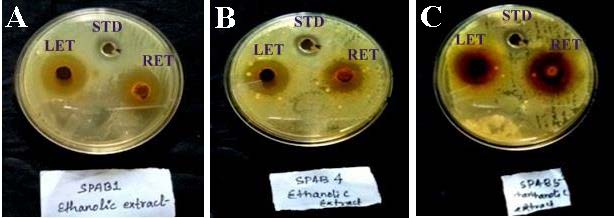
Globally, the gastroenteritis or diarrhoea has become a more significant problem today due to infection caused by foodborne/ waterborne pathogen Vibrio cholera. In this concern, an investigation was carried out to evaluate the vibriocidal potential of the different solvent extracts of leaf and rhizome of Maranta arundinacea under in vitro condition. For this, aqueous, methanolic, ethanolic and hexane extracts of both leaf and rhizome of M. arundinacea were tested against the pre-isolated strains of Vibrio cholerae such as SPAB1, SPAB4 and SPAB5 by agar well diffusion and minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) method. All the solvent extracts of both leaf and rhizome were found to be active against the tried strains of V. cholera however, ethanolic extract showed maximum inhibitory effect against SPAB1 strain with an inhibition zone of 26.23 ± 0.53 mm (MIC of 80.00 ± 10.06 µg/ ml) and 24.27 ± 0.12 mm (MIC of 100.00 ± 12.82 µg/ ml) in rhizome and leaf samples, respectively. Then, the effectiveness was followed in SPAB4 and SPAB5 however, it was not much more significant to that of SPAB1. Therefore, it was suggested that the rhizome and leaf extracts which proved to be potentially effective can be used as the natural alternative for the treatment of diarrhoea caused by Vibrio infection.