1. Introduction
Today’s concepts of space and time were coined by Albert Einstein. His theory of SR [
1] is based on a flat spacetime with an indefinite (not positive-semidefinite) distance function. SR is often interpreted in Minkowski spacetime (MS) because Hermann Minkowski’s geometric interpretation [
4] was very successful in explaining relativistic effects. Predicting the lifetime of muons [
5] is one example that demonstrates the power of SR. General relativity (GR) [
2] includes gravitation and is based on a curved spacetime with a pseudo-Riemannian metric. GR is supported, for example, by the deflection of starlight during a solar eclipse [
6] and by the high accuracy of GPS. Quantum field theory [
7] unifies classical field theory, SR, and quantum mechanics, but not GR.
We call our theory “Euclidean relativity” and build it on these three postulates: (1) In Euclidean spacetime (ES), all energy is moving radially away from an origin at the speed of light. (2) The laws of physics have the same form in each observer’s “reality” (orthogonal projections of ES to his proper 3D space and to his proper flow of time). (3) All energy is “wavematter” (electromagnetic wave packet and matter in one). Our first postulate is stronger than the second SR postulate. The speed of light is both absolute and universal. Everything is moving through ES at the speed . Moving through MS at the speed is a pointless concept as objects at rest in 3D space would then move in time at one second per one second. Our second postulate is the same as the first SR postulate, except that there is no limitation to inertial frames and that we distinguish ES from an observer’s reality. Our third postulate makes relativity compatible with quantum mechanics.
We aren’t the first physicists to investigate ER: In the early 1990s, Montanus already described ES [
8]. He also formulated electrodynamics and gravitational lensing in ES [
9]. Almeida compared trajectories in MS with trajectories in ES [
10]. Gersten demonstrated that the Lorentz transformation in SR becomes an SO(4) rotation in ER [
11]. van Linden studied energy and momentum in ES [
12]. Pereira claimed a “hypergeometrical universe”, where matter is made from deformed space [
13]. Yet none of these models identifies the issue in Einstein’s concept of time, and they all run into paradoxes (discussed in
Section 4) because they don’t project ES to an observer’s reality. Only Machotka added a “boundedness postulate” to avoid paradoxes [
14], but it sounds rather contrived. We overcome such paradoxes by limiting reality in our
second postulate.
An observer’s reality is only created by projecting ES orthogonally to his proper 3D space and to his proper flow of time.
It is instructive to compare our theory with Newton’s physics and Einstein’s physics. In Newton’s physics, all objects are moving through 3D space as a function of an independent time. The speed of matter is
. In Einstein’s physics, all objects are moving through 4D spacetime given by 3D space and time, where time is linked to, but different from space (time is measured in seconds). The speed of matter is
. In our theory, all objects are moving through 4D ES given by four symmetric distances (all distances are measured in light seconds), where time is only a subordinate quantity. The 4D speed of everything is
. Kant’s philosophy [
15] was inspired by Newton’s physics. Our theory will have a huge impact on physics and philosophy. Replacing the concept of time is probably the biggest intervention since the formulation of quantum mechanics.
2. An Issue in Einstein’s Concept of Time
Today’s concept of time traces back to Albert Einstein. We thus call it “Einstein time”
. § 1 of SR [
1] is an instruction of how to synchronize two clocks at the positions P and Q. At “P time”
, an observer sends a light pulse from P towards Q. At “Q time”
, it is reflected at Q towards P. At “P time”
, it is back at P. Both clocks synchronize if
In § 3 of SR [
1], Einstein derives the Lorentz transformation for two systems moving relative to each other at a constant speed. The coordinates
of an event in a system K are transformed to the coordinates
of that event in a system K’ by
where the system K’ is moving relative to K in the axis
and at the constant speed
. The factor
is the Lorentz factor.
Equations (1) and (2a–d) are correct for one observer R in K describing his reality. Because of the relativity postulate, we can write down a similar set of equations for one observer B in K’ describing his reality. So, all theories that are consistent with SR (such as electrodynamics) will be valid for either observer. SR works well for each observer describing his reality, but Einstein time has an issue. It arranges all events in the universe in a 1D line on my watch, yet neither cosmology nor quantum mechanics care about my watch. Einstein time is egocentric: It considers the watch of an observer (“ego”) the center of time, just as the geocentric model considers Earth (“geo”) the center of the solar system. This analogy (and the pun “ego/geo”) should give food for thought to all skeptics.
In order to find an alternative concept of time, we now take a closer look at the effect of time dilation. In § 4 of SR [
1], Einstein derives that there is a dilation in Einstein time: The clock of an observer B in K’ is slow with respect to the clock of an observer R in K by the factor
. Time dilation has been experimentally confirmed. So, any alternative concept must recover it and the same
.
Now watch out as the next sentences are our entrance to ER: Most physicists aren’t aware that there are two variables in which this time dilation can show up for the same (!) observer R. Einstein and Minkowski assumed that the clock of B is slow with respect to R in
(proper time of B), which belongs to B.
Yet, as we explain next, it can also be slow with respect to R in (proper time of R), which belongs to R.
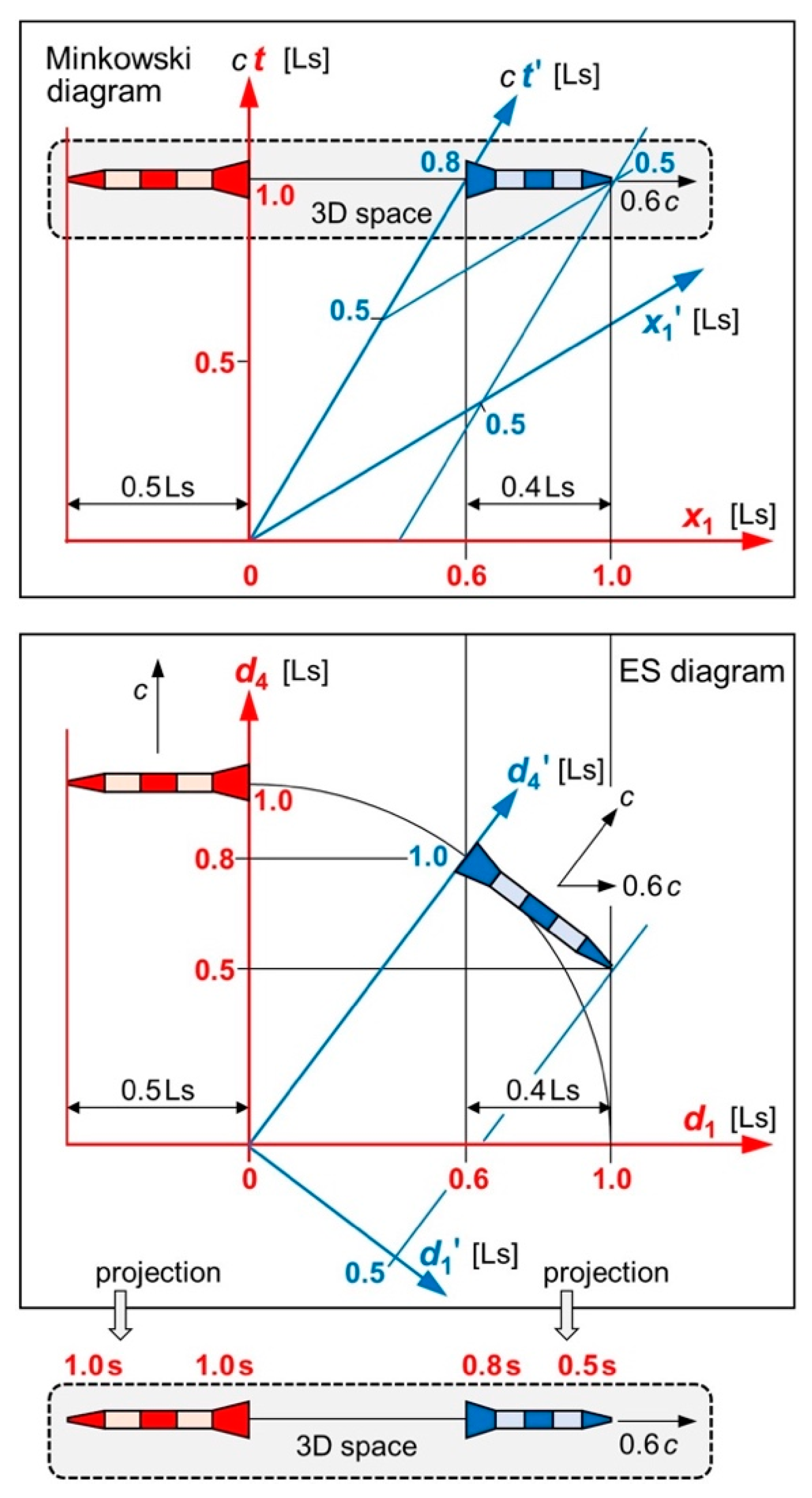
Figure 1 top illustrates a Minkowski diagram of two identical rockets—except for their color—with a proper length of 0.5 Ls (light seconds). They started at the origin and move relative to each other in the axis
at a speed of
. We choose these very high values to visualize relativistic effects. We show that moment when the red rocket has moved 1 s in
. Observer R is in the rear end of the red rocket r. His/her view is the red frame with the coordinates
and
. Observer B is in the rear end of the blue rocket b. His/her view is the blue frame with the coordinates
and
. Only for visualization do we draw our rockets in 2D although their width is in the dimensions
or
(not displayed in
Figure 1). For R, the blue rocket contracts to 0.4 Ls
because of length contraction. For B, the rear end of the blue rocket has moved only 0.8 s in
because of time dilation.
It is well known that simultaneity isn’t absolute in SR. In
Figure 1 top, R synchronized all clocks inside r and b according to § 2 of SR [
1]:
. In this diagram, clocks inside b display a different time for B:
and
. Clocks that are synchronized for R aren’t synchronized for B. Yet we must assume that B would also synchronize all clocks inside r and b. To depict the reality of B, we must draw a second Minkowski diagram (not shown here) where clocks inside r aren’t synchronized for R. Since we need two diagrams, we can’t take the measurements of R and B seriously
at once. In SR, there is no “at once for both”. Each observer claims
just for himself that all clocks are synchronized.
In experimental physics, we are used to take measurements of all observers seriously at once. We can do so if we claim:
Each observer measures clocks inside his own rocket as synchronous, while he measures all moving clocks as asynchronous. We get to this “Euclidean time” by replacing the asymmetric axes
and
with symmetric distances
and
, and by rotating rocket b thereafter. We end up with an ES diagram (
Figure 1 center), in which “0.8” and “0.5” show up in
(which belongs to R). In MS, R measures the time of R in
and the time of B in
. In ES, R uses the same variable
for measuring the time of R and for measuring the time of B.
In either case (MS and ES), the clock of B is slow with respect to R. In MS, it is slow with respect to R in
(which belongs to B). In ES, it is slow with respect to R in
related to
(which belongs to R).
Be aware that R can never measure himself. He either calculates from Equation (2d), or else he observes that a clock which was moving relative to him is slow in thereafter. So, R just can’t tell whether the clock of B is running slow with respect to himself in or else in . Common sense tells us that two identical clocks run the same whether or not they move relative to each other. This is true only in ES where Euclidean time is absolute. Only by projecting to does the clock of B become slow with respect to R.
3. Introducing Euclidean Time and Euclidean Spacetime
The indefinite distance function in MS can be rewritten as a Euclidean metric.
where
for
and
. The roles of Einstein time
(proper time of one observer) and Euclidean time
(proper time of all objects/observers) have switched: All invariants are now based on
, while the fourth dimension in all vectors is now based on
. The switch affects all equations of physics. Equation (3b) must not be confused with the “Wick rotation” which replaces
by
, but keeps
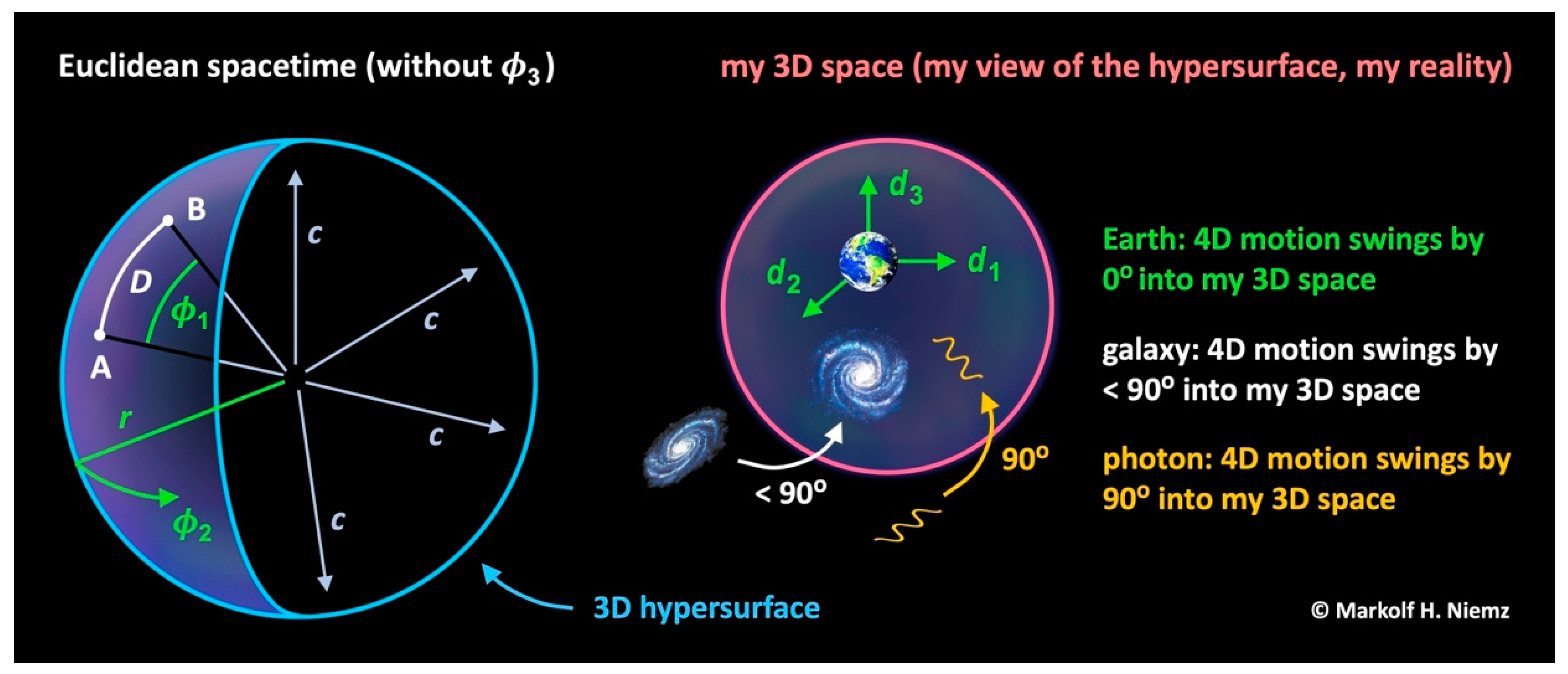
as the invariant. Because of the Euclidean metric in Equation (3b), we can imagine that we live in the 3D hypersurface of a 4D hypersphere. This hypersphere is expanding radially from some absolute point O at the speed of light. For each observer, the Cartesian ES coordinates
are projected to his proper 3D space.
The 3D hypersurface is absolute, but the proper 3D space is relative.
We define
as the radius
of the hypersphere divided by
. Euclidean time isn’t egocentric, but universal, because its origin O is an absolute point! We define a 4D vector “flow of time”
, where
points from O to an object. The absolute value
of this vector is universal, but its 4D orientation is unique. For each object, time flows in a unique 4D direction related to its position. The coordinates
are also projected to an observer’s proper flow of time.
Euclidean time is absolute, but the proper flow of time is relative.
Equation (4a) tells us that Euclidean time is only a subordinate quantity derived from covered distance. Time isn’t fundamental to physics as already claimed by other authors [
16]. Distance and speed are more significant than time. So, we suggest to choose new units for speed and time.
should be specified in its own new unit to be given.
should be specified in “light seconds per this new unit”. Be aware that these new units won’t affect how clocks are running. So, all of our clocks will measure Euclidean time, too.
ES is an open 4D manifold with a Euclidean metric. We can describe ES either in four hyperspherical coordinates (), where each is a hyperspherical angle and is radial distance from an origin—or in four symmetric, Cartesian coordinates (), where each is axial distance from an origin. and all are “spatial and temporal distance in one”. Distance isn’t covered as a function of independent time. Only by covering distance is Euclidean time passing by. All distances are measured in light seconds (Ls) by odometers. There is no need to calibrate the odometers because light seconds in ES are absolute. The symmetry of all supports the idea of natural units. “Space” and “time” in everyday life are only interpretations of distance.
ES serves as a “master reference frame”: Each observer’s reality is created by projecting ES orthogonally to his proper 3D space and to his proper flow of time. Einstein time is the proper time of just one observer. Euclidean time is the proper time of all objects/observers. In SR and GR, the object’s proper time deviates from the observer’s proper time. In ER, all objects/observers share the same time and the same 3D hypersurface, but each object/observer has a proper flow of time and a proper 3D space.
Hyperspherical coordinates are good for grasping the big picture in cosmology. We claim that a huge amount of energy was injected into ES at some point that we take as its origin O. Right here our first postulate comes into play: In ES, all energy is moving radially away from the origin O at the speed of light. Hyperspherical coordinates have the great benefit of reducing all that is ever happening to one formula: All energy is covering radial distance
which, divided by Euclidean time
, is equal to the speed
. So, this formula is the Theory of Everything (TOE), yet in hyperspherical coordinates.
One may argue that Equation (4b) couldn’t be a TOE as it wouldn’t address the dynamics in 3D space. We disagree. In hyperspherical coordinates, there is indeed no motion within the hypersurface because everything is moving radially at the same speed. Yet, as we will demonstrate in
Section 5.6, all dynamics in 3D space is pure geometry.
Matching the symmetry simplifies physics. Equation (4b) describes all action in hyperspherical coordinates.
Cartesian ES coordinates are good for projecting ES to an observer’s reality. They are calculated from hyperspherical coordinates by
In our ES diagrams, we often choose Cartesian coordinates in which an object starts moving from some origin P other than O. Because of the ES symmetry, we are free to label all four axes. We always assume: coincides with an object’s proper flow of time. Below our ES diagrams, we project ES to an observer’s proper 3D space. Here we are free to label the axis that we project to. We assume: There is relative motion only in and . So, our Cartesian ES diagrams display and , while our 3D projections display .
The projections of
to
and to
are orthogonal:
are equal to
(this is why there is no need to replace the concept of space), while there is
only for clocks moving in the axis
.
All odometers measure , and all clocks measure , but the distance covered by a moving clock is projected to an observer’s axis . This is why all moving clocks are slow in his flow of time (which is his Einstein time). The Cartesian 4D velocity
has four components
. From Equation (3b), we get
4. Geometric Effects in Euclidean Spacetime
We consider the same two rockets as in
Figure 1. Observer R (or B) in the rear end of the red rocket r (or else blue rocket b) uses
(or else
) as coordinates.
span the 3D space of R, and
span the 3D space of B.
relates to the Einstein time of R, and
relates to the Einstein time of B. The rockets move relative to each other in either 3D space at the constant speed
(
Figure 2 bottom). As just explained, all 3D motion is in
(or else
). Our ES diagrams (
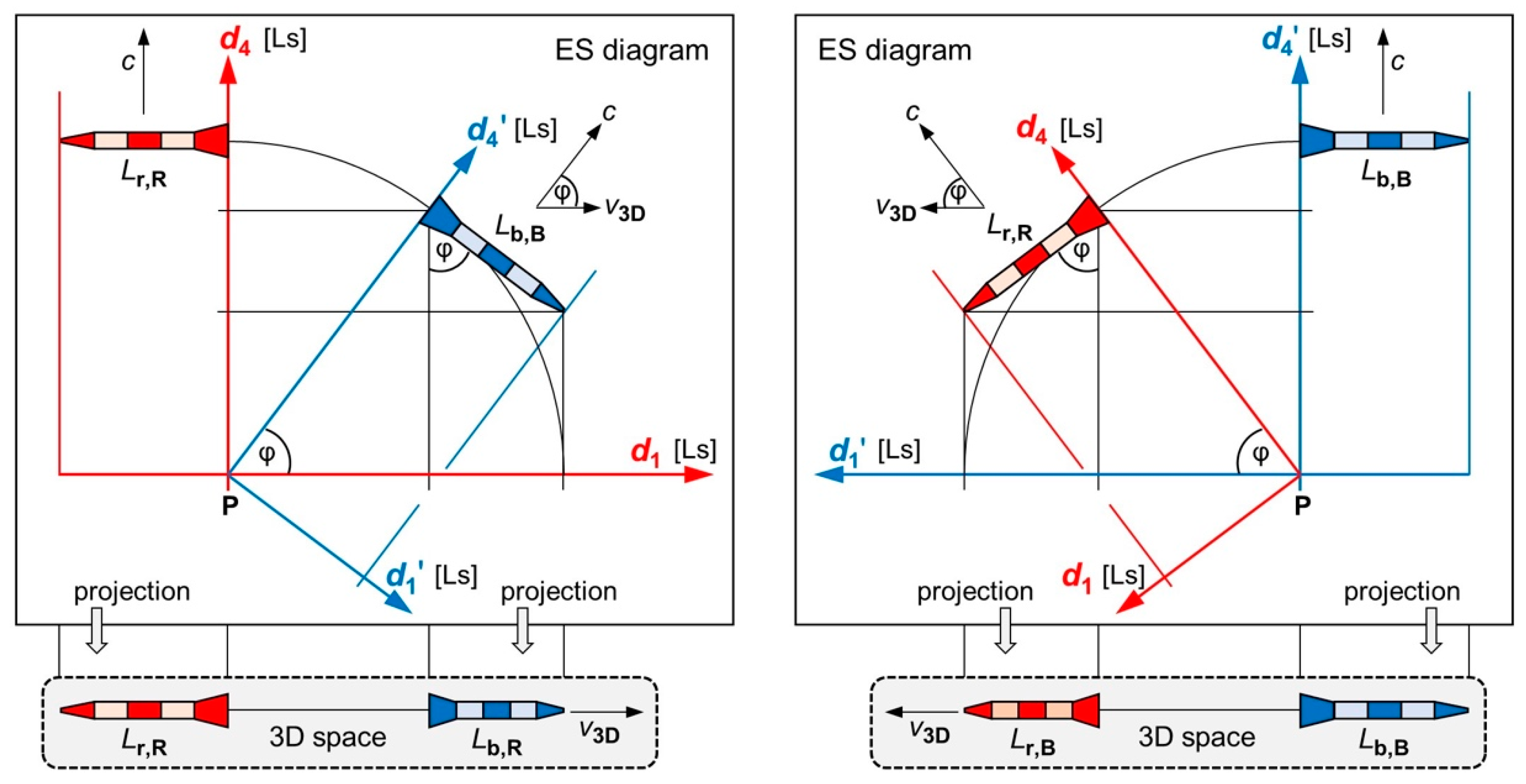
Figure 2 top) must fulfill these requirements: (1) According to our first postulate, both rockets must move at the speed
. (2) Our second postulate must be fulfilled. (3) Both rockets started at the same point P. There is only one way of how to draw our ES diagrams: We must rotate the two reference frames with respect to each other. Only a rotation guarantees full symmetry, so that the laws of physics have the same form in the 3D spaces of R and of B.
We now verify two effects in ES: (1) Since B moves relative to R, the proper 3D space of B is rotated with respect to the proper 3D space of R
causing length contraction. (2) Since B moves relative to R, the time of B and the time of R flow in different directions
causing time dilation. We define
(or
) as length of the rocket
as measured by the observer R (or else B). In a first step, we project the blue rocket in
Figure 2 top left to the axis
.
where
is the same Lorentz factor as in SR. The blue rocket appears contracted to observer R by the factor
.
Figure 2.
ES diagrams and 3D projections for two identical rockets. All axes are in Ls (light seconds). Top left and top right: In the ES diagrams, both rockets are moving at the speed , but in different directions. Bottom left: Projection to the 3D space of R. The relative speed is . The blue rocket contracts to . Bottom right: Projection to the 3D space of B. The red rocket contracts to .
Figure 2.
ES diagrams and 3D projections for two identical rockets. All axes are in Ls (light seconds). Top left and top right: In the ES diagrams, both rockets are moving at the speed , but in different directions. Bottom left: Projection to the 3D space of R. The relative speed is . The blue rocket contracts to . Bottom right: Projection to the 3D space of B. The red rocket contracts to .
We now ask: Which distances will R observe in his axis
? For the answer, we mentally continue the rotation of the blue rocket in
Figure 2 top left until it is pointing vertically down (
) and serves as R’s ruler in the axis
. In the projection to the 3D space of R, this ruler contracts to zero: The axis
“is suppressed” (disappears) for R. In a second step, we project the blue rocket in
Figure 2 top left to the axis
.
where
(or
) is the distance that B has moved in
(or else
). With
(full symmetry in ES) and the substitutions
and
, we get
where
(or
) is the distance that R (or else B) has moved in the Einstein time
of R. Equation (11) tells us that the clock of B is slow with respect to R in the variable
, and not in
. There is no Euclidean time dilation because
is absolute (
). At first, we thought: Einstein time is just an inconvenient concept. But when we realized that ER outperforms SR and GR (see
Section 5), we concluded that the issue in Einstein time is real.
Be aware that the Lorentz factor
in Equations (8) and (11) is the same as in SR. The factor
and thus length contraction and time dilation are recovered in ER despite its Euclidean metric. This is no surprise because Weyl showed that the generators of the Lorentz group are 4D rotations [
17]. Montanus [
8] and Gersten [
11] already proved that the Lorentz transformation is recovered in ER. So, we don’t repeat the proof here.
Predictions made by SR are correct because the Lorentz transformation is equivalent to a 4D rotation. Gersten [
11] interprets the Lorentz transformation as an SO(4) rotation in a “mixed space”
with the primed axis
. This is mathematically correct, but we dislike the term “mixed”. It makes us believe that untransformed and transformed coordinates would be mixed. Gersten writes that this mix causes “difficulties of interpretation” (page 1246 in [
11]). Because of these difficulties, ER has not been taken seriously up to the present day! We solve them by recalling that the roles of
and
have switched in ER:
(not ) is taken as the fourth coordinate of an event. So,
is the untransformed (!) coordinate of that event, and we must indeed transform
. There is no “mixed space”.
In order to understand how an acceleration in 3D space manifests itself in ES, let us assume that the blue rocket b in
Figure 3 accelerates in the axis
. According to Equation (6), the speed
of b must then increase at the expense of its speed
.
So, b is rotating and moving along a curved trajectory in Cartesian ES coordinates. Any acceleration of an object in 3D space relates to a 4D rotation and a curved trajectory in Cartesian ES coordinates.
Up next, we demonstrate that the ES geometry can also improve our understanding of gravitation. Let us imagine that Earth is located to the right of the blue rocket in
Figure 3 bottom. We assume that the blue rocket is accelerating in the gravitational field of Earth. Equation (6), which we applied for drawing
Figure 3, tells us: If an object accelerates in the axis
of an observer, it automatically decelerates in his axis
(in his flow of time).
Understanding gravitation is still one of the biggest challenges of physics. Gravitational waves [
18] support the idea of GR that gravitation is a property of spacetime, but they might be predicted by ER, too. Particle physics is still considering gravitation a force that has not yet been unified with the other three forces.
We claim that curved trajectories in Cartesian ES coordinates replace “curved spacetime” in GR. Equation (6) is the key equation which relates a motion in
to a motion in
. To support our claim, we now calculate the time dilation in the gravitational field of Earth. Clock A is far away from Earth and is emitting time signals at infinitesimally short intervals. Receiver B (mass
and starting at the position of A) is approaching Earth and detecting these signals. The kinetic energy of B is
where
is the speed of B in the axis
of A,
is the gravitational constant,
is the mass of Earth, and
is the distance of B to Earth’s center. By applying Equation (6), we get
where
is the speed of B in the axis
of A. With
and
(there is no steady axis
because of the accelerated motion of B), we get
where
(or
) is the distance that A (or else B) has moved in the Einstein time
of A in between consecutive time signals. There is gravitational time dilation only in Einstein time. The dilation factor
is the same as in GR [
2]. It has the same form as
if we set
equal to
. Be aware that Equation (16) is independent of
. So, Equation (16) applies whether or not B is still moving relative to A.
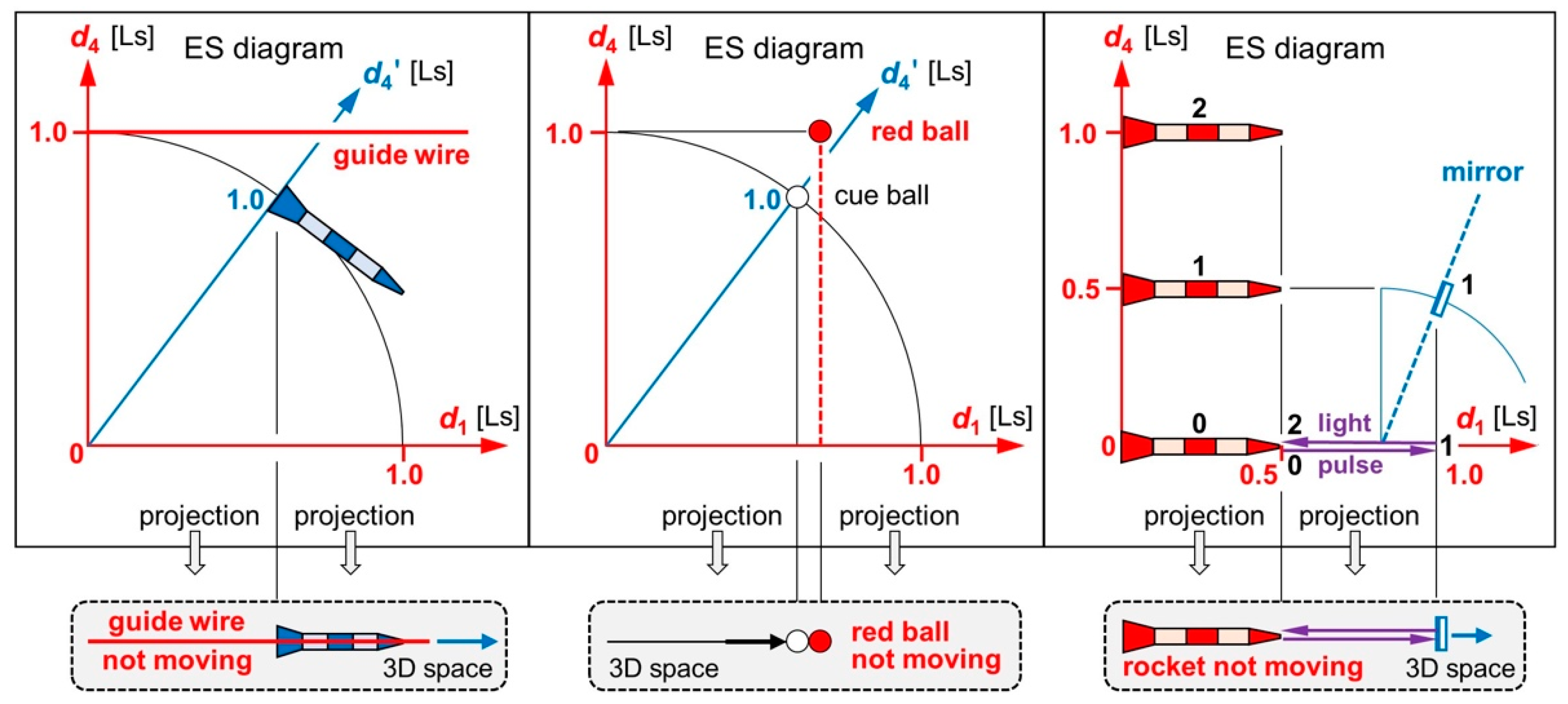
We finish this section by discussing three instructive paradoxes (
Figure 4). They demonstrate the benefit of our concept “distance” and of the projections from ES to an observer’s reality. Problem 1: A rocket moves along a guide wire. In ES, rocket and wire move at the speed
. We assume that the wire moves in some axis
. As the rocket moves along the wire, its speed in
must be slower than
. Wouldn’t the wire eventually be outside the rocket? Problem 2: In billiards, a cue ball is hit to collide with the red ball. In ES, cue ball and red ball move at the speed
. We assume that the red ball moves in some axis
. As the cue ball covers spatial distance to the red ball, its speed in
must be slower than
. How can the balls collide if their
values never match? Problem 3: A mirror is passing a rocket. An observer in the rocket’s tip sends a light pulse to the mirror and tries to detect the reflection. In ES, all objects move at the speed
, but in different directions. We assume that the rocket moves in some axis
. How can the observer detect the reflection?
The questions in the last paragraph seem to imply that there are geometric paradoxes in ER, but there aren’t. The fallacy in all problems lies in the assumption that there would be four observable (spatial) dimensions. Yet just three distances of ES are observable! We solve all problems by projecting 4D ES orthogonally to 3D space (
Figure 4). Then the axis
is suppressed.
The projection tells us what an observer’s reality is like because “suppressing ” is equivalent to “length contraction makes disappear”. Suppressed distance is felt as time. We easily verify in 3D space: The guide wire remains within the rocket; the cue ball collides with the red ball; the light pulse is reflected back to the observer. Other ER models [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13] run into paradoxes as they don’t project ES to an observer’s proper 3D space.
5. Solving 15 Fundamental Mysteries of Physics
Why should we know about ER and the master frame ES if SR and GR work so well for each observer? In this section, we demonstrate that ER outperforms SR and GR in the understanding of time, time’s arrow, , cosmology, and quantum mechanics.
5.1. Solving the Mystery of Time
Euclidean time is radial distance
from an origin (site of the Big Bang, see
Section 5.6) divided by
.
Time originates from the Big Bang rather than from my watch. Since time flows in countless 4D directions, the metaphor of “time being a 1D line” is limited in scope. Unlike our definition of Euclidean time, there is no definition of Einstein time other than “what I read on my watch” (attributed to Albert Einstein himself).
5.2. Solving the Mystery of Time’s Arrow
“Time’s arrow” is a synonym for time moving only forward. The arrow emerges from the Big Bang: The 4D vectors “flow of time” can’t be reversed because radial momentum provided by the Big Bang drives all energy irreversibly away from the origin O.
5.3. Solving the Mystery of
In SR, where forces are absent, the total energy
of an object is given by
where
is an object’s kinetic energy in 3D space and
is its “energy at rest”. SR doesn’t tell us why there is a
in the energy of objects that in SR never move at the speed of light. ER gives us this missing clue and is thus superior to SR:
is the kinetic energy of moving through the fourth dimension. The
in Equation (17) is strong evidence that everything is moving through ES at the speed
, while it is at rest in its proper 3D space. There is also
where
and
are the momenta of an object in ES and in 3D space. Dividing Equation (18) by
gives us the vector addition of an object’s momentum in its proper 3D space
and its momentum of moving through the fourth dimension.
5.4. Solving the Mystery of Relativistic Effects
In SR, length contraction and time dilation can be derived from the Lorentz transformation, but the physical cause of these relativistic effects remains in the dark. ER discloses that they stem from projecting the master frame ES to an observer’s reality.
5.5. Solving the Mystery of Gravitational Time Dilation
Equation (16) tells us: The Einstein time of an object in a gravitational field passes by more slowly with respect to an observer who is very far away from the center of the field. The object’s curved trajectory in Cartesian ES coordinates is projected to his proper 3D space (here the object accelerates) and to his proper flow of time (here the object decelerates). Curved trajectories in Cartesian ES coordinates replace “curved spacetime” in GR.
5.6. Solving the Mystery of the Cosmic Microwave Background
Now we are ready for our new model of cosmology based on ER. There is no need to create ES. It exists just like numbers. Because of some reason that we don’t know, there was a Big Bang. In today’s model of cosmology, it makes no sense to ask where it occurred: Because space inflated from a singularity, it occurred everywhere. In ES, the Big Bang can be localized at what we take as “origin O”. It injected a huge amount of energy into ES all at once. Ever since has all this energy been moving radially away at the speed .
During the initial stage after the Big Bang, there was a huge amount of concentrated energy in ES. In the projection to any proper 3D space, this energy created a very hot and dense plasma. While the plasma was expanding, it cooled down. During the recombination of plasma particles, electromagnetic radiation was emitted that we observe as cosmic microwave background (CMB) [
19]. At a temperature of roughly 3,000 K, hydrogen atoms formed. According to today’s model of cosmology, this stage was reached approximately 380,000 years “after” the Big Bang. In ER, these are 380,000 light years “away from” the Big Bang. The value “380,000” still needs to be recalculated if the universe has always been expanding at the constant speed
.
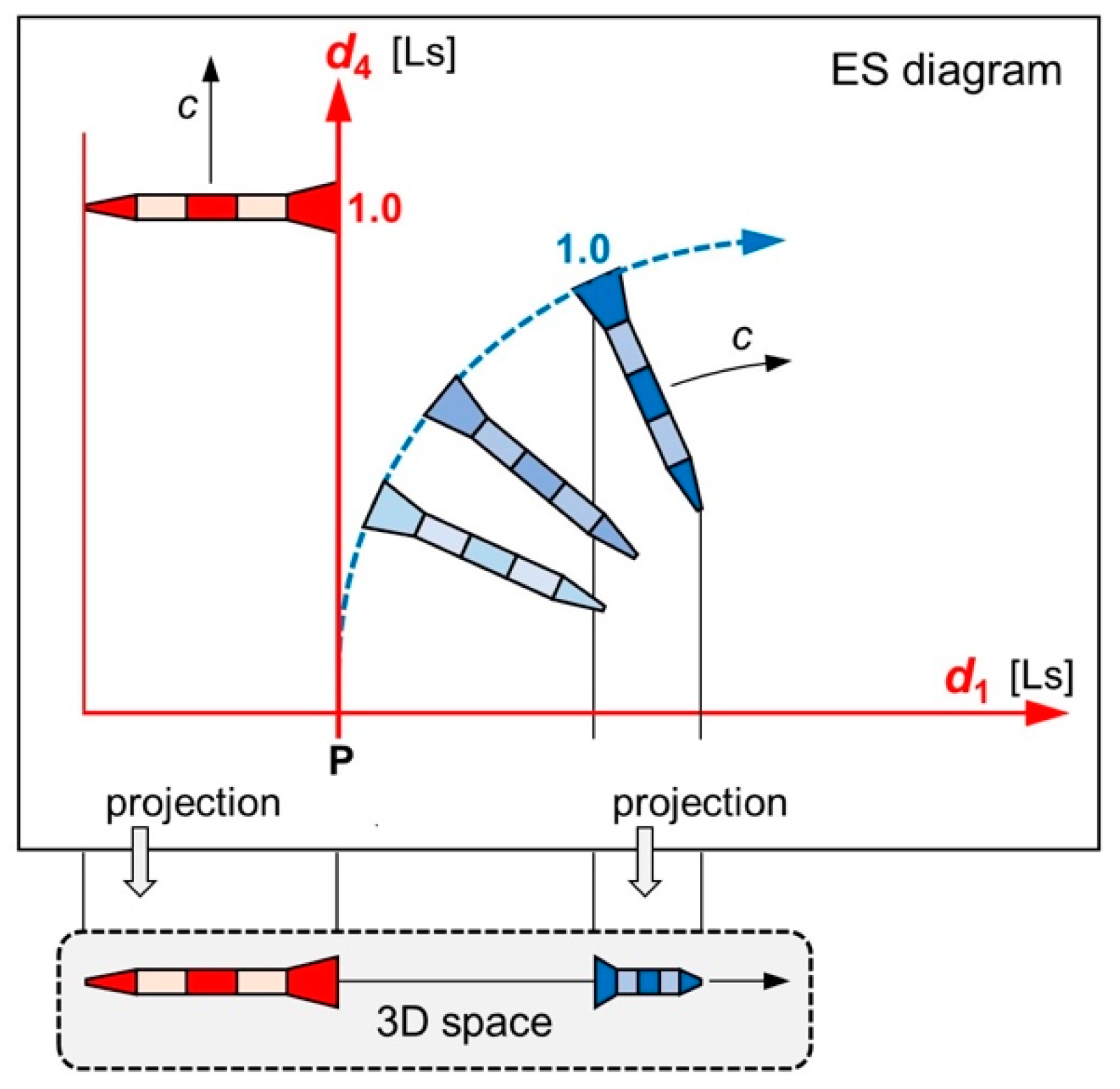
Yet why is the CMB so isotropic? Here is our answer: The CMB is so isotropic because it is “swinging” equally from ES into all three dimensions of my 3D space (
Figure 5). To grasp the process of swinging, we mentally continue the rotation of the blue rocket in
Figure 2 top left until it is pointing vertically down. We then mentally replace this blue rocket with a photon and finally look at its projection to my 3D space. Here is what we learn from this thought experiment: In each photon, I actually observe energy from ES whose 4D motion swings “completely” (by an angle of
) into my 3D space.
Our eyes aren’t made for
perceiving all four dimensions of ES. Yet we can
conceive of them with our brain by employing our trick: rotating that blue rocket in
Figure 2 top left and looking at its projection to 3D space. This trick tells us that the process of swinging covers both operations: “Swinging” is one word for the combined action of rotating and projecting. In my 3D space, I observe the final result of this combined action.
We learned that a photon is energy whose 4D motion swings completely into my 3D space (
). Matter is energy whose 4D motion swings “partly” (by an angle of
) into my 3D space (
). The swing angle of Earth is
as it doesn’t move relative to myself (
).
We would be mistaken if we thought that the pure radial motion of energy in hyperspherical coordinates would prevent objects in my 3D space from moving towards each other. If the blue rocket in
Figure 2 top left reverses its speed
, it will meet the red rocket again in the 3D projection. All dynamics in 3D space is pure geometry!
Photons are moving in my view of the hypersurface at the speed , while the entire hypersurface is expanding at the speed . One may ask: Doesn’t a photon then exceed the speed ? No, it doesn’t. Speeds in my view of the hypersurface must not be added to the speed of the hypersurface itself. Each photon that I observe is energy from ES whose 4D motion swings completely into my 3D space. That is to say: In the speed of each photon, I already see the speed of the hypersurface.
5.7. Solving the Mystery of Hubble’s Law
The 3D speed
at which a galaxy A is moving away from a galaxy B or from Earth relates to their distance
as
relates to the radius
of the hypersurface (
Figure 5).
where
is the Hubble constant,
is in km/s, and
is in Mpc. There it is! Equation (19) is Hubble’s law [
20]:
The farther a galaxy, the faster it is moving away from Earth. We derived it from the geometry of an expanding hypersurface. Because of Equation (4a), there is
. So, it does make sense to speak of a “Hubble function”
. Be aware that we must be very careful with the popular metaphor of an inflating balloon. The 3D hypersurface shown in
Figure 5 only looks like the surface of a 3D sphere because the angle
can’t be displayed in such a 2D illustration.
5.8. Solving the Mystery of the Flat Universe
Because the entire hypersurface is expanding at the speed of light (
Figure 5), the radial dimension disappears for any observer inside the hypersurface. Together with this dimension, the 4D curvature of the 3D hypersurface disappears as well. He observes a flat 3D universe. His situation compares to that of an ant: Since it observes just two dimensions of space, the 3D curvature of Earth’s 2D surface disappears for the ant.
5.9. Solving the Mystery of Cosmic Inflation
Many physicists believe that an inflation of space in the early universe [
21,
22] would explain the isotropic CMB, the flatness of the universe, and large-scale structures (inflated from quantum fluctuations). We showed that an expanding 3D hypersurface can explain the first two of these observations. It also explains the third observation if we only assume that there had been quantum fluctuations in energy in the early hypersurface. Ever since have the impacts of all these quantum fluctuations been expanding at the speed of light.
Cosmic inflation is a redundant concept.
5.10. Solving the Mystery of Competing Hubble Constants
There are several methods of calculating the Hubble constant
, but unfortunately the results vary from one method to another. Here we consider measurements of the CMB made with the
Planck space telescope [
23]. We compare them with calculations of calibrated distance ladder techniques (measurement of distance and redshift of celestial objects) using the
Hubble space telescope [
24]. By taking the ES geometry into account, we now explain why the values of
obtained by these two teams don’t even match within the specified error margins. According to team A [
23], there is
. According to team B [
24], there is
.
Team B made efforts to minimize the error margin by optimizing the distance measurements. Yet, as we will prove now, misinterpreting the redshift measurements causes a systematic error in team B’s calculation of
. Let us assume that 67.66 km/s/Mpc would be today’s value of
. Here we simulate a supernova at a distance of
from Earth. It is moving at the 3D speed
away from Earth. Equation (19) gives us
where the redshift parameter
tells us how any wavelength
of the supernova’s light is either
passively stretched by an expanding space (team B)—or how it is redshifted by the Doppler effect of objects that are
actively receding in ES (our model).
In this and the next paragraph, we demonstrate that team B will measure a too-high value
, and thus calculate a too-high value
, and thus calculate a too-high value
.
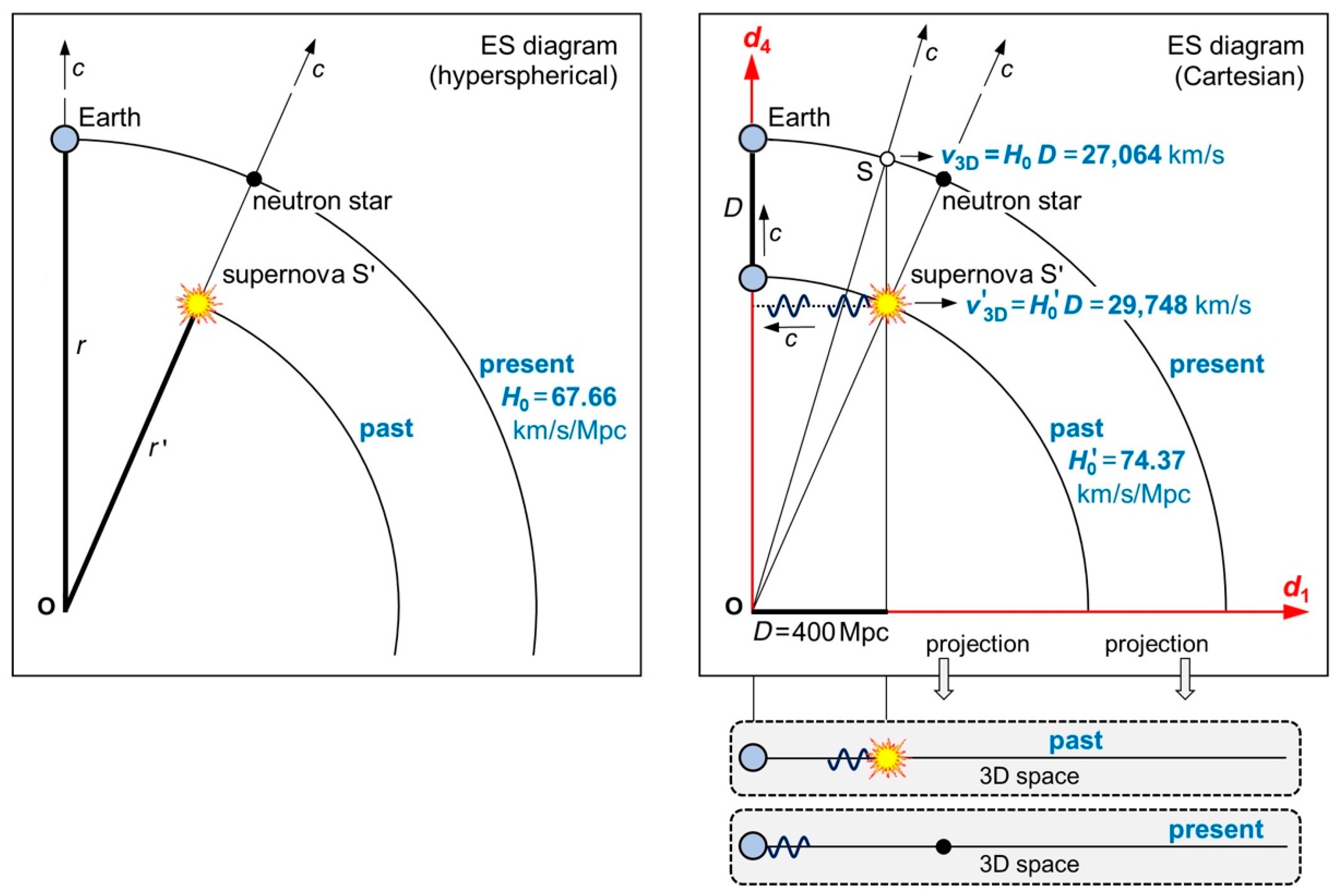
Figure 6 left shows the geometry of the supernova and Earth in hyperspherical coordinates. There is one circle called “past”, where the supernova occurred, and a second circle called “present”, where its light is observed on Earth. Today, this supernova has turned into a neutron star.
Figure 6 top right shows the same geometry, but in Cartesian coordinates. Since everything is moving through ES at the speed
, Earth has moved the distance
in
when the supernova’s light arrives. Hence, team B is receiving data from a time
when there was a different radius
and a different Hubble constant
.
Because of this higher value and of Equation (19), all data measured and calculated by team B relate to a higher 3D speed
for the same
. So, because of Equation (21) this is going to happen: Team B measures a redshift of
, which is indeed higher than 0.0903. Because of this too-high value of
, team B will calculate
from Equation (21) and thus
from Equation (19). Hence, team B will conclude that 74.37 km/s/Mpc would be today’s value
. In truth, team B ends up with a value
of the past because it isn’t aware of Equation (22) and of the ES geometry shown in
Figure 6.
Figure 6.
ES diagrams for team B’s calculation of the Hubble constant. The location of the Big Bang serves as the origin O. Left: We assume that 67.66 km/s/Mpc would be today’s value of the Hubble constant (present). A supernova S’ occurred in the past when the radius of the hypersurface was smaller than today’s radius . Right: Team B observes S’ and measures a distance of 400 Mpc. Since the occurrence of S’, Earth has also moved 400 Mpc, but in the axis . Team B calculates a Hubble constant of the past (74.37 km/s/Mpc). A supernova S occurring today (same distance, small white circle) recedes slower (27,064 km/s) than a supernova S’ in the past (29,748 km/s)
Figure 6.
ES diagrams for team B’s calculation of the Hubble constant. The location of the Big Bang serves as the origin O. Left: We assume that 67.66 km/s/Mpc would be today’s value of the Hubble constant (present). A supernova S’ occurred in the past when the radius of the hypersurface was smaller than today’s radius . Right: Team B observes S’ and measures a distance of 400 Mpc. Since the occurrence of S’, Earth has also moved 400 Mpc, but in the axis . Team B calculates a Hubble constant of the past (74.37 km/s/Mpc). A supernova S occurring today (same distance, small white circle) recedes slower (27,064 km/s) than a supernova S’ in the past (29,748 km/s)
For a shorter distance of
, Equation (22) tells us that team B’s Hubble constant
deviates from team A’s Hubble constant
by only 0.009 percent. Yet when plotting
versus
for various distances (we chose 50 Mpc, 100 Mpc, 150 Mpc, ..., and 450 Mpc as we didn’t have the raw distance data used by [
24]), the resulting slope (team B’s Hubble constant) is 8 to 9 percent higher than team A’s Hubble constant. We kindly ask team B to improve its calculation by eliminating the systematic error in the redshift measurement. It must adjust the calculated speed
to today’s speed
by converting Equation (22) to
We conclude:
The redshift is caused by the Doppler effect of objects that are actively receding in ES. Matching the two competing values of
(team B’s published value is indeed 8 to 9 percent higher than team A’s value) is probably the strongest proof of our theory. Team A’s value is correct:
. If the 3D hypersurface has been expanding uniformly at the speed
, the age of today’s universe is equal to
. In this case, its age wouldn’t be 13.8 billion years [
25], but 14.5 billion years. The adjusted age would explain the observation that there are stars out there as old as 14.5 billion years [
26].
As pointed out in
Section 3, there is no motion within the hypersurface in hyperspherical coordinates. This is why we can’t draw the path of the supernova’s light in
Figure 6 left. Only in Cartesian ES coordinates (
Figure 6 top right) can we display the light’s path horizontally as we already did in
Figure 4 top right. In order to see an observer’s reality, we have to project Cartesian ES coordinates to his proper 3D space (
Figure 6 bottom right).
Of course, team B is well aware of the fact that the supernova’s light was emitted in the past. Yet in the Lambda-CDM model, all that counts is the timespan during which light is traveling from the supernova to Earth. Along the way, its wavelength is passively stretched by expanding space. So, the total redshift is only developing during the journey to Earth. We can put it this way: The redshift parameter starts from zero and increases continuously during the journey to Earth. The fact that the supernova occurred long ago in the past at a time is irrelevant for team B’s calculation.
In ER, the moment (when a supernova occurs) is significant, but the timespan (during which light is traveling to Earth) is irrelevant. The wavelength of the supernova’s light is initially redshifted by the Doppler effect. During its journey to Earth, the parameter remains constant. Here we can put it this way: The redshift parameter is tied up at the moment “in a package” and sent to Earth, where it is measured. In the Lambda-CDM model, space itself is expanding. In ER, a hypersurface is expanding in ES. The hypersurface isn’t expanding space, but energy that is actively receding from the origin O.
5.11. Solving the Mystery of Dark Energy
The CDM model of cosmology assumes an expanding space to explain the distance-dependent recession of celestial objects. Meanwhile, it has been extended to the Lambda-CDM model, where Lambda is the cosmological constant. Cosmologists are now favoring an accelerating expansion [
27,
28] over a uniform expansion. This is because the calculated recession speeds deviate from values predicted by Equation (19) if
is taken as an averaged constant. The deviations increase with distance
and are compensated by assuming an accelerating expansion of space. Such an acceleration would stretch the wavelength even more and thus increase the recession speeds according to Equation (21).
Our model gives a much simpler explanation for the deviations from Hubble’s law: Because of Equation (4a), there is
. So,
isn’t a constant.
from each past is higher than today’s value. The older the considered redshift data are, the more will
deviate from today’s value
, and the more will
deviate from
. The small white circle in
Figure 6 top right helps us understand these deviations: If a new supernova S occurred today at the same distance
as the mapped supernova S’ in the past, then S would recede slower (27,064 km/s) than S’ (29,748 km/s) just because of the different values of
and
. As long as the ES geometry is unknown, the too-high redshifts are attributed to an accelerating expansion of space. Now that we know about the ES geometry, we can attribute different redshifts to data from different pasts.
We conclude that any expansion of space—uniform as well as accelerating—is only virtual. There is no accelerating expansion of the universe even if a Nobel Prize was given “for the discovery of the accelerating expansion of the Universe through observations of distant supernovae” [
29]. This phrasing actually contains two misconceptions: (1) In the Lambda-CDM model, the term “universe” implies space, but space isn’t expanding at all. (2) There is a uniform expansion of a 3D hypersurface (which is receding energy), but no accelerating expansion whatsoever.
Expansion of space is a redundant concept.
The term “dark energy” [
30] was coined to come up with a cause for an accelerating expansion of space. Because there is no accelerating expansion of space,
dark energy is a redundant concept, too. It has never been observed anyway. Radial momentum provided by the Big Bang drives all energy away from the origin O. So, the receding hypersurface is driven by itself rather than by dark energy.
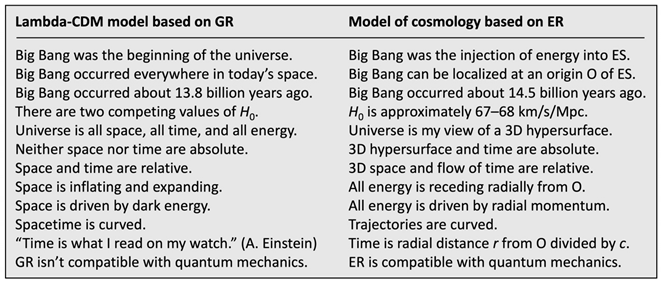
Table 1 summarizes huge differences in the meaning of the Big Bang, universe, space, and time. In the Lambda-CDM model, the Big Bang was the beginning of the universe. In our model, the Big Bang was the injection of energy into ES. In the Lambda-CDM model, the universe is all space, all time, and all energy. In our model, the universe is my view of a 3D hypersurface (of receding energy). In the Lambda-CDM model, spacetime is curved. In our model, curved trajectories in Cartesian ES coordinates relate to accelerations in an observer’s proper 3D space and in his proper flow of time. While the Lambda-CDM model isn’t compatible with quantum mechanics, our model is compatible.
5.12. Solving the Mystery of the Wave–Particle Duality
We can’t tell which solved mystery is the most important one. Yet the wave–particle duality has certainly kept physicists busy since it was first discussed by Niels Bohr and Werner Heisenberg [
31]. The Maxwell equations tell us that electromagnetic waves are oscillations of an electromagnetic field that move through 3D space at the speed of light
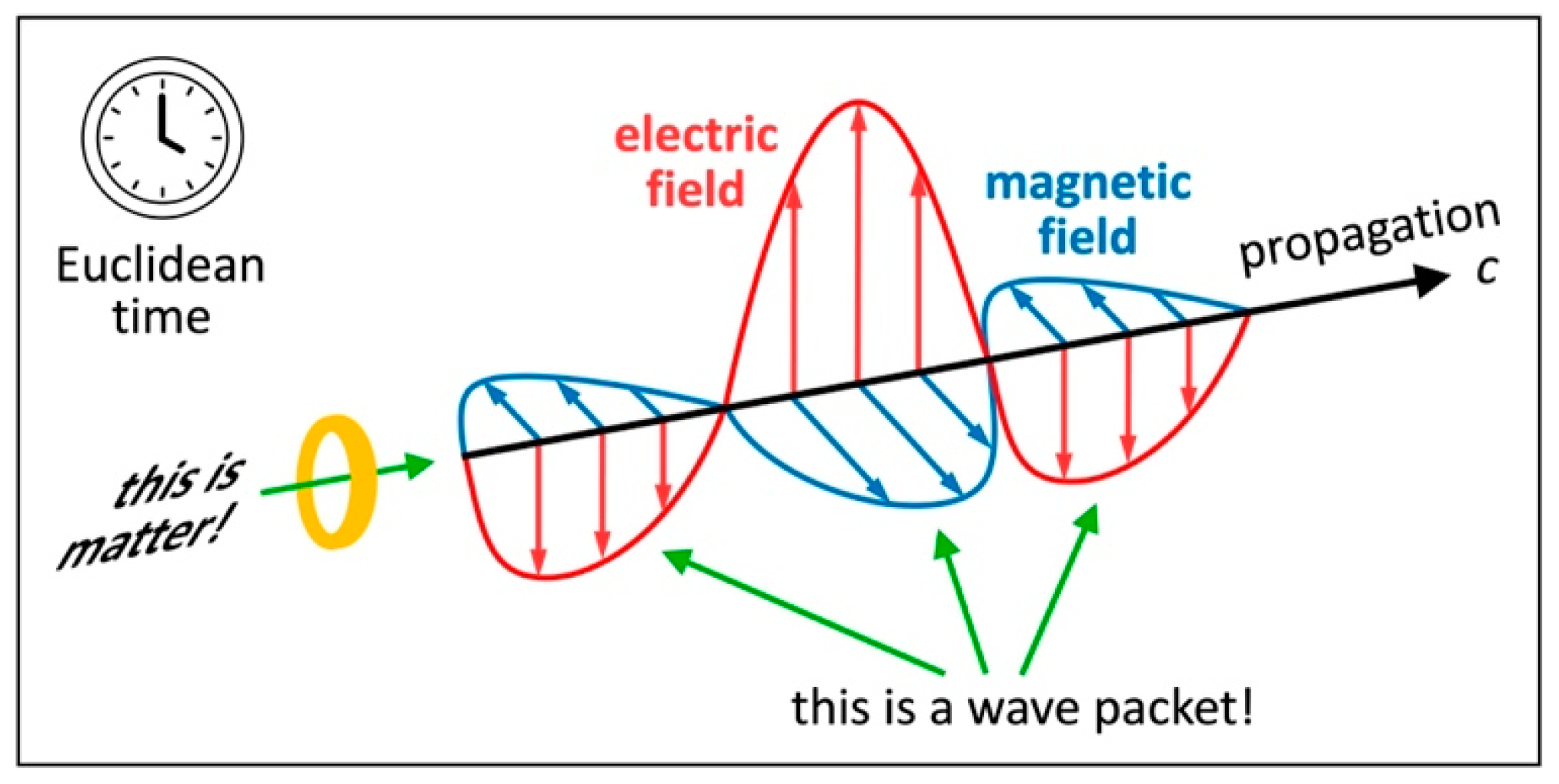
. In some experiments, objects behave like “waves” (electromagnetic wave packets). But in other experiments, the same objects behave like particles. In today’s physics, an object can’t be both at once because waves distribute energy in space over time, while the energy of particles is localized in space at a given time. This is why we added our third postulate: All energy is “wavematter” (electromagnetic wave packet and matter in one). By combining our concepts of distance and wavematter, we now demonstrate:
Waves and particles are actually the same thing (energy), but seen from two perspectives.
Figure 7 illustrates in Cartesian ES coordinates what our new concept of wavematter is all about. If I observe a wavematter (we call it the “external view”), this wavematter comes in four orthogonal dimensions: It propagates in my axis
at some speed
, and it oscillates in my axes
(electric field) and
(magnetic field); propagating and oscillating are functions of Euclidean time
(related to my fourth axis
). So, I can observe how this wavematter is propagating and oscillating:
I deem it wave.
From its own perspective (we call it the “internal view” or the “in-flight view”), each wavematter propagates in its axis at the speed . Yet because of length contraction at the speed , the axis is suppressed for this wavematter. So, its own propagating and oscillating disappears for itself: It deems itself matter at rest. It still observes the other objects propagating and oscillating in its proper 3D space as it keeps on feeling Euclidean time, while it is invisibly propagating in its axis . We conclude that there is an external view and an internal view of each wavematter. Be aware that “wavematter” isn’t just another word for the duality, but a generalized concept of energy disclosing why there is a wave–particle duality in an observer’s proper 3D space. In today’s physics, there is no reference frame moving at the speed and thus no internal view of a photon.
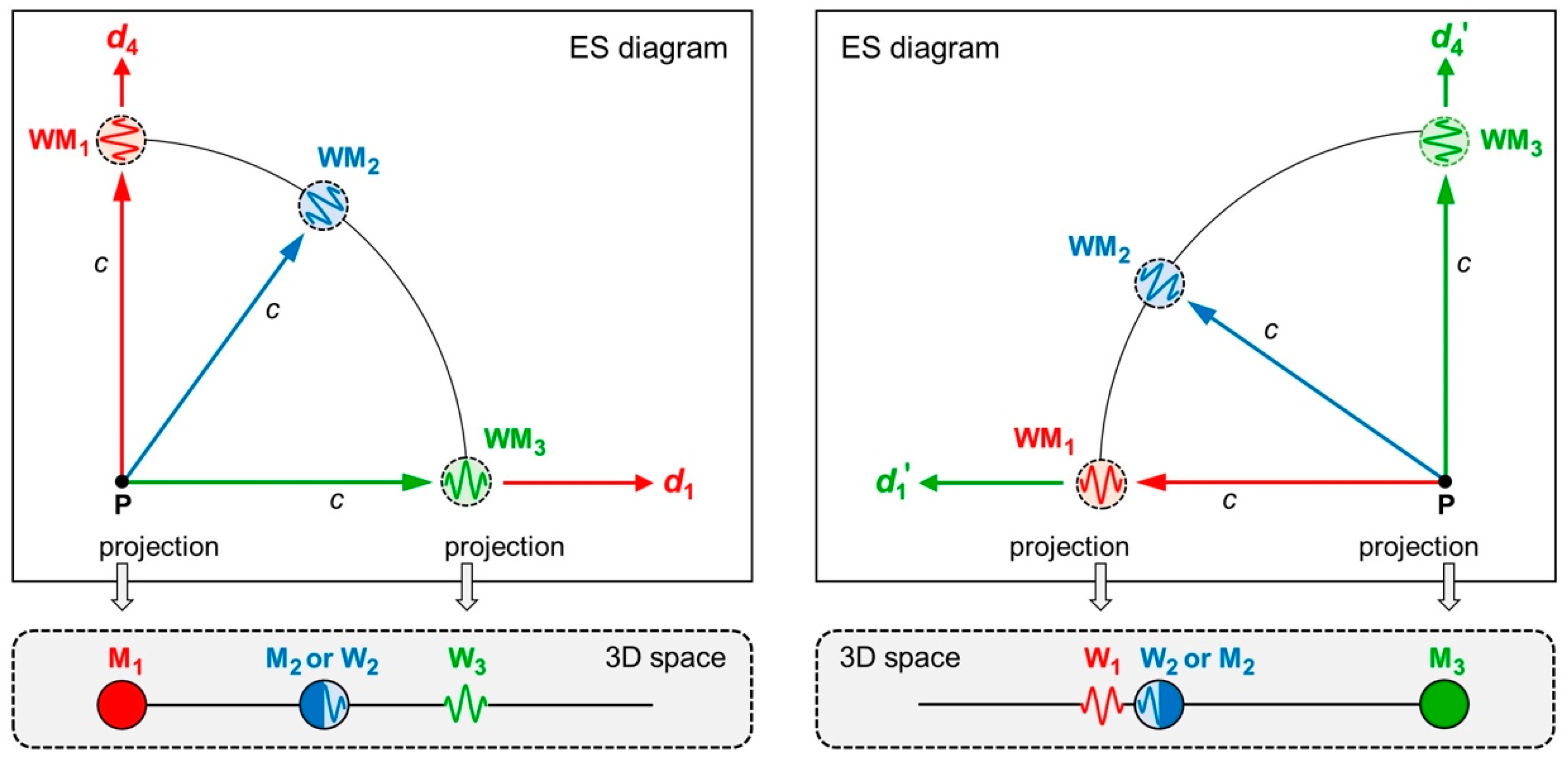
As an example, we now investigate the symmetry in three wavematters
,
, and
. We assume that they are all moving away from the same point P in ES, but in different directions (
Figure 8 top left).
are Cartesian coordinates in which
moves only in
. Hence,
is that axis which
deems time multiplied by
, and
span
’s 3D space (
Figure 8 bottom left). As the axis
disappears because of length contraction,
deems itself matter at rest (
).
moves orthogonally to
.
are Cartesian coordinates in which
moves only in
(
Figure 8 top right). In this case,
is that axis which
deems time multiplied by
, and
span
’s 3D space (
Figure 8 bottom right). As the axis
disappears because of length contraction,
also deems itself matter at rest (
).
Yet how do and move in each other’s view? We must fulfill our first two postulates and the requirement that they both started at the same point P. There is only one way of how to draw our ES diagrams: We must rotate the two reference frames with respect to each other. Only a rotation guarantees full symmetry, so that the laws of physics have the same form in the 3D spaces of and of . As the rotation angle is , ’s 4D motion swings completely into ’s 3D space. So, deems wave (), while deems wave (). Regarding , we split its 4D motion into a motion parallel to ’s motion (internal view) and a motion orthogonal to ’s motion (external view). So, deems either matter () or wave ().
The secret to understanding our new concepts “distance” and “wavematter” is all in
Figure 8. Here we see how they go hand in hand: We claim the symmetry of all four Cartesian coordinates in ES and, on top of that, the symmetry of waves and matter.
What I deem wave, deems itself matter. Just as distance is spatial and temporal distance in one, so is wavematter wave and matter in one. Here is a compelling reason for this unique claim of our theory: Einstein taught that energy is equivalent to mass. Full symmetry of waves and matter is a consequence of this equivalence. As the axis
disappears because of length contraction, the energy in a propagating wave “condenses” to mass in matter at rest.
In a double-slit experiment, an observer detects coherent waves that pass through a double-slit and produce some pattern of interference on a screen. We already know that he observes wavematters from ES whose 4D motion swings by an angle of into his proper 3D space. He deems all these wavematters waves because he isn’t tracking through which slit each wavematter is passing. If he did, the interference pattern would disappear immediately. So, he is a typical external observer.
The photoelectric effect is quite different. Of course, one can externally witness how one photon releases one electron from a metal surface. But the physical effect itself (“Do I have enough energy to release one electron?”) is all up to the photon’s view. Only if the photon’s energy exceeds the binding energy of an electron is this electron released. So, we must interpret the photoelectric effect from the internal view of each wavematter. Here its view is crucial! It behaves like a particle, which is commonly called “photon”.
The wave–particle duality is also observed in matter, such as electrons [
32]. According to our third postulate, electrons are wavematter, too. From the internal view (if I track them), electrons are particles: “Which slit will I go through?” From the external view (if I don’t track them), electrons behave more like waves. Because I automatically track slow objects, I deem all macroscopic wavematters matter: Their speed in my 3D space is rather low compared with the speed of light thus favoring the internal view. This justifies drawing solid rockets and celestial objects in most of our ES diagrams.
5.13. Solving the Mystery of Quantum Entanglement
The term “entanglement” [
33] was coined by Erwin Schrödinger when he published his comment on the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox [
34]. The three authors argued that quantum mechanics wouldn’t provide a complete description of reality. John Bell proved that quantum mechanics is incompatible with local hidden-variable theories [
35]. Schrödinger’s word creation didn’t solve the paradox, but demonstrates up to the present day the difficulties that we have in comprehending quantum mechanics. Several experiments have meanwhile confirmed that entangled particles violate the concept of locality [
36,
37,
38]. Ever since has quantum entanglement been considered a non-local effect.
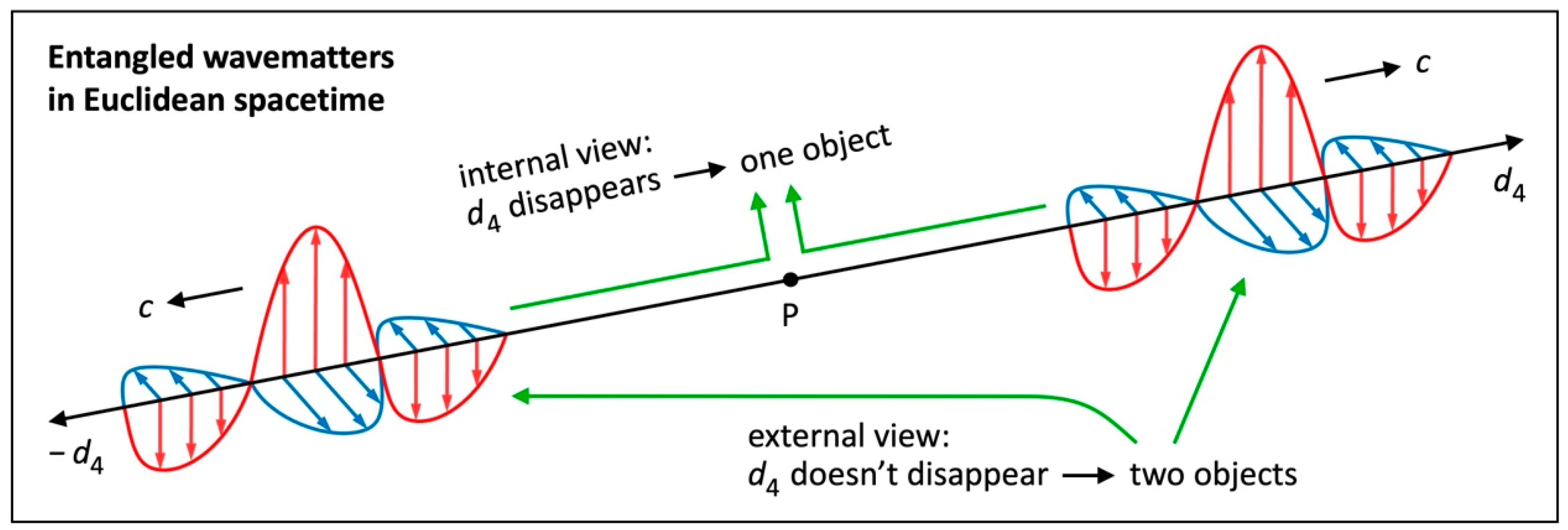
We will now “untangle” quantum entanglement
without the issue of non-locality. All we need to do is discuss quantum entanglement in ES.
Figure 9 illustrates two wavematters that were created at once at the same point P and move away from each other in opposite directions at the speed
. We claim that these wavematters are entangled. We assume that these wavematters are moving in the axes
and
, respectively. If they are observed by a third wavematter that is moving in a direction other than
, they are deemed two objects. This third wavematter can’t understand how the entangled wavematters are able to communicate with each other in no time. This is again the external view.
And here comes the internal (in-flight) view in ES: For each entangled wavematter in
Figure 9, the axis
disappears because of length contraction at the speed
. That is to say: In the projection to their
common 3D space spanned by
, either wavematter deems itself at the very same position as its twin.
From either perspective, they are one object that has never been separated. This is why they communicate with each other in no time! Entanglement is another strong evidence that everything is moving through ES at the speed
. Our solution to entanglement isn’t limited to photons. Electrons or atoms can be entangled as well. They move at a speed
in my 3D space, but in their axis
they also move at the speed
. We conclude:
Even non-locality is a redundant concept.
5.14. Solving the Mystery of Spontaneity
In spontaneous emission, a photon is emitted by an excited atom. Prior to the emission, the photon’s energy was moving with the atom. After the emission, this energy is moving by itself. Today’s physics can’t explain how this energy is boosted to the speed in no time. In ES, both atom and photon are moving at the speed . So, there is no need to boost any energy to the speed . All it takes is energy from ES whose 4D motion swings by an angle of into an observer’s proper 3D space—and this energy speeds off all at once. In absorption, a photon is spontaneously absorbed by an atom. Today’s physics can’t explain how the photon’s energy is slowed down to the atom’s speed in no time. In ES, both photon and atom are moving at the speed . So, there is no need to slow down any energy. Similar arguments apply to pair production and annihilation. We consider spontaneity another clue that everything is moving through ES at the speed .
5.15. Solving the Mystery of the Baryon Asymmetry
According to the Lambda-CDM model, almost all matter in the universe was created shortly after the Big Bang. Only then was the temperature high enough to enable the pair production of baryons and antibaryons. Yet the density was also very high so that baryons and antibaryons should have annihilated each other again. Since we do observe a lot more baryons than antibaryons today (also known as the “baryon asymmetry”), it is assumed that more baryons than antibaryons must have been produced in the early universe [
39]. However, an asymmetry in pair production has never been observed.
Our theory offers a unique solution to the baryon asymmetry: Since each wavematter deems itself matter, there was matter in 3D space right after the Big Bang. Pair production isn’t needed to create matter, and an asymmetry in pair production isn’t needed to explain the baryon asymmetry. There is much less antimatter than matter because antimatter is created only in pair production. One may ask why wavematter doesn’t deem itself antimatter, but this question is missing the point. Energy has two faces: wave and matter. “Antimatter” is matter, too, but with the opposite electric charge.
6. Conclusions
To this day, all attempts to unify GR and quantum mechanics have failed miserably. In Sects. 5.1 through 5.15, ER solves mysteries which SR and GR either haven’t solved in 100+ years—or that have meanwhile been solved, but only by applying concepts (cosmic inflation, expansion of space, dark energy, non-locality) that we proved to be redundant. Now we let Occam’s razor, a powerful tool in science, do its job: Because ER outperforms SR and GR, Occam’s razor knocks out Einstein time and these four redundant concepts. We also conclude: ER is compatible with quantum mechanics. Egocentric Einstein time prevents physicists from grasping the big picture in cosmology and quantum mechanics. We glimpse “behind the curtain” if we only replace Einstein time with Euclidean time.
Since SR and GR have been experimentally confirmed many times over, they are considered two of the greatest achievements of physics. We proved that their concept of time is flawed. Albert Einstein, one of the most brilliant physicists ever, wasn’t aware of ER. It was a wise decision to award him with the Nobel Prize for his theory of the photoelectric effect [
40] rather than for SR or GR. We campaign for ER as it penetrates to a deeper level. For the first time ever, mankind understands the nature of time: We live in the 3D hypersurface of an expanding 4D hypersphere—its radius, divided by the speed of light, is time! Just imagine: The human brain is able to grasp the idea that our energy is moving through ES at the speed of light.
With that said, conflicts of mankind become all so small.
ER solves 15 mysteries at once: (1) time, (2) time’s arrow, (3) , (4) relativistic effects, (5) gravitational time dilation, (6) CMB, (7) Hubble’s law, (8) flat universe, (9) cosmic inflation, (10) competing Hubble constants, (11) dark energy, (12) wave–particle duality, (13) quantum entanglement, (14) spontaneity, (15) baryon asymmetry. These 15 solutions are 15 confirmations of ER. It isn’t unusual that new concepts give many answers at once. For quantum leaps in understanding, we must question existing concepts. It certainly was to our advantage that we weren’t dazzled by the success of SR and GR. Einstein sacrificed absolute space and time. We sacrifice the absoluteness of waves and matter, but we restore absolute time and pair it with an absolute hypersurface. Quantum leaps can’t be planned. They just happen like the spontaneous emission of a photon. ☺
We introduced new concepts of time, distance, and energy: (1) There is absolute time. (2) Spatial and temporal distance aren’t two, but one [
41]. (3) Wave and matter aren’t two, but one. We explained these concepts and confirmed how powerful they are. We can even tell the source of their power:
symmetry and beauty. Once you have cherished this beauty, you will never let it go again. Yet to cherish it, you first need to give yourself a little push—accepting that an observer’s reality is only created by projecting ES to his proper 3D space and to his proper flow of time. Questions like “Why would reality only be a projection?” must not be asked in physics.
The magic of “reality being a projection” compares to the magic of “reality being a probability function”. The latter is well accepted.
It looks like philosopher Plato was right with his
Allegory of the Cave [
42]: Mankind experiences a projection that is blurred because of quantum mechanics! We would be mistaken if we thought that the concepts of nature were on the same level as all the tangible realities perceived by us. Our advice: Think of a problem in physics and try to solve it in ER. We predict that ER covers gravitational waves, too. Our new concepts lay the groundwork for ER. Anyone is welcome to join us. Hopefully, physics will be improved.
Figure 1.
Minkowski diagram, ES diagram, and 3D projection for two identical rockets. Top: The Minkowski diagram depicts the reality of just one observer (here: of R who synchronizes all clocks inside both rockets). Our diagram doesn’t depict the reality of B who would also synchronize these clocks. Center: The ES diagram can be projected to either reality. Bottom: Projection to the 3D space of R.
Figure 1.
Minkowski diagram, ES diagram, and 3D projection for two identical rockets. Top: The Minkowski diagram depicts the reality of just one observer (here: of R who synchronizes all clocks inside both rockets). Our diagram doesn’t depict the reality of B who would also synchronize these clocks. Center: The ES diagram can be projected to either reality. Bottom: Projection to the 3D space of R.
Figure 3.
ES diagram and 3D projection for two identical rockets. Top: In the ES diagram, the red rocket moves in the steady axis . The blue rocket accelerates in the axis . Bottom: Projection to the 3D space of R. The red rocket is “at rest”. The blue rocket accelerates against the red rocket
Figure 3.
ES diagram and 3D projection for two identical rockets. Top: In the ES diagram, the red rocket moves in the steady axis . The blue rocket accelerates in the axis . Bottom: Projection to the 3D space of R. The red rocket is “at rest”. The blue rocket accelerates against the red rocket
Figure 4.
Graphical solutions to three geometric paradoxes. Left: A rocket moves along a guide wire. In 3D space, the guide wire remains within the rocket. Center: A cue ball is hit to collide with the red ball. In 3D space, the cue ball collides with the red ball. Right: An observer in a rocket’s tip tries to detect the reflection of a light pulse. Between two snapshots (0–1 or 1–2), rocket, mirror, and light pulse move 0.5 Ls in ES. In 3D space, the light pulse is reflected back to the observer.
Figure 4.
Graphical solutions to three geometric paradoxes. Left: A rocket moves along a guide wire. In 3D space, the guide wire remains within the rocket. Center: A cue ball is hit to collide with the red ball. In 3D space, the cue ball collides with the red ball. Right: An observer in a rocket’s tip tries to detect the reflection of a light pulse. Between two snapshots (0–1 or 1–2), rocket, mirror, and light pulse move 0.5 Ls in ES. In 3D space, the light pulse is reflected back to the observer.
Figure 5.
Model of cosmology based on ER (not to scale). Artwork illustrating how a 3D hypersurface is expanding in ES. Left: Non-observable ES in hyperspherical coordinates (). The angle can’t be displayed here. Hubble’s law is derived from the geometry of the hypersurface. Right: My 3D space in Cartesian coordinates (), which is my view of the hypersurface and my reality. The axis (related to time) disappears because of length contraction
Figure 5.
Model of cosmology based on ER (not to scale). Artwork illustrating how a 3D hypersurface is expanding in ES. Left: Non-observable ES in hyperspherical coordinates (). The angle can’t be displayed here. Hubble’s law is derived from the geometry of the hypersurface. Right: My 3D space in Cartesian coordinates (), which is my view of the hypersurface and my reality. The axis (related to time) disappears because of length contraction
Figure 7.
Concept of wavematter. Artwork illustrating how one object can be deemed wave or matter. Wavematter comes in four orthogonal dimensions: propagation, electric field, magnetic field, and Euclidean time. Each wavematter deems itself matter at rest (internal or in-flight view). If it is observed by some other wavematter (external view), it is deemed wave.
Figure 7.
Concept of wavematter. Artwork illustrating how one object can be deemed wave or matter. Wavematter comes in four orthogonal dimensions: propagation, electric field, magnetic field, and Euclidean time. Each wavematter deems itself matter at rest (internal or in-flight view). If it is observed by some other wavematter (external view), it is deemed wave.
Figure 8.
ES diagrams and 3D projections for three wavematters. Top left: ES in coordinates where moves in . Top right: ES in coordinates where moves in . Bottom left: Projection to ’s 3D space. deems itself matter at rest () and wave (). Bottom right: Projection to ’s 3D space. deems itself matter at rest () and wave ()
Figure 8.
ES diagrams and 3D projections for three wavematters. Top left: ES in coordinates where moves in . Top right: ES in coordinates where moves in . Bottom left: Projection to ’s 3D space. deems itself matter at rest () and wave (). Bottom right: Projection to ’s 3D space. deems itself matter at rest () and wave ()
Figure 9.
Quantum entanglement in ES. Artwork illustrating internal view and external view. For each displayed wavematter, the axis disappears because of length contraction. It deems its twin and itself one object (internal view). For a third wavematter that is moving in a direction other than , the axis doesn’t disappear. It deems the displayed wavematters two objects (external view)
Figure 9.
Quantum entanglement in ES. Artwork illustrating internal view and external view. For each displayed wavematter, the axis disappears because of length contraction. It deems its twin and itself one object (internal view). For a third wavematter that is moving in a direction other than , the axis doesn’t disappear. It deems the displayed wavematters two objects (external view)
Table 1.
Comparing the Lambda-CDM model with our model of cosmology.
Table 1.
Comparing the Lambda-CDM model with our model of cosmology.