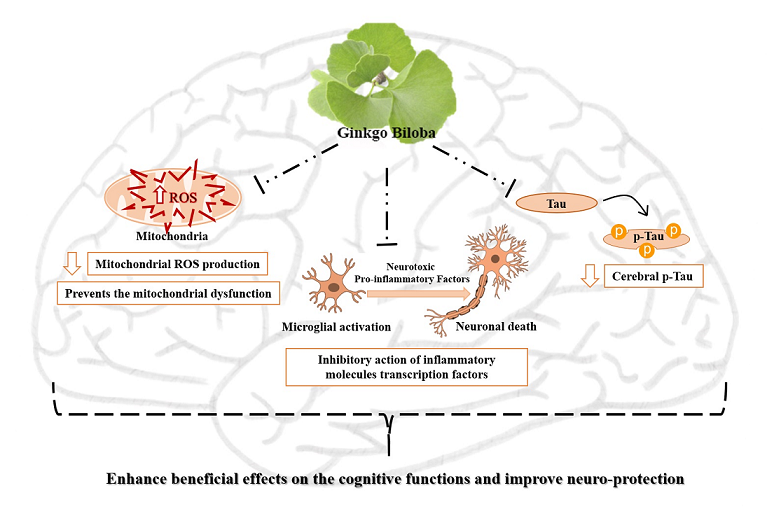
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and mild dementia are a clinically relevant health problem in the elderly and Alzheimer's disease being the most common neurodegenerative disorder. Furthermore, MCI and mild dementia are characterized by a deterioration of cognitive function and their diagnosis is mainly based on cognitive examination and, the prognosis of the disease seems to be an essential reason for the diagnosis, because there is a high risk of cognitive decline in the two syndromes. This review describes the effectiveness of Ginkgo biloba (EGb761®) leaf extract for the treatment of dementia syndrome and EGb761® combination therapy with other medications for symptomatic dementia. Tebonin® is a drug of plant origin based on the active ingredient “Ginkgo biloba”. This drug has shown encouraging results, improving cognitive function, neuropsychiatric disorders and consequent reduction of caregiver stress and maintenance of autonomy in patients with age-related cognitive decline, MCI and mild dementia. Nowadays, there is little evidence to support the efficacy of EGb761® combination therapy with anti-dementia drugs and, therefore, more evidence is needed to evaluate the role of EGb761® in mixed therapy.