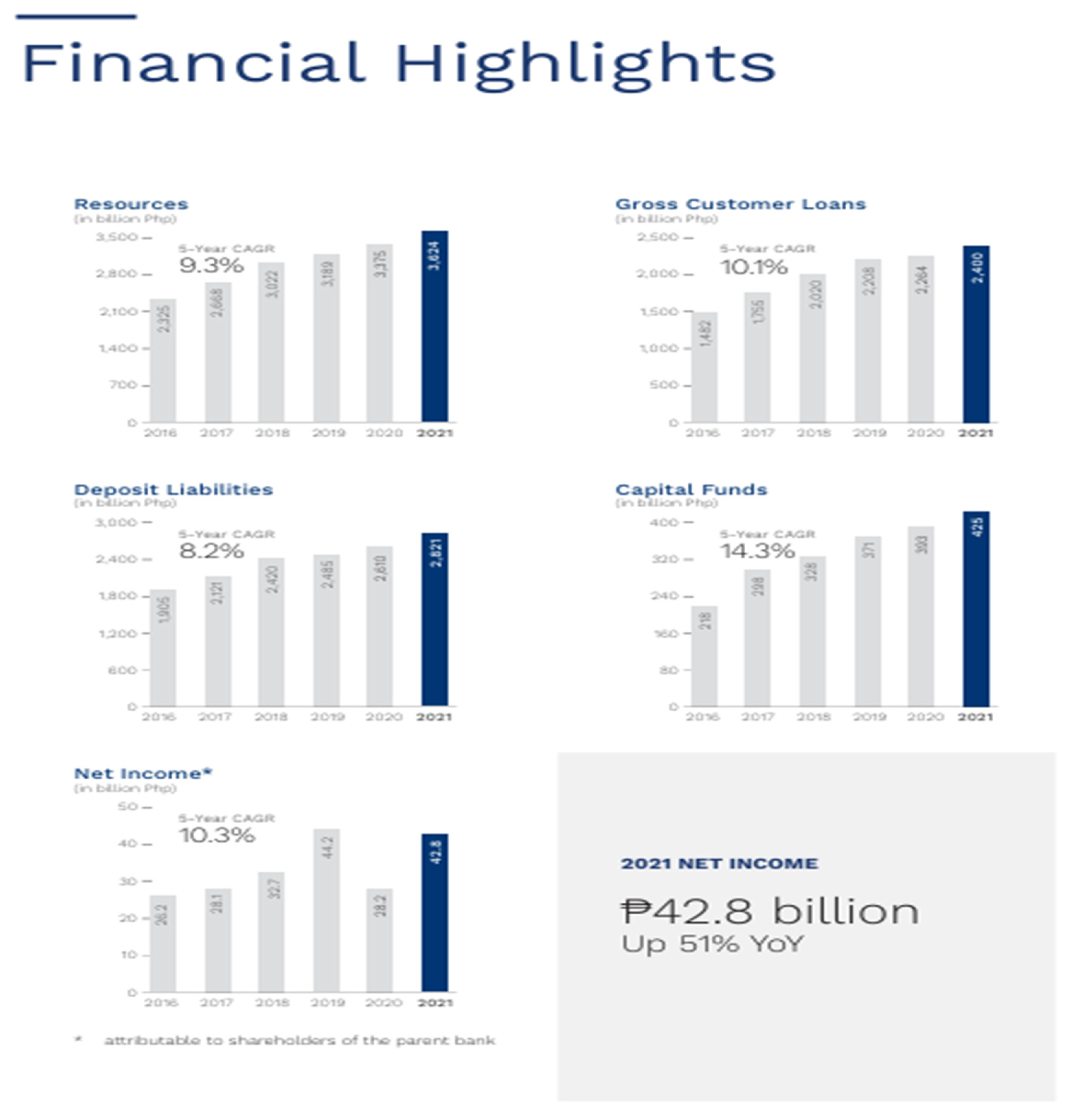
Following the implementation of comprehensive risk management measures, BDO Unibank achieved significant improvements reflected in its financial and operational results. By the end of 2021, BDO recorded a net income of PHP 42.8 billion, representing a remarkable 51% increase from the previous year. Loan portfolios grew by 6%, while deposits increased by 8%, driven largely by growth in low-cost CASA deposits, which reached a record ratio of 85%. Additionally, BDO successfully completed its Next Gen IT Transformation Program, enhancing its digital banking capabilities, improving cybersecurity through biometric and QR code-enabled ATMs, and rolling out BDO Pay, the Philippines' first bank-backed mobile wallet with over half a million enrolled users since its launch in 2021. Asset quality stabilized, with a Gross Non-Performing Loans (NPL) ratio declining to 2.8%, supported by an increased NPL coverage of 111%. These results indicate substantial improvements following the bank’s strategic response to earlier crises.
Comparing these actual outcomes with initial expectations, BDO largely met and, in some cases, exceeded anticipated improvements. The bank effectively enhanced its financial resilience, regained consumer confidence, and achieved robust financial performance despite the challenging environment. Operationally, expected outcomes, such as improved cybersecurity and operational reliability from the IT infrastructure upgrades, were achieved, as evidenced by the successful launch and wide customer adoption of BDO Pay, fully digital account openings, and cardless ATM transactions with biometrics. The actual improvements in customer deposits, liquidity, and profitability metrics significantly surpassed the modest recovery initially anticipated in the wake of the COVID-19 disruptions.
The implemented solutions proved highly effective, as demonstrated by BDO’s rapid recovery in profitability, improved financial stability, and enhanced customer trust. The successful completion of the Next Gen IT Transformation Program notably strengthened operational resilience and cybersecurity preparedness, significantly reducing system downtimes and mitigating cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Adoption of ISO 27001 standards significantly improved the bank’s compliance framework, thereby reducing regulatory exposure. Nonetheless, the implementation faced challenges, notably the considerable financial and logistical investments required for technological upgrades and employee training. The complexity of aligning internal processes with new cybersecurity measures posed initial hurdles but was effectively managed through comprehensive governance oversight by the Board and specialized committees. Overall, the measures adopted have positioned BDO strongly for future growth and risk management, solidifying its resilience and reinforcing its leadership in the Philippine banking sector
Conclusion
The case study analyzed the risk management approach at BDO Unibank, highlighting its exposure to financial, operational, and compliance risks following significant cyber fraud incidents and service disruptions in 2021 and 2022. The cyber fraud attack severely impacted customer trust, caused financial losses, and exposed vulnerabilities in the bank’s cybersecurity infrastructure. Operational disruptions, particularly system downtimes, further undermined customer satisfaction. To address these challenges, BDO implemented a comprehensive Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) approach, significantly investing in advanced cybersecurity measures, including multi-factor authentication, biometric and QR-enabled ATMs, real-time fraud detection, and customer education campaigns. Furthermore, BDO completed the Next Gen IT Transformation Program, improving operational agility and resilience. Compliance frameworks were reinforced by adopting international standards such as ISO 27001, which enhanced regulatory adherence and strengthened internal controls. As a result, BDO’s performance markedly improved, with net income rising by 51%, loan growth of 6%, and deposit growth of 8%, underscoring successful recovery and restored customer trust.
The case revealed critical insights emphasizing that robust risk management is fundamental in navigating and recovering from severe disruptions. It highlighted the need for continuous improvement, agility in response to emerging threats, and strict adherence to global security standards. Increased dependency on digital channels underscores the necessity of operational resilience and proactive cybersecurity preparedness. The effective response demonstrated by BDO showcased the importance of strategic oversight at the Board and senior management level, emphasizing the value of a strong, integrated governance structure. Continuous customer education was also identified as essential in strengthening customer trust and mitigating cybersecurity threats.
Recommendations
For BDO Unibank and similar financial organizations encountering comparable challenges, the following recommendations are suggested:
1. Invest Continuously in Cybersecurity and Digital Resilience
Regularly upgrade security infrastructure and adopt emerging technologies such as AI-driven fraud detection and blockchain-based transaction verification to proactively identify and prevent threats.
2. Enhance Workforce Capability through Regular Training
Implement ongoing training programs to develop employees’ competencies in managing new and complex risk landscapes, aligning with Rodriguez’s (2024) recommendation that workforce development is vital to sustaining a robust ABCD (AI, Blockchain, Cloud, Data) technology culture.
3. Strengthen Compliance and Governance Frameworks
Consistently apply international best practices like the COSO and ISO 27001 frameworks, ensuring comprehensive internal controls, effective governance, and continuous risk monitoring.
4. Promote Customer Education and Awareness
Maintain active customer education programs emphasizing fraud prevention, digital security best practices, and responsible financial behaviors.
5. Build Agile Risk Governance Structures
Strengthen the ERM framework by ensuring the Board of Directors and specialized committees remain actively engaged, quickly adapting to changing regulatory environments and emerging industry trends.
References
- Annual Report of BDO (2021). https://www.bdo.com.ph/content/dam/bdounibank/en-ph/about-bdo/disclosures/asm/2022/2021-annual-report.pdf.
- Banco De Oro (2025). Enterprise Risk Management, https://www.bdo.com.ph/about-bdo/corporate-governance/enterprise-risk-management.
- Brown, J. , Duane, M. & Schuermann, T. (2019). What is enterprise risk management? In the Journal of Risk Management in Financial Institutions, Volume 12, Issue 4. [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F., & Júnior, W. (2015). INFORMATION SECURITY AND ISO 27001, 3. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.M. (2024). The AI, Blockchain, Cloud and Data (ABCD) technology integration in the Philippines: A literature review. Journal of Interdisciplinary Perspectives. [CrossRef]
- Wonglimpiyarat, J. (2017). Technology auditing and risk management of technology incubators/science parks. World Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Sustainable Development, 13, 44-56. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).