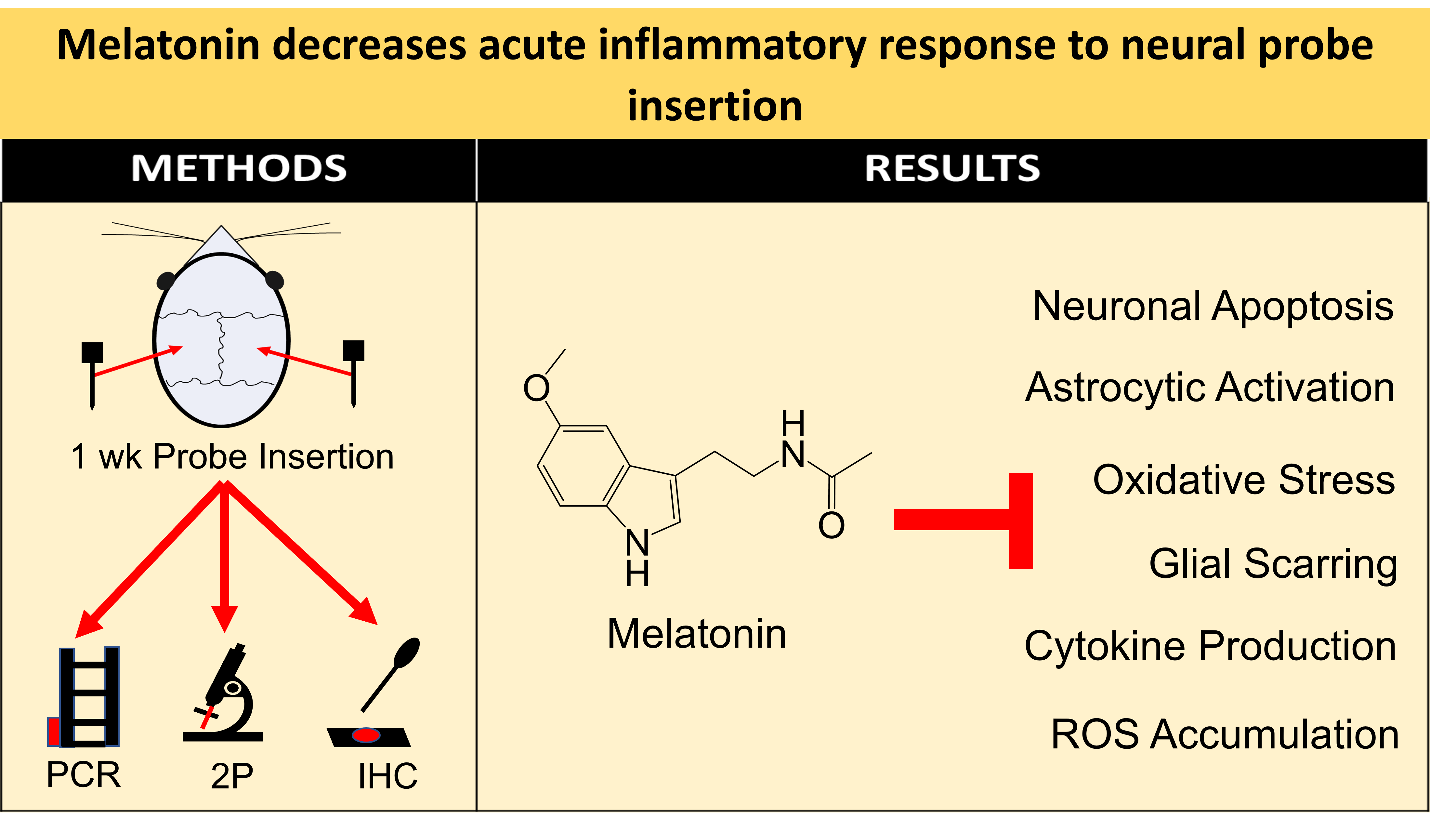
Neural electrode insertion trauma impedes the recording and stimulation capabilities of numerous diagnostic and treatment avenues. Implantation leads to the activation of inflammatory markers and cell types, which is detrimental to neural tissue health and recording capabilities. Oxidative stress and inflammation at the implant site have been shown to decrease with chronic administration of antioxidant melatonin at week 16, but its effects on the acute landscape have not been studied. To assess the effect of melatonin administration in the acute phase, specifically the first week post-implantation, we utilized histological and q-PCR methods to quantify cellular and molecular indicators of inflammation and oxidative stress as well as two-photon microscopy to track the microglial responses in real-time. Histological results indicate that melatonin effectively maintained neuron density surrounding the electrode, inhibited accumulation and activation of microglia, astrocytes, and reduced oxidative tissue damage. The expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α and IL-6, were significantly reduced in melatonin-treated animals. Additionally, microglia encapsulation of the implant surface was inhibited by melatonin as compared to control animals following implantation. Our results combined with previous research suggest that melatonin is a particularly suitable drug for modulating inflammatory activity around neural electrode implants both acutely and chronically, translating to more stable and reliable interfaces.