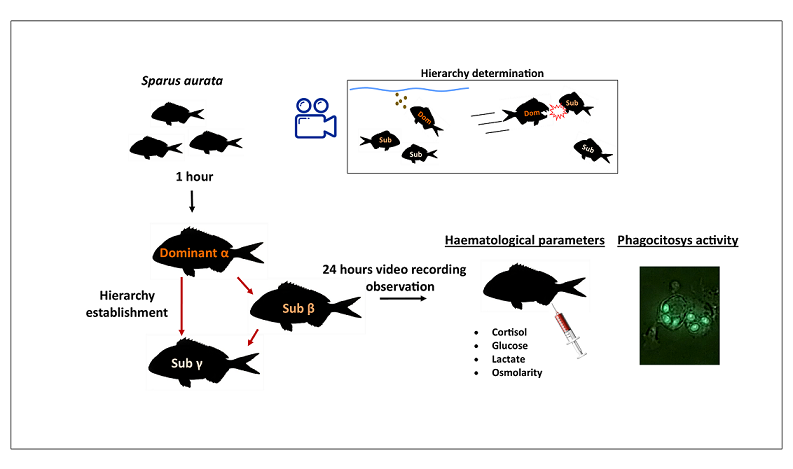
Abstract: Social stress can affect the ability of the fish to respond to various stressors, such as pathogens or environmental variations. In this paper, the effects of social stress on gilt-head bream (Sparus aurata) were investigated. To study the effects of physiological stress, we evaluated biochemical and cellular parameters as cortisol, glucose, lactate, osmolarity and phagocytosis 24 hours after the establishment of social hierarchy. Social hierarchy was determined and characterised by behavioural observation (aggressive acts and feeding order) of the specimens (dominant “α”, subordinate “β” and “γ”). After the establishment of the social hierarchy, we observed that the levels of plasma cortisol and other biochemical stress markers (glucose and lactate) were higher in subordinate individuals than in dominant ones. In addition, the modulation of phagocytic activity of the peritoneal cavity cells (PEC) demonstrated that social stress appeared to affect the immune response. At last, principal component analysis clearly separated the subordinate fish groups from the dominant groups based on stress markers and phagocytic activity of the peritoneal exudates cells.