1. Introduction
Entanglement is one of the most complex phenomena of quantum mechanics. Entanglement has been considered theoretically with no interaction. [
1] Meanwhile, all the similar particles can be entangled. [
1] The possibility for entanglement in the brain has been considered by the researchers. [
2] Many studies have been carried out about brain quantum behavior as well. [
3,
4,
5,
6]
Various neurotransmitters are secreted in human brain for different aims and also human brain has neuroplasticity property. Dopamine role in learning as well as brain reward system are fully known. [
7] Furthermore, music effect for neuroplasticity property is known and studied completely. [
8]
Extrasensory behaviors can be surveyed within brain quantum behaviors. [
9] Love and increase in dopamine secretion are directly related. [
10]
Without performing precise tests the brain’s extrasensory behaviors can’t be related to quantum phenomena. Often performing scientific tests in this field are confronted with many problems like non reliability of the events. Complexities of quantum phenomena such as entanglement are hidden in space-time structure.[
11] Consequently, time role is considerable for appearing of quantum behaviors.
Precise test were carried out based on the music effect and neuroplasticity property. Quantum entanglement was investigated in terms of dopamine secretion increase level in the brain. In addition, various information was sent and received based on information compression. On this basis, several Software are in the process of designing for compressing, decoding and sending information.
2. Test one
Human eyes enjoy looking at the equal and paired numbers in digital clocks. Observation of pair numbers causes to activate reward and error system in the brain; as a result, biological clocks of dependent neurons regulate their activities on the basis of observing clock pair numbers. By increasing neurotransmitter levels depending on thinking, specified thoughts were related to this phenomenon.The pair clocks were observed by calling a special memory from a particular person. Simultaneously the participating individuals in this test listened to the same pieces of the minor scale. On the basis of neuroplasticity property in the brain, the time and number of pair clocks observations became more after a while. Never these individuals had met. Then, afterward, these individuals had textual conversations.These individuals observed their photos as well. After a month, daily ordinary conversations were stopped, and the same pieces were heard again.
3. Entanglement between two brains’ particles
Each time that individual ‘A’ is thinking about individual ‘B’, individual ‘B’ looks at clock pair numbers unconsciously after a short time. A deeper relationship was found due to this phenomenon. Different thoughts were compressed by the brain and sent like worry, love, nostalgia, happiness, and... For example, individual ‘A’ worried about the problems of individual ‘B’, ‘A’ looked at the clock at 12:12. The individual ‘B’ understood ‘A’ worries, and looked at the clock at 12:21. After 12:21, ’A’ became calm. This phenomenon follows quantum entanglement completely and expresses the matter that particles in man’s brain can entangle with other particles without any interaction.
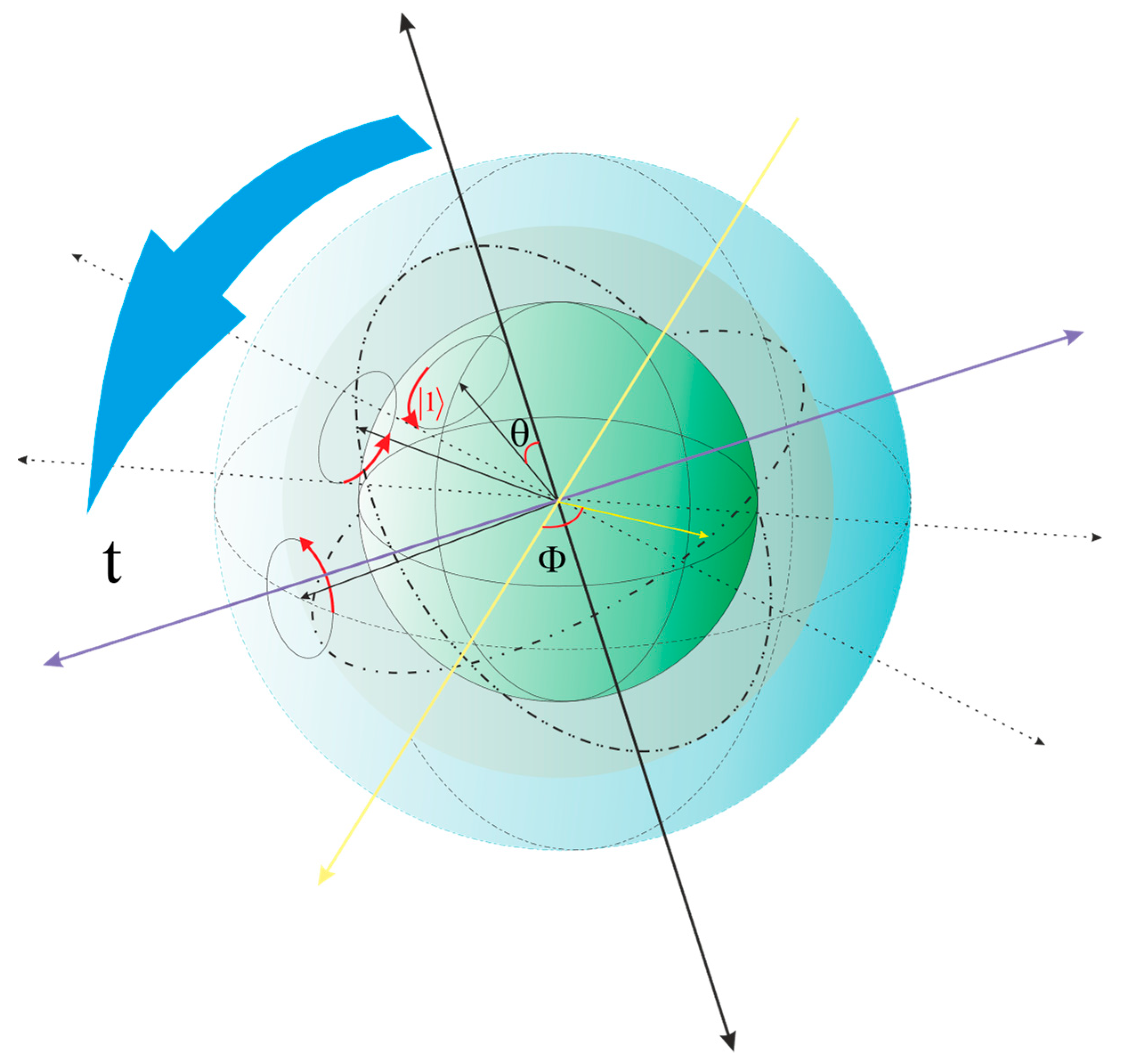
Figure 1.(3.1) The time lifting of the feedback is due to decoding based on the structure six-dimensional space-time, of Qubits by the brain. The more complex point was not observing some numbers in some of the testing days. For example, the time 10:01 and the response 10:10 was not observed at all in several days, or only once in a day the pair numbers were observed.
4. Decoding and sending information
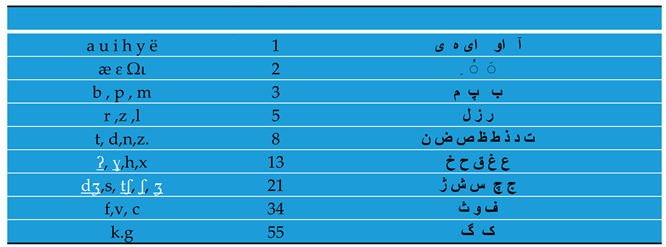
Finally, a key was designed for decoding information. Words were classified on the basis of the Fibonacci sequence which is a component of neurons' fractal structure. Letters were categorized in terms of expression.
Table (1) This key has semantic generality in language. For example, the numbers related to the words like sorrow, grief, pain,...are related mathematically. This relationship between words' meanings is related to the manner of semantic storage of words in the brain. As a result, each number was related to a meaning based on the existing structure of language. These meanings are both positive and negative.
Table (2). A lot of information is stored in one neuron pulse. Similar pulses have similar effects. Accordingly, the human brain classifies related concepts based on the fact of the surrounding world.
Other numbers are also related to the above numbers semantically. By summing the internal component of each number we obtain the above numbers. For example, the number ‘36’ is equal to the word ‘love’ in the Persian language. This number is related to the meaning of the holiness. (4.1)
By using this key, information was sent between the brains of two persons, received and decoded.
Using the relationship of numbers with reflective thinking in the individual ‘A’, different meanings and information were transferred and received through observations. Meanings of numbers and methods of word compression were taught to the individuals. After teaching, sending information without observation of numbers became possible and this case approves quantum entanglement between two brains’ particles.
5. Results
Brain activity differs depending on the surrounding environment. On this basis symmetrical environments geometrically can play an essential role for improving brain operation. On the basis of quantum entanglement, the compressed information can be sent and received between two brains immediately. The human brain classifies words in terms of its related meaning. The numerical structure of the surrounding environment has meaning in brain. Symmetry and beauties of nature and environment are dependent on geometry and mathematics. Thus, observation of these symmetries or non-observation have effect on decision making and thinking. Semantic compression of information play an important role for improvement of sending information by quantum entanglement. Numbers constitute the structure of the universe. Disorder in environment is a factor for not thinking regularly. This problem had a direct effect on the test. Human brain can organize and classify the problems related to thinking in terms of order, symmetry and mathematics. Sometimes solving the problems related to chaotic thinking is dependent on quantum mechanics and environment mathematics. On this basis, observation of symmetries and numbers in nature had similar results in individuals. For example, observation of several birds’ flight was a response to the person’s thinking in the same immediately. It is evident that brain knows the response before mentioning the question that is only describable only by wave function in quantum mechanics. Quantum entanglement is related to the space-time structure of six-dimensional.
Acknowledgements
The author expresses gratitude to God, and Dr.M.T and Dr.Lh.R and E.t.S.Sattar their professors for their helpful discussions and valuable comments.
References
- Blasiak, P.; Markiewicz, M. Entangling three qubits without ever touching. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M.P. Quantum cognition: The possibility of processing with nuclear spins in the brain. Ann. Phys. 2015, 362, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.M.; Stapp, H.P.; Beauregard, M. Quantum physics in neuroscience and psychology: a neurophysical model of mind–brain interaction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1309–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, F. Synaptic Quantum Tunnelling in Brain Activity. NeuroQuantology 2008, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarlacı, S. A Historical View of the Relation Between Quantum Mechanics and the Brain: A NeuroQuantologic Perspective. NeuroQuantology 2010, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkoski, Spase, and Viktor Jirsa. "Renormalization of the brain connectome: Duality of particle and wave." bioRxiv (2020).
- Pessiglione, M.; Seymour, B.; Flandin, G.; Dolan, R.J.; Frith, C.D. Dopamine-dependent prediction errors underpin reward-seeking behaviour in humans. Nature 2006, 442, 1042–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münte, Thomas F , Eckart Altenmüller, and Lutz Jäncke. "The musician's brain as a model of neuroplasticity.". Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2002, 3, 473–478. [CrossRef]
- Fingelkurts, A. A. , Fingelkurts, A. A., Neves, C. F., & Kallio-Tamminen, T. Brain-mind operational architectonics: At the boundary between quantum physics and Eastern metaphysics. Physics of Life Reviews 2019, 31, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Mizuno, K.; Sasaki, A.T.; Wada, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Ishii, A.; Tajima, K.; Tsuyuguchi, N.; Watanabe, K.; Zeki, S.; et al. Imaging the passionate stage of romantic love by dopamine dynamics. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S. K. The balance In the six dimensions of space-time description of quantum mechanics phenomena and nature of time. Journal of Physics: Theories and Applications, 2022, 7. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).