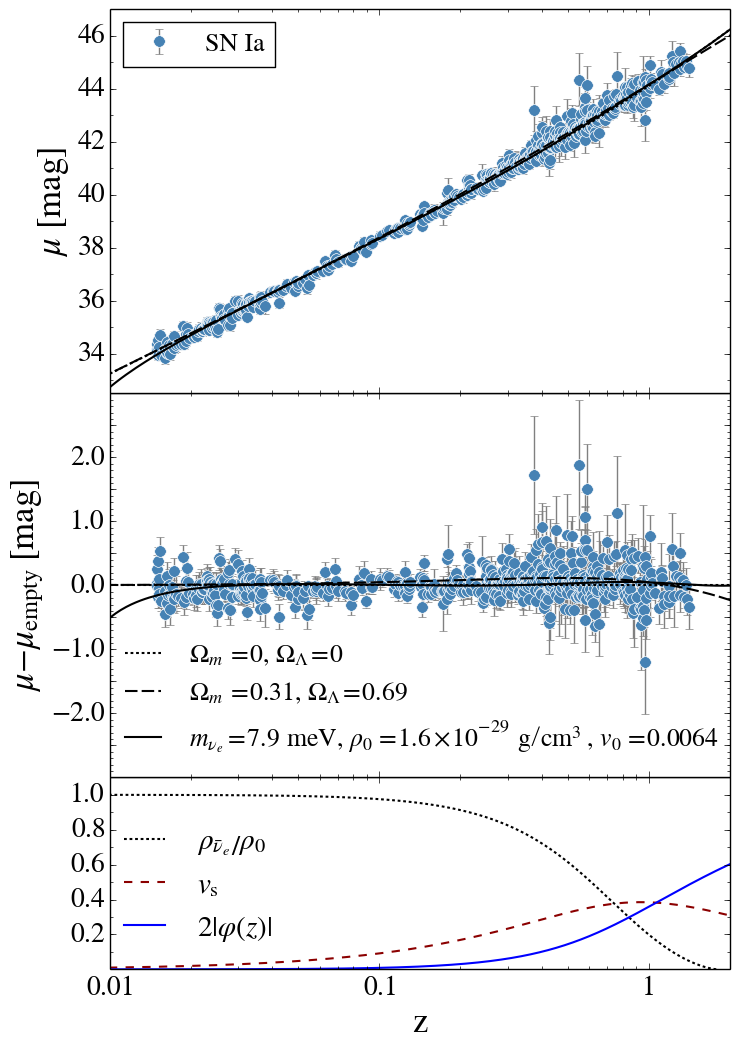
A new model of cosmology is proposed, where the state of high energy density commonly associated with the big bang is generated by the collapse of an antineutrino star that has exceeded its Chandrasekhar limit. To allow the first neutrino stars and antineutrino stars to form naturally from an initial quantum vacuum state, matter and antimatter are assumed to gravitationally repel. In this scenario, a degenerate antineutrino star in effective hydrostatic equilibrium has a density that is similar to the dark energy density of the ΛCDM model. When viewed from the core, such a star could today accelerate matter radially and emit the isothermal cosmic microwave background radiation, which addresses the horizon and flatness problems. This model and the ΛCDM model are in similar quantitative agreement with supernova distance measurements. The presented model is also in qualitative agreement with observed large-scale anisotropy and inhomogeneity, which distinguishes it from the ΛCDM model.