Submitted:
25 July 2023
Posted:
26 July 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Animal and Cellular Models of PCOS
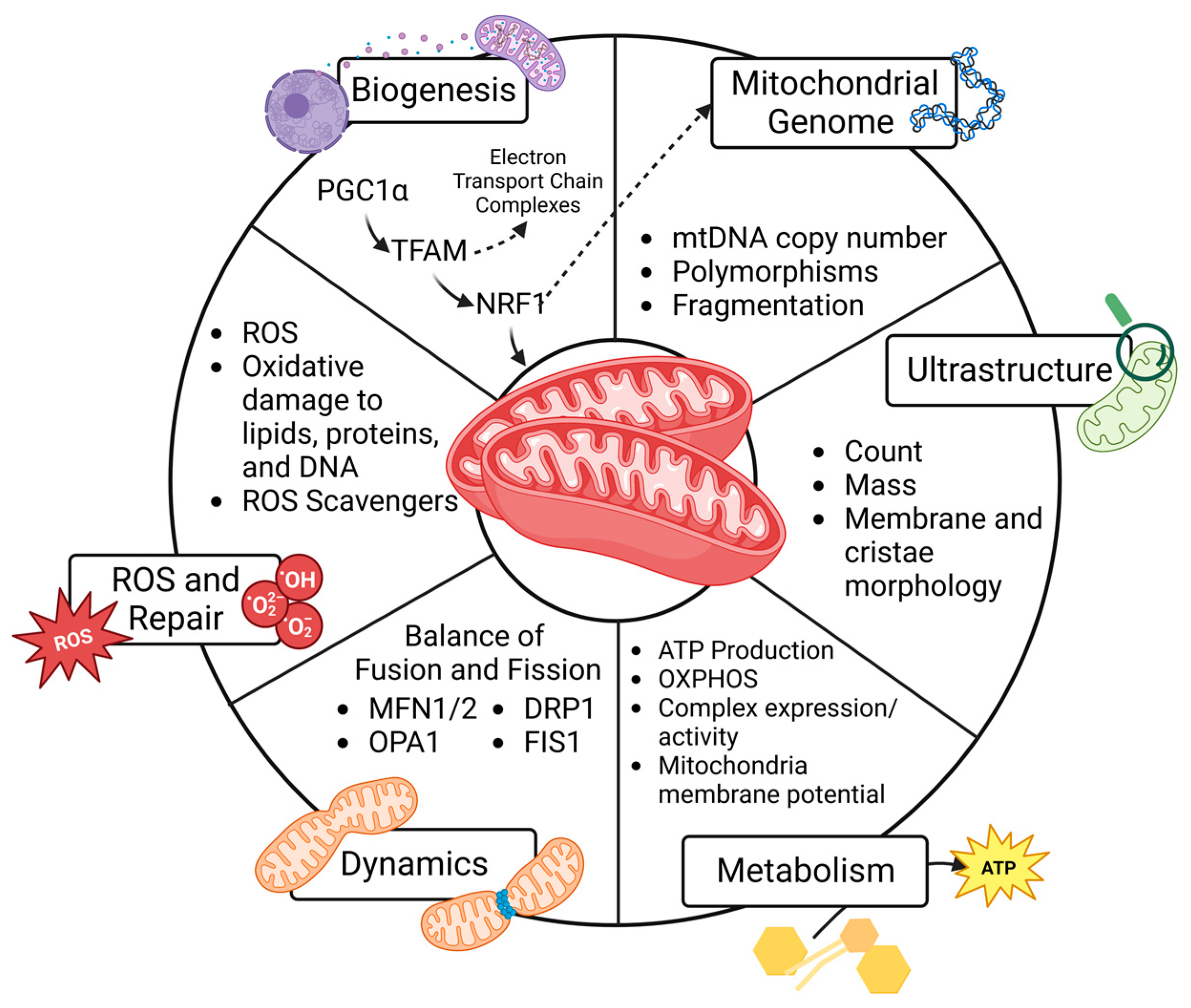
4. Mitochondrial Function and Cell Fate
4.1. Mitochondrial Biogenesis
4.2. Mitochondrial Genome
4.3. Ultrastructure
4.4. Metabolism
4.5. Dynamics
4.6. Reactive Oxygen Species and Repair
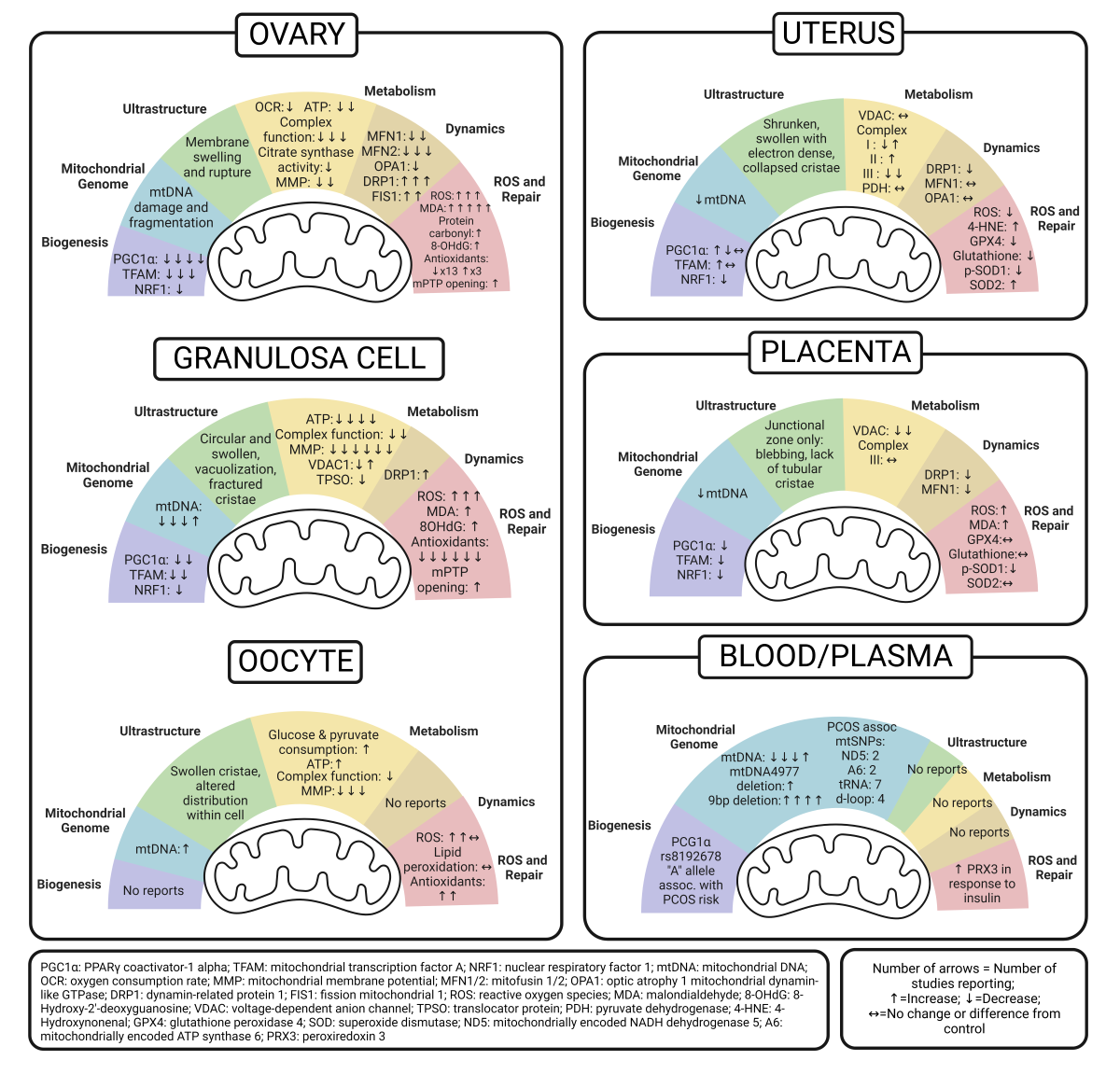
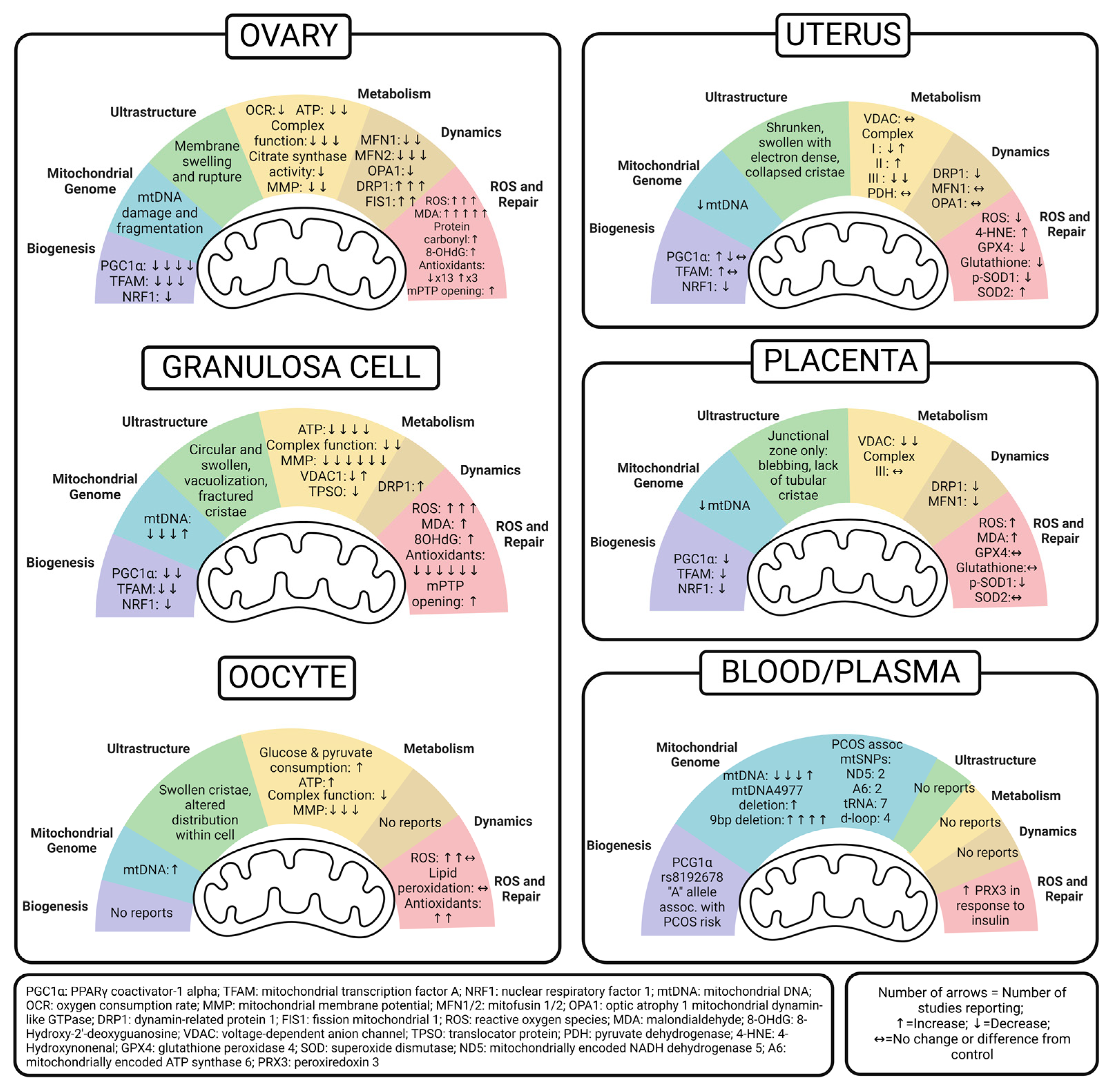
5. Ovary Mitochondria in PCOS
5.1. Whole Ovary
| Mitochondrial Function | Effect of PCOS Condition on Mitochondrial Function | Model - Species | PCOS Model/Diagnosis | Treatment timeframe | Method | Therapeutic Intervention | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biogenesis | Decreased PGC1 |
Rat | IP Letrozole + HFD | 21 days, 21 days, 35 days, 12 weeks | qPCR, WB | Cangfudaotan (IG) and metformin (IG) increased PGC1 to control levels | [1] |
| Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | WB | [2] | |||
| Mouse | SQ DHT | 35 days | WB | Overexpressing SIRT3 in vivo increased PGC1 back to control levels | |||
| Mouse | HF/HGD (58% kcal fat + sucrose) | 12 weeks | qPCR | Neurokinin-B antagonist increased PGC1 back to control levels | [3] | ||
| Decreased TFAM | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | WB | 1) L-carnitine (LC) + acetyl-L-carnitine (ACL) 2) LC and ACL plus propionyl-L-carnitine Both formulations increased TFAM compared to DHEA alone and controls |
[4] | |
| Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | WB | [2] | |||
| Mouse | HF/HGD (58% kcal fat + sucrose) | 12 weeks | qPCR | Neurokinin-B antagonist increased TFAM back to control levels | [3] | ||
| Decreased NRF1 | Mouse | HF/HGD (58% kcal fat + sucrose) | 12 weeks | qPCR | Neurokinin-B antagonist increased NRF1 back to control levels | [3] | |
| Mitochondrial Genome | Increased mtDNA fragmentation | Rat | On day 22 of HFD (46% fat), OG letrozole | 21 days | qPCR | Cangfudaotan (IG) and metformin (IG) decreased mtDNA damage and fragmentation | [1] |
| Ultrastructure | Membrane swelling & ruptures | Rat | IP Letrozole + HFD | 21 days | EM | % of total damaged mitochondria decreased with both metformin (IG) or cangfudaotan (IG) but were still higher than control levels | [1] |
| Metabolism | Increased basal, maximal and ATP-linked OCR, proton leak | Mice - offspring | DHT injection in dams post coitus, assessed pup neonatal ovaries | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | XF (Agilent) of whole neonatal ovaries | [5] | |
| Decreased OCR, RCR | Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | Oxytherm Clark-type electrode on isolated mitochondria | Cangfudaotan (IG) increased OCR, RCR | [1] | |
| Decreased ATP | Rat | On day 22 of HFD (46% fat), OG letrozole | 21 days | Colorimetric ATP assay | SeNP alone and in combination with metformin increased ATP (most increase in combination) | [6] | |
| Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | ATP assay | Cangfudaotan (IG) increased ATP levels | [1] | ||
| No difference in ATP | Mice - offspring | DHT injection in dams post coitus, assessed pup neonatal ovaries | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | XF (Agilent) of whole neonatal ovaries | [5] | ||
| Decreased activity of mitochondrial complex enzymes | Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | Complex enzymes activity assay | Cangfudaotan (IG) increased mitochondrial complex activity | [1] | |
| Decreased Complex I activity | Rat | On day 22 of HFD (46% fat), OG letrozole | 21 days | Complex I enzyme activity assay | SeNP alone and in combination with metformin increased Complex 1 activity (most increase in combination) | [6] | |
| Rat | SQ DHEA | 20 days | Bushen Huatan Granules (OG) increased activity of complex I | [7] | |||
| Decreased Complex III, IV activity | SQ DHEA | 20 days | Complex III, IV enzyme activity assays | Bushen Huatan Granules (OG) increased activity of complex III and IV | [7] | ||
| Decreased Complex IV (Cox6a2 subunit) | Mice - offspring | DHT injection in dams post coitus, assessed pup neonatal ovaries | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | RNAseq | [5] | ||
| Decreased citrate synthase activity | Rat | Letrozole (OG) | 21 days | Citrate synthase activity assay | Metformin (OG) and sodium selenite (OG) increased mitochondrial citrate synthase activity but was still lower than control group | [8] | |
| Decreased MMP | Rat | On day 22 of HFD (46% fat), OG letrozole | 21 days |
JC-1 staining | SeNP alone and in combination with metformin increased MMP (most increase in combination) | [6] | |
| Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | Cangfudaotan (IG) or metformin (IG) increased MMP | [1] | ||||
| Dynamics | Decreased MFN1 | Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | qPCR/WB | Cangfudaotan (IG) or metformin (IG) increased MFN1 | [1] |
| Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | WB | [2] | |||
| Decreased MFN2 | Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | qPCR/WB | Cangfudaotan (IG) or metformin (IG) increased MFN2 | [1] | |
| Rat | Letrozole (OG) | 21 days | qPCR/ELISA kit | Metformin (OG) and sodium selenite (OG) increased MFN2, but still lower than control group | [8] | ||
| Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | WB | [2] | |||
| Decreased OPA1 | Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | qPCR/WB | Cangfudaotan (IG) or metformin (IG) increased OPA1 | [1] | |
| Increased DRP1 | Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | qPCR/WB | Cangfudaotan (IG) or metformin (IG) decreased DRP1 | [1] | |
| Rat | Letrozole (OG) | 21 days | qPCR/ELISA kit | Metformin (OG) and sodium selenite (OG) decreased DRP1, but still higher than control group | [8] | ||
| Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | WB | [2] | |||
| Increased FIS1 | Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | qPCR/WB | Cangfudaotan (IG) or metformin (IG) decreased FIS1 | [1] | |
| Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | WB | [2] | |||
| ROS & Repair | Increased ROS | Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | DCF staining | Cangfudaotan (IG) or metformin (IG) decreased ROS | [1] |
| Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | Activity to produce superoxide anion assay | [2] | |||
| Increased mitochondrial superoxide | Rat | SQ DHEA | 20 days | MitoSOX staining | Bushen Huatan Granules (OG) decreased mitochondrial superoxide | [7] | |
| Increased lipid peroxidation | Rat | On day 22 of HFD (46% fat), OG letrozole | 21 days | MDA assay | SeNP alone or in combination with metformin decreased lipid peroxidation | [6] | |
| Rat | Letrozole (OG) | 21 days | Metformin (OG) and sodium selenite (OG) decreased lipid peroxidation, but still higher than control group | [8] | |||
| Rat | SQ DHEA | 21 days | [9] | ||||
| Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | [2] | ||||
| Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | Genistein decreased lipid peroxidation | [10] | |||
| Increased protein oxidation | Rat | Letrozole (OG) | 21 days | DNPH reaction assay | Metformin (OG) and sodium selenite (OG) decreased protein oxidation, but still higher than control group | [8] | |
| Increased DNA oxidation | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | 8-OHdG ELISA | Genistein decreased DNA oxidation levels | [10] | |
| Decreased antioxidant capacity | Rat | Letrozole (OG) | 21 days | Ferric reducing antioxidant power assay | Metformin (OG) and sodium selenite (OG) increased antioxidant capacity, but still lower than control group | [8] | |
| Decreased SOD activity | Rat | On day 22 of HFD (46% fat), OG letrozole | 21 days | SOD enzyme activity assay | SeNP alone or in combination with metformin increased SOD levels | [6] | |
| Rat | SQ DHEA | 21 days | [9] | ||||
| Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | Genistein increased SOD | [10] | |||
| Decreased SOD1 | Mouse | HF/HGD (58% kcal fat + sucrose) | 12 weeks | qPCR | Neurokinin-B antagonist increased SOD1 | [3] | |
| Increased SOD2 (MnSOD) | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | WB | 1) LC + ACL & 2) LC, ACL + propionyl-L-carnitine both decreased SOD2 | [4] | |
| Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | WB | [2] | |||
| Decreased GSH | Rat | On day 22 of HFD (46% fat), OG letrozole | 21 days | GSH level | SeNP alone or in combination with metformin increased GSH levels | [6] | |
| Decreased GSH-Px (GPx) | Rat | Letrozole (OG) | 21 days | GPx enzyme activity assay | Metformin (OG) and sodium selenite (OG) increased GPx activity, but still lower than control group | [8] | |
| Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | GSH-Px level | Genistein increased GSH-Px | [10] | ||
| Increased GSH-Px | Rat | IG Letrozole | 21 days | GSH-Px enzyme activity assay | [2] | ||
| Decreased GR | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | GR enzyme activity assay | [10] | ||
| Decreased GSH:GSSG ratio | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | GSH and GSSG level | Genistein increased GSH:GSSG ratio | [10] | |
| Decreased CAT activity | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | CAT enzyme activity assay | Genistein increased CAT activity | [10] | |
| Rat | SQ DHEA | 21 days | [9] | ||||
| Mouse | HF/HGD (58% kcal fat + sucrose) | 12 weeks | qPCR | Neurokinin-B antagonist increased CAT expression | [3] | ||
| Increased opening of mPTP | Rat | IP letrozole + HFD | 21 days | Mitochondrial Membrane Pore Channel Colorimetric Assay | Canfudaton (IG) or metformin (IG) decreased opening of mPTP | [1] | |
| Increased levels of Cytochrome C in cytosol than in mitochondria | Rat | SQ DHEA | 20 days | WB | Bushen Huatan Granules (OG) decreased levels of Cytochrome C in cytosol fraction compared to mitochondrial fraction | [7] |
5.2. Granulosa Cell
| Mitochondrial Function | Effect of PCOS on Mitochondrial Function | Model - Species | PCOS Model/Diagnosis | Treatment timeframe | Method | Therapeutic Intervention | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biogenesis | Decreased PGC1 | Cell line KGN | 500mM DHT | 24 hours | WB | Overexpression of SIRT3 (cell transfection) increased PGC1 levels comparable to controls | [11] |
| Cell line KGN | Palmitic Acid + DHT | Various | qPCR | si-NK3R increased PGC1 | [3] | ||
| Decreased TFAM | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days prior to puberty | qPCR | Vitamin D3 (100mM for 24 hours) increased TFAM | [12] | |
| Cell line KGN | Palmitic Acid + DHT | Various | qPCR | si-NK3R increased TFAM | [3] | ||
| Decreased NRF1 | Cell line KGN | Palmitic Acid + DHT | Various | qPCR | si-NK3R increased NRF1 | [3] | |
| Mitochondrial Genome | Decreased mtDNA copy number |
Mouse | SQ DHT | 20 days prior to puberty | qPCR | Vitamin D3 (100mM for 24 hours) increased mtDNA copy number | [12] |
| Rat | SQ DHEA | 20 days | qPCR (mtND1:beta-globin) | [13] | |||
| Human | Rotterdam | qPCR (mtND1:beta-actin) | [14] | ||||
| Increased mtDNA copy number | Cell line KGN | 500nM DHT | 24 hours | qPCR | Overexpression of SIRT3 decreased mtDNA copy number, but increased back to DHT-exposed levels with PGC1a inhibitor | [11] | |
| Ultrastructure | Disorganized cristae, vacuoles, less electron dense | Mouse - offspring | DHT injection post coitus, assessed pup neonatal GCs | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | TEM | [5] | |
| Mitochondrial aggregated distribution, cristae dissolution and fracture, presence of vacuoles (66.66% abnormal mitochondria compared to 0% in controls) | Rat | SQ DHEA | 20 days | TEM | [13] | ||
| Mitochondrial swelling and membrane defects | Mouse | SQ DHT | 35 days | TEM | Melatonin reduced mitochondrial swelling and membrane defects | [15] | |
| Mitochondrial swelling and membrane defects | Human | Rotterdam | TEM | [15] | |||
| Less rod-shaped mitochondria, more circular/constricted mitochondria | Rat | Continuous-release DHT pellet implant | 1 month (83μg/day) | TEM | eCG increased rod-shaped mitochondria & decreased circular/constricted mitochondria | [16] | |
| Decreased mitochondria amount | Human | Rotterdam | Nonyl acridine orange (NAC) flow cytometry | [17] | |||
| Decreased mitochondrial mass, increased mitochondrial fragmentation, constrained cell expansion | Human | Rotterdam | pLV-mitoDsRed plasmid transfection (tags ATP synthase) and imaging | [17] | |||
| Metabolism | Decreased ATP levels | Mouse | 100 μM DHEA | 12 hours | ATP assay | Genistein increased ATP levels but still lower than controls. Additional treatment with NRF2 inhibitor ML385 decreased ATP levels compared to genistein alone, but was still higher than DHEA group | [10] |
| Rat | SQ DHEA | 20 days | [13] | ||||
| Cell line KGN | 500nM DHT | 24 hours | Overexpression of SIRT3 increased ATP, but addition of PGC1a inhibitor reversed this effect | [11] | |||
| Human | Rotterdam | [14] | |||||
| Decreased Complex I, III, IV activity | Rat | Testosterone (10-5 M) | 24 hours | Complex I/III/IV activity assay | 6 hour incubation with serum from rats receiving Bushen Huatan Granules treatment led to increased activity of complex I, III, IV | [7] | |
| Decreased NDUFB8 (Complex I subunit) and ATP5j (ATP synthase subunit) | Rat | SQ DHEA | 20 days | qPCR/WB | [13] | ||
| Decreased MMP | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | JC-1 flow cytometry | Genistein increased MMP but still lower than controls. Additional treatment with NRF2 inhibitor ML385 had similar MMP to DHEA group | [10] | |
| Cell line KGN | 500nM DHT | 24 hours | JC-1 staining | Overexpression of SIRT3 increased MMP, but addition of PGC1a inhibitor reversed this effect | [11] | ||
| Cell line KGN | 500nM DHT | 24 hours | Melatonin (1000pM for 24 hrs) increased MMP | [15] | |||
| Human | Rotterdam | TMRE flow cytometry | [17] | ||||
| Human | Rotterdam | Mitotracker Red flow cytometry |
[17] | ||||
| Human | Rotterdam | JC-1 Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Kit | [14] | ||||
| Increased VDAC1 | Rat | IG letrozole | 21 days | WB | [2] | ||
| Decreased VDAC1 | Human | Rotterdam | qPCR/ICC | [18] | |||
| Decreased TSPO | Human | Rotterdam | qPCR/ICC | [18] | |||
| Dynamics | Increased DRP1 | Rat | Continuous-release DHT pellet implant | 1 month (83μg/day) | WB | [16] | |
| ROS & Repair | Increased ROS | Mouse | 100 μM DHEA | 12 hours | DCFH-DA flow cytometry | Genistein decreased ROS | [10] |
| Human | Rotterdam | DCFH-DA | [14] | ||||
| Increased mitochondrial superoxide | Cell line KGN | 500nM DHT | 24 hours | MitoSOX staining | Overexpression of SIRT3 decreased mitochondrial superoxide, but addition of PGC1-a inhibitor reversed this outcome | [11] | |
| Increased lipid peroxidation | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | MDA assay | Genistein decreased lipid peroxidation | [10] | |
| Increased DNA oxidation | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | 8-OHdG ELISA | Genistein decreased 8-OhdG levels | [10] | |
| Decreased SOD, GSH-Px, GR, GSH:GSSG ratio | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | SOD, GR enzyme activity assays/GSH-Px, GSH:GSSG content assays | Genistein increased SOD, CAT, GSH-Px, GSH:GSSG ratio | [10] | |
| Decreased SOD1 | Cell line KGN | Palmitic Acid + DHT | Various | qPCR | si-NK3R increased SOD1 | [3] | |
| Decreased CAT | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | CAT enzyme activity assay | Genistein increased CAT | [10] | |
| Cell line KGN | Palmitic Acid + DHT | Various | qPCR | si-NK3R increased CAT | [3] | ||
| Upregulation of UPR-MT (mitochondrial unfolded protein response) proteins | Human | Rotterdam | qPCR | [19] | |||
| Increased opening of mPTP | Cell line KGN | 500nM DHT | 24 hours | Mitochondrial permeability transition pore assay | Melatonin (1000pM for 24 hrs) decreased opening of mPTP | [15] |
5.3. Oocyte
| Mitochondrial Function | Effect of PCOS on Mitochondrial Function | Model - Species | PCOS Model/Diagnosis | Treatment timeframe | Method | Therapeutic Intervention | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biogenesis | No Reports | ||||||
| Mitochondrial Genome | Increased mtDNA copy number | Mouse | Controlled-release DHT pellet implant | 90 days (2.75μg/day) | qPCR (mtCO1:tubulin) | [20] | |
| No difference in mtDNA copy number | Mouse – offspring | DHT injection in dam post coitus, assessed post pubertal pup oocytes | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | qPCR (mtCO1:tubulin) | [5] | ||
| Ultrastructure | Disorganized cristae, vacuoles, less electron dense | Mouse – offspring | DHT injection in dam post coitus, assessed post pubertal pup oocytes | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | TEM | [5] | |
| Mitochondria with malformed cristae with concentric circles, swollen or loss of cristae | Mouse | Controlled-release DHT pellet implant | 90 days (2.75μg/day) | SEM | [20] | ||
| Mitochondria have swollen cristae, no electron dense contents and are vacuolated | Mice – offspring | DHT injection in dams post coitus, assessed post pubertal pup oocytes | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | TEM | [21] | ||
| Abnormal mitochondria distribution | Human/ Mouse | EVs isolated from PCOS patients with non-hyperandrogenic phenotype were co-cultured with control murine oocytes | Mitochondrial Red Fluorescent Probe | [22] | |||
| Metabolism | Increased glucose, pyruvate consumption | Human | Rotterdam | Ultra-microfluorometric assay | [23] | ||
| Increased ATP levels | Mice | Controlled-release DHT pellet implant | 90 days (2.75μg/day) | ATP assay | [20] | ||
| No difference in ATP levels | Mice – offspring | DHT injection in dams post coitus, assessed post pubertal pup oocytes | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | [21] | |||
| Decreased mitochondrial complex I genes (ND1,ND2,ND5) | Mice | Controlled-release DHT pellet implant | 90 days (2.75μg/day) | qPCR | [20] | ||
| Increased mitochondrial complex I and IV genes (ND1, ND6 & CO1, CO2, CO3) | Mice – offspring | DHT injection in dams post coitus, assessed post pubertal pup oocytes | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | [21] | |||
| Decreased MMP | Mice | Controlled-release DHT pellet implant | 90 days (2.75μg/day) | JC-1 staining | [20] | ||
| Rat | DHEA injection (interscapular region) | 20 days | Rat-to-mouse BAT xenotransplant increased MMP | [24] | |||
| Mice – offspring | DHT injection in dams post coitus, assessed post pubertal pup oocytes | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | [21] | ||||
| ROS & Repair | Increased ROS | Rat | DHEA injection (interscapular region) | 20 days | ROS assay using DCFH-DA | Rat-to-mouse BAT xenotransplant decreased ROS level | [24] |
| Human | EVs isolated from PCOS patients with non-hyperandrogenic phenotype were co-cultured with control murine oocytes | DCHF-DA staining | [22] | ||||
| Mice – offspring | DHT injection in dams post coitus, assessed post pubertal pup oocytes | GD 16.5, 17.5, 18.5 | CellROX staining | [21] | |||
| No differences in ROS | Mice | Controlled-release DHT pellet implant | 90 days (2.75μg/day) | [20] | |||
| No differences in lipid peroxidation | Mice | Controlled-release DHT pellet implant | 90 days (2.75μg/day) | BODIPYC11® 581/591 staining | [20] | ||
| Increased CAT | Human | EVs isolated from PCOS patients with non-hyperandrogenic phenotype were co-cultured with control murine oocytes | qPCR | [22] | |||
| Increased GSS | Human | EVs isolated from PCOS patients with non-hyperandrogenic phenotype were co-cultured with control murine oocytes | qPCR | [22] |
6. Uterus Mitochondria in PCOS
| Mitochondrial Function | Effect of PCOS on Mitochondrial Function | Model/ Species | PCOS Model/ Diagnosis | Treatment timeframe | Method | Reference | Therapeutic Intervention | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biogenesis | Increased PGC-1α | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | WB | [1] | ||
| No change in PGC-1α | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 0.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [2] | |||
| Decreased PGC-1α | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [3] | |||
| Increased TFAM | Human | Rotterdam Criteria | WB | [4] | ||||
| No change in TFAM | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 or GD 14.5 | qPCR | [2,3] | |||
| Decreased NRF1 | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [3] | |||
| Mitochondrial Genome | Decreased mtDNA copy number | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [3] | ||
| Ultrastructure | Decreased TOMM20 | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | IHC | [1] | L-carnitine/acetyl-L-carnitine returned levels closer to control | [1] |
| Increased prohibitin I | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 14.5 | WB | [5] | |||
| Shrunken mitochondria | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | TEM | [6] | |||
| Swollen mitochondria | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 or GD 14.5 | TEM | [2,5] | N-acetyl-cysteine improved but didn't fully rescue morphology but also impaired mitochondria in controls; flutamide decreased number of small swollen mitochondria but cristae remained disorganized | [2,5] | |
| Electron dense and collapsed cristae | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 or GD 14.5 | TEM | [2,5,6] | |||
| Metabolism | No difference in VDAC | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 14.5 | WB | [5] | N-acetyl-cysteine didn't change VDAC but did decrease it in controls | [5] |
| Decreased Complex I | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 14.5 | WB | [5] | N-acetyl-cysteine normalized | [5] | |
| Increased Complex I | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 0.5 - GD 13.5 | WB | [2] | Flutamide normalized | [2] | |
| Increased Complex II | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 0.5 - GD 13.5 | WB | [2] | Flutamide normalized | [2] | |
| Decreased Complex III | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | WB | [3,5] | N-acetyl-cysteine normalized | [5] | |
| No difference in PDH | Human | Rotterdam Criteria | WB | [4] | ||||
| Dynamics | Decreased DRP1 (Fission) | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [3] | ||
| No change in MFN1 (Fusion) | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [3] | |||
| No change in OPA1 (Fusion) | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [3] | |||
| ROS and Repair | Increased 4-HNE adducts | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | IHC | [1] | L-carnitine/acetyl-L-carnitine returned levels closer to control | [1] |
| Reduced ROS levels | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | OxiSelect In Vitro ROS/RNS assay | [3] | |||
| Reduced GPX4 | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | WB, IHC | [6] | |||
| Reduced glutathione | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | Glutathione/ glutathione + glutathione disulfide assay | [6] | |||
| Reduced phosphorylated SOD1 | Rat | IP DHT+INS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | WB | [3] | |||
| Increased SOD2 | Mouse | SQ DHEA | 20 days | WB | [1] | Propionyl-L-carnitine altered levels | [1] |
7. Placenta Mitochondria in PCOS
| Mitochondrial Function | Effect of PCOS on Mitochondrial Function | Treatment timeframe | Method | Therapeutic Intervention | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biogenesis | Decreased PGC-1α | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [80] | |
| Decreased TFAM | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [80] | ||
| Decreased NRF1 | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [80] | ||
| Mitochondrial Genome | Decreased mtDNA copy number | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [80] | |
| Ultrastructure | Mitochondrial blebbing | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 and GD 14.5 | TEM | [80,81,89] | |
| Lack of tubular cristae | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 or GD 14.5 | TEM | [81,89] | ||
| Decreased intracristal dilatation | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | TEM | [80] | ||
| Morphology changes limited to junctional zone; little change in the labyrinth zone | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 or GD 14.5 | TEM | High dose NAC abolished damaged morphology in junctional zone but had no effect in labyrinth zone | [81,89] | |
| Metabolism | No change in Complex III expression | GD 7.5 - GD 14.5 | WB | Low dose NAC decreased Complex I abundance | [81] |
| Decreased VDAC | GD 7.5 - GD 14.5 | WB | High dose NAC increased VDAC abundance | [80,81] | |
| Dynamics | Decreased MFN1 (Fusion) | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [80] | |
| Decreased DRP1 (Fission) | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | qPCR | [80] | ||
| ROS and Repair | Increased ROS | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | OxiSelect In Vitro, ROS/RNS assay | [80] | |
| Increased MDA | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | MDA ELISA | [80] | ||
| Increased cytosolic NRF2 and decreased nuclear NRF2 in basal zone | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | WB, IHC | [80] | ||
| Reduced phosphorylated SOD1 and p-SOD1:SOD1 ratio | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | WB | [80] | ||
| No difference in SOD2 abundance | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | WB | [80] | ||
| No difference in GPX4 abundance | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | WB | [89] | ||
| Less GPX4 in junctional and labyrinth zones | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | IHC | [89] | ||
| No GPX4 in nuclei of spongiotrophoblasts, cytotrophoblasts, and synctiotrophoblasts | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | IHC | [89] | ||
| No difference in glutathione | GD 7.5 - GD 13.5 | Glutathione/ glutathione + glutathione disulfide assay | [89] |
8. Peripheral Markers of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in PCOS
| Mitochondrial Function | Effect of PCOS on Mitochondrial Function | Method | Therapeutic Intervention | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biogenesis | Reduced "GG"(WT) frequency of PGC-1α rs8192678 polymorphism | PCR, RFLP Analysis | [90] | |
| No difference in TFAM genotype or allele frequency | PCR, RFLP Analysis | [90] | ||
| Mitochondrial Genome | Lower mtDNA copy number | qPCR | [92,93,94] | |
| Higher mtDNA copy number | qPCR | [91] | ||
| Negative association between mtDNA copy number and fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, waist circumference, and triglycerides | Pearson correlation coefficient | [94] | ||
| Positive association between mtDNA copy number and quantitative insulin-sensitivity check index (QUICKI) and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) | Pearson correlation coefficient | [94] | ||
| No correlation between mtDNA copy number and anthropometric measure nor 8-OHdG | qPCR, 8OH-dG ELISA kit | Metformin decreased mtDNA copy number at 6 and 12 months of treatment | [95] | |
| Higher mtDNA4977 deletion rate | qPCR | [91] | ||
| Higher frequency of a 9bp deletion | qPCR | [49,96,97,98,99] | ||
| ND5 gene polymorphisms: T12811C, T12338C | qPCR | [97,100,101] | ||
| A6 gene polymorphisms: G8584A, C8684T | qPCR | [97,98,100] | ||
| Unique tRNA variants and higher frequency of variants for Cys and Leu tRNAs | qPCR | [92,97,100] | ||
| Greater frequency of D-loop SNPs C150T, T146C, A189G, and D310 | PCR, Mitomap and mtDB mitochondria databases | [49,93] | ||
| Carriers of AA genotype of PGC1a polymorphism rs8192678 and D-loop SNPs A189G and D310 had lower mtDNA | PCR, Mitomap and mtDB mitochondria databases | [90,93] | ||
| Ultrastructure | No Reports | |||
| Metabolism | No Reports | |||
| Dynamics | No Reports | |||
| ROS and Repair | Decreased PRX3 2-3h post-OGTT | ELISA | [103] | |
| Positive correlation between PRX3 at 2h post-OGTT and insulin at 1h post-OGTT | Spearman correlation analysis | [103] |
9. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Genazzani, A.D.; Genazzani, A.R. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome as Metabolic Disease: New Insights on Insulin Resistance. touchREV Endocrinol 2023, 19, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joham, A.E.; Norman, R.J.; Stener-Victorin, E.; Legro, R.S.; Franks, S.; Moran, L.J.; Boyle, J.; Teede, H.J. Polycystic ovary syndrome. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2022, 10, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet Regional Health –, E. Polycystic ovary syndrome: What more can be done for patients? The Lancet Regional Health - Europe 2022, 21, 100524. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) and Diabetes. Available online: (accessed on July 12 2023).
- Deswal, R.; Narwal, V.; Dang, A.; Pundir, C.S. The Prevalence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Brief Systematic Review. J Hum Reprod Sci 2020, 13, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, E.A.; Kauffman, A.S. The Role of the Brain in the Pathogenesis and Physiology of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Med Sci (Basel) 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, R.P.; Bachega, T.; Mendonça, B.B.; Gomes, L.G. An update of genetic basis of PCOS pathogenesis. Arch Endocrinol Metab 2018, 62, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, N.; Khan, S.Z.; Shaikh, R. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and genetic predisposition: A review article. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X 2019, 3, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeger, K.M.; Dokras, A.; Piltonen, T. Update on PCOS: Consequences, Challenges, and Guiding Treatment. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2020, 106, e1071–e1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Ullah, A.; Basit, S. Genetic Basis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Current Perspectives. Appl Clin Genet 2019, 12, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teede, H.J.; Misso, M.L.; Costello, M.F.; Dokras, A.; Laven, J.; Moran, L.; Piltonen, T.; Norman, R.J. Recommendations from the international evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril 2018, 110, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderpoor, N.; Shorakae, S.; de Courten, B.; Misso, M.L.; Moran, L.J.; Teede, H.J. Metformin and lifestyle modification in polycystic ovary syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Human Reproduction Update 2016, 22, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.F.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Y.H.; Ding, T.; Batterham, R.L.; Qu, F.; Hardiman, P.J. Pharmacologic therapy to induce weight loss in women who have obesity/overweight with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Obes Rev 2018, 19, 1424–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, W.; Bordewijk, E.M.; Legro, R.S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Gao, J.; Morin-Papunen, L.; Homburg, R.; König, T.E.; et al. First-line ovulation induction for polycystic ovary syndrome: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update 2019, 25, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legro, R.S.; Driscoll, D.; Strauss, J.F., 3rd; Fox, J.; Dunaif, A. Evidence for a genetic basis for hyperandrogenemia in polycystic ovary syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 14956–14960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepto, N.K.; Cassar, S.; Joham, A.E.; Hutchison, S.K.; Harrison, C.L.; Goldstein, R.F.; Teede, H.J. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome have intrinsic insulin resistance on euglycaemic-hyperinsulaemic clamp. Hum Reprod 2013, 28, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreich, A.K.; Moley, K.H. Developmental and Transmittable Origins of Obesity-Associated Health Disorders. Trends in genetics 2017, 33, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, S.M.D.F.M.S.; Berga, S.L.M.D. Does PCOS have developmental origins? Fertility and sterility 2012, 97, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risal, S.; Pei, Y.; Lu, H.; Manti, M.; Fornes, R.; Pui, H.P.; Zhao, Z.; Massart, J.; Ohlsson, C.; Lindgren, E.; et al. Prenatal androgen exposure and transgenerational susceptibility to polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Med 2019, 25, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insler, V.; Lunenfeld, B. Polycystic ovarian disease: a challenge and controversy. Gynecol Endocrinol 1990, 4, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azziz, R.; Adashi, E.Y. Stein and Leventhal: 80 years on. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2016, 214, 247.e241–247.e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EvidenceHunt. Available online: https://evidencehunt.com/ (accessed on).
- International Protein Nomenclature Guidelines. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/doc/internatprot_nomenguide/ (accessed on 2004 - 2023 Jul 19).
- Song, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Cai, Z.; Yu, C. Androgen Excess Induced Mitochondrial Abnormality in Ovarian Granulosa Cells in a Rat Model of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 789008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, L.D. Mitochondrial biogenesis: An update. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 4892–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.F.; Hamilton, K.L. A perspective on the determination of mitochondrial biogenesis. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2012, 302, E496–E499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.W.; Turnbull, D.M. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in human disease. Nat Rev Genet 2005, 6, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigl, S.; Paradiso, A.; Tommasi, S. Mitochondria and familial predisposition to breast cancer. Curr Genomics 2013, 14, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Ji, X.; Yuan, Q.; Su, L.; Guo, X.; Gu, X.; Xing, J. NGS-based accurate and efficient detection of circulating cell-free mitochondrial DNA in cancer patients. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisserier, M.; Shanmughapriya, S.; Rai, A.K.; Gonzalez, C.; Brojakowska, A.; Garikipati, V.N.S.; Madesh, M.; Mills, P.J.; Walsh, K.; Arakelyan, A.; et al. Cell-Free Mitochondrial DNA as a Potential Biomarker for Astronauts' Health. J Am Heart Assoc 2021, 10, e022055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trecarichi, A.; Duggett, N.A.; Granat, L.; Lo, S.; Malik, A.N.; Zuliani-Álvarez, L.; Flatters, S.J.L. Preclinical evidence for mitochondrial DNA as a potential blood biomarker for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. PLOS ONE 2022, 17, e0262544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfanner, N.; Warscheid, B.; Wiedemann, N. Mitochondrial proteins: from biogenesis to functional networks. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2019, 20, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, N. Mitochondrial Structure and the Practice of Cell Biology in the 1950s. Journal of the History of Biology 1995, 28, 381–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, R.C.B. The Structure of Mitochondria. Transactions of the American Microscopical Society 1975, 94, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zick, M.; Rabl, R.; Reichert, A.S. Cristae formation—linking ultrastructure and function of mitochondria. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 2009, 1793, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühlbrandt, W. Structure and function of mitochondrial membrane protein complexes. BMC Biology 2015, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, G.A.; Frey, T.G. Recent structural insight into mitochondria gained by microscopy. Micron 2000, 31, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinazzi, M.; Casarin, A.; Pertegato, V.; Salviati, L.; Angelini, C. Assessment of mitochondrial respiratory chain enzymatic activities on tissues and cultured cells. Nature Protocols 2012, 7, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Else, A.J.; Barnes, S.J.; Danson, M.J.; Weitzman, P.D. A new spectrophotometric assay for citrate synthase and its use to assess the inhibitory effects of palmitoyl thioesters. Biochem J 1988, 251, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benard, G.; Bellance, N.; James, D.; Parrone, P.; Fernandez, H.; Letellier, T.; Rossignol, R. Mitochondrial bioenergetics and structural network organization. J Cell Sci 2007, 120, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, B.; Lewis, N.; Adeniyi, T.; Leese, H.J.; Brison, D.R.; Sturmey, R.G. Application of extracellular flux analysis for determining mitochondrial function in mammalian oocytes and early embryos. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 16778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoshan-Barmatz, V.; De Pinto, V.; Zweckstetter, M.; Raviv, Z.; Keinan, N.; Arbel, N. VDAC, a multi-functional mitochondrial protein regulating cell life and death. Mol Aspects Med 2010, 31, 227–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorova, L.D.; Popkov, V.A.; Plotnikov, E.Y.; Silachev, D.N.; Pevzner, I.B.; Jankauskas, S.S.; Babenko, V.A.; Zorov, S.D.; Balakireva, A.V.; Juhaszova, M.; et al. Mitochondrial membrane potential. Analytical Biochemistry 2018, 552, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilokani, L.; Nagashima, S.; Paupe, V.; Prudent, J. Mitochondrial dynamics: overview of molecular mechanisms. Essays Biochem 2018, 62, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemirli, N.; Morel, E.; Molino, D. Mitochondrial Dynamics in Basal and Stressful Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernas, L.; Scorrano, L. Mito-Morphosis: Mitochondrial Fusion, Fission, and Cristae Remodeling as Key Mediators of Cellular Function. Annual Review of Physiology 2016, 78, 505–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, F.; Ryan, M.T. The constriction and scission machineries involved in mitochondrial fission. Journal of Cell Science 2017, 130, 2953–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.P. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem J 2009, 417, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosa, A.; Ghani, M.; O'Neill, H.C. Genetic associations with polycystic ovary syndrome: the role of the mitochondrial genome; a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Pathol 2022, 75, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, R.S.; Nemoto, S.; Finkel, T. Mitochondria, oxidants, and aging. Cell 2005, 120, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.L.; Tai, H.; Xiao, X.S.; Zhang, S.Y.; Cui, S.C.; Qi, S.B.; Hu, D.D.; Zhang, L.N.; Kuang, J.S.; Meng, X.S.; et al. Cangfudaotan decoction inhibits mitochondria-dependent apoptosis of granulosa cells in rats with polycystic ovarian syndrome. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 962154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Roles of HIF-1α/BNIP3 mediated mitophagy in mitochondrial dysfunction of letrozole-induced PCOS rats. J Mol Histol 2022, 53, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Fernando, T.; Zhu, X.; Shi, Y. The overexpression of neurokinin B-neurokinin 3 receptor system exerts direct effects on the ovary under PCOS-like conditions to interfere with mitochondrial function. Am J Reprod Immunol 2023, 89, e13663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Emidio, G.; Rea, F.; Placidi, M.; Rossi, G.; Cocciolone, D.; Virmani, A.; Macchiarelli, G.; Palmerini, M.G.; D'Alessandro, A.M.; Artini, P.G.; et al. Regulatory Functions of L-Carnitine, Acetyl, and Propionyl L-Carnitine in a PCOS Mouse Model: Focus on Antioxidant/Antiglycative Molecular Pathways in the Ovarian Microenvironment. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Cheng, J.; Wu, T.; Sun, L. SIRT3 ameliorates polycystic ovary syndrome through FOXO1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. Endocrine 2023, 80, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabah, H.M.; Mohamed, D.A.; Mariah, R.A.; Abd El-Khalik, S.R.; Khattab, H.A.; AbuoHashish, N.A.; Abdelsattar, A.M.; Raslan, M.A.; Farghal, E.E.; Eltokhy, A.K. Novel insights into the synergistic effects of selenium nanoparticles and metformin treatment of letrozole - induced polycystic ovarian syndrome: targeting PI3K/Akt signalling pathway, redox status and mitochondrial dysfunction in ovarian tissue. Redox Rep 2023, 28, 2160569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsky, M.; Merkison, J.; Hosseinzadeh, P.; Yang, L.; Bruno-Gaston, J.; Dunn, J.; Gibbons, W.; Blesson, C.S. Fetal programming of polycystic ovary syndrome: Effects of androgen exposure on prenatal ovarian development. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2021, 207, 105830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Pan, C.S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.L.; Yan, L.; Anwaier, G.; Wang, X.Y.; Yan, L.L.; Fan, J.Y.; Li, D.; et al. The Ameliorating Effects of Bushen Huatan Granules and Kunling Wan on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Induced by Dehydroepiandrosterone in Rats. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 525145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atef, M.M.; Abd-Ellatif, R.N.; Emam, M.N.; Abo El Gheit, R.E.; Amer, A.I.; Hafez, Y.M. Therapeutic potential of sodium selenite in letrozole induced polycystic ovary syndrome rat model: Targeting mitochondrial approach (selenium in PCOS). Arch Biochem Biophys 2019, 671, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Zeng, Z.; Tang, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, F.; Zhou, L.; Xia, W.; Zhu, C.; Rao, M. Humanin regulates oxidative stress in the ovaries of polycystic ovary syndrome patients via the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Mol Hum Reprod 2021, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zheng, L.W.; Wang, Y.S.; Huang, J.C.; Yang, Z.Q.; Yue, Z.P.; Guo, B. Genistein exhibits therapeutic potential for PCOS mice via the ER-Nrf2-Foxo1-ROS pathway. Food Funct 2021, 12, 8800–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, Z.; Bakhshalizadeh, S.H.; Nasr Esfahani, M.H.; Akbari Sene, A.; Najafzadeh, V.; Soleimani, M.; Shirazi, R. Effect of Vitamin D3 on Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Granulosa Cells Derived from Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Int J Fertil Steril 2020, 14, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, X. The effects of mitochondrial dysfunction on energy metabolism switch by HIF-1α signalling in granulosa cells of polycystic ovary syndrome. Endokrynol Pol 2020, 71, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. Melatonin enhances SIRT1 to ameliorate mitochondrial membrane damage by activating PDK1/Akt in granulosa cells of PCOS. J Ovarian Res 2021, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, R.; Mazier, H.L.; Nivet, A.L.; Reunov, A.A.; Lima, P.; Wang, Q.; Fiocco, A.; Isidoro, C.; Tsang, B.K. Ovarian mitochondrial dynamics and cell fate regulation in an androgen-induced rat model of polycystic ovarian syndrome. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreerangaraja Urs, D.B.; Wu, W.H.; Komrskova, K.; Postlerova, P.; Lin, Y.F.; Tzeng, C.R.; Kao, S.H. Mitochondrial Function in Modulating Human Granulosa Cell Steroidogenesis and Female Fertility. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazloomi, S.; Sanoeei Farimani, M.; Tayebinia, H.; Karimi, J.; Amiri, I.; Abbasi, E.; Khodadadi, I. The Association of Mitochondrial Translocator Protein and Voltage-Dependent Anion Channel-1 in Granulosa Cells with Estradiol Levels and Presence of Immature Follicles in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J Reprod Infertil 2022, 23, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, M.; Herraiz, S.; Cakiroglu, Y.; Garcia-Velasco, J.A.; Tiras, B.; Pacheco, A.; Rabadan, S.; Kohls, G.; Barrio, A.I.; Pellicer, A.; et al. Distress response in granulosa cells of women affected by PCOS with or without insulin resistance. Endocrine 2023, 79, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, N.R.; Zhou, B.; Hosseinzadeh, P.; Schutt, A.; Gibbons, W.E.; Blesson, C.S. Hyperandrogenemia alters mitochondrial structure and function in the oocytes of obese mouse with polycystic ovary syndrome. F S Sci 2021, 2, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, N.R.; Zhou, B.; Schutt, A.K.; Gibbons, W.E.; Blesson, C.S. Prenatal androgen induced lean PCOS impairs mitochondria and mRNA profiles in oocytes. Endocr Connect 2020, 9, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayev, E.; Seli, E. Oocyte mitochondrial function and reproduction. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 2015, 27, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, M.; Yao, H.; Cui, M.; Gong, X.; Wang, L.; Sui, C.; Zhang, H. Inhibition of Oocyte Maturation by Follicular Extracellular Vesicles of Nonhyperandrogenic PCOS Patients Requiring IVF. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2023, 108, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.E.; Maruthini, D.; Tang, T.; Balen, A.H.; Picton, H.M. Metabolism and karyotype analysis of oocytes from patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod 2010, 25, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.R.; Chen, L.J.; Cai, J.Y.; Xia, Z.R.; Zeng, W.T.; Wang, Z.B.; Chen, X.C.; Hu, F.; et al. Rat BAT xenotransplantation recovers the fertility and metabolic health of PCOS mice. J Endocrinol 2021, 248, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, I.M.; Baracat, M.C.; Simões Mde, J.; Simões, R.S.; Baracat, E.C.; Soares, J.M., Jr. Endometrium in women with polycystic ovary syndrome during the window of implantation. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992) 2011, 57, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, P.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Vestin, E.; Brännström, M.; Shao, L.R.; et al. Differential Expression Patterns of Glycolytic Enzymes and Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis in PCOS Patients with Endometrial Hyperplasia, an Early Hallmark of Endometrial Cancer, In Vivo and the Impact of Metformin In Vitro. Int J Biol Sci 2019, 15, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmerini, M.G.; Macchiarelli, G.; Cocciolone, D.; Mascitti, I.A.; Placidi, M.; Vergara, T.; Di Emidio, G.; Tatone, C. Modulating Morphological and Redox/Glycative Alterations in the PCOS Uterus: Effects of Carnitines in PCOS Mice. Biomedicines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N.; Wu, X.; Brännström, M.; et al. Increased uterine androgen receptor protein abundance results in implantation and mitochondrial defects in pregnant rats with hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance. J Mol Med (Berl) 2021, 99, 1427–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Jia, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Cui, P.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N.; Han, Y.; et al. Hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance induce gravid uterine defects in association with mitochondrial dysfunction and aberrant reactive oxygen species production. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2019, 316, E794–e809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xu, H.; Hu, M.; Guo, X.; Jia, W.; Liu, G.; Li, J.; Cui, P.; Lager, S.; et al. Hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance-induced fetal loss: evidence for placental mitochondrial abnormalities and elevated reactive oxygen species production in pregnant rats that mimic the clinical features of polycystic ovary syndrome. J Physiol 2019, 597, 3927–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Liang, M.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N.; Wu, X.; Ma, H.; Brännström, M.; et al. Suppression of uterine and placental ferroptosis by N-acetylcysteine in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome. Mol Hum Reprod 2021, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemers, Kyle M.; Baack, Michelle L. The importance of placental lipid metabolism across gestation in obese and non-obese pregnancies. Clinical Science 2023, 137, 31–34. [CrossRef]
- Kirtana, A.; Seetharaman, B. Comprehending the Role of Endocrine Disruptors in Inducing Epigenetic Toxicity. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2022, 22, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczuko, M.; Kikut, J.; Komorniak, N.; Bilicki, J.; Celewicz, Z.; Ziętek, M. The Role of Arachidonic and Linoleic Acid Derivatives in Pathological Pregnancies and the Human Reproduction Process. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, C.; Lazzeroni, P.; Merli, S.; Patianna, V.D.; Viaroli, F.; Cirillo, F.; Amarri, S.; Street, M.E. From Placenta to Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome: The Role of Adipokines. Mediators Inflamm 2016, 2016, 4981916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Sun, B.; Qiao, S.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lin, Y.; Hou, L. Elevated maternal androgen is associated with dysfunctional placenta and lipid disorder in newborns of mothers with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril 2020, 113, 1275–1285.e1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, G.; Maliqueo, M.; Crisosto, N.; Echiburú, B.; Sir-Petermann, T.; Lara, H.E. Metformin increases norepinephrine transporter expression in placenta of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2017, 21, 3482–3489. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, A.S.; Smith, Y.R.; Padmanabhan, V. A Narrative Review of Placental Contribution to Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019, 104, 5299–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Jia, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Cui, P.; Li, X.; Lager, S.; et al. Hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance modulate gravid uterine and placental ferroptosis in PCOS-like rats. J Endocrinol 2020, 246, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, T.V.; Govatati, S.; Deenadayal, M.; Shivaji, S.; Bhanoori, M. Polymorphisms in the TFAM and PGC1-α genes and their association with polycystic ovary syndrome among South Indian women. Gene 2018, 641, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Hu, B.; Shi, W.; Guo, F.; Xu, C.; Li, S. Mitochondrial DNA 4977 bp Deletion in Peripheral Blood Is Associated With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 675581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, N.; Hamzah, I.H.; Al-Gharrawi, S.A.R. Polycystic ovary syndrome dependency on mtDNA mutation; copy Number and its association with insulin resistance. BMC Res Notes 2019, 12, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, T.V.; Govatati, S.; Deenadayal, M.; Sisinthy, S.; Bhanoori, M. Impact of mitochondrial DNA copy number and displacement loop alterations on polycystic ovary syndrome risk in south Indian women. Mitochondrion 2019, 44, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Chung, D.J.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, M.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Im, J.A.; Lee, D.C.; Lee, J.W. Mitochondrial DNA copy number in peripheral blood in polycystic ovary syndrome. Metabolism 2011, 60, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.K.; Chou, C.H.; Chang, C.H.; Chen, S.U.; Ho, H.N.; Chen, M.J. Changes in peripheral mitochondrial DNA copy number in metformin-treated women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a longitudinal study. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2020, 18, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.-p.; Wang, Y.; Mao, W.-w.; Zhang, X.-w.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, Q.-f. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) and Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs) in mtDNA D-loop and CO II- tRNALys Intergenic Region with PCOS. Journal of reproduction and contraception 2011, 22, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, G.; Ding, Y.; Feng, G.; Yu, L.; Jiang, Y. Analysis of mitochondrial DNA sequence variants in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Archives of gynecology and obstetrics 2012, 286, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, G.; Feng, G.; Leng, J.; Yu, L.; Jiang, Y. 9-bp Deletion Homoplasmy in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Revealed by Mitochondrial Genome-Mutation Screen. Biochemical genetics 2010, 48, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xia, B.-H.; Zhang, C.-J.; Zhuo, G.-C. Mitochondrial tRNALeu(UUR) C3275T, tRNAGln T4363C and tRNALys A8343G mutations may be associated with PCOS and metabolic syndrome. Gene 2018, 642, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Xia, B.-H.; Zhang, C.-J.; Zhuo, G.-C. Mutations in mitochondrial tRNA genes may be related to insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. American journal of translational research 2017, 9, 2984–2996. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.U.; Zhuo, G.; Zhang, C.; Leng, J. Point mutation in mitochondrial tRNA gene is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome and insulin resistance. Molecular medicine reports 2016, 13, 3169–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Ji, D.; Liu, Y.; Deng, X.; Zou, W.; Liang, D.; Du, Y.; Zong, K.; Jiang, T.; Li, M.; et al. Polymorphisms of mtDNA in the D-loop region moderate the associations of BMI with HOMA-IR and HOMA-β among women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a cross-sectional study. J Assist Reprod Genet 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Li, T.T.; Yu, A.Q.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Kaifu, T. Plasma level of peroxiredoxin 3 in patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome. BMC Endocr Disord 2019, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





