Submitted:
21 April 2025
Posted:
22 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
- Transmission: The transmission system is based on a looped structure. Transmission lines are usually protected by relays installed at one or two ends that continuously monitor voltages and currents. The conventional methods often used in fault diagnosis of transmission lines are the traveling wave method and the impedance measurement-based method. The most frequent protection method is distance protection. The methods in this category can be further classified into two sub-categories: methods that use measurements from one terminal of the transmission line and methods that use measurements taken from both terminals [1,2,32,41].
- Distribution: It is the most affected part of the power system since faults at these levels account for about 80% of service interruptions to end-users. Traditionally, the default protection against faults in distribution networks is the overcurrent scheme. In contrast to transmission lines, the distribution networks are usually non-homogeneous, with branches and loads along a feeder, which make the fault location more difficult [1]. A very basic method of fault location uses visual inspection, which cannot be used if the fault is on an insulated cable. Conventional methods, proposed in literature or implemented in practice, use measured voltages and currents and may be divided into three categories [1]: methods based on traveling waves, methods using high frequency components of voltages and currents, and methods using fundamental frequency voltages and currents. The last method, also classified as impedance-based method, consists of calculating line impedances as seen from the line terminals and estimating distances of the faults. Impedance-based methods are popular among utilities, because of their ease of implementation.
II. Concepts and Definitions on Artificial Intelligence and Fault Diagnosis
2.1. Artificial Intelligence Concepts
- ➢
- Supervised learning: An algorithm is trained using data tagged with a label so that an algorithm can successfully learn from it. Training labels help the model know how to classify data in the desired manner. Two types of models can be distinguished in this group: classification and prediction. Classification models are used to assign test data into specific categories. Regression models use an algorithm to understand the relationship between dependent and independent variables, and can be used to predict numerical values from different data points.
- ➢
- Unsupervised learning: Unlabeled data are used to train an algorithm; the algorithm finds patterns in the data itself and creates its own data clusters. Unsupervised learning can be used to find patterns in data that are currently unknown.
- ➢
- Reinforcement learning: It is a technique in which positive and negative values are assigned to desired and undesired actions. The goal is to encourage programs to avoid the negative training examples and seek out the positive learning how to maximize rewards through trial and error.
- ➢
- Semi-supervised learning: It uses a mix of labeled and unlabeled data to train an algorithm. In this process, the algorithm is first trained with a small amount of labeled data before being trained with a much larger amount of unlabeled data.
- ➢
- Ensemble methods: They make use of several ML algorithms to improve the performance that can be achieved with the use of a single algorithm. Ensemble learning constructs a set of hypotheses generated by several base learners that are used together to solve a single problem and provide better generalizability than individual base learners.
- Metaheuristic methods are a type of algorithm characterized by their ability to solve optimization problems by mimicking natural phenomena or human intelligence [72,73]. They are used to find approximate optimal solutions to complex and highly nonlinear optimization problems for which no deterministic approach is able to handle in an acceptable amount of time. The particle swarm optimization (PSO), the ant colony optimization (ACO), the genetic algorithm (GA), the tabu search method or the simulated annealing method are some of the most popular algorithms. A significant effort has also been carried out to review this group of methods, see references [74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81]. It is worth mentioning that reference [79] provides a list of more than 500 metaheuristics algorithms, and it is not complete since some additional methods have been proposed; see, for instance, [82].
- Rule-based systems, also referred to as expert systems (ESs), are a group of techniques that allow the direct integration of human knowledge. An expert system is a computer software that emulates the process used by human experts when they solve problems [83]. By developing a set of if-then rules, the system is able to decide based on the rules given by an expert. Besides the Boolean logic, fuzzy logic has also been used in rule-based systems; its main advantage is the description of variables and relations in human linguistics. A fuzzy system normally consists of three basic parts [84]: (1) fuzzification, where the input signals are mapped onto a fuzzy membership function using a membership degree; (2) inference, where the calculated degrees of membership are integrated into IF-THEN fuzzy rules; (3) defuzzification, which creates an output signal that the physical system is able to handle. For more information on this AI subfield, see [85,86,87,88,89].
2.2. Fault Diagnosis Concepts
- fault detection is the task of recognizing the occurrence of a fault;
- fault classification is the identification of the fault type;
- fault isolation is the process of isolating the faulty part of the network after a successful detection;
- fault location is the task of localizing the fault (i.e. branch, zone, location point);
- service restoration is the process aimed at returning the system to normal operating conditions; that is, a task carried out to restore the service in healthy zones after detecting and isolating a permanent fault in the system.
2.3. Scope of the Paper
III. Application of Artificial Intelligence Techniques to Power System Studies
IV. Fault Diagnosis of Power Systems Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques
4.1 . Introduction
- Transform methods: The frequency characteristics of current and voltage signals during a fault change with time, and they can be very useful for detecting, classifying and locating a fault. A variety of methods used to analyze frequency characteristics of time-domain signals have been proposed. Some of the most popular transform methods are the Fourier transform (FT), the wavelet transform (WT), and the S transform (ST). Since time-domain signals and frequency-domain coefficients are both discrete, in practice the most popular approaches use this condition for feature extraction; they are the discrete Fourier transform (DFT), the fast Fourier transform (FFT), or the discrete wavelet transform (DWT).
- Modal transformations: They transform/decouple three-phase quantities into components that can be used to further characterize fault types or to obtain detection and location indices. A list of popular transformations includes the Clark transformation, the Clarke-Concordia transformation, and the Karrenbauer transformation.
- Dimensionality reduction: This approach maps the data from the original high-dimensional space onto a low-dimensional subspace in which the variance of the data can be best accounted. The reduction is usually performed by means of principal component analysis (PCA), and can be combined with other methods.
- Other methods: To reduce the computational burden associated with the above listed methods, other approaches have been proposed. They are based on the RMS values of phase and zero sequence currents, the normalized ratios of maximum absolute values of currents for two different phases, or the ratios of phase angle differences between phases plus the ratio of zero sequence current amplitude to positive sequence current amplitude [9]. Mathematical morphology is another option that is being adopted as a feature extraction technique for detection and classification of faults [219]. For a comparison of feature extraction techniques, see this last reference.
- Prominent techniques: They used one of the following three approaches for feature extraction: wavelet transform, ANNs, and fuzzy logic.
- Hybrid techniques: They are based on a combination of two or more approaches of the previous group (e.g., neuro-fuzzy technique, wavelet and ANN technique, wavelet and fuzzy-logic technique, wavelet and neuro-fuzzy technique).
- Modern techniques: They are based on other AI techniques (e.g., SVM, GA, PCA, or DT) or use modern technologies to either measure signals or process extracted signal features (FPGA-based implementation, PMU-based protection scheme, pilot scheme).
- Techniques based on fundamental-frequency currents and voltages: These techniques assume that the calculated impedance of the faulted-line segment is a measure of the distance to fault. When applied to a two-terminal line, they can be classified considering the available measurements: waveforms from one or both ends; complete or incomplete measurements (voltage or current) from a particular line end. Methods using one-end impedance techniques do not need communication means and their implementation into digital protective relays or digital fault recorders is rather simple. However, the algorithms will be more accurate if information from the two line terminals is available; therefore, if communication channels are at the disposal, then two-terminal fault-location methods should be used since low-speed communications are sufficient. Besides, two-end techniques exhibit more accuracy without any assumption about external networks (i.e., impedances of the equivalent sources).
- Techniques based on traveling-wave phenomenon: These techniques use voltage and current waves, traveling at the speed of light from the fault towards the line terminals; they can be very accurate, but also complex and expensive due to the required high sampling frequency.
- Techniques based on high-frequency components of currents and voltages: These techniques are also complex and expensive since they require specially tuned filters for measuring high-frequency components.
- AI-based techniques: Although ANN-based methods for fault location have been developed for more than forty years, it has been during the last two decades when a significant effort has been dedicated to fault-location techniques both in transmission and distribution networks using AI methods. A high number of review papers focused on this subject has been published during this period; see references [8,9,14,15,16,22,24,25,30,33,34,36,225,226].
4.2. Fault Location Methods for Transmission Systems
- There is a high number of AI techniques that can be useful to faults diagnosis of power systems. Remember that the topics covered in this survey are focused on faults/failures that can affect overhead lines and insulated cables only.
- None of the selected papers deals with automatic AI-based fault diagnosis of transmission-level insulated cables.
- Only a small percentage of papers deal with a complete fault diagnosis procedure (i.e., detection, classification and location). Actually, the fault location seems to be the task to which a lower number of papers has been dedicated.
- Supervised ML techniques (i.e., NN, SVM, DT) are the most popular group of AI applications.
| Ref. | Authors | Year | Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | Daang et al. | 2024 | Fault detection in transmission lines |
| [36] | Kanwal and Jiriwibhakorn | 2024 | Fault detection, classification, and location in transmission lines |
| [35] | Shukla and Deepa | 2024 | Fault classification in transmission lines |
| [33] | Liu et al. | 2023 | Fault location in transmission lines |
| [32] | Shakiba et al. | 2023 | Fault detection, classification, and location in transmission lines |
| [31] | Jena et al. | 2023 | Fault detection, classification, and location in underground cables |
| [30] | Rezapour et al. | 2023 | Fault location in distribution grids |
| [8] | De La Cruz et al. | 2023 | Fault location in smart distribution grids and MGs |
| [43] | Baharozu et al. | 2023 | High impedance fault location |
| [28] | Shafiullah et al. | 2022 | Comparison of ML techniques for distribution grid fault analysis |
| [26] | Srivastava et al. | 2022 | Fault detection, isolation, and restoration in distribution grids |
| [25] | Stefanidou-Voziki et al. | 2022 | Fault classification and location in distribution grids |
| [24] | Dashti et al. | 2021 | Fault prediction and location in smart distribution grids and MGs |
| [23] | Vaish et al. | 2021 | Fault detection, isolation, and restoration in power systems |
| [22] | Mukherjee et al. | 2021 | Fault detection, classification, and location in transmission lines |
4.3. Fault Location Methods for Distribution Systems
- As for research related to transmission systems, a high number of AI techniques has also been applied to faults diagnosis of distribution systems.
- Only a small percentage of works deals with a complete fault diagnosis procedure (i.e., detection, classification and location).
- Supervised ML techniques are again the most popular option for authors interested in this field.
| Ref. | Authors | Year | Task | Technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [326] | Anwar et al. | 2025 | Fault detection | RF, LSTM, and kNN |
| [325] | Nayak et al. | 2024 | Fault detection and classification | CWT and 2D-CNN |
| [324] | Wu et al. | 2024 | Fault classification and location | PNMCN |
| [323] | Turanli and Yakut | 2024 | Fault classification | 1D-CNN |
| [322] | Jia et al | 2024 | Fault location | CEEMDAN, MSA, and ConvGRU |
| [321] | de Alencar et al. | 2024 | Fault classification | ICA and CNN |
| [320] | Alhanaf et al. | 2024 | Fault detection and classification | Hybrid CNN-LSTM |
| [319] | Najafzadeh et al. | 2024 | Fault detection, classification, and location | WHO-RF/DT, ANFIS |
| [318] | Ukwuoma et al. | 2024 | Fault detection, classification, and location | MSAN, DGNN, and MLP |
| [317] | Chen and Liu | 2024 | Fault detection | FuzREANN |
| [316] | Mampilly and Sheeba | 2023 | Fault detection and classification | WT and ICNN-BOA |
| [315] | Bhattacharya and Nigam | 2023 | Fault detection and classification | RF, DT, XGB, LGBM |
| [314] | Altaie et al. | 2023 | Fault detection | Several ML techniques |
| [313] | Alhanaf et al. | 2023 | Fault detection, classification, and location | ANN, DNN |
| [312] | Khan et al. | 2023 | Fault classification and location | VAE and SVM, kNN, RF, DT |
| [311] | Biswas et al. | 2023 | Fault detection and classification | VMD and CNN |
| [310] | Zhang and Wang | 2023 | Fault classification | GLDA-CE |
| [308] | Goni et al. | 2023 | Fault detection and classification | ELM |
| [307] | Sahoo and Samal | 2023 | Fault detection and classification | DNN |
| [306] | Thomas et al. | 2023 | Fault detection and location | CNN |
| [305] | Rajesh et al. | 2022 | Fault detection and classification | TSVD-HUA-RPNN |
| [304] | Fahim et al. | 2022 | Fault detection and classification | DBN |
| [303] | Hong et al. | 2022 | Fault classification and location | CNN |
| [302] | França et al. | 2022 | Fault classification | MLPN, RBF, SVM, DT |
| [300] | Gutierrez-Rojas et al. | 2022 | Fault classification | DM-DFT and QARMA |
| [298] | Arranz et al. | 2021 | Fault location | ST and ANN |
| [297] | Fahim et al. | 2021 | Fault detection and classification | WT and CNSF |
| [296] | Rafique et al. | 2021 | Fault detection and classification | e2e learning and LSTM |
| [295] | Mukherjee et al | 2021 | Fault detection and location | PCA |
| [294] | Hassani et al. | 2021 | Fault classification | kGAN and kNN, SVM |
| [293] | Mukherjee et al. | 2021 | Fault classification | PCA |
| [292] | Belagoune et al. | 2021 | Fault detection, classification, and location | DRNN-LSTM |
| [291] | Srikanth and Koley | 2021 | Fault classification | ST and 3D CNN |
| [290] | Haq et al. | 2021 | Fault detection and classification | DWT and ELM |
| [289] | Vyasa et al. | 2021 | Fault detection and classification | DWT and ChNN |
| [288] | Han et al. | 2021 | Fault classification | GSV-CDA-CNN |
| Ref. | Authors | Year | Task | Technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [433] | Shafei et al. | 2024 | Fault detection, classification and location | PT-PFPT and CNN |
| [432] | Arsoniadis and Nikolaidis | 2024 | Fault location | WSN and SVM/ERM |
| [431] | Barkhi et al. | 2024 | Fault detection and classification in MGs | SVM |
| [430] | Krishnamurthy et al. | 2024 | Fault classification | RF |
| [429] | Yildiz and Abur | 2024 | Fault detection and location | CNN |
| [428] | Fan et al. | 2024 | Fault location | VGAE-GraphSAGE |
| [427] | Basher et al. | 2024 | Fault classification and location in MGs | DWT with DTE-LDA |
| [426] | Bhagwat et al. | 2024 | Fault detection, classification and location | Customised ANN |
| [425] | Awasthi et al. | 2024 | Fault classification | kNN |
| [424] | Liang et al. | 2024 | Fault location | Multi-head GAT |
| [423] | Zhou et al. | 2024 | Fault classification and location | CNN |
| [422] | Cieslak et al. | 2024 | HIF classification in MGs | TNN |
| [421] | Li | 2024 | HIF detection and location | CNN-LSTM |
| [419] | Mampilly and Sheeba | 2024 | Fault detection and classification in MGs | EWT-HCRNN-POA |
| [418] | Awasthi et al. | 2024 | Fault classification | Shallow ANN |
| [417] | Bhatnagar et al. | 2024 | Fault detection and classification | CNN-LSTM-AM |
| [416] | Mbey et al. | 2023 | Fault detection and classification | LSTM-ANFIS |
| [415] | Mirshekali et al. | 2023 | Fault location | Spectrogram and CNN-CN |
| [408] | Yang and Yang | 2023 | Fault classification | STFT and CNN-FDTW |
| [407] | Kurup et al. | 2023 | Fault detection and classification | CNN and SVM |
| [406] | Mo et al. | 2023 | Fault classification and location | Super-resolution and GNN |
| [405] | Haydaroğlu and Gümüş | 2023 | Fault detection | Cauchy-M and RVFLN |
| [404] | Rizeakos et al. | 2023 | Fault classification and location | CWT and CNN |
| [403] | Yuan and Jiao | 2023 | Fault detection | Hybrid CNN-LSTM |
| [398] | Dashtdar et al. | 2023 | Fault location | GA |
| [397] | Hu et al. | 2023 | Fault classification and location | STGCN |
| [396] | da Silva Santos et al. | 2022 | Fault detection and classification | DWT and FIS |
| [395] | Moloi et al. | 2022 | Fault classification and location | WPD and SVM |
| [394] | Ahmadipour et al. | 2022 | Fault detection and classification in MGs | MODWPT-ALPSO-SVM |
| [393] | Granado Fornás et al. | 2022 | Fault detection and classification | TDR, GAF, and GAN |
| [389] | Rai et al. | 2022 | HIF detection and classification | TNN-CNN |
| [385] | Carvalho et al. | 2022 | HIF classification | HOS-FDR with ANN |
| [383] | Mirshekali et al. | 2022 | Fault location | NCFS and SVM |
| [382] | Swaminathan et al. | 2021 | Fault classification and location in cables | CNN-LSTM |
| [381] | de Freitas and Coelho | 2021 | Fault location | GNN |
| [380] | Gilanifar et al. | 2021 | Fault classification | MTLS-LR |
| [378] | Yu et al. | 2021 | Fault location | SIG-CNN |
| [376] | Okumus and Nuroglu | 2021 | Fault location | WT-FWHT and RF |
| [374] | Baloch and Muhammad | 2021 | Fault detection and classification in MGs | HT, LR and AB |
4.4. Fault Location Methods for DC Systems
V. Discussion
- This paper holds the concept Artificial Intelligence in its title. Interestingly, future developments in this field, namely in generative AI [474], might make unnecessary the effort to create such type of documents since it cannot be discarded that a survey paper like the current one could be easily generated by taking advantage of future developments of AI.
- What is AI and what is not is another important aspect. Although part of Section 2 was dedicated to clarifying this aspect, the fact is that AI concepts has been classified using different approaches in many previous works. For instance, some authors include game theory as a subfield of AI; see, for instance, [193]. Neither game theory nor other popular approaches (i.e. multi-agent system) were considered in this survey.
- The availability of massive datasets and open-source code, the development of efficient algorithms, and the continuous improvement of computing power are some of the aspects that have made possible the application of AI algorithms.
- The number of papers related to fault diagnosis (i.e., detection, classification and location of faults) in power systems is about several thousand. Although this review has only covered papers related to AI-based techniques, some selection has been unavoidable. Obviously, it is debatable the way in which the papers included in this survey have been selected.
| Ref. | Authors | Year | Task | Techniques |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [473] | Liu et al. | InPress | Traveling wave fault location in MMC-based HVDC systems | GWO-VMD |
| [472] | Fayazi et al. | 2025 | Fault detection and classification in parallel HVAC/HVDC transmission lines | DT and FEI |
| [471] | Akbari and Shadlu | 2024 | Fault detection, classification and location in VSC-based HVDC systems | PCA-DWT and ANFIS |
| [470] | Pragati et al. | 2024 | Fault detection and classification in VSC-based HVDC systems | ST-RNN and TEO |
| [469] | Yousaf et al. | 2024 | Fault detection in MMC-based HVDC systems | DWT and Enhanced ANN with Bagging |
| [468] | Yousaf et al. | 2024 | Fault detection in MMC-based HVDC systems | LSTM-DWT |
| [467] | Yu et al. | 2024 | Fault location in DC distribution systems | Multivariate information fusion |
| [466] | Deb and Jain | 2024 | Fault detection and classification in low-voltage DC microgrids | BEL and cosine kNN |
| [465] | Salehimehr et al | 2024 | Fault detection and location in low-voltage DC microgrids | CS-RT and LSTM |
| [463] | Hameed et al. | 2024 | Fault detection and classification in MMC-based HVDC systems | HHO and ANN |
| [462] | Jawad and Abid | 2023 | Fault detection in VSC-based HVDC systems | ACO-DWT and ANN |
| [461] | Gnanamalar et al. | 2023 | Fault detection, classification and location in VSC-HVDC systems | HHT plus CNN-SVM |
| [460] | Psaras et al. | 2023 | Fault location in HVDC systems | GA in frequency domain |
| [459] | Jawad and Abid | 2022 | Fault detection in VSC-based HVDC systems | GWO and ANN |
| [458] | Ghashghaei and Akhbari | 2021 | Fault detection and classification in CSC-HVDC systems | SVM and KNN |
| [457] | Yang et al. | 2021 | Fault detection and location in MMC-based HVDC systems | CWT and Deep-RNN |
| [456] | Roy | 2021 | Fault detection and location in HVDC systems | DOST-PNN and FDST-BPNN |
| [455] | Wang et al. | 2021 | Fault location in VSC-based HVDC transmission lines | VMD-TEO and CNN-LSTM |
| [454] | Ye et al. | 2021 | Fault location in MMC-based HVDC systems | WT and DBN |
| [453] | Wu et al. | 2021 | Fault location in MMC-based HVDC systems | SVM-CEEMDAN |
- 5.
- Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones, have emerged as an option for inspection of overhead lines and for detection of faults [475,476]. UAV-mounted sensors can be a data source for accurate visual and thermal inspection of overhead lines. There is an increasing interest in the application of AI-based techniques to the detection and classification of overhead line faults using data from UAVs [477,478,479,480,481,482,483].
- 6.
- AI-based methods exhibit some potential for improving accuracy and adaptability to diverse fault conditions; however, their practical implementation is challenging. Consider, for example, a fault location scheme using a traveling wave-based approach combined with ANNs; such technique requires extensive training data and high computational burden, in addition to a continuous adaptation to varying system configurations. This can be especially difficult for distribution networks with high renewable penetration since they require innovative fault location techniques that can handle bidirectional power flows.
- 7.
- The practical implementation of AI-based techniques for detecting, classifying and locating faults will be parallel to advances in software and hardware. Training data for supervised ML techniques can be easily derived from computer simulations, which should be carried out using sophisticated software tools and very accurate power system component models. A similar conclusion can be derived from hardware implementation: AI-based techniques require powerful and flexible microprocessors that could be easily reprogrammed considering the experience obtained from both the actual power system and its computer representation. Real-time simulation platforms will be of much help in deploying the new techniques. Consider that many works have been based on results derived from rather small test systems, and many authors did not include the representation of instrument transformers (i.e., current and voltage transformers) in the system models. Therefore, it is advisable to be careful about some conclusions.
- 8.
- An aspect that has to be considered for selecting an adequate technique is the data that can be available, and this will depend on the various technologies installed in the system under study. The modern SG offers sufficient availability of data for the implementation of an accurate AI-based fault diagnosis technique. That is, an aspect that can affect a fault diagnosis scheme based on an AI technique is the monitoring system implemented in the actual power grid. The grid becomes smarter as the number of monitoring nodes increases. The way in which a practical fault location scheme will be developed and implemented depends on this aspect and on the skills of the available communication system. From a theoretical point of view estimating the faulted section in a distribution system would be a very easy task if a monitor has been installed in each grid node and a low-latency communication network is available; in practice, such an ideal scenario would be too expensive and hardly justifiable.
- 9.
- The faulty section of a power system can be easily and quickly estimated by means of an expert system if powerful monitoring and low-latency communication systems have been installed in the grid. A combination of an ES and a ML-based technique might be a practical solution for detecting, classifying and location faults in smart grids.
- 10.
- As discussed in subsection 4.1, a fault-location function can be part of a microprocessor-based protective relay, and a fault locator can be a supplementary device that can estimate the fault location in an overhead line or an insulated cable. Presently, a fault locator is also a device manually handled by maintenance crews to estimate the location of faults, mainly in underground cables.
- 11.
- Although most (if not all) of the works reported in this survey are based on computer simulation, the survey has not covered some important aspects such as the applied software simulation tools or the sources from which data for training ML techniques come from. As for simulation tools, it has already been mentioned that most works are based on MATLAB and EMTP-like tools. In general, data for training ML-based approaches come from simulations carried out by the authors; however, it is worth mentioning that some dataset repositories are available for helping researchers in the development of predictive models. Some works that could be useful to readers interested in this subject were presented in references [484,485,486,487,488].
- 12.
- Although a significant effort has been made to date and very useful experience is already available on the application of AI-based techniques to detect, classify and locate faults in lines and cables, it is not easy to select the best combination of techniques. A very good method for locating faults in a distribution system based on a rather limited system model should not be selected as a winner: although the combination of techniques selected for each task (i.e. feature extraction, detection, classification, location) can be useful for future work, it could also exhibit poor performance when using a more accurate and sophisticated system model.
- 13.
- The number of AI algorithms applied to power system studies is steadily increasing. The list of the latest techniques include transfer learning, graph learning, deep attention mechanism, deep reinforcement learning, or physics-guided neural networks. Some of these developments address some limitations of neural networks (e.g., overfitting, low data efficiency, low adaptivity, or physical inconsistency).
- 14.
- Quantum computing is an emerging technology that will be extremely useful in AI-based applications for which high performance computing power is a requirement [489,490,491,492]. Although not much experience is available to date, some interesting works on fault diagnosis of power systems has already been presented [493,494,495,496].
- 15.
- Since AI systems are prone to cyberattacks, risk evaluation can be crucial before their implementation. In complex transmission and distribution grids, associated with the vulnerability of SCADA systems and communication networks, which interconnect countless smart devices (meters, sensors, etc.), cybersecurity becomes a critical issue. Attacks to SG equipment (e.g., data breaches, data manipulation, unauthorized access, denial of service, man-in-the-middle, false data injection, malware introduction, etc.) can cause large-scale damage. Some recent works, see [497,498], offer a broad perspective on these risks and alert to the need for investment in strengthening security and mitigating potential damage. Besides, with their increasing autonomy, AI systems are acquiring skills that can be dangerous even for themselves; therefore, risk evaluation of their capabilities before implementation is becoming another critical issue [499].
VI. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| List of Acronyms | |
| AC: alternating current | HIF: high impedance fault |
| ACO: ant colony optimization | HLLE: Hessian locally linear embedding |
| AB: AdaBoost | HOS: higher-order statistics |
| AI: artificial intelligence | HT: Hilbert transform |
| ALPSO: augmented Lagrangian particle swarm optimization | HUA: human urbanization algorithm |
| AM: attention mechanism | HVAC: high voltage alternating current |
| ANFIS: adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system | HVDC: high voltage direct current |
| ANN: artificial neural network | ICNN: improved convolution neural network |
| BEL: bagged ensemble learner | KMC: K-means clustering |
| BOA: bees optimization algorithm | kGAN: knockoff generative adversarial network |
| BPNN: backpropagation neural network | kNN: k-nearest neighbour |
| CAE: convolutional auto-encoder | LDA: linear discriminant analysis |
| CDA: cross-domain adaption | LGBM: light gradient boosting machine |
| CE: characteristic entropy | LR: logistic regression |
| CEEMDAN: complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise | LSTM: long short-term memory |
| ChNN: Chebyshev neural network | MG: microgrid |
| CN: Capsule network | MIF: multivariate information fusion |
| CNN: convolutional neural network | ML: machine learning |
| CNSF: capsule network with sparse filtering | MLP: multi-linear perceptron network |
| ConvGRU: convolutional gate recurrent unit | MLPN: multi-layer perceptron neural network |
| CS: compressed sensing | MMC: modular multilevel converter |
| CSC: current source converter | MODWPT: maximal overlap discrete wavelet packet transform |
| CWT: continuous wavelet transform | MRA: multiresolution analysis |
| DBN: deep belief network | MSA: mantis search algorithm |
| DC: direct current | MSAN: multi-scale attention network |
| DER: distributed energy resource | MTLS-LR: multi-task latent structure learning |
| DFT: discrete Fourier transform | NCFS: neighborhood component feature selection |
| DG: distributed generation | NN: neural network |
| DGNN: deep graph neural network | PCA: principal component analysis |
| DL: deep learning | PFPT: Piecewise Function Put Together algorithm |
| DM-DFT: delta method discrete Fourier transform | PMU: phasor measurement unit |
| DNN: deep neural network | PNMCN: pose normalized multioutput convolutional nets |
| DOST: discrete orthonormal S-transform | PNN: probabilistic neural network |
| DRNN: deep recurrent neural network | POA: pelican optimization algorithm |
| DT: decision tree | PSO: particle swarm optimization |
| DTE: decision tree ensemble | PT: Park’s transformation |
| DWT: discrete wavelet transform | QARMA: quantitative association rule mining algorithm |
| e2e: end to end learning | QL: Q-learning |
| ELM: extreme learning machine | RBF: radial basis function neural network |
| EMS: energy management services | RF: random forest |
| ERM: ensemble regression mode | RMS: root mean square |
| ES: expert system | RNN: recurrent neural network |
| EWT: empirical wavelet transform | RPNN: recurrent perceptron neural network |
| FDIR: fault detection, isolation, and service restoration | RT: regression tree |
| FDR: Fisher’s discriminant ratio | RVFLN: random vector functional link network |
| FDST: Fast discrete S-transform | SA: simulated annealing |
| FDTW: fast dynamic time warping | SCADA: supervisory control and data acquisition |
| FEI: fault energy index | SG: smart grid |
| FFT: fast Fourier transform | SIG: signal to image |
| FIS: fuzzy inference system | ST: S-transform/Stockwell transform |
| FLISR: fault location, isolation, and service restoration | STFT: short-time Fourier transform |
| FLR: fuzzy linear regression | STGCN: spatiotemporal graph convolutional network |
| FPGA: field programmable gate array | SVM: support vector machine |
| FPI: fault passage indicator | TDR: time-domain reflectometry |
| FT: Fourier transform | TEO: Teager energy operator |
| FuzREANN: fuzzy reinforcement encoder adversarial neural networks | TNN: transformer neural network |
| FWHT: fast Walsh Hadamard transform | TS: tabu search |
| GA: genetic algorithm | t-SNE: t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding |
| GAF: Gramian angular field transform | TSVD: truncated singular value decomposition |
| GAN: generative adversarial network | UAV: unmanned aerial vehicle |
| GAT: graph attention network | VAE: variational encoder |
| GLDA: global and local discriminant analysis | VGAE: variational graph auto-encoder |
| GMM: Gaussian mixture model | VSC: voltage source converter |
| GNN: graph neural network | VMD: variational mode decomposition |
| GSV: gradient similarity visualization | WPD: wavelet packet decomposition |
| GWO: grey wolf optimization | WSN: wavelet scattering network |
| HCRNN: hybrid convolutional recurrent neural network | WT: wavelet transform |
| HHO: Harris Hawks optimization | XAI: explainable artificial intelligence |
| HHT: Hilbert–Huang transform | XGB: XGBoost |
| Note: For the sake of clarity, a list of acronyms (already defined here) has been attached to some tables of the paper. | |
References
- Mohan Saha, M.; Izykowski, J.; Rosolowski, E. Fault Location on Power Networks; Springer: London, UK, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G.; Dong, X.; Chen, X.; Tong, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S. Fault Location and Service Restoration for Electrical Distribution Systems; John Wiley: Singapore, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Santoso, S.; Ananthan, S.N. Fault Location on Transmission and Distribution Lines. Principles and Applications; John Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Bompard, E.; Huang, T.; Wu, Y.; Cremenescu, M. Classification and trend analysis of threats origins to the security of power systems. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2013, 50, 50-64. [CrossRef]
- Buchholz, B.M.; Styczynski, Z. Smart Grids-Fundamentals and Technologies in Electricity Networks, 2nd Edition, Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Refaat, S.S.; Ellabban, O.; Bayhan, S.; Abu-Rub, H.; Blaabjerg, F.; Begovic, M.M. Smart Grid and Enabling Technologies; John Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M. Fundamentals of Smart Grid Systems; Academic Press, 2022. [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz, J.; Gómez-Luna, E.; Ali, M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M. Fault location for distribution smart grids: Literature overview, challenges, solutions, and future trends. Energies 2023, 16(5), 2280. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Huang, C.; He, J. Fault detection, classification and location for transmission lines and distribution systems: a review on the methods. High Voltage 2016, 1(1), 25-33. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Dash, Y. An overview of transmission line protection by artificial neural network: Fault detection, fault classification, fault location, and fault direction discrimination. Advances in Artificial Neural Systems 2014, 2014, 230382. [CrossRef]
- Aleem, S.A.; Shahid, N.; Naqvi¸ I.H. Methodologies in power systems fault detection and diagnosis. Energy Syst. 2015, 6, 85-108. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.H.; Zanghi, R.; Fortes, M.Z.; Sotelo, G.G.; Silva, R.B.M.; Souza, J.C.S.; Guimarães, C.H.C.; Gomes Jr., S. A survey on intelligent system application to fault diagnosis in electric power system transmission lines. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 136, 135-153. [CrossRef]
- Hare, J.; Shi, X.; Gupta, S.; Bazzi, A. Fault diagnostics in smart micro-grids: A survey. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 60, 1114-1124. [CrossRef]
- Personal, E.; García, A.; Parejo, A.; Larios, D.F.; Biscarri, F.; León, C. A comparison of impedance-based fault location methods for power underground distribution systems. Energies 2016, 9(12), 1022. [CrossRef]
- Bahmanyar, A.; Jamali, S.; Estebsari, A.; Bompard, E. A comparison framework for distribution system outage and fault location methods. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 145, 19-34. [CrossRef]
- Gururajapathy, S.S.; Mokhlis, H.; Illias, H.A. Fault location and detection techniques in power distribution systems with distributed generation: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 74, 949-958. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.P.; Ray, P. Fault detection, location and classification of a transmission line. Neural Comput. & Applic. 2018, 30, 1377-1424. [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Benrabah, A.; Alquthami, T.; Akmal, M. A review of fault diagnosing methods in power transmission systems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10(4), 1312. [CrossRef]
- Fahim, S.R.; Sarker, S.K.; Muyeen, S.M.; Sheikh, M.R.I.; Das, S.K. Microgrid fault detection and classification: Machine learning based approach, comparison, and reviews. Energies 2020, 13(13), 3460. [CrossRef]
- Labrador Rivas, A.E.; Abrão, T. Faults in smart grid systems: Monitoring, detection and classification. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 189, 106602. [CrossRef]
- Mnyanghwalo, D.; Kundaeli, H.; Kalinga, E.; Hamisi, N. Deep learning approaches for fault detection and classifications in the electrical secondary distribution network: Methods comparison and recurrent neural network accuracy comparison. Cogent Engineering 2021, 7, 1857500. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Kundu, P.K.; Das, A. Transmission line faults in power system and the different algorithms for identification, classification and localization: A brief review of methods. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2021, 102, 855-877. [CrossRef]
- Vaish, R.; Dwivedi, U.D.; Tewari, S.; Tripathi, S.M. Machine learning applications in power system fault diagnosis: Research advancements and perspectives. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2021, 106, 104504. [CrossRef]
- Dashti, R.; Daisy, M.; Mirshekali, H.; Shaker, H.R.; Aliabadi, M.H. A survey of fault prediction and location methods in electrical energy distribution networks. Measurement 2021, 184, 109947. [CrossRef]
- Stefanidou-Voziki, P.; Sapountzoglou, N.; Raison, B.; Dominguez-Garcia, J.L. A review of fault location and classification methods in distribution grids. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 209, 108031. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, I.; Bhat, S.; Vardhan, B.V.S.; Bokde, N.D. Fault detection, isolation and service restoration in modern power distribution systems: A review. Energies 2022, 15, 7264. 15(19), 7264. [CrossRef]
- Krivohlava, Z.; Chren, S.; Rossi, B. Failure and fault classification for smart grids. Energy Inform. 2022, 5, 33. [CrossRef]
- Shafiullah, M.; AlShumayri, K.A.; Alam, M.S. Machine learning tools for active distribution grid fault diagnosis. Advances in Engineering Software 2022, 173, 103279. [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Kim, Y.H. Chapter 4-Machine Learning Techniques for Power System Application: Fault Analysis, In Power System Protection in Future Smart Grids; Ustun, T.S., Ed.; Academic Press, 2024; pp. 59-80. [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, H.; Jamali, S.; Bahmanyar, A. Review on artificial intelligence-based fault location methods in power distribution networks. Energies 2023, 16(12), 4636. [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.; Mishra, D.P.; Salkuti, S.R. Fault Detection, Classification, and Location in Underground Cables. In Power Quality in Microgrids: Issues, Challenges and Mitigation Techniques. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 1039; Salkuti, S.R., Ray, P., Singh, A.R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 195-215. [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, F.M.; Azizi, S.M.; Zhou, M.; Abusorrah, A. Application of machine learning methods in fault detection and classification of power transmission lines: a survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 5799-5836. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, D.; Vasilev, S.; Wang, B.; Lu, D.; Terzija, V. Model-based transmission line fault location methods: A review. Int. Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems 2023, 153, 109321. [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, S.; Jiriwibhakorn, S. Artificial intelligence based faults identification, classification, and localization techniques in transmission lines-A review. IEEE Latin America Transactions 2023, Vol. 21, no. 12, pp. 1291-1305. [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.K.; Deepa, K. Deep learning techniques for transmission line fault classification - A comparative study. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15(2), 102427. [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, S.; Jiriwibhakorn, S. Advanced fault detection, classification, and localization in transmission lines: A comparative study of ANFIS, neural networks, and hybrid methods. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 49017-49033. [CrossRef]
- Daang, J.A.M.; Omas-As, A.M.; Arboleda, E.R. Advancements in fault detection techniques for transmission lines: A literature review. Int. Journal of Research Publication and Reviews 2024, 5(7), 553-572. [CrossRef]
- Sonagra, K.A.; Vyas, B.Y. A review: Methods of fault detection, identification and location in conventional and active AC power distribution system. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 2025, 10, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.R. Statistical techniques in power systems fault diagnostic: Classifications, challenges, and strategic recommendations. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 239, 111279. [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, Y.; Subbaiyan, T. Intelligent fault diagnosis in power systems: A comparative analysis of machine learning-based algorithms. Expert Systems with Applications 2025, 265, 125945. [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Santoso, S.; Gaikwad, A.; Patel, M. Impedance-based fault location in transmission networks: Theory and application. IEEE Access 2014, 2, pp. 537-557. [CrossRef]
- Hamatwi, E.; Imoru, O.: Kanime, M.; Kanelombe, H.S.A. Comparative analysis of high impedance fault detection techniques on distribution networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 25817-25834. [CrossRef]
- Baharozu, E.; Ilhan, S.; Soykan, G. High impedance fault localization: A comprehensive review. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 214, 108892. [CrossRef]
- Mishra M.; Panigrahi, R.R. Taxonomy of high impedance fault detection algorithm. Measurement 2019, 148, 106955. [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, A.; Ginn, H.L.; Mohammadpour, H.A. High impedance fault detection: A review. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 143, 376-388. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.A.; Rao, N.D. Artificial neural network based fault diagnostic system for electric power distribution feeders. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 1995, 35, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Tomsovic, K.; Liu, C.C.; Ackerman, P.; Pope, S. An expert system as a dispatchers' aid for the isolation of line section faults. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1987, 2(3), 736-743. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Osaka, S.; Suzuki, H.; Kawakami, J. Experiences of expert systems for power system operation and planning. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 1989, 22(17), pp. 151-156. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Hope, G.S.; Malik, O.P. Expert systems in electric power systems: A bibliographical survey. IEEE Trans. on Power Systems 1989, 4(4), 1355-1362. [CrossRef]
- Dillon T.S.; Laughton, M.A. Expert System Applications in Power Systems; Prentice Hall, 1990. ISBN 0132957671.
- Bretthauer, G.; Handschin, E.; Hoffmann, W. Expert systems application to power systems - State-of-the-art and future trends. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 1992, 25(1), pp. 463-468. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Dillon, T. State-of-the-art of expert system applications to power systems. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 1992, 14(2-3), 86-96. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dillon, T. A second generation expert system for fault diagnosis, Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 1992, 14(2-3), 212-216. [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.P. Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems in Power Engineering. In Expert Systems in Engineering Applications; Tzafestas, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993; pp. 160-178. [CrossRef]
- Huneault, M.; Rosu, C.; Manoliu, R.; Galiana, F.D. A study of knowledge engineering tools in power engineering applications. IEEE Trans. on Power Systems 1994, 9(4), 1825-1832. [CrossRef]
- Burrell P.; Inman, D. An expert system for the analysis of faults in an electricity supply network: problems and achievements. Computers in Industry 1998, 37, pp. 113-123. [CrossRef]
- Turing, A.M. Computing machinery and intelligence, Mind 1950, 49, 433-460. [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J.; Minsky, M.L.; Rochester, N.; Shannon, C.E. A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence, August 31, 1955. AI Magazine 2006, 27(4), 12-14. [CrossRef]
- Russell S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach; 4th ed., Pearson, 2021. ISBN: 978-1-292-40113-3.
- Liu, J.; Kong, X.; Xia, F.; Bai, X.; Wang, L.; Qing, Q.; Lee, I. Artificial intelligence in the 21st century, IEEE Access 2018, 6, 34403-34421. [CrossRef]
- Kühl, N.; Schemmer, M.; Goutier, M.; Satzger, G. Artificial intelligence and machine learning, Electron. Markets 2022, 32, 2235-2244. [CrossRef]
- Xu Y. et al., Artificial intelligence: A powerful paradigm for scientific research, The Innovation 2021, 2(4), 100179. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. On defining artificial intelligence, Journal of Artificial General Intelligence 2019, 10(2), 1-37. [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.; Prins, C.; Schrijvers, E. Chapter 2-Artificial Intelligence: Definition and Background. In Mission AI. Research for Policy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 15-41, . [CrossRef]
- Ertel, W. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence. 3rd Edition, Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Lucci, S.; Musa, S.M.; Kopec, D. Artificial Intelligence in the 21st Century, Mercury Learning and Information: Berlin, Boston, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. ISBN 978-0-262-01802-9.
- Kubat, M. An Introduction to Machine Learning; 3rd Edition, Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, D. Applied Machine Learning; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Deisenroth, M.P.; Faisal, A.A.; Ong, C.S. Mathematics for Machine Learning; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.V. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence; 2nd Edition, Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Oliva, D.; Houssein, E.H.; Hinojosa, S.; Eds. Metaheuristics in Machine Learning: Theory and Applications, Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H., Eds., Comprehensive Metaheuristics. Algorithms and Applications, Academic Press, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Abdel-Basset, L. Abdel-Fatah, and A.K. Sangaiah, Chapter 10-Metaheuristic algorithms: A comprehensive review, In Computational Intelligence for Multimedia Big Data on the Cloud with Engineering Applications; Sangaiah, A.K., Sheng, M., Zhang, Z., Eds.; Academic Press, 2018; pp. 185-231. [CrossRef]
- Dokeroglua, T.; Sevinc, E.; Kucukyilmaz, T.; Cosar, A. A survey on new generation metaheuristic algorithms. Computers & Industrial Engineering 2019, 137, 106040. [CrossRef]
- Ezugwu, A.E.; Shukla, A.K.; Nath, R.; Akinyelu, A.A.; Agushaka, J.O.; Chiroma, H.; Muhuri, P.K. Metaheuristics: a comprehensive overview and classification along with bibliometric analysis. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 4237-4316. [CrossRef]
- Lagaros, N.D.; Plevris, V.; Kallioras, N.A. The mosaic of metaheuristic algorithms in structural optimization. Arch. Computat. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 5457-5492. [CrossRef]
- Tomar, V.; Bansal, M.; Singh, P. Metaheuristic algorithms for optimization: A brief review. Engineering Proceedings 2023, 59(1), 238. [CrossRef]
- Rajwar, K.; Deep, K.; Das, S. An exhaustive review of the metaheuristic algorithms for search and optimization: taxonomy, applications, and open challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 13187-13257. [CrossRef]
- Barrera-García, J.; Cisternas-Caneo, F.; Crawford, B.; Gómez Sánchez, M.; Soto, R. Feature selection problem and metaheuristics: A systematic literature review about its formulation, evaluation and applications. Biomimetics 2024, 9(1), 9. [CrossRef]
- Houssein, E.H.; Saeed, M.K.; Hu, G.; Al-Sayed, M.M. Metaheuristics for solving global and engineering optimization problems: Review, applications, open issues and challenges. Arch. Computat. Methods Eng. 2024, 31, 4485-4519. [CrossRef]
- Abdollahzadeh B. et al., Puma optimizer (PO): a novel metaheuristic optimization algorithm and its application in machine learning. Cluster Comput. 2024, 27, 5235-5283. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P. Introduction to Expert Systems. 3rd Edition, Addison-Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. ISBN 978-0-201-87686-4.
- Trillas E.; Eciolaza, L. Fuzzy Logic. An Introductory Course for Engineering Students. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Leondes, C.T., Ed., Knowledge-Based Systems Techniques and Applications. 4 volumes, Academic Press: London, UK, 2000. ISBN 0-12-443875-X.
- Leondes, C.T., Ed. Expert Systems. The Technology of Knowledge Management and Decision Making for the 21st Century. 6 volumes, Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002. ISBN 0-12-443880-6.
- Liebowitz, J., Ed., The Handbook of Applied Expert Systems, CRC Press: London; UK, 1997. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Nagpal, G. Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems. Mercury Learning and Information: Berlin, Boston, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Fields, R. From past to present: a comprehensive technical review of rule-based expert systems from 1980-2021. ACM Southeast Conf. 2022, Virtual Event. [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436-444. [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Mahmood, A. Review of deep learning algorithms and architectures. IEEE Access 2019, 7, pp. 53040-53065. [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L. et al., Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions, J Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H. Deep learning: A comprehensive overview on techniques, taxonomy, applications and research directions. SN Computer Science 2021, 2, 420. [CrossRef]
- Dean, J. A golden decade of deep learning: Computing systems & applications. Daedalus 2022, 151(2), 58-74. [CrossRef]
- Grohs, P.; Kutyniok, G., Eds., Mathematical Aspects of Deep Learning. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Jentzen, A.; Kuckuck, B.; von Wurstemberger, P. Mathematical Introduction to Deep Learning: Methods, Implementations, and Theory. arXiv:2310.20360v1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ramón, M.; Ajith, M.; Kurup, A.R. Deep Learning: A Practical Introduction, John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. ISBN: 978-1-119-86188-1.
- Liquet, B.; Moka, S.; Nazarathy, Y. The Mathematical Engineering of Deep Learning, Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Tuinema, B.W.; Rueda Torres, J.L.; Stefanov, A.I.; Gonzalez-Longatt, F.M.; van der Meijden, M.A.M.M. Probabilistic Reliability Analysis of Power Systems. A Student’s Introduction, Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, R.; Terzija, V. Power system restoration: a literature review from 2006 to 2016. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2016, 4(3), 332-341. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.P. Review of methodology and best practice of power system restoration plan. Energy Internet 2024, 1(2), 123-140. [CrossRef]
- Zidan, A.; Khairalla, M.; Abdrabou A.M.; Khalifa, T.; Shaban, K.; Abdrabou, A. Fault detection, isolation, and service restoration in distribution systems: State-of-the-art and future trends. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8(5), 2170-2185. [CrossRef]
- Mwifunyi, R.J.; Kissaka, M.M.; Mvungi, N.H. Distributed approach in fault localisation and service restoration: State-of-the-Art and future direction. Cogent Engineering 2019, 6, 1628424. [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.M.; Kandari, R. Microgrids: Modeling, Control, and Applications, Academic Press, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, B.F.; Sakaguchi, T. Artificial intelligence in power system operations. Proc. IEEE 1987, 75(12), 1678-1685. [CrossRef]
- CIGRE TF 38-06-06 (Niebur, D., Convenor:), Artificial neural networks for power systems. A literature survey, Int. Journal of Engineering Intelligent Systems for Electrical Engineering and Communications 1993, 1(3), 133-158.
- Vankayala, V.S.S.; Rao, N.D. Artificial neural networks and their applications to power systems-a bibliographical survey. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 1993, 28(1), 67-79. [CrossRef]
- Madan, S.; Bollinger, K.E. Applications of artificial intelligence in power systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 1997, 41(2), 117-131. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Song, Y. Artificial neural networks in power systems. I. General introduction to neural computing. Power Engineering Journal 1997, 11(3), 129-134. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Song, Y. Artificial neural networks in power systems. II. Types of artificial neural networks. Power Engineering Journal 1998, 12(1), 41-47. [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Song, Y. Artificial neural networks in power systems. III. Examples of applications in power systems. Power Engineering Journal 1998, 12(6), 279-287. [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Applications of artificial neural-networks for energy systems, Applied Energy 2000, 67(1-2), 17-35. [CrossRef]
- Wehenkel, L. Chapter 31-Automatic Learning Approaches for Electric Power Systems, In Knowledge-Based Systems. Techniques and Applications, Vol. 3, Leondes, C.T., Ed., Academic Press, 2000; pp. 977-1036. [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.C. Overview and literature survey on artificial neural networks applications to power systems (1992-2004). Journal of the Institution of Engineers (India). Part EL 2006, 86(1), 282-296.
- Mellita, A.; Kalogirou, S.A. Artificial intelligence techniques for photovoltaic applications: A review. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 2008, 34(5), 574-632. [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.; Liu, C.C. AI in Power Systems and Energy Markets (Guest Editors' Introduction). IEEE Intelligent Systems 2011, 26(2), 5-8. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, L.H.; Moghavvemi, M.; Almurib, H.A.F.; Steinmayer, O. Current state of neural networks applications in power system monitoring and control. Int. Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems 2013, 51, 134-144. [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.Q., Khosravi, A. A review on artificial intelligence based load demand forecasting techniques for smart grid and buildings. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 50, 1352-1372. [CrossRef]
- Zahraee, S.M.; Assadi, M.K.; Saidur, R. Application of artificial intelligence methods for hybrid energy system optimization. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 66, 617-630. [CrossRef]
- Bose, B.K. Artificial intelligence techniques in smart grid and renewable energy systems—some example applications. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105(11), 2262-2273. [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.; Pinto, T.; Lezama, F.; Morais, H. Survey on complex optimization and simulation for the new power systems paradigm. Complexity 2018, 2018(1), 2340628. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Han, X.; Deng, C. Review on the research and practice of deep learning and reinforcement learning in smart grids. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems 2018, 4(3), 362-370. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, Q.; Yao, W. Framework for artificial intelligence analysis in large-scale power grids based on digital simulation. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems 2018, 4(4), 459-468. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Yu, T. A new generation of AI: A review and perspective on machine learning technologies applied to smart energy and electric power systems. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 1928-1973. [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Ma, S.; Li, Q.; Gong, X.; Wang, F.Y. Application of AI techniques in monitoring and operation of power systems. Front. Energy 2019, 13, 71-85. [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Salimi, M.; Faizollahzadeh Ardabili, S.; Rabczuk, T.; Shamshirband, S.; Varkonyi-Koczy, A.R. State of the art of machine learning models in energy systems, a systematic review. Energies 2019, 12(7), 1301. [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.N.; Mekhilef, S.; Mokhlis, H.; Shah, N.M. Review on forecasting of photovoltaic power generation based on machine learning and metaheuristic techniques. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13(7), 1009-1023. [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, L.; Ditsworth, M.; Niraula, M.; Caicedo Narvaez, C.; Fahimi, B. Machine learning based energy management system for grid disaster mitigation. IET Smart Grid 2019, 2(2), 172-182. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L. Detection of power grid disturbances and cyber-attacks based on machine learning. Journal of Information Security and Applications 2019, 46, 42-52. [CrossRef]
- Menke, J.H.; Dipp, M.; Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Schäfer, F.; Braun, M. Chapter 13-Applications of Artificial Neural Networks in the Context of Power Systems. In Artificial Intelligence Techniques for a Scalable Energy Transition; Sayed-Mouchaweh, M., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 345-373. [CrossRef]
- Ozcanli, A.K.; Yaprakdal, F.; Baysal, M. Deep learning methods and applications for electrical power systems: A comprehensive review. Int. J Energy Res. 2020, 44(10), 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, R.C. Deep reinforcement learning for power system applications: An overview. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems 2020, 6(1), 213-225. [CrossRef]
- Jumani, T.A.; Mustafa, M.W.; Alghamdi, A.S.; Rasid, M.M.; Alamgir, A.; Awan, A.B. Swarm intelligence-based optimization techniques for dynamic response and power quality enhancement of AC microgrids: A comprehensive review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 75986-76001. [CrossRef]
- Saqib Ali, S.; Jun Choi, B. State-of-the-art artificial intelligence techniques for distributed smart grids: A review. Electronics 2020, 9(6), 1030. [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.A.; Ouahada, K.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. A review of machine learning approaches to power system security and stability. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 113512-113531. [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, K.; Kandasamy, P.; Ramanathan, S. Deep learning and reinforcement learning approach on microgrid. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30(10), e12531. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.S.; Dong, W.; Yang, Q. Machine learning driven smart electric power systems: Current trends and new perspectives. Applied Energy 2020, 272, 115237. [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, I.; Robu, V.; Couraud, B.; Kirli, D.; Norbu, S.; Kiprakis, A.; Flynn, D.; Elizondo-Gonzalez, S.; Wattam, S. Artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches to energy demand-side response: A systematic review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2020, 130, 109899. [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, L.; Karangelos, E.; Wehenkel, L. Recent developments in machine learning for energy systems reliability management. Proc. IEEE 2020, 108(9), 1656-1676. [CrossRef]
- Sayghe, A.; Hu, Y.; Zografopoulos, I.; Liu, X.R.; Dutta, R.G.; Jin, Y.; Konstantinou, C. Survey of machine learning methods for detecting false data injection attacks in power systems. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3(5), 581-595. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Yao, W.; Li, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tang, Y.; Wen, J. Artificial intelligence techniques for stability analysis and control in smart grids: Methodologies, applications, challenges and future directions. Applied Energy 2020, 278, 115733. [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Hu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. Reinforcement learning and its applications in modern power and energy systems: A review. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 2020, 8(6), 1029-1042. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Nayak, J.; Naik, B.; Abraham, A. Deep learning in electrical utility industry: A comprehensive review of a decade of research. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2020, 96, 104000. [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Sun, M.; Dabbaghjamanesh, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Chapter 7-Advanced Machine Learning Applications to Modern Power Systems, In New Technologies for Power System Operation and Analysis; Jiang, H., Zhang, Y., Muljadi E., Eds., Academic Press, 2020; pp. 209-257. [CrossRef]
- Farhoumandi, M.; Zhou, Q.; Shahidehpour, M. A review of machine learning applications in IoT-integrated modern power systems. The Electricity Journal 2021, 34(1), 106879. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, T.; Li, C.; Huang, W. Machine learning for power system protection and control. The Electricity Journal 2021, 34(1), 106881. [CrossRef]
- Aminifar, F.; Teimourzadeh, S.; Shahsavari, A.; Savaghebi, M.; Golsorkhi, M.S. Machine learning for protection of distribution networks and power electronics-interfaced systems. The Electricity Journal 2021, 34(1), 106886. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, L. Machine learning approaches to the unit commitment problem: Current trends, emerging challenges, and new strategies. The Electricity Journal 2021, 34(1), 106889. [CrossRef]
- Wu, T., Wang, J. Artificial intelligence for operation and control: The case of microgrids. The Electricity Journal 2021, 34(1), 106890. [CrossRef]
- Perera, A.T.D., Kamalaruban, P. Applications of reinforcement learning in energy systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2021, 137, 110618. [CrossRef]
- Khodayar, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Khodayar, M.E. Deep learning in power systems research: A review. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems 2021, 7(2), 209-220. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dai, N.; Song, Y.; Chen, H. Artificial intelligence in sustainable energy industry: Status quo, challenges and opportunities. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 289, 125834. [CrossRef]
- Omitaomu, O.A.; Niu, H. Artificial intelligence techniques in smart grid: A survey. Smart Cities 2021, 4(2), 548-568. [CrossRef]
- Massaoudi, M.; Abu-Rub, H.; Refaat, S.S.; Chihi, I.; Oueslati, F.S. Deep learning in smart grid technology: A review of recent advancements and future prospects. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 54558-54578. [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Herodotou, H.; Mohsin, S.M.; Javaid, N.; Ashraf, N.; Aslam, S. A survey on deep learning methods for power load and renewable energy forecasting in smart microgrids. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2021, 144, 110992. [CrossRef]
- Miraftabzadeh, S.M.; Longo, M.; Foiadelli, F.; Pasetti, M.; Igual, R. Advances in the application of machine learning techniques for power system analytics: A survey. Energies 2021, 14(16), 4776. [CrossRef]
- Donti, P.L.; Kolter, J.Z. Machine learning for sustainable energy systems. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 2021, 46, 719-747. [CrossRef]
- Barja-Martinez, S.; Aragüés-Peñalba, M.; Munné-Collado, Í.; Lloret-Gallego, P.; Bullich-Massagué, E.; Villafafila-Robles, R. Artificial intelligence techniques for enabling Big Data services in distribution networks: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2021, 150, 111459. [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.; Babazadeh, D.; Becker, C. Applications of artificial intelligence in distribution power system operation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 150098-150119. [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, A.; Dhawale, P.G.; Kumbhar, S.; Patil, U.; Magdum, P. A comprehensive review: Machine learning and its application in integrated power system. Energy Reports 2021, 7, 5467-5474. [CrossRef]
- Onen, A. Role of artificial intelligence in smart grids (Editorial). Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 231. [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Bak-Jensen, B.; Radhakrishna Pillai, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. A review of graph neural networks and their applications in power systems. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 2022, 10(2), 345-360. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Terzija, V. Review on deep learning applications in frequency analysis and control of modern power system. Int. Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems 2022, 136, 107744. [CrossRef]
- Forootan, M.M.; Larki, I.; Zahedi, R.; Ahmadi, A. Machine learning and deep learning in energy systems: A review. Sustainability 2022, 14(8), 4832. [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wu, Q.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A.; Zhao, J.; Xu, X.; Abulanwar, S.M.; Cao, D. Applications of artificial intelligence in renewable energy systems (Editorial). IET Renew. Power Gener. 2022, 16, 1279-1282. [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Kavousi-Fard, A.; Dabbaghjamanesh, M.; Karim, M. A survey on deep learning role in distribution automation system: A new collaborative learning-to-learning (L2L) concept. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 81220-81238. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qu, G.; Tang, Y.; Low, S.; Li, N. Reinforcement learning for selective key applications in power systems: recent advances and future challenges. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13(4), 2935-2958. [CrossRef]
- Machlev, R.; Heistrene, L.; Perl, M.; Levy, K.Y.; Belikov, J.; Mannor, S.; Levron, Y. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) techniques for energy and power systems: Review, challenges and opportunities. Energy and AI 2022, 9, 100169. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ling, J.; Lin, M. Artificial intelligence in renewable energy: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis. Energy Reports 2022, 8, 14072-14088. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, D.; Tariq, R.; Bassam, A.; Ullah, F.; AlGhamdi, A.S.; Alshamrani, S.S. Energetics systems and artificial intelligence: Applications of industry 4.0. Energy Reports 2022, 8, 334-361. [CrossRef]
- Aminifar, F.; Abedini, M.; Amraee, T.; Jafarian, P.; Samimi, M.H.; Shahidehpour, M. A review of power system protection and asset management with machine learning techniques. Energy Syst. 2022, 13, 855-892. [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, J. Applications of physics-informed neural networks in power systems - A review. IEEE Trans. Power Systems 2023, 38(1), 572-588. [CrossRef]
- Entezari, A.; Aslani, A.; Zahedi, R.; Noorollahi, Y. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in energy systems: A bibliographic perspective. Energy Strategy Reviews 2023, 45, 101017. [CrossRef]
- Muqeet, H.A.; Liaqat, R.; Jamil, M.; Khan, A.A. A state-of-the-art review of smart energy systems and their management in a smart grid environment. Energies 2023, 16(1), 472. [CrossRef]
- Franki, V.; Majnaric, D; Viškovic, A. A comprehensive review of artificial intelligence (AI) companies in the power sector. Energies 2023, 16(3), 1077. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pinson, P.; Chatzivasileiadis, S.; Panteli, M.; Strbac, G.; Terzija, V. On machine learning-based techniques for future sustainable and resilient energy systems. IEEE Trans. Sustainable Energy 2023, 14(2), 1230-1243. [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Zhang, Y. Artificial intelligence applications in electric distribution systems: Post-pandemic progress and prospect. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(12), 6937. [CrossRef]
- Markovic, M.; Bossart, M.; Hodge, B.M. Machine learning for modern power distribution systems: Progress and perspectives. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy 2023, 15, 032301. [CrossRef]
- Pinto, T.; Artificial Intelligence as a booster of future power systems (Editorial). Energies 2023, 16(5), 2347. [CrossRef]
- Strielkowski, W.; Vlasov, A.; Selivanov, K.; Muraviev, K.; Shakhnov, V. Prospects and challenges of the machine learning and data-driven methods for the predictive analysis of power systems: A review. Energies 2023, 16(10), 4025. [CrossRef]
- Khodayar, M.; Regan, J. Deep neural networks in power systems: A review. Energies 2023, 16(12), 4773. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, Y.; Xu, R.; Lim, B.; Wu, J.; Gao, J. A review for green energy machine learning and AI services. Energies 2023, 16(15), 5718. [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Liang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, J.; Wen, F.; Dong, Z.Y. Deep learning for cybersecurity in smart grids: Review and perspectives. Energy Conversion and Economics 2023, 4(4), 233-251. [CrossRef]
- IEEE PSRC WG C43 (Hu, Y., Chair), Practical Applications of Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning in Power System Protection and Control; IEEE Technical Report PES-TR112, 2023. Available online: https://www.pes-psrc.org/kb/report/117.pdf (accessed on 09 April 2025).
- Akhtar, S.; Adeel, M.; Iqbal, M.; Namoun, A.; Tufail, A.; Kim, K.H. Deep learning methods utilization in electric power systems. Energy Reports 2023, 10, 2138-2151. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, U.; Pathak, A.; Kumar, A.; Mondal, S. Applications of artificial intelligence in power system operation, control and planning: a review. Clean Energy 2023, 7(6), 1199-1218. [CrossRef]
- Heymann, F.; Quest, H.; Lopez Garcia, T.; Ballif, C.; Galus, M. Reviewing 40 years of artificial intelligence applied to power systems - A taxonomic perspective. Energy and AI 2024, 15, 100322. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Seon, J.; Hwang, B.; Kim, S.; Sun, Y.; Kim, J. Recent trends and issues of energy management systems using machine learning. Energies 2024, 17(3), 624. [CrossRef]
- Akter, A.; Zafir, E.I.; Dana, N.H.; Joysoyal, R.; Sarker, S.K.; Li, L.; Muyeen, S.M.; Das, S.K.; Kamwa, I. A review on microgrid optimization with meta-heuristic techniques: Scopes, trends and recommendation. Energy Strategy Reviews 2024, 51, 101298. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Huang, R.; Huang, Q.; Li, A.; Guddanti, K. Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning Technology in Power System Applications. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Report PNNL-35735, 2024. Available online: https://www.pnnl.gov/main/publications/external/technical_reports/PNNL-35735.pdf (accessed on 09 April 2025).
- Porawagamage, G.; Dharmapala, K.; Sebastian Chaves, J.; Villegas, D.; Rajapakse, A. A review of machine learning applications in power system protection and emergency control: opportunities, challenges, and future directions. Front. Smart Grids 2024, 3. [CrossRef]
- Hallmann, M.; Pietracho, R.; Komarnicki, P. Comparison of artificial intelligence and machine learning methods used in electric power system operation. Energies 2024, 17(11), 2790. [CrossRef]
- Zahraoui, Y.; Korõtko, T.; Rosin, A.; Mekhilef, S.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Stojcevski, A.; Alhamrouni, I. AI applications to enhance resilience in power systems and microgrids-A review. Sustainability 2024, 16(12), 4959. [CrossRef]
- Saffari, M.; Khodayar, M. Spatiotemporal deep learning for power system applications: A survey. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 93623-93657. [CrossRef]
- Alhamrouni, I.; Kahar, N.H.A.; Salem, M.; Swadi, M.; Zahroui, Y.; Kadhim, D.J.; Mohamed, F.A.; Nazari, M.A. A comprehensive review on the role of artificial intelligence in power system stability, control, and protection: insights and future directions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14(14), 6214. [CrossRef]
- Judge, M.A.; Franzitta, V.; Curto, D.; Guercio, A.; Cirrincione, G.; Khattak, H.A. A comprehensive review of artificial intelligence approaches for smart grid integration and optimization. Energy Conversion and Management: X 2024, 24, 100724. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Singh, J.G. A comprehensive review on deep learning techniques in power system protection: Trends, challenges, applications and future directions. Results in Engineering 2025, 25, 103884. [CrossRef]
- Ongsakul, W.; Vo, D.N. Artificial Intelligence in Power System Optimization, CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL; USA, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Sidorov, D., Ed. Machine Learning for Energy Systems, MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. ISBN 978-3-03943-383-4.
- Sayed-Mouchaweh, M., Ed. Artificial Intelligence Techniques for a Scalable Energy Transition, Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Godoy Simões, M. Artificial Intelligence for Smarter Power Systems: Fuzzy Logic and Neural Networks, IET: London, UK, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Nazari-Heris, M.; Asadi, S.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Abdar, M.; Jebelli, H.; Sadat-Mohammadi, M., Eds. Application of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods to Power System Problems. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Padmanaban, S.; Palanisamy, S.; Chenniappan, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B., Eds., Artificial Intelligence-based Smart Power Systems, John Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.Y.; Aleem, S.H.E.A.; Yadav, A., Eds. Artificial Intelligence Applications in Electrical Transmission and Distribution Systems Protection. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL; USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.; Padmanaban, S.; Alhelou, H.H.; Mahela, O.P.; Rajkumar, S., Eds. Artificial Intelligence-Based Energy Management Systems for Smart Microgrids. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Mellit, A.; Kalogirou, S. Handbook of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Photovoltaic Systems, Modeling, Control, Optimization, Forecasting and Fault Diagnosis. Academic Press, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Leonowicz, Z.; Jasinski, M., Eds. Machine Learning and Data Mining Applications in Power Systems, MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2022. ISBN 978-3-0365-4178-5.
- Wang, G.; Xie, J.; Wang, S. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Power System Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis. MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2023. ISBN 978-3-0365-8411-9.
- Padmanaban, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Padmanandam, K.; Dhanaraj, R.K.; Balusamy, B. Eds. Smart Energy and Electric Power Systems. Current Trends and New Intelligent Perspectives, Elsevier, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Tamrakar, S.; Mewada, A.; Gupta, S.K., Eds. Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Power Systems Operations and Analysis, Auerbach: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Du, Y. Deep Learning for Power System Applications. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Azad, S.; Nazari-Heris, M., Eds. Artificial Intelligence in the Operation and Control of Digitalized Power Systems. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Adadi, A.; Berrada, M. Peeking inside the black-box: A survey on explainable artificial intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access 2018, 6, 52138-52160. [CrossRef]
- Samek, W.; Montavon, G.; Vedaldi, A.; Hansen, L.K.; Müller K.R., Eds. Explainable AI: Interpreting, Explaining and Visualizing Deep Learning, Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Barredo Arrieta A. et al., Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Information Fusion 2020, 58, 82-115. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Jeon, G.; Piccialli, F. From artificial intelligence to explainable artificial intelligence in industry 4.0: A survey on what, how, and where. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics 2022, 18(8), 5031-5042. [CrossRef]
- Saarela, M.; Podgorelec, V. Recent applications of explainable AI (XAI): A systematic literature review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14(19), 8884. [CrossRef]
- Furse, C.M.; Kafal, M.; Razzaghi, R.; Shin, Y.J. Fault diagnosis for electrical systems and power networks: A review. IEEE Sensors Journal 2021, 21(2), 888-906. [CrossRef]
- Godse, R.; Bhat, S. Mathematical morphology-based feature-extraction technique for detection and classification of faults on power transmission line. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 38459-38471. [CrossRef]
- Nsaif, Y.M.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Ayob, A.; Yusof, Y.; Hussain, A. Fault detection and protection schemes for distributed generation integrated to distribution network: Challenges and suggestions. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 142693-142717. [CrossRef]
- Hamatwi, E.; Imoru, O.; Kanime, M.M.; Kanelombe, H.S.A. Comparative analysis of high impedance fault detection techniques on distribution networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 25817-25834. [CrossRef]
- Taft, J.D. Fault Intelligence: Distribution Grid Fault Detection and Classification, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Report PNNL-27602, 2017. Available online: https://gridarchitecture.pnnl.gov/media/white-papers/FaultIntelligence_PNNL.pdf (accessed on 09 April 2025).
- Prasad, A.; Edward, J.B.; Ravi, K. A review on fault classification methodologies in power transmission systems: Part-I. Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology 2018, 5, 48-60. [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Edward, J.B.; Ravi, K. A review on fault classification methodologies in power transmission systems: Part-II. Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology 2018, 5, 61-67. [CrossRef]
- Lotfifard, S.; Kezunovic, M.; Mousavi, M.J. A systematic approach for ranking distribution systems fault location algorithms and eliminating false estimates. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28(1), 285-293. [CrossRef]
- Sheta, A.N.; Abdulsalam, G.M.; Eladl, A.A. A survey of fault location techniques for distribution networks. Mansoura Engineering Journal 2020, 45(2), 12-22. [CrossRef]
- CIGRE WG B5.52 (Sefidpour, S., Convenor), Analysis and Comparison of Fault Location Systems in AC Power Networks, CIGRE Technical Brochure 854, 2021.
- IEEE Std C37.114-2014, IEEE Guide for Determining Fault Location on AC Transmission and Distribution Lines, Revision of IEEE Std C37.114-2004, January 2015. [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.J.; Russell, B.D. Classification of faults and switching events by inductive reasoning and expert system methodology. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1989, 4(3), 1631-1637. [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, T.S.; Singh, H.; Sachdev, M.S. Design, implementation and testing of an artificial neural network based fault direction discriminator for protecting transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1995, 10(2), 697-706. [CrossRef]
- Mazon, A.J.; Zamora, I.; Miñambres, J.F.; Zorrozua, M.A.; Barandiaran, J.J.; Sagastabeitia, K. A new approach to fault location in two-terminal transmission lines using artificial neural networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2000, 56, 261-266. [CrossRef]
- Youssef, O.A.S. Combined fuzzy-logic wavelet-based fault classification technique for power system relaying, IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19(2), 582-589. [CrossRef]
- Gracia, J.; Mazon, A.J.; Zamora, I. Best ANN structures for fault location in single-and double-circuit transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2005, 20(4), 2389-2395. [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.K.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.B.; Klöckl, B. Wavelet and neuro-fuzzy based fault location for combined transmission systems. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2007, 29(6), 445-454. [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, S. Decision tree-based fault zone identification and fault classification in flexible AC transmissions-based transmission line. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2009, 3(5), 425-436. [CrossRef]
- Elbaset, A.A.; Hiyama, T. Fault detection and classification in transmission lines using ANFIS. The Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan 2009, 129(7), 705-713. [CrossRef]
- Sadeh, J.; Afradi, H. A new and accurate fault location algorithm for combined transmission lines using adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2009, 79(11), 1538-1545. [CrossRef]
- Jamehbozorg, A.; Shahrtash, S.M. A decision-tree-based method for fault classification in single-circuit transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25(4), 2190-2196. [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, K.; Kumarappan, N. Accurate fault location on EHV lines using both RBF based support vector machine and SCALCG based neural network. Expert Systems with Applications 2010, 37(12), 8822-8830. [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhang, J. A dependency graph approach for fault detection and localization towards secure smart grid. IEEE Trans. on Smart Grid 2011, 2(2), 342-351. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.A.; Chuang, C.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Hung, C.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Hsiao, Y.T. A Hybrid Framework for fault detection, classification, and location—Part I: Concept, structure, and methodology. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2011, 26(3), 1988-1998. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.A.; Chuang, C.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Hung, C.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Hsiao, Y.T. A Hybrid framework for fault detection, classification, and location—Part II: Implementation and test results. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2011, 26(3), 1999-2008. [CrossRef]
- Yusuff, A.A.; Jimoh, A.A.; Munda, J.L. Determinant-based feature extraction for fault detection and classification for power transmission lines. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2011, 5(12), 1259-1267. [CrossRef]
- Ekici, S. Support vector machines for classification and locating faults on transmission lines. Applied Soft Computing 2012, 12(6), 1650-1658. [CrossRef]
- Moravej, Z.; Khederzadeh, M.; Pazoki, M. New combined method for fault detection, classification, and location in series-compensated transmission line. Electric Power Components and Systems 2012, 40(9), 1050-1071. [CrossRef]
- Livani, H.; Evrenosouglu, C.Y. A fault classification and localization method for three-terminal circuits using machine learning. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28(4), 2282-2290. [CrossRef]
- Livani, H.; Evrenosoglu, C.Y. A machine learning and wavelet-based fault location method for hybrid transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5(1), 51-59. [CrossRef]
- Hessine, M.B.; Saber, S.B. Accurate fault classifier and locator for EHV transmission lines based on artificial neural networks. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2014, 2014(1), 240565. [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.; Quiles, E.; García, E.; Morant, F.; Correcher, A. A modular neural network scheme applied to fault diagnosis in electric power systems. The Scientific World Journal 2014, 2014(1), 176463. [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Lin, S.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Qian, Q. A rough membership neural network approach for fault classification in transmission lines. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2014, 61, 429-439. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W.; Wu, Z. Fault detection, identification, and location in smart grid based on data-driven computational methods. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5(6), 2947-2956. [CrossRef]
- Gopakumar, P.; Reddy, M.J.B.; Mohanta, D.K. Adaptive fault identification and classification methodology for smart power grids using synchronous phasor angle measurements. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2015, 9(2), 133-145. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Swetapadma, A. A novel transmission line relaying scheme for fault detection and classification using wavelet transform and linear discriminant analysis. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2015, 6(1), 199-209. [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Sharma, S.K.; Singh, R. Fault detection and classification in electrical power transmission system using artificial neural network. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 334. [CrossRef]
- Zin, A.A.M.; Saini, M.; Mustafa, M.W.; Sultan, A.R. New algorithm for detection and fault classification on parallel transmission line using DWT and BPNN based on Clarke’s transformation. Neurocomputing 2015, 168, 983-993. [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Edward, J.B.; Roy, C.S.; Divyansh, G.; Kumar, A. Classification of faults in power transmission lines using fuzzy-logic technique. Indian Journal of Science and Technology 2015, 8(30), 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Hasheminejad, S.; Seifossadat, S.G.; Razaz, M.; Joorabian, M. Traveling-wave-based protection of parallel transmission lines using Teager energy operator and fuzzy systems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10(4), 1067-1074. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Saini, D.; Saxena, A. Fault detection and classification in transmission line using wavelet transform and ANN. Bulletin of Electrical Engineering and Informatics 2016, 5(3), 284-295. [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.; Mishra, D.P. Support vector machine based fault classification and location of a long transmission line. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal 2016, 19(3), 1368-1380. [CrossRef]
- Manassero Jr., G.; Santo, S.G.D.; Gutierrez Rojas, D. Fault location in series-compensated transmission lines based on heuristic method. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 140, 950-957. [CrossRef]
- Abdelgayed, T.S.; Morsi, W.G.; Sidhu, T.S. A new approach for fault classification in microgrids using optimal wavelet functions matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. on Smart Grid 2017, 9(5), 4838-4846. [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.; Sharma, R. Transmission line fault classification using modified fuzzy Q learning. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11(16), 4041-4050. [CrossRef]
- Asadi Majd, A.; Samet, H.; Ghanbari, T. k-NN based fault detection and classification methods for power transmission systems. Prot. Control Mod. Power. Syst. 2017, 2, 32. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Bao, Z. Data-based line trip fault prediction in power systems using LSTM networks and SVM. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 7675-7686. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Fink, O.; Sansavini, G. Combined fault location and classification for power transmission lines fault diagnosis with integrated feature extraction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electronics 2018, 65(1), 561-569. [CrossRef]
- Abdelgayed, T.S.; Morsi, W.G.; Sidhu, T.S. Fault detection and classification based on co-training of semisupervised machine learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electronics 2018, 65(2), 1595-1605. [CrossRef]
- Akmaz, D.; Mamiş, M.S.; Arkan, M.; Tağluk, M.E. Transmission line fault location using traveling wave frequencies and extreme learning machine. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 155, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Abdelgayed, T.S.; Morsi, W.G.; Sidhu, T.S. A new harmony search approach for optimal wavelets applied to fault classification. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9(2), 521-529. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A. Ultrafast transmission line fault detection using a DWT based ANN. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54(2), 1182-1193. [CrossRef]
- Wani, N.S.; Singh, R.P. A novel approach for the detection, classification and localization of transmission lines faults using wavelet transform and support vector machines classifier. Int. Journal of Engineering & Technology 2018, 7(2), 56-62. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Hu, J.; He, J. Detection and classification of transmission line faults based on unsupervised feature learning and convolutional sparse autoencoder. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9(3), 1748-1758. [CrossRef]
- Ntalampiras, S. Fault diagnosis for smart grids in pragmatic conditions. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9(3), 1964-1971. [CrossRef]
- Swetapadma, A.; Yadav, A. A novel single-ended fault location scheme for parallel transmission lines using k-nearest neighbor algorithm. Computers & Electrical Engineering 2018, 69, 41-53. [CrossRef]
- Kalu, O.O.; Madueme, T.C. Application of artificial neural network (ANN) to enhance power systems protection: a case of the Nigerian 330 kV transmission line. Electr. Eng. 2018, 100, 1467-1479. [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Vahidi, B.; Hosseinian, S.H. Fault location on a series-compensated three-terminal transmission line using deep neural networks. IET Science, Measurement & Technology 2018, 12(6), 746-754. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Yao, L.; Su, M.; Huang, X. A novel fault location method for a cross-bonded HV cable system based on sheath current monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18(10), 3356. 18(10), 3356. [CrossRef]
- Aneke, J.I.; Ezechukwu, O.A.; Ebune, R.U. Artificial intelligence based fault detection and classification in transmission lines. IRE Journals 2018, 2(4), 38-46.
- Mustari, M.R.; Hashim, M.N.; Osman, M.K.; Ahmad, A.R.; Ahmad, F.; Ibrahim, M.N. Fault location estimation on transmission lines using neuro-fuzzy system. Procedia Computer Science 2019, 163, 591-602. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Deka, D.; Chertkov, M.; Wang, M. Real-time faulted line localization and PMU placement in power systems through convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34(6), 4640-4651. [CrossRef]
- Sahani, M.; Dash, P.K. Fault location estimation for series-compensated double-circuit transmission line using parameter optimized variational mode decomposition and weighted P-norm random vector functional link network. Applied Soft Computing 2019, 85, 105860. [CrossRef]
- Aker, E.; Othman, M.L.; Veerasamy, V.; bin Aris, I.; Wahab, N.I.A.; Hizam, H. Fault detection and classification of shunt compensated transmission line using discrete wavelet transform and Naive Bayes classifier. Energies 2020, 13(1), 243. [CrossRef]
- Sahani, M.; Dash, P.K. Fault location estimation for series-compensated double-circuit transmission line using EWT and weighted RVFLN. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2020, 88, 103336. [CrossRef]
- Raval, P.D.; Pandya, A.S. A hybrid PSO-ANN-based fault classification system for EHV transmission lines. IETE Journal of Research 2020, 68(4), 3086-3099. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.H.; Zanghi, R.; Fortes, M.Z.; Gomes Jr., S.; da Silva, A.P.A. Probabilistic transmission line fault diagnosis using autonomous neural models. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 185, 106360. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Shi, M.; Yang, J.; Miao, H. Fault location method based on SVM and similarity model matching. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2020, 2020, 2898479. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Y. Power system fault classification and prediction based on a three-layer data mining structure. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 200897-200914. [CrossRef]
- Fahima, S.R.; Sarker, Y.; Sarker, S.K.; Sheikha, M.R.I.; Das, S.K. Self attention convolutional neural network with time series imaging based feature extraction for transmission line fault detection and classification. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 187, 106437. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Miao, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Yin, H. Faulted-phase classification for transmission lines using gradient similarity visualization and cross-domain adaption-based convolutional neural network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 191, 106876. [CrossRef]
- Vyasa, B.Y.; Maheshwarib, R.P.; Das, B. Versatile relaying algorithm for detection and classification of fault on transmission line. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 192, 106913. [CrossRef]
- Haq, E.U.; Jianjun, H.; Li, K.; Ahmad, F.; Banjerdpongchai, D.; Zhang, T. Improved performance of detection and classification of 3-phase transmission line faults based on discrete wavelet transform and double-channel extreme learning machine. Electr. Eng. 2021, 103, 953-963. [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, P.; Koley, C. A novel three-dimensional deep learning algorithm for classification of power system faults. Computers & Electrical Engineering 2021, 91, 107100. [CrossRef]
- Belagoune, S.; Bali, N.; Bakdi, A.; Baadji, B.; Atif, K. Deep learning through LSTM classification and regression for transmission line fault detection, diagnosis and location in large-scale multi-machine power systems. Measurement 2021, 177, 109330. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Kundu, P. K.; Das, A. A differential signal-based fault classification scheme using PCA for long transmission lines. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2021, 102, 403-414. [CrossRef]
- Hassani, H.; Razavi-Far, R.; Saif, M.; Palade, V. Generative adversarial network-based scheme for diagnosing faults in cyber-physical power systems. Sensors 2021, 21(15), 5173. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A; Kundu, P.; Das, A. A supervised principal component analysis-based approach of fault localization in transmission lines for single line to ground faults. Electr. Eng. 2021, 103, 2113-2126. [CrossRef]
- Rafique, F.; Fu, L.; Mai, R. End to end machine learning for fault detection and classification in power transmission lines. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 199, 107430. [CrossRef]
- Fahim, S.R.; Sarker, S.K.; Muyeen, S.M.; Das, S.K.; Kamwa, I. A deep learning based intelligent approach in detection and classification of transmission line faults. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2021, 133, 107102. [CrossRef]
- Arranz, R.; Paredes, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Muñoz, F. Fault location in transmission system based on transient recovery voltage using Stockwell transform and artificial neural networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 201, 107569. [CrossRef]
- Shadi, M.R.; Ameli, M.T.; Azad, S. A real-time hierarchical framework for fault detection, classification, and location in power systems using PMUs data and deep learning. Int. Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems 2022, 134, 107399. [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Rojas, D.; Christou, I.T.; Dantas, D.; Narayanan, A.; Nardelli, P.H.J.; Yang, Y. Performance evaluation of machine learning for fault selection in power transmission lines. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2022, 64, 859-883. [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Xiong, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. Universal transparent artificial neural network-based fault section diagnosis models for power systems. Advanced Theory and Simulations 2022, 5(4), 2100402. [CrossRef]
- França, I.A.; Vieira, C.W.; Ramos, D.C.; Sathler, L.H.; Carrano, E.G. A machine learning-based approach for comprehensive fault diagnosis in transmission lines. Computers and Electrical Engineering 2022, 101, 108107. [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Nhung-Nguyen, H.; Kwon, J.; Lee, H. Deep-learning based fault events analysis in power systems. Energies 2022, 15(15), 5539. [CrossRef]
- Fahim, S.R.; Muyeen, S.M.; Mannan, M.A.; Sarker, S.K.; Das, S.K.; Al-Emadi, N. Uncertainty awareness in transmission line fault analysis: A Deep learning based approach. Applied Soft Computing 2022, 128, 109437. [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, P.; Kannan, R.; Vishnupriyan, J.; Rajani, B. Optimally detecting and classifying the transmission line fault in power system using hybrid technique. ISA Transactions 2022, 130, 253-264. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.B.; Chaudhari, S.G.; Shihabudheen, K.V.; Verma, N.K. CNN-based transformer model for fault detection in power system networks. IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement 2023, 72, 2504210. [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Samal, S.K. Online fault detection and classification of 3-phase long transmission line using machine learning model. Multiscale and Multidiscip. Model. Exp. and Des. 2023, 6, 135-146. [CrossRef]
- Goni, M.O.F.; Nahiduzzaman, M.; Anower, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Ahsan, M.; Haider, J.; Shahjalal, M. Fast and accurate fault detection and classification in transmission lines using extreme learning machine. e-Prime-Advances in Electrical Engineering, Electronics and Energy 2023, 3, 100107. [CrossRef]
- Kulikov, A.; Loskutov, A.; Bezdushniy, D.; Petrov, I. Decision tree models and machine learning algorithms in the fault recognition on power lines with branches. Energies 2023, 16(14), 5563. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, N. Transmission line fault classification based on spatiotemporal characteristic analysis with global and local discriminant analysis. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal 2023, 45, 101476. [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Nayak, P.K.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Pradhan, G. An intelligent fault detection and classification technique based on variational mode decomposition-CNN for transmission lines installed with UPFC and wind farm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 223, 109526. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Asad, B.; Vaimann, T.; Kallaste, A.; Pomarnacki, R.; Hyunh, V.K. Improved fault classification and localization in power transmission networks using VAE-generated synthetic data and machine learning algorithms. Machines 2023, 11(10), 963. [CrossRef]
- Alhanaf, A.S.; Balik, H.H.; Farsadi, M. Intelligent fault detection and classification schemes for smart grids based on deep neural networks. Energies 2023, 16(22), 7680. [CrossRef]
- Altaie, A.S.; Majeed, A.A.; Abderrahim, M.; Alkhazraji, A. Fault detection on power transmission line based on wavelet transform and scalogram image analysis. Energies 2023, 16(23), 7914. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Nigam, M.K. Energy efficient fault detection and classification using hyperparameter-tuned machine learning classifiers with sensors. Measurement: Sensors 2023, 30, 100908. [CrossRef]
- Mampilly, M.K.; Sheeba, V.S. Detection and classification of power system fault in IEEE 30 bus network using wavelet transform and novel hybrid Bees Bayesian Optimization algorithm based Improved Convolution Neural Network (ICNN). Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments 2023, 60, 103413. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, C. Soft computing based smart grid fault detection using computerised data analysis with fuzzy machine learning model. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems 2024, 41, 100945. [CrossRef]
- Ukwuoma, C.C.; Cai, D.; Bamisile, O.; Chukwuebuka, E.J.; Favour, E.; Emmanuel, G.S.A.; Caroline, A.; Abdi, S.F. Power transmission system’s fault location, detection, and classification: Pay close attention to transmission nodes. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2024, 156, 109771. [CrossRef]
- Najafzadeh, M.; Pouladi, J.; Daghigh, A.; Beiza, J.; Abedinzade, T. Fault detection, classification and localization along the power grid line using optimized machine learning algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2024, 17, 49. [CrossRef]
- Alhanaf, A.S.; Farsadi, M.; Balik, H.H. Fault detection and classification in ring power system with DG penetration using hybrid CNN-LSTM. IEEE Access 2024, 12, pp. 59953-59975. [CrossRef]
- de Alencar, G.T.; dos Santos, R.C.; Neves, A. A fault recognition method for transmission systems based on independent component analysis and convolutional neural networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 229, 110105. [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Yao, L.; Yang, G. A new fault location method for high-voltage transmission lines based on ICEEMDAN-MSA-ConvGRU model. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2024, 18(16), 2650-2668. [CrossRef]
- Turanli, O.; Yakut, Y.B. Classification of faults in power system transmission lines using deep learning methods with real, synthetic, and public datasets. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14(20), 9590. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Nan, D.; Cui, Q.; Li, W. Fault location and fault cause identification method for transmission lines based on pose normalized multioutput convolutional nets. IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement 2024, 74, 3500412. [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.; Das, S.R.; Mallick, R.K.; Mishra, S.; Althobaiti, A.; Mohammad, A.; Aymen, F. 2D-convolutional neural network based fault detection and classification of transmission lines using scalogram images. Heliyon 2024, 10(19), e38947. [CrossRef]
- Anwar, T.; Mu, C.; Yousaf, M.Z.; Khan, W.; Khalid, S.; Hourani, A.O.; Zaitsev, I. Robust fault detection and classification in power transmission lines via ensemble machine learning models. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2549. [CrossRef]
- Ebron, S.; Lubkeman, D.L.; White, M. A neural network approach to the detection of incipient faults on power distribution feeders. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1990, 5(2), 905-914. [CrossRef]
- Eickhoff, F.; Handschin, E.; Hoffmann, W. Knowledge based alarm handling and fault location in distribution networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1992, 7(2), 770-776. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.A.; Rao, N.D. Artificial neural network based fault diagnostic system for electric power distribution feeders. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 1995, 35(1), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Bi, T.; Yan, Z.; Wen, F.; Ni, Y.; Shen, C.M.; Wu, F.F.; Yang, Q. On-line fault section estimation in power systems with radial basis function neural network. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2002, 24(4), 321-328. [CrossRef]
- Thukaram, D.; Khincha, H.P.; Vijaynarasimha, H.P. Artificial neural network and support vector Machine approach for locating faults in radial distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2005, 20(2), 710-721. [CrossRef]
- Chunju, F.; Li, K.K.; Chan, W.L.; Weiyong, Y.; Zhaoning, Z. Application of wavelet fuzzy neural network in locating single line to ground fault (SLG) in distribution lines. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2007, 29(6), 497-503. [CrossRef]
- Mora-Florez, J.; Barrera-Nuez, V.; Carrillo-Caicedo, G. Fault location in power distribution systems using a learning algorithm for multivariable data analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2007, 22(3), 1715-1721. [CrossRef]
- Pourahmadi-Nakhli, M.; Safavi, A.A. Path characteristic frequency-based fault locating in radial distribution systems using wavelets and neural networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2011, 26(2), 772-781. [CrossRef]
- Baqui, I.; Zamora, I.; Mazón, J.; Buigues, G. High impedance fault detection methodology using wavelet transform and artificial neural networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2011, 81(7), 1325-1333. [CrossRef]
- Aslan, Y. An alternative approach to fault location on power distribution feeders with embedded remote-end power generation using artificial neural networks. Electr. Eng. 2012, 94, 125-134. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, Z.Y.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.B.; Qian, Q.Q. An ANFIS-based fault classification approach in power distribution system. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2013, 49, 243-252. [CrossRef]
- Livani, H.; Evrenosoglu, C.Y. A machine learning and wavelet-based fault location method for hybrid transmission lines. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5(1), 51-59. [CrossRef]
- Rafinia, A.; Moshtagh, J. A new approach to fault location in three-phase underground distribution system using combination of wavelet analysis with ANN and FLS. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2014, 55, 261-274. [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; You, D.; Yin, X.; Wang, K.; Wu, J. An improved fault-location method for distribution system using wavelets and support vector regression. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2014, 55, 467-472. [CrossRef]
- Barakat, S.; Eteiba, M.B.; Wahba, W.I. Fault location in underground cables using ANFIS nets and discrete wavelet transform. Journal of Electrical Systems and Information Technology 2014, 1(3), 198-211. [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yuan, R.; Xiao, Z.; Li, T.; Wang, K.L.L. Fault location in loop distribution network using SVM technology. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2015, 65, 254-261. [CrossRef]
- De Santis, E.; Livi, L.; Sadeghian, A.; Rizzi, A. Modeling and recognition of smart grid faults by a combined approach of dissimilarity learning and one-class classification. Neurocomputing 2015, 170, 368-383. [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Khooban, M.H.; Niknam, T. Fast fault detection and classification based on a combination of wavelet singular entropy theory and fuzzy logic in distribution lines in the presence of distributed generations. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2016, 78, 455-462. [CrossRef]
- Adewole, A.C.; Tzoneva, R.; Behardien, S. Distribution network fault section identification and fault location using wavelet entropy and neural networks. Applied Soft Computing 2016, 46, 296-306. [CrossRef]
- Aslan, Y.; Yağan, Y.E. Artificial neural-network-based fault location for power distribution lines using the frequency spectra of fault data. Electr. Eng. 2017, 99, 301-311. [CrossRef]
- Tonelli-Neto, M.S.; Decanini, J.G.M.S.; Lotufo, A.D.P.; Minussi, C.R. Fuzzy based methodologies comparison for high-impedance fault diagnosis in radial distribution feeders. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11(6), 1557-1565. [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Linh, N.V. Statistical feature extraction for fault locations in nonintrusive fault detection of low voltage distribution systems. Energies 2017, 10(5), 611. [CrossRef]
- Shafiullah, M.; Abido, M.A.; Al-Hamouz, Z. Wavelet-based extreme learning machine for distribution grid fault location. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11(17), 4256-4263. [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Costa, P.; Gouvea, M.; Lacerda, A.; Alves, F.; Leite, D. High impedance fault detection in power distribution systems using wavelet transform and evolving neural network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 154, 474-483. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Rout, P.K. Detection and classification of micro-grid faults based on HHT and machine learning techniques. IET Gener., Transm. Distrib. 2018, 12(2), 388-397. [CrossRef]
- Shafiullah, M.; Abido, M.A. S-transform based FFNN approach for distribution grids fault detection and classification. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 8080-8088. [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, D.; Zambroni de Souza, A.C.; da Silveira, P.M. Fault identification based on artificial immunological systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 156, 24-34. [CrossRef]
- De Santis, E.; Rizzi, A.; Sadeghian, A. A cluster-based dissimilarity learning approach for localized fault classification in smart grids. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation 2018, 39, 267-278. [CrossRef]
- Khaleghi, A.; Oukati Sadegh, M.; Ghazizadeh-Ahsaee, M.; Mehdipour Rabori, A. Transient fault area location and fault classification for distribution systems based on wavelet transform and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). Power Engineering and Electrical Engineering 2018, 16(2), 155-166. [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, B.K.; Yadav, A. An intelligent fault detection and classification scheme for distribution lines integrated with distributed generators. Computers and Electrical Engineering 2018, 69, 28-40. [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Lanxiang, S.; Jianchang, L.; Haibin, Y.; Xiaoming, Z.; Lin, G.; Yingwei, Z. Fault diagnosis and location method for active distribution network based on artificial neural network. Electric Power Components and Systems 2018, 46(9), 987-998. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J.Q.; Hou, Y.; Lam, A.Y.S.; Li, V.O.K. Intelligent fault detection scheme for microgrids with wavelet-based deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. on Smart Grid 2019, 10(2), 1694-1703. [CrossRef]
- AsghariGovar, S.; Pourghasem, P.; Seyedi, H. High impedance fault protection scheme for smart grids based on WPT and ELM considering evolving and cross-country faults. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2019, 107, 412-421. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ravishankar, J.; Phung, T. Wavelet transform-based feature extraction for detection and classification of disturbances in an islanded micro-grid. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13(11), 2077-2087. [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Yang, N.; Chen, W. Deep-learning-based fault classification using Hilbert-Huang transform and convolutional neural network in power distribution systems. IEEE Sensors Journal 2019, 19(16), 6905-6913. [CrossRef]
- Lima, É.M.; Brito, N.S.D.; de Souza, B.A. High impedance fault detection based on Stockwell transform and third harmonic current phase angle. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 175, 105931. [CrossRef]
- Patcharoen, T.; Ngaopitakkul, A. Fault classifications in distribution systems consisting of wind power as distributed generation using discrete wavelet transforms. Sustainability 2019, 11(24), 7209. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xie, Z.; Huang, X. Fault location of distribution network base on improved cuckoo search algorithm. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 2272-2283. [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, J.; Masoodzadeh, F.; Roshandel, E. Fault detection and classification in smart grids using augmented K-NN algorithm. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1627. [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.U.; Ospina, J.; Faruque, M.O. Fault classification and location identification in a smart DN using ANN and AMI with real-time data. The Journal of Engineering 2020, 2020(1), 19-28. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; He, J. Fault location in power distribution systems via deep graph convolutional networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2020, 38(1), 119-131. DOI: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2951964.
- Janjic, A.; Velimirovic, L. Integrated fault location and isolation strategy in distribution networks using Markov decision process. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 180, 106172. [CrossRef]
- Mamuya, Y.D.; Lee, Y.D.; Shen, J.W.; Shafiullah, M.; Kuo, C.C. Application of machine learning for fault classification and location in a radial distribution grid. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10(14), 4965. [CrossRef]
- Jamali, S.; Bahmanyar, A.; Ranjbar, S. Hybrid classifier for fault location in active distribution networks, Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2020, 5, 17. [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Gao, J.; Shao, X.; Chen, D. Location of single-line-to-ground fault using 1-D convolutional neural network and waveform concatenation in resonant grounding distribution systems. IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement 2020, 70, 3501009. [CrossRef]
- Gimenez Ledesma, J.J.; do Nascimento, K.B.; Ramos de Araujo, L.; Ribeiro Penido, D.R. A two-level ANN-based method using synchronized measurements to locate high-impedance fault in distribution systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 188, 106576. [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, M.; Mehmood, F.; Abid, M.; Khan, A.Q.; Gul, S.T.; Khan, A.S. High impedance fault detection and isolation in power distribution networks using support vector machines. Journal of King Saud University-Engineering Sciences 2020, 32(8), 524-535. [CrossRef]
- Baloch, S.; Muhammad, M.S. An intelligent data mining-based fault detection and classification strategy for microgrid. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 22470-22479. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, Q. Fault diagnosis in distributed power-generation systems using wavelet based artificial neural network. European Journal of Electrical Engineering 2021, 23(1), 53-59. [CrossRef]
- Okumus, H.; Nuroglu, F.M. A random forest-based approach for fault location detection in distribution systems. Electr. Eng. 2021, 103, 257-264. [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Londhe, N.D.; Raj, R. Fault classification in power system distribution network integrated with distributed generators using CNN. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 192, 106914. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, M.; Ji, T.; Wu, Q.H. Fault location in distribution system using convolutional neural network based on domain transformation. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems 2021, 7(3), 472-484. [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.; Hojatpanah, F.; Ajaei, F.B.; Grolinger, K. Deep learning for high-impedance fault detection: Convolutional autoencoders. Energies 2021, 14(12), 3623. [CrossRef]
- Gilanifar, M.; Wang, H.; Cordova, J.; Erman Ozguven, E.; Strasser, T.I.; Arghandeh, R. Fault classification in power distribution systems based on limited labeled data using multi-task latent structure learning. Sustainable Cities and Society 2021, 73, 103094. [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, J.T.; Coelho, F.G.F. Fault localization method for power distribution systems based on gated graph neural networks. Electr. Eng. 2021, 103, 2259-2266. [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, R.; Mishra, S.; Routray, A.; Swain, S.C. A CNN-LSTM-based fault classifier and locator for underground cables. Neural Comput. & Applic. 2021, 33, 15293-15304. [CrossRef]
- Mirshekali, H.; Dashti, R.; Keshavarz, A.; Shaker, H.R. Machine learning-based fault location for smart distribution networks equipped with micro-PMU. Sensors 2022, 22(3), 945. [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, A.; Dashti, R.; Deljoo, M.; Shaker, H.R. Fault location in distribution networks based on SVM and impedance-based method using online databank generation. Neural Comput. & Applic. 2022, 34, 2375-2391. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.G.S.; Almeida, A.R.; Ferreira, D.D.; Ferreira dos Santos Jr., B.; Vasconcelos, L.H.P.; de Oliveira Sobreira, D. High-impedance fault modeling and classification in power distribution networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 204, 107676. [CrossRef]
- Souhe, F.G.Y.; Boum, A.T.; Ele, P.; Mbey, C.F.; Kakeu, V.Jr.F. Fault detection, classification and location in power distribution smart grid using smart meters data. Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2022, 26(1), 23-34. [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Rao, T.C.; Tulasi Ram, S.S.; Subrahmanyam, J.B.V. Neural network with adaptive evolutionary learning and cascaded support vector machine for fault localization and diagnosis in power distribution system. Evol. Intel. 2022, 15, 1171-1182. [CrossRef]
- Azeroual, M. et al., Fault location and detection techniques in power distribution systems with distributed generation: Kenitra City (Morocco) as a case study. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 209, 108026. [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.; Hojatpanah, F.; Ajaei, F.B.; Guerrero, J.M., Grolinger, K. Deep learning for high-impedance fault detection and classification: transformer-CNN. Neural Comput. & Applic. 2022, 34, 14067-14084. [CrossRef]
- Tavoosi, J.; Shirkhani, M.; Azizi, A.; Din, S.U.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Mobayen, S. A hybrid approach for fault location in power distributed networks: Impedance-based and machine learning technique. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 210, 108073. [CrossRef]
- Dashtdar, M.; Bajaj, M.; Hosseinimoghadam, S.M.S.; Mérsheâkáér, H. Fault location in distribution network by solving the optimization problem using genetic algorithm based on the calculating voltage changes. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 8757-8783. [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, D.; Tang, X.; Duan, P.; Liu, S. Double convolutional neural network for fault identification of power distribution network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 210, 108085. [CrossRef]
- Granado Fornás, J.; Herrero Jaraba, J.E.; Llombart Estopiñan, A.; Saldana, J. Detection and classification of fault types in distribution lines by applying contrastive learning to GAN encoded time-series of pulse reflectometry signals. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 110521-110536. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadipour, M.; Othman, M.M.; Bo, R.; Salam, Z.; Ridha, H.M.; Hasan, K. A novel microgrid fault detection and classification method using maximal overlap discrete wavelet packet transform and an augmented Lagrangian particle swarm optimization-support vector machine. Energy Reports 2022, 8, 4854-4870. [CrossRef]
- Moloi, K.; Ndlela, N.W.; Davidson, I.E. Fault classification and localization scheme for power distribution network, Appl. Sci. 2022, 12(23), 11903. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Santos, A.; Faria, L.T.; Lopes, M.L.M.; Lotufo, A.D.P.; Minussi, C.R. Efficient methodology for detection and classification of short-circuit faults in distribution systems with distributed generation, Sensors 2022, 22(23), 9418. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, J.; Cao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. Fault location and classification for distribution systems based on deep graph learning methods. Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 2023, 11(1), 35-51. [CrossRef]
- Dashtdar, M.; Hussain, A.; Al Garni, H.Z.; Masud, A.A.; Haider, W.; Aboras, K.M.; Kotb, H. Fault location in distribution network by solving the optimization problem based on power system status estimation using the PMU. Machines 2023, 11(1), 109. [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, D.; Yi, S. Real-time machine learning-based fault detection, classification, and locating in large scale solar energy-based systems: Digital twin simulation. Solar Energy 2023, 251, 77-85. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Fault location method for an active distribution network based on a hierarchical optimization model and fault confidence factors. Electronics 2023, 12(6), 1314. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.B.; Shihabudheen K.V. Neural architecture search algorithm to optimize deep Transformer model for fault detection in electrical power distribution systems. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 120, 105890. [CrossRef]
- Tsotsopoulou, E.; Karagiannis, X.; Papadopoulos, T.; Chrysochos, A.; Dyśko, A.; Hong, Q.; Tzelepis, D. Advanced fault location scheme for superconducting cables based on deep learning algorithms. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 147, 108860. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Jiao, Z. Faulty feeder detection for single phase-to-ground faults in distribution networks based on patch-to-patch CNN and feeder-to-feeder LSTM. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 147, 108909. [CrossRef]
- Rizeakos, V.; Bachoumis, A.; Andriopoulos, N.; Birbas, M.; Birbas, A. Deep learning-based application for fault location identification and type classification in active distribution grids. Applied Energy 2023, 338, 120932. [CrossRef]
- Haydaroğlu, C.; Gümüş, B. Fault detection in distribution network with the Cauchy-M estimate-RVFLN method. Energies 2023, 16(1), 252. [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.; Peng, Y.; Wei, W.; Xi, W.; Cai, T. SR-GNN based fault classification and location in power distribution network. Energies 2023, 16, 433. [CrossRef]
- Kurup, A.R.; Summers, A.; Bidram, A.; Reno, M.J.; Martínez-Ramón, M. Ensemble models for circuit topology estimation, fault detection and classification in distribution systems. Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks 2023, 34, 101017. [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.C.; Yang, J.M. Fault classification in distribution systems using deep learning with data preprocessing methods based on fast-DTW and short-time Fourier transform, IEEE Access 2023, 11, pp. 63612-63622. [CrossRef]
- Atencia-De la Ossa, J.; Orozco-Henao, C.; Marín-Quintero, J. Master-slave strategy based in artificial intelligence for the fault section estimation in active distribution networks and microgrids. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 148, 108923. [CrossRef]
- Han, S.R.; Kim, Y.S. A fault identification method using LSTM for a closed-loop distribution system protective relay. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2023, 148, 108925. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xie, D.; Shao, N.; Ding, W.; Dong, Y. Novel faulted-section location method for active distribution networks of new-type power systems. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13(14), 8521. [CrossRef]
- Hojabri, M.; Nowak, S.; Papaemmanoui, A. ML-based intermittent fault detection, classification, and branch identification in a distribution network. Energies 2023, 16, 6023. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qi, Z.; Cui, P.; Xie, M.; Din, J. Detection of single-phase-to-ground faults in distribution networks based on Gramian angular field and improved convolutional neural networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 221, 109501. [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, H.; Gu, C.; Zhou, Y.; He, X. Fault detection and classification in solar based distribution systems in the presence of deep learning and social spider method. Solar Energy 2023, 262, 111868. [CrossRef]
- Mirshekali, H.; Keshavarz, A.; Dashti, R.; Hafezi, S.; Shaker, H.R. Deep learning-based fault location framework in power distribution grids employing convolutional neural network based on capsule network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 223, 109529. [CrossRef]
- Mbey, C.F.; Kakeu, V.Jr.F.; Boum, A.T.; Souhe, F.G.Y. Fault detection and classification using deep learning method and neuro-fuzzy algorithm in a smart distribution grid. The Journal of Engineering 2023, 2023(11), e12324. [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, M.; Yadav, A.; Swetapadma, A. Integrating distributed generation and advanced deep learning for efficient distribution system management and fault detection. Arab J Sci Eng 2024, 49, 7095-7111. [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Singh, G.; Ahamad, N. Fault identification in distributed generation system using shallow ANN model. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2024, 105, 131-145. [CrossRef]
- Mampilly, B.J.; Sheeba, V.S. An empirical wavelet transform based fault detection and hybrid convolutional recurrent neural network for fault classification in distribution network integrated power system. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 77445-77468. [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Pei, D. Power line fault diagnosis based on convolutional neural networks. Heliyon 2024, 10(8), e29021. [CrossRef]
- Li, X. High impedance fault location in power distribution systems using deep learning and micro phasor measurements units (μPMU). Multiscale and Multidiscip. Model. Exp. and Des. 2024, 7, 1045-1056. [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, D.A.G.; Moreto, M.; Lazzaretti, A.E.; Macedo Jr., J.R. High impedance fault classification in microgrids using a transformer-based model with time series harmonic synchrophasors under data quality issues. Neural Comput. & Applic. 2024, 36, 14017-14034. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Kazemi, N.; Musilek, P. Distribution grid fault classification and localization using convolutional neural networks. Smart Grids and Sustainable Energy 2024, 9, 24. [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Z. Fault location method for distribution networks based on multi-head graph attention networks. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1395737. [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Singh, G.; Ahamad, N. Classifying electrical faults in a distribution system using k-nearest neighbor (KNN) model in presence of multiple distributed generators, J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2024, 105, 621-634. [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, A.; Dutta, S.; Jadoun, V.K.; Veerendra, A.S.; Sahu, S.K. A customised artificial neural network for power distribution system fault detection. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2024, 18(11), 2105-2118. [CrossRef]
- Basher, B.G.; Ghanem, A.; Abulanwar, S.; Hassan, M.K.; Rizk, M.E.M. Fault classification and localization in microgrids: Leveraging discrete wavelet transform and multi-machine learning techniques considering single point measurements. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 231, 110362. [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Xia, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Fault location method of distribution network based on VGAE-GraphSAGE, Processes 2024, 12(10), 2179. [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, T.; Abur, A. Convolutional neural network-assisted fault detection and location using few PMUs. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 235, 110705. [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Thangavel, S.; Dhanalakshmi, R.; Khushi, S.N. Fault classification in power system with inverter-interfaced renewable energy resources using machine learning. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 2024, 35, 1019-1038. [CrossRef]
- Barkhi, M.; Pourhossein, J.; Hosseini, S.A. Integrating fault detection and classification in microgrids using supervised machine learning considering fault resistance uncertainty. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28466. [CrossRef]
- Arsoniadis, C.G.; Nikolaidis, V.C. A machine learning based fault location method for power distribution systems using wavelet scattering networks. Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks 2024, 40, 101551. [CrossRef]
- Shafei, A.P.; Silva, J.F.A.; Monteiro, J. Convolutional neural network approach for fault detection and characterization in medium voltage distribution networks. e-Prime - Advances in Electrical Engineering, Electronics and Energy 2024, 10, 100820. [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.V.S.M. et. al. Efficient fault detection and categorization in electrical distribution systems using hessian locally linear embedding on measurement data. Measurement: Energy 2025, 5, 100035. [CrossRef]
- Muniappan, M. A comprehensive review of DC fault protection methods in HVDC transmission systems. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2021, 6, 1. [CrossRef]
- Pragati, A.; Mishra, M.; Rout, P.K.; Gadanayak, D.A.; Hasan, S.; Prust, B.R. A comprehensive survey of HVDC protection system: Fault analysis, methodology, issues, challenges, and future perspective. Energies 2023, 16 (11), 4413. [CrossRef]
- Farkhani, J.S.; Çelik, O.; Ma, K.; Bak, B.R.; Chen, Z. A comprehensive review of potential protection methods for VSC multi-terminal HVDC systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2024, 192, 114280. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Pragati, A.; Gadanayak, D.A.; Parida, T. Signal processing and artificial intelligence based HVDC network protection: A systematic and state-up-the-art review. e-Prime-Advances in Electrical Engineering, Electronics and Energy 2024, 8, 100606. [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.Z.; Liu, H.; Raza, A.; Baig, M.B. Primary and backup fault detection techniques for multi-terminal HVdc systems: a review. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020, 14(22), 5261-5276. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.C.; Honorato, T.R.; Lopes, F.V.; Silva, K.M.; Gonçalves, H.N.G.V. Evaluation of travelling wave-based fault location methods applied to HVDC systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 189, 106619. [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.A.; Caneloi dos Santos, R.; Yang, Q.; Li, J. Analyses of different approaches for detecting, classifying and locating faults in a three-terminal VSC-HVDC system. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2022, 135, 107514. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.M.; Yadav, A. Complete protection scheme for fault detection, classification and location estimation in HVDC transmission lines using support vector machines. IET Sci., Meas. Technol. 2017, 11(3), 279-287. [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, W. An intelligent algorithm for fault location on VSC-HVDC system, Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2018, 94, 116-123. [CrossRef]
- Hossam-Eldin, A.; Lotfy, A.; Elgamal, M.; Ebeed, M. Artificial intelligence-based short-circuit fault identifier for MT-HVDC systems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2018, 12(10), 2436-2443. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Fu, Y. Fault-line selection and fault-type recognition in DC systems based on graph theory. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2018, 3, 27. [CrossRef]
- Zhang M.; Wang, H. Fault location for MMC-MTDC transmission lines based on least squares-support vector regression. J. Eng. 2019, 2019(16), 2125-2130. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, H.; Shi, S.; Dong, X. Fault location in AC transmission lines with back-to-back MMC-HVDC using ConvNets. J. Eng. 2019, 2019(16), 2430-2434. [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.S.; Santos, R.C.; Torres, J.A.; Coury, D.V. An accurate method for fault location in HVDC systems based on pattern recognition of DC voltage signals. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 170, pp. 64-71. [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Chen, M.J.; Chen, D.Y. A novel HVDC double-terminal non-synchronous fault location method based on convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Power Del. 2019, 34(3), 848-857. [CrossRef]
- Abdali, A.; Mazlumi, K.; Noroozian, R. High-speed fault detection and location in DC microgrids systems using multi-criterion system and neural network. Applied Soft Computing 2019, 79, 341-353. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Swetapadma, A.; Panigrahi, C.; Dasgupta, A. A method for fault section identification in high voltage direct current transmission lines using one end measurements. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 172, 140-151. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Ahmed, H.O.A.; Darwish, M.; Nandi, A.K. Fault detection and classification in MMC-HVDC systems using learning methods. Sensors 2020, 20, 4438. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Lan, S.; Xiao, S.J.; Yuan, Y.B. Single pole-to-ground fault location system for MMC-HVDC transmission lines based on active pulse and CEEMDAN. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 42226-42235. [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Lan, S.; Xiao, S.J.; Yuan, Y. Single pole-to-ground fault location method for MMC-HVDC system using wavelet decomposition and DBN. IEEJ Trans. on Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2021, 16(2), 238-247. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, Y.; Li, L. A single-terminal fault location method for HVDC transmission lines based on a hybrid deep network. Electronics 2021, 10(3), 255. [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.B. Fault identification and determination of its location in a HVDC system based on feature extraction and artificial neural network. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2021, 102, 351-361. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Santos, R.; Huang, K.; Igic, P. Intelligent fault detection and location scheme for modular multi-level converter multi-terminal high-voltage direct current. High Voltage 2021, 6(1), 125-137. [CrossRef]
- Ghashghaei, S.; Akhbari, M. Fault detection and classification of an HVDC transmission line using a heterogenous multi-machine learning algorithm, IET Gener. Transmi. Distrib. 2021, 15(16), 2319-2332. [CrossRef]
- Jawad, R.S.; Abid, H.; Fault detection in HVDC system with gray wolf optimization algorithm based on artificial neural network. Energies 2022, 15(20), 7775. [CrossRef]
- Psaras, V.; Tzelepis, D.; Burt, G. HVDC grid fault location method using genetic algorithm on reconstructed frequency-domain voltage profiles. Int. Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems 2023, 144, 108429. [CrossRef]
- Gnanamalar, A.J.; Bhavani, R.; Arulini, A.S.; Veerraju, M.S. CNN-SVM based fault detection, classification and location of multi-terminal VSC-HVDC system. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 18, 3335-3347. [CrossRef]
- Jawad, R.S.; Abid, H. HVDC fault detection and classification with artificial neural network based on ACO-DWT method. Energies 2023, 16(3), 1064. [CrossRef]
- Hameed, O.H.H.; Kutbay, U.; Rahebi, J.; Hardalaç, F.; Mahariq, I. Enhancing fault detection and classification in MMC-HVDC systems: Integrating Harris Hawks Optimization algorithm with machine learning methods. Int. Trans. on Electrical Energy Systems 2024, 1, 6677830. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Qiao, H.; Zhou, S.; Qin, L. An improved fault localization method for direct current filters in HVDC systems: development and application of the DRNCNN model. Machines 2024, 12(3), 185. [CrossRef]
- Salehimehr, S.; Miraftabzadeh, S.M.; Brenna, M. A novel machine learning-based approach for fault detection and location in low-voltage DC microgrids. Sustainability 2024, 16(7), 2821. [CrossRef]
- Deb, A.; Jain, A.K. An effective data-driven machine learning hybrid approach for fault detection and classification in a standalone low-voltage DC microgrid. Electrical Engineering 2024, 106, 6199-6212. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, S. Fault location method for DC distribution network based on multivariate information fusion. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 233, 110518. [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.Z.; Singh, A.R.; Khalid, S.; Bajaj, M.; Kumar, B.H.; Zaitsev, I. Bayesian-optimized LSTM-DWT approach for reliable fault detection in MMC-based HVDC systems. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17968. [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.Z.; Singh, A.R.; Khalid, S.; Bajaj, M.; Kumar, B.H.; Zaitsev, I. Enhancing HVDC transmisión line fault detection using disjoint bagging and bayesian optimization with artificial neural networks and scientometric insights. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23610. [CrossRef]
- Pragati, A.; Gadanayak, D.A.; Mishra, M. Fault detection and fault phase identification in a VSC-MT-HVDC link using Stockwell transform and Teager energy operator, Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 236, 110937. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, E.; Shadlu, M.S. An intelligent ANFIS-based fault detection, classification, and location model for VSC-HVDC systems based on hybrid PCA-DWT signal processing technique. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2024, 120, 109763. [CrossRef]
- Fayazi, M.; Saffarian, A.; Joorabian, M.; Monadi, M. An AI-based fault detection and classification method for hybrid parallel HVAC/HVDC overhead transmission lines. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2025, 238, 111083. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. et al., A highly accurate double-ended traveling wave fault location method using GWO-VMD and the Hilbert transform for offshore MMC-MTDC grids, Smart Power & Energy Security, in Press.
- He, R.; Cao, J.; Tan, T. Generative artificial intelligence: A historical perspective. National Science Review 2025. 12(5), nwaf050. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, D. A Review of UAV Power Line Inspection. In Advances in Guidance, Navigation and Control. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 644; Yan, L., Duan, H., Yu, X., Eds.; Springer, Singapore, 2022; pp. 3147-3159. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.; Ham, J.W.; Lee, J.K.; Oh, K.Y. Fault diagnosis of power transmission lines using a UAV-mounted smart inspection system, IEEE Access 2020, 8, 149999-150009. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.N.; Jenssen R.; Roverso, D. Automatic autonomous vision-based power line inspection: A review of current status and the potential role of deep learning. Int. Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2018, 99, 107-120. [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Y.; Choe, C.W.C.; Goh, H.H.; Low, Y.W.; Cheah, D.Y.S.; Pang, C. Power transmission line fault detection and diagnosis based on artificial intelligence approach and its development in UAV: A review. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering 2021, 46, 9305-9331. [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Xie, Z.; Mao, W.; Li, B.; Shan, Y.; Wei, B.; Zeng, H. Research on edge intelligent recognition method oriented to transmission line insulator fault detection. Int. Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems 2022, 139, 108054. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, D.; Zhou, B. A survey of intelligent transmission line inspection based on unmanned aerial vehicle. Artificial Intelligence Review 2023, 56, 173-201. [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, Q. Development of power transmission line detection technology based on unmanned aerial vehicle image vision. SN Appl. Sci. 2023, 5, 72. [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.; Cunha, T.; Dias, A.; Moreira, A.P.; Almeida, J. UAV visual and thermographic power line detection using deep learning. Sensors 2024, 24(17), 5678. [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, B.; Eylence, M.; Özmen, M.M. Detection of Faults in High Voltage Power Transmission Lines Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle with Artificial Intelligence Methods. In Innovative Methods in Computer Science and Computational Applications in the Era of Industry 5.0. ICAIAME 2023. Engineering Cyber-Physical Systems and Critical Infrastructures, vol 9; Hemanth, D.J., Kose, U., Patrut, B., Ersoy, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 141-150. [CrossRef]
- Jovicic, E.; Primorac, D.; Cupic, M.; Jovic, A. Publicly available datasets for predictive maintenance in the energy sector: A review, IEEE Access 2023, 11, 73505-73520. [CrossRef]
- Sticht, C.R.; Bukowski, S.A. Power System Waveform Datasets for Machine Learning; Idaho National Laboratory. INL/RPT-23-76029-Revision-0, 2024. Available online: https://inldigitallibrary.inl.gov/sites/STI/STI/Sort_83657.pdf (accessed on 09 April 2025).
- Singh, M.P.; Sinha, N. Data creation techniques and data-oriented models for dynamic security assessment of power system. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 5787-5800. [CrossRef]
- Gillioz, M.; Dubuis, G.; Jacquod, P. A large synthetic dataset for machine learning applications in power transmission grids. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 168. [CrossRef]
- Venzke, A.; Molzahn, D.K.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Efficient creation of datasets for data-driven power system applications. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 190, 106614. [CrossRef]
- Martín-Guerrero, J.D.; Lamata, L. Quantum machine learning: A tutorial. Neurocomputing 2022, 470, 457-461. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, M. Quantum Computing-An Emerging Computing Paradigm. In Emerging Computing: From Devices to Systems. Computer Architecture and Design Methodologies; Aly, M.M.S., Chattopadhyay, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp.145-167. [CrossRef]
- Peral-García, D.; Cruz-Benito, J.; García-Peñalvo, F.J. Systematic literature review: Quantum machine learning and its applications. Computer Science Review 2024, 51, 100619. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J. A comprehensive review of quantum machine learning: from NISQ to fault tolerance. Reports on Progress in Physics 2024, 87(11), 116402. https://doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/ad7f69.
- Ajagekar, A.; You, F. Quantum computing based hybrid deep learning for fault diagnosis in electrical power systems. Applied Energy 2021, 303, 117628. [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Yu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D. Fault location of distribution network based on the quantum ant colony algorithm. Research Square 2023. [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Lu, H.; Li, B. Fault location of untransposed double-circuit transmission lines based on an improved Karrenbauer matrix and the QPSO algorithm. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2023, 8, 44. [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhao J.; Shu, T.; Wen F. Power system fault diagnosis with quantum computing and efficient gate decomposition. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16991. [CrossRef]
- Nambundo, J.M.; Gomes, O.; Souza, A.; Machado, R. Cybersecurity and major cyber threats of smart meters: A systematic mapping review. Energies 2025, 18(6), 1445. [CrossRef]
- Tatipatri N.; Arun, S.L. A comprehensive review on cyber-attacks in power systems: Impact analysis, detection, and cyber security. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 18147-18167. [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y. et al. Managing extreme AI risks amid rapid progress. Science 2024, 384, 842-845. [CrossRef]
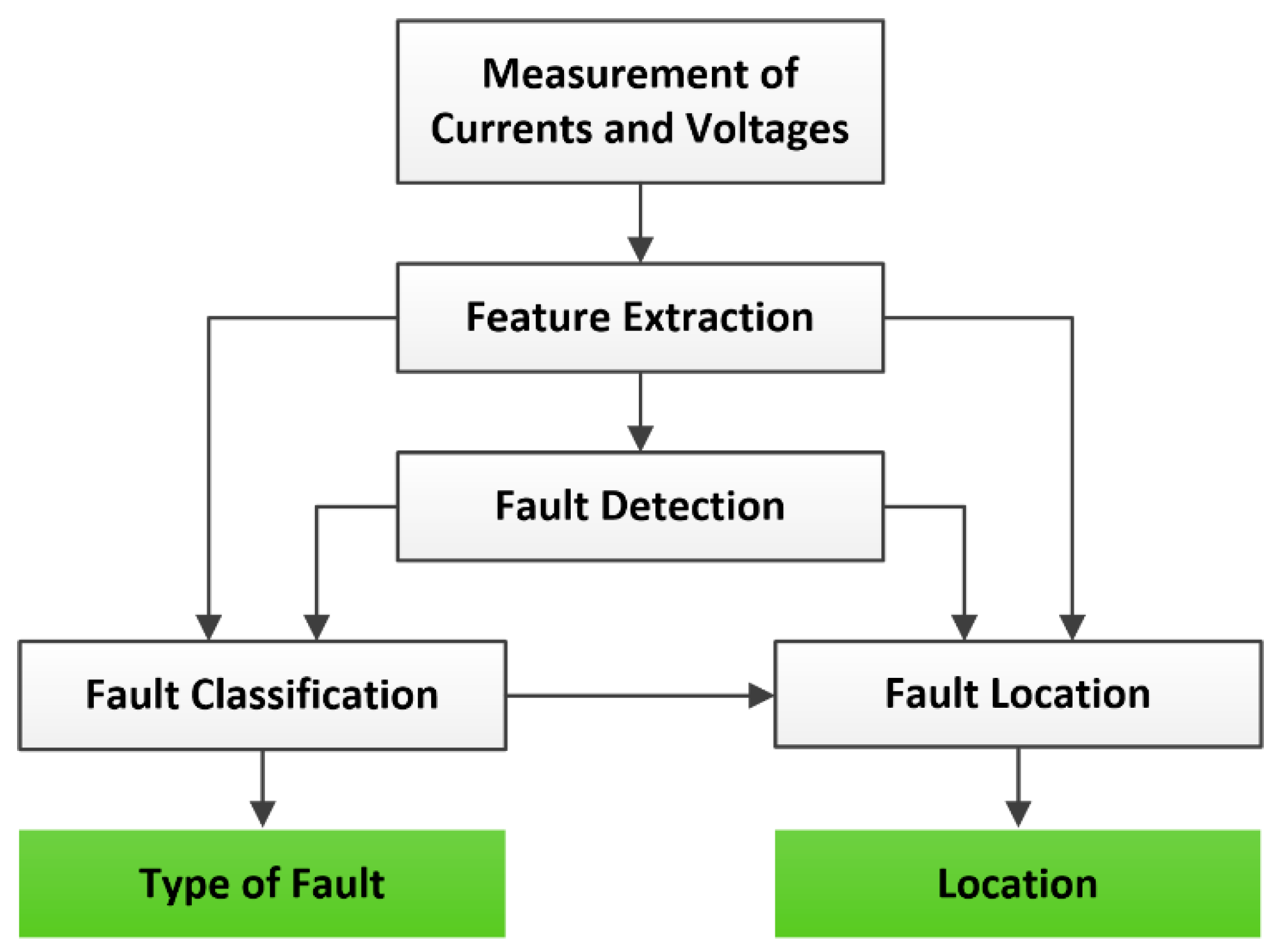
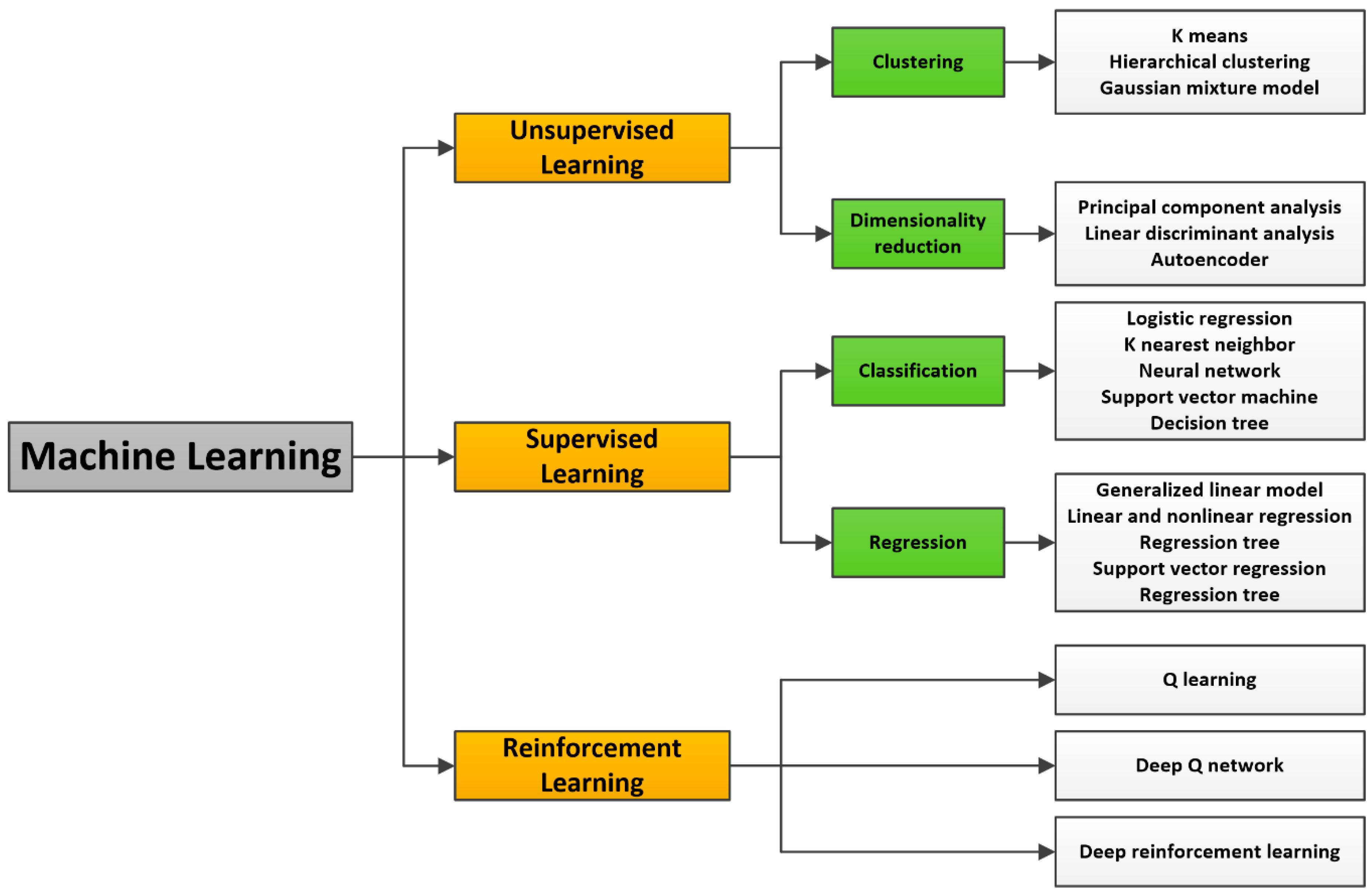
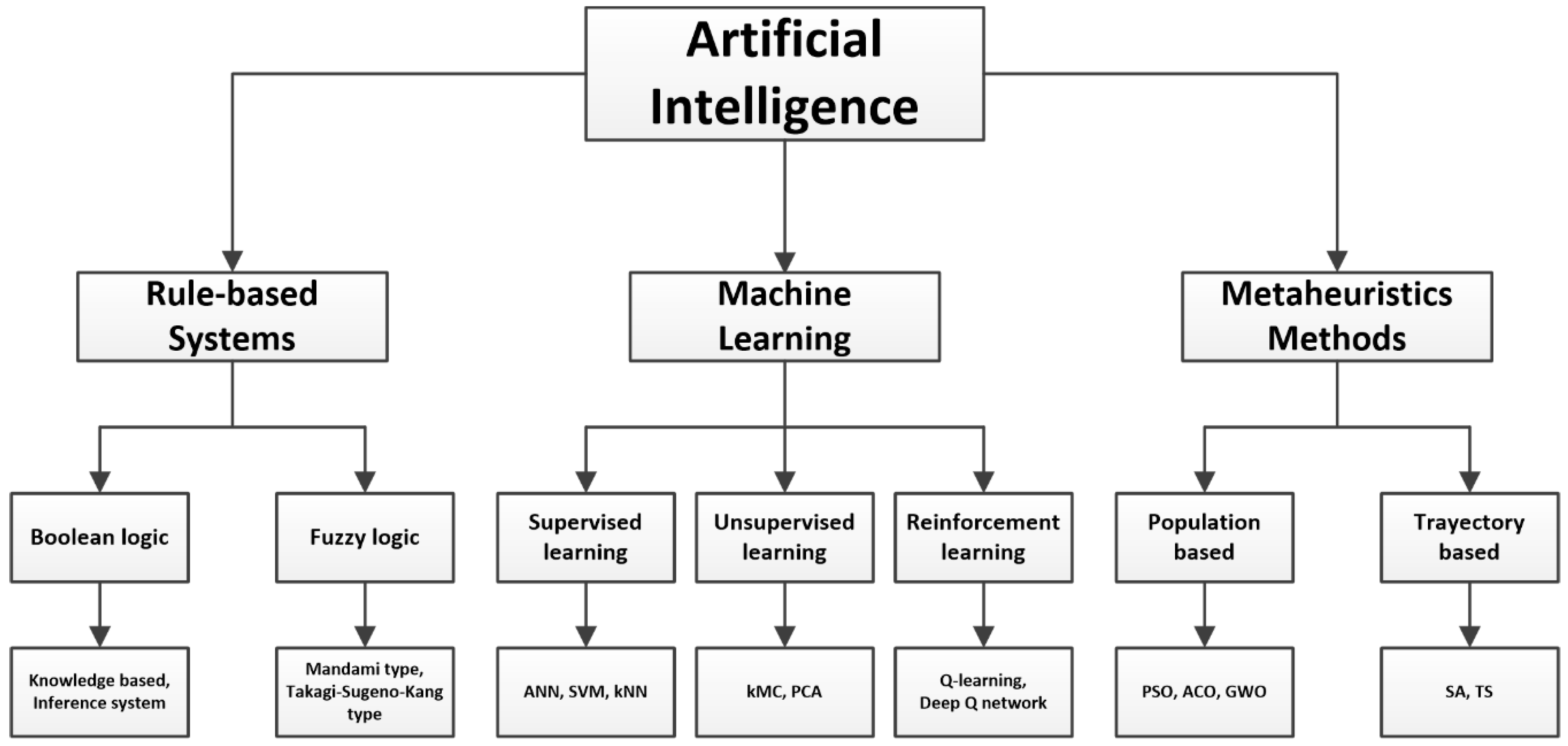
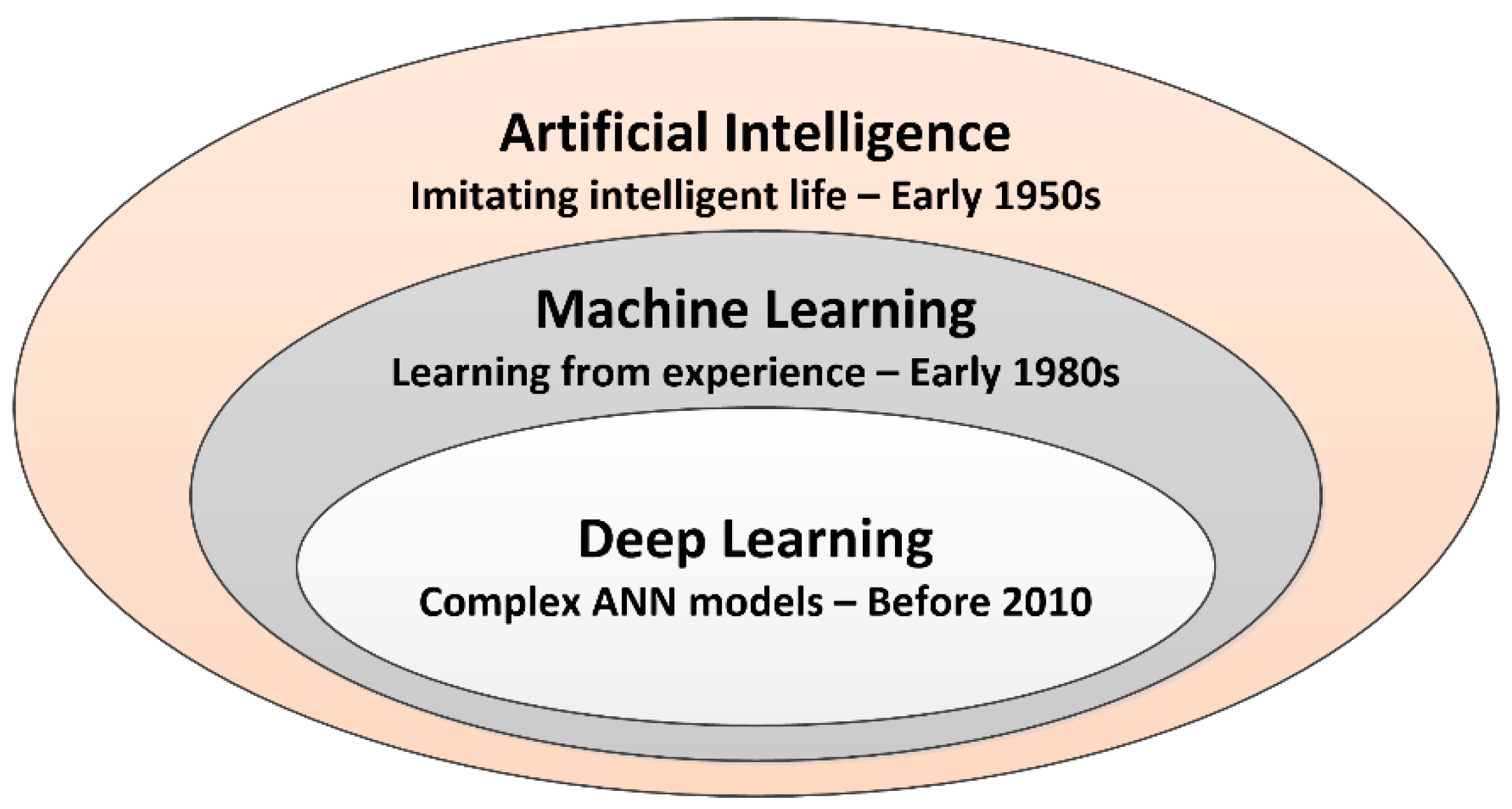
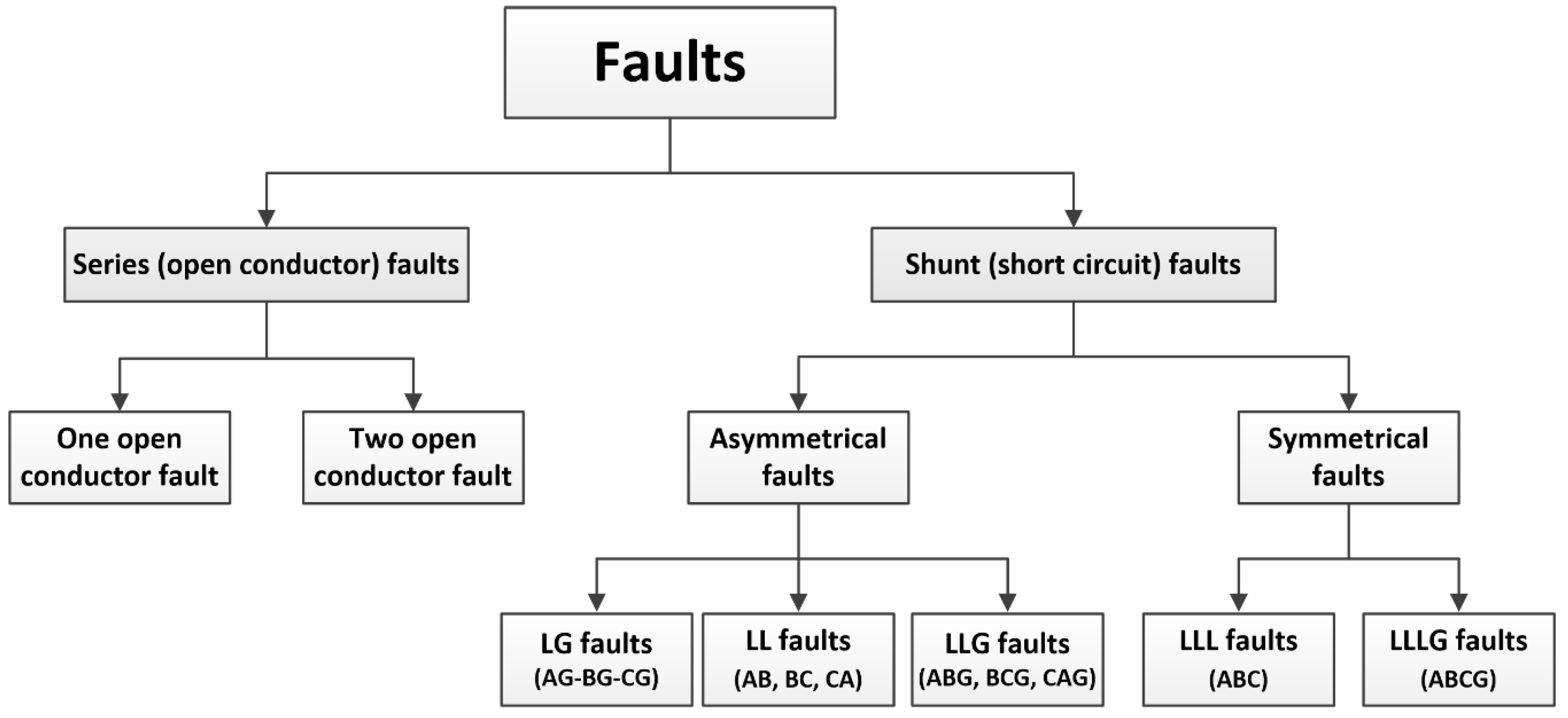
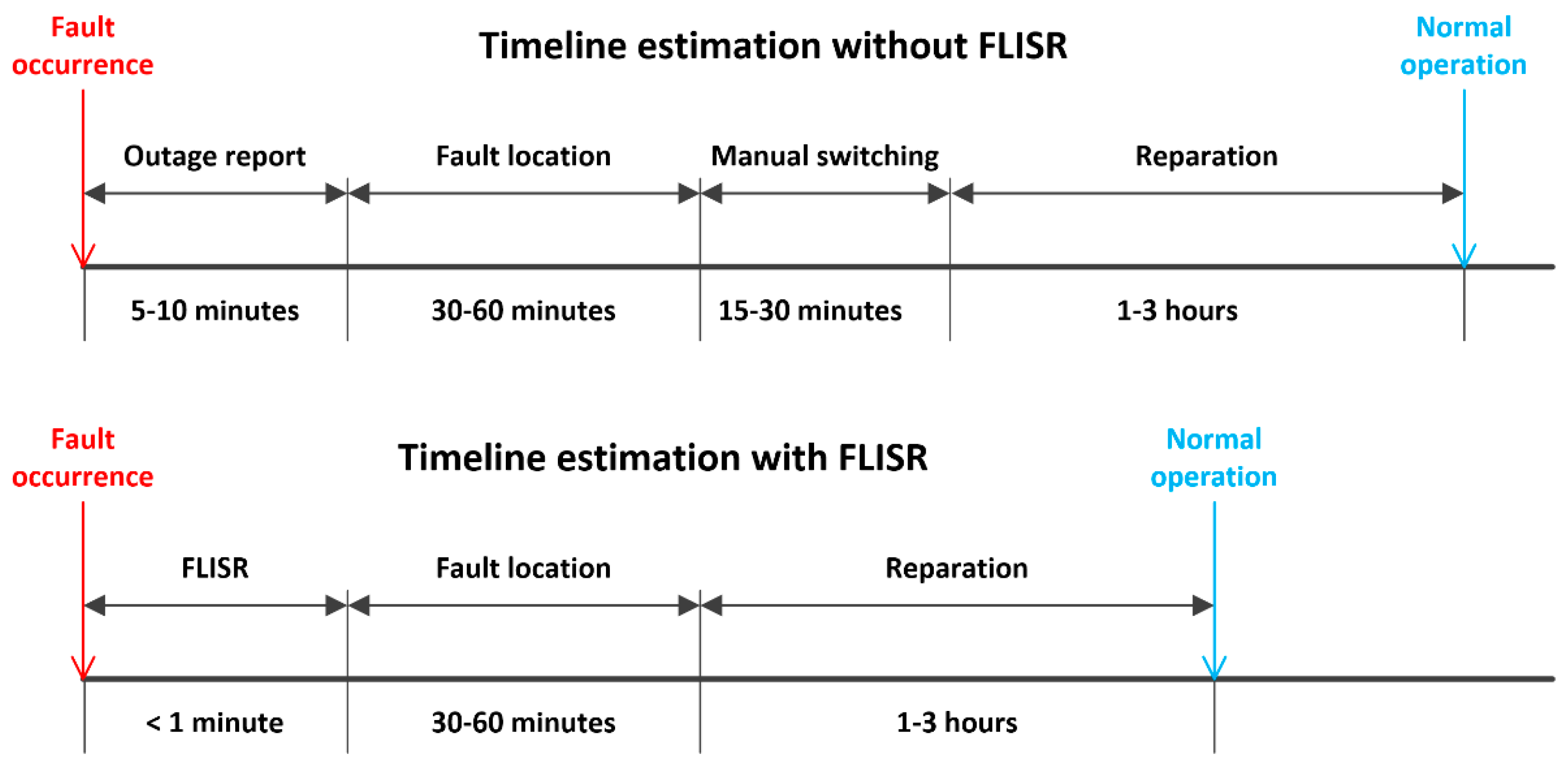
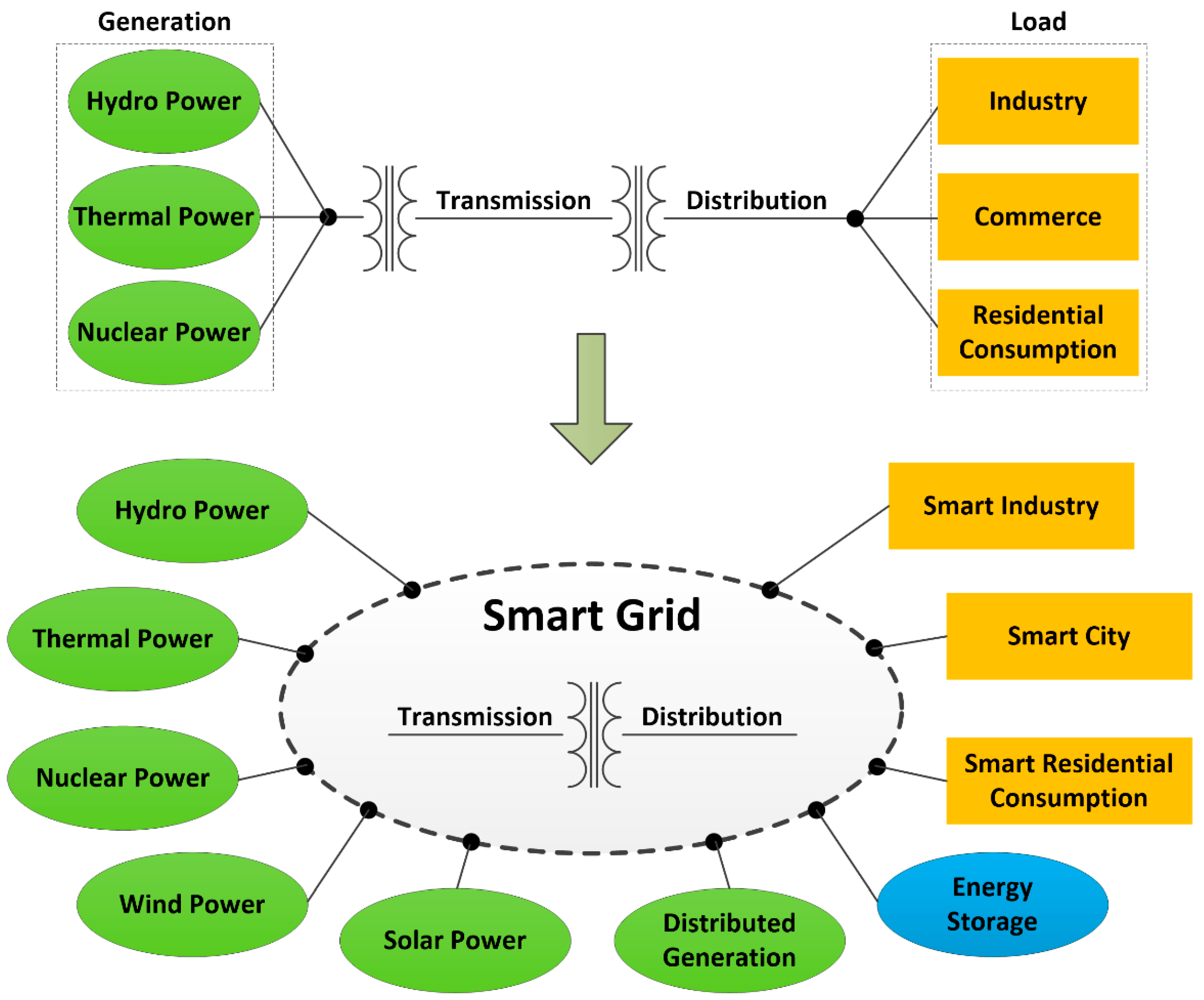
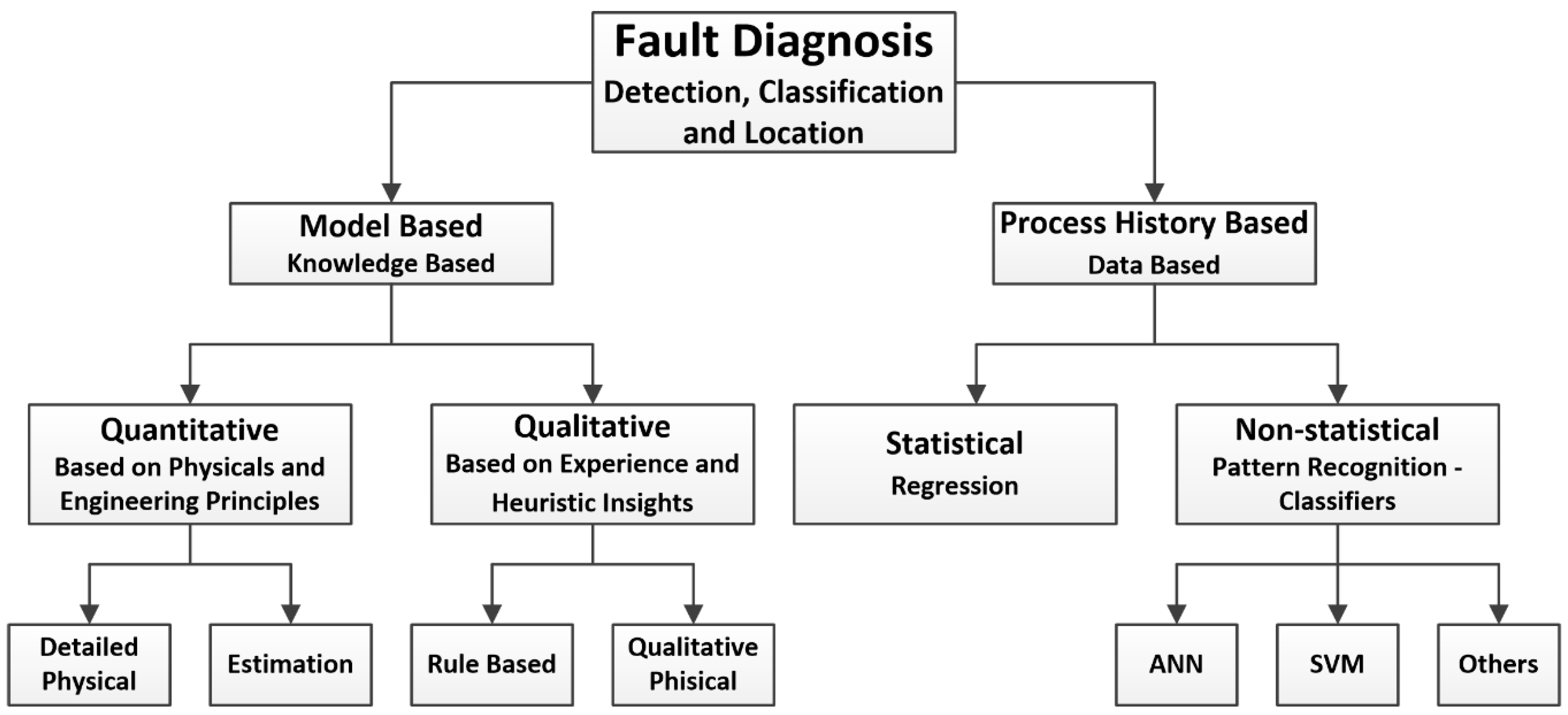
| Ref. | Authors | Year | Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| [197] | Mishra and Singh | 2025 | Overview of AI applications to power system protection |
| [196] | Judge et al. | 2024 | Overview of AI applications to SG integration and optimization |
| [195] | Alhamrouni et al. | 2024 | AI applications to power system stability, control, and protection |
| [193] | Zahraoui et al. | 2024 | Overview of AI applications to resilience in power systems and MGs |
| [192] | Hallmann et al. | 2024 | Overview of AI applications to power system operation |
| [191] | Porawagamage et al. | 2024 | Overview of power system protection and control |
| [190] | Chen et al. | 2024 | Overview of AI applications to power system studies |
| [189] | Akter et al. | 2024 | Microgrid optimization using meta-heuristic techniques |
| [188] | Lee et al. | 2024 | Overview of ML applications to energy management systems |
| [187] | Heymann et al. | 2024 | Overview of AI applications to power system studies |
| [186] | Pandey et al. | 2023 | AI applications to power system operation, control and planning |
| [185] | Akhtar et al. | 2023 | Overview of DL applications to power systems |
| [183] | Ruan et al. | 2023 | Overview of DL applications to cybersecurity studies |
| [182] | Mehta et al. | 2023 | Overview of AI applications to green energy studies |
| [180] | Strielkowski et al. | 2023 | Overview of ML applications to predictive analysis of power systems |
| [178] | Markovic et al. | 2023 | Overview of ML applications to distribution system studies |
| [177] | Chung and Zhang | 2023 | Overview of AI applications to distribution system studies |
| [176] | Wang et al. | 2023 | Overview of ML applications to power system resilience studies |
| [175] | Franki et al. | 2023 | Overview of AI applications to power system studies |
| [173] | Entezari et al. | 2023 | Survey of AI applications to energy systems studies |
| [171] | Aminifar et al. | 2022 | Overview of AI applications to power system protection |
| [170] | Ahmad et al. | 2022 | Overview of AI applications to energy systems |
| [169] | Zhang, Ling, and Lin | 2022 | Bibliometric analysis of AI applications in renewable energy |
| [167] | Chen et al. | 2022 | Survey of RL applications to power system studies |
| [166] | Jafari et al. | 2022 | Survey of DL applications to distribution automation studies |
| [164] | Forootan et al. | 2022 | Overview of AI applications to energy systems |
| [160] | Kumbhar et al. | 2021 | Overview of ML applications to power systems |
| [159] | Stock et al. | 2021 | Overview of AI applications to distribution system operation |
| [158] | Barja-Martinez et al. | 2021 | Overview of AI applications to distribution systems |
| [157] | Donti and Kolter | 2021 | Overview of ML applications to energy systems |
| [156] | Miraftabzadeh et al. | 2021 | Survey of ML applications to power system studies |
| [155] | Aslam et al. | 2021 | Survey of DL applications to MG studies |
| [154] | Massaoudi et al. | 2021 | Survey of DL applications to smart grid studies |
| [153] | Omitaomu and Niu | 2021 | Survey of AI applications to smart grid studies |
| [151] | Khodayar et al. | 2021 | Survey of DL applications to power system studies |
| [150] | Perera and Kamalaruban | 2021 | Survey of RL applications to energy system studies |
| [149] | Wu and Wang | 2021 | Overview of AI applications to MG operation and control |
| [144] | Feng et al. | 2021 | Overview of ML applications to power system studies |
| Application | Description | AI Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Demand Forecasting | Predicts energy demand to optimize power generation and distribution. | ML (FLR, SVM, RF, KMC) DL (RNNs, LSTM, DNNs) |
| Grid Management | Real-time monitoring and control of power grids to detect and predict faults, manage loads, and optimize electricity flow. | ML (FLR, SVM, KMC, QL) |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Predicts the generation capacity of renewable sources based on weather conditions, improving grid stability and optimizing renewable use. | ML (FLR, SVM, RF, KMC) DL (RNNs, LSTM, DNNs) |
| Energy Storage Management | Optimizes charging and discharging cycles of energy storage systems, prolonging battery life and reducing costs. | ML (SVM, KMC, QL) DL (RNNs, LSTM, DNNs) |
| Predictive Maintenance | Analyzes sensor data to predict equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. | ML (RF) DL (LSTM, DNNs) |
| Energy Efficiency | AI-driven systems in buildings and industries optimize energy use by learning consumption patterns and implementing efficiency measures. | ML (FLR, SVM, RF, KMC) |
| Fault Diagnosis | Quickly identifies and diagnoses faults in the power system, enabling faster responses and preventing equipment damage. | ML (SVM, RF, KMC) DL (RNNs, DNNs) |
| Energy Trading | Forecasts prices, optimizes trading strategies and manages risks in energy trading platforms. | ML (FLR, SVM, RF) DL (RNNs, LSTM, DNNs) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





