Submitted:
16 April 2025
Posted:
18 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Ammonia and Hydrogen Characteristics in ICEs
2.1. Ammonia as a Fuel
2. Ammonia Blended Technologies
2.1. Ammonia Blends with Hydrocarbon Fuels
2.2. Ammonia Blends with Hydrogen
3. Fuel Injection Strategies for the Combustion Process
3.1. Ammonia Injection Strategies for ICEs Engine
3.2. Hydrogen Injection Strategies for ICES Engine
4. Conclusion
- The mechanical approaches for ammonia combustion have mitigated the common challenges in a few studies. As an example, with the addition of a new ignition system or the introduction of a second fuel, minimum ignition energy can be decreased. Only the addition of a combustion promoter can markedly improve flame speed.
- Mixing ammonia with hydrogen has relatively fewer adverse effects than other fuel blend combinations at the same time promotes combustion characteristics of ammonia. Both ammonia and hydrogen have very high octane rating which allows burning them on higher compression ratio engines that improves thermal efficiency and engine performance.
- An ammonia doping ratio of about 10% has been reported to provide inhibitive combustion and operating efficiency of the ammonia-doped hydrogen engines. However, it may not make the most efficient use of space and energy and raises additional safety concerns. Hydrogen production can help save resources wastage, mitigate safety issues, and ensure the efficient working of hydrogen-ammonia engines.
- Ammonia decomposition for hydrogen production has been revealed to be a feasible method for supplying hydrogen, as it allows the elimination of hydrogen storage, which lowers the costs and the required amount of equipment. However, this approach is still limited by several factors including the decrease in hydrogen production when ammonia flow and consumption rise because the residence time of ammonia in the catalyst is short.
Author Contributions
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aTDC | After Top Dead Center |
| bTDC | Before Top Dead Center |
| CA | Crank Angle |
| CI | Compression Ignition (engine) |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide |
| CO₂ | Carbon Dioxide |
| DEE | Diethyl Ether |
| DME | Dimethyl Ether |
| DI | Direct Injection |
| EEOI | Energy Efficiency Operational Index (used in maritime emissions) |
| GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
| H₂ | Hydrogen |
| HCCI | Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition |
| HRR | Heat Release Rate |
| ICE | Internal Combustion Engine |
| IMO | International Maritime Organization |
| LBV | Laminar Burning Velocity |
| MJ/kg | Megajoules per kilogram (energy density) |
| NH₃ | Ammonia |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| NO₂ | Nitrogen Dioxide |
| NOₓ | Nitrogen Oxides (collective term for NO, NO₂, N₂O) |
| N₂O | Nitrous Oxide |
| PFI | Port Fuel Injection |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| SI | Spark Ignition (engine) |
| SOₓ | Sulfur Oxides |
| TDC | Top Dead Center |
| Vol.% | Volume Percentage |
References
- Yapicioglu, Arda; Dincer, Ibrahim. A review on clean ammonia as a potential fuel for power generators. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2019, 103, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehade, G. , & Dincer, I. Progress in green ammonia production as potential carbon-free fuel. Fuel, 2021, 299, 120845. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Goryong; Cho, Kwonhae. A study on the change of EEOI before and after modifying bulbous at the large container ship adopting low speed operation. Journal of the Korean Society of Marine Engineering. 2017, 41, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senecal, Peter & Leach, Felix. (2019). Diversity in transportation: Why a mix of propulsion technologies is the way forward for the future fleet. Results in Engineering. 4. 100060. [CrossRef]
- Vidal, Carlos & Lamas, María & Rodriguez, Juan de Dios & Abbas, Amr. (2022). Possibilities of Ammonia as Both Fuel and NOx Reductant in Marine Engines: A Numerical Study. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 10. 43. [CrossRef]
- Seediek, Ibrahim & Elgohary, Mohamed & Ammar, Nader. (2015). The hydrogen-fuelled internal combustion engines for marine applications with a case study. Brodogradnja. 66. 23-38.
- Jensen, Jens Oluf & Vestbø, A.P. & Li, Q. & Bjerrum, N.J.. (2007). The energy efficiency of onboard hydrogen storage. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 446. 723-728. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Mei & Wang, Yuegu & Chu, Yuchun & Tang, Youning & Tian, Koukou & Zheng, Songsheng & Chen, Jin & Wang, Zhaolin. (2019). Ammonia as an environmentally benign energy carrier for the fast growth of China. Energy Procedia. 158. 4986-4991. [CrossRef]
- Wan, Zhijian & Tao, Youkun & Shao, Jing & Zhang, Yinghui & You, Hengzhi. (2021). Ammonia as an effective hydrogen carrier and a clean fuel for solid oxide fuel cells. Energy Conversion and Management. 228. 113729. [CrossRef]
- Al-Aboosi, Fadhil & El-Halwagi, Mahmoud & Moore, Margaux & Nielsen, Rasmus. (2021). Renewable ammonia as an alternative fuel for the shipping industry. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering. 31. 100670. [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamed, Khaled H.M. & Dincer, Ibrahim, 2021. A novel ammonia solid oxide fuel cell-based powering system with on-board hydrogen production for clean locomotives, Energy, Elsevier, vol. 220(C). [CrossRef]
- Mørch, C. S. , Bjerre, A., Gøttrup, M. P., Sorenson, S. C., & Schramm, J. (2011). Ammonia/Hydrogen Mixtures in an SI-Engine: Engine performance and analysis of a proposed fuel system. Fuel. 2011;90:854-864. [CrossRef]
- Valera-Medina, A., Xiao, H., Owen-Jones, M., David, W.I.F., Bowen, P.J.. 2018. Ammonia for power”, Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 69 : 63–102, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Lhuillier, Charles & Brequigny, Pierre & Contino, Francesco & Mounaïm-Rousselle, Christine. (2019). Combustion Characteristics of Ammonia in a Modern Spark-Ignition Engine. [CrossRef]
- Starkman, E.S. , Newhall, H.K., Sutton, R.D., Maguire, T., & Farbar, L. (1966). Ammonia as a spark ignition engine fuel: theory and application. SAE paper 660155, 1966.
- Liu, Rui & Ting, David & Checkel, M.. (2003). Ammonia as a Fuel for SI Engine. SAE Technical Papers. [CrossRef]
- Li, Jun & Huang, Hongyu & Kobayashi, Noriyuki & He, Zhaohong & Nagai, Yoshihiro. (2014). Study on using hydrogen and ammonia as fuels: Combustion characteristics and NOx formation. International Journal of Energy Research. 38. 1214-1223. [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, M. F & Dincer, I., (2018). Development and assessment of a new hybrid vehicle with ammonia and hydrogen, Applied Energy, Elsevier, vol. 219(C), pages 226-239. [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Kyunghyun & Zacharakis-Jutz, George & Kong, Song-Charng. (2014). Effects of gaseous ammonia direct injection on performance characteristics of a spark-ignition engine. Applied Energy. 116. 206–215. [CrossRef]
- Niki, Yoichi & Nitta, Yoshifuru & Sekiguchi, Hidenori & Hirata, Koichi. (2019). Diesel Fuel Multiple Injection Effects on Emission Characteristics of Diesel Engine Mixed Ammonia Gas Into Intake Air. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power. 141. [CrossRef]
- Lhuillier, Charles & Brequigny, Pierre & Contino, Francesco & Mounaïm-Rousselle, Christine. (2019). Performance and Emissions of an Ammonia-Fueled SI Engine with Hydrogen Enrichment. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D., & Song, H.H. (2018). Development of combustion strategy for the internal combustion engine fueled by ammonia and its operating characteristics. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 32, 1905-1925.
- Nozari, Hadi & Karabeyoglu, Arif. (2015). Numerical study of combustion characteristics of ammonia as a renewable fuel and establishment of reduced reaction mechanisms. Fuel. 159. 223-233. [CrossRef]
- Lhuillier, Charles & Brequigny, Pierre & Contino, Francesco & Mounaïm-Rousselle, Christine. (2020). Experimental investigation on ammonia combustion behavior in a spark-ignition engine by means of laminar and turbulent expanding flames. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute. 38. 5859-5868. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D., Li, J., Huang, H., Chen, Y., He, Z., & Deng, L. (2020). Progress in ammonia combustion and reaction mechanism. Chemistry, 83(6), 508-515.
- Dimitriou, Pavlos & Javaid, Rahat. (2020). A review of ammonia as a compression ignition engine fuel. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 45. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Yuan & Zhu, Jizhen & Mao, Yebing & Raza, Mohsin & Qian, Yong & Yu, Liang & Lu, Xingcai. (2020). Low-temperature auto-ignition characteristics of NH3/diesel binary fuel: Ignition delay time measurement and kinetic analysis. Fuel. 281. 118761. [CrossRef]
- Yapicioglu, Arda & Dincer, Ibrahim. (2018). Performance assesment of hydrogen and ammonia combustion with various fuels for power generators. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 43. [CrossRef]
- Mounaïm-Rousselle, Christine & Brequigny, Pierre. (2020). Ammonia as Fuel for Low-Carbon Spark-Ignition Engines of Tomorrow's Passenger Cars. Frontiers in Mechanical Engineering. 6. 70. [CrossRef]
- Lan, Rong & Irvine, John & Tao, Shanwen. (2012). Ammonia and related chemicals as potential indirect hydrogen storage materials. Fuel and Energy Abstracts. 37. [CrossRef]
- Lamb, Krystina & Dolan, Michael & Kennedy, Danielle. (2019). Ammonia for hydrogen storage; A review of catalytic ammonia decomposition and hydrogen separation and purification. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 44. [CrossRef]
- Koike, Makoto & Miyagawa, H. & Suzuoki, T. & Ogasawara, K.. (2012). Ammonia as a hydrogen energy carrier and its application to internal combustion engines. [CrossRef]
- Splitter, Derek & Szybist, James. (2014). Intermediate Alcohol-Gasoline Blends, Fuels for Enabling Increased Engine Efficiency and Powertrain Possibilities. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr.. 7. 10-4271. [CrossRef]
- Ayvalı, T. , Edman Tsang, S. C., & Van Vrijaldenhoven, T. (2021). The Position of Ammonia in Decarbonising Maritime Industry: An Overview and Perspectives: Part I: Technological advantages and the momentum towards ammonia-propelled shipping. Johnson Matthey technology review, 65(2), 275-290.
- Abedin, Ahmed & Radenahmad, Nikdalila & Cheok, Quentin & Shams, Shahriar & Kim, Jung & Azad, Abul. (2016). Ammonia-fed fuel cells: A comprehensive review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 60. 822-835. [CrossRef]
- Langella, Giuseppe & de Joannon, Mara & Sabia, Pino & Iodice, Paolo & Amoresano, Amedeo. (2022). Ammonia as a fuel for internal combustion engines: latest advances and future challenges. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 2385. 012036. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Hideaki & Hayakawa, Akihiro & Somarathne, Kapuruge Don Kunkuma & Okafor, Ekenechukwu. (2018). Science and technology of ammonia combustion. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute. 37. [CrossRef]
- Kurien, Caneon & Mittal, Mayank. (2022). Review on the production and utilization of green ammonia as an alternate fuel in dual-fuel compression ignition engines. Energy Conversion and Management. 251. 114990. [CrossRef]
- Long Liu, Yue Wu, Yang Wang. (2022). Numerical investigation on the combustion and emission characteristics of ammonia in a low-speed two-stroke marine engine, Fuel, Volume 314, 2022, 122727, ISSN 0016-2361.
- Looijenga, J. Y. (2020). The feasibility of zero-emission ferries in the Wadden Sea (Doctoral dissertation, PhD thesis. Delft: TU Delft).
- Mestemaker, B. T. W. , Castro, M. G., Van Der Blom, E. C., Cornege, H. J., & Visser, K. (2019, July). Zero emission vessels from a shipbuilders perspective. In 2nd International Conference on Smart & Green Technology for the Future of Marine Industries (SMATECH 2019)–Conference Proceedings (pp. 11-12).
- Rachele Lamioni, Cristiana Bronzoni, Marco Folli, Leonardo Tognotti, Chiara Galletti. (2023). Impact of H2-enriched natural gas on pollutant emissions from domestic condensing boilers: numerical simulations of the combustion chamber, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 48, Issue 51, 2023, Pages 19686-19699, ISSN 0360-3199.
- Ciniviz, M. and Kose, H. (2012). Hydrogen Use in Internal Combustion Engine: A Review. International Journal of Automotive Engineering and Technologies, 2012, Vol. 1, Issue 1, pp. 1-15.
- Heywood, J. (2018). Internal combustion engine fundamentals.
- Koch, E. J. J. I. P. (1945). Ammonia–a fuel for motor buses. J. Inst. Pet, 31(213), 498.
- Cornelius, W. , Huellmantel, L. W., & Mitchell, H. R. (1966). Ammonia as an engine fuel. SAE Transactions, 300-326.
- Gray Jr, James T., Edward Dimitroff, Nelson T. Meckel, and R. D. Quillian Jr. "Ammonia fuel—engine compatibility and combustion." SAE Transactions (1967): 785-807.
- Pearsall, T. J., & Garabedian, C. G. (1968). Combustion of anhydrous ammonia in diesel engines. SAE Transactions, 3213-3221.
- Lhuillier, Charles & Brequigny, Pierre & Contino, Francesco & Mounaïm-Rousselle, Christine. (2020). Experimental study on ammonia/hydrogen/air combustion in spark ignition engine conditions. Fuel. 269. 117448. 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117448.
- Duynslaegher, C., Jeanmart, H., & Vandooren, J. (2010, September). Ammonia Combustion in spark ignition engine conditions. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual NH3 Fuel Conference, Romulus, MI, USA (pp. 26-28).
- Gross, Christopher & Kong, Song-Charng. (2013). Performance characteristics of a compression-ignition engine using direct-injection ammonia–DME mixtures. Fuel. 103. 1069-1079. [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere da Rocha, Rodolfo & Ramos, Carlos & Costa, Mário & Bai, Xue-Song. (2019). Combustion of NH3/CH4/Air and NH3/H2/Air Mixtures in a Porous Burner: Experiments and Kinetic Modeling. Energy & Fuels. XXXX. [CrossRef]
- Niki, Yoichi & Yoo, Dong-Hoon & Hirata, Koichi & Sekiguchi, Hidenori. (2016). Effects of Ammonia Gas Mixed Into Intake Air on Combustion and Emissions Characteristics in Diesel Engine. V001T03A004. [CrossRef]
- Reiter, Aaron & Kong, Song-Charng. (2011). Combustion and emissions characteristics of compression-ignition engine using dual ammonia-diesel fuel. Fuel. 90. 87-97. [CrossRef]
- Xiaowei Xu & Enlong Liu & Neng Zhu & Fanfu Liu & Feng Qian, 2022. Review of the Current Status of Ammonia-Blended Hydrogen Fuel Engine Development, Energies, MDPI, vol. 15(3), pages 1-19, January.
- Haputhanthri, Shehan. (2014). Ammonia Gasoline Fuel Blends: Feasibility Study of Commercially Available Emulsifiers and Effects on Stability and Engine Performance. SAE Technical Papers. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Tay, Kun & Yang, W.M. & Chou, S.K. & Zhou, Dezhi & Li, Jing & Wenbin, Yu & Zhao, Feiyang & Mohan, Balaji. (2017). Effects of Injection Timing and Pilot Fuel on the Combustion of a Kerosene-diesel/Ammonia Dual Fuel Engine: A Numerical Study. Energy Procedia. 105. 4621-4626. [CrossRef]
- Frigo, Stefano & Gentili, Roberto. (2013). Analysis of the behaviour of a 4-stroke Si engine fuelled with ammonia and hydrogen. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 38. 1607–1615. [CrossRef]
- Otomo, Junichiro & Koshi, Mitsuo & Mitsumori, Teruo & Iwasaki, Hiroshi & Yamada, Koichi. 2018. Chemical kinetic modeling of ammonia oxidation with improved reaction mechanism for ammonia/air and ammonia/hydrogen/air combustion. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 43. [CrossRef]
- Frigo, Stefano & Gentili, Roberto & Angelis, Franco. (2014). Further Insight into the Possibility to Fuel a SI Engine with Ammonia plus Hydrogen. SAE Technical Papers. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Pozzana, Giuseppe & Bonfanti, Neri & Frigo, Stefano & Doveri, Nicolò & Dario, Paolo & Mattoli, Virgilio & Ragnoli, Marina. (2012). A Hybrid Vehicle Powered by Hydrogen and Ammonia. SAE Technical Papers. 4. [CrossRef]
- Comotti, Massimiliano & Frigo, Stefano. (2015). Hydrogen generation system for ammonia-hydrogen fuelled internal combustion engines. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 40. 10673-10686. [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Kyunghyun & Zacharakis-Jutz, George & Kong, Song-Charng. (2014). Performance enhancement of ammonia-fueled engine by using dissociation catalyst for hydrogen generation. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 39. 2390-2398. [CrossRef]
- Boretti, Albert. (2012). Novel heavy duty engine concept for operation dual fuel H2–NH3. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 37. 7869–7876. [CrossRef]
- Pochet, Maxime & Truedsson, Ida & Foucher, F. & Jeanmart, Hervé & Contino, Francesco. (2017). Ammonia-Hydrogen Blends in Homogeneous-Charge Compression-Ignition Engine. SAE Technical Papers. 2017-24-0087. [CrossRef]
- Issayev, Gani & Giri, Binod & Elbaz, A. & Shrestha, Krishna Prasad & Mauss, Fabian & Roberts, William & Farooq, Aamir. (2020). Combustion behavior of ammonia blended with diethyl ether. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute. [CrossRef]
- Grannell, Shawn & Assanis, Dennis & Bohac, Stanislav & Gillespie, Donald. (2008). The Fuel Mix Limits and Efficiency of a Stoichiometric, Ammonia, and Gasoline Dual Fueled Spark Ignition Engine. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power-transactions of The Asme - J ENG GAS TURB POWER-T ASME. 130. [CrossRef]
- Reiter, Aaron & Kong, Song-Charng. (2010). Diesel Engine Operation Using Ammonia as a Carbon-Free Fuel. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Internal Combustion Engine Division (Publication) ICE. [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Kyunghyun & Zacharakis-Jutz, George & Kong, Song-Charng. (2014). Performance characteristics of compression-ignition engine using high concentration of ammonia mixed with dimethyl ether. Applied Energy. 113. 488-499. [CrossRef]
- Haputhanthri, Shehan & Maxwell, Timothy & Fleming, John & Austin, Chad. (2015). Ammonia and Gasoline Fuel Blends for Spark Ignited Internal Combustion Engines. Journal of Energy Resources Technology. 137. [CrossRef]
- Nash, D. & Aklil, D. & Johnson, E. & Gazey, R. & Ortisi, V. (2012). Hydrogen Storage. [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, M.F. & Dincer, Ibrahim. (2018). Comparative assessments of two integrated systems with/without fuel cells utilizing liquefied ammonia as a fuel for vehicular applications. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 43. 4597-4608. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H. & Kim, J.H. & Park, J.H. & Kwon, O.C. (2010). Study on properties of laminar premixed hydrogen-added ammonia/air flames for hydrogen production. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 35. 1054-1064. [CrossRef]
- Koike, Makoto & Suzuoki, Tetsunori. (2019). In-line adsorption system for reducing cold-start ammonia emissions from engines fueled with ammonia and hydrogen. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 44. [CrossRef]
- Du, Wang & Ji, Changwei & Wang, Shuofeng & Yang, Jinxin & Wang, Zhe. (2020). Numerical study of the premixed ammonia-hydrogen combustion under engine-relevant conditions. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 46. [CrossRef]
- Bro, K. and Pedersen, P. 1977. Alternative Diesel Engine Fuels: An Experimental Investigation of Methanol, Ethanol, Methane and Ammonia in a D.I. Diesel Engine with Pilot Injection, SAE Technical Paper 770794, 1977.
- Chiong, Meng-Choung & Chong, Cheng Tung & Ng, Jo-Han & Mashruk, Syed & Chong, William & Samiran, N. & Mong, Guo & Valera-Medina, Agustin. (2021). Advancements of combustion technologies in the ammonia-fuelled engines. Energy Conversion and Management. 244. 114460. [CrossRef]
- Niki, Yoichi & Nitta, Yoshifuru & Sekiguchi, Hidenori & Hirata, Koichi. (2019). Diesel Fuel Multiple Injection Effects on Emission Characteristics of Diesel Engine Mixed Ammonia Gas Into Intake Air. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power. 141. [CrossRef]
- Lamas, M.I. & Vidal, Carlos. (2019). NOx Reduction in Diesel-Hydrogen Engines Using Different Strategies of Ammonia Injection. Energies. 12. 1255. [CrossRef]
- Galdo, Lamas & Castro-Santos, Laura & Vidal, Carlos. (2020). Numerical Analysis of NOx Reduction Using Ammonia Injection and Comparison with Water Injection. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 8. 109. [CrossRef]
- Lamas MI, Rodriguez CG.. (2017). Numerical model to analyze NOx reduction byammonia injection in diesel-hydrogen engines. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017;42(41):26132–41.
- Lesmana, Herry & Zhang, Zhezi & Li, Xianming & Zhu, Mingming & Xu, Wenqiang & Zhang, Dongke. (2019). NH3 as a Transport Fuel in Internal Combustion Engines: A Technical Review. Journal of Energy Resources Technology. 141. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Ali & Shioji, M. & Nakai, Yasuyuki & Ishikura, Wataru & Tabo, Eizo. (2007). Performance and combustion characteristics of a direct injection SI hydrogen engine. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 32. 296-304. [CrossRef]
- Verhelst, Sebastian & Demuynck, Joachim & Sierens, Roger & Scarcelli, Riccardo & Matthias, Nicholas & Wallner, Thomas. (2013). Update on the Progress of Hydrogen-Fueled Internal Combustion Engines. [CrossRef]
- Yip HL, Srna A, Yuen ACY, Kook S, Taylor RA, Yeoh GH, Medwell PR, Chan QN. (2019). A Review of Hydrogen Direct Injection for Internal Combustion Engines: Towards Carbon-Free Combustion. Applied Sciences, 2019; 9(22):4842-1-4842-30.
- Ozcanli, Mustafa & Baş, Oğuz & Akar, Mustafa & Yıldızhan, Şafak & Serin, Hasan. (2018). Recent studies on hydrogen usage in Wankel SI engine.
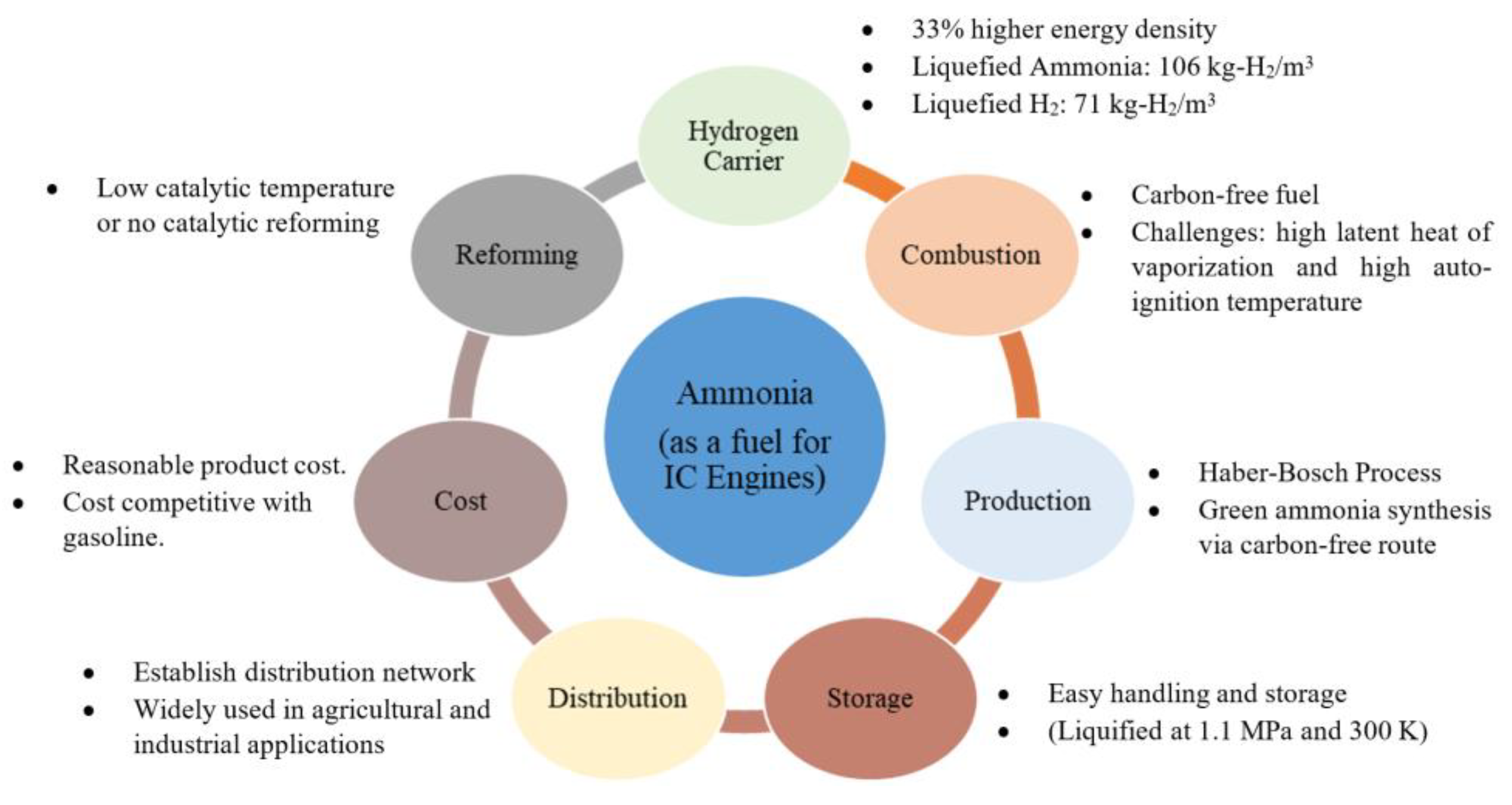
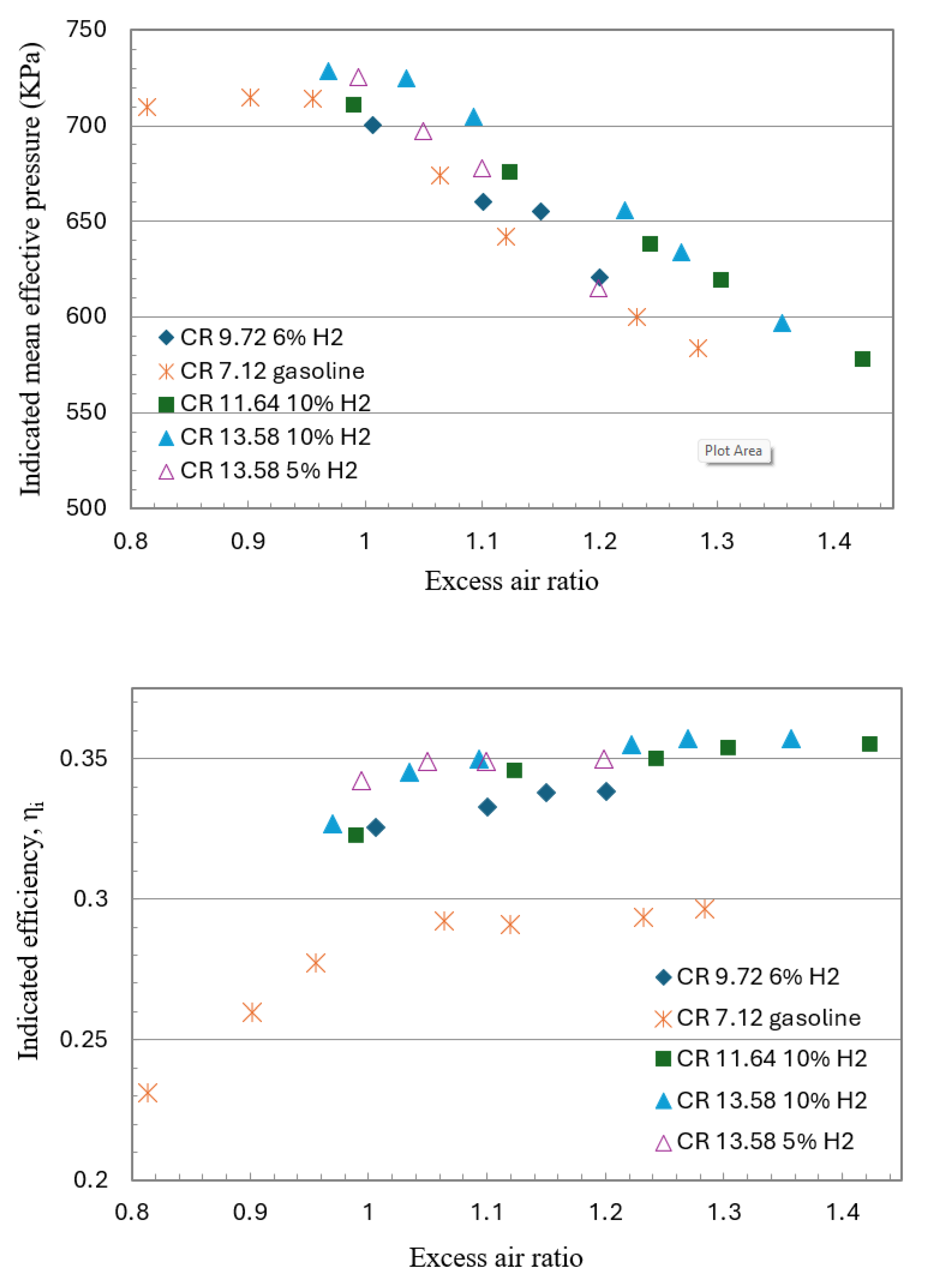
| Species | Units | Ammonia | Hydrogen | Gasoline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage | - | Liquid | Compressed | Liquid |
| Lower heating value | MJ/Kg | 18.8 | 120.0 | 44.5 |
| Laminar flame velocity | m/s | 0.015 | 3.51 | 0.58 |
| Flammability limits, gas in air | Vol.% | 15-28 | 4.7-75 | 0.6-8 |
| Autoignition temperature | °C | 651 | 500-577 | 230 |
| Absolute min. ignition energy | mg | 8.0 | 0.018 | 0.14 |
| Octane number Minimum Ignition Energy, Explosion limit (volume ratio) |
- mj % |
>130 680 16~28 |
>100 0.02 4.5~75 |
90-98 0.20 1.4~7.6 |
| Main Authors | Year | Engine (SI/CI) | Focuses and Progress |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emerio Kroch [45] | 1942 | Diesel oil | The first utilization of liquid anhydrous ammonia for motor buses in Belgium. |
| Cornelius W et al. [46] | 1960s | SI/CI | Examining factors such as material requirements, corrosive properties, and combustion characteristics for Ammonia. |
| Gray Jr JT et al.[47] | |||
| Pearsall TJ and Garabedian CG [48] | Conducting multiple studies by the US Army to increase fuel independence. |
| Main Authors | Year | Type | Focuses and Progress |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reiter A. J. et al. [54] | 2011 | Experiment | Demonstrated dual-fuel CI operation with ammonia-diesel; reduced CO₂ emissions but faced ignition delay and efficiency trade-offs. |
| Gross CW, Kong SC [51] | 2013 | Experiment | Studied CI engine using direct-injection ammonia–DME blends; improved ignition and combustion performance with higher DME content. |
| Haputhanthri SO [56] | 2014 | Experiment | Evaluated ammonia-gasoline blends with emulsifiers; showed improved fuel stability and potential for engine performance enhancement. |
| Niki Y. et al. [53] | 2016 | Experiment | Investigated ammonia mixed into intake air in diesel engines; found improved combustion and reduced emissions, with challenges in ammonia control. |
| Tay, K.L. et al. [57] | 2017 | Simulation | Numerically studied injection timing and pilot fuel effects in a kerosene-diesel/ammonia dual-fuel engine; found improved combustion and efficiency with optimized injection strategies. |
| Valera-Medina, A et al [13] | 2018 | Review | Reviewed the use of ammonia as a fuel for power generation, focusing on its potential to reduce CO₂ emissions. |
| Niki Y. et al. [20] | 2019 | Experiment | Investigated the effects of multiple diesel fuel injections in a diesel engine with ammonia mixed into intake air; found reduced emissions and improved combustion performance with optimized injection strategies. |
| Dimitriou P, Javaid R. [26] | 2020 | Review | Reviewed ammonia as a CI engine fuel; highlighted challenges in combustion control and emissions, while emphasizing its potential for reducing CO₂. |
| Main Authors | Year | Type | Focuses and Progress |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mørch CS [12] | 2011 | Experiment | Examined ammonia/hydrogen mixtures in an SI engine, improving combustion efficiency and emissions control, and proposing a modified fuel system for optimized dual-fuel use. |
| Boretti AA [64] | 2012 | Experiment | Proposed a novel heavy-duty engine concept using a dual-fuel H2–NH3 system. The study highlighted the potential for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, while addressing the technical challenges of ammonia and hydrogen combustion in heavy-duty engines. |
| Pozzana G et al. [61] | 2012 | Experiment | Explored a hybrid vehicle powered by hydrogen and ammonia, focusing on the integration of these fuels for improved vehicle efficiency and reduced environmental impact. The study assessed the potential benefits and challenges of using hydrogen-ammonia combinations in hybrid vehicle applications. |
| Frigo S Gentili R [58] | 2012 | Experiment | Analyzed the performance of a 4-stroke SI engine fueled with ammonia and hydrogen. The study highlighted improved combustion characteristics and emission reductions, while discussing the challenges related to ammonia’s ignition properties and the need for optimized fuel management. |
| Frigo, S et al. [60] | 2014 | Experiment | Further explored the feasibility of fueling an SI engine with ammonia and hydrogen. Highlighting improvements in engine efficiency and emission reductions, while addressing challenges such as ignition delay and fuel mixture control. |
| Ryu K et al. [19] | 2014 | Experiment | Studying the combustion and emissions of an SI engine with direct ammonia injection and port-injected gasoline showed enhanced power performance, making it comparable to a gasoline engine. |
| Ryu K et al. [63] | 2014 | Experiment | Studied direct ammonia injection in a spark-ignition engine; found improved combustion efficiency and reduced CO₂ emissions, but challenges with ignition control and lower energy content. |
| Comotti M [62] | 2015 | Description | Developed a hydrogen generation system for ammonia-hydrogen fueled engines, improving fuel efficiency and emissions while addressing integration challenges. |
| Otomo, J et al. [59] | 2018 | Description | Developed a chemical kinetic model for ammonia oxidation with an improved reaction mechanism for ammonia/air and ammonia/hydrogen/air combustion, enhancing the understanding of combustion characteristics and efficiency. |
| Langella G et al [36] | 2022 | Description | Reviewed the latest advances and future challenges of using ammonia as a fuel for internal combustion engines, highlighting its potential for reducing emissions and the technical barriers such as combustion efficiency and NOx control. |
| Authors | Year | Mixture composition of fuel | Engine type | Main findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Issayev et al. [66] | 2020 | 95-80% NH3/5-20% DEE | CI | Studied ammonia blended with diethyl ether, showing improved combustion efficiency and emissions for alternative fuel applications. |
| Reiter and Kong [68] | 2010 | 95% NH3/5% diesel | CI | Investigated diesel engine operation using ammonia as a carbon-free fuel, demonstrating potential for reduced emissions and highlighting operational challenges. |
| Reiter and Kong [54] | 2011 | 60% NH3/40% diesel; 40% NH3/60% diesel | CI | Examined the combustion and emissions of a compression-ignition engine using dual ammonia-diesel fuel, finding improved combustion efficiency and reduced emissions, with some challenges in ignition control. |
| Gross and Kong [51] | 2013 | 20% NH3/80% DME; 40% NH3/60% DME | CI | Studied a compression-ignition engine using direct-injection ammonia-DME mixtures, finding improved performance and reduced emissions, with challenges in optimizing the fuel mixture. |
| Ryu et al. [69] | 2014 | 60% NH3/40% DME; 40% NH3/60% DME | CI | Investigated a compression-ignition engine using high ammonia concentrations mixed with dimethyl ether, finding enhanced performance and reduced emissions, with challenges in controlling combustion stability. |
| Pochet et al. [65] | 2017 | 70 vol% NH3 + H2 | CI | Explored ammonia-hydrogen blends in a homogeneous-charge compression-ignition engine, showing improved combustion efficiency and reduced emissions, with a focus on optimizing fuel mixture and engine operation. |
| Bro and Pedersen [76] | 1977 | Methanol (84%), Ethanol (80%), Methane (62%), Ammonia (87%)and Diesel | CI | Studied ammonia as an alternative fuel in a diesel engine, noting lower emissions but challenges with ignition and efficiency. |
| Authors | Year | Mixture composition of fuel | Engine type | Main findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grannell et al. [67] | 2008 | 70% NH3/30% gasoline | SI | Explored the fuel mix limits and efficiency of a stoichiometric ammonia and gasoline dual-fueled spark ignition engine, highlighting challenges in maintaining efficiency while using ammonia as a fuel. |
| Haputhanthri et al. [70] | 2015 | Gasoline + 30 vol% ethanol or methanol + 17.35 vol% NH3 | SI | Studied ammonia-gasoline blends in spark-ignited engines, showing potential for better fuel efficiency and lower emissions. |
| Ezzat and Dincer [72] | 2018 | 80% NH3/20% H2 | - | Compared two systems using liquefied ammonia for vehicular applications, with and without fuel cells. The study assessed performance, efficiency, and environmental impact, demonstrating the viability of ammonia as a sustainable vehicle fuel. |
| Lee and al. [73] | 2010 | Fuel equivalence ratio of 0.60-1.67 mole fraction of H2 | - | Studied laminar premixed hydrogen-ammonia/air flames for hydrogen production. The research revealed the combustion properties of ammonia-hydrogen blends, contributing to hydrogen generation for sustainable energy systems. |
| Koike and Suzuoki [74] | 2019 | 40% NH3/60% H2 | SI | Developed an in-line adsorption system to reduce cold-start ammonia emissions in ammonia-hydrogen fueled engines, improving environmental performance and emission control. |
| Du et al. [75] | 2021 | NH3/40-60% H2 | SI | Conducted a numerical study on premixed ammonia-hydrogen combustion under engine-relevant conditions, optimizing combustion efficiency and emissions in ammonia-hydrogen powered engines. |
| Lhuillier et al. [49] | 2020 | NH3/0-60% H2 | SI | Studied ammonia/hydrogen/air combustion in a spark ignition engine, showing improved combustion efficiency but challenges with emissions control. |
| Main Authors | Year | Engine | Type | Focuses and Progress |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lamas & Rodriguez [81] | 2017 | CI | Simulation | Developed a numerical model to analyze NOx reduction through ammonia injection in diesel-hydrogen engines, demonstrating potential for emissions control. |
| Lee & Song [22] | 2018 | - | Experiment | Developed a combustion strategy for ammonia-fueled internal combustion engines, examining its operating characteristics and potential for enhanced performance. |
| Niki et al. [78] | 2019 | CI | Experiment | Studied the effects of multiple diesel fuel injections on emission characteristics in a diesel engine with ammonia gas mixed into the intake air, finding improvements in emission control. |
| Lesmana H et al. [82] | 2019 | CI | Review | A technical review assessing the existing understanding of using ammonia as a fuel in internal combustion engines, either in its pure form or combined with other fuels |
| Lamas MI, Rodriguez CG [79] | 2019 | CI | Simulation | Investigating different fuel injection configurations, such as parabolic, triangular, and rectangular shapes to reduce NOx emissions in internal combustion engines. |
| Lamas et al. [80] | 2020 | CI | Simulation | explored the reduction of NOx emissions by nearly 80% in a marine diesel engine using direct ammonia injection into the cylinder, comparing this approach with water injection. |
| Chiong M C et al. [77] | 2021 | SI/CI engine & gas turbine | Experiment | Advancements in ammonia combustion to make it a viable option for sustainable energy in engines and turbines. |
| Main Authors | Year | Engine | Type | Focuses and Progress |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mohammadi A et al. [83] | 2007 | SI | Experiment | Studied the performance and combustion of a direct injection SI hydrogen engine, showing efficiency gains but highlighting combustion control challenges. |
| Verhelst S et al. [84] | 2013 | SI/CI | Description | The progress of hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engines was reviewed, highlighting advancements in combustion efficiency, emissions reduction, and the challenges of hydrogen storage and engine design. |
| Ozcanli, M et al. [86] | 2018 | SI | Description | The study reviews recent research on hydrogen usage in Wankel spark-ignition (SI) engines, focusing on performance improvements, combustion characteristics, and emission reductions associated with hydrogen as a fuel. |
| Yip HL et al [85] | 2019 | SI/CI | Description | The review explores hydrogen direct injection in engines, focusing on its potential for carbon-free combustion, performance, and emission reduction challenges. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





