Submitted:
22 April 2025
Posted:
22 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
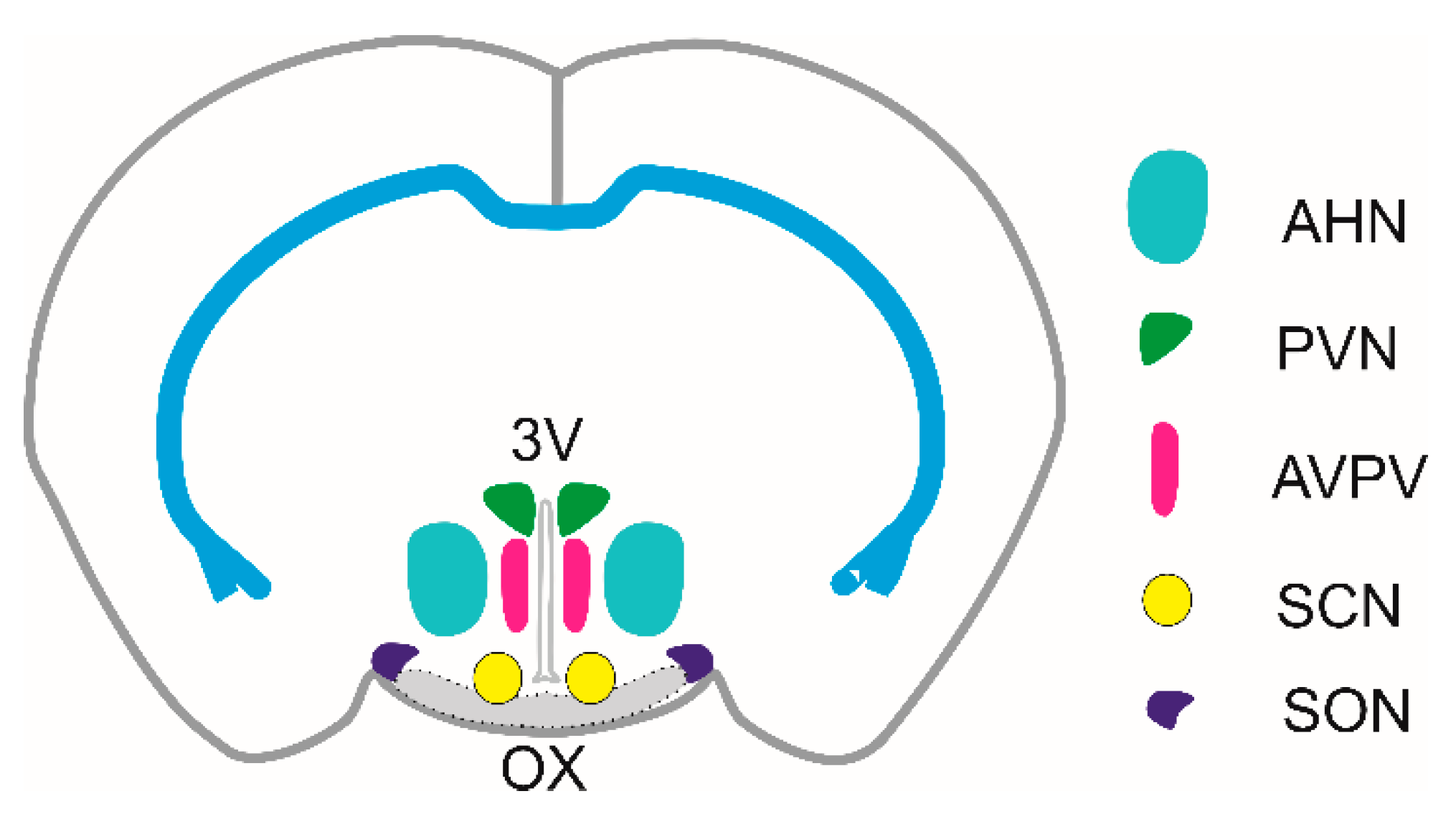
2. Nuclei and Neuron Types in the Hypothalamus
2.1. Supraoptic Nucleus (SON)
2.2. Paraventricular Nucleus (PVN)
2.3. Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
2.4. Anteroventral Periventricular Nucleus (AVPV)
2.5. Anterior Hypothalamic Nucleus (AHN)
2.6. Arcuate Nucleus (ARC)
2.7. Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus (VMH)
2.8. Dorsomedial Hypothalamic Nucleus (DMH)
2.9. Tuberomammilary Nucleus (TMN)
2.10. Lateral Hypothalamic Area (LHA)
3. Sources of Extracellular ATP in the Brain
4. A Brief Overview of Purinergic P2X1-7 Receptors
5. Expression and Function of P2X in Hypothalamic Nuclei
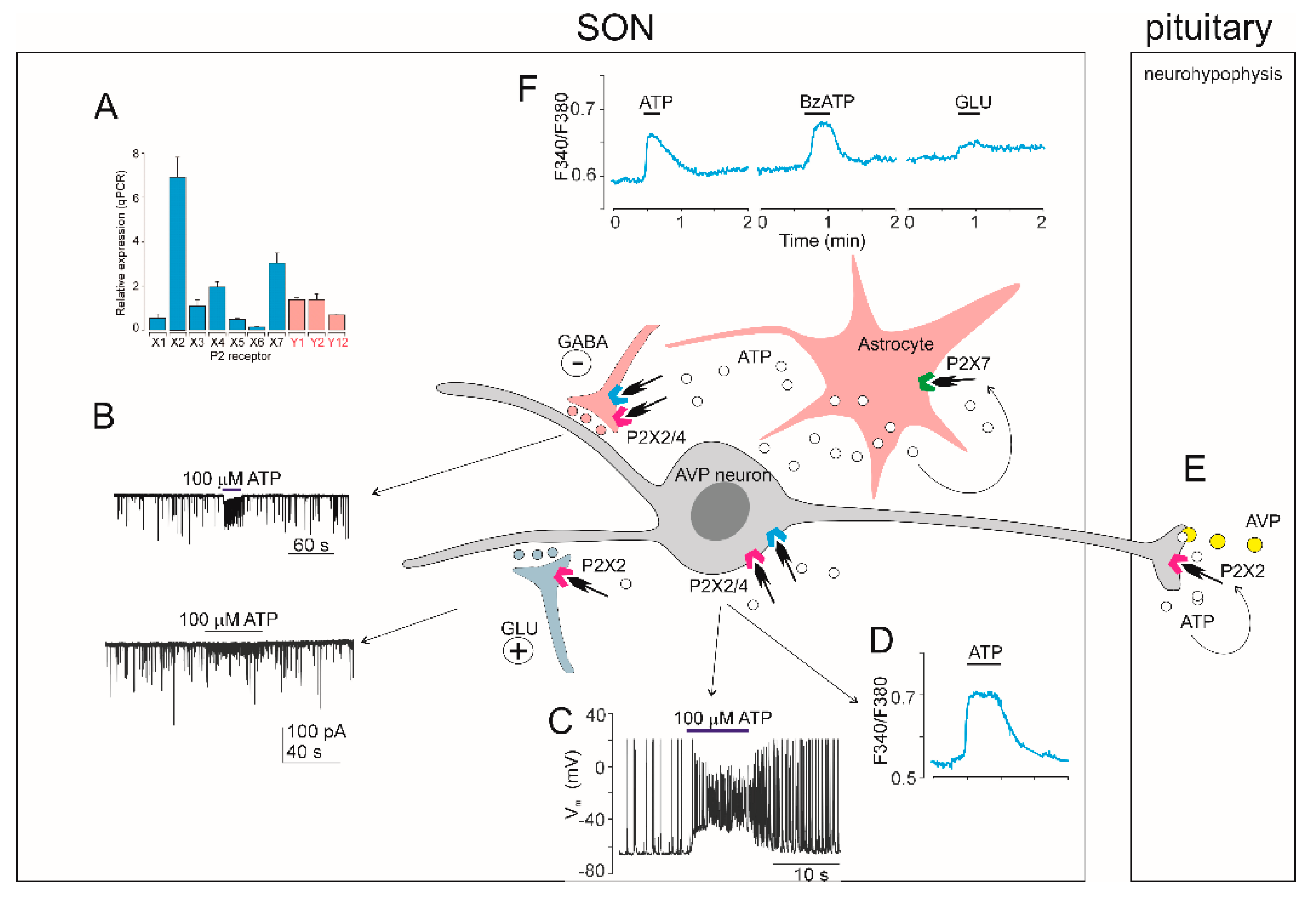
5.1. SON
5.1.1. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in SON
5.1.2. P2X Activity in SON Cells Studied by Intracellular Calcium Measurements
5.1.3. P2X Activity in SON Cells Studied by Using Electrophysiology
5.1.4. Functional Relevance of ATP Acting on P2X in the SON
5.2. PVN
5.2.1. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in PVN
5.2.2. P2X Activity in Magnocellular PVN Neurons Studied by Using Electrophysiology
5.2.3. P2X Activity in Parvocellular PVN Neurons Studied by Using Electrophysiology
5.2.4. Functional Relevance of ATP Acting at P2X in the PVN
5.3. SCN
5.3.1. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in the SCN
5.3.2. P2X Activity in SCN Cells Studied by Intracellular Calcium Measurements
5.3.3. P2X Activity in SCN Neurons Studied by Using Electrophysiology
5.3.4. Functional Relevance of ATP Acting at P2X in the SCN
5.4. AVPV
5.4.1. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in GnRH Neurons of AVPV
5.4.2. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in Kisspeptin Neurons of AVPV
5.4.3. P2X Activity in GnRH and Kisspeptin Neurons in AVPV Studied by Intracellular Calcium Measurements
5.4.4. P2X Activity in GnRH and Kisspeptin Neurons Studied by Using Electrophysiology
5.4.5. Functional Relevance of ATP Acting at P2X in the AVPV
5.5. AHN
5.5.1. Expression of P2X in the AHN
5.5.2. Functional Relevance of ATP in the AHN
5.6. ARC
5.6.1. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in ARC
5.6.2. P2X Activity in ARC Cells Studied by Intracellular Calcium Measurements
5.6.3. P2X Activity in ARC Cells Studied Using Electrophysiology
5.6.4. Role of ATP Acting in ARC Physiology
5.7. VMH
5.7.1. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in the VMH
5.7.2. P2X Activity in VMH Cells Studied by Intracellular Calcium Measurements
5.7.3. P2X Activity in VMH Cells Studied by Using Electrophysiology
5.7.4. Functional Role of ATP Acting at P2 Receptors in the VMH
5.8. DMH
5.8.1. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in DMH
5.8.2. P2X Activity in DMH Cells Studied by Intracellular Calcium Measurements
5.8.3. P2X Activity in DMH Cells Studied by Using Electrophysiology
5.8.4. Functional Relevance of ATP Acting on P2 Receptors in the DMH
5.9. TMN
5.9.1. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in TMN
5.9.2. P2X Activity in TMN Cells Studied by Electrophysiology
5.9.3. Functional Relevance of ATP Acting at P2X in the TMN
5.10. LHA
5.10.1. Expression of P2X mRNA and Protein in the LHA
5.10.2. P2X Activity in LHA Cells Studied by Electrophysiology
5.10.3. Functional Relevance of ATP Acting at P2X in the LHA
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Abbreviations
| ADP | adenosine-5'-diphosphate |
| AgRP | agouti-related peptide |
| AMP | adenosine-5'-monophosphate |
| ATP | adenosine-5'-triphosphate |
| ATPγS | adenosine 5'-O-(2-thiotriphosphate) |
| 2MeSATP | 2-methylthio-adenosine triphosphate |
| AMPA | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole propionic acid |
| αβmeATP | α,β-methyleneadenosine 5′-triphosphate |
| AHN | anterior hypothalamic nucleus |
| ARC | arcuate nucleus |
| AVP | arginine vasopressin |
| AVPV | anteroventral periventricular nucleus |
| BBG | brilliant blue G |
| BzATP | 3´-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyladenosine-5´-triphosphate |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| DMH | dorsomedial hypothalamic nukleus |
| DYN | dynorphin peptide |
| GABA | γ-aminobutyric acid |
| GABAA | GABA receptor type A |
| GFP | green fluorescent protein |
| GnRH | gonadotropin-releasing hormone |
| Kiss1R | kisspeptin receptor |
| LHA | lateral hypothalamic area |
| mIPSC | miniature inhibitory postsynaptic current |
| mEPSC | iniature excitatory postsynaptic current |
| MnPO | median preoptic nukleus |
| nNOS | neuronal nitric oxide synthase |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| MPOA | medial preoptic area |
| NPP1 | ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 |
| NPY | neuropeptide Y |
| P1 | purinergic receptor type 1 |
| P2X | purinergic receptor type 2 (ionotropic) |
| P2Y | purinergic receptor type 2 (metabotropic) |
| POA | preoptic area |
| PPADS | pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2', 4'-disulfonic acid |
| PVN | paraventricular nucleus |
| SCN | supraschiasmatic nucleus |
| SON | supraoptic nucleus |
| VMH | ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus |
| VTM | ventral tuberomammillary nucleus |
| TMN | tuberomammillary nucleus |
References
- Russell, J.A. Fifty Years of Advances in Neuroendocrinology. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 2018, 2. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Jimenez, J.G. and O. De Jesus, Hypothalamic Dysfunction, in StatPearls. 2024: Treasure Island (FL) with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Orlando De Jesus declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
- Steuernagel, L.; Lam, B.Y.H.; Klemm, P.; Dowsett, G.K.C.; Bauder, C.A.; Tadross, J.A.; Hitschfeld, T.S.; Martin, A.d.R.; Chen, W.; de Solis, A.J.; et al. HypoMap—a unified single-cell gene expression atlas of the murine hypothalamus. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 1402–1419. [CrossRef]
- Collo, G.; North, R.; Kawashima, E.; Merlo-Pich, E.; Neidhart, S.; Surprenant, A.; Buell, G. Cloning OF P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of an extended family of ATP-gated ion channels. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2495–2507. [CrossRef]
- Tasker, J.G.; Oliet, S.H.R.; Bains, J.S.; Brown, C.H.; Stern, J.E. Glial Regulation of Neuronal Function: From Synapse to Systems Physiology. J. Neuroendocr. 2011, 24, 566–576. [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, I.; Bhattaracharya, A.; Ivetic, M.; Bendova, Z.; Zemkova, H. Circadian ATP Release in Organotypic Cultures of the Rat Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Is Dependent on P2X7 and P2Y Receptors. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 192. [CrossRef]
- Collo, G.; Neidhart, S.; Kawashima, E.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.; North, R.; Buell, G. Tissue distribution of the P2X7 receptor. Neuropharmacology 1997, 36, 1277–1283. [CrossRef]
- Genzen, J.R.; Platel, J.-C.; Rubio, M.E.; Bordey, A. Ependymal cells along the lateral ventricle express functional P2X7 receptors. Purinergic Signal. 2009, 5, 299–307. [CrossRef]
- Loesch, A., On P2X receptors in the brain: microvessels. Dedicated to the memory of the late Professor Geoffrey Burnstock (1929-2020). Cell Tissue Res, 2021. 384(3): p. 577-588.
- Caruso, V.; Zuccarini, M.; Di Iorio, P.; Muhammad, I.; Ronci, M. Metabolic Changes Induced by Purinergic Signaling: Role in Food Intake. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guan, J.; Yin, S.; Liu, F. The role of ATP in sleep-wake regulation: In adenosine-dependent and -independent manner. Sleep Med. 2024, 119, 147–154. [CrossRef]
- Lemos, J.R.; Custer, E.E.; Ortiz-Miranda, S. Purinergic receptor types in the hypothalamic-neurohypophysial system. J. Neuroendocr. 2018, 30. [CrossRef]
- Zemková, H.; Balík, A.; Jindřichová, M.; Vávra, V. Molecular structure of purinergic P2X receptors and their expression in hypothalamus and pituitary. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57 Suppl 3, S23–S38. [CrossRef]
- Stojilkovic, S.S. Purinergic regulation of hypothalamopituitary functions. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 460–468. [CrossRef]
- Bjelobaba, I.; Janjic, M.M.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Purinergic signaling pathways in endocrine system. Auton. Neurosci. 2015, 191, 102–116. [CrossRef]
- Stojilkovic, S.S.; Zemkova, H. P2X receptor channels in endocrine glands. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Membr. Transp. Signal. 2013, 2, 173–180. [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G. Purinergic signalling in endocrine organs. Purinergic Signal. 2014, 10, 189–231. [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Avakian, G.A.; Von Gall, C. The Role of Purinergic Receptors in the Circadian System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3423. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., et al., The circadian regulation of extracellular ATP. Purinergic Signal, 2023. 19(1): p. 283-295.
- Chen, Y.-H.; Lin, S.; Jin, S.-Y.; Gao, T.-M. Extracellular ATP Is a Homeostatic Messenger That Mediates Cell–Cell Communication in Physiological Processes and Psychiatric Diseases. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 97, 41–53. [CrossRef]
- Møller, M.; Busch, J.R.; Jacobsen, C.; Lundemose, S.B.; Lynnerup, N.; Rath, M.F.; Banner, J. The accessory magnocellular neurosecretory system of the rostral human hypothalamus. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 487–498. [CrossRef]
- Voisin, D.L.; E Herbison, A.; A Poulain, D. Central inhibitory effects of muscimol and bicuculline on the milk ejection reflex in the anaesthetized rat.. J. Physiol. 1995, 483, 211–224. [CrossRef]
- Moos, F.C. GABA-induced facilitation of the periodic bursting activity of oxytocin neurones in suckled rats.. J. Physiol. 1995, 488, 103–114. [CrossRef]
- Brussaard, A.B.; Devay, P.; Leyting-Vermeulen, J.L.; Kits, K.S. Changes in properties and neurosteroid regulation of GABAergic synapses in the supraoptic nucleus during the mammalian female reproductive cycle. J. Physiol. 1999, 516, 513–524. [CrossRef]
- Jourdain, P.; Israel, J.-M.; Dupouy, B.; Oliet, S.H.R.; Allard, M.; Vitiello, S.; Theodosis, D.T.; Poulain, D.A. Evidence for a Hypothalamic Oxytocin-Sensitive Pattern-Generating Network Governing Oxytocin NeuronsIn Vitro. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 6641–6649. [CrossRef]
- Oliet, S.H. and C.W. Bourque, Mechanosensitive channels transduce osmosensitivity in supraoptic neurons. Nature, 1993. 364(6435): p. 341-3.
- Israel, J.-M.; Poulain, D.A.; Oliet, S.H.R. Glutamatergic Inputs Contribute to Phasic Activity in Vasopressin Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1221–1232. [CrossRef]
- Choe, K.Y.; Han, S.Y.; Gaub, P.; Shell, B.; Voisin, D.L.; Knapp, B.A.; Barker, P.A.; Brown, C.H.; Cunningham, J.T.; Bourque, C.W. High Salt Intake Increases Blood Pressure via BDNF-Mediated Downregulation of KCC2 and Impaired Baroreflex Inhibition of Vasopressin Neurons. Neuron 2015, 85, 549–560. [CrossRef]
- Pow, D.; Morris, J. Dendrites of hypothalamic magnocellular neurons release neurohypophysial peptides by exocytosis. Neuroscience 1989, 32, 435–439. [CrossRef]
- Sabatier, N.; Caquineau, C.; Dayanithi, G.; Bull, P.; Douglas, A.J.; Guan, X.M.M.; Jiang, M.; Van der Ploeg, L.; Leng, G. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Stimulates Oxytocin Release from the Dendrites of Hypothalamic Neurons While Inhibiting Oxytocin Release from Their Terminals in the Neurohypophysis. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10351–10358. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.H.; Intorre, A.A.; French, J.A. Vasopressin and Oxytocin Reduce Food Sharing Behavior in Male, but Not Female Marmosets in Family Groups. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 181–181. [CrossRef]
- Iovino, M.; Messana, T.; Tortora, A.; Giusti, C.; Lisco, G.; Giagulli, V.A.; Guastamacchia, E.; De Pergola, G.; Triggiani, V. Oxytocin Signaling Pathway: From Cell Biology to Clinical Implications. Endocrine, Metab. Immune Disord. - Drug Targets 2021, 21, 91–110. [CrossRef]
- Martucci, L.L.; Launay, J.-M.; Kawakami, N.; Sicard, C.; Desvignes, N.; Dakouane-Giudicelli, M.; Spix, B.; Têtu, M.; Gilmaire, F.-O.; Paulcan, S.; et al. Endolysosomal TPCs regulate social behavior by controlling oxytocin secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2023, 120. [CrossRef]
- Hu, H., C.A. Zarate, Jr., and J. Verbalis, Arginine vasopressin in mood disorders: A potential biomarker of disease pathology and a target for pharmacologic intervention. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, 2024.
- Ludwig, M. Dendritic Release of Vasopressin and Oxytocin. J. Neuroendocr. 1998, 10, 881–895. [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Ludwig, M. Neurotransmitters and peptides: whispered secrets and public announcements. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 5625–5632. [CrossRef]
- Kombian, S.B.; Hirasawa, M.; Mouginot, D.; Pittman, Q.J. Chapter 18 Modulation of synaptic transmission by oxytocin and vasopressin in the supraoptic nucleus. In Vasopressin and Oxytocin: From Genes to Clinical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume, 139, pp. 235–246. [CrossRef]
- Kombian, S.B.; Hirasawa, M.; Mouginot, D.; Chen, X.; Pittman, Q.J. Short-Term Potentiation of Miniature Excitatory Synaptic Currents Causes Excitation of Supraoptic Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 83, 2542–2553. [CrossRef]
- Brussaard, A.B.; Kits, K.S. Changes in GABAA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Transmission in Oxytocin Neurons during Female Reproduction: Plasticity in a Neuroendocrine Context. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1999, 868, 677–680. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tripathi, P.K.; Armstrong, W.E. Differences in spike train variability in rat vasopressin and oxytocin neurons and their relationship to synaptic activity. J. Physiol. 2007, 581, 221–240. [CrossRef]
- Sladek, C.D.; Kapoor, J.R. Neurotransmitter/Neuropeptide Interactions in the Regulation of Neurohypophyseal Hormone Release. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 171, 200–209. [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, W.E. The neurophysiology of neurosecretory cells. J. Physiol. 2007, 585, 645–647. [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.; Brown, C.H.; A Russell, J. Physiological pathways regulating the activity of magnocellular neurosecretory cells. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 57, 625–655. [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Bourque, C.W. Functional N-Methyl-D-Aspartate and Non-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptors are Expressed by Rat Supraoptic Neurosecretory Cells in vitro. J. Neuroendocr. 1991, 3, 509–514. [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, I.; Kabashima, N.; Ibrahim, N.; Setiadji, S.V.; Ueta, Y.; Yamashita, H. Pre- and postsynaptic modulation of the electrical activity of rat supraoptic neurones. Exp. Physiol. 2000, 85, 145s–151s. [CrossRef]
- Wuarin, J.; Dudek, F. Patch-clamp analysis of spontaneous synaptic currents in supraoptic neuroendocrine cells of the rat hypothalamus. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 2323–2331. [CrossRef]
- Decavel, C.; Curras, M. Increased expression of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit, NR1, in immunohistochemically identified magnocellular hypothalamic neurons during dehydration. Neuroscience 1997, 78, 191–202. [CrossRef]
- Boudaba, C.; Di, S.; Tasker, J.G. Presynaptic Noradrenergic Regulation of Glutamate Inputs to Hypothalamic Magnocellular Neurones. J. Neuroendocr. 2003, 15, 803–810. [CrossRef]
- Iremonger, K.J.; Benediktsson, A.M.; Bains, J.S. Glutamatergic synaptic transmission in neuroendocrine cells: Basic principles and mechanisms of plasticity. Front. Neuroendocr. 2010, 31, 296–306. [CrossRef]
- Vilhena-Franco, T.; Valentim-Lima, E.; Reis, L.C.; Elias, L.L.K.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Mecawi, A.S. Role of AMPA and NMDA receptors on vasopressin and oxytocin secretion induced by hypertonic extracellular volume expansion. J. Neuroendocr. 2018, 30, e12633. [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.H., Magnocellular Neurons and Posterior Pituitary Function. Compr Physiol, 2016. 6(4): p. 1701-1741.
- Ferguson, A.V.; Latchford, K.J.; Samson, W.K. The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus – a potential target for integrative treatment of autonomic dysfunction. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 717–727. [CrossRef]
- Rasiah, N.P., S.P. Loewen, and J.S. Bains, Windows into stress: a glimpse at emerging roles for CRH(PVN) neurons. Physiol Rev, 2023. 103(2): p. 1667-1691.
- Sawchenko, P.E., et al., The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and the functional neuroanatomy of visceromotor responses to stress. Prog Brain Res, 1996. 107: p. 201-22.
- Simmons, D.M.; Swanson, L.W. Comparison of the spatial distribution of seven types of neuroendocrine neurons in the rat paraventricular nucleus: Toward a global 3D model. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 516, 423–441. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Coote, J.H. Influence of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus on cardiovascular neurones in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of the rat. J. Physiol. 1998, 513, 521–530. [CrossRef]
- Shafton, A.D.; Ryan, A.; Badoer, E. Neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus send collaterals to the spinal cord and to the rostral ventrolateral medulla in the rat. Brain Res. 1998, 801, 239–243. [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.; Nemeroff, C. The CRF System as a Therapeutic Target for Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1045–1054. [CrossRef]
- Marsh, N.; Marsh, A.A.; Lee, M.R.; Hurlemann, R. Oxytocin and the Neurobiology of Prosocial Behavior. Neurosci. 2020, 27, 604–619. [CrossRef]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Cuesta-Marti, C.; Lopez-Salas, A.; Chruścicka-Smaga, B.; Crespo-Ramírez, M.; Tesoro-Cruz, E.; Palacios-Lagunas, D.A.; de la Mora, M.P.; Schellekens, H.; Fuxe, K. The oxytocin receptor represents a key hub in the GPCR heteroreceptor network: potential relevance for brain and behavior. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1055344. [CrossRef]
- Santoso, P.; Nakata, M.; Ueta, Y.; Yada, T. Suprachiasmatic vasopressin to paraventricular oxytocin neurocircuit in the hypothalamus relays light reception to inhibit feeding behavior. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2018, 315, E478–E488. [CrossRef]
- Vargas, Y.; Tron, A.E.C.; Rodríguez, A.R.; Uribe, R.M.; Joseph-Bravo, P.; Charli, J.-L. Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone and Food Intake in Mammals: An Update. Metabolites 2024, 14, 302. [CrossRef]
- Barrett-Jolley, R.; Nunn, N.; Womack, M.; Dart, C. Function and Pharmacology of Spinally-Projecting Sympathetic Pre-Autonomic Neurones in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 9, 262–277. [CrossRef]
- Strecker, G.J.; Wuarin, J.-P.; Dudek, F.E. GABAA-Mediated Local Synaptic Pathways Connect Neurons in the Rat Suprachiasmatic Nucleus. J. Neurophysiol. 1997, 78, 2217–2220. [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.Y.; Eichler, V.B. Loss of a circadian adrenal corticosterone rhythm following suprachiasmatic lesions in the rat. Brain Res. 1972, 42, 201–206. [CrossRef]
- Stephan, F.K.; Zucker, I. Circadian Rhythms in Drinking Behavior and Locomotor Activity of Rats Are Eliminated by Hypothalamic Lesions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1972, 69, 1583–1586. [CrossRef]
- Sumová, A.; Trávnícková, Z.; Peters, R.; Schwartz, W.J.; Illnerová, H. The rat suprachiasmatic nucleus is a clock for all seasons.. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1995, 92, 7754–7758. [CrossRef]
- Reppert, S.M., A clockwork explosion! Neuron, 1998. 21(1): p. 1-4.
- Lee, H.S.; Billings, H.J.; Lehman, M.N. The Suprachiasmatic Nucleus: A Clock of Multiple Components. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2003, 18, 435–449. [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.Y.; Card, J.P. Visual Pathways and the Entrainment of Circadian Rhythmsa. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1985, 453, 123–133. [CrossRef]
- Jacomy, H.; Burlet, A.; Bosler, O. Vasoactive intestinal peptide neurons as synaptic targets for vasopressin neurons in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Double-label immunocytochemical demonstration in the rat. Neuroscience 1999, 88, 859–870. [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, M.; Enoki, R.; Mazuski, C.N.; Jones, J.; Evans, J.A.; Azzi, A. Network-Mediated Encoding of Circadian Time: The Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN) from Genes to Neurons to Circuits, and Back. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15192–15199. [CrossRef]
- Inouye, S.T.; Kawamura, H. Persistence of circadian rhythmicity in a mammalian hypothalamic "island" containing the suprachiasmatic nucleus.. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1979, 76, 5962–5966. [CrossRef]
- Groos, G.; Hendriks, J. Circadian rhythms in electrical discharge of rat suprachiasmatic neurones recorded in vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 1982, 34, 283–288. [CrossRef]
- Pennartz, C.M.A.; de Jeu, M.T.G.; Bos, N.P.A.; Schaap, J.; Geurtsen, A.M.S. Diurnal modulation of pacemaker potentials and calcium current in the mammalian circadian clock. Nature 2002, 416, 286–290. [CrossRef]
- Stephens, S.B.Z.; Kauffman, A.S. Estrogen Regulation of the Molecular Phenotype and Active Translatome of AVPV Kisspeptin Neurons. Endocrinology 2021, 162. [CrossRef]
- Spergel, D.J. Modulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Neuron Activity and Secretion in Mice by Non-peptide Neurotransmitters, Gasotransmitters, and Gliotransmitters. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 329. [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Yu, Q.; Guo, W.; He, C.; Burnstock, G.; Xiang, Z. P2X receptors are expressed on neurons containing luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone in the mouse hypothalamus. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 458, 32–36. [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.K.; Chiappa, S.A.; Fink, G.; Sherwood, N.M. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone surge in pro-oestrous rats. Nature 1976, 264, 461–463. [CrossRef]
- Baca-Alonso, J.J.A. and J.L. Quintanar, The effect of gonadotropin-releasing hormone on the nervous system. Neuro Endocrinol Lett, 2024. 45(3): p. 188-196.
- Bakker, J., Can kisspeptin be a new treatment for sexual dysfunction? Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2025.
- Messager, S.; Chatzidaki, E.E.; Ma, D.; Hendrick, A.G.; Zahn, D.; Dixon, J.; Thresher, R.R.; Malinge, I.; Lomet, D.; Carlton, M.B.L.; et al. Kisspeptin directly stimulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone release via G protein-coupled receptor 54. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2005, 102, 1761–1766. [CrossRef]
- de Roux, N., et al., Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism due to loss of function of the KiSS1-derived peptide receptor GPR54. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003. 100(19): p. 10972-6.
- Sliwowska, J.H.; Woods, N.E.; Alzahrani, A.R.; Paspali, E.; Tate, R.J.; Ferro, V.A. Kisspeptin a potential therapeutic target in treatment of both metabolic and reproductive dysfunction. J. Diabetes 2024, 16, e13541. [CrossRef]
- Boulant, J.A.; Hardy, J.D. The effect of spinal and skin temperatures on the firing rate and thermosensitivity of preoptic neurones. J. Physiol. 1974, 240, 639–660. [CrossRef]
- Bouret, S.G.; Draper, S.J.; Simerly, R.B. Formation of Projection Pathways from the Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus to Hypothalamic Regions Implicated in the Neural Control of Feeding Behavior in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2797–2805. [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.B.; Brownlow, M.L.; Araújo, B.B.; Garnica-Siqueira, M.C.; Zaia, D.A.M.; Leite, C.M.; Zaia, C.T.B.V.; Uchoa, E.T. Arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus contributes to the hypophagic effect and plasma metabolic changes induced by vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide. Neurochem. Int. 2022, 155, 105300. [CrossRef]
- Fioramonti, X.; Lorsignol, A.; Taupignon, A.; Pénicaud, L. A New ATP-Sensitive K+ Channel–Independent Mechanism Is Involved in Glucose-Excited Neurons of Mouse Arcuate Nucleus. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2767–2775. [CrossRef]
- Mehay, D.; Silberman, Y.; Arnold, A.C. The Arcuate Nucleus of the Hypothalamus and Metabolic Regulation: An Emerging Role for Renin–Angiotensin Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7050. [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, K.M.; Saunders, S.E.; Antunes, V.R.; Boychuk, C.R. Insulin activates parasympathetic hepatic-related neurons of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus through mTOR signaling. J. Neurophysiol. 2025, 133, 320–332. [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, J.; Han, S.Y.; Piet, R.; McLennan, T.; Kane, G.M.; Ng, J.; Porteous, R.W.; Kim, J.S.; Colledge, W.H.; Iremonger, K.J.; et al. Definition of the hypothalamic GnRH pulse generator in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, E10216–E10223. [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Hagihara, M.; Miyamichi, K.; Japan Dynamics of pulsatile activities of arcuate kisspeptin neurons in aging female mice. eLife 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Koysombat, K.; Tsoutsouki, J.; Patel, A.H.; Comninos, A.N.; Dhillo, W.S.; Abbara, A. Kisspeptin and neurokinin B: roles in reproductive health. Physiol. Rev. 2025, 105, 707–764. [CrossRef]
- Sawchenko, P.; Swanson, L. The organization of noradrenergic pathways from the brainstem to the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei in the rat. Brain Res. Rev. 1982, 4, 275–325. [CrossRef]
- Mezey, E., et al., Distribution of the pro-opiomelanocortin derived peptides, adrenocorticotrope hormone, alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and beta-endorphin (ACTH, alpha-MSH, beta-END) in the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res, 1985. 328(2): p. 341-7.
- Morgane, P.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Li, C.-S.; Smith, D.V. Electrophysiological studies of feeding and satiety centers in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1961, 201, 838–844. [CrossRef]
- King, B.M. The rise, fall, and resurrection of the ventromedial hypothalamus in the regulation of feeding behavior and body weight. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 87, 221–244. [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.H., et al., Crosstalk between P2X4 and GABA-A receptors determines synaptic efficacy at central synapses. J Biol Chem, 2011.
- Cheung, C.C.; Kurrasch, D.M.; Liang, J.K.; Ingraham, H.A. Genetic labeling of steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1) neurons in mice reveals ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH) circuitry beginning at neurogenesis and development of a separate non-SF-1 neuronal cluster in the ventrolateral VMH. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 521, 1268–1288. [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, S.; Roy, S.C.; Briski, K.P. Dorsomedial Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone Neuron Steroidogenic Factor-1 Gene Targets in Female Rat. ASN Neuro 2024, 16, 2403345. [CrossRef]
- Fosch, A.; Zagmutt, S.; Casals, N.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, R. New Insights of SF1 Neurons in Hypothalamic Regulation of Obesity and Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6186. [CrossRef]
- Bellinger, L.L. and L.L. Bernardis, The dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus and its role in ingestive behavior and body weight regulation: lessons learned from lesioning studies. Physiol Behav, 2002. 76(3): p. 431-42.
- Brasil, T.F.S.; Lopes-Azevedo, S.; Belém-Filho, I.J.A.; Fortaleza, E.A.T.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Corrêa, F.M.A. The Dorsomedial Hypothalamus Is Involved in the Mediation of Autonomic and Neuroendocrine Responses to Restraint Stress. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1547. [CrossRef]
- DiMicco, J.A., et al., The dorsomedial hypothalamus and the response to stress: part renaissance, part revolution. Pharmacol Biochem Behav, 2002. 71(3): p. 469-80.
- Sakai, K.; Takahashi, K.; Anaclet, C.; Lin, J.-S. Sleep-waking discharge of ventral tuberomammillary neurons in wild-type and histidine decarboxylase knock-out mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 53. [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Inagaki, N.; Itowi, N.; Yamatodani, A. Histaminergic neuron system in the brain: Distribution and possible functions. Brain Res. Bull. 1991, 27, 367–370. [CrossRef]
- Mickelsen, L.E.; Bolisetty, M.; Chimileski, B.R.; Fujita, A.; Beltrami, E.J.; Costanzo, J.T.; Naparstek, J.R.; Robson, P.; Jackson, A.C. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of the lateral hypothalamic area reveals molecularly distinct populations of inhibitory and excitatory neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 642–656. [CrossRef]
- Colldén, G.; Mangano, C.; Meister, B. P2X2 purinoreceptor protein in hypothalamic neurons associated with the regulation of food intake. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 62–78. [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Caballero, C.; Jara, J.; Luarte, L.; Jiménez, Y.; Teske, J.; Perez-Leighton, C. Control of motivation for sucrose in the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus by dynorphin peptides and the kappa opioid receptor. Appetite 2024, 200, 107504. [CrossRef]
- Bernardis, L.L.; Bellinger, L.L. The lateral hypothalamic area revisited: Neuroanatomy, body weight regulation, neuroendocrinology and metabolism. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1993, 17, 141–193. [CrossRef]
- Bonnavion, P.; Mickelsen, L.E.; Fujita, A.; de Lecea, L.; Jackson, A.C. Hubs and spokes of the lateral hypothalamus: cell types, circuits and behaviour. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 6443–6462. [CrossRef]
- Samson, W.K.; Taylor, M.M.; Follwell, M.; Ferguson, A.V. Orexin actions in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: physiological consequences and cellular correlates. Regul. Pept. 2001, 104, 97–103. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, R.; Young, S.L.; Cox, V.C. Analgesia for formalin-induced pain by lateral hypothalamic stimulation. Brain Res. 1991, 563, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Lee, B.; Inyang, K.; Bemis, H.; Bugescu, R.; Laumet, G.; Leinninger, G. Neurotensin-expressing lateral hypothalamic neurons alleviate neuropathic and inflammatory pain via neurotensin receptor signaling. Neurobiol. Pain 2024, 16, 100172. [CrossRef]
- Beamer, E.; Conte, G.; Engel, T. ATP release during seizures – A critical evaluation of the evidence. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 151, 65–73. [CrossRef]
- Jurányi, Z.; Sperlágh, B.; Vizi, E. Involvement of P2 purinoceptors and the nitric oxide pathway in [3H]purine outflow evoked by short-term hypoxia and hypoglycemia in rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1999, 823, 183–190. [CrossRef]
- Godoy, P.A.; Ramírez-Molina, O.; Fuentealba, J. Exploring the Role of P2X Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1330. [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, P.B.; Knappenberger, J.; Segal, M.; Bennett, M.V.L.; Charles, A.C.; Kater, S.B. ATP Released from Astrocytes Mediates Glial Calcium Waves. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 520–528. [CrossRef]
- Fields, R.D. and B. Stevens, ATP: an extracellular signaling molecule between neurons and glia. Trends Neurosci, 2000. 23(12): p. 625-33.
- Inoue, K.; Koizumi, S.; Tsuda, M. The role of nucleotides in the neuron–glia communication responsible for the brain functions. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1447–1458. [CrossRef]
- Abbracchio, M.P.; Burnstock, G.; Verkhratsky, A.; Zimmermann, H. Purinergic signalling in the nervous system: an overview. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 19–29. [CrossRef]
- Lalo, U.; Palygin, O.; Verkhratsky, A.; Grant, S.G.N.; Pankratov, Y. ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD-95 multi-protein complex. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep33609. [CrossRef]
- Araque, A.; Parpura, V.; Sanzgiri, R.P.; Haydon, P.G. Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 208–215. [CrossRef]
- Crosby, K.M.; Murphy-Royal, C.; Wilson, S.A.; Gordon, G.R.; Bains, J.S.; Pittman, Q.J. Cholecystokinin Switches the Plasticity of GABA Synapses in the Dorsomedial Hypothalamus via Astrocytic ATP Release. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 8515–8525. [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, X.-J.; Li, S. Mutant Huntingtin Impairs BDNF Release from Astrocytes by Disrupting Conversion of Rab3a-GTP into Rab3a-GDP. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 8790–8801. [CrossRef]
- Lazarowski, E.R., et al., Molecular mechanisms of purine and pyrimidine nucleotide release. Adv Pharmacol, 2011. 61: p. 221-61.
- Lazarowski, E.R. Vesicular and conductive mechanisms of nucleotide release. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 359–373. [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Fredholm, B.B.; Verkhratsky, A. Adenosine and ATP Receptors in the Brain. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 973–1011. [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.-H.; Schlichter, R. Synaptic corelease of ATP and GABA in cultured spinal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 241–245. [CrossRef]
- Nörenberg, W.; Illes, P. Neuronal P2X receptors: localisation and functional properties. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 324–339. [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.; Rhee, J.S.; Kubota, H.; Akaike, N.; Akaike, N. Developmental changes in P2X purinoceptors on glycinergic presynaptic nerve terminals projecting to rat substantia gelatinosa neurones. J. Physiol. 2001, 536, 505–519. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.J., et al., Dual presynaptic control by ATP of glutamate release via facilitatory P2X1, P2X2/3, and P2X3 and inhibitory P2Y1, P2Y2, and/or P2Y4 receptors in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci, 2005. 25(27): p. 6286-95.
- Burnstock, G., Purinergic cotransmission. Exp Physiol, 2009. 94(1): p. 20-4.
- Vavra, V.; Bhattacharya, A.; Zemkova, H. Facilitation of glutamate and GABA release by P2X receptor activation in supraoptic neurons from freshly isolated rat brain slices. Neuroscience 2011, 188, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Gordon, G.R.J.; Baimoukhametova, D.V.; A Hewitt, S.; Rajapaksha, W.R.A.K.J.S.; E Fisher, T.; Bains, J.S. Norepinephrine triggers release of glial ATP to increase postsynaptic efficacy. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1078–1086. [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, M.; Brambilla, R.; D'Ambrosi, N.; Volonté, C.; Matteoli, M.; Verderio, C.; Abbracchio, M.P. Nucleotide-mediated calcium signaling in rat cortical astrocytes: Role of P2X and P2Y receptors. Glia 2003, 43, 218–230. [CrossRef]
- Pascual, O.; Casper, K.B.; Kubera, C.; Zhang, J.; Revilla-Sanchez, R.; Sul, J.-Y.; Takano, H.; Moss, S.J.; McCarthy, K.; Haydon, P.G. Astrocytic Purinergic Signaling Coordinates Synaptic Networks. Science 2005, 310, 113–116. [CrossRef]
- Pangršič, T.; Potokar, M.; Stenovec, M.; Kreft, M.; Fabbretti, E.; Nistri, A.; Pryazhnikov, E.; Khiroug, L.; Giniatullin, R.; Zorec, R. Exocytotic Release of ATP from Cultured Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28749–28758. [CrossRef]
- Stout, C.E.; Costantin, J.L.; Naus, C.C.G.; Charles, A.C. Intercellular Calcium Signaling in Astrocytes via ATP Release through Connexin Hemichannels. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10482–10488. [CrossRef]
- Schenk, U.; Westendorf, A.M.; Radaelli, E.; Casati, A.; Ferro, M.; Fumagalli, M.; Verderio, C.; Buer, J.; Scanziani, E.; Grassi, F. Purinergic control of T cell activation by ATP released through pannexin-1 hemichannels. Sci. Signal. 2008, 1, ra6. [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R., et al., Pannexin 1: the molecular substrate of astrocyte "hemichannels". J Neurosci, 2009. 29(21): p. 7092-7.
- Li, S.; Bjelobaba, I.; Yan, Z.; Kucka, M.; Tomić, M.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Expression and Roles of Pannexins in ATP Release in the Pituitary Gland. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 2342–2352. [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; Sofroniew, M.V. Diversity of astrocyte functions and phenotypes in neural circuits. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 942–952. [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, M.; Hirayama, Y.; Fujishita, K.; Shibata, K.; Shinozaki, Y.; Shigetomi, E.; Takeda, A.; Le, H.P.N.; Hayashi, H.; Hiasa, M.; et al. Anti-Depressant Fluoxetine Reveals its Therapeutic Effect Via Astrocytes. EBioMedicine 2018, 32, 72–83. [CrossRef]
- North, R.A. Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 1013–1067. [CrossRef]
- Nicke, A.; Bäumert, H.G.; Rettinger, J.; Eichele, A.; Lambrecht, G.; Mutschler, E.; Schmalzing, G. P2X1 and P2X3 receptors form stable trimers: a novel structural motif of ligand-gated ion channels. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3016–3028. [CrossRef]
- Pelegrin, P.; Surprenant, A. Pannexin-1 mediates large pore formation and interleukin-1β release by the ATP-gated P2X7 receptor. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 5071–5082. [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.H., et al., Crosstalk between P2X4 and GABA-A receptors determines synaptic efficacy at central synapses. J Biol Chem, 2011. 256: p. 19993-20004.
- Queme, L.F.; Weyler, A.A.; Cohen, E.R.; Hudgins, R.C.; Jankowski, M.P. A dual role for peripheral GDNF signaling in nociception and cardiovascular reflexes in the mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2019, 117, 698–707. [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S. Molecular physiology of p2x receptors and atp signalling at synapses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 165–174. [CrossRef]
- Stojilkovic, S.S.; Tomić, M.; He, M.; Yan, Z.; Koshimizu, T.; Zemkova, H. Molecular Dissection of Purinergic P2X Receptor Channels. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2005, 1048, 116–130. [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; Proctor, W.R.; Dunwiddie, T.V.; Labarca, C.; Lester, H.A. Allosteric Control of Gating and Kinetics at P2X4Receptor Channels. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 7289–7299. [CrossRef]
- Coddou, C.; Yan, Z.; Obsil, T.; Huidobro-Toro, J.P.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Activation and Regulation of Purinergic P2X Receptor Channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 641–683. [CrossRef]
- Coddou, C.; Stojilkovic, S.S.; Huidobro-Toro, J.P. Allosteric modulation of ATP-gated P2X receptor channels. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 22, 335–354. [CrossRef]
- Stokes, L.; Bidula, S.; Bibič, L.; Allum, E. To Inhibit or Enhance? Is There a Benefit to Positive Allosteric Modulation of P2X Receptors? Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 627. [CrossRef]
- Illes, P.; Müller, C.E.; Jacobson, K.A.; Grutter, T.; Nicke, A.; Fountain, S.J.; Kennedy, C.; Schmalzing, G.; Jarvis, M.F.; Stojilkovic, S.S.; et al. Update of P2X receptor properties and their pharmacology: IUPHAR Review 30. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 178, 489–514. [CrossRef]
- Sivcev, S.; Kudova, E.; Zemkova, H. Neurosteroids as positive and negative allosteric modulators of ligand-gated ion channels: P2X receptor perspective. Neuropharmacology 2023, 234, 109542. [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, B.R.; Lynch, K.J.; Touma, E.; Niforatos, W.; Burgard, E.C.; Alexander, K.M.; Park, H.S.; Yu, H.; Metzger, R.; Kowaluk, E.; et al. Pharmacological characterization of recombinant human and rat P2X receptor subtypes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 376, 127–138. [CrossRef]
- Samways, D.S.K.; Li, Z.; Egan, T.M. Principles and properties of ion flow in P2X receptors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 6. [CrossRef]
- Oury, C.; Toth-Zsamboki, E.; Van Geet, C.; Thys, C.; Wei, L.; Nilius, B.; Vermylen, J.; Hoylaerts, M.F. A Natural Dominant Negative P2X1 Receptor Due to Deletion of a Single Amino Acid Residue. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 22611–22614. [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.J., et al., Molecular and functional characterization of human P2X(2) receptors. Mol Pharmacol, 1999. 56(6): p. 1171-81.
- Zhong, Y.; Dunn, P.M.; Xiang, Z.; Bo, X.; Burnstock, G. Pharmacological and molecular characterization of P2X receptors in rat pelvic ganglion neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 771–781. [CrossRef]
- Haustein, M.D.; Kracun, S.; Lu, X.-H.; Shih, T.; Jackson-Weaver, O.; Tong, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, X.W.; O’dell, T.J.; Marvin, J.S.; et al. Conditions and Constraints for Astrocyte Calcium Signaling in the Hippocampal Mossy Fiber Pathway. Neuron 2014, 82, 413–429. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Bahia, P.K.; Patil, M.; Sutton, S.; Sowells, I.; Hadley, S.H.; Kollarik, M.; Taylor-Clark, T.E. Development of a Mouse Reporter Strain for the Purinergic P2X2Receptor. eneuro 2020, 7. [CrossRef]
- Grohmann, M.; Schumacher, M.; Günther, J.; Singheiser, S.M.; Nußbaum, T.; Wildner, F.; Gerevich, Z.; Jabs, R.; Hirnet, D.; Lohr, C.; et al. BAC transgenic mice to study the expression of P2X2 and P2Y1 receptors. Purinergic Signal. 2021, 17, 449–465. [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek-Hájek, K.; Lörinczi, É.; Hausmann, R.; Nicke, A. Molecular and functional properties of P2X receptors—recent progress and persisting challenges. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 8, 375–417. [CrossRef]
- Hugel, S.; Schlichter, R. Presynaptic P2X Receptors Facilitate Inhibitory GABAergic Transmission between Cultured Rat Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 2121–2130. [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S.; Gittermann, D.; Cockayne, D.A.; Jones, A. ATP Modulation of Excitatory Synapses onto Interneurons. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7426–7437. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.; Neidhart, S.; Holy, C.; North, R.A.; Buell, G.; Surprenant, A. Coexpression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits can account for ATP-gated currents in sensory neurons. Nature 1995, 377, 432–435. [CrossRef]
- Finger, T.E.; Danilova, V.; Barrows, J.; Bartel, D.L.; Vigers, A.J.; Stone, L.; Hellekant, G.; Kinnamon, S.C. ATP Signaling Is Crucial for Communication from Taste Buds to Gustatory Nerves. Science 2005, 310, 1495–1499. [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, L.-P.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Hu, H.-H.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.-J.; Xiong, W.-C.; et al. Astrocyte-derived ATP modulates depressive-like behaviors. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 773–777. [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.E.; Lü, W.; Oosterheert, W.; Shekhar, M.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Gouaux, E. X-ray structures define human P2X3 receptor gating cycle and antagonist action. Nature 2016, 538, 66–71. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Akopian, A.N.; Sivilottit, L.; Colquhoun, D.; Burnstock, G.; Wood, J.N. A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature 1995, 377, 428–431. [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.P. and E.W. McCleskey, Desensitization, recovery and Ca(2+)-dependent modulation of ATP-gated P2X receptors in nociceptors. Neuropharmacology, 1997. 36(9): p. 1303-8.
- North, R.A., P2X3 receptors and peripheral pain mechanisms. J Physiol, 2004. 554(Pt 2): p. 301-8.
- Ding, S.; Zhu, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X. P2X3 receptor involvement in endometriosis pain via ERK signaling pathway. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0184647–e0184647. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-B.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.-G.; Wang, X.-D.; Yang, B.-L.; Zhu, G.-C.; Zhou, C.-F.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.-X. Effects of 1,8-cineole on neuropathic pain mediated by P2X2 receptor in the spinal cord dorsal horn. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7909. [CrossRef]
- North, R.A., P2X receptors. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 2016. 371(1700).
- Silva-Ramos, M., et al., Activation of Prejunctional P2x2/3 Heterotrimers by ATP Enhances the Cholinergic Tone in Obstructed Human Urinary Bladders. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2020. 372(1): p. 63-72.
- Khakh, B.S.; North, R.A. P2X receptors as cell-surface ATP sensors in health and disease. Nature 2006, 442, 527–532. [CrossRef]
- Kawate, T.; Michel, J.C.; Birdsong, W.T.; Gouaux, E. Crystal structure of the ATP-gated P2X4 ion channel in the closed state. Nature 2009, 460, 592–598. [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, O.S.; Paramasivam, A.; Yu, J.C.H.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.D. Regulation of P2X4 receptors by lysosomal targeting, glycan protection and exocytosis. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 3838–3849. [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zou, Y.; Zhong, X.Z.; Cao, Q.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, M.X.; Murrell-Lagnado, R.; Dong, X.-P. P2X4 Forms Functional ATP-activated Cation Channels on Lysosomal Membranes Regulated by Luminal pH. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17658–17667. [CrossRef]
- Jelínkova, I.; Vávra, V.; Jindrichova, M.; Obsil, T.; Zemkova, H.W.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Identification of P2X4 receptor transmembrane residues contributing to channel gating and interaction with ivermectin. Pfl?gers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2008, 456, 939–950. [CrossRef]
- Buell, G.; Lewis, C.; Collo, G.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. An antagonist-insensitive P2X receptor expressed in epithelia and brain.. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 55–62. [CrossRef]
- Jelínková, I.; Yan, Z.; Liang, Z.; Moonat, S.; Teisinger, J.; Stojilkovic, S.S.; Zemková, H. Identification of P2X4 receptor-specific residues contributing to the ivermectin effects on channel deactivation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 349, 619–625. [CrossRef]
- Le, K.T., K. Babinski, and P. Seguela, Central P2X4 and P2X6 channel subunits coassemble into a novel heteromeric ATP receptor. J Neurosci, 1998. 18(18): p. 7152-9.
- Seguela, P.; Haghighi, A.; Soghomonian, J.; Cooper, E. A novel neuronal P2x ATP receptor ion channel with widespread distribution in the brain. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 448–455. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Cronin, C.G.; Scranton, V.L.; Jacobson, K.A.; Liang, B.T.; Verma, R. Neuroprotective and neuro-rehabilitative effects of acute purinergic receptor P2X4 (P2X4R) blockade after ischemic stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 329, 113308–113308. [CrossRef]
- Montilla, A.; Mata, G.P.; Matute, C.; Domercq, M. Contribution of P2X4 Receptors to CNS Function and Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5562. [CrossRef]
- Kotnis, S.; Bingham, B.; Vasilyev, D.V.; Miller, S.W.; Bai, Y.; Yeola, S.; Chanda, P.K.; Bowlby, M.R.; Kaftan, E.J.; Samad, T.A.; et al. Genetic and Functional Analysis of Human P2X5 Reveals a Distinct Pattern of Exon 10 Polymorphism with Predominant Expression of the Nonfunctional Receptor Isoform. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 77, 953–960. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Burnstock, G.; Xiang, Z.; He, C. Developmental expression of P2X5 receptors in the mouse prenatal central and peripheral nervous systems. Purinergic Signal. 2012, 9, 239–248. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xu, X.; Gao, X.; Burnstock, G.; He, C.; Xiang, Z. Expression of P2X5 receptors in the mouse CNS. Neuroscience 2008, 156, 673–692. [CrossRef]
- Ryten, M.; Dunn, P.M.; Neary, J.T.; Burnstock, G. ATP regulates the differentiation of mammalian skeletal muscle by activation of a P2X5 receptor on satellite cells. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 158, 345–355. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kajikawa, T.; Walsh, M.C.; Takegahara, N.; Jeong, Y.H.; Hajishengallis, G.; Choi, Y. The purinergic receptor P2X5 contributes to bone loss in experimental periodontitis. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 468–473. [CrossRef]
- Soto, F.; Garcia-Guzman, M.; Karschin, C.; Stühmer, W. Cloning and Tissue Distribution of a Novel P2X Receptor from Rat Brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 223, 456–460. [CrossRef]
- North, R., P2X receptors: a third major class of ligand-gated ion channels. . Ciba Found Symp, 1996. 198: p. 91-105.
- King, B.F., et al., Coexpression of rat P2X2 and P2X6 subunits in Xenopus oocytes. J Neurosci, 2000. 20(13): p. 4871-7.
- Torres, G.E.; Egan, T.M.; Voigt, M.M. Identification of a Domain Involved in ATP-gated Ionotropic Receptor Subunit Assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 22359–22365. [CrossRef]
- Surprenant, A., et al., The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7). Science, 1996. 272(5262): p. 735-8.
- Virginio, C.; MacKenzie, A.; Rassendren, F.A.; North, R.A.; Surprenant, A. Pore dilation of neuronal P2X receptor channels. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 315–321. [CrossRef]
- Cheewatrakoolpong, B.; Gilchrest, H.; Anthes, J.C.; Greenfeder, S. Identification and characterization of splice variants of the human P2X7 ATP channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 332, 17–27. [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, E.; Cirillo, M.; Woltersdorf, R.; Falzoni, S.; Chiozzi, P.; Pellegatti, P.; Callegari, M.G.; Sandonà, D.; Markwardt, F.; Schmalzing, G.; et al. Trophic activity of a naturally occurring truncated isoform of the P2X7 receptor. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 3393–3404. [CrossRef]
- Di Virgilio, F.; Schmalzing, G.; Markwardt, F. The Elusive P2X7 Macropore. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 392–404. [CrossRef]
- Gelin, C.F., A. Bhattacharya, and M.A. Letavic, P2X7 receptor antagonists for the treatment of systemic inflammatory disorders. Prog Med Chem, 2020. 59: p. 63-99.
- Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Sebastián-Serrano, Á.; García, L.D.D.; Díaz-Hernández, M. Neuronal P2X7 Receptor: Involvement in Neuronal Physiology and Pathology. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 7063–7072. [CrossRef]
- Kopp, R.; Krautloher, A.; Ramírez-Fernández, A.; Nicke, A. P2X7 Interactions and Signaling – Making Head or Tail of It. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 183. [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.; Stokes, L.; Sluyter, R. The P2X7 Receptor Channel: Recent Developments and the Use of P2X7 Antagonists in Models of Disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 638–675. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Lord, B.; Grigoleit, J.-S.; He, Y.; Fraser, I.; Campbell, S.N.; Taylor, N.; Aluisio, L.; O’connor, J.C.; Papp, M.; et al. Neuropsychopharmacology of JNJ-55308942: evaluation of a clinical candidate targeting P2X7 ion channels in animal models of neuroinflammation and anhedonia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2586–2596. [CrossRef]
- Czamara, D.; Müller-Myhsok, B.; Lucae, S. The P2RX7 polymorphism rs2230912 is associated with depression: A meta-analysis. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 82, 272–277. [CrossRef]
- Deussing, J.M. and E. Arzt, P2X7 Receptor: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Depression? Trends Mol Med, 2018. 24(9): p. 736-747.
- Bhattacharya, A.; Biber, K. The microglial ATP-gated ion channel P2X7 as a CNS drug target. Glia 2016, 64, 1772–1787. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Ceusters, M. Targeting neuroinflammation with brain penetrant P2X7 antagonists as novel therapeutics for neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 45, 234–235. [CrossRef]
- Illes, P.; Verkhratsky, A.; Tang, Y. Pathological ATPergic Signaling in Major Depression and Bipolar Disorder. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 12, 331. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., et al., P2X7 receptor: a potential target for treating comorbid anxiety and depression. Purinergic Signal, 2024.
- Jimenez-Pacheco, A.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.; Arribas-Blázquez, M.; Sanz-Rodriguez, A.; Olivos-Oré, L.A.; Artalejo, A.R.; Alves, M.; Letavic, M.; Miras-Portugal, M.T.; Conroy, R.M.; et al. Transient P2X7 Receptor Antagonism Produces Lasting Reductions in Spontaneous Seizures and Gliosis in Experimental Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 5920–5932. [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek-Hajek, K.; Zhang, J.; Kopp, R.; Grosche, A.; Rissiek, B.; Saul, A.; Bruzzone, S.; Engel, T.; Jooss, T.; Krautloher, A.; et al. Re-evaluation of neuronal P2X7 expression using novel mouse models and a P2X7-specific nanobody. eLife 2018, 7. [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.; Gomez-Villafuertes, R.; Benito-León, M.; de la Torre, M.M.; Olivos-Oré, L.A.; Arribas-Blazquez, M.; Gomez-Gaviro, M.V.; Azcorra, A.; Desco, M.; Artalejo, A.R.; et al. Salient brain entities labelled in P2rx7-EGFP reporter mouse embryos include the septum, roof plate glial specializations and circumventricular ependymal organs. Anat. Embryol. 2021, 226, 715–741. [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, I.; Tanaka, K.; Hattori, Y.; Uezono, Y.; Harayama, N.; Noguchi, J.; Ueta, Y.; Izumi, F.; Yamashita, H. Evidence that multiple P2X purinoceptors are functionally expressed in rat supraoptic neurones. J. Physiol. 1999, 514, 351–367. [CrossRef]
- Housley, G.D.; Kanjhan, R.; Raybould, N.P.; Greenwood, D.; Salih, S.G.; Järlebark, L.; Burton, L.D.; Setz, V.C.M.; Cannell, M.B.; Soeller, C.; et al. Expression of the P2X2Receptor Subunit of the ATP-Gated Ion Channel in the Cochlea: Implications for Sound Transduction and Auditory Neurotransmission. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 8377–8388. [CrossRef]
- Vulchanova, L.; Arvidsson, U.; Riedl, M.; Wang, J.; Buell, G.; Surprenant, A.; A North, R.; Elde, R. Differential distribution of two ATP-gated channels (P2X receptors) determined by immunocytochemistry.. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1996, 93, 8063–8067. [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Bo, X.; Oglesby, I.; Ford, A.; Burnstock, G. Localization of ATP-gated P2X2 receptor immunoreactivity in the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res. 1998, 813, 390–397. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Vavra, V.; Svobodova, I.; Bendova, Z.; Vereb, G.; Zemkova, H. Potentiation of Inhibitory Synaptic Transmission by Extracellular ATP in Rat Suprachiasmatic Nuclei. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 8035–8044. [CrossRef]
- Lommen, J.; Stahr, A.; Ingenwerth, M.; Ali, A.A.H.; von Gall, C. Time-of-day-dependent expression of purinergic receptors in mouse suprachiasmatic nucleus. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 369, 579–590. [CrossRef]
- Loesch, A.; Miah, S.; Burnstock, G. Ultrastructural localisation of ATP-gated P2X2 receptor immunoreactivity in the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system.. J. Neurocytol. 1999, 28, 495–504. [CrossRef]
- Knott, T.K.; Velázquez-Marrero, C.; Lemos, J.R. ATP elicits inward currents in isolated vasopressinergic neurohypophysial terminals via P2X2 and P2X3 receptors. Pfl?gers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2005, 450, 381–389. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Bunstock, G.; He, C.; Xiang, Z. P2X receptors are differentially expressed on vasopressin- and oxytocin-containing neurons in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of rat hypothalamus. Histochem. 2008, 131, 29–41. [CrossRef]
- Knott, T.K.; Hussy, N.; Cuadra, A.E.; Lee, R.H.; Ortiz-Miranda, S.; Custer, E.E.; Lemos, J.R. Adenosine Trisphosphate Appears to Act via Different Receptors in Terminals Versus Somata of the Hypothalamic Neurohypophysial System. J. Neuroendocr. 2012, 24, 681–689. [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; He, C.; Burnstock, G. P2X5 receptors are expressed on neurons containing arginine vasopressin and nitric oxide synthase in the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res. 2006, 1099, 56–63. [CrossRef]
- Loesch, A.; Burnstock, G. Immunoreactivity to P2X6 receptors in the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system: an ultrastructural study with extravidin and colloidal gold-silver labelling. Neuroscience 2001, 106, 621–631. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.A.; Song, Z.; Stevens, W.; Sladek, C.D. Sustained stimulation of vasopressin and oxytocin release by ATP and phenylephrine requires recruitment of desensitization-resistant P2X purinergic receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 297, R940–R949. [CrossRef]
- Cuadra, A.E.; Custer, E.E.; Bosworth, E.L.; Lemos, J.R. P2X7 Receptors in Neurohypophysial Terminals: Evidence for their Role in Arginine-Vasopressin Secretion. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 229, 333–342. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Levy, A.; Lightman, S. Activation of specific ATP receptors induces a rapid increase in intracellular calcium ions in rat hypothalamic neurons. Brain Res. 1994, 641, 249–256. [CrossRef]
- Troadec, J.D., et al., ATP-evoked increases in [Ca2+]i and peptide release from rat isolated neurohypophysial terminals via a P2X2 purinoceptor. J Physiol, 1998. 511(Pt 1): p. 89-103.
- Song, Z.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Sladek, C.D. ATP increases intracellular calcium in supraoptic neurons by activation of both P2X and P2Y purinergic receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R423–R431. [CrossRef]
- Espallergues, J.; Solovieva, O.; Técher, V.; Bauer, K.; Alonso, G.; Vincent, A.; Hussy, N. Synergistic activation of astrocytes by ATP and norepinephrine in the rat supraoptic nucleus. Neuroscience 2007, 148, 712–723. [CrossRef]
- Sladek, C.D.; Song, Z. Diverse Roles of G-Protein Coupled Receptors in the Regulation of Neurohypophyseal Hormone Secretion. J. Neuroendocr. 2011, 24, 554–565. [CrossRef]
- Day, T.A.; Sibbald, J.R.; Khanna, S. ATP mediates an excitatory noradrenergic neuron input to supraoptic vasopressin cells. Brain Res. 1993, 607, 341–344. [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, H.; Bourque, C.W. P2 purinoceptor-mediated depolarization of rat supraoptic neurosecretory cells in vitro.. J. Physiol. 1995, 489, 805–811. [CrossRef]
- Ivetic, M.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Zemkova, H. P2X2 Receptor Expression and Function Is Upregulated in the Rat Supraoptic Nucleus Stimulated Through Refeeding After Fasting. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 284. [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Tsushima, H.; Matsuda, T. Antidiuretic Effects of ATP Induced by Microinjection into the Hypothalamic Supraoptic Nucleus in Water-Loaded and Ethanol-Anesthetized Rats. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 66, 445–450. [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, J.R.; Sladek, C.D. Purinergic and Adrenergic Agonists Synergize in Stimulating Vasopressin and Oxytocin Release. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8868–8875. [CrossRef]
- Buller, K.; Khanna, S.; Sibbald, J.; Day, T. Central noradrenergic neurons signal via atp to elicit vasopressin responses to haemorrhage. Neuroscience 1996, 73, 637–642. [CrossRef]
- Sperlagh, B.; Mergl, Z.; Juranyi, Z.; Vizi, E.; Makara, G. Local regulation of vasopressin and oxytocin secretion by extracellular ATP in the isolated posterior lobe of the rat hypophysis. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 160, 343–350. [CrossRef]
- Knott, T.K.; Marrero, H.G.; Custer, E.E.; Lemos, J.R. Endogenous ATP potentiates only vasopressin secretion from neurohypophysial terminals. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 217, 155–161. [CrossRef]
- Custer, E.E.; Knott, T.K.; Cuadra, A.E.; Ortiz-Miranda, S.; Lemos, J.R. P2X Purinergic Receptor Knockout Mice Reveal Endogenous ATP Modulation of Both Vasopressin and Oxytocin Release from the Intact Neurohypophysis. J. Neuroendocr. 2012, 24, 674–680. [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Ohkubo, J.; Katoh, A.; Ohno, M.; Ishikura, T.; Kakuma, T.; Yoshimatsu, H.; Murphy, D.; Ueta, Y. A c-fos-Monomeric Red Fluorescent Protein 1 Fusion Transgene is Differentially Expressed in Rat Forebrain and Brainstem after Chronic Dehydration and Rehydration. J. Neuroendocr. 2013, 25, 478–487. [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.S.; Green, E.W.; Zhao, Y.; van Ooijen, G.; Olmedo, M.; Qin, X.; Xu, Y.; Pan, M.; Valekunja, U.K.; Feeney, K.A.; et al. Peroxiredoxins are conserved markers of circadian rhythms. Nature 2012, 485, 459–464. [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, H.B.; Ji, L.L.; Cunningham, J.T. Role of superior laryngeal nerve and Fos staining following dehydration and rehydration in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 1053–1058. [CrossRef]
- Carreño, F.R.; Walch, J.D.; Dutta, M.; Nedungadi, T.P.; Cunningham, J.T. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Tyrosine Kinase B Pathway Mediates NMDA Receptor NR2B Subunit Phosphorylation in the Supraoptic Nuclei Following Progressive Dehydration. J. Neuroendocr. 2011, 23, 894–905. [CrossRef]
- Lucio-Oliveira, F.; Traslaviña, G.; Borges, B.; Franci, C. Modulation of the activity of vasopressinergic neurons by estrogen in rats refed with normal or sodium-free food after fasting. Neuroscience 2015, 284, 325–336. [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Gourine, A.; Spyer, K.; Barden, J.; Lawrence, A. Localisation of p2x2 receptor subunit immunoreactivity on nitric oxide synthase expressing neurones in the brain stem and hypothalamus of the rat: a fluorescence immunohistochemical study. Neuroscience 2003, 121, 411–419. [CrossRef]
- Cham, J.L.; Owens, N.C.; Barden, J.A.; Lawrence, A.J.; Badoer, E. P2X purinoceptor subtypes on paraventricular nucleus neurones projecting to the rostral ventrolateral medulla in the rat. Exp. Physiol. 2006, 91, 403–411. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Neto, H.; Ribeiro, I.; Moreira, T.; Yao, S.; Antunes, V. Purinergic P2 receptors in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus are involved in hyperosmotic-induced sympathoexcitation. Neuroscience 2017, 349, 253–263. [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Jiang, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Xia, C.; Guan, R.; Shen, L.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, D. Microglial P2X7 receptor in the hypothalamic paraventricular nuclei contributes to sympathoexcitatory responses in acute myocardial infarction rat. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 587, 22–28. [CrossRef]
- Jacques-Silva, M.C.; Bernardi, A.; Rodnight, R.; Lenz, G. ERK, PKC and PI3K/Akt Pathways Mediate Extracellular ATP and Adenosine-Induced Proliferation of U138-MG Human Glioma Cell Line. Oncology 2004, 67, 450–459. [CrossRef]
- Bains, J.S. and S.H. Oliet, Glia: they make your memories stick! Trends Neurosci, 2007. 30(8): p. 417-24.
- Gordon, G.R.; Iremonger, K.J.; Kantevari, S.; Ellis-Davies, G.C.; MacVicar, B.A.; Bains, J.S. Astrocyte-Mediated Distributed Plasticity at Hypothalamic Glutamate Synapses. Neuron 2009, 64, 391–403. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Neto, H.C.; Antunes, V.R.; Stern, J.E. Purinergic P2 and glutamate NMDA receptor coupling contributes to osmotically driven excitability in hypothalamic magnocellular neurosecretory neurons. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 3531–3547. [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, A.; Burnstock, G.; Gibb, A. The single-channel properties of purinergic P2X ATP receptors in outside-out patches from rat hypothalamic paraventricular parvocells. Pfl?gers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2001, 443, 115–122. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Neto, H.C.; Antunes, V.R.; Stern, J.E. ATP stimulates rat hypothalamic sympathetic neurons by enhancing AMPA receptor-mediated currents. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 114, 159–169. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bernstein, A.M.; Wong, A.; Lu, X.-H.; Khoja, S.; Yang, X.W.; Davies, D.L.; Micevych, P.; Sofroniew, M.V.; Khakh, B.S. P2X4 Receptor Reporter Mice: Sparse Brain Expression and Feeding-Related Presynaptic Facilitation in the Arcuate Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 8902–8920. [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Tsushima, H.; Matsuda, T. Antidiuretic effects of purinoceptor agonists injected into the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of water-loaded, ethanol-anesthetized rats. Neuropharmacology 1992, 31, 585–592. [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.C.; Bonagamba, L.G.; Machado, B.H. Modulation of arterial pressure by P2 purinoceptors in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of awake rats. Auton. Neurosci. 2010, 158, 79–85. [CrossRef]
- Mińczuk, K.; Schlicker, E.; Krzyżewska, A.; Malinowska, B. Angiotensin 1-7 injected into the rat paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus increases blood pressure and heart rate via various receptors. Neuropharmacology 2024, 266, 110279. [CrossRef]
- Busnardo, C.; Ferreira-Junior, N.C.; Cruz, J.C.; Machado, B.H.; Correa, F.M.A.; Resstel, L.B.M. Cardiovascular responses to ATP microinjected into the paraventricular nucleus are mediated by nitric oxide and NMDA glutamate receptors in awake rats. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 1411–1421. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Neto, H.C.; Yao, S.T.; Antunes, V.R. Purinergic and glutamatergic interactions in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus modulate sympathetic outflow. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 337–349. [CrossRef]
- Barad, Z.; Jacob-Tomas, S.; Sobrero, A.; Lean, G.; Hicks, A.-I.; Yang, J.; Choe, K.Y.; Prager-Khoutorsky, M. Unique Organization of Actin Cytoskeleton in Magnocellular Vasopressin Neurons in Normal Conditions and in Response to Salt-Loading. eneuro 2020, 7. [CrossRef]
- Balapattabi, K.; Little, J.T.; Farmer, G.E.; Cunningham, J.T. High salt loading increases brain derived neurotrophic factor in supraoptic vasopressin neurones. J. Neuroendocr. 2018, 30, e12639–e12639. [CrossRef]
- Sá, R.W.M.; Theparambil, S.M.; dos Santos, K.M.; Christie, I.N.; Marina, N.; Cardoso, B.V.; Hosford, P.S.; Antunes, V.R. Salt-loading promotes extracellular ATP release mediated by glial cells in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of rats. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 124, 103806. [CrossRef]
- Haam, J.; Halmos, K.C.; Di, S.; Tasker, J.G. Nutritional State-Dependent Ghrelin Activation of Vasopressin Neurons via Retrograde Trans-Neuronal–Glial Stimulation of Excitatory GABA Circuits. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 6201–6213. [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Cheng, G.; Bi, Q.; Lu, C.; Sun, Q.; Li, L.; Chen, N.; Hu, M.; Lu, H.; Xu, X.; et al. Microglia in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus sense hemodynamic disturbance and promote sympathetic excitation in hypertension. Immunity 2024, 57, 2030–2042.e8. [CrossRef]
- Kanjhan, R.; Housley, G.D.; Burton, L.D.; Christie, D.L.; Kippenberger, A.; Thorne, P.R.; Luo, L.; Ryan, A.F. Distribution of the P2X2 receptor subunit of the ATP-gated ion channels in the rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 407, 11–32. [CrossRef]
- Lommen, J.; Detken, J.; Harr, K.; von Gall, C.; Ali, A.A.H. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Purinergic P2 Receptors in the Mouse Hippocampus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8078. [CrossRef]
- Cipolla-Neto, J.; Skorupa, A.; Ribeiro-Barbosa, É.; Bartol, I.; Mota, S.R.; Afeche, S.; Delagrange, P.; Guardiola-Lemaitre, B.; Canteras, N. The Role of the Retrochiasmatic Area in the Control of Pineal Metabolism. Neuroendocrinology 1999, 69, 97–104. [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S., Y. Ishida, and S. Inouye, Circadian rhythms of adenosine triphosphate contents in the suprachiasmatic nucleus, anterior hypothalamic area and caudate putamen of the rat--negative correlation with electrical activity. Brain Res, 1994. 664(1-2): p. 237-40.
- Womac, A.D.; Burkeen, J.F.; Neuendorff, N.; Earnest, D.J.; Zoran, M.J. Circadian rhythms of extracellular ATP accumulation in suprachiasmatic nucleus cells and cultured astrocytes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 30, 869–876. [CrossRef]
- Hastings, M.H.; Maywood, E.S.; Brancaccio, M. The Mammalian Circadian Timing System and the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus as Its Pacemaker. Biology 2019, 8, 13. [CrossRef]
- McArthur, A.J.; Hunt, A.E.; Gillette, M.U. Melatonin Action and Signal Transduction in the Rat Suprachiasmatic Circadian Clock: Activation of Protein Kinase C at Dusk and Dawn*. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 627–634. [CrossRef]
- Marpegan, L.; Swanstrom, A.E.; Chung, K.; Simon, T.; Haydon, P.G.; Khan, S.K.; Liu, A.C.; Herzog, E.D.; Beaulé, C. Circadian Regulation of ATP Release in Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8342–8350. [CrossRef]
- Burkeen, J.F.; Womac, A.D.; Earnest, D.J.; Zoran, M.J. Mitochondrial Calcium Signaling Mediates Rhythmic Extracellular ATP Accumulation in Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8432–8440. [CrossRef]
- Dworak, M.; McCarley, R.W.; Kim, T.; Kalinchuk, A.V.; Basheer, R. Sleep and Brain Energy Levels: ATP Changes during Sleep. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9007–9016. [CrossRef]
- Buell, G.; Collo, G.; Rassendren, F. P2X Receptors: An Emerging Channel Family. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 2221–2228. [CrossRef]
- Terasawa, E.; Keen, K.L.; Grendell, R.L.; Golos, T.G. Possible Role of 5′-Adenosine Triphosphate in Synchronization of Ca2+ Oscillations in Primate Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Neurons. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 2736–2747. [CrossRef]
- Vastagh, C.; Rodolosse, A.; Solymosi, N.; Liposits, Z. Altered Expression of Genes Encoding Neurotransmitter Receptors in GnRH Neurons of Proestrous Mice. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 230. [CrossRef]
- Bjelobaba, I.; Nedeljkovic, N.; Subasic, S.; Lavrnja, I.; Pekovic, S.; Stojkov, D.; Rakic, L.; Stojiljkovic, M. Immunolocalization of ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (NPP1) in the rat forebrain. Brain Res. 2006, 1120, 54–63. [CrossRef]
- Inoue, N.; Hazim, S.; Tsuchida, H.; Dohi, Y.; Ishigaki, R.; Takahashi, A.; Otsuka, Y.; Yamada, K.; Uenoyama, Y.; Tsukamura, H. Hindbrain Adenosine 5-Triphosphate (ATP)-Purinergic Signaling Triggers LH Surge and Ovulation via Activation of AVPV Kisspeptin Neurons in Rats. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 2140–2152. [CrossRef]
- Constantin, S.; Klenke, U.; Wray, S. The Calcium Oscillator of GnRH-1 Neurons Is Developmentally Regulated. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3863–3873. [CrossRef]
- Bosma, M.M. Ion channel properties and episodic activity in isolated immortalized gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons. J. Membr. Biol. 1993, 136, 85–96. [CrossRef]
- Koshimizu, T.-A.; Tomic, M.; Koshimizu, M.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Identification of Amino Acid Residues Contributing to Desensitization of the P2X2 Receptor Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12853–12857. [CrossRef]
- Barnea, A.; Cho, G.; Katz, B.M. A putative role for extracellular ATP: Facilitation of67copper uptake and of copper stimulation of the release of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone from median eminence explants. Brain Res. 1991, 541, 93–97. [CrossRef]
- Zsarnovszky, A.; Bartha, T.; Frenyo, L.V.; Diano, S. NTPDases in the neuroendocrine hypothalamus: Possible energy regulators of the positive gonadotrophin feedback. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2009, 7, 63–63. [CrossRef]
- He, M.-L.; Gonzalez-Iglesias, A.E.; Tomic, M.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Release and extracellular metabolism of ATP by ecto-nucleotidase eNTPDase 1–2 in hypothalamic and pituitary cells. Purinergic Signal. 2005, 1, 135–144. [CrossRef]
- Allen-Worthington, K.; Xie, J.; Brown, J.L.; Edmunson, A.M.; Dowling, A.; Navratil, A.M.; Scavelli, K.; Yoon, H.; Kim, D.-G.; Bynoe, M.S.; et al. The F0F1 ATP Synthase Complex Localizes to Membrane Rafts in Gonadotrope Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 30, 996–1011. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.P.; Kratzmeier, M.; Levy, A.; A McArdle, C.; Poch, A.; Day, A.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Lightman, S.L. Evidence for a role of pituitary ATP receptors in the regulation of pituitary function.. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1995, 92, 5219–5223. [CrossRef]
- Tomić, M.; Jobin, R.M.; Vergara, L.A.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Expression of Purinergic Receptor Channels and Their Role in Calcium Signaling and Hormone Release in Pituitary Gonadotrophs. 1996, 271, 21200–21208. [CrossRef]
- Zemkova, H.; Balik, A.; Jiang, Y.; Kretschmannova, K.; Stojilkovic, S.S. Roles of Purinergic P2X Receptors as Pacemaking Channels and Modulators of Calcium-Mobilizing Pathway in Pituitary Gonadotrophs. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 1423–1436. [CrossRef]
- Gourine, A.V.; Melenchuk, E.V.; Poputnikov, D.M.; Gourine, V.N.; Spyer, K.M. Involvement of purinergic signalling in central mechanisms of body temperature regulation in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 2047–2055. [CrossRef]
- Klir, J.J.; McClellan, J.L.; Kluger, M.J. Interleukin-1 beta causes the increase in anterior hypothalamic interleukin-6 during LPS-induced fever in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1994, 266, R1845–R1848. [CrossRef]
- Alexander, V.G.; Gourine, A.V.; Dale, N.; Gourine, V.N.; Spyer, K.M. Fever in systemic inflammation: roles of purines. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 1011–22. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, V.B.; Hart, J.; Wewers, M.D. ATP-stimulated Release of Interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18 Requires Priming by Lipopolysaccharide and Is Independent of Caspase-1 Cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3820–3826. [CrossRef]
- Hide, I., et al., Extracellular ATP triggers tumor necrosis factor-alpha release from rat microglia. J Neurochem, 2000. 75(3): p. 965-72.
- Gourine, A.V.; Poputnikov, D.M.; Zhernosek, N.; Melenchuk, E.V.; Gerstberger, R.; Spyer, K.M.; Gourine, V.N. P2 receptor blockade attenuates fever and cytokine responses induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 139–145. [CrossRef]
- Gourine, A.V.; Dale, N.; Llaudet, E.; Poputnikov, D.M.; Spyer, K.M.; Gourine, V.N. Release of ATP in the central nervous system during systemic inflammation: real-time measurement in the hypothalamus of conscious rabbits. J. Physiol. 2007, 585, 305–316. [CrossRef]
- Seidel, B.; Bigl, M.; Franke, H.; Kittner, H.; Kiess, W.; Illes, P.; Krügel, U. Expression of purinergic receptors in the hypothalamus of the rat is modified by reduced food availability. Brain Res. 2006, 1089, 143–152. [CrossRef]
- Steculorum, S.M.; Timper, K.; Ruud, L.E.; Evers, N.; Paeger, L.; Bremser, S.; Kloppenburg, P.; Brüning, J.C. Inhibition of P2Y6 Signaling in AgRP Neurons Reduces Food Intake and Improves Systemic Insulin Sensitivity in Obesity. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 1587–1597. [CrossRef]
- Pollatzek, E.; Hitzel, N.; Ott, D.; Raisl, K.; Reuter, B.; Gerstberger, R. Functional expression of P2 purinoceptors in a primary neuroglial cell culture of the rat arcuate nucleus. Neuroscience 2016, 327, 95–114. [CrossRef]
- Wakamori, M.; Sorimachi, M. Properties of native P2X receptors in large multipolar neurons dissociated from rat hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. Brain Res. 2004, 1005, 51–59. [CrossRef]
- Steculorum, S.M.; Paeger, L.; Bremser, S.; Evers, N.; Hinze, Y.; Idzko, M.; Kloppenburg, P.; Brüning, J.C. Hypothalamic UDP Increases in Obesity and Promotes Feeding via P2Y6-Dependent Activation of AgRP Neurons. Cell 2015, 162, 1404–1417. [CrossRef]
- Sorimachi, M.; Ishibashi, H.; Moritoyo, T.; Akaike, N. Excitatory effect of ATP on acutely dissociated ventromedial hypothalamic neurons of the rat. Neuroscience 2001, 105, 393–401. [CrossRef]
- Kittner, H.; Franke, H.; Harsch, J.I.; El-Ashmawy, I.M.; Seidel, B.; Krügel, U.; Illes, P. Enhanced food intake after stimulation of hypothalamic P2Y1receptors in rats: modulation of feeding behaviour by extracellular nucleotides. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 2049–2056. [CrossRef]
- Burnstock, G.; Gentile, D. The involvement of purinergic signalling in obesity. Purinergic Signal. 2018, 14, 97–108. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Rong, P. Transcutaneous auricular vagal nerve stimulation inhibits hypothalamic P2Y1R expression and attenuates weight gain without decreasing food intake in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104. [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Sorimachi, M.; Akaike, N. Excitatory effects of ATP on rat dorsomedial hypothalamic neurons. Brain Res. 2004, 1009, 234–237. [CrossRef]
- Kittner, H.; Franke, H.; Fischer, W.; Schultheis, N.; Krügel, U.; Illes, P. Stimulation of P2Y1 Receptors Causes Anxiolytic-like Effects in the Rat Elevated Plus-maze: Implications for the Involvement of P2Y1 Receptor-Mediated Nitric Oxide Production. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002, 28, 435–444. [CrossRef]
- Vorobjev, V.S.; Sharonova, I.N.; Haas, H.L.; A Sergeeva, O. Expression and function of P2X purinoceptors in rat histaminergic neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 1013–1019. [CrossRef]
- Vorobjev, V.S.; Sharonova, I.N.; A Sergeeva, O.; Haas, H.L. Modulation of ATP-induced currents by zinc in acutely isolated hypothalamic neurons of the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 919–926. [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, K.; Ishibashi, H.; Akaike, N. ATP-induced inward current in neurons freshly dissociated from the tuberomammillary nucleus. J. Neurophysiol. 1994, 71, 868–873. [CrossRef]
- Wollmann, G.; Acuna-Goycolea, C.; Pol, A.N.v.D. Direct Excitation of Hypocretin/Orexin Cells by Extracellular ATP at P2X Receptors. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 94, 2195–2206. [CrossRef]
- Florenzano, F.; Viscomi, M.T.; Mercaldo, V.; Longone, P.; Bernardi, G.; Bagni, C.; Molinari, M.; Carrive, P. P2X2R purinergic receptor subunit mRNA and protein are expressed by all hypothalamic hypocretin/orexin neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 498, 58–67. [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.-H.; Role, L.W. Coordinate Release of ATP and GABA at In VitroSynapses of Lateral Hypothalamic Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 4794–4804. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




