Submitted:
22 April 2025
Posted:
22 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
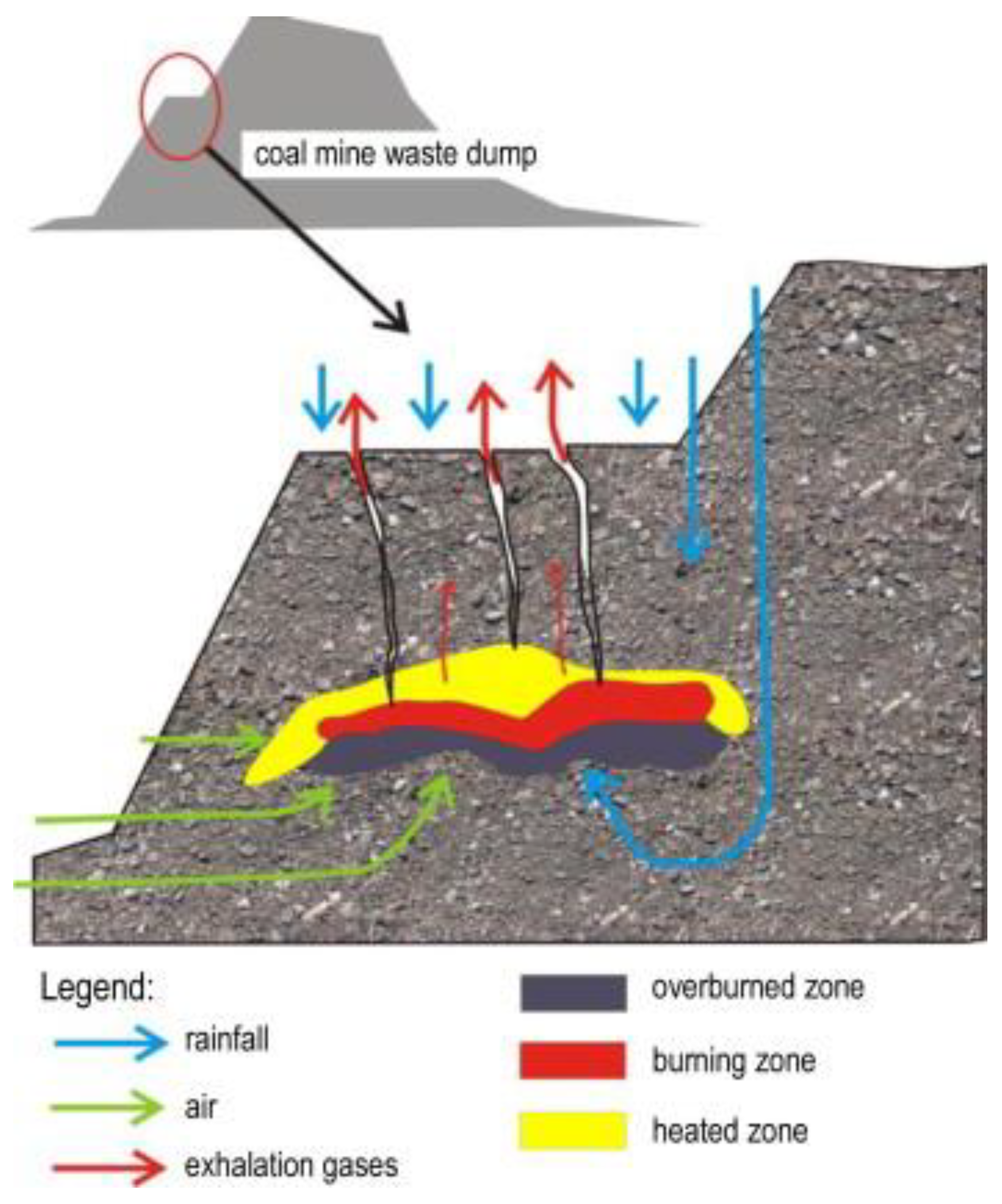
2. Mechanisms of Spontaneous Combustion in Mine Waste Dumps
- -
- Coal Rank: higher-rank coals (e.g., anthracite) have lower susceptibility to spontaneous combustion than low-rank coals (e.g., lignite). Coal is a porous material characterized by a complex structure with numerous active sites on its surface. These sites can continuously adsorb oxygen molecules from the surrounding air. During this process, coal undergoes low-temperature oxidation, which results in the gradual release of gaseous products and heat. Under certain conditions—such as restricted ventilation, high ambient temperatures, and sufficient coal mass—this heat can accumulate faster than it dissipates. As a result, the temperature of the coal gradually rises, potentially reaching the critical threshold at which spontaneous combustion occurs [47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54].
- -
- Particle Size: fine coal particles with increased surface area are more prone to oxidation. The particle size and porosity of coal significantly influence its specific surface area. A larger specific surface area enhances the contact between coal and oxygen, thereby increasing both the reaction rate and the efficiency of heat transfer. As the particle size decreases, the tendency for spontaneous heating increases—studies have shown that a reduction in particle size can raise this tendency by approximately 12–14% [14,52,55,56,57,58,59,60].
- -
- -
- Ambient conditions: high ambient temperatures and oxygen availability accelerate self-heating [19,73,74,75,76,77,78,79]. Additionally, external heat sources, such as mentioned wildfires, human activities such as removal/ reconstruction of the mine waste dump or wind flow, delivering air to the self-heating cells, can initiate combustion [21,80,81,82,83,84].
3. Thermal Effects on Geotechnical Properties
4. Monitoring and Mitigation Strategies Combating Spontaneous Combustion
4.1. Monitoring Techniques
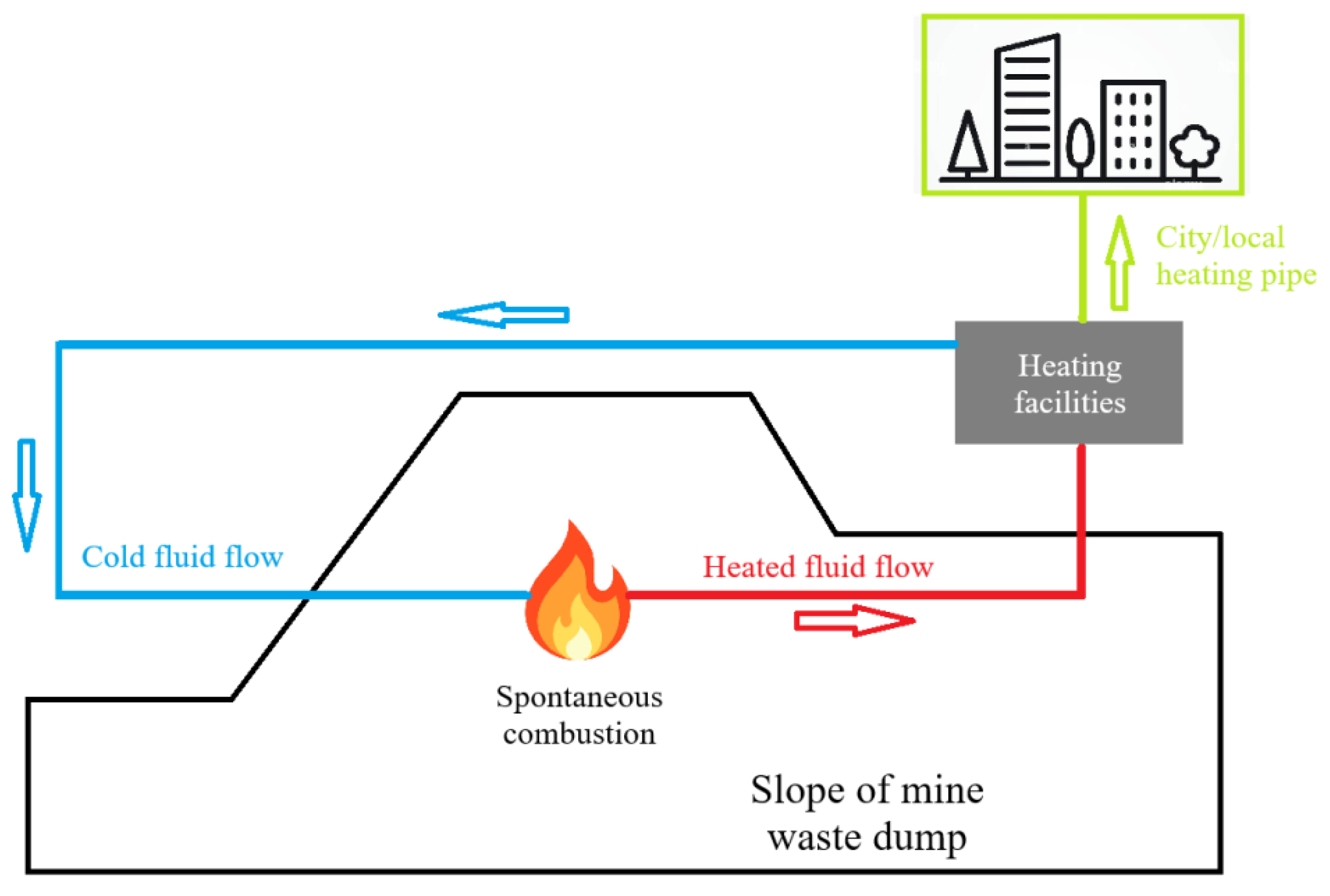
4.2. Mitigation Strategies
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NIK - Najwyższa Izba Kontroli (Supreme Audit Office). Securing and managing post-mining waste dumps (in Polish), 2019. Available online: https://www.nik.gov.pl/kontrole/P/18/067/.
- GUS - Główny Urząd Statystyczny (Central Statistical Office). Environmental Protection; Statistical Information and Studies. Statistical Publishing House: Warsaw, Poland, 2012.
- Wasilewski, S. Monitoring the thermal and gaseous activity of coal waste dumps. Environmental Earth Sciences 2020, 79, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, P. Risk Assessment Considerations in the Donetsk Basin. Mine Closure and Spoil Dumps. The Environment & Security Initiative (ENVSEC): Arendal, Norway, 2009.
- Querol, X.; Zhuang, X.; Font, O.; Izquierdo, M.; Alastuey, A.; Castro, I.; van Drooge, B.L.; Moreno, T.; Grimalt, J.O.; Elvira, J.; Cabañas, M.; Bartroli, R.; Hower, J.C.; Ayora, C.; Plana, F.; López-Soler, A. Influence of soil cover on reducing the environmental impact of spontaneous coal combustion in coal waste gobs: A review and new experimental data. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2011, 11, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.K.; Yu, M.G.; Lu, L.X. Experimental study on explosive mechanism of spontaneous combustion gangue dump. J. Coal Sci. Eng. 2009, 4, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, K.; Drebenstedt, C.; Zhao, J. Environment influences and extinguish technology of spontaneous combustion of coal gangue heap of Baijigou Coal Mine in China. Energy Procedia 2017, 136, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Yan, H.; Zhou, N.; Yao, Y.; Guo, Y. Underground Disposal of Coal Gangue Backfill in China. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokoupilová, P.; Sracek, O.; Losos, Z. Geochemical behaviour and mineralogical transformations during spontaneous combustion of a coal waste pile in Oslavany, Czech Republic. Mineralogical Magazine 2007, 71(4), 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chou, C.L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zheng, C. Trace element emissions from spontaneous combustion of gob piles in coal mines, Shanxi, China, International Journal of Coal Geology 2008, 73, 1, 52-62. [CrossRef]
- Žáček V.; Skála, R. Chapter 5 - Mineralogy of Burning-Coal Waste Piles in Collieries of the Czech Republic. Coal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective, 2015, pp. 109-159, Edited by Glenn B. Stracher, Anupma Prakash, Ellina V. Sokol. [CrossRef]
- Ciesielczuk, J. Chapter 16 - Coal Mining and Combustion in the Coal Waste Dumps of Poland. Coal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective, 2015, pp. 463-473, Editor(s): Glenn B. Stracher, Anupma Prakash, Ellina V. Sokol. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Nakano, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.D. Trace element partitioning behavior of coal gangue-fired CFB plant: Experimental and equilibrium calculation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15469–15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, S.; Bainbridge, N.; Carras, J.; Lilley, W.; Roberts, C.; Saghafi, A.; Williams, D. Chapter 1 - Spontaneous Combustion in Open-Cut Coal Mines: Australian Experience and Research. Coal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective, 2015, pp. 1-36, Editor(s): Glenn B. Stracher, Anupma Prakash, Ellina V. Sokol. [CrossRef]
- Sýkorová, I.; Kříbek, B.; Havelcová, M.; Machovič, V.; Špaldoňová, A.; Lapčák, L.; Knésl, I.; Blažek, J. Radiation- and self-ignition induced alterations of Permian uraniferous coal from the abandoned Novátor mine waste dump (Czech Republic). International Journal of Coal Geology 2016, 1, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y. liu Z.; Yan D. A review on the mechanism, risk evaluation, and prevention of coal spontaneous combustion in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2017, 24, 23453–23470. [CrossRef]
- Kříbek, B.; Sýkorová, I.; Veselovský, F.; Laufek, F.; Malec, J.; Knésl, I.; Majer, V. Trace element geochemistry of self-burning and weathering of a mineralized coal waste dump: The Novátor mine, Czech Republic. International Journal of Coal Geology 2017, 173, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onifade, M.; Genc, B. A review of spontaneous combustion studies – South African context. International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment 2018, 33(8), 527–547. [CrossRef]
- Onifade, M.; Genc, B. A review of research on spontaneous combustion of coal. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology 2020, 3, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádudvari, Á.; Fabiańska, M.J.; Misz-Kennan, M.; Ciesielczuk, J.; Kowalski, A. Investigation of organic material self-heating in oxygen-depleted condition within a coal-waste dump in Upper Silesia Coal Basin, Poland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2020, 27, 8285–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoliński, A.; Dombek, V.; Pertile, E.; Drobek, L.; Gogola, K.; Żechowska, S.; Magdziarczyk, M. An analysis of self-ignition of mine waste dumps in terms of environmental protection in industrial areas in Poland. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nádudvari, Á.; Abramowicz, A.; Fabiańska, M.; Misz-Kennan, M.; Ciesielczuk, J. Classification of fires in coal waste dumps based on Landsat, Aster thermal bands and thermal camera in Polish and Ukrainian mining regions. Int J Coal Sci Technol 2021, 8, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, A.; Rahmonov, O.; Chybiorz, R. Environmental Management and Landscape Transformation on Self-Heating Coal-Waste Dumps in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin. Land 2021, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, N.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Tong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Temperature Distribution Regularity and Dynamic Evolution of Spontaneous Combustion Coal Gangue Dump: Case Study of Yinying Coal Mine in Shanxi, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, K.; Koner, R. Mine Waste Dump Stability Monitoring Using the Combination of Drone Technology and 3D Numerical Modelling. In: Agnihotri, A.K., Reddy, K.R., Bansal, A. (eds) Sustainable Infrastructures. EGRWSE 2023. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, Springer, Singapore, 2025, vol. 355. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, B.; Shao, Y.; Tang, C. Experimental and numerical investigation of the effect of the urban heat island on slope stability. Bull Eng Geol Environ 2013, 72, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tong, F.; Tian, B.; Tian, W. Influence of atmospheric temperature on shallow slope stability. Environ Earth Sci 2019, 78, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, S.; Puig-Polo, C.; Lloret, A.; Vaunat, J.; Hürlimann, M. Effect of climate change on slope stability: a numerical analysis using predictions of the Catalan Pyrenees. A: International Symposium on Landslides. "International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering Online Library: 13th International Symposium on Landslides ( XIII ISL)". International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (ISSMGE), 2021, pp. 1-8.
- Thota, S.K.; Vahedifard, F. Stability analysis of unsaturated slopes under elevated temperatures, Engineering Geology 2021, 293, 106317. [CrossRef]
- Bai, G. X. Study on Thermodynamic Characteristics and Heat Transfer Method of Uncontrolled Fire in Coal Mine Gangue Mountain Spontaneous Combustion Based on System Dynamics. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 5953322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracko, T.; Zlender, B.; Jelusic, P. Implementation of Climate Change Effects on Slope Stability Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, Q.; Li, D.; Wang, N. Response of thermal conductivity of loess after high temperature in northern Shaanxi burnt rock area, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2023, 30, 33475–33484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakun-Mazor, D. Rock slope stability under temperature fluctuations. In M. Hassan (Ed.), Avantgarde reliability implications in civil engineering. Intech Open 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.R.; Chang, R.E.; Yang, Y.S.; Yeh, H.F. Environmental Temperature Effect on Hydraulic Behavior and Stability of Shallow Slopes. Environments 2023, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loche, M.; Scaringi, G. Temperature and shear-rate effects in two pure clays: Possible implications for clay landslides. Results in Engineering 2023, 20, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarropoulos, P.N.; Makrakis, N.; Tsompanakis, Y. Climate Change Impact on the Stability of Soil Slopes from a Hydrological and Geotechnical Perspective. GeoHazards 2024, 5, 1190–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loche, M.; Scaringi, G. Assessing the influence of temperature on slope stability in a temperate climate: A nationwide spatial probability analysis in Italy. Environmental Modelling & Software 2025, 183, 106217. [CrossRef]
- Abbate, A.; Longoni, L.; Ivanov, V.I.; Papini, M. Wildfire Impacts on Slope Stability Triggering in Mountain Areas. Geosciences 2019, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo Santos, L.M.; Correia, A.J.P.M.; Coelho, P.A.L.F. Post-wildfire slope stability effects and mitigation: a case study from hilly terrains with unmanaged forest. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wakai, A.; Costa, S. Bushfire effects on soil properties and post-fire slope stability: the case of the 2015 Wye River-Jamieson Track bushfire. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2024 [preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Juha, S.; Pertti, A.; Heikkilä, A.; Risto, T.; Iris, V.; Jyrki, I.; Mikael, R.; Kalevi, A. Risk and mitigation of self-heating and spontaneous combustion in underground coal storage. J Loss Prev Process Ind. 2012, 25, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ren, S.; Deng, J.; Shu, C. Comparative analysis of thermokinetic behavior and gaseous products between first and second coal spontaneous combustion. Fuel 2018, 227, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różański, Z. Fire hazard in coal waste dumps – selected aspects of the environmental impact IOPConference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2018, 174(1), 012013. [CrossRef]
- Moshood, O.; Bekir, G.; Abisola, R.; Andrew, M.; Thapelo, N. Influence of antioxidants on spontaneous combustion and coal properties. Process Safety Environ Protect. 2021, 148, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Division of coal spontaneous combustion stages and selection of indicator gases. PLoS One 2022, 17(4), e0267479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuna-Gwoździewicz, P. Emission of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from the Exhalation Zones of Thermally Active Mine Waste Dumps. Journal of Sustainable Mining 2013, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.; Choi, H.; Kim, S.; Yoo, J.; Chun, D.; Rhim, J.; Lim, J.; Lee, S. A comparison of spontaneous combustion susceptibility of coal according to its rank. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohalik, N.K.; Lester, E.; Lowndes, I.S. Review of experimental methods to determine spontaneous combustion susceptibility of coal—Indian context. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2017, 31, 301–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, A.; Sereshki, F.; Ataei, M. Presenting an engineering classification system for coal spontaneous combustion potential. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2017, 4, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Pramanik, S.; Dey, S.; Panigrahi, G.; Jana, DK. Fire monitoring in coal mines using wireless underground sensor network and interval type-2 fuzzy logic controller. Int J Coal Sci Technol 2019, 6(2), 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A. K.; Choudhury, D. Spontaneous Combustion in Relation to Drying of Low Rank Coal. International Journal of Coal Preparation and Utilization 2020, 42(5), 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádudvari, A.; Kozielska, B.; Abramowicz, A.; Fabiańska, M.; Ciesielczuk, J.; Cabała, J.; Krzykawski, T. Heavy metal- and organic-matter pollution due to self-heating coal-waste dumps in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin (Poland). Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 412, 125244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q. Numerical simulation study on coal spontaneous combustion: Effect of porosity distribution. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2023, 195, 472–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádudvari, A.; Krzykawski, T.; Jabłońska, M.; Fabiańska, M.; Skrzyńska, K.; Abramowicz, A.; Książek, M.; Ciesielczuk, J. Organic minerals in a self-heating coal-waste dump in Upper Silesia, Poland: Structure, formation pathways and environmental issues. International Journal of Coal Geology 2024, 281, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogola, K.; Rogala, T.; Magdziarczyk, M.; Smoliński, A. The Mechanisms of Endogenous Fires Occurring in Extractive Waste Dumping Facilities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wu, J.; Lian, C. Jianjun Wang, Jilai Rao, Renjun Feng, Yong Chen. Investigating the effect of coal particle size on spontaneous combustion and oxidation characteristics of coal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2022, 29, 16113–16122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Nie, B.; Kong, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yin, F.; Gong, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y. Experimental investigation of coal particle size on the kinetic properties of coal oxidation and spontaneous combustion limit parameters, Energy 2023, 270, 126890. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Amini, S.H. Systematic investigation on the effect of particle size on low-rank coal spontaneous combustion under various extrinsic conditions. Fuel 2023, 2, 126844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Mishra, D.P.; Mohalik, N.K.; Ray, S.K.; Pandey, J.K. Effect of depth and particle size on spontaneous combustion of coal in deep underground mines of Jharia coalfield. Journal of Sustainable Mining 2025, 24, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z. Influence of Different Particle Sizes on Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics of Coal. Solid Fuel Chem. 2025, 59, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadioğlu, Y.; Varamaz, M. The effect of moisture content and air-drying on spontaneous combustion characteristics of two Turkish lignitesa. Fuel 2003, 13, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamish, B.B.; Hamilton, G.R. Effect of moisture content on the R70 self-heating rate of Callide coal. International Journal of Coal Geology 2005, 64, 1–2, 133-138. [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Thiruppathiraja, C.; Kim, S.; Rhim, Y.; Lim, J.; Lee, S. Moisture readsorption and low temperature oxidation characteristics of upgraded low rank coal. Fuel Processing Technology 2011, 10, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliff, D.; Brady, D.; Watkinson, M. Developments in the management of spontaneous combustion in Australian underground coal mines. Paper presented at: Underground coal mines, 14 th Coal Operators’ Conference. Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 2014, Australian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy and Mine Managers’ Association of Australia; pp. 330–338.
- Arisoy, A.; Beamish, B. Mutual effects of pyrite and moisture on coal self-heating rates and reaction rate data for pyrite oxidation. Fuel 2015, 139, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Qin, B.; Xin, H.; Qin, X.; Chen, K. Exploring effect of waterimmersion on the structure and low-temperature oxidation ofcoal: a case study of Shendong long flame coal, China. Fuel 2018, 234, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, A.; Sereshki, F.; Ataei, M. The simultaneous effect of moisture and pyrite oncoal spontaneous combustion using CPT and R70 test methods. Rudarsko-Geološko-Naftni Zbornik 2019, 34(3), 1–12.
- Qu, Z.; Sun, F.; Gao, J.; Pei, T.; Qie, Z.; Wang, L.; Pi, X.; Zhao, G.; Wu, S. A new insight into the role of coal adsorbed water in low-temperature oxidation: Enhanced·OH radical generation. Combustion and Flame 2019, 208, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lv, C.; Bai, Z.; Deng, J.; Kang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Shu, C.M. Synergistic acceleration effect of coal spontaneous combustion caused by moisture and associated pyrite. Fuel 2021, 304, 121458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Xi, K.; Lu, L.; Li, X. Investigation of the influence of moisture during coal self-heating. Fuel 2022, A, 124581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Li, X.; Xi, K. Study on the reactivity of oxygen-containing functional groups in coal with and without adsorbed water in low-temperature oxidation. Fuel 2021, 304, 121454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhai, F.; Yao, D.; Deng, J.; Shu, P.; Duan, Z. Study on the Thermal Effects and Characteristics of Free Radical Evolution in Coal Oxidation at Different Moisture Content. Fire 2024, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y. Effects of pyrite on the spontaneous combustion of coal. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2015, 2, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Sasaki, K. Effects of temperature gradient and particle size on self-ignition temperature of low-rank coal excavated from inner Mongolia, ChinaR. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6190374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Effects of thermal boundary conditions on spontaneous combustion of coal under temperature-programmed conditions. Fuel 2021, 295, 120591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Bai, Z.; Deng, J.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y. Study on the dynamic evolution law of spontaneous coal combustion in high-temperature regions. Fuel 2022, 314, 123036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, H.; Huang, G.; Lu, B.; Yu, C.; Zou, J. Experimental study on the effect of room temperature pre-oxidized time on spontaneous combustion characteristics of coal. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 22035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Shi, X.; Jiang, L.; Deng, C.; Nian, J.; Gao, Y. Study on the Effect of External Air Supply and Temperature Control on Coal Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Miao, G.; Li, P.; Wang, G. Investigation of the effect of different distilled water, rainwater and seawater mass ratios on coal spontaneous combustion characteristics. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 900, 165878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghtaderi, B.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Kennedy, E.M. Effects of Wind Flow on Self-Heating Characteristics of Coal Stockpiles. Process Safety and Environmental Protection 2000, 6, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misz-Kennan, M.; Tabor, A. Chapter 15 - The Thermal History of Select Coal-Waste Dumps in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin, Poland. in: Coal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective. Editor(s): Glenn B. Stracher, Anupma Prakash, Ellina V. Sokol Elsevier, 2015, pp. 431-462. [CrossRef]
- Jendruś, R. Chemical and physical aspects of fires on coal waste dumps. Zeszyty Naukowe Wyższej Szkoły Technicznej w Katowicach 2016, 8, 131–149. [Google Scholar]
- Batugin, A.S.; Kobylkin, A.S.; Musina, V.R. Effect of geodynamic setting on spontaneous combustion of coal waste dumps. Eurasian Mining 2019, 2, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtacha-Rychter, K.; Smolinski, A. Coal oxidation with air stream of varying oxygen content and flow rate—Fire gas emission profile. Fire Saf. J. 2020, 116, 103182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, M.; Usher, B. Management of spontaneous combustion for metalliferous mines. In Proceedings: 10th International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage andIMWA 2015 (Chapter 2). 28 April – 1 May 2015. Santiago, Chile.
- Jiang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhou, B.; Cai, J. Study on spontaneous combustion characteristics of waste coal gangue hill. Combustion Science and Technology 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Lei, P.; Zhang, Y. Experimental investigation of temperature distribution and spontaneous combustion tendency of coal gangue stockpiles in storage. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotóns, V.; Tomás, R.; Ivorra, S.; Alarcón, J.C. Temperature influence on the physical and mechanical properties of a porous rock: San Julian's calcarenite. Engineering Geology 2013, 167, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Engineering Properties of Rocks, Second Edition, Butterworth-Heinemann, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, J.; Faramarzi, L.; Darbor, M.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Ferdosi, B. The effects of temperature on mechanical properties of rocks. International Journal of Mining and Geo-Engineering 2020, 54(2), 147-152. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, Z.; McLennan, J.; Gu, B.; Ta, X. Influence of temperature on physical and mechanical properties of a sedimentary rock: Coal measure mudstone. Thermal Science 2021, 25(1), 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksala, T. Numerical Modeling of Temperature Effect on Tensile Strength of Granitic Rock. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ibáñez, V.; Garrido, M.E.; Hidalgo Signes, C.; Basco, A.; Miranda, T.; Tomás, R. Thermal Effects on the Drilling Performance of a Limestone: Relationships with Physical and Mechanical Properties. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, W.H.; Scussiato, T.; Vagnon, F.; Ferrero, A.M.; Migliazza, M.R.; Ramis, J.; de Queiroz, P.I.B. On the Thermal Stresses Due to Weathering in Natural Stones. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarro, R.; Pérez-Rey, I.; Tomás, R.; Alejano, L.R.; Hernández-Gutiérrez, L.E.; Mateos, R.M. Effects of Wildfire on Rockfall Occurrence: A Review through Actual Cases in Spain. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Wang, M.K.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y. Evaluating the effects of temperature on soil hydraulic and mechanical properties in the collapsing gully areas of south China. CATENA 2022, 218, 106549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S. Temperature dependence of mechanical properties and damage evolution of hot dry rocks under rapid cooling. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2024, 2, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, B.; Luo, J.; Zhang, A.; Hao, G. Effect of Temperature Gradient on Compressive Strength and Strain Characteristics of Coarse-Grained Frozen Soil. Geofluids 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, P.; Guo, X.; Li, M.; Zhu, F. Physical and Mechanical Properties and Damage Mechanism of Sandstone at High Temperatures. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, G.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, X.; Luo, Y. The impact of high temperature on mechanical properties and behaviors of sandstone. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1322495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhlisin, M.; Khiyon, K.N. The Effects of Cracking on Slope Stability. Jour. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 91(6), 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, Q.; Liu, X. Slope Crack Propagation Law and Numerical Simulation of Expansive Soil under Wetting–Drying Cycles. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Shen, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Mei, G. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 189, 022014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalia, D.; Mochtar, I.B.; Mochtar, N.E. Application of a New Concept of Cracked Soils in Slope Stability Analysis with Heavy Rain and the Pattern of Cracks as the Governing Factors. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering. (Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering). Springer. 2020, 53, 601–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.; Sarkar, K.; Singh, A.K.; Chawla, S. Preliminary slope stability analysis and discontinuities driven susceptibility zonation along a crucial highway corridor in higher Himalaya, India. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 801–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarafza, M.; Akgün, H.; Ghazifard, A.; Asghari-Kaljahi, E.; Rahnamarad, J.; Derakhshani, R. Discontinuous rock slope stability analysis by limit equilibrium approaches – a review. International Journal of Digital Earth 2021, 14(12), 1918–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yu, J.; Yuan, R.; Wang, W.; Nikitas, N. Stability and failure mechanisms in three-dimensional cracked slope: Static and dynamic analysis. Computers and Geotechnics 2022, 144, 104626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Beiranvand, P.; Mohammadiasl, M.; Hassanvand, A. Influence of surface cracks on the stability of cracked soil slope. International Journal for Computational Civil and Structural Engineering 2022, 18(4), 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, L. Research on Fracture Mechanism and Stability of Slope with Tensile Cracks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Rai, R.; Singh, T.N. The Effect of Discontinuity Orientation and Thickness of the Weathered Layer on the Stability of Lesser Himalayan Rock Slope. J Geol Soc India 2022, 98, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Grasselli, G.; Liu, Q.; Tang, X.; Abdelaziz, A. The role of discontinuities in rock slope stability: Insights from a combined finite-discrete element simulation. Computers and Geotechnics 2022, 147, 104788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-E’Bayat, M.; Guner, D.; Sherizadeh, T.; Asadizadeh, M. Numerical Investigation for the Effect of Joint Persistence on Rock Slope Stability Using a Lattice Spring-Based Synthetic Rock Mass Model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xiu, Z.; Han, J.; Meng, F.; Wang, F.; Ji, H. Characterization and Stability Analysis of Rock Mass Discontinuities in Layered Slopes: A Case Study from Fushun West Open-Pit Mine. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Abdullah, R.A.; Ullah, A.; Sa’ari, R.; Mahmood, S.; Rehman, H.; Rehman, S.; Sari, M. Discontinuity characterization for slope stability assessment using combined aerial photogrammetry, and geophysics approach. Nat Hazards 2025, 121, 3581–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Gao, L.; Qi, Y.; Hu, H. Exploring Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics and Structural Disparities of Coal Induced by Igneous Rock Erosion. Fire 2024, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbeshie, A.A.; Abugre, S.; Atta-Darkwa, T.; Awuah, R. A review of the effects of forest fire on soil properties. J. For. Res. 2022, 33, 1419–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q. Experimental Study on Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics of Large Coal Particles after Soaking. ACS Omega 2022, 15, 13102–13111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudzińska, A. The Effect of Pore Volume of Hard Coals on Their Susceptibility to Spontaneous Combustion. Journal of Chemistry 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, T.; Wang, J.G.; Gao, F.; Ju, Y.; Jiang, C. A thermally sensitive permeability model for coal-gas interactions including thermal fracturing and volatilization. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 32, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qin, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhao, J. Experimental research on dynamic variation of permeability and porosity of low-rank inert-richcoal under stresses. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 28124–28135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xueqing, Z.; Wen, Y.; Haihui, X.; Sherong, H.; Yu, S. Pore structure and its impact on susceptibility to coal spontaneous combustion based on multiscale and multifractal analysis. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, M.H.; Shi, S.; Zhang, T. Influence of Thermal Cracking Permeability Enhancement in Spontaneously Combustible Coalbed Methane Reservoirs on the Characteristics of Coal Spontaneous Combustion. Combustion Science and Technology 2021, 195(2), 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Huang, Q.; Shi, Q. Research on the evolution of pore and fracture structures during spontaneous combustion of coal based on CT 3D reconstruction. Energy 2022, 260, 125033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Liang, Y.; Tian, F.; Guo, B. Analytical Prediction of Coal Spontaneous Combustion Tendency: Pore Structure and Air Permeability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, H.; Wu, G. Study on the Effect of Pore Evolution on the Coal Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics in Goaf. Fire 2024, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, J.; Kumar, D.; Mishra, R.; Mohalik, N.; Khalkho, A.; Singh, V. Application of thermography technique for assessment and monitoring of coal mine fire: A special reference to Jharia coal field, Jharkhand, India. International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2013, 1, 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Wen, H.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X. A method for evaluating the spontaneous combustion of coal by monitoring various gases. Process Safety and Environmental Protection 2019, 2019, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Wang, D.; Cao, K.; Si, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Treatment of smouldering coal refuse piles: an application in China. Environmental Technology 2019, 41(23), 3105–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewińska-Preis, L.; Szram, E.; Fabiańska, M.J.; Nádudvari, A.; Misz-Kennan, M.; Abramowicz, A.; Kruszewski, Ł.; Kita, A. Selected ions and major and trace elements as contaminants in coal-waste dump water from the Lower and Upper Silesian Coal Basins (Poland). Int J Coal Sci Technol 2021, 8, 790–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewski, S.; Skotniczny, P. Mining waste dumps—modern monitoring of thermal and gas activities. Min Resour Manag Gospodarka Surowcami Mineralnymi 2015, 31(1):155–182. [CrossRef]
- Jendruś, R. Environmental Protection in Industrial Areas and Applying Thermal Analysis to Coal Dumps. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies 2017, 26(1), 137-146. [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, A.; Chybiorz, R. Fire detection based on a series of thermal images and point measurements: the case study of coal-waste dumps. Int Arch Photogram Rem Sens Spatial Inf Sci XLII-1/W2,9–12, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Garvie, A.; Donaldson, K.; Williams, B.; Chapman, J. A demonstration of the cessation of spontaneous combustion in a coal overburden spoil pile', in AB Fourie & M Tibbett (eds), Mine Closure 2019: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Mine Closure, Australian Centre for Geomechanics, Perth, 2019, pp. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fang, X.; Du, F.; Tan, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, C. Three-dimensional distribution and oxidation degree analysis of coal gangue dump fire area: A case study. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 772, 145606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádudvari, Á.; Abramowicz, A.; Ciesielczuk, J.; Cabała, J.; Misz-Kennan, M.; Fabiańska, M. Self-Heating Coal Waste Fire Monitoring and Related Environmental Problems: Case Studies from Poland and Ukraine. J. Environ. Geogr. 2021, 14, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, X.; Luo, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, J. Detection of Spontaneous Combustion Areas of Coal Gangue Dumps and Comprehensive Governance Technologies: A Case Study. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R. Coal fire mapping from satellite thermal IR data—A case example in Jharia Coalfield, Jharkhand, India. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. 2006, 2, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xia, Q. An integrated methodology for monitoring spontaneous combustion of coal waste dumps based on surface temperature detection. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 122, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hao, M.; Wang, Y.; Dang, L.; Guo, Y. Multi-Scale Coal Fire Detection Based on an Improved Active Contour Model from Landsat-8 Satellite and UAV Images. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 449. [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; She, J.; Liu, G.; Ma, D.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, B. Coal fire identification and state assessment by integrating multitemporal thermal infrared and InSAR remote sensing data: A case study of Midong District, Urumqi, China, ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2022, 190, 144-164. [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, O.; Defer, D.; Antczak, E.; Duthoit, B. Infraredthermography applied to spontaneous combustionmonitoring of coal tips. At Conference: 7th International Conference of Quantitative Infrared ThermographyAt: Rhode, St Génèse, Belgium 2004. [CrossRef]
- Nádudvari, Á. Thermal mapping of self-heating zones on coal waste dumps in Upper Silesia (Poland)—A case study. International Journal of Coal Geology 2014, 128, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Cui, X.; Sun, G.; Qian, A.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W. Approach of detecting coal fires by unmanned aerial vehicle thermal infrared remote sensing technology. Saf. Coal Mines 2017, 12, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Hu, Z. A review of UAV monitoring in mining areas: Current status and future perspectives. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2019, 6, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, S.; Shao, H.; Liao, Q.; Fan, Y. Experimental study of the effects of stacking modes on the spontaneous combustion of coal gangue. Process Safety and Environmental Protection 2019, 123, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, X.; Luo, Z.; Guan, T. Application of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) thermal infrared remote sensing to identify coal fires in the Huojitu coal mine in Shenmu City, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 1, 13895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoro, A.C.; Fernandes, J.; Santos, P.; Duarte, L.; Gonçalves, J.A.; Flores, D. Monitoring of soil movement in a self-burning coal waste pile with UAV imagery. Earth Resources and Environmental Remote Sensing/GIS Applications XI, International Society for Optics and Photonics 2020, 11534, p. 115340. [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, R.; Wang, D.; Zhong, X. Three-dimensional-imaging thermal surfaces of coal fires based on UAV thermal infrared data. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2021, 42(2), 672–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Hao, M.; Yan, S.; Dang, L.; Peng, B. Accuracy assessment and scale effect investigation of UAV thermography for underground coal fire surface temperature monitoring. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2021, 102, 102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, R.; Wang, D.; Zhong, X. Three-dimensional-imaging thermal surfaces of coal fires based on UAV thermal infrared data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 2, 672–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q,; Hu, Z. Monitoring and early warning the spontaneous combustion of coal waste dumps supported by unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing. Coal Science and Technology 2023,51, 2, 412−421. [CrossRef]
- Anghelescu, L.; Diaconu, B.M. Advances in Detection and Monitoring of Coal Spontaneous Combustion: Techniques, Challenges, and Future Directions. Fire 2024, 7, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Yang, T.; Deng, R.; Shao, H. Monitoring Burning Coal Gangue Dump Based on the 3-D Thermal Infrared Model," in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2024, 17, 8979-8995. [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Ma, G.; Li, L.; Li, J. An Optimized Detection Approach to Subsurface Coalfield Spontaneous Combustion Areas Using Airborne Magnetic Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesjak, J.; Calderini, D.F. Increased night temperature negatively affects grain yield, biomass and grain number in Chilean quinoa. Frontiers in Plant Science 2017, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, R.; Gullström, M.; Mangora, M.M.; Mtolera, M.S.P.; Björk, M. High midday temperature stress has stronger effects on biomass than on photosynthesis: A mesocosm experiment on four tropical seagrass species. Ecology and Evolution 2018, 8(9), 4508–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, N.; Li, W.; Gu, X.; Liu, Y. Biomass estimation for semiarid vegetation and mine rehabilitation using worldview-3 and sentinel-1 SAR imagery. Remote Sensing 2019, 11(23), 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.H.; Jhou, Y.J.; Wu, C.W.; Chang, Y.S. Growth, physiological, and antioxidant characteristics in green and red Perilla frutescens varieties as affected by temperature-and water-stressed conditions. Scientia Horticulturae 2020, 274, 109682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, A.K.; Rahmonov, O.; Fabiańska, M.J.; Nádudvari, Á.; Chybiorz, R.; Michalak, M. Changes in soil chemical composition caused by self-heating of a coal-waste dump. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4340–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Ding, B.; Yang, X. Vegetation growth status as an early warning indicator for the spontaneous combustion disaster of coal waste dump after reclamation: An unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Yang, X.; Ding, B.; Chen, C. Monitoring potential spontaneous combustion in a coal waste dump after reclamation through UAV RGB imagery-based on alfalfa aboveground biomass (AGB). Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2728–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Lin, Z.; Ren, H. Assessing Potential Spontaneous Combustion of Coal Gangue Dumps after Reclamation by Simulating Alfalfa Heat Stress Based on the Spectral Features of Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, L. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-Based Vegetation Restoration Monitoring in Coal Waste Dumps after Reclamation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, N.; Moolman, C. Develop methods to prevent and control spontaneous combustion associated with mining and subsidence. Coaltech, 2003.
- Smith, M.A.; Glasser, D. Spontaneous combustion of carbonaceous stockpiles. Part 2. Factors affecting the rate of the low-temperature oxidation reaction. Fuel 2005, 84, 1161-1170. [CrossRef]
- Pone, J.D.N.; Hein, K.A.A.; Stracher, G.B.; Annegarn, H.J.; Finkelman, R.B.; Blake, D.R.; McCormack, J.K.; Schroder, P. The spontaneous combustion of coal and its by-products in the Witbank and Sasolburg coalfields of South Africa. International Journal of Coal Geology 2007, 72, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, H.; Uludag, S.; Chabedi, K. Prevention and Control of Spontaneous Combustion, Best Practice Guidelines for Surface Coal Mines in South Africa. CoalTech Research Association, 2011.
- Misz-Kennan, M.; Gardocki, M.; Tabor, A. Chapter 13 - Fire Prevention in Coal Waste Dumps: Exemplified by the Rymer Cones, Upper Silesian Coal Basin, Poland. in: Coal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective. Editor(s): Glenn B. Stracher, Anupma Prakash, Ellina V. Sokol Elsevier, 2015, pp. 349-385. [CrossRef]
- Gałaś, A.; Abramowicz, A.; Kot-Niewiadomska, A.; Misz-Kennan, M.; Gałaś, S. Sozology instead of ecology, other direction for ecosystem services and environmental protection-on the example of the Silesian–Kraków region, Southern Poland. GeoJournal 2024, 89, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carras, J.N.; Day, S.J.; Saghafi, A.; Williams, D.J. Greenhouse gas emissions from low-temperature oxidation and spontaneous combustion at open-cut coal mines in Australia. International Journal of Coal Geology 2009, 78, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, S.J.; Carras, J.N.; Fry, R.; Williams, D.J. Greenhouse gas emissions from Australian open-cut coal mines: contribution from spontaneous combustion and low-temperature oxidation. Environ Monit Assess 2010, 166, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, S.T. Anatomy of Subsurface Coal Fires: A Case Study of a Coal Fire on the Southern Ute Indian Reservation. PhD dissertation. Stanford University, US, 2011, pp. 190.
- Kim, AG. United States Bureau of Mines: study and control of fires in abandoned mines and waste banks. In Coal and Peat Fires: A Global Perspective. Coal - Geology and Combustion, eds. Stracher GB, Prakash A, Sokol EV. Vol 1. Oxford, UK: Elsevier, 2011, pp. 267−305. [CrossRef]
- Kuenzer, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.;, Jia, Y.; Dech, S. Coal fires revisited: the Wuda Coal Field in the aftermath of extensive coal fire research and accelerating extinguishing activities. International Journal of Coal Geology 2012, 102, 75−86. [CrossRef]
- Singh, RVK. Spontaneous heating and fire in coal mines. Procedia Engineering 2013, 62, 78−90. [CrossRef]
- Sloss, L.L. Assessing and Managing Spontaneous Combustion of Coal. London, UK: IEA Clean Coal Centre. 2015.
- Calizaya, F.; Nelson, M.G.; Bateman, C.; Jha, A. Pressure Balancing Techniques to Control Spontaneous Combustion. 2016 SME Annual Conference and Expo: the future for Mining in a Data-Driven World, Phoenix, Arizona, USA. Englewood, Colorado, USA: Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration Inc. 2016, pp. 261−64.
- Ozdogan, M.V.; Turan, G.; Karakus, D,.; Onur, A.H.; Konak G.; Yalcin, E. Prevention of spontaneous combustion in coal drifts using a lining material: a case study of the Tuncbilek Omerler underground mine, Turkey. Journal of the Southern African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy 2018, 188(2), 149−56. [CrossRef]
- Versilov, S.O.; Vil'bitskaya N.A.; Kurdashov V.M. Increase of Efficiency of Extinguishing of Rock Dumps on the Surface of Coal Mines. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 272, 022236. [CrossRef]
- Hallman, DS. A review of coal mine fire extinguishment methods. Emergency Management Science and Technology 2024, 4, e005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Ren, W.; Wang, D.; Song, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Application of three-phase foam to fight an extraordinarily serious coal mine fire. International Journal of Coal Geology. [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Tang, X.; Hu, X. Controlling coal fires using the three-phase foam and water mist techniques in the Anjialing Open Pit Mine, China. Natural Hazards 2015, 75(2), 1833−1852. [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.V.; Kuprin, D.S.; Abduragimov, I.M.; Kuprin, G.N.; Serebriyakov, E., Vinogradov, V.V. Silica foams for fire prevention and firefighting. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2016, 8(1), 294−301. [CrossRef]
- Rabajczyk, A.; Zielecka, M.; Gniazdowska, J. Application of nanotechnology in extinguishing agents. Materials 2022, 15, 8876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallman, D.S. Foamed Backfilling for Combatting Mine Fires. Environmental Geotechnics 2022, 9(5), 310−317. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qin, B.; Shi, Q.; Hao, M.; Shao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, Z. Study on the adsorption of cement particles on surfactant and its effect on the characteristics of inorganic curing foam for prevention of coal spontaneous combustion in a goaf. Fuel 2023, 333(2), 126407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, H.; Chen, C.; Guo, J.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, D. Research Status and Development Trend of Coal Spontaneous Combustion Fire and Prevention Technology in China: A Review. ACS Omega 2024, 20, 1727–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, C.J.R.; Gupta, R.; Morris, J.; McCartney, J.S. Municipal solid waste landfills as geothermal heat sources. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2013, 19, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmi, G.; Zarrella, A.; Zuanetti, A.; De Carli, M. Use of Municipal Solid Waste Landfill as Heat Source of Heat Pump. Energy Procedia 2016, 101, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Sun, M.; Ducoste, J.J.; Benson, C.H.; Luettich, S.; Castaldi, M.J.; Barlaz, M.A. Heat Generation and Accumulation in Municipal Solid Waste Landfills. Environmental Science & Technology 2017, 51, 21, 12434-12442. [CrossRef]
- Utami, A.; Aji, N.; Fadyah, A.; Ghifari, A.; Anam, M.B.; Ramadhani, S.; Rasyid, F.H.; Maulana, R.R. Geothermal energy solid waste management: Source, type of waste, and the management. 2nd INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON EARTH SCIENCE, MINERAL, AND ENERGY 2019, 2245, 1, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. [CrossRef]
- DOE, EERE. Waste-to-Energy from Municipal Solid Wastes, 2019. Available online: energy.gov/eere/bioenergy /articles/waste-energy-municipal-solid-wastes-report.
- Manjunatha, G.S.; Chavan, D.; Lakshmikanthan, P.; Swamy, R.; Kumar, S. Estimation of heat generation and consequent temperature rise from nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins and fats in municipal solid waste landfills in India. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 707, 135610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, C.; Denney, J.; Mbonimpa, E.G.; Slagley, J.; Bhowmik, R. A review on municipal solid waste-to-energy trends in the USA. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2020, 119, 109512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.L.; Onnen, M.T.; Yeşiller, N.; Kopp, K.B. Heat energy potential of municipal solid waste landfills: Review of heat generation and assessment of vertical extraction systems. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2022, 167, 112835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B. Thermal properties of municipal solid waste components and their relative significance for heat retention, conduction, and thermal diffusion in landfills. Journal of Environmental Management 2023, B, 116651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadario, N.; Gabriel Filho, L.R.A.; Cremasco, C.P.; Santos, F.A.d.; Rizk, M.C.; Mollo Neto, M. Waste-to-Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste: Global Scenario and Prospects of Mass Burning Technology in Brazil. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiński, S.; Dębowski, M. Municipal Solid Waste as a Renewable Energy Source: Advances in Thermochemical Conversion Technologies and Environmental Impacts. Energies 2024, 17, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardane, V.; Anggraini, V.; Tran, MV.; Mirzababaei, M; Syamsir, A. Heat mitigation in basal compacted clay liners in municipal solid waste landfills. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2024, 31, 63262–63286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
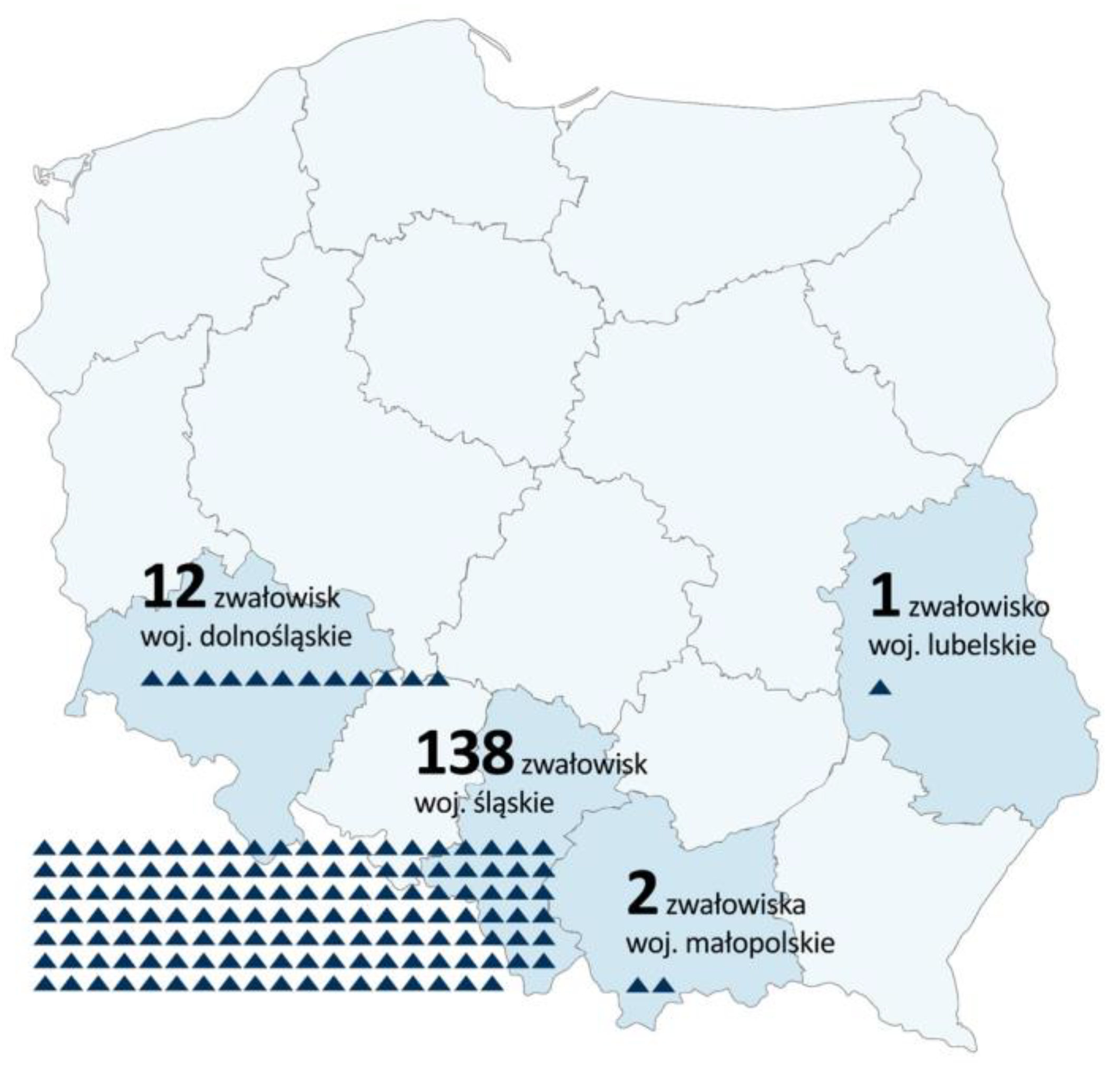
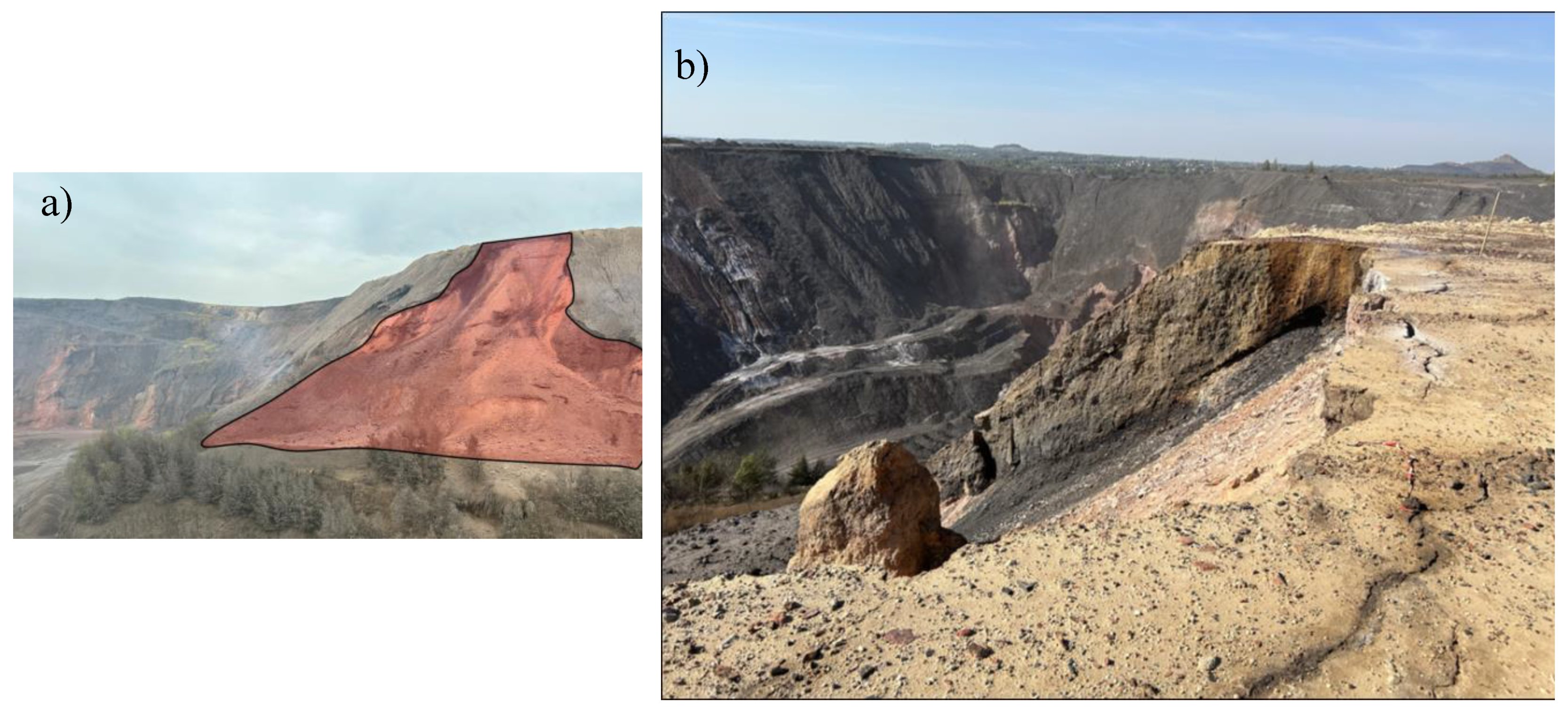


| FoS | Slope angle, ° | |||
| 23 | 26.6 | 31 | ||
| Crack orientation and length | No cracks/fractures | 1.45 | 1.19 | 1.0 |
| 6 m long, the dip angle close to the slope surface | 1.18 | 1.04 | 0.98 | |
| 12 m long, the dip angle close to the slope surface | 1.03 | 0.86 | 0.83 | |
| 6 m, dip angle of 90° (vertical) | 1.33 | 1.09 | 1.0 | |
| 12 m, dip angle of 90° (vertical) | 1.27 | 1.05 | 0.89 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





