Submitted:
21 April 2025
Posted:
21 April 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
1. Methodology of Derivation
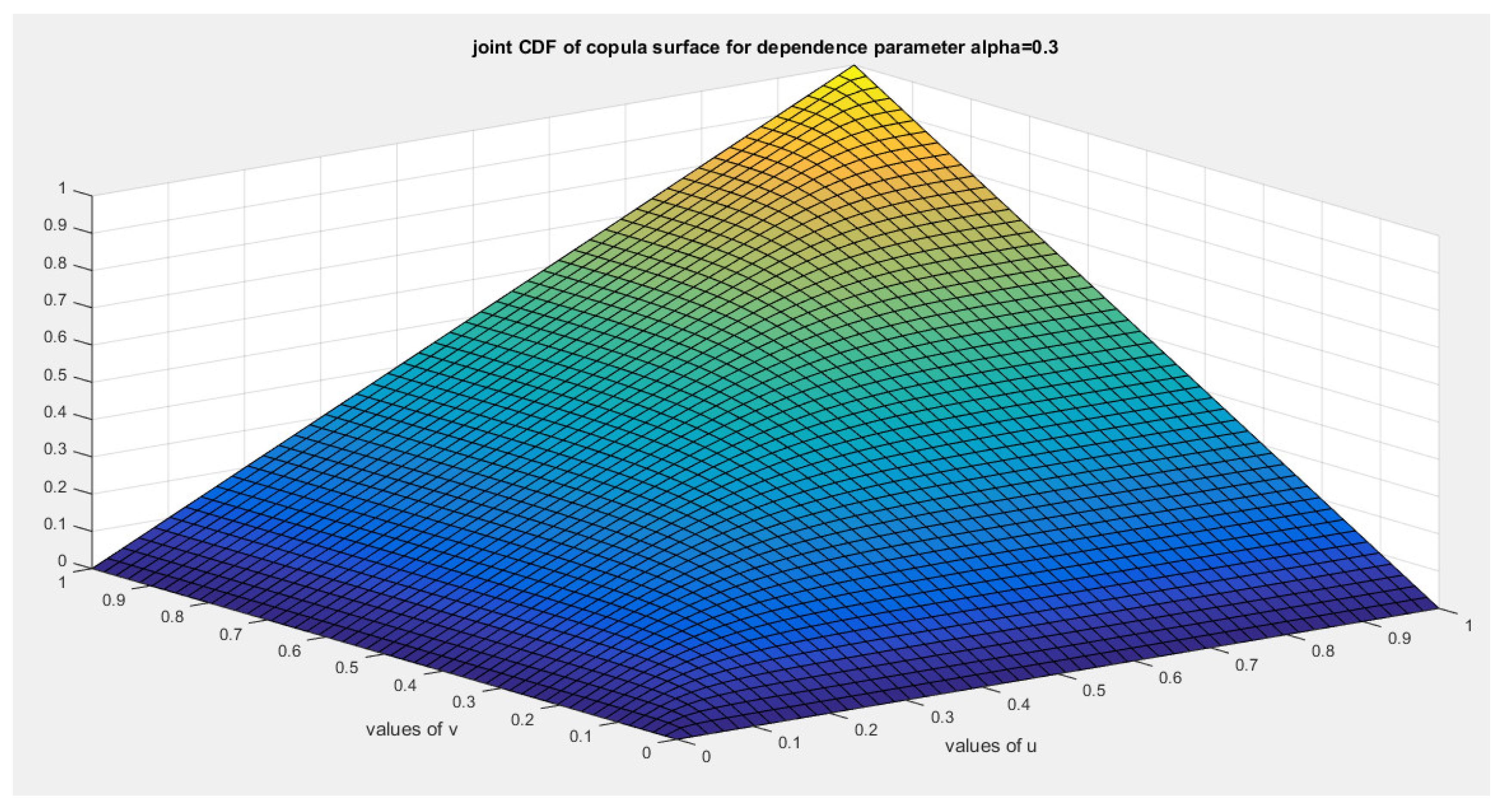
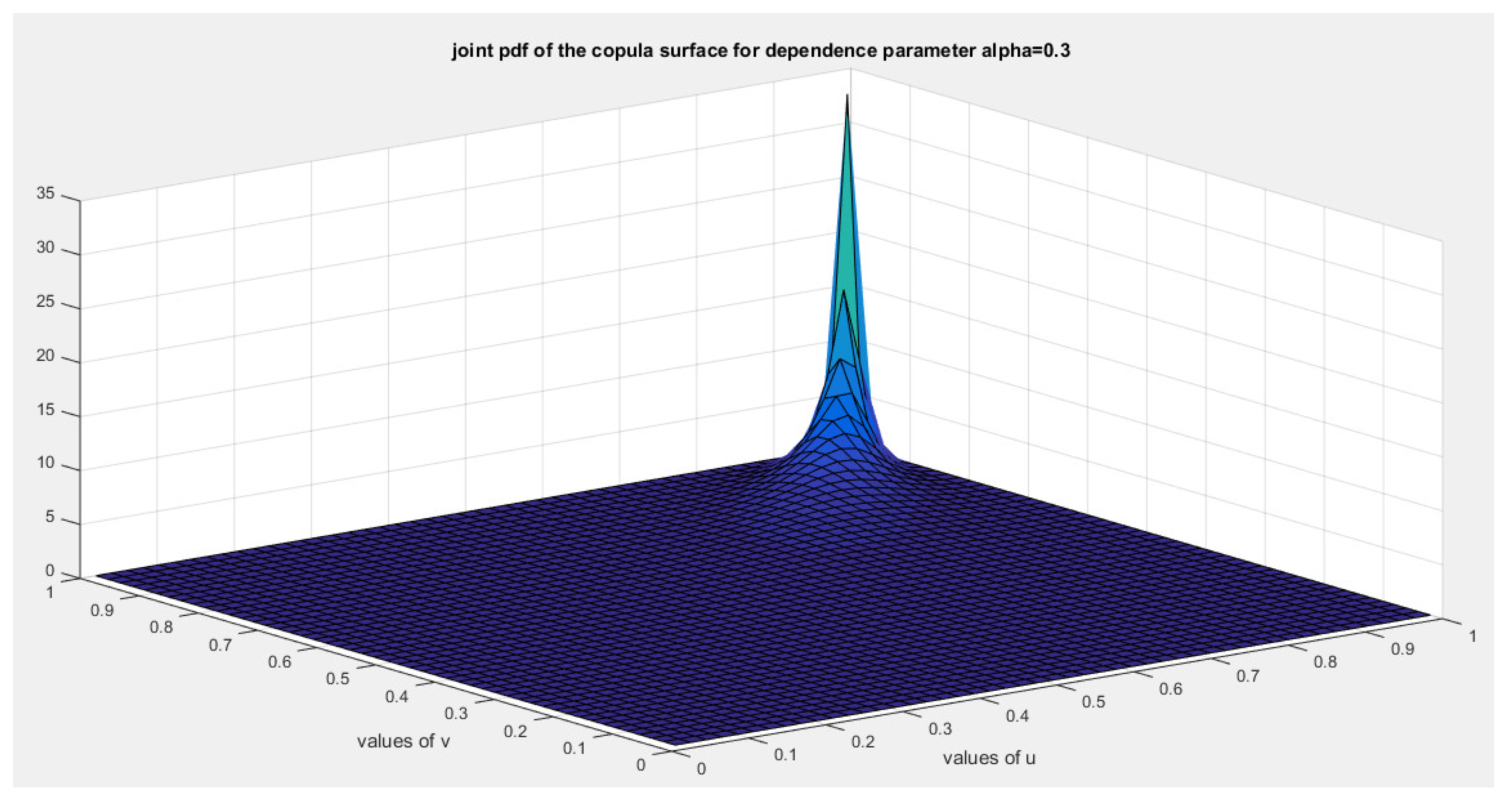
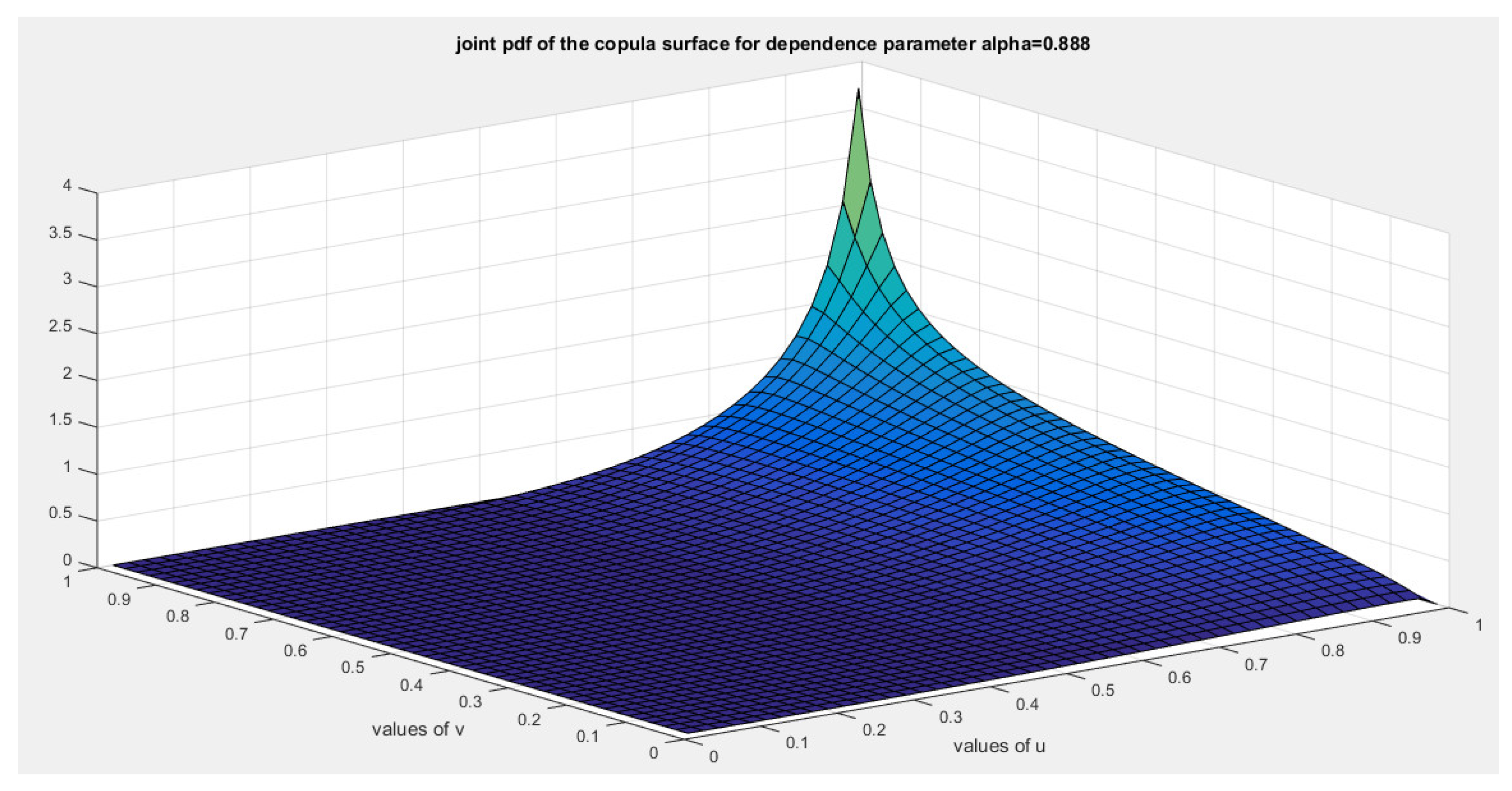
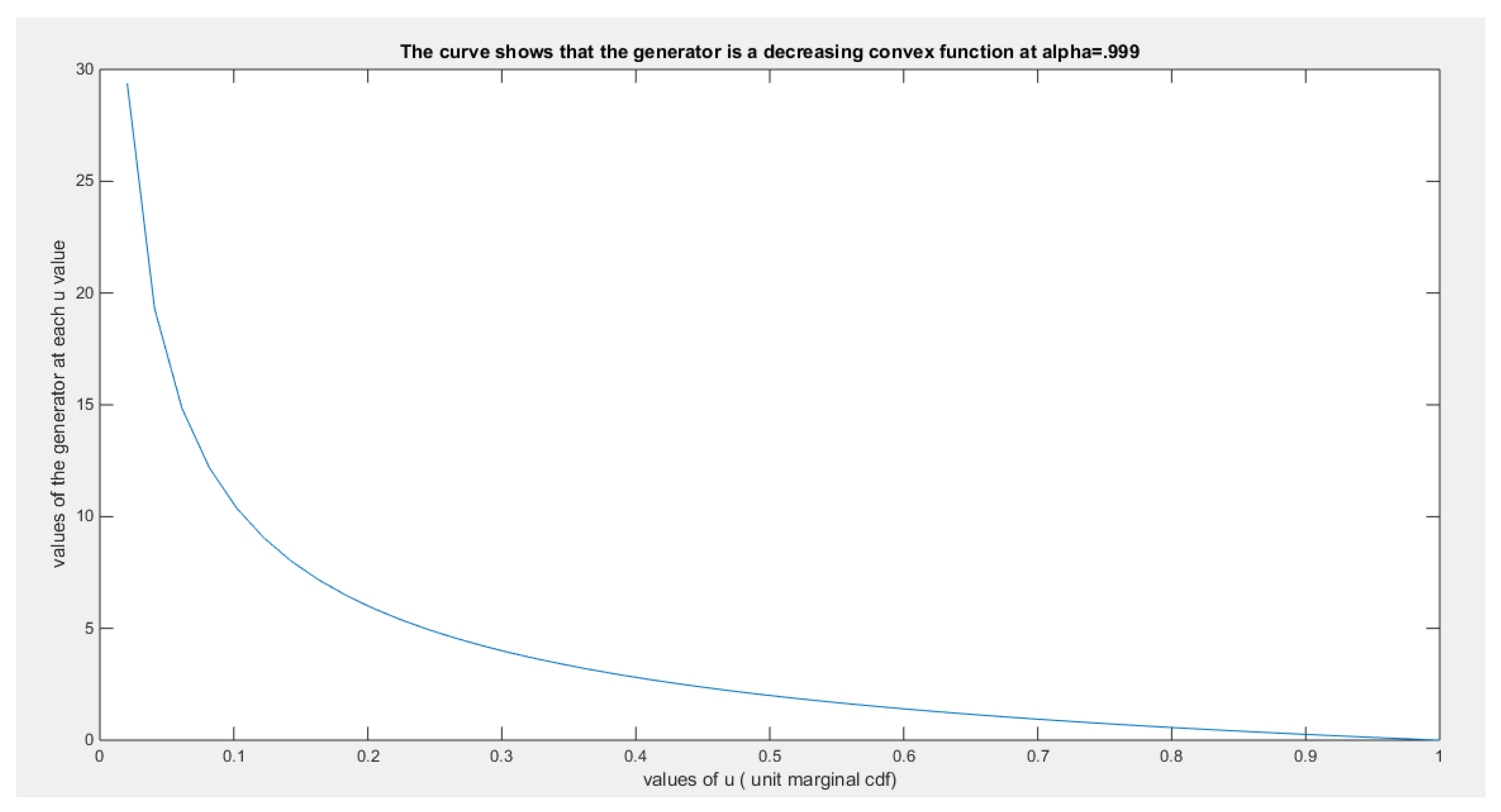
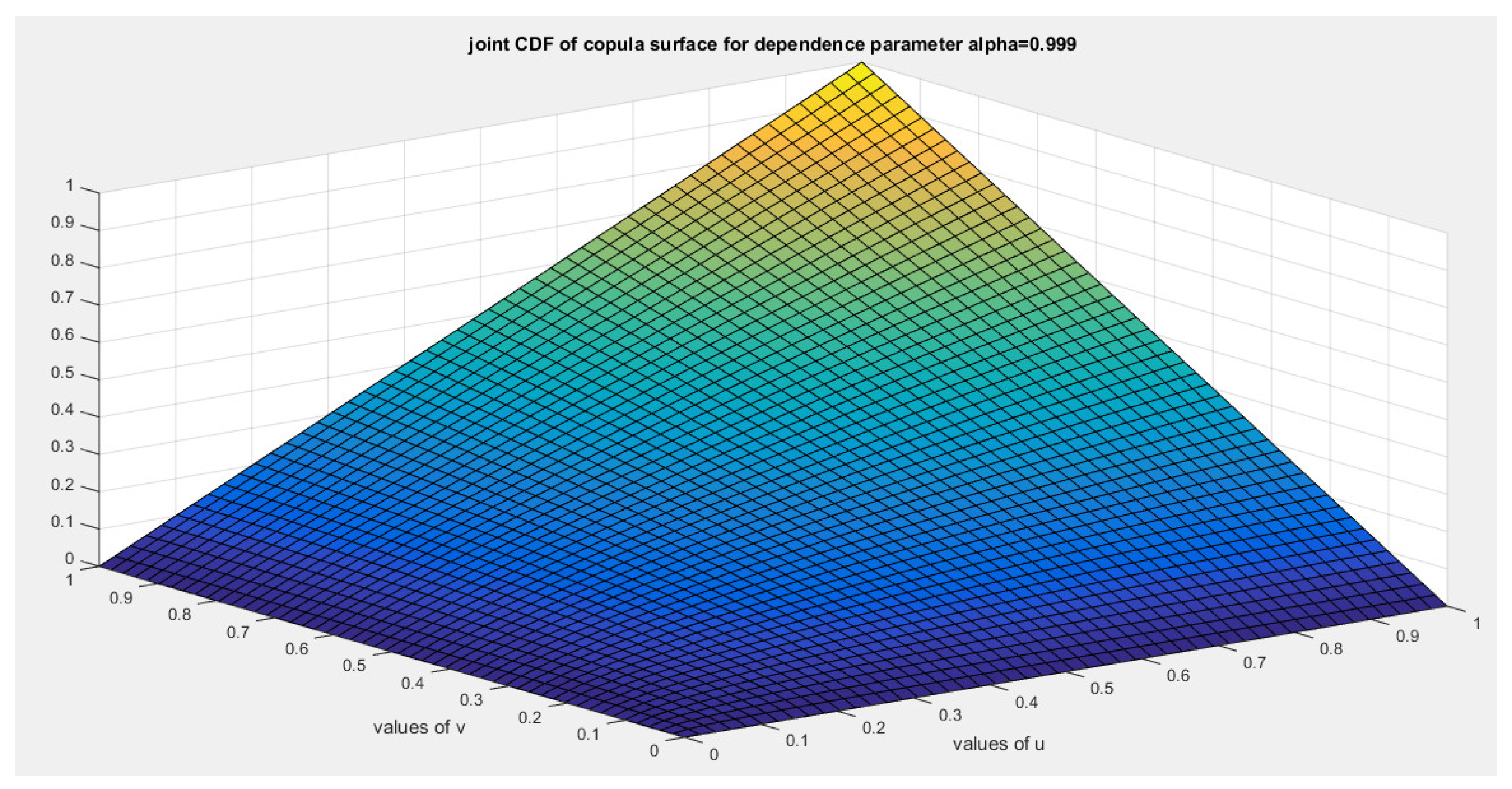
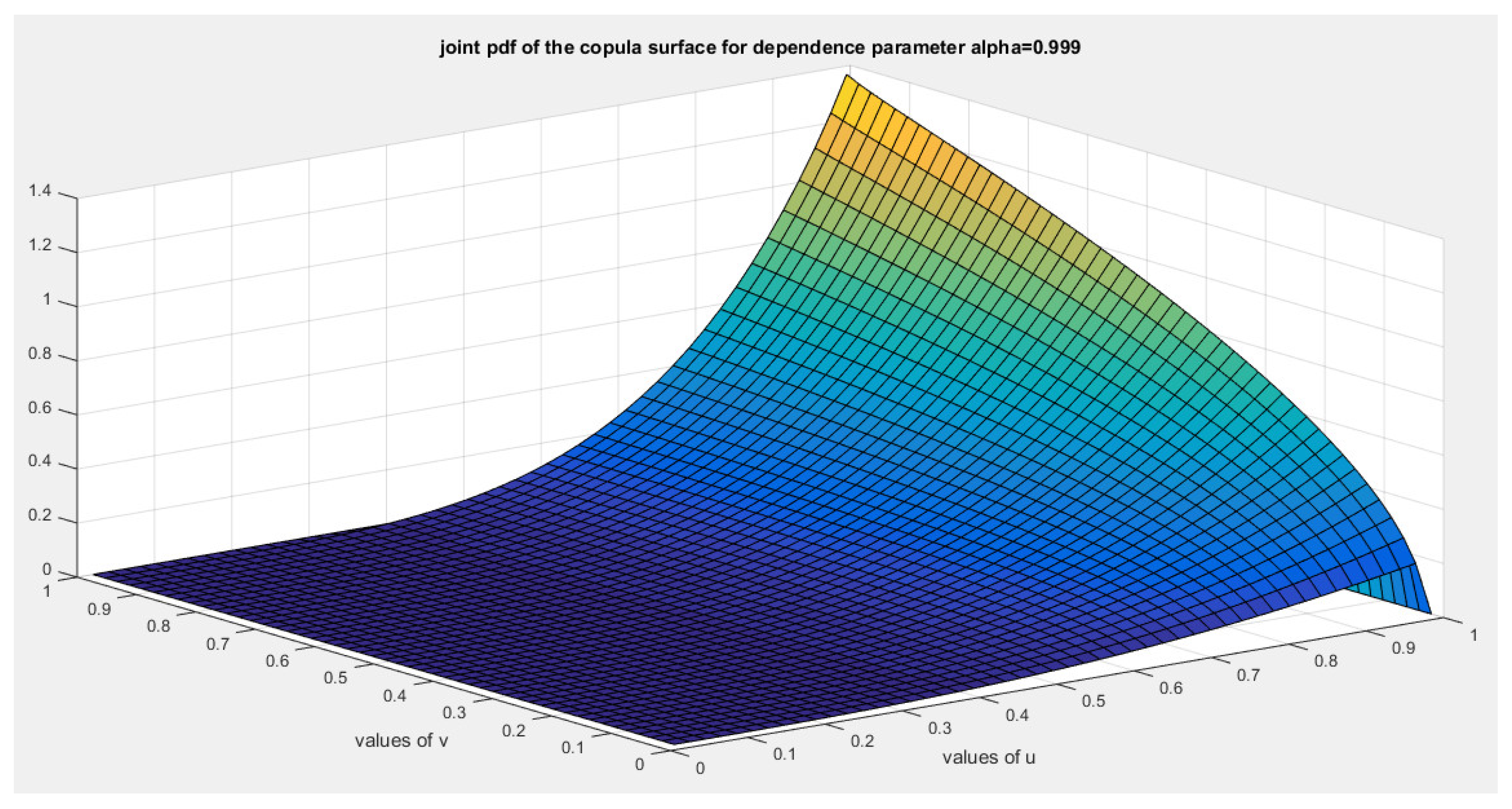
2. The Generator
- 1)
- 2)
- 3)
-
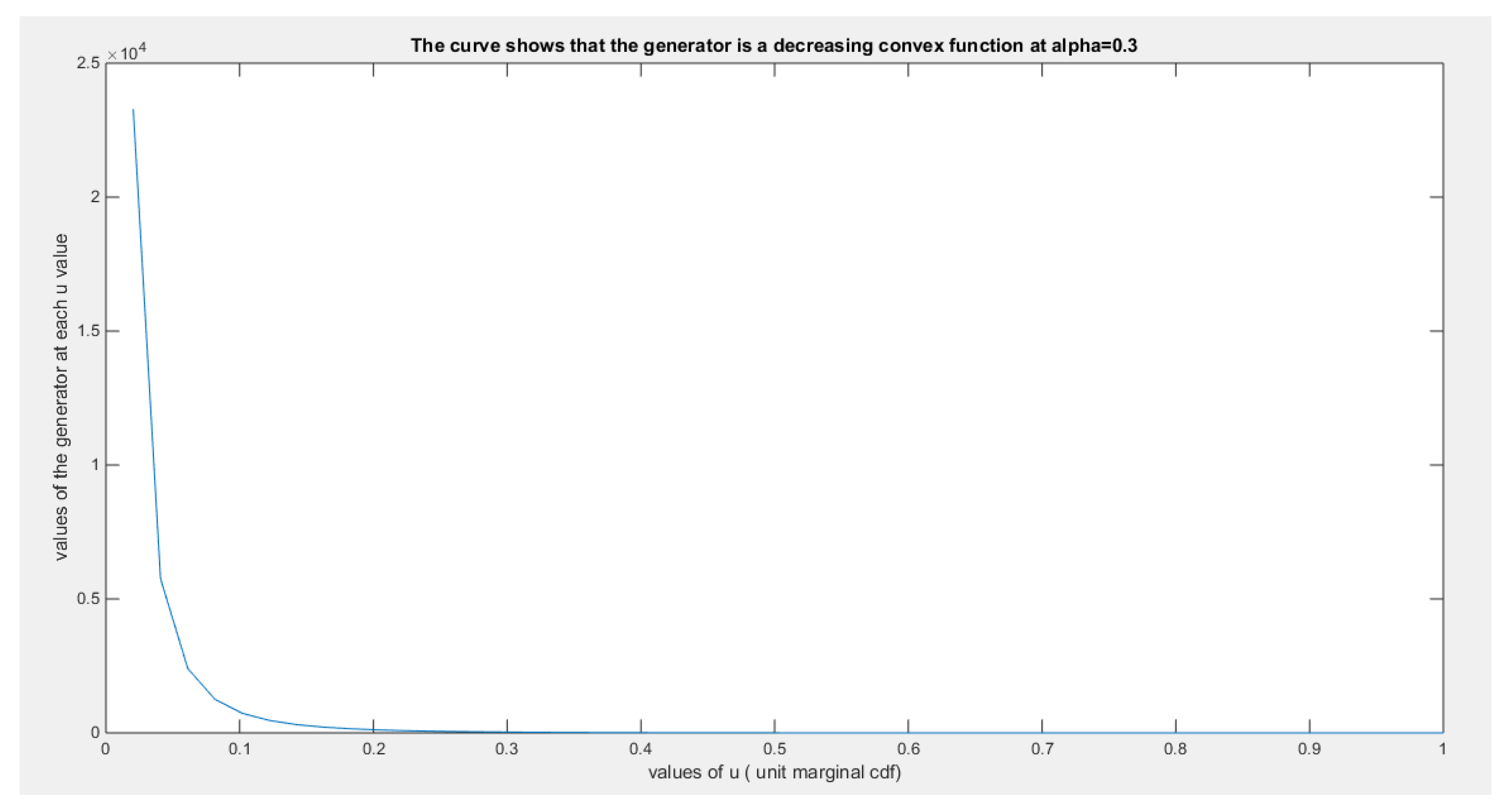
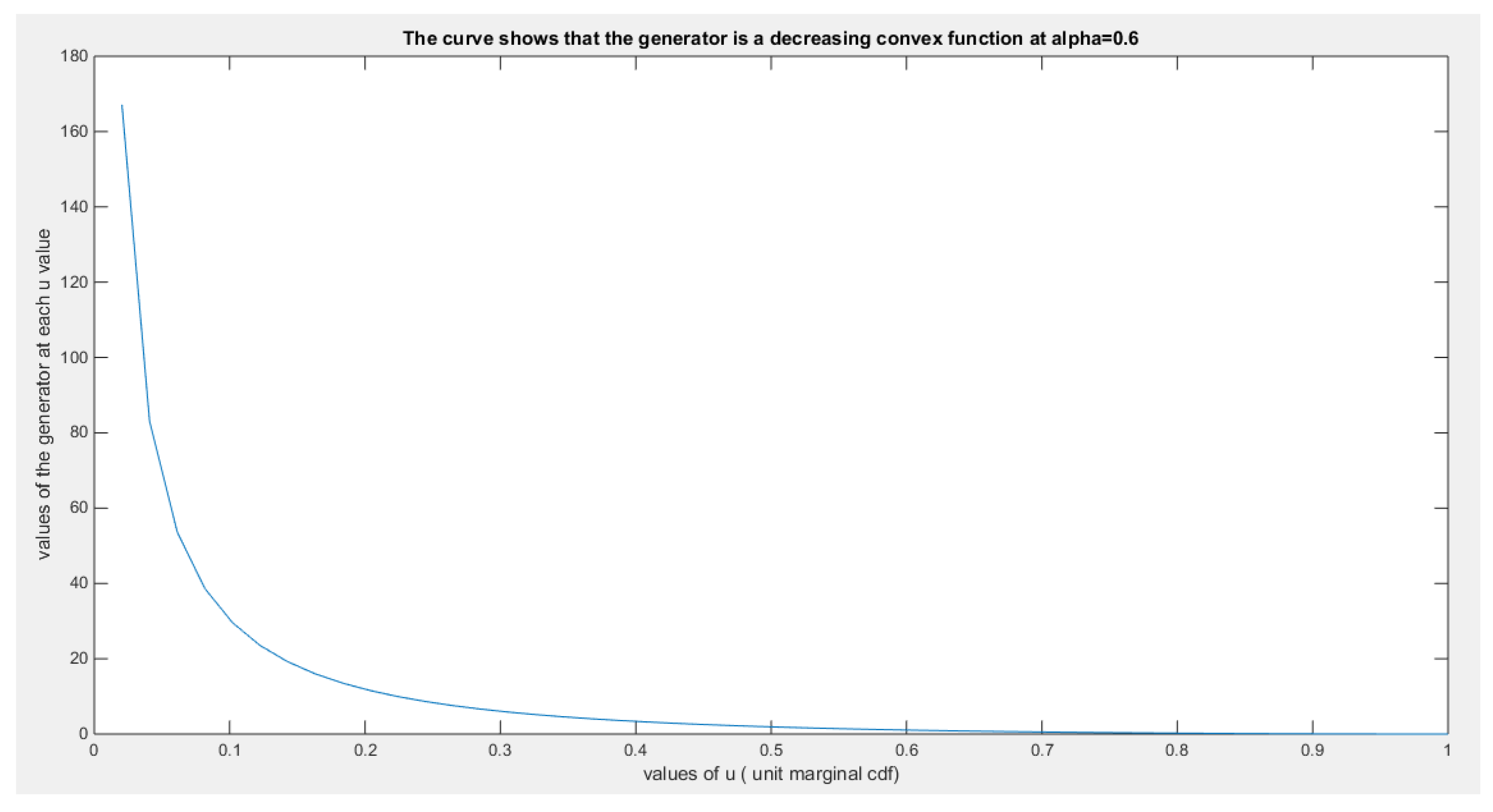
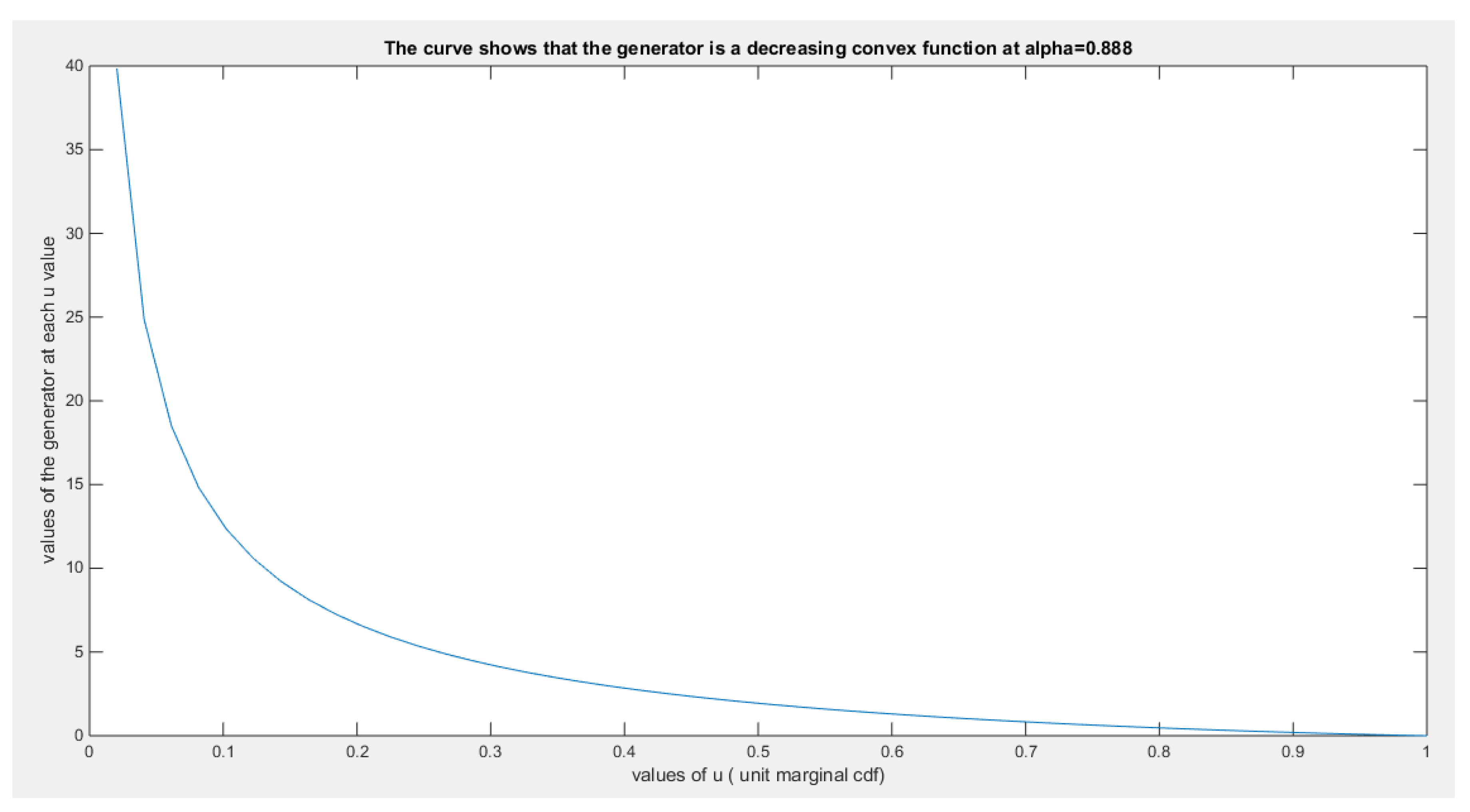
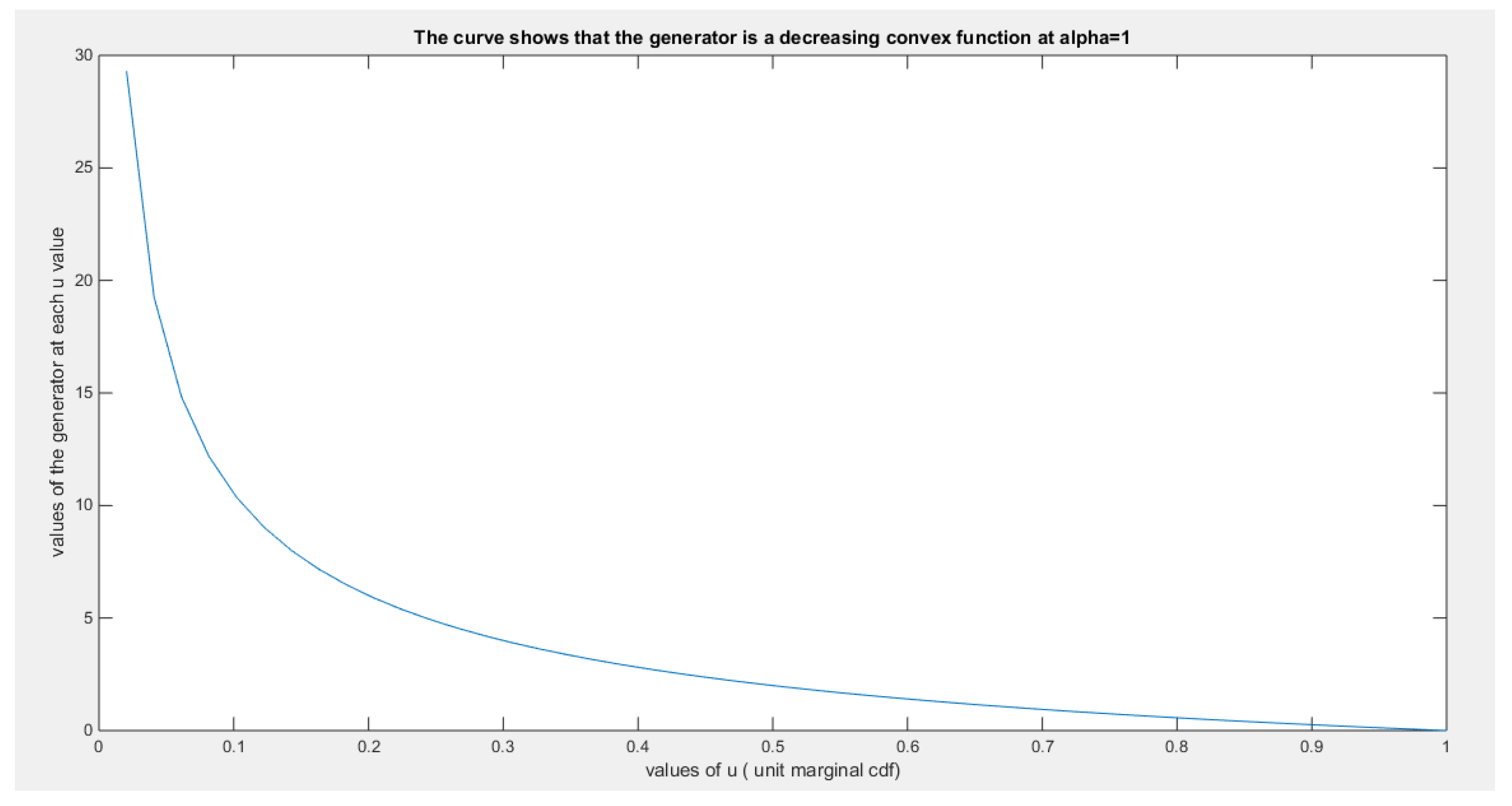
This ensures that the generator is a decreasing function in u.
- 4)
-
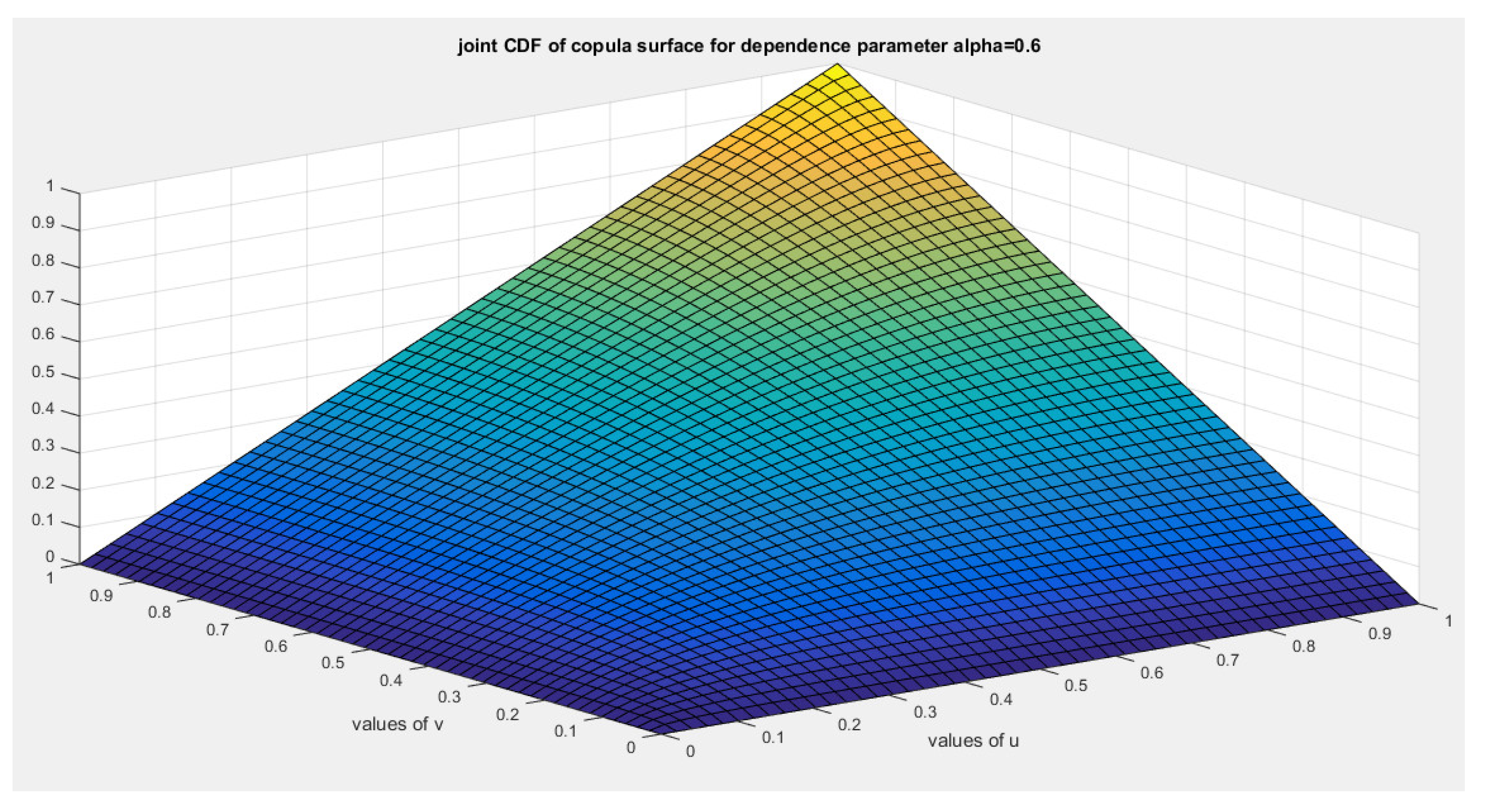
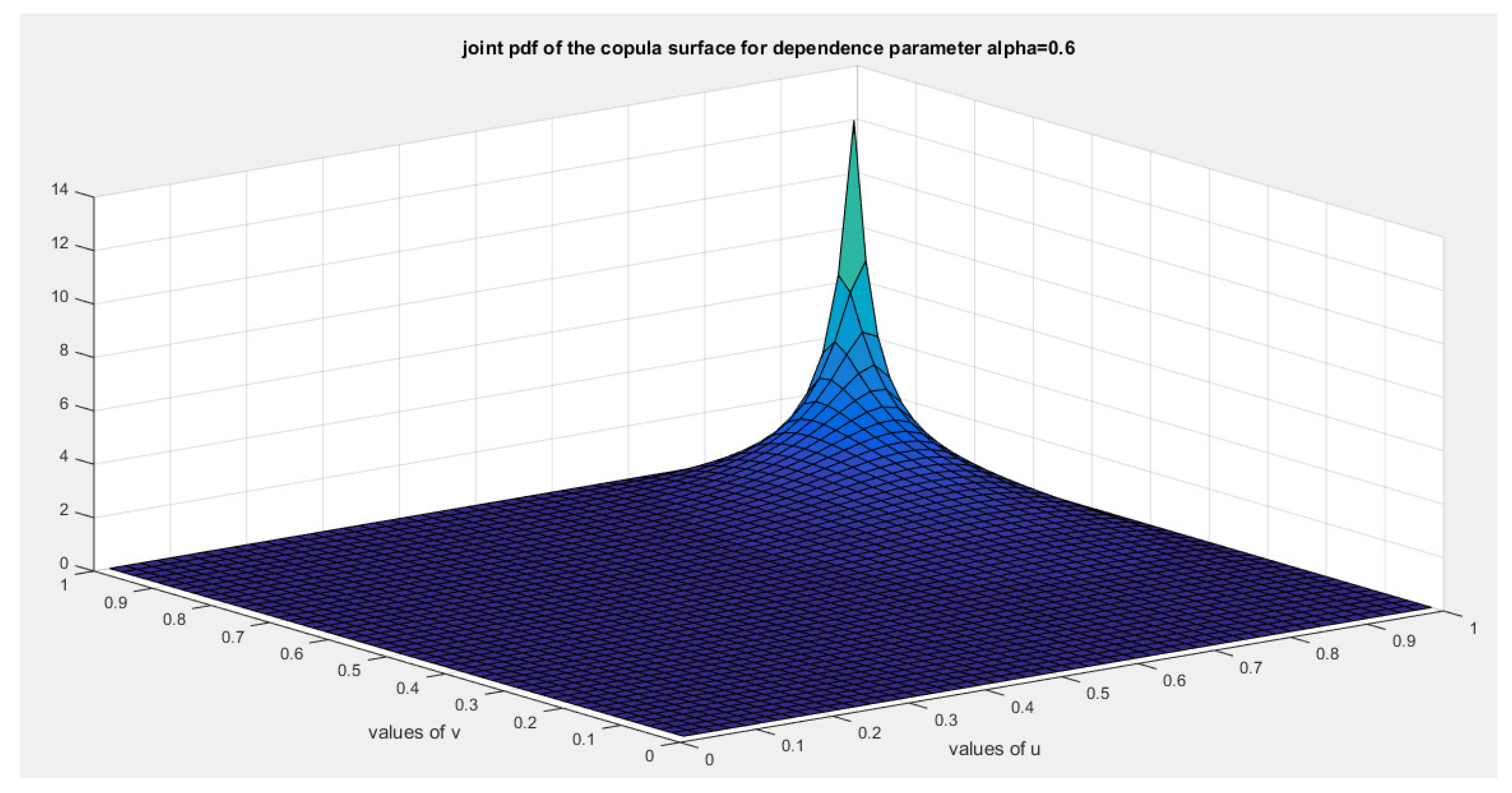
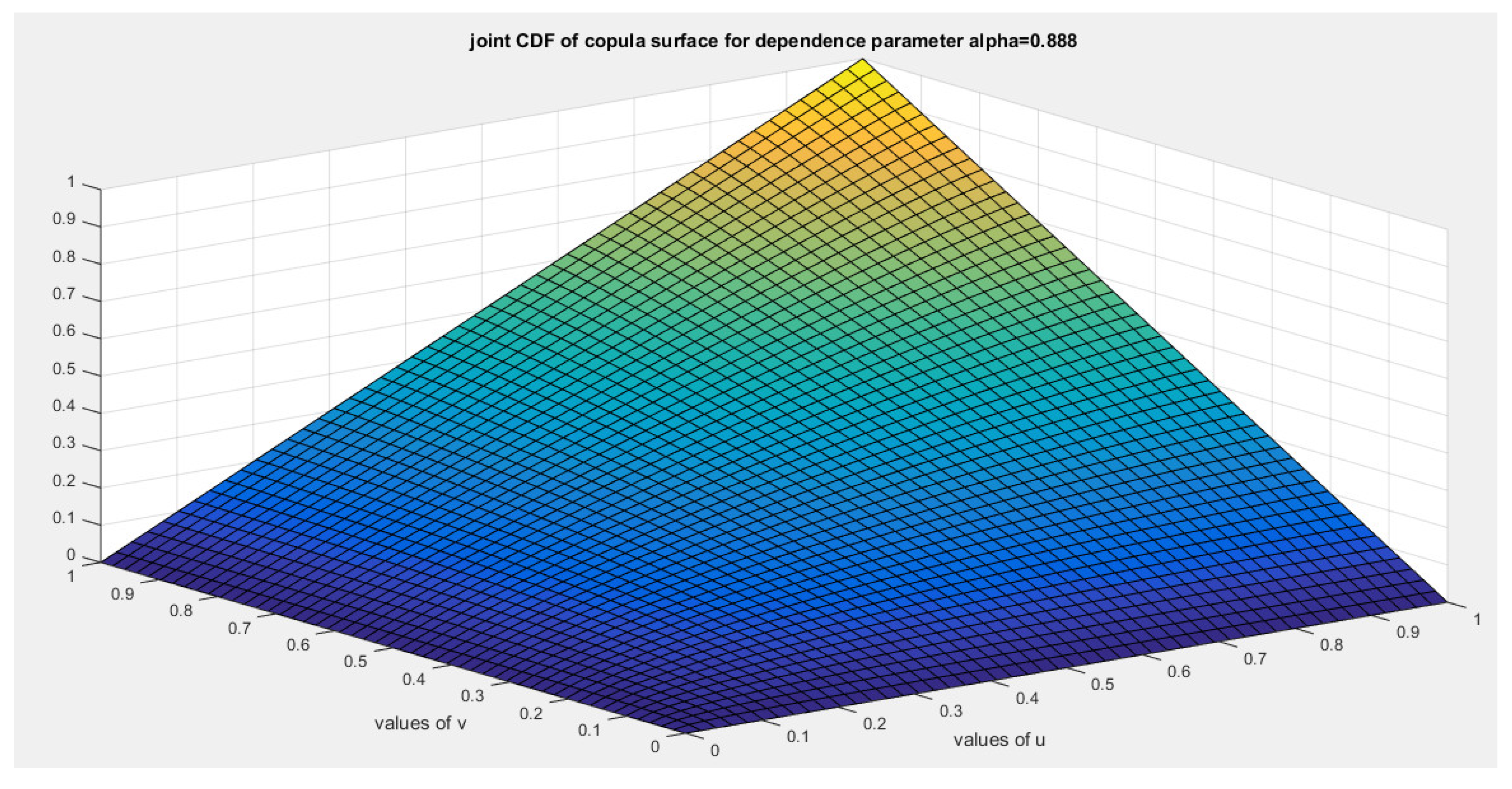
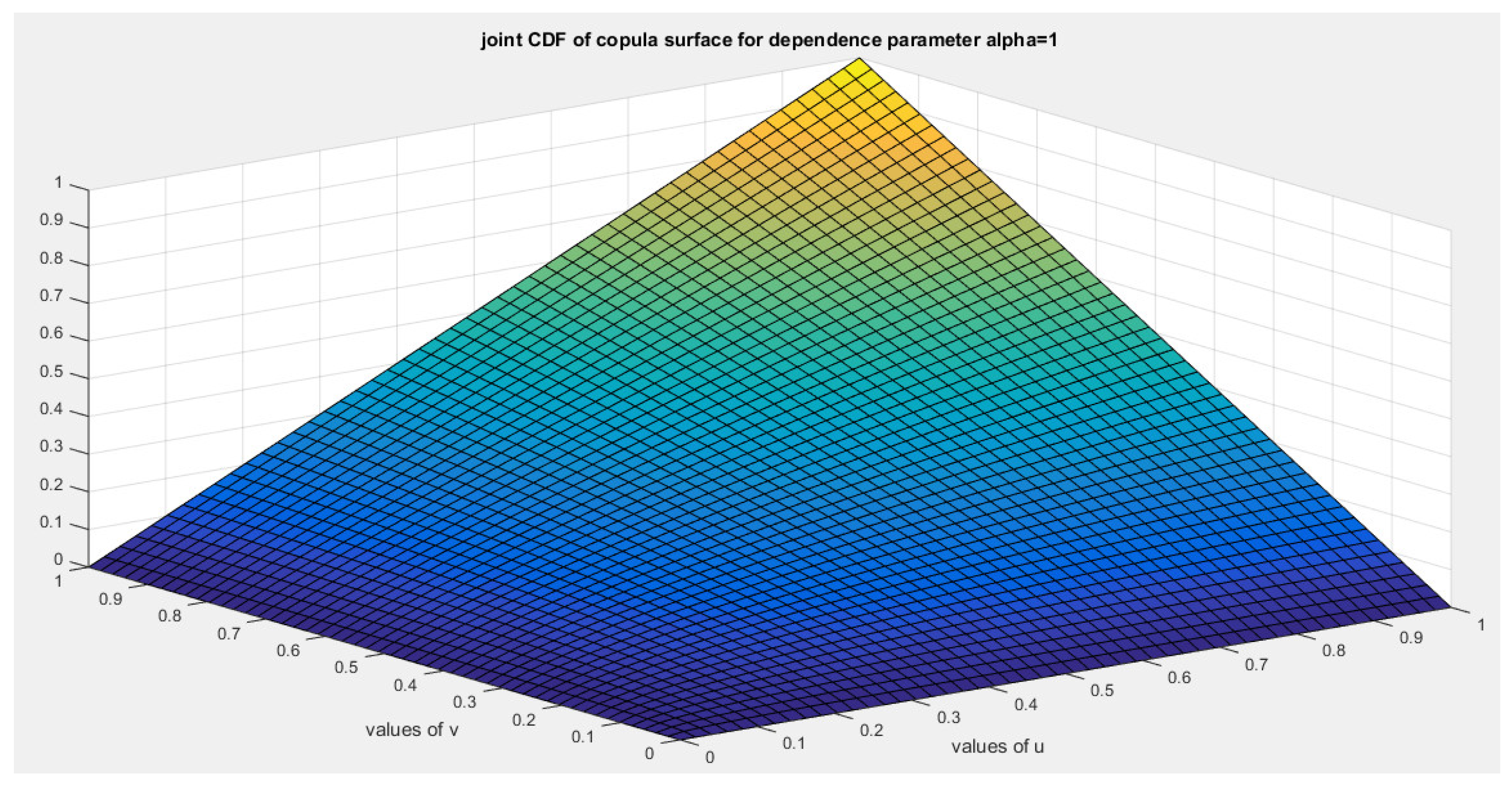
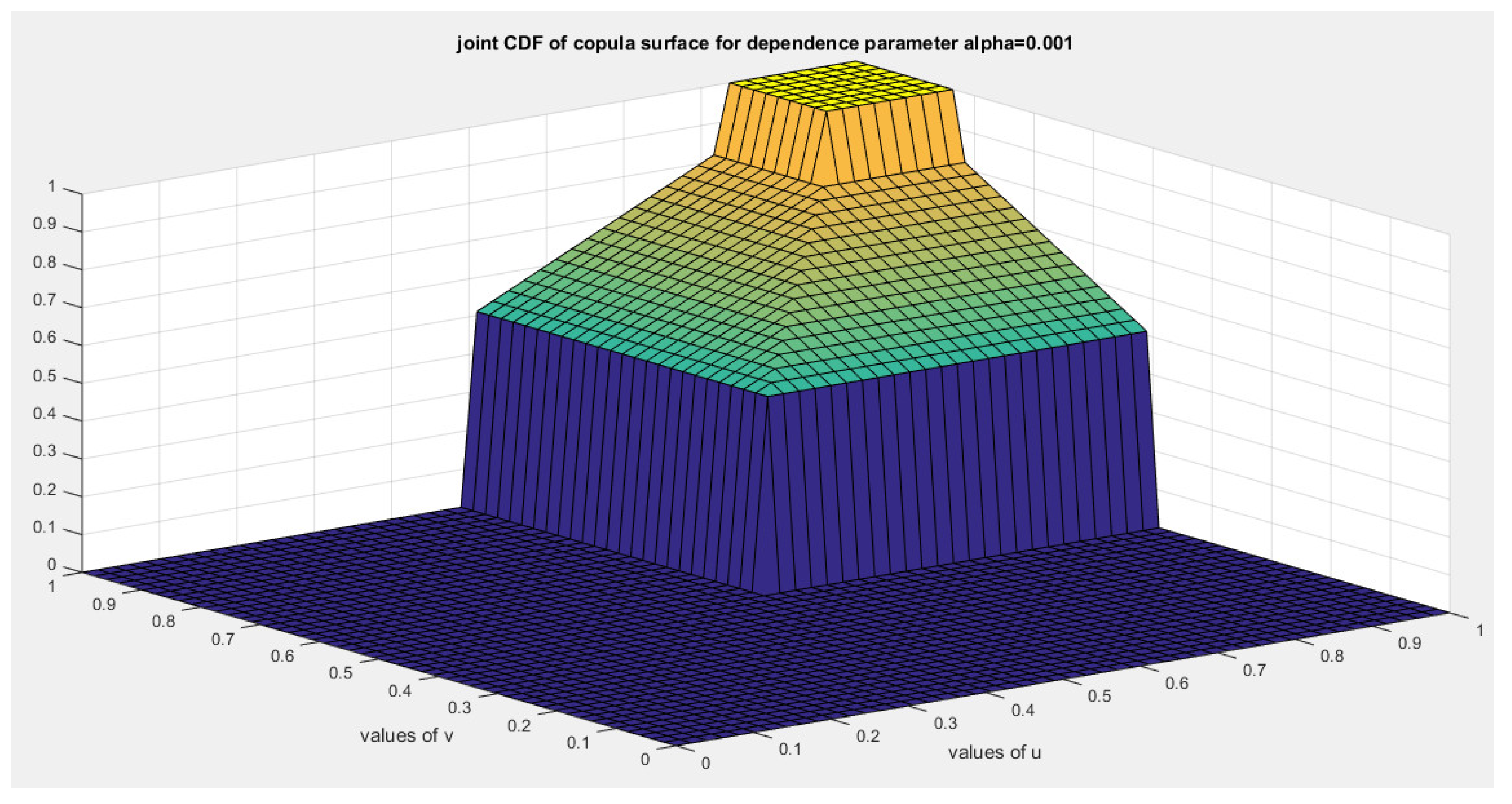
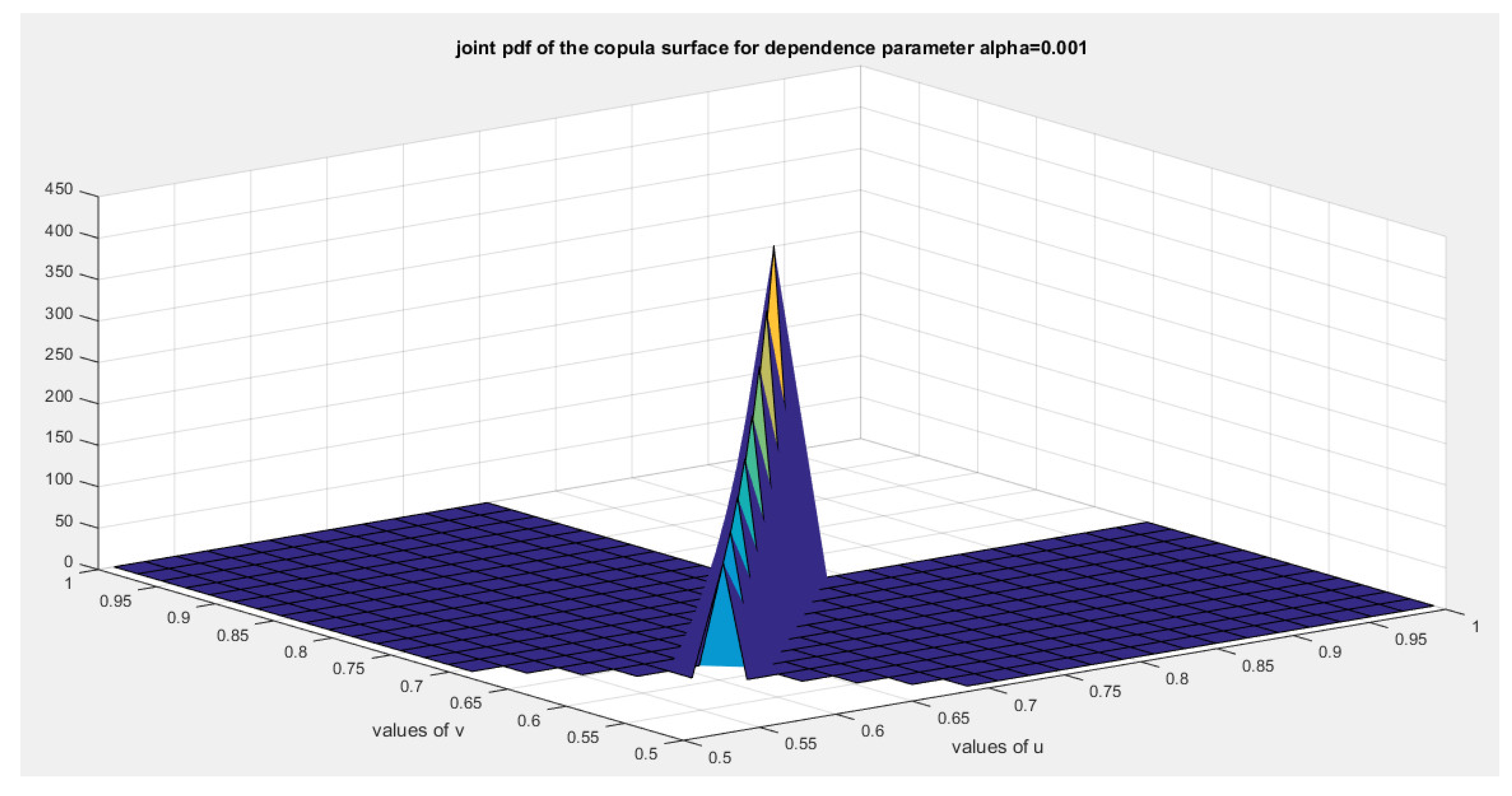
This ensures that the generator is a convex function atFor bivariate distribution with uniform marginal CDF (u) and (v), the generators are shown in equations (10-12)
3. The Inverse Generator
4. Kendall Tau Measure of Dependency
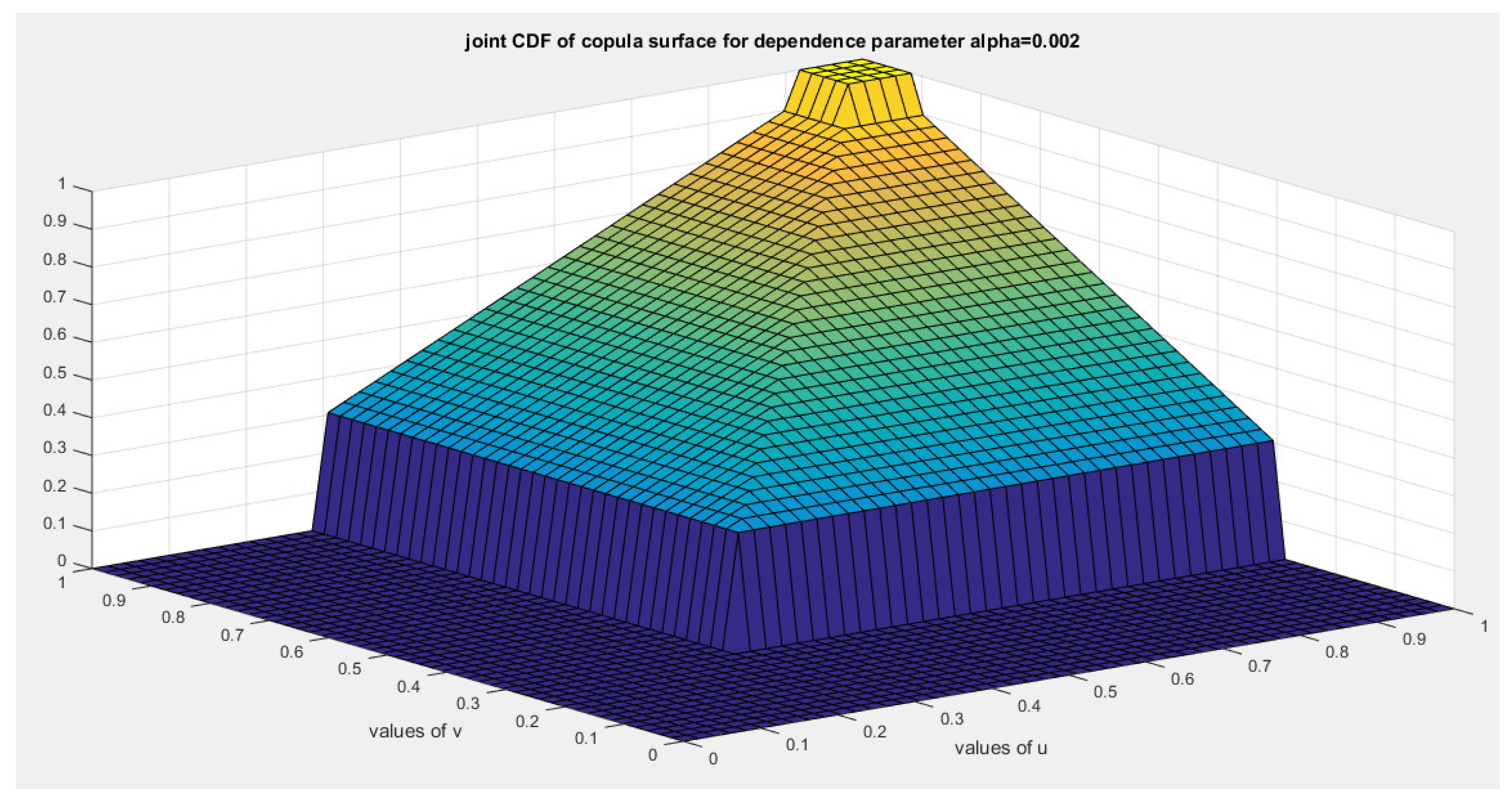
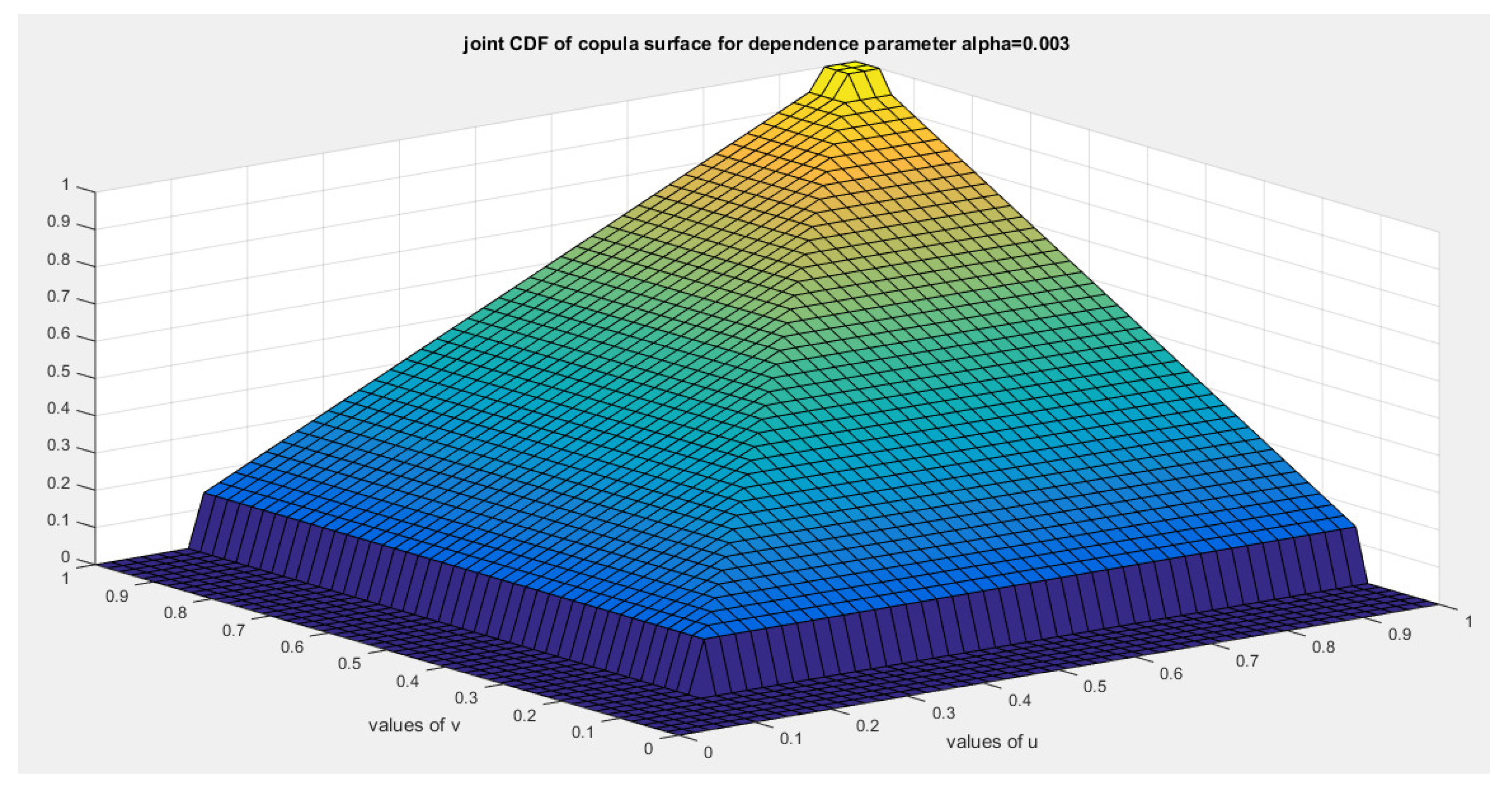
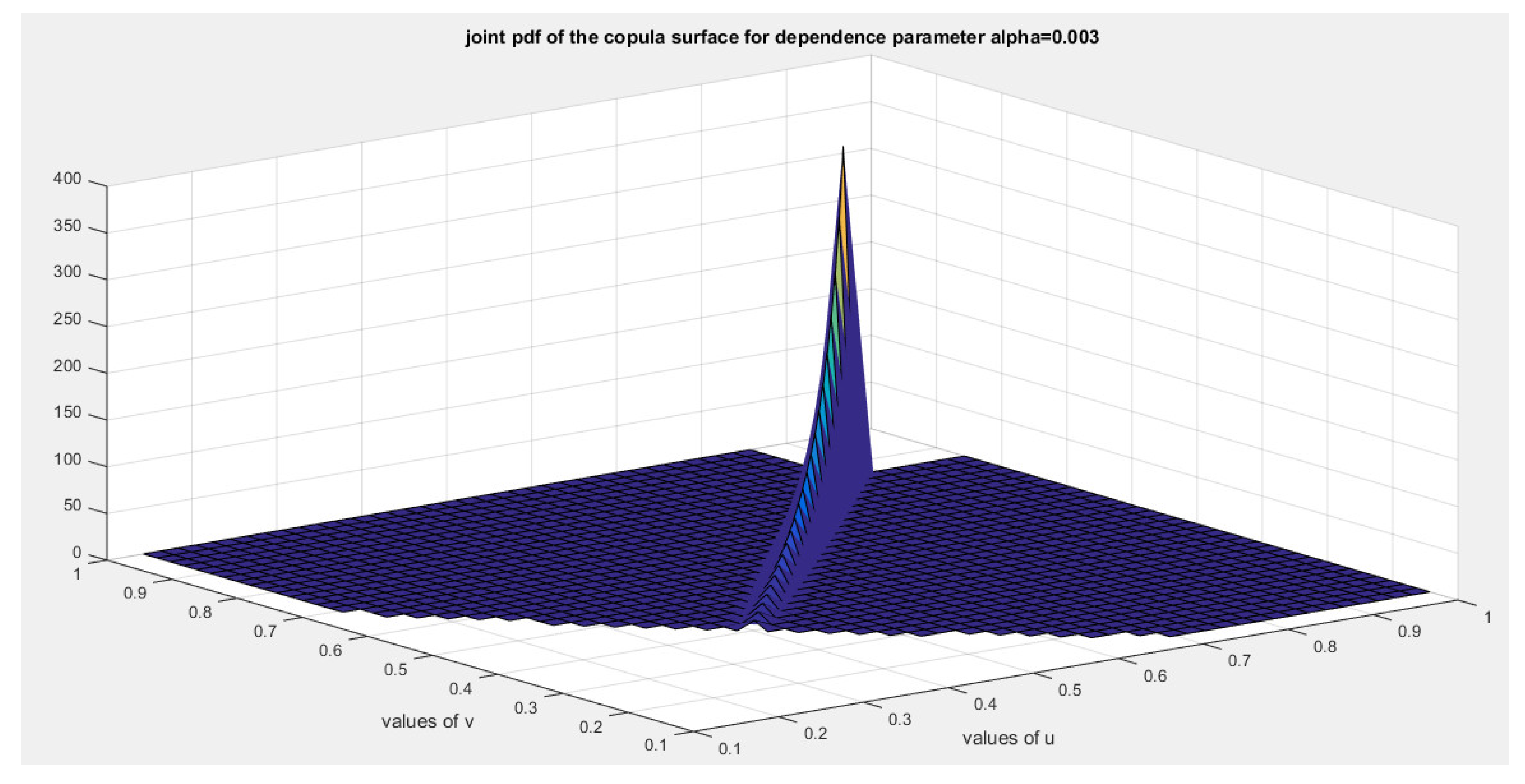
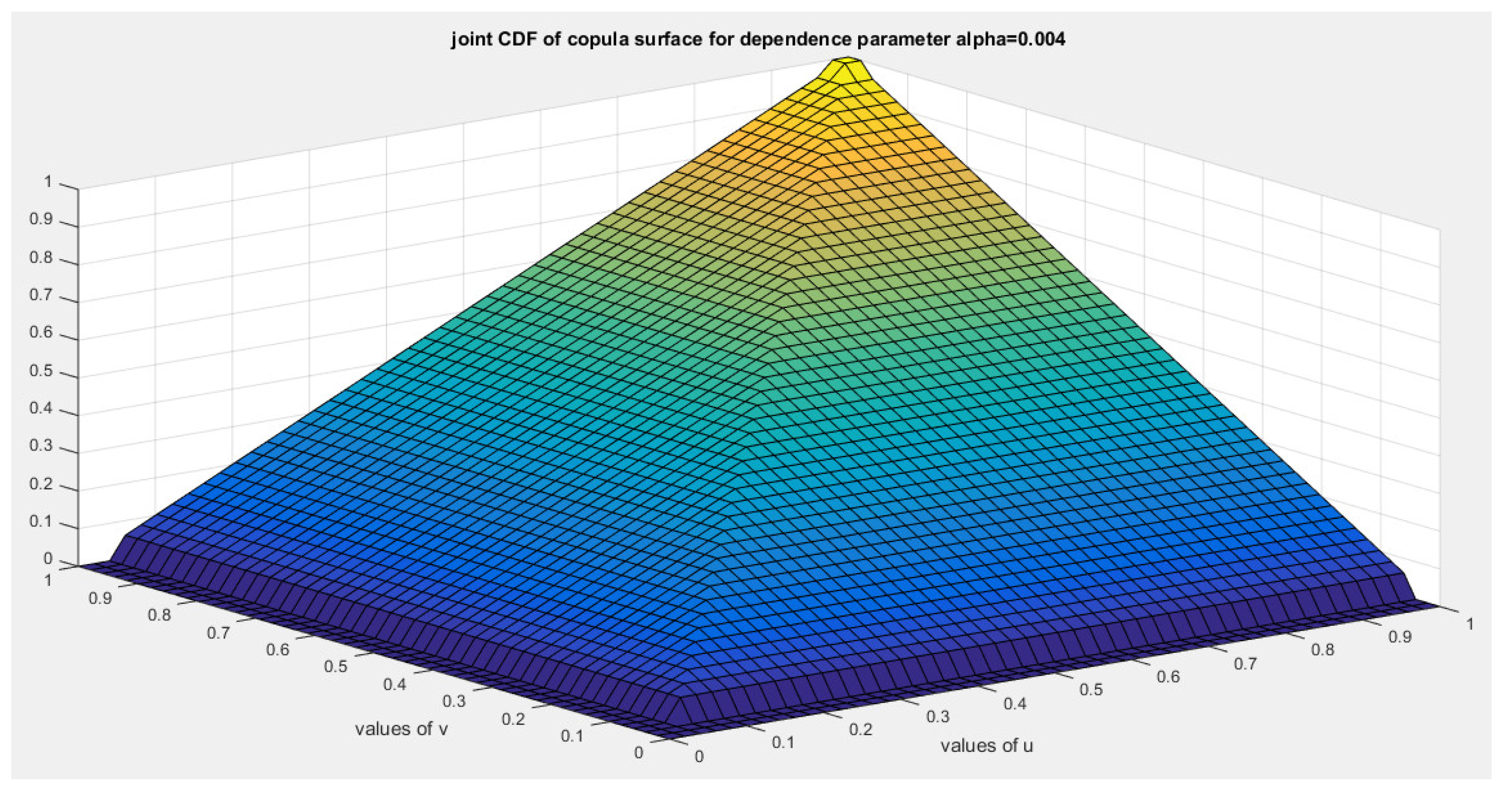
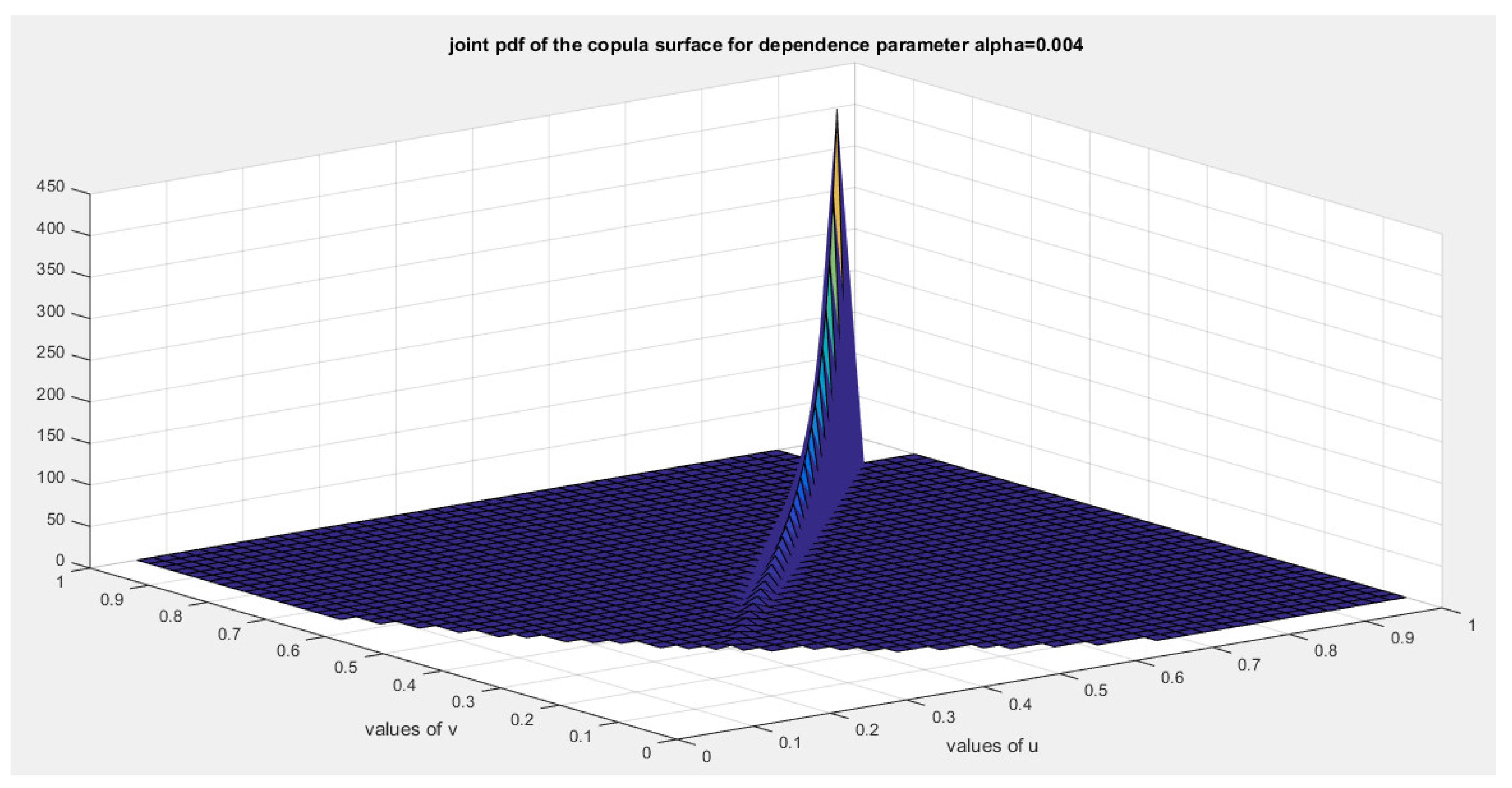
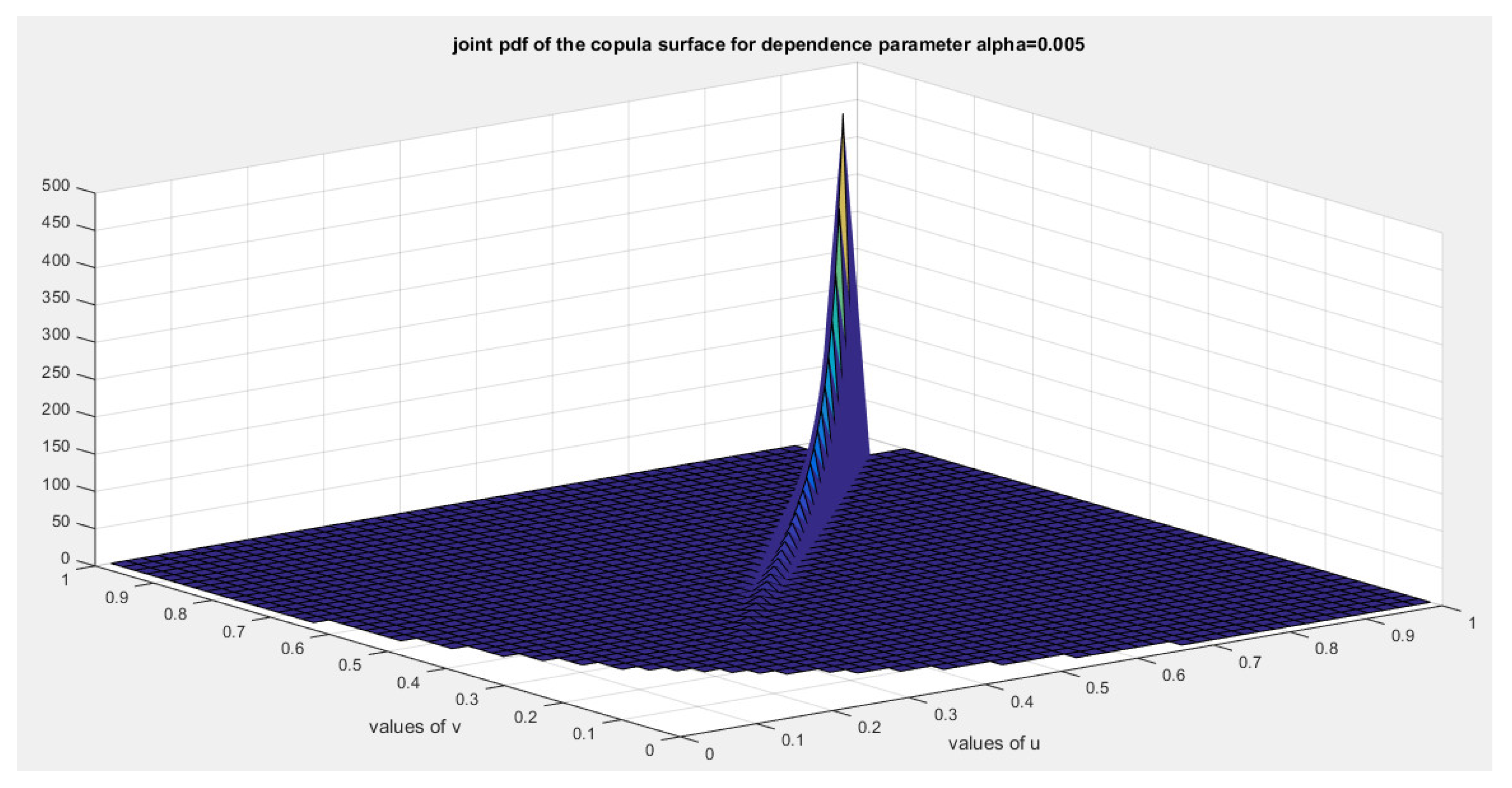
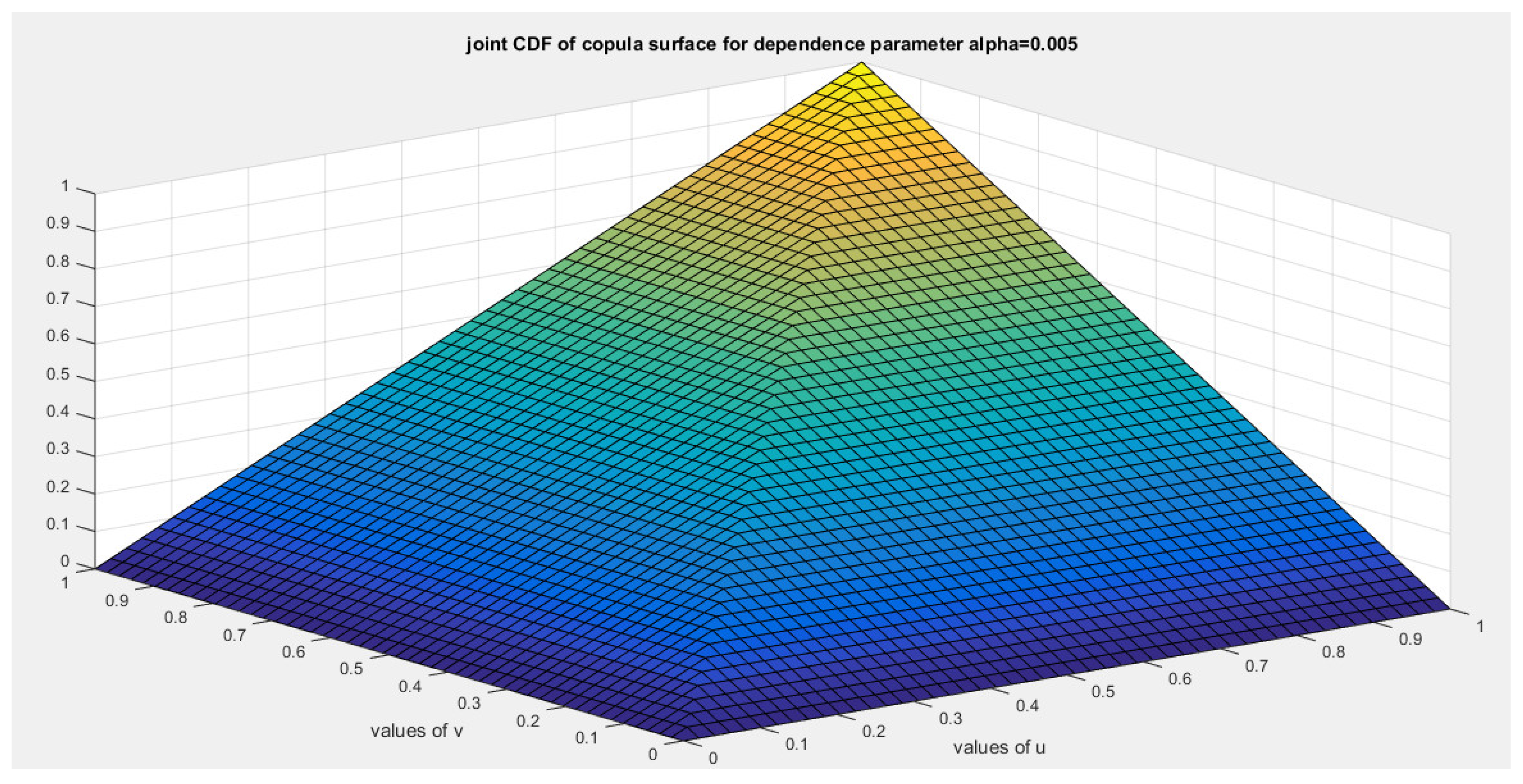
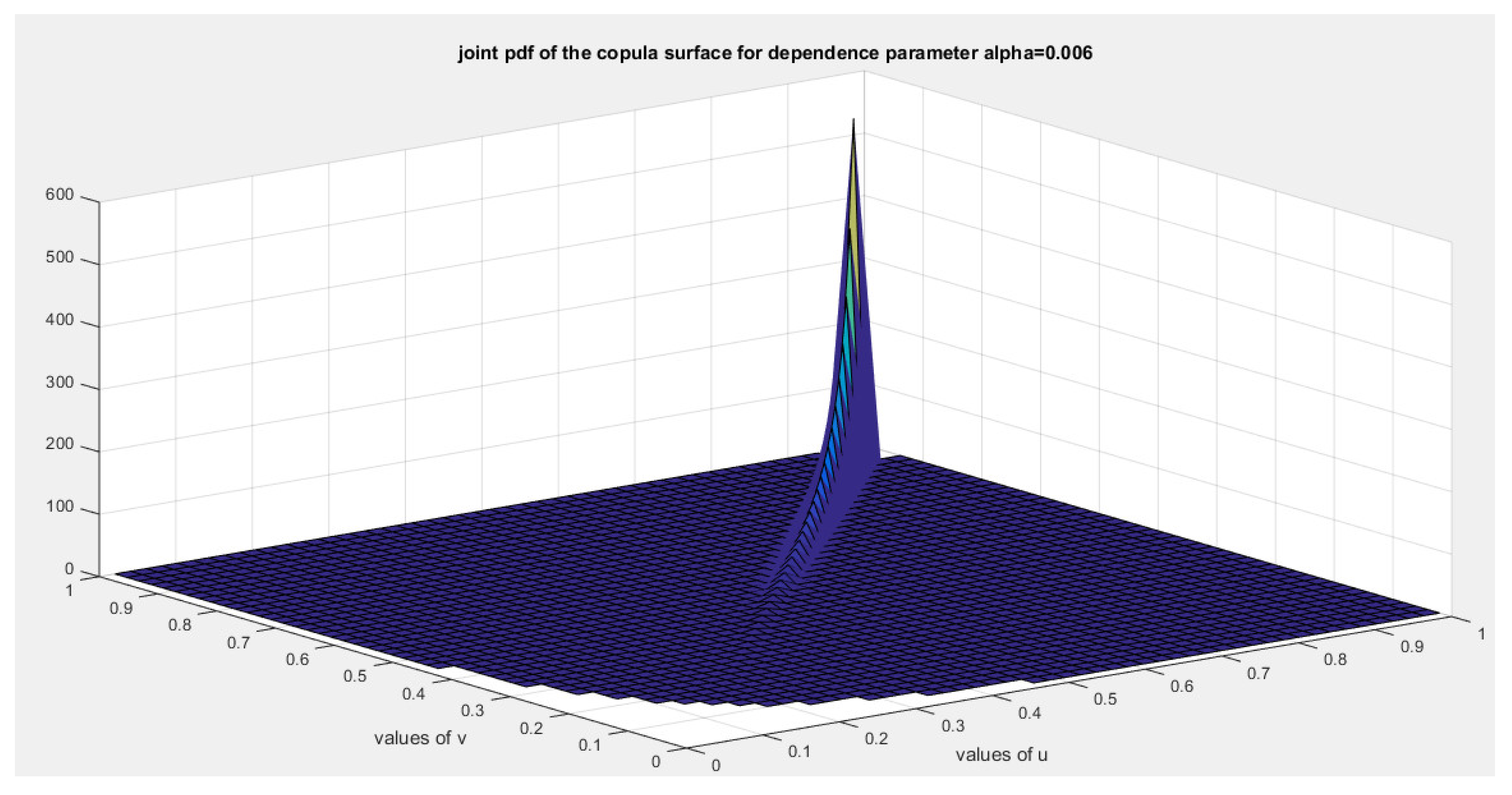
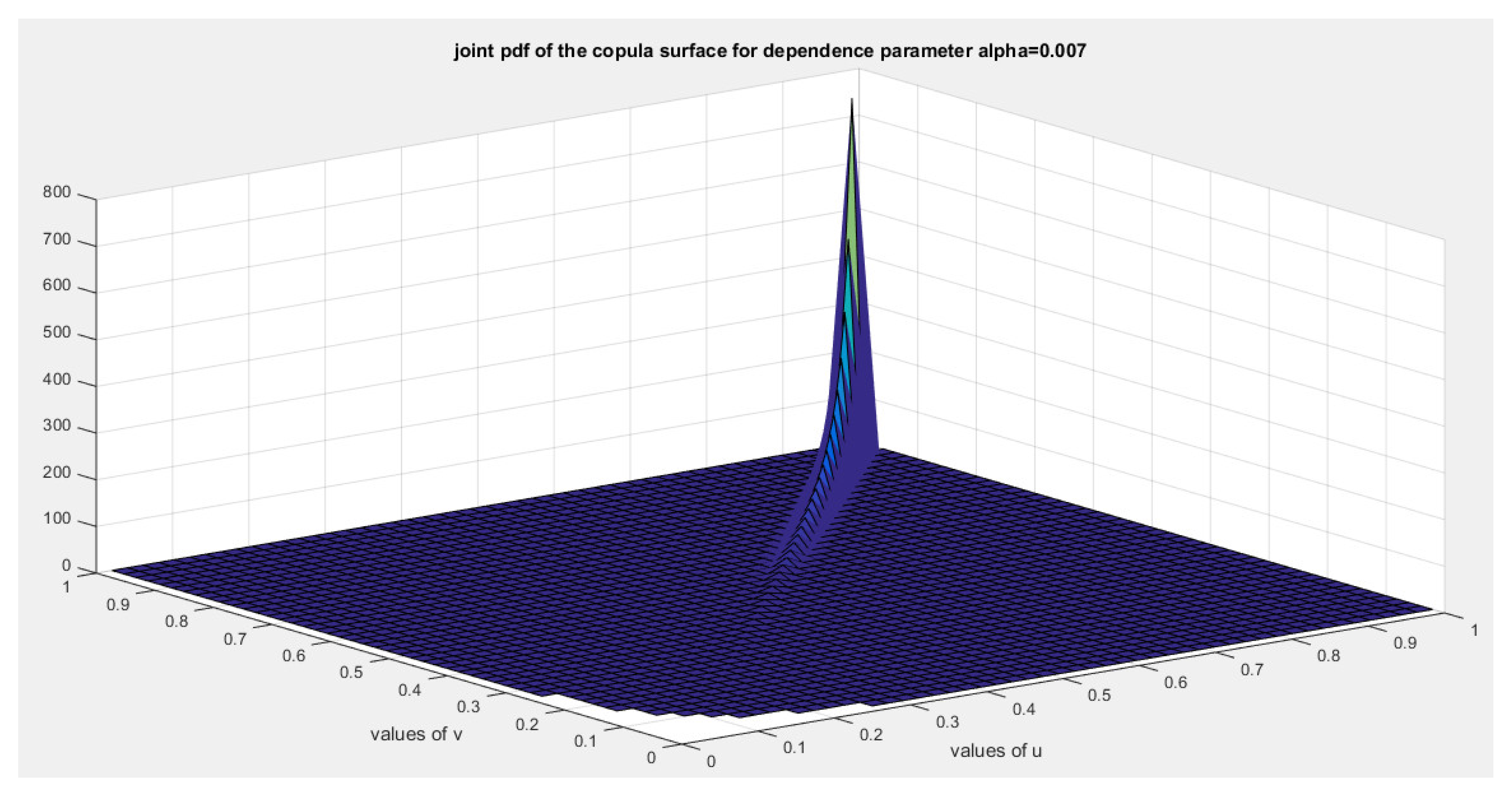
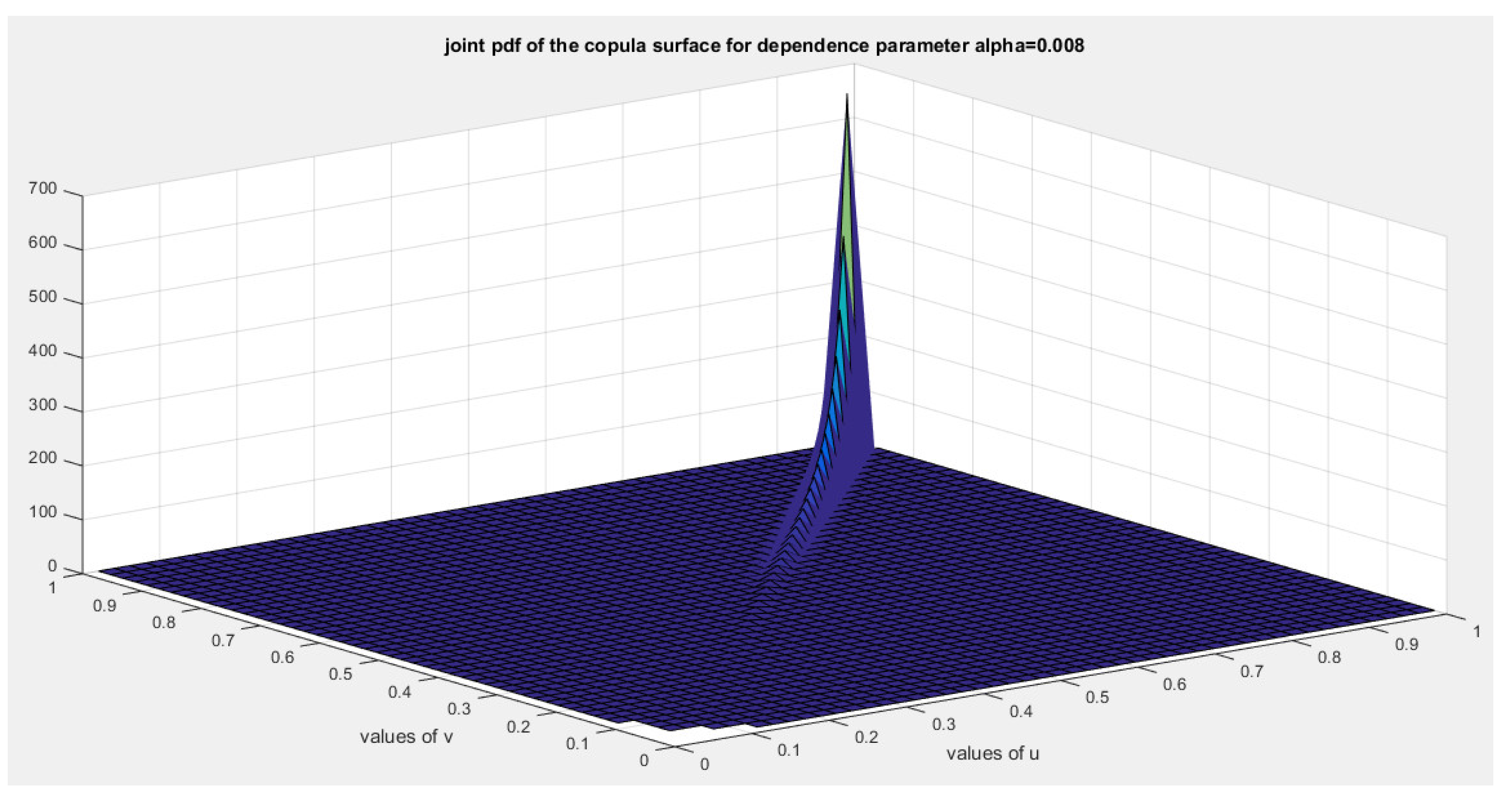
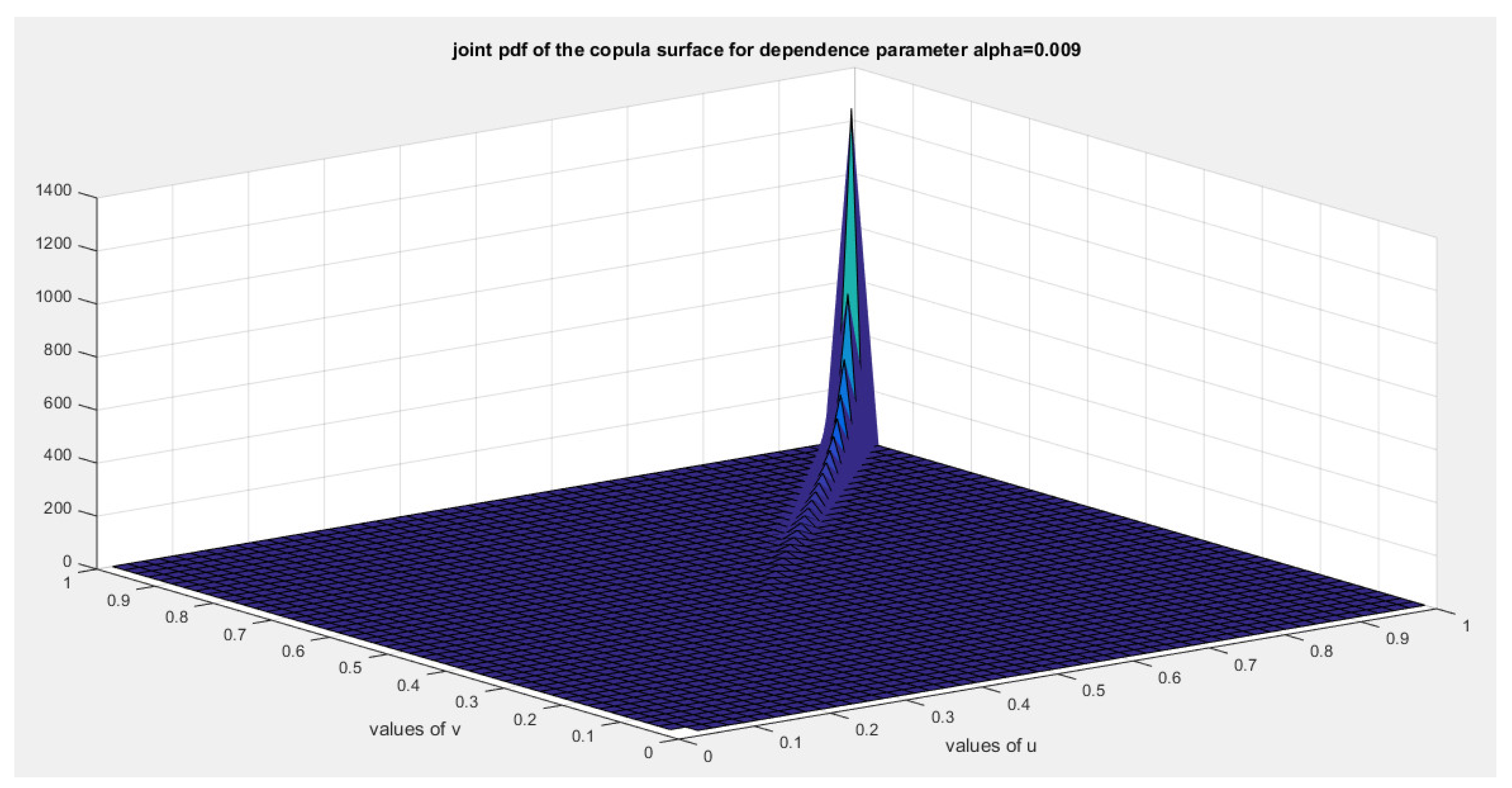
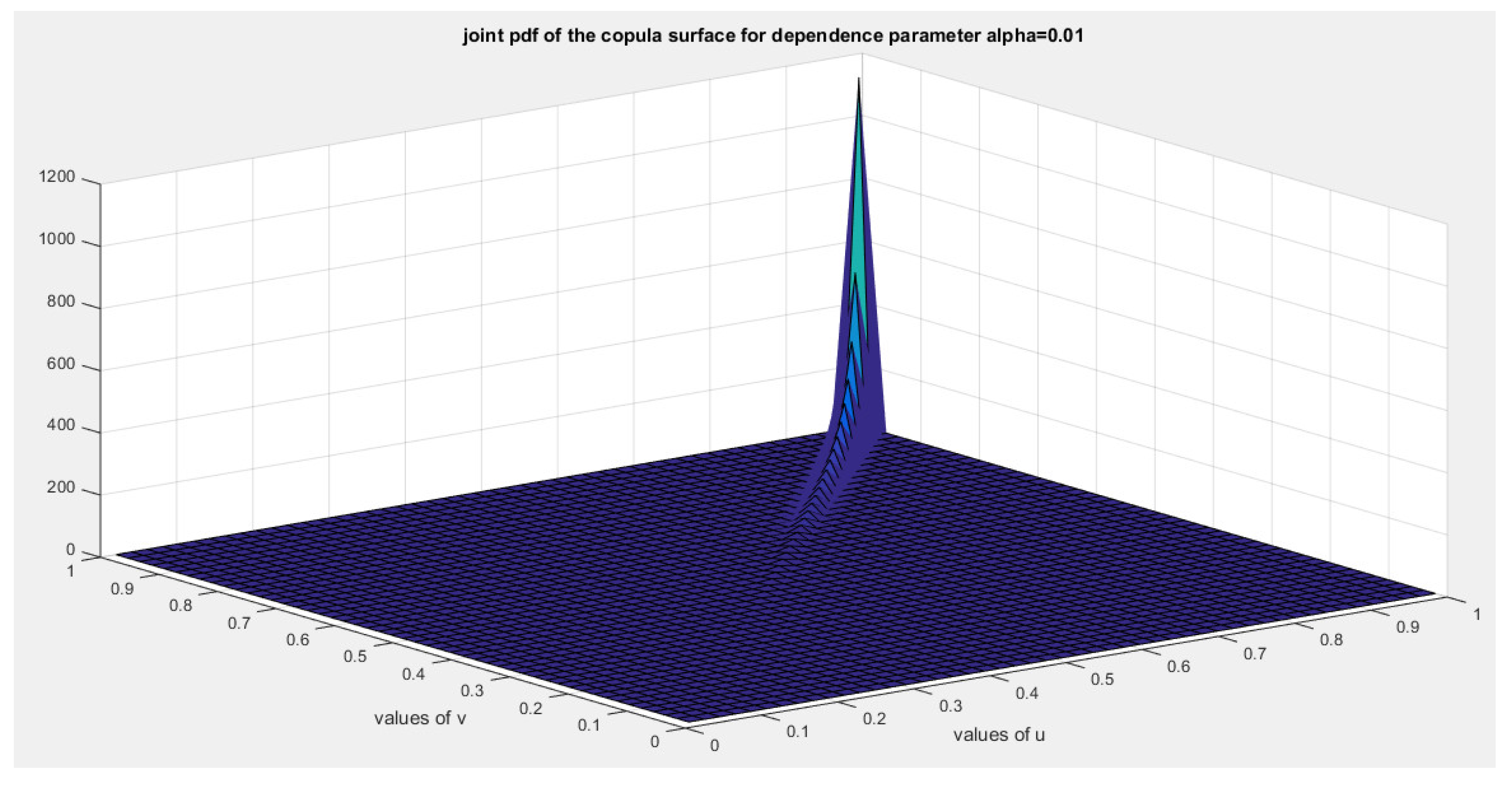
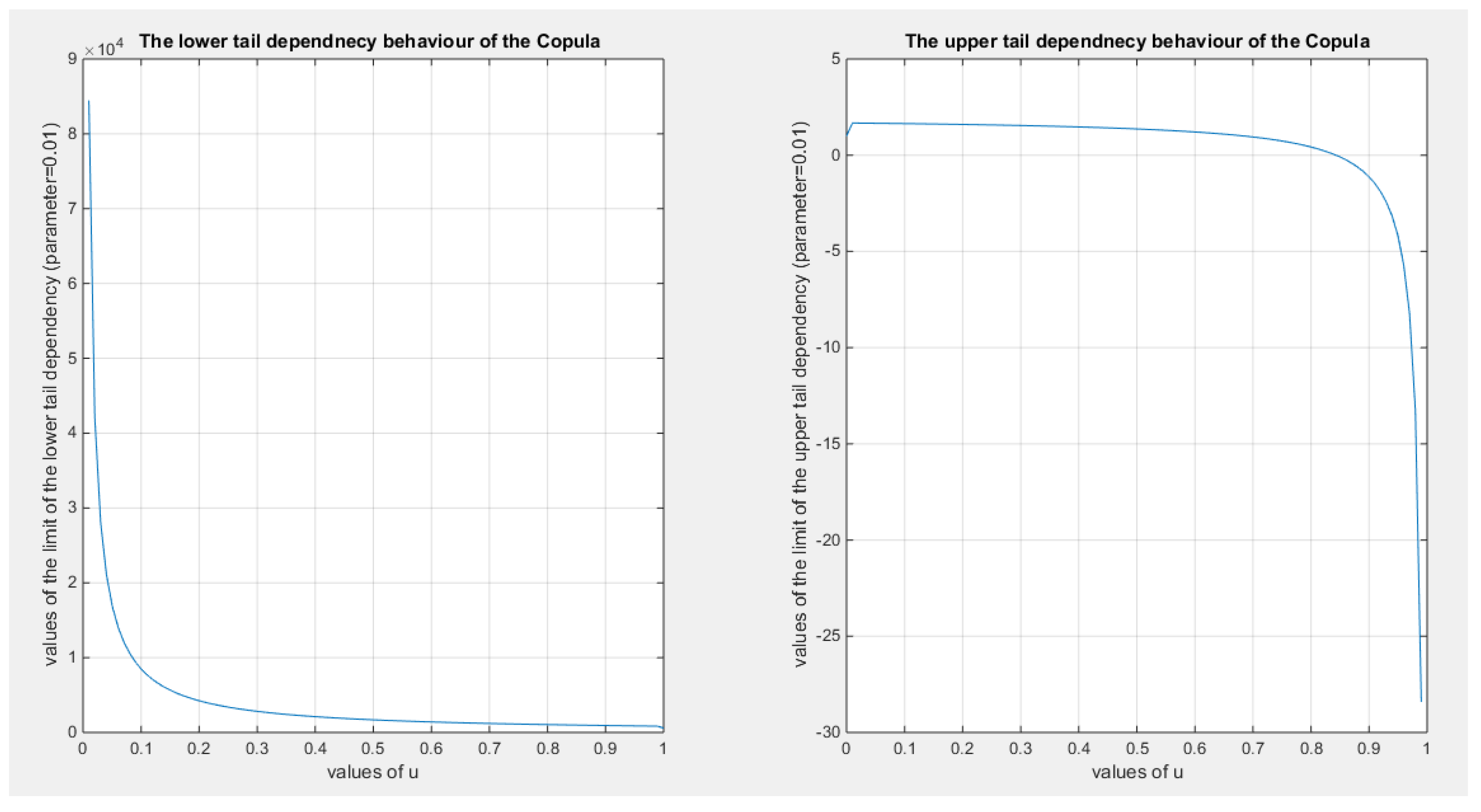
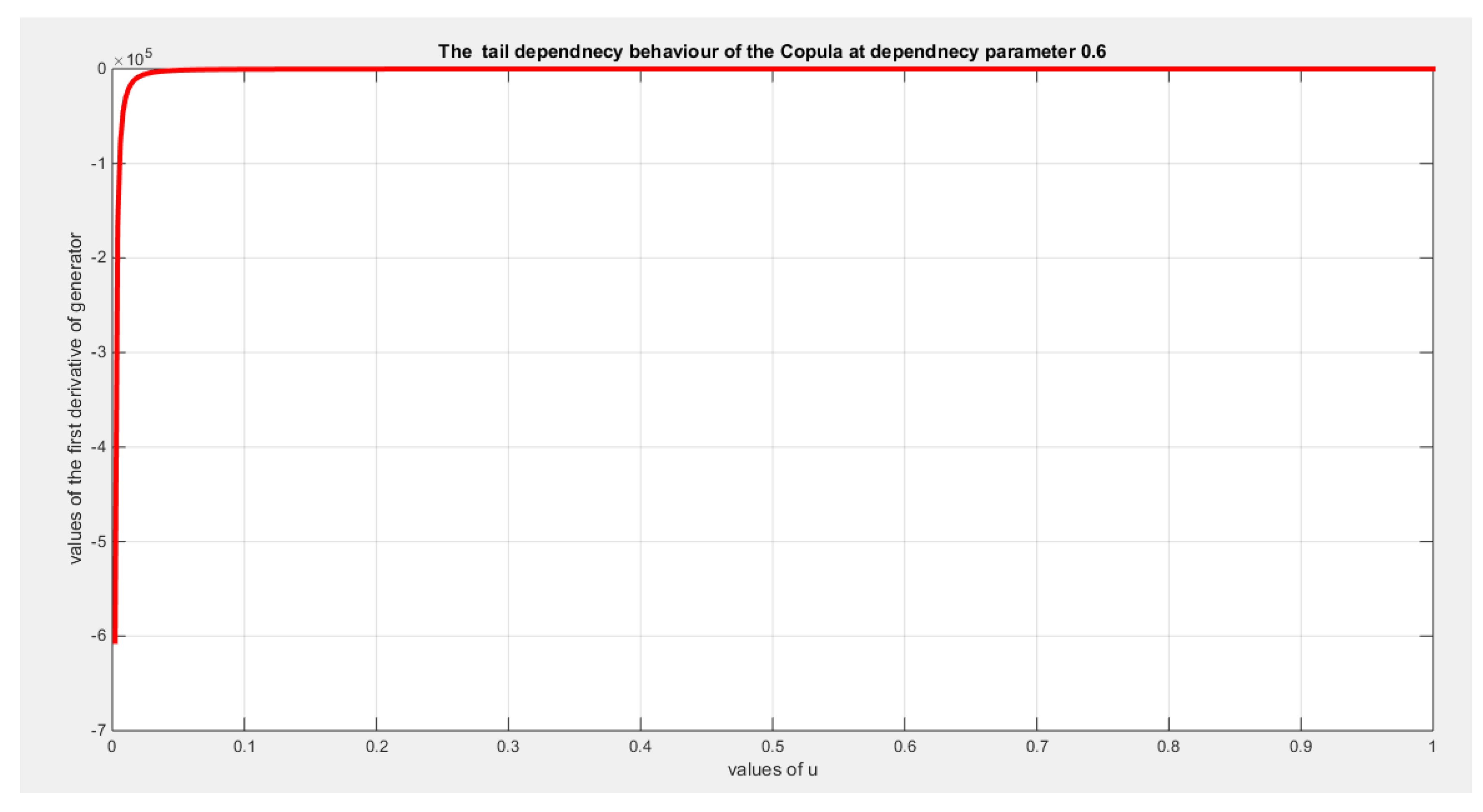
5. Tail Dependency
6. Conclusions
Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Consent for Publication
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsina, C. Franks, M. F., & Schweizer, B. (2006). Associative Functions.Triangular Norms and Copulas. World Scientific, Singapore.
- Attia, I. M. (2025). New Three Different Generators for Constructing New Three Different Bivariate Copulas. Preprint.org. [CrossRef]
- Attia, M.I. (2024). A Novel Unit Distribution Named as Median Based Unit Rayleigh (MBUR):Properties and Estimations. Preprints.Org, Preprint, 7 October 2024(7 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Cherubini, U. Luciano, E., & Vecchiato, W. (2004). Copula Methods In Finance. John Wiley and Sons.
- Cuadras, C. M. , Fortiana, J., & Rodriguez-Lallena, J. A. (2002). Distributions with Given Marginals and Statistical Modellings. Kluwer. Distributions with Given Marginals and Statistical Modellings.
- Drouet-Mari, D. , & Kotz, S. (2001). Correlation and Dependence. Imperial College Press.
- Durante, F. , & Sempi, C. (2015). Principles of Copula Theory. CRC Press.
- Embrechts, P. Lindskog, F., & Mcneil, A. (2003). Modelling Dependence with Copulas and Applications to Risk Management. In Handbook of Heavy Tailed Distributions in Finance (pp. 329–384). Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Frees, E. W. , & Valdez, E. A. Understanding Relationships Using Copulas. North American Actuarial Journal 1998, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genest, C. (2005a). Preface (Vol. 33). Candian Journal of statistics.
- Genest, C. (2005b). Preface (Vol. 37). Insurance: Mathematics and Economics.
- Genest, C. , & Mackay, J. The Joy of Copulas: Bivariate Distributions with Uniform Marginals. The American Statistician 1986, 40, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genest, C. , Rémillard, B., & Beaudoin, D. Goodness-of-fit tests for copulas: A review and a power study. Insurance: Mathematics and Economics 2009, 44, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, P. , Durante, F., & Hardle, W. (2013). Copula in Mathematical and Quantitative Finance. Springer Verlag.
- Jaworski, P. , Durante, F., Hardle, W., & Rychlik, T. (2010). Copula Theory and Its Applications: Proceedings of the Workshop held in Warsaw. (Lecture Notes in Statistics, Vol. 198). Springer Verlag.
- Joe, H. Families of min-stable multivariate exponential and multivariate extreme value distributions. Statistics & Probability Letters 1990, 9, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, H. Parametric Families of Multivariate Distributions with Given Margins. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 1993, 46, 262–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, H. (1997). Multivariate Models and Dependence Concepts. Chapman and Hall.
- Joe, H. (2014). Dependence Modeling with Copulas. CRC Press.
- Joe, H. , & Hu, T. Multivariate Distributions from Mixtures of Max-Infinitely Divisible Distributions. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 1996, 57, 240–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, N. , Anjos, U. D., & Mendes, B. V. D. M. Copulas: A Review and Recent Developments. Stochastic Models 2006, 22, 617–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, N. , & Paiva, D. Copula-based regression models: A survey. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference 2009, 139, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, J. F. & Scherer, M. (2014). Finanial Engineering with Copula Explained. Palgrave Macmillan.
- Malevergne, Y. , & Sornette, D. (2006). Extreme Financial Risks: From Dependence to Risk Management. Springer Verlag.
- Manner, H. , & Reznikova, O. A Survey on Time-Varying Copulas: Specification, Simulations, and Application. Econometric Reviews 2012, 31, 654–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, A. J. , Frey, R., & Embrechts, P. (2005). Quantitative Risk Management: Concepts, Techniques and Tools. Princeton University Press.
- Nadarajah, S. , Afuecheta, E., & Chan, S. A Compendium of Copulas. Statistica 2018, 77, 279–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelsen, R. B. (2002). Concordance and Copulas: A Survey. In C. M. Cuadras, J. Fortiana, & J. A. Rodriguez-Lallena (Eds.), Distributions With Given Marginals and Statistical Modelling (pp. 169–177). Springer Netherlands. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R. B. (2006). An Introduction to Copulas. Springer Verlag.
- Ozun, A. , & Cifter, A. Estimating Portfolio Risk with Conditional Joe-Clayton Copula: An Empirical Analysis with Asian Equity Markets The IUP Journal of Financial Economics 2007, 28–41.
- Patton, A. J. A review of copula models for economic time series. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 2012, 110, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, G. , Michele, C. D., Kottegoda, N. T., & Rosso, R. (2007). Extremes in nature. An approach Using Copulas. Springer Verlag.
- Schweizer, B. (1991). Thirty Years of Copulas. In G. Dall’Aglio, S. Kotz, & G. Salinetti (Eds.), Advances in Probability Distributions with Given Marginals (pp. 13–50). Springer Netherlands. [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, B. , & Sklar, A. (2005). Probabilistic Metric Space. Dover, Mineola.
- Sklar, A. Random Variables, Joint distribution functions, and copulas. Kybernetika 1973, 9, 449–460. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




